Lecture 16 - Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy: Coughs & Colds
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
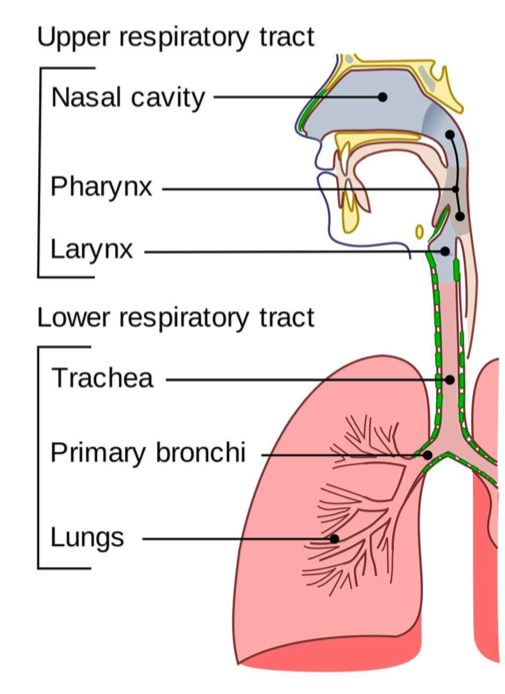
Respiratory tract infections
Upper respiratory tract
Cold, cough, flu, tonsillitis, sinusitis and hay fever
Lower respiratory tract
Bronchitis, pneumonia and influenza
Colds
Can be caused by over 200 different viruses
Incubation 1-4 day s and symptomatic 3-4 days
Signs & Symptoms - upper respiratory tract
Causes inflammation in the lining of the nose
Nasal congestion
Rhinorrhoea: runny nose
Sneezing
Sore throat & cough
Signs & symptoms - lower respiratory tract
Cough
Increased mucous production
Pain/discomfort
Voicr change if larynx involved
Airflow obstruction: muscular/mucous onstruction
Haemoptysis (coughing up blood) - serious
Management of Cold
Anti-tussive: cough suppressant
Mild pain killers e.g. paracetamol
Sore throat sprays - numb the pain, contain anaesthetics
Antihistamines: as deconhestants or sedation in night preparations
Steam inhalation: menthol, eucalyptus
Influenza
Influenza virus A,B or C - A and B most common
Epidemic nature & incubation phase 1-3 days
Early symptoms resemble cold
Distinguished by fever
May be severe
In pandemic can be high mortality
Contagious - first 3 days after symptoms begon
Spread of cold and flu
With each cough, about 1.5L of air is expelled - contains 3000 saliva droplets
Travels at speed of about 50mph
Sneezes can travel up to 100mph and create around 100000 droplets
Classification of cough: duration
Acute - less than 3 weeks
Dry: pneumonia, cold/flu, asthma
Chesty: cold and flu
Subacute - 3-8 weeks
Asthma, post infection airway inflammation, postnasal drip
Chronic - more than 8 weeks
Dry: medicines, allergy, reflux
Chesty: infection, asthma, lung cancer, COPD
Coughs: dry vs chesty
Dry:
Non productive, tickly or tight
No mucous/ sputum production
Chesty:
Mucous production
Clear, yellow/green, blood
Treatment of cough
Variable ways depending on cause
Most involves self-care
If caused by virus can’t be treated with antibiotics
Cough suppressant
Centrally acting - codeine, pholcodine, dextromethrophan
Expectrorants
Hydration, ammonium salts, guafenesin, ipecuanha, citric acid, etc
Demulcents
Honey, glycerin, syrup, coat pharyngeal mucosa
Cough suppressants - dry cough
Codein is the standard - normal dose 15-30mg
Dextromethorphan now widely used - dose range in adults 15-30mg
Demulcent linctuses - act in pharynx to reduce irritation and sensation of sensory receptors
Expectorants - chesty cough
Increased productivity of the cough
Direct stimulant action in respiratory tract
Indirect activation of p-sympathetic tone secondary to gastro-intestinal irritation
Water is an expectorant - hydration of mucous to reduce viscosity
Guaifenesin
Widely used - readily absorbed from oral dose
Plasma half life is 1 hour
Well tolerated and free of major side-effects
Reported dose 100-200 mg every 2-4 hours
No clear evidence of efficacy
Best practice in children
Non-pharmacological interventions - fluids and rest
Fever and pain - paracetamol, ibuprofen
Nasal congection - saline nasal drops, vapour rubs, steam inhalation
Cough - warm clear fluids, lemon and honey drink
Symptoms persist - referral to GP
Cough preparation for children
Very little is available or should be used
Under 6 - don’t use antitussives, expectorants, nasal decongestanats, antihistamines
Codeine - not to be used in children under 18
OTC supply
Who? - age important
What? - determine history & symptoms
Other factors e.g. environemental
What’s the nature?
How long?
Has action been taken and is it appropriate?
Medication?
Lung cancer warning signs
Cough more than 3 weeks
Worsening or change in long-standing cough
Repeated or persistent chest infections
Blood in phelgm (haemoptysis)
Unexplained persistent breathlessnes
Unexplained persistent tiredness or lack of energy
Unexplained persistent weight loss
Persistent chest and/or shoulder pain
Unexplained persistent hoarseness
Unexplained swelling of the face and neck