[APK2100C] Chapter 23
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Functions of the Digestive System
- Food Consumption
- Food Digestion into Nutrient Molecules
- Nutrient Absorption into Blood
- Waste Elimination
2 Divisions of the Digestive System
(1) Alimentary Canal or GI Tract
(2) Accessory Digestive Organs
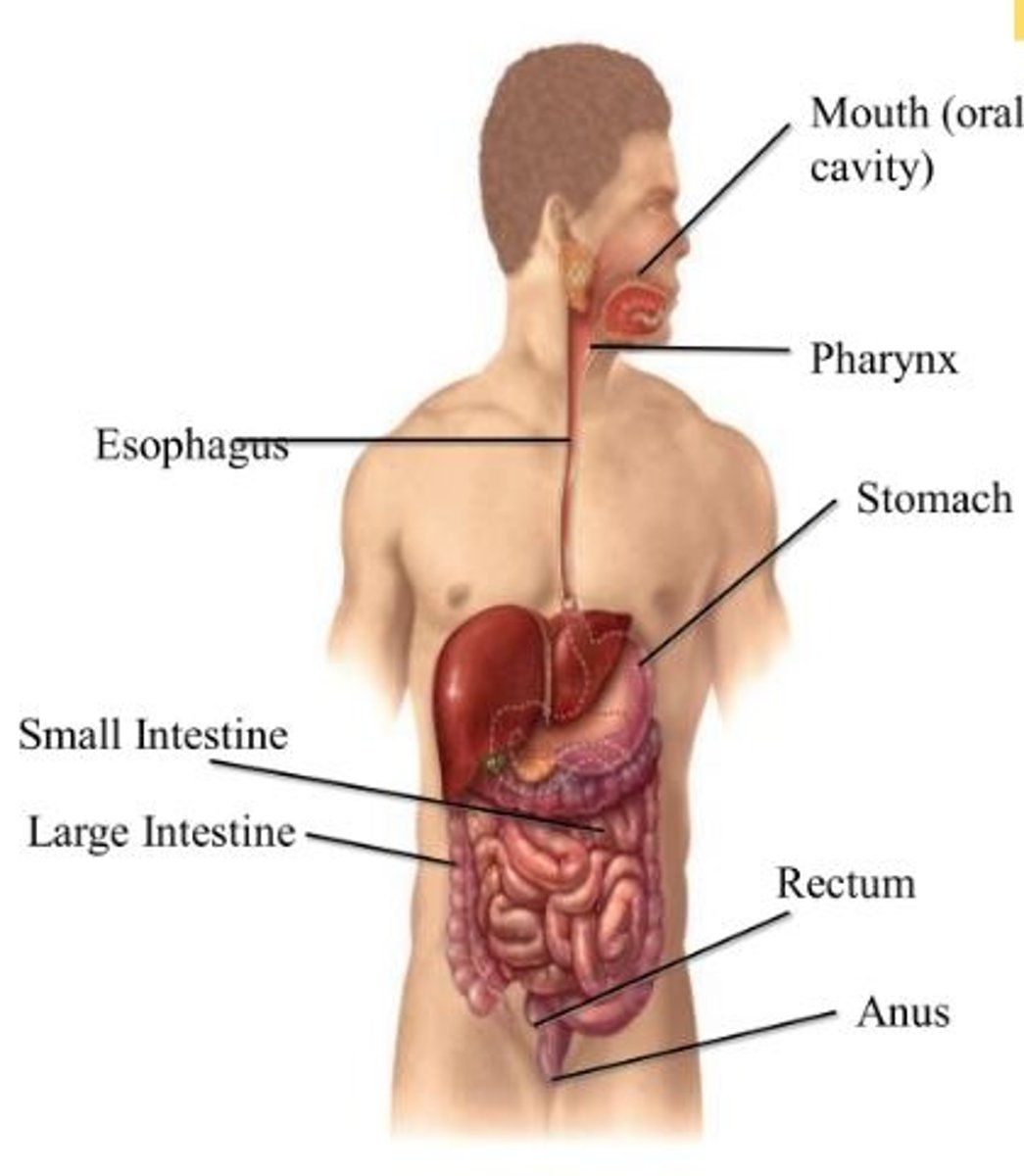
Alimentary Canal (GI Tract)
- Hollow 'tube' running from the mouth to anus where food travels along
Oral Cavity -> Esophagus -> Stomach -> Small Intestine -> Large Intestine -> Anus
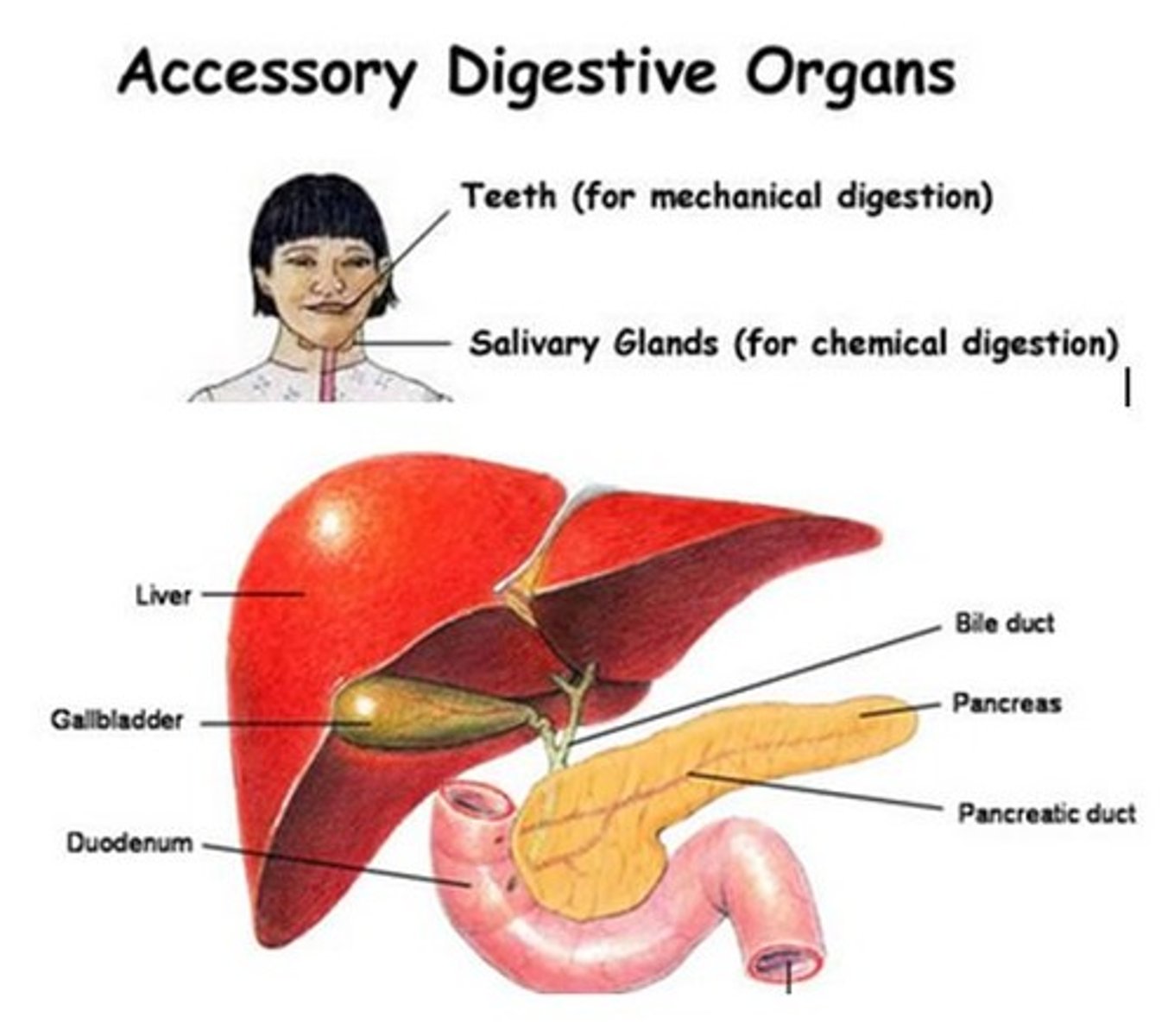
Accessory Digestive Organs
- Responsible for secreting digestive enzymes and aiding in digestion
Salivary Glands + Teeth + Pancreas + Liver + Gallbladder
Ingestion
Intake of food via the mouth
Mechanical Breakdown of Food
(1) Chewing -> Mouth
(2) Churning -> Stomach
(3) Segmentation -> Small Intestine
Propulsion of Food
(1) Swallowing -> Oropharynx
(2) Peristalsis -> Esophagus + Stomach + Small Intestine + Large Intestine
Digestion
Breakdown of food in the stomach into nutrients by enzymes + water
Absorption
Water mainly is absorbed in the intestines and sent into blood vessels/lymph vessels
Defecation
Elimination of waste product out of the anus in the form of feces
9 Abdominal Regions
As shown in the picture
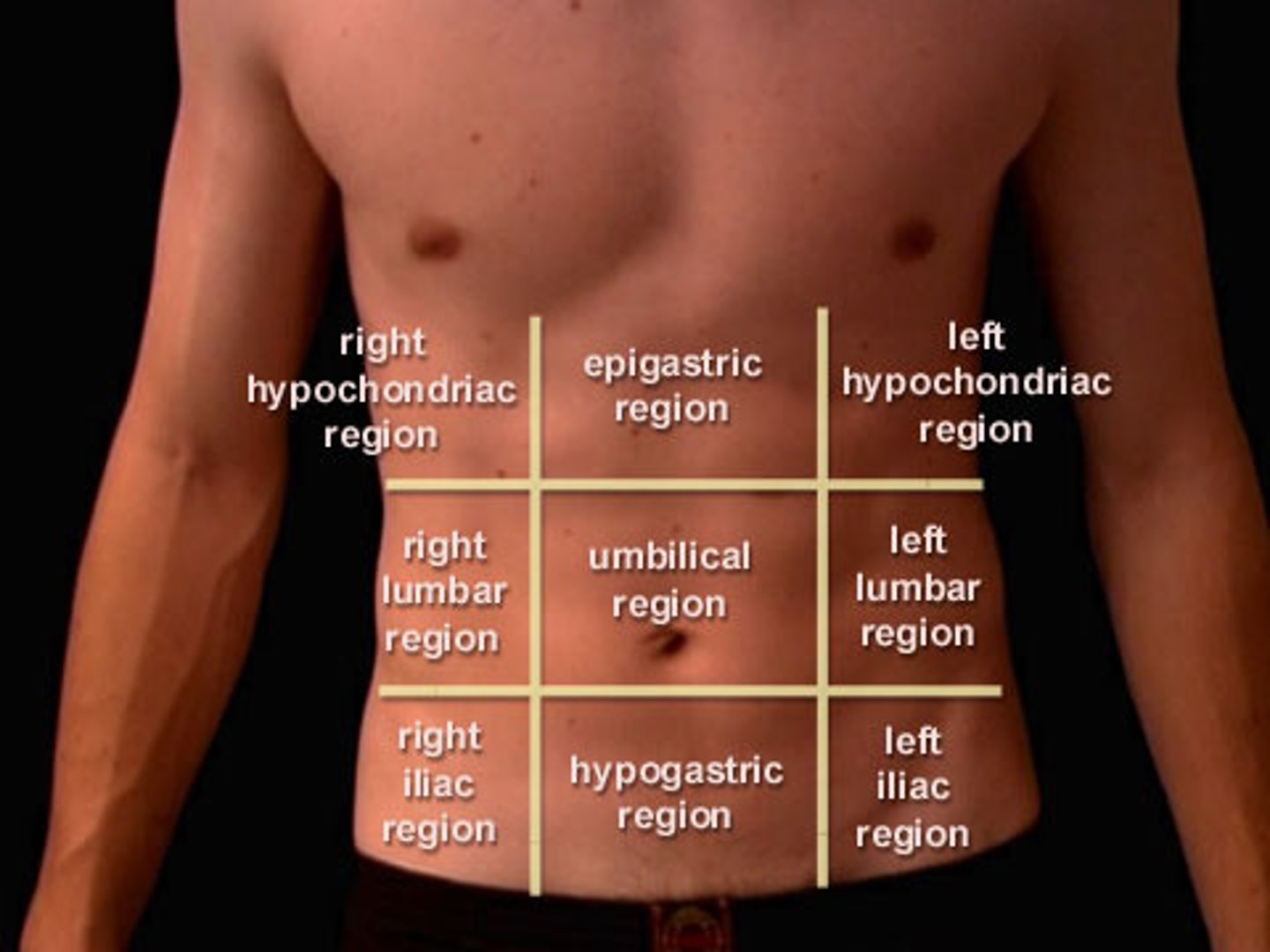
Organs Associated w/ Each Abdominal Region
[R. Hypochondriac] Liver + Gallbladder
[Epigastric] Stomach
[L. Hypochondriac] Part of the Diaphragm
[R. Lumbar] Ascending Colon of Large Intestine
[Umbilical] Transverse Colon of LI + Small Intestine
[L. Lumbar] Descending Colon of Large Intestine
[R. Iliac (Inguinal)] Cecum + Appendix
[Hypogastric (Pubic)] Urinary Bladder
[L. Iliac (Inguinal)] Initial Part of the Sigmoid Colon
![<p>[R. Hypochondriac] Liver + Gallbladder<br>[Epigastric] Stomach<br>[L. Hypochondriac] Part of the Diaphragm<br><br>[R. Lumbar] Ascending Colon of Large Intestine<br>[Umbilical] Transverse Colon of LI + Small Intestine<br>[L. Lumbar] Descending Colon of Large Intestine<br><br>[R. Iliac (Inguinal)] Cecum + Appendix<br>[Hypogastric (Pubic)] Urinary Bladder<br>[L. Iliac (Inguinal)] Initial Part of the Sigmoid Colon</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f8cca54e-0a4a-4f25-bcb1-fdd37627274c.jpg)
True or False: Involuntary movements of the GI tract are responsible by smooth muscle lining its organ walls
True
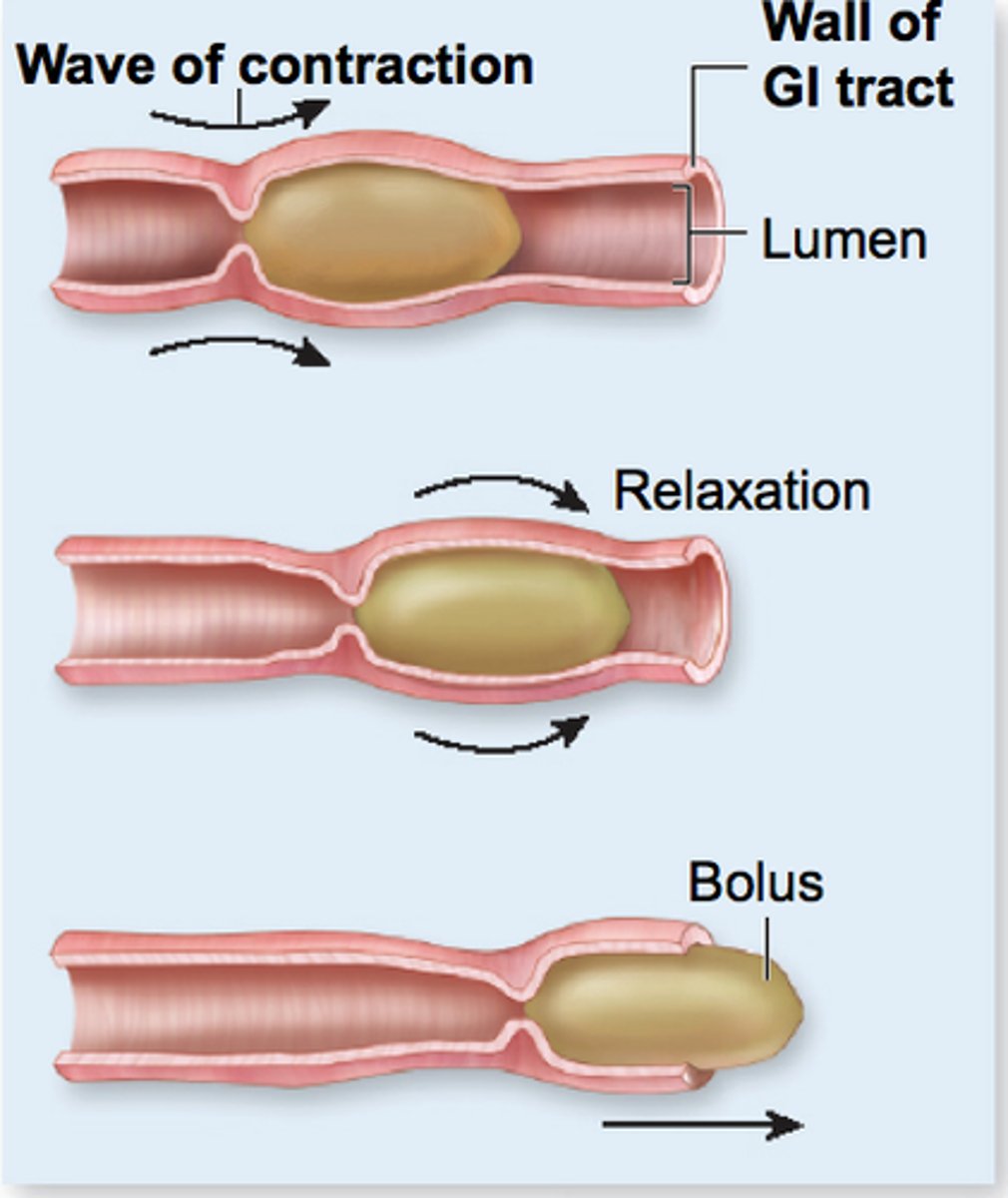
Peristalsis
- Adjacent segments of GI tract organs alternately contract + relax
- Moves food along the tract distally
- Occurs in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
Segmentation
- Nonadjacent segments of GI tract organs alternately contract + relax
- Moves food forward then backward to aid mechanical breakdown (food mixing and slow food propulsion occur)
- Occurs in the small intestine
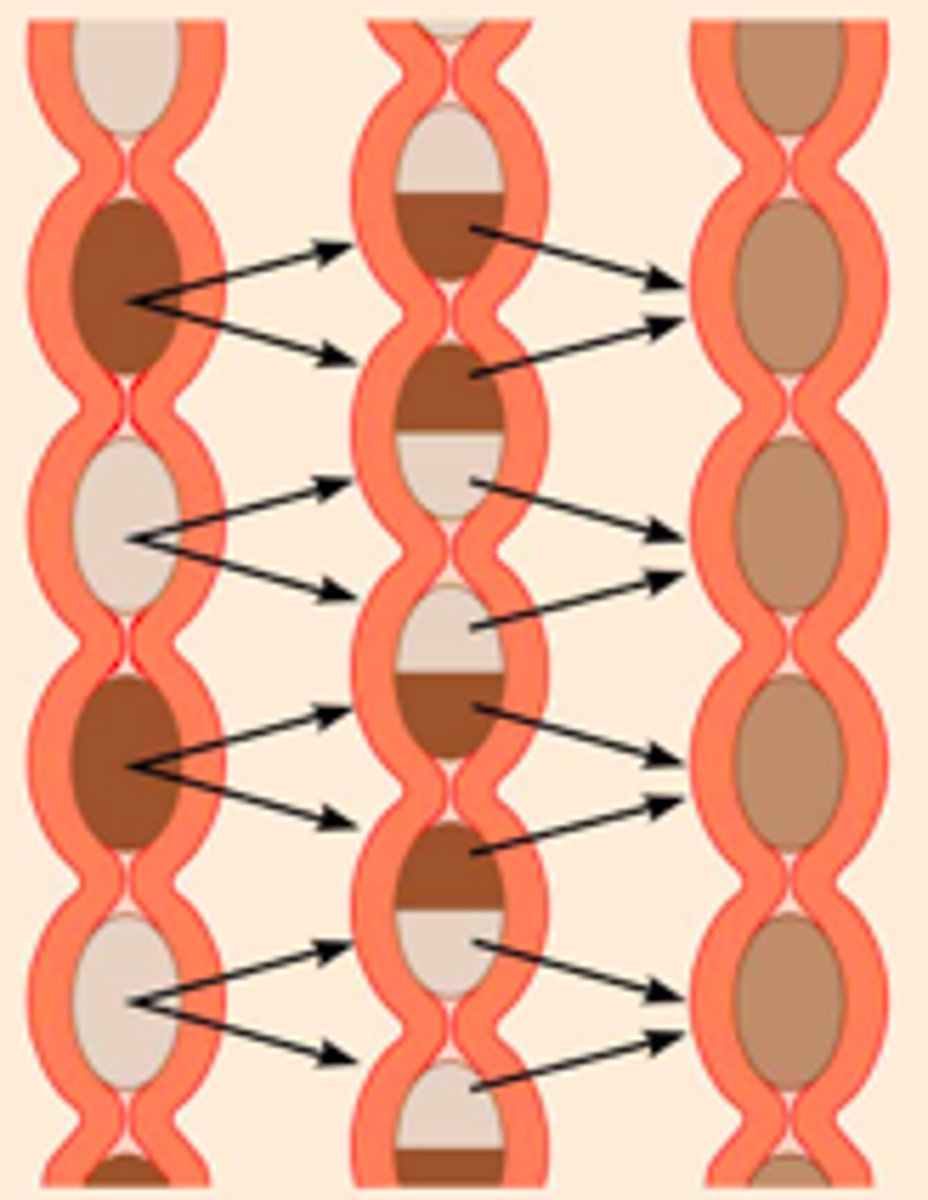
How many tissue layers line the walls of the GI tract organs?
4 layers*
*Serosa layer will be explained on a different card
Mucosa (Mucous Membrane)
- Lines the lumen w/ epithelium + lamina propria
- Contains muscularis mucosae (type of smooth muscle) that contracts to flick stuck food on the lumen
Submucosa
Highly elastic CT w/ vessels + nerves
Muscularis Externa
Circular/longitudinal smooth muscle responsible for peristalsis + segmentation
Serosa
- Visceral peritoneum
- Does NOT cover the esophagus because the organ is not within the abdominal cavity
Peritoneum
- Serous membrane of the abdominopelvic cavity
- Visceral layer + parietal layer + peritoneal cavity w/ serous fluid
Mesentery
- Fused double layer of peritoneum
- Functions to hold organs in place, store adipose (fat), and provide a route for vessels to/from other organs
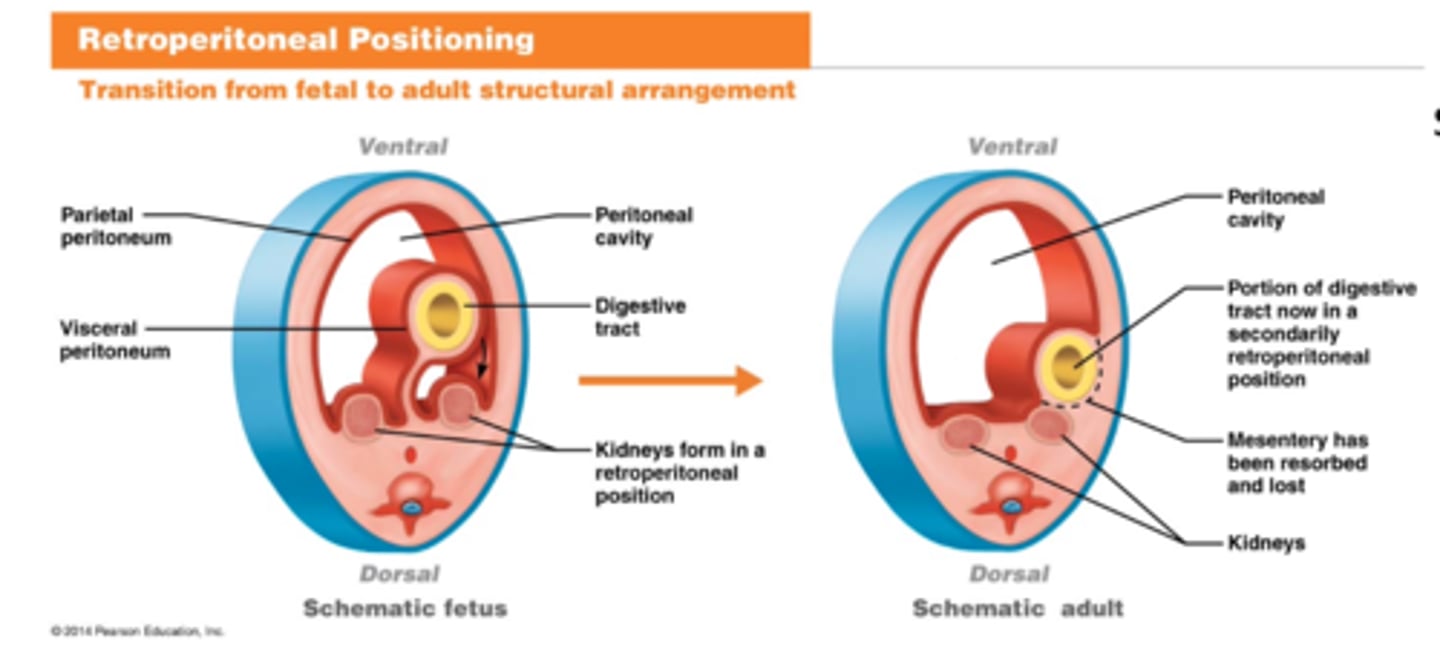
Retroperitoneal Positioning
Organs being pushed posteriorly (dorsal) during peritoneal development from a fetus to an adult
Intraperitoneal Organs
- Organs surrounded by peritoneum (most lay in abdominal cavity)
- Attached to body wall by mesenteries
Names of Ventral Mesenteries
(1) Falciform Ligament
(2) Lesser Omentum
Names of Dorsal Mesenteries
(1) Transverse Mesocolon
(2) Greater Omentum
(3) Mesentery Proper
(4) Sigmoid Mesocolon
Name All Intraperitoneal Organs w/ their Mesenteries
- Liver -> Falciform ligament + Lesser omentum
- Stomach -> Greater/Lesser omentum
- Ileum and Jejunum -> Mesentery proper
- Transverse Colon -> Transverse mesocolon
- Sigmoid Colon -> Sigmoid mesocolon
Secondarily Retroperitoneal Organs
- Organs that lay behind the peritoneal (abdominal) cavity
- Lacks a mesentery
Name All Retroperitoneal Organs
**These DO NOT have mesenteries
- Duodenum
- Ascending Colon
- Descending Colon
- Rectum
- Pancreas
Upper/Lower Lip
Pieces of tissue covering the oral cavity on the external surface
Oral Vestibule
Space between the lips and the external teeth
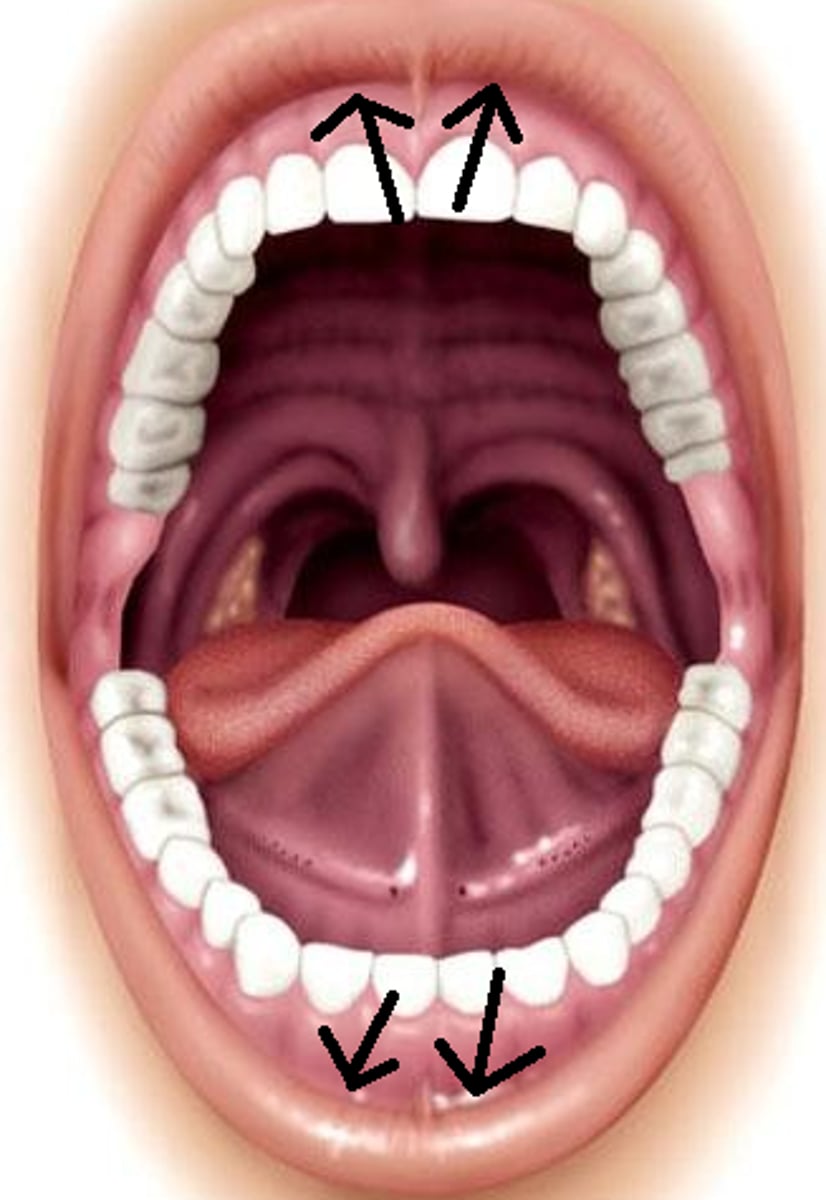
Oral Cavity
Inner space of the mouth
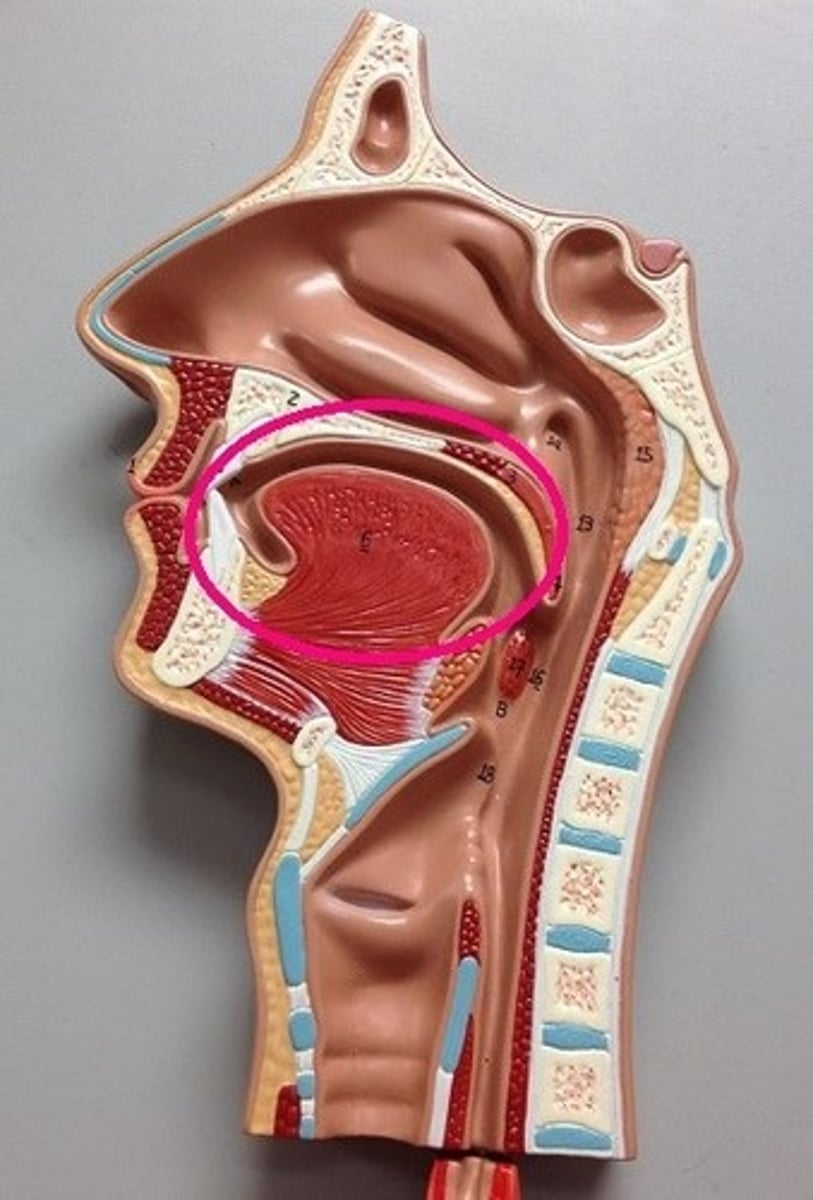
Gingivae (Gums)
Helps secure the teeth in place
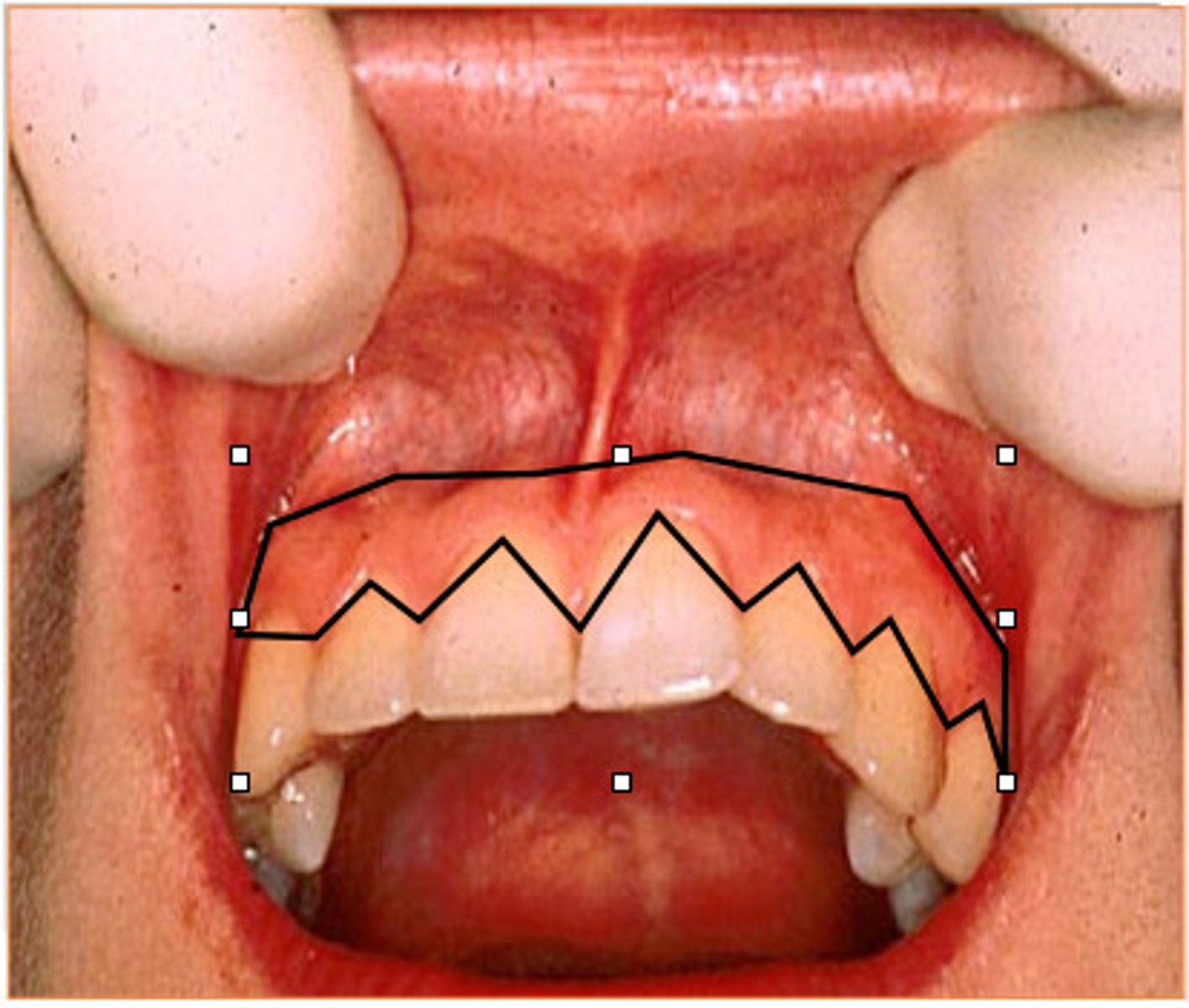
Tongue
- Forms the floor of the oral cavity
- Aids in speech, mastication, and movement of materials
Lingual Frenulum
- Stalk of tissue attaching the tongue to the floor of the mouth
- Takes part in tongue movement for pronunciation
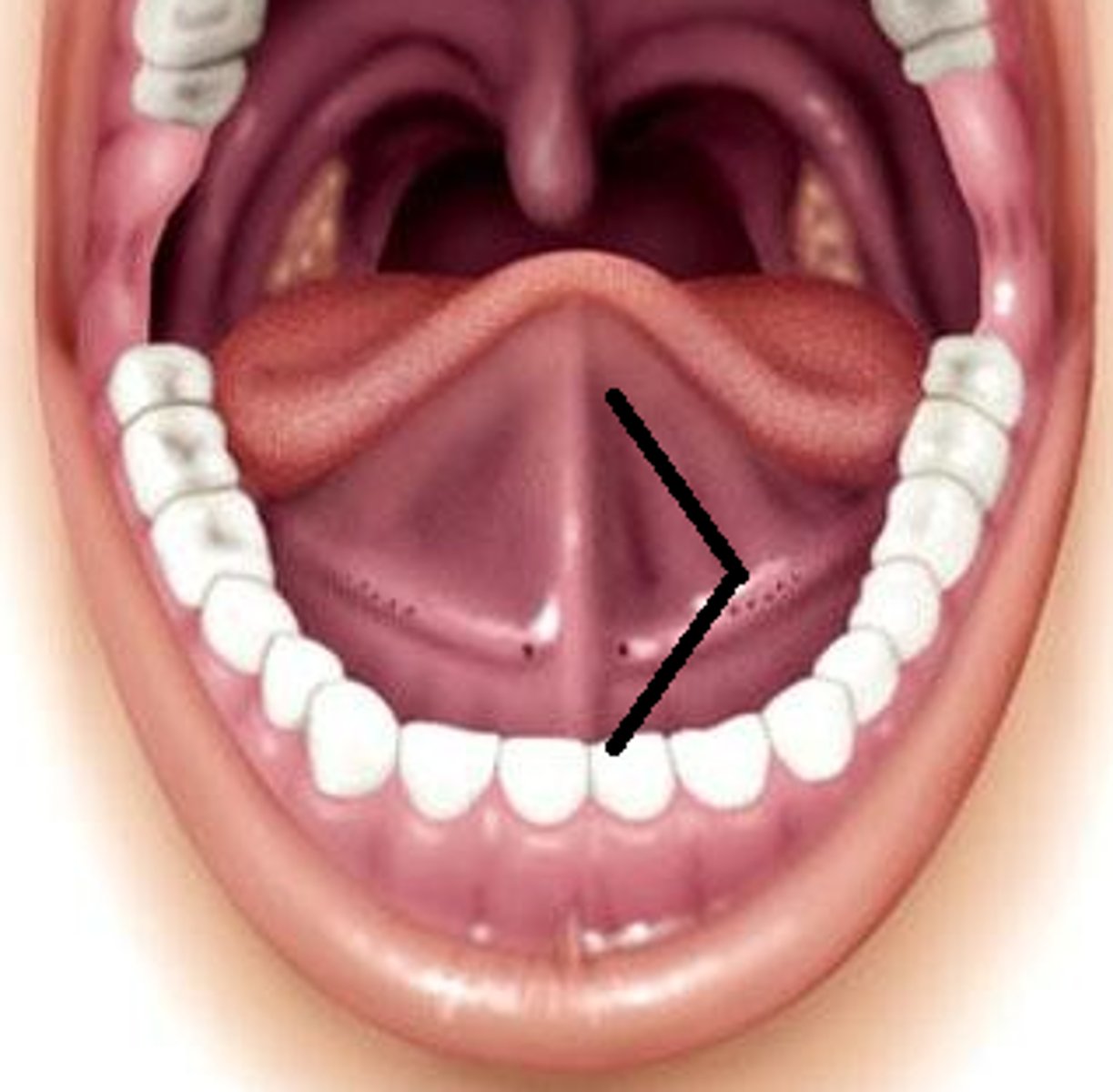
Superior/Inferior Frenulum
Attaches the lips to the gums
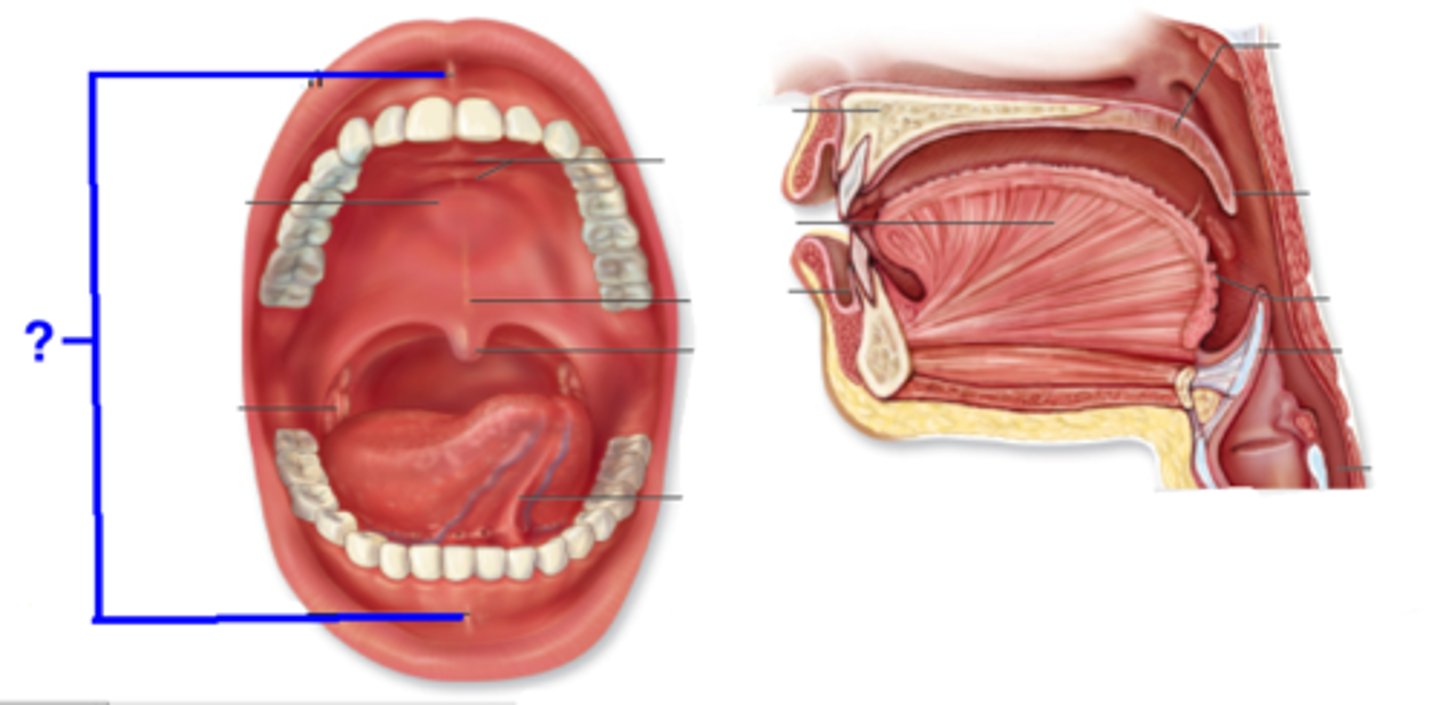
Hard Palate
Made of bone to aid in mechanical breakdown of food
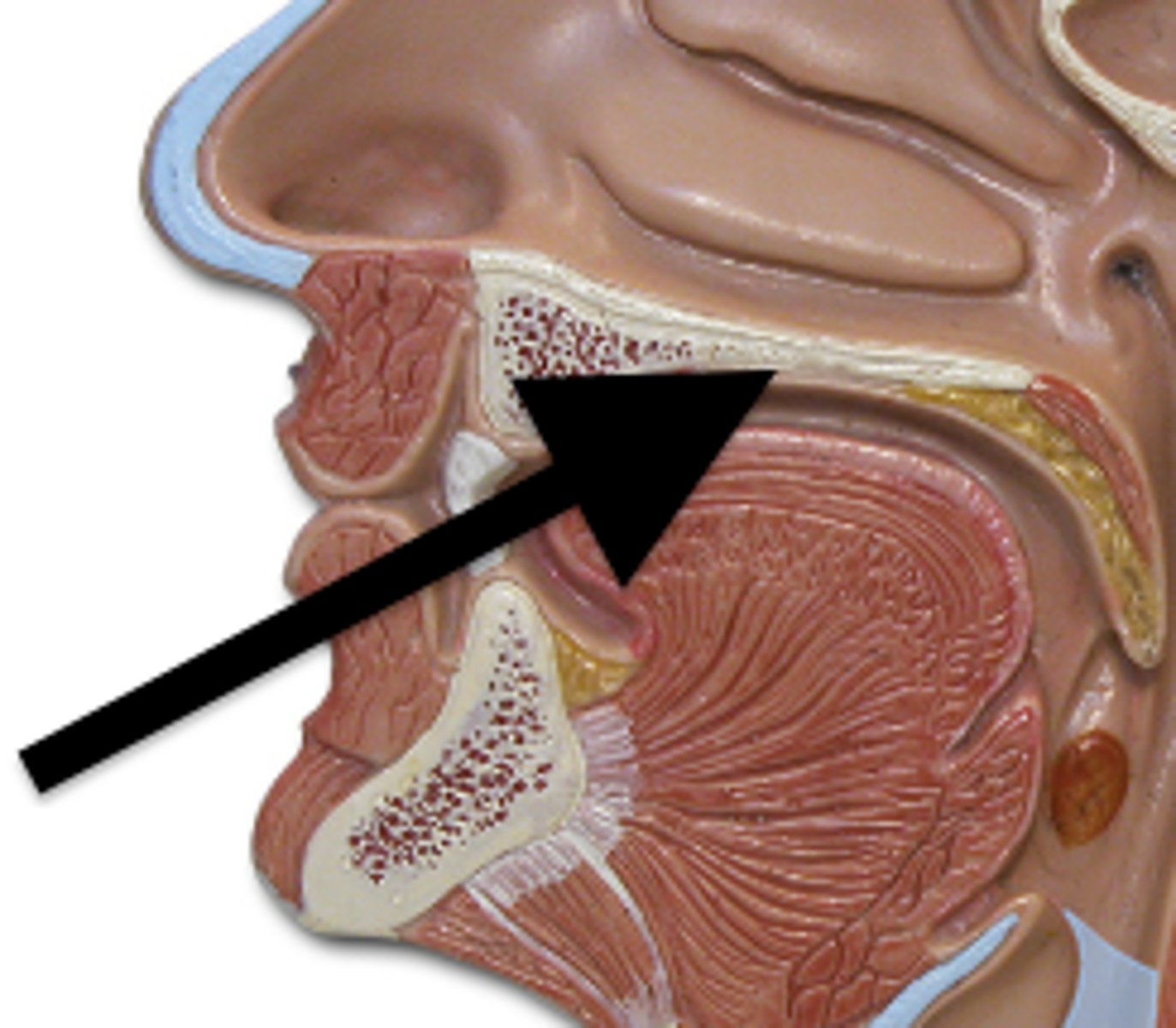
Soft Palate
Separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity
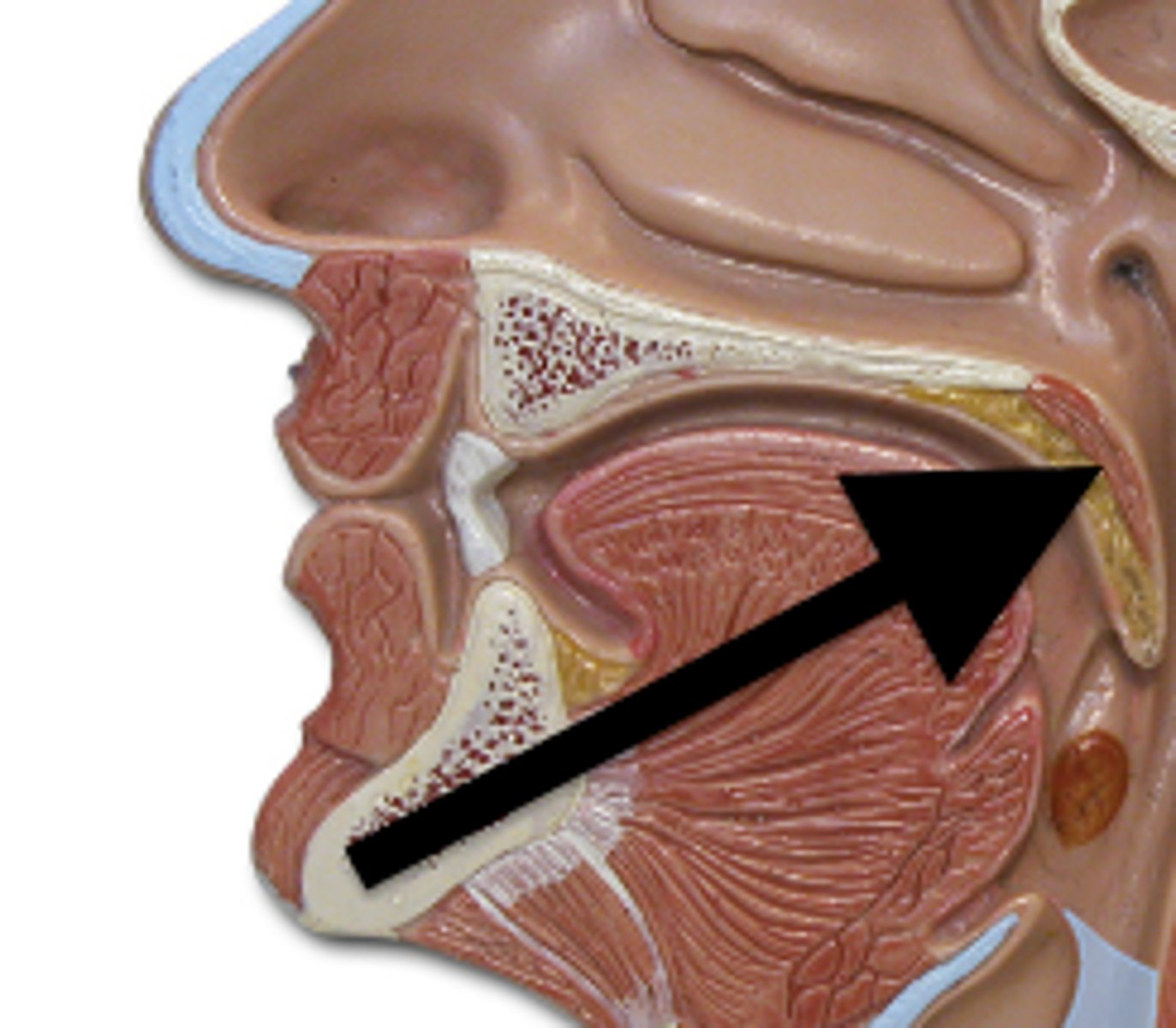
Uvula
Extension of the soft palate responsible for gag-reflexes
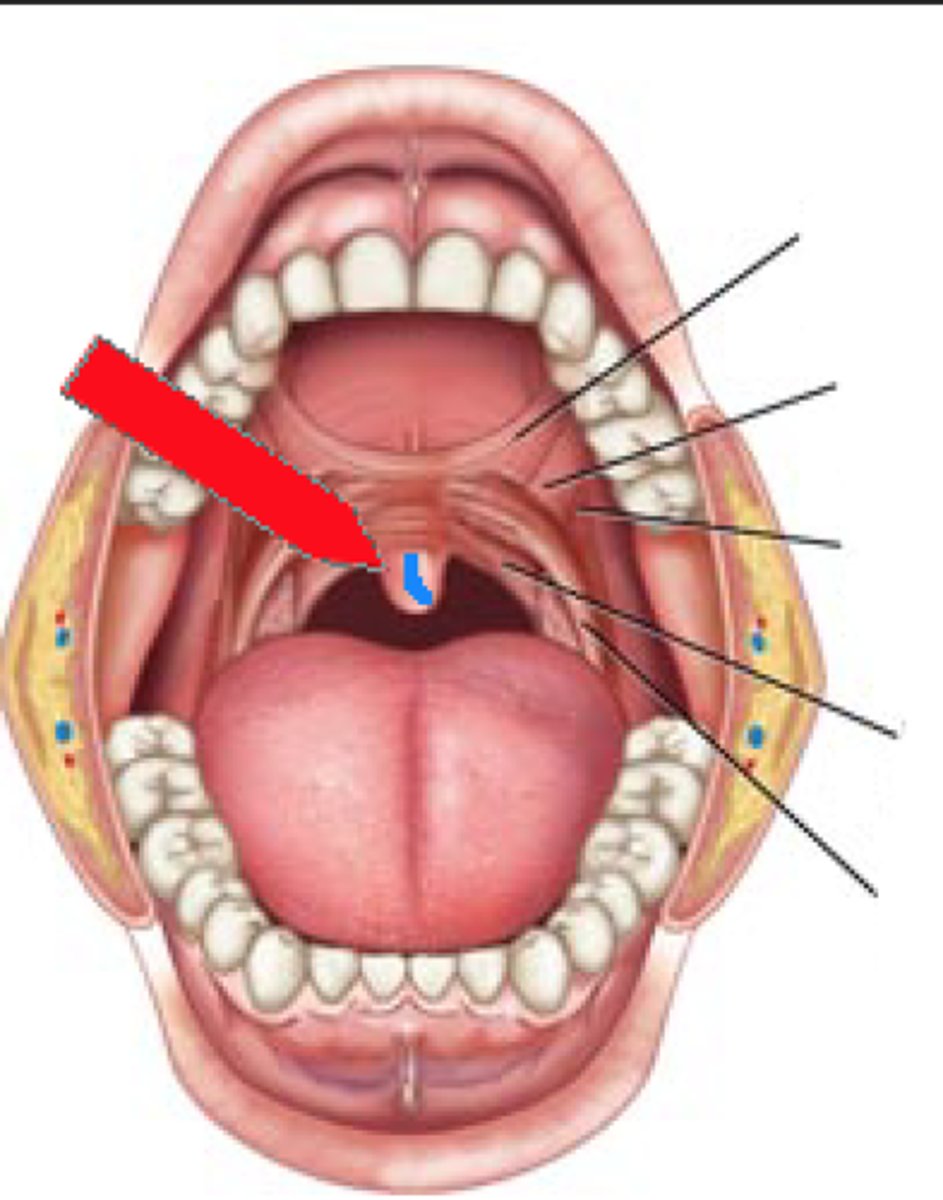
Palatoglossal + Palatopharyngeal Arches
Structures to help attach the soft palate to the tongue
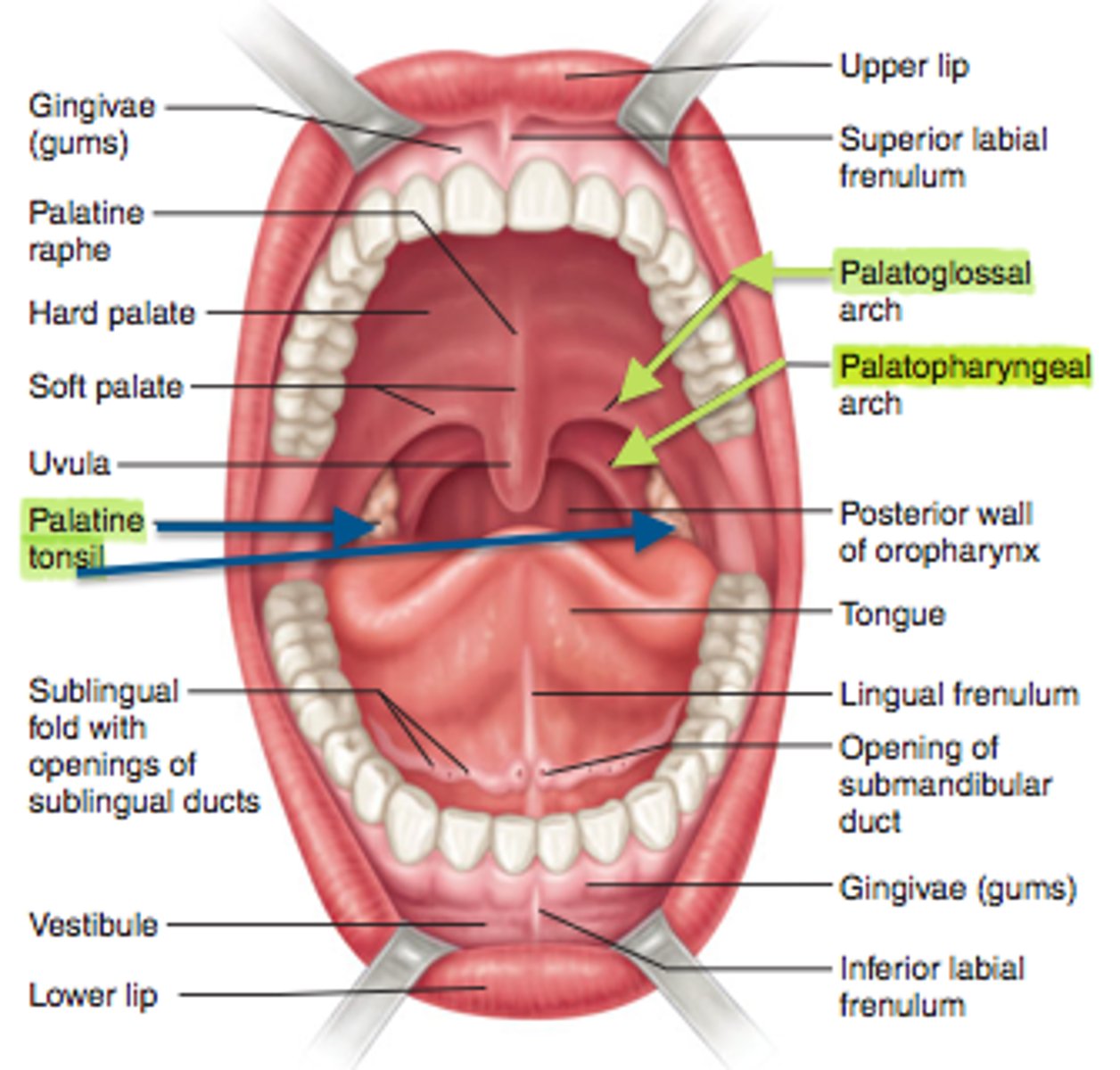
3 Types of Salivary Glands
*NOT part of the GI Tract
**All contain ducts that secrete salivary enzymes into the oral cavity
(1) Sublingual Gland
(2) Submandibular Gland
(3) Parotid Gland
Sublingual Gland
Located directly under the tongue
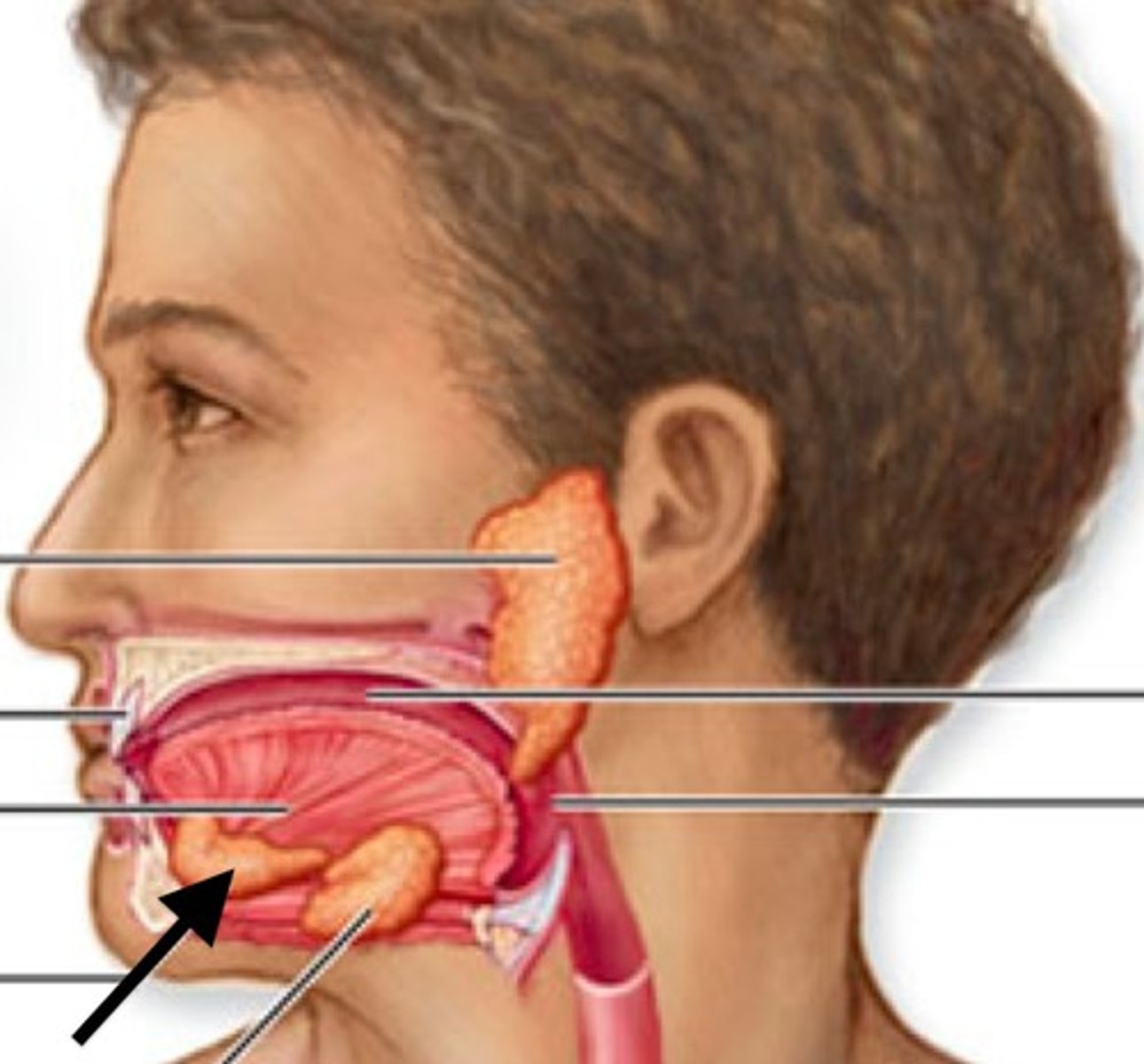
Submandibular Gland
Located within the mandible
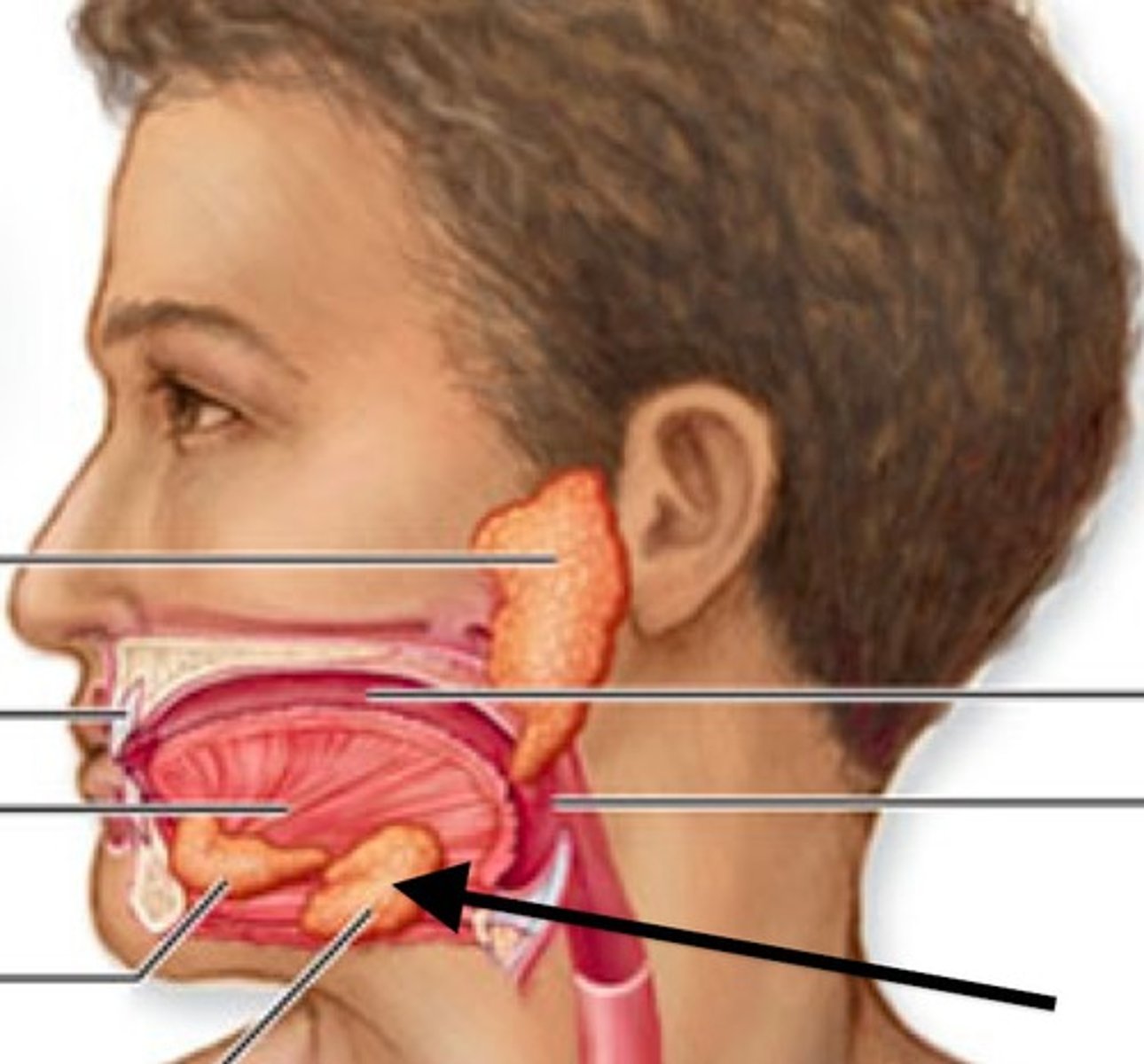
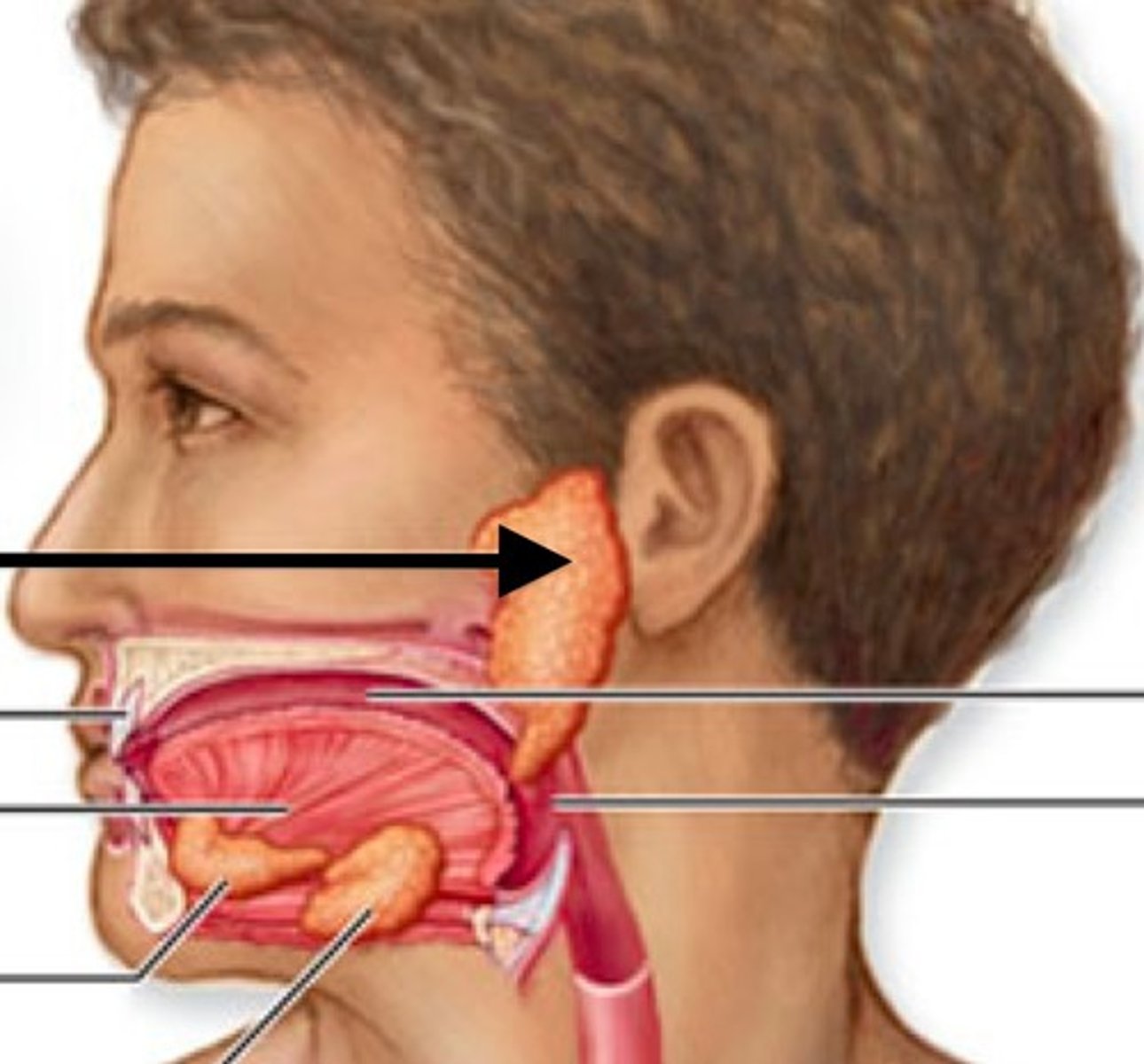
Parotid Gland
Largest salivary gland located posterior to the cheek
Filiform Papilla
- Helps the tongue grab onto food
- NO taste buds
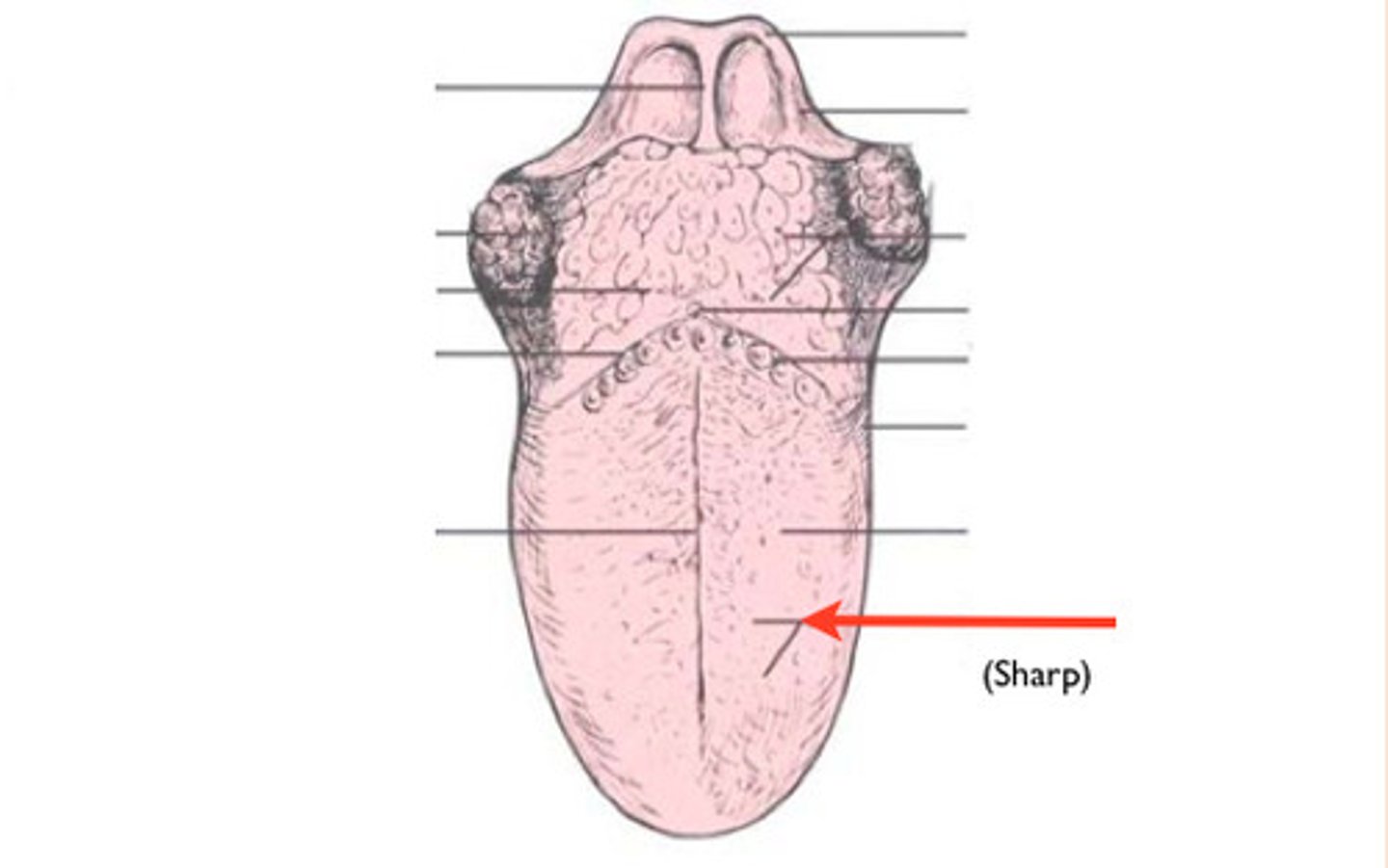
Fungiform Papilla
Mushroom-shaped bumps on the tongue that CONTAIN taste buds
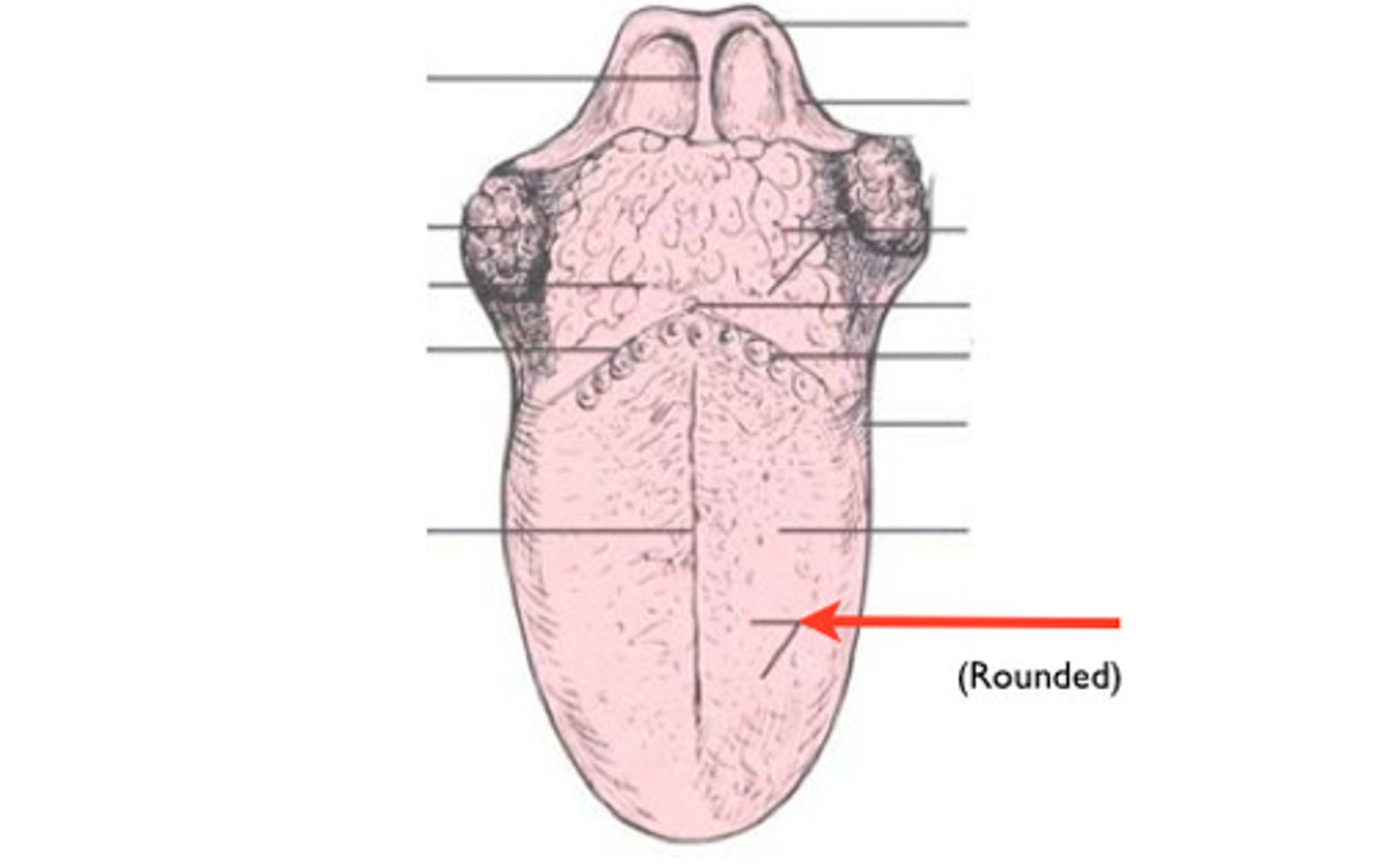
Medial Sulcus
Groove separating the 2 sides of the tongue (dorsum)
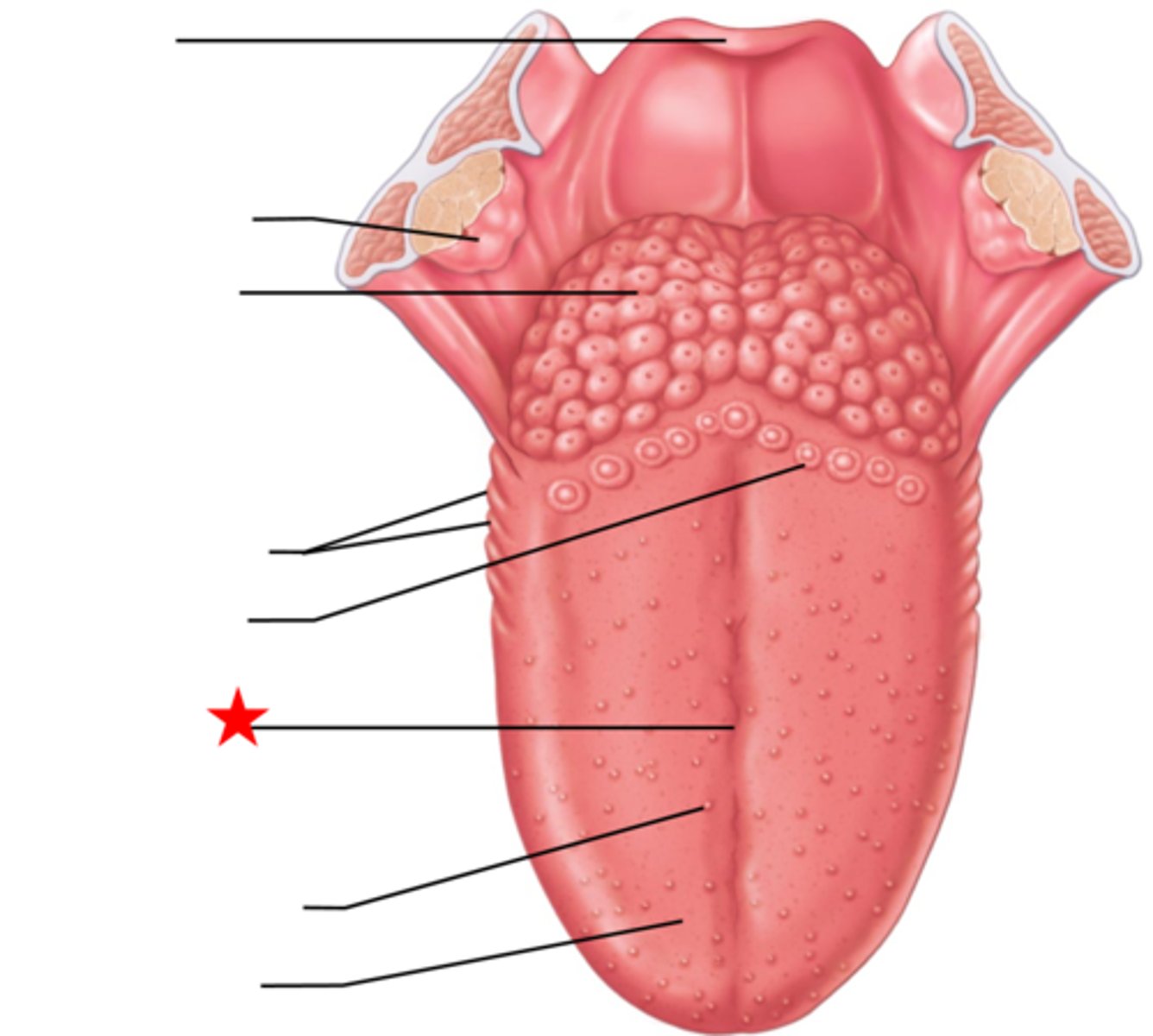
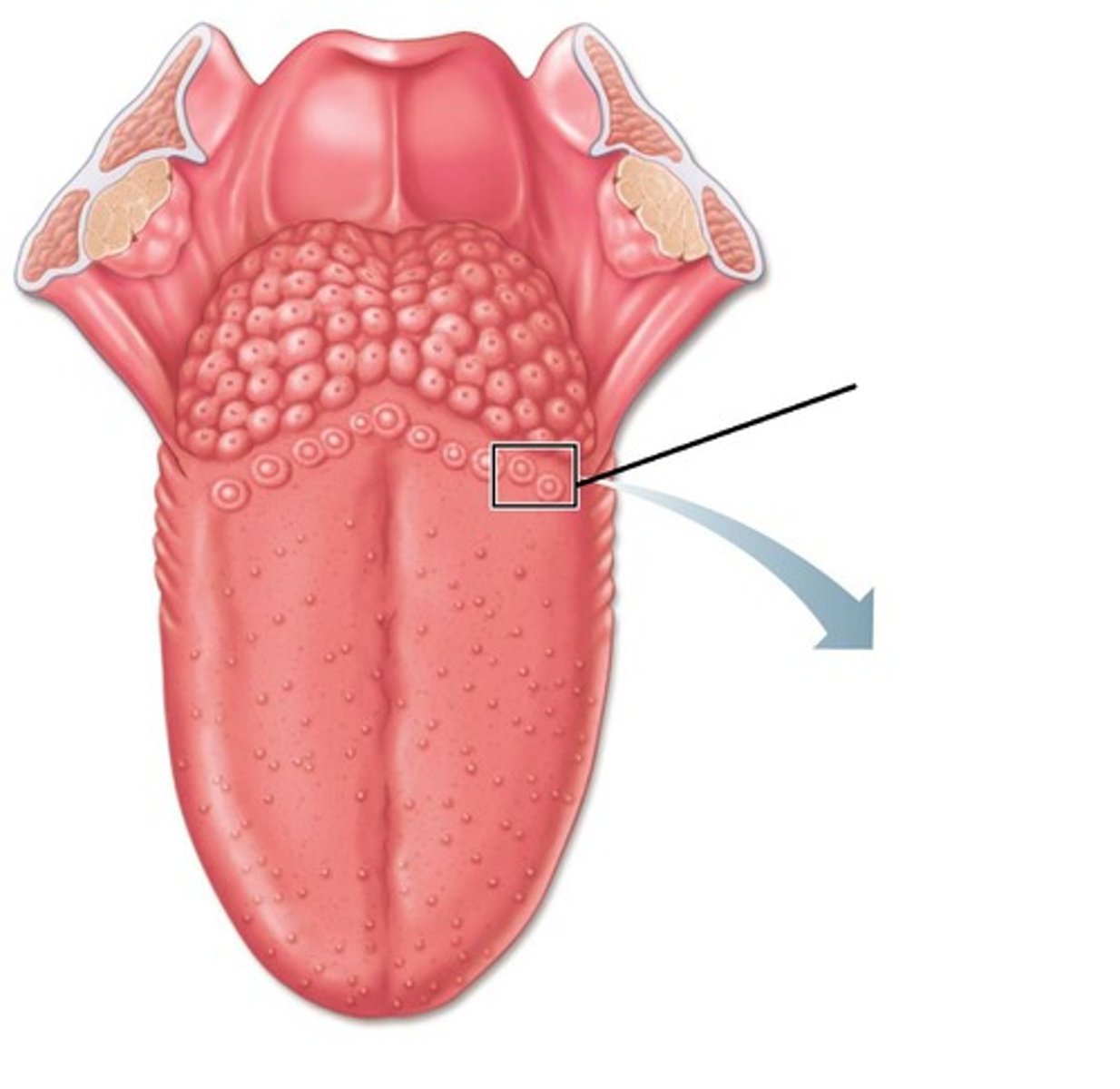
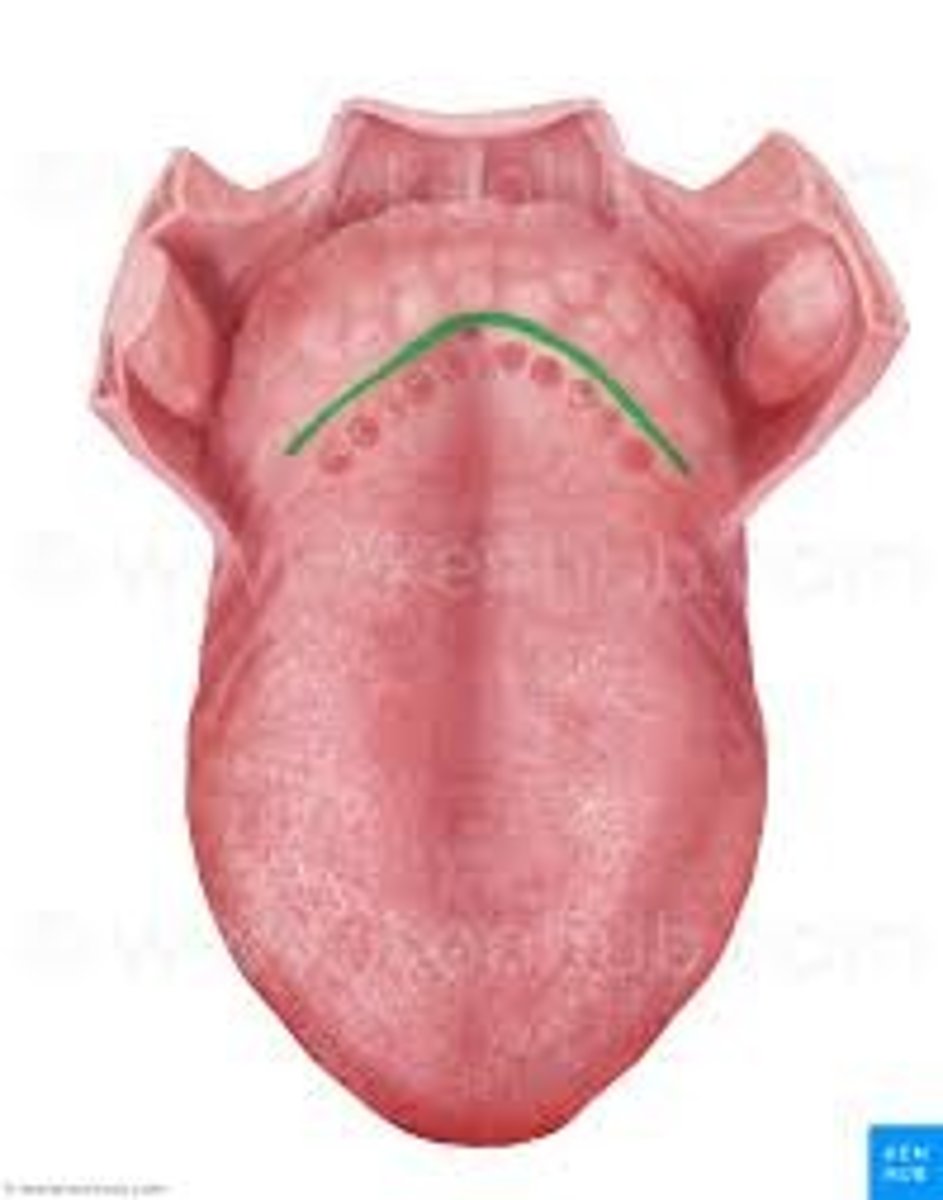
Vallate Papilla
Only found at the posterior end of the tongue and CONTAINS taste buds
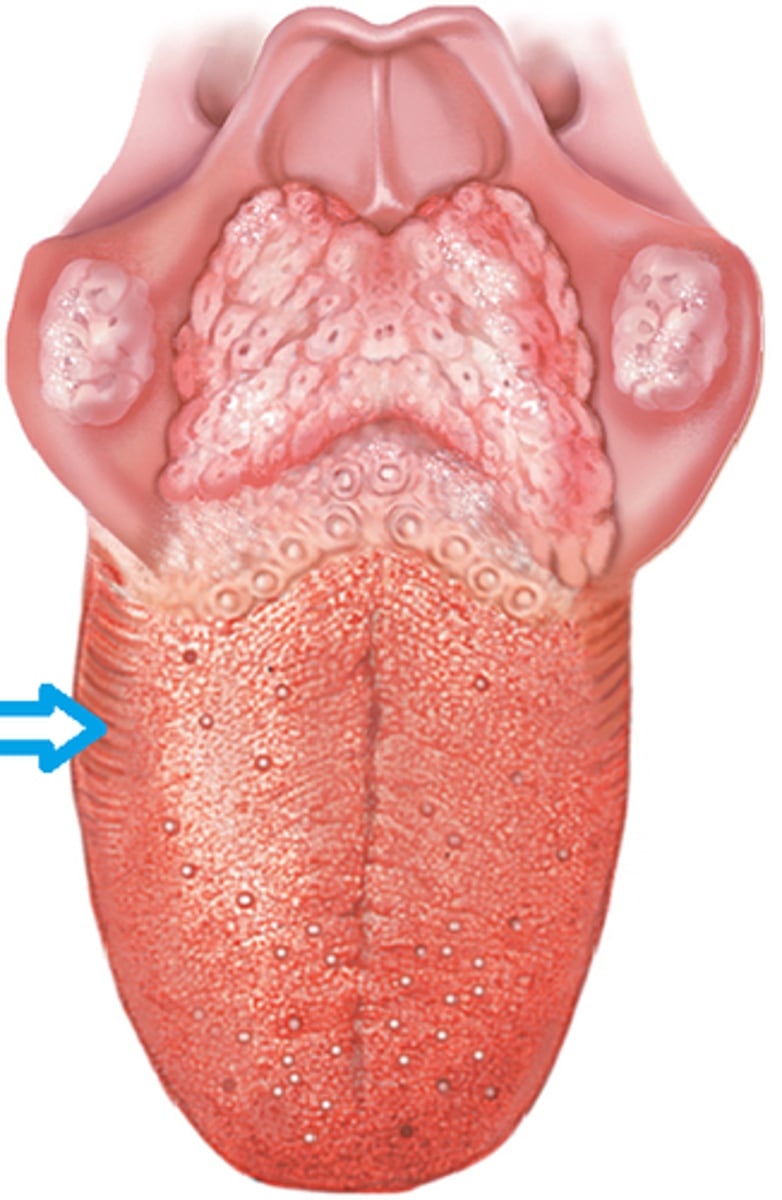
Foliate Papilla
-Ridges found along the posterior side of the tongue
- NO taste buds
Terminal Sulcus
Groove that defines the tongue from the pharynx
Internal Muscles of the Tongue
- Fascicles of muscles running in multiple directions to change the tongue shape
- NOT attached to bones
External Muscles of the Tongue
- Muscles responsible for changing tongue position
- Attached to bones of the skull + hyoid
- Ex: Genioglossus
Pharynx
- Passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
- Muscles are used to contract in sequence to complete the swallowing process
Suprahyoid Muscles
- Located above the hyoid bone
- Lifts the larynx to position it under the epiglottis
Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscles
Pushes food into the esophagus
Infrahyoid Muscles
- Located below the hyoid bone
- Returns the larynx back to its original position
Esophagus
- Collapsible muscular tube extending from the pharynx to the stomach
- Contains NO serosa
Histology of the Esophagus
[Mucosa] Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
[Submucosa] Mucous Glands
[Muscularis Externa] Skeletal to Smooth Muscles
Stomach
- Widest part of the GI Tract
- Temporarily stores food and churns it into chyme
- First site of protein breakdown
Fundus of Stomach
Dome-shaped part
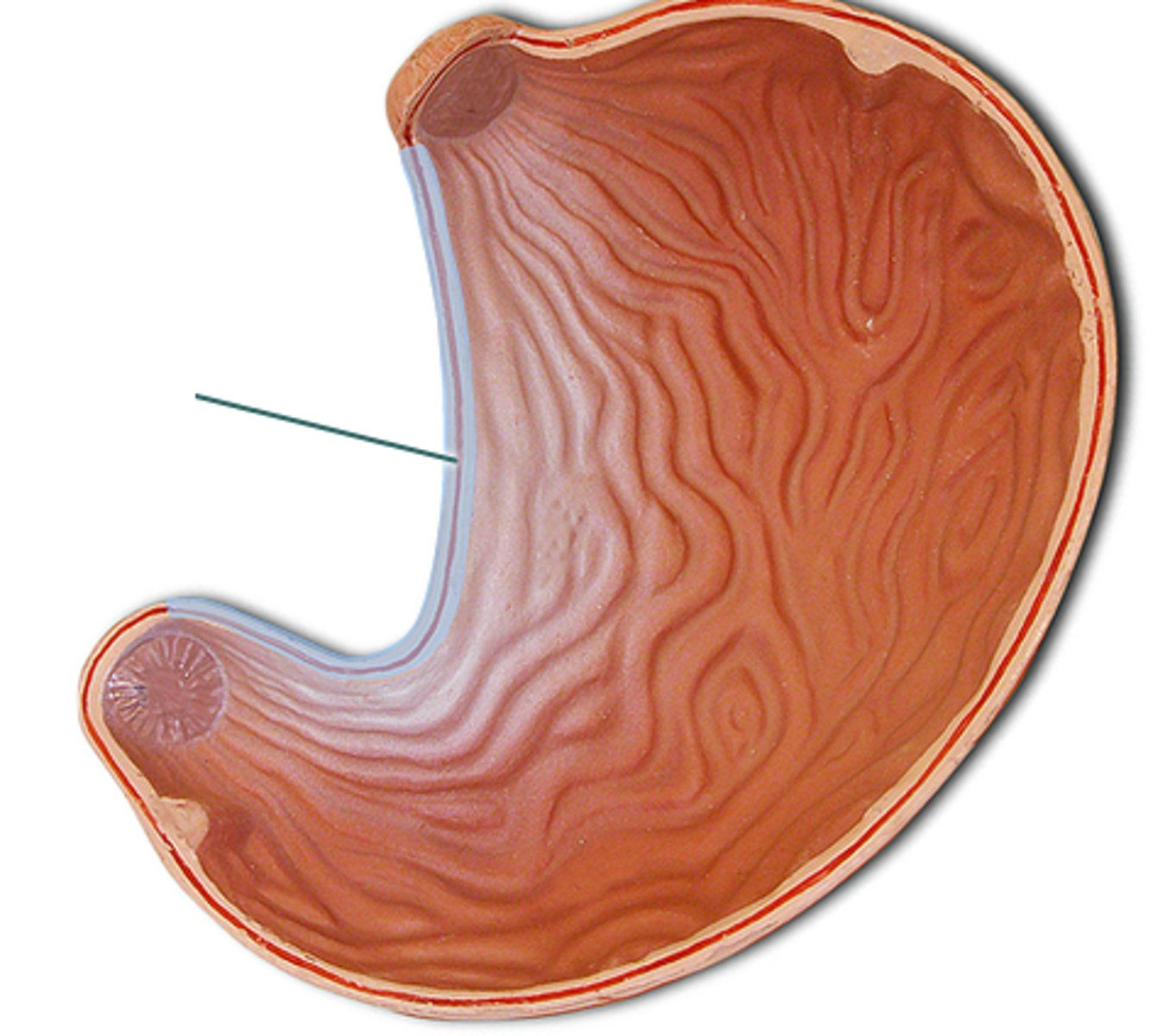
Lesser Curvature of Stomach
Concave surface of the stomach
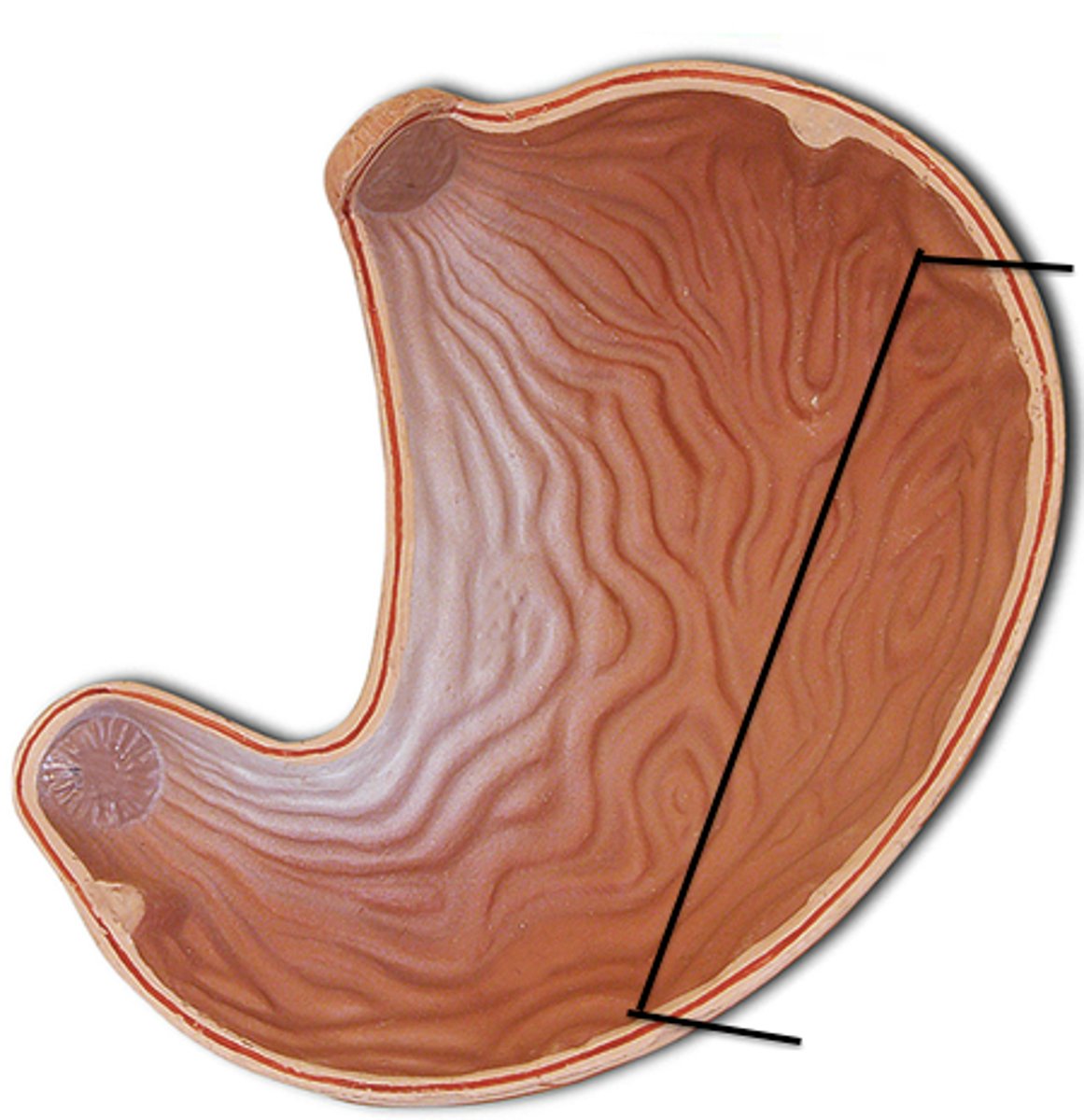
Greater Curvature of Stomach
Convex surface of the stomach
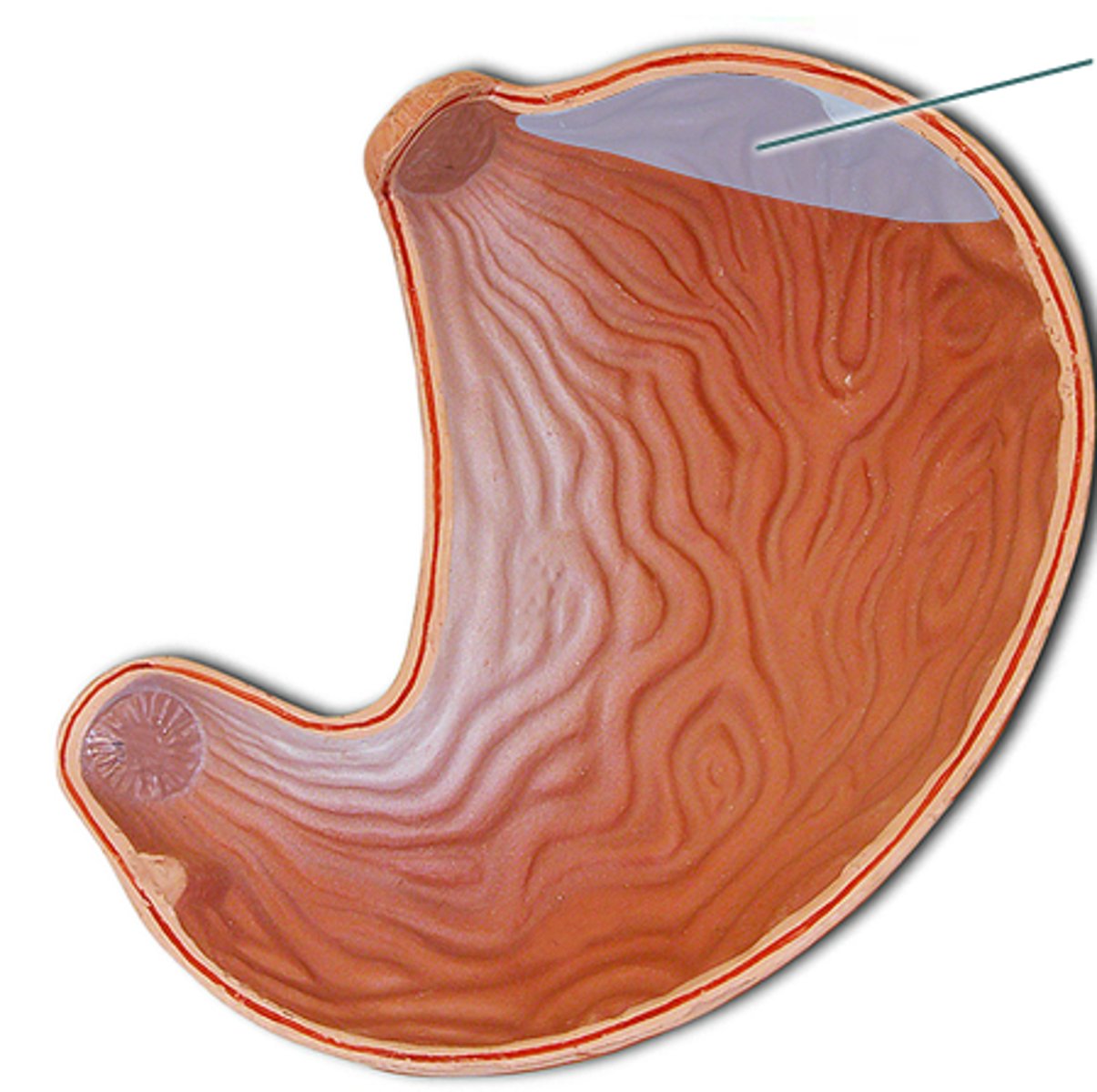
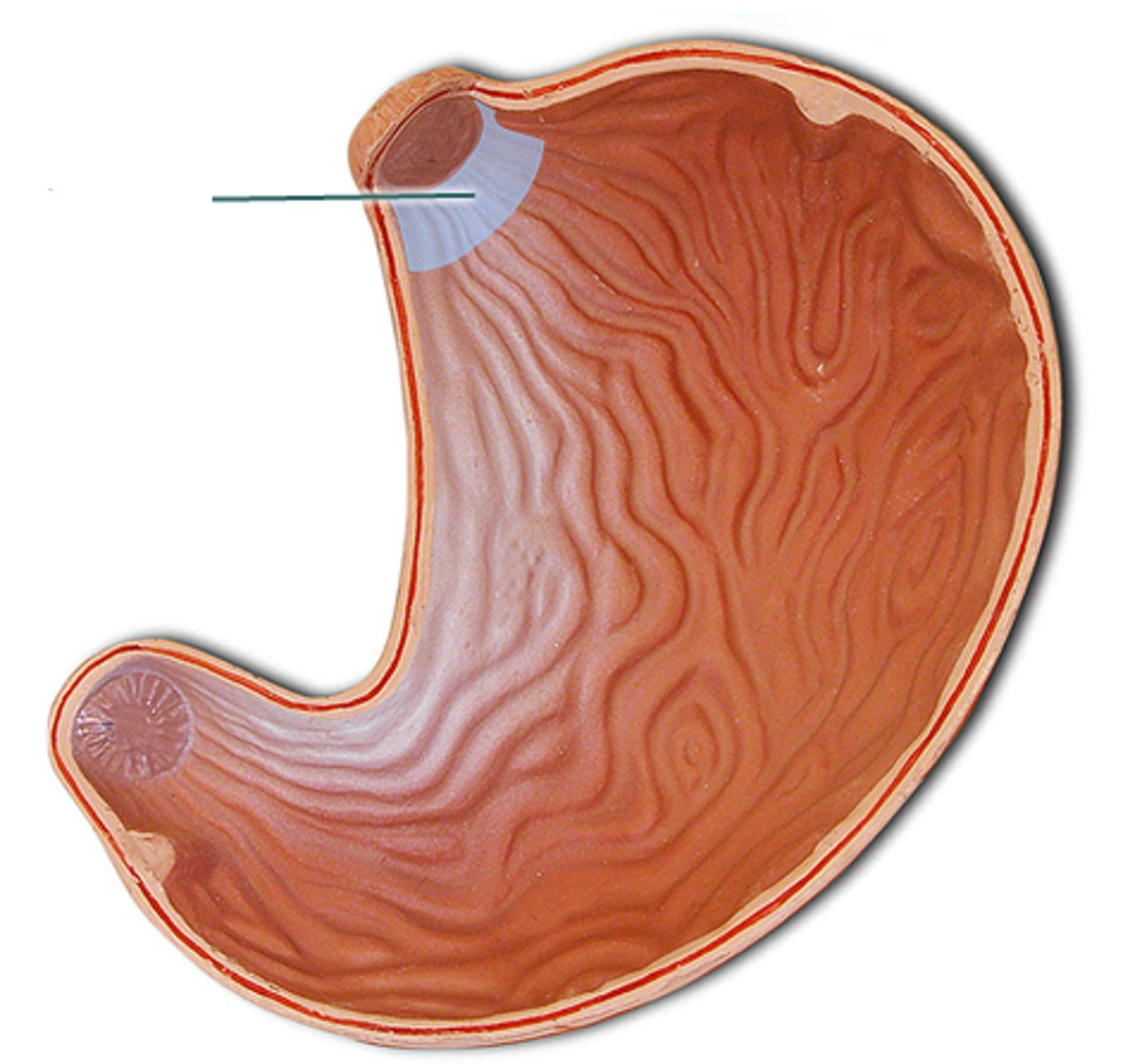
Cardia of Stomach
Tapering region where the esophagus transitions into the stomach
3 Layers of Muscularis Externa in Stomach
[Superficial to Deep]
(1) Longitudinal
(2) Circular
(3) Oblique
![<p>[Superficial to Deep]<br><br>(1) Longitudinal<br>(2) Circular<br>(3) Oblique</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49658664-b0f5-4b86-82f5-fa2ae606354d.jpg)
Tapering Regions of Stomach to Small Intestine
Pyloric Antrum -> Pyloric Canal -> Pyloris (contains the pyloric sphincter)
Gastric Pit
Superficial layer containing only surface epithelium (mucous cells)
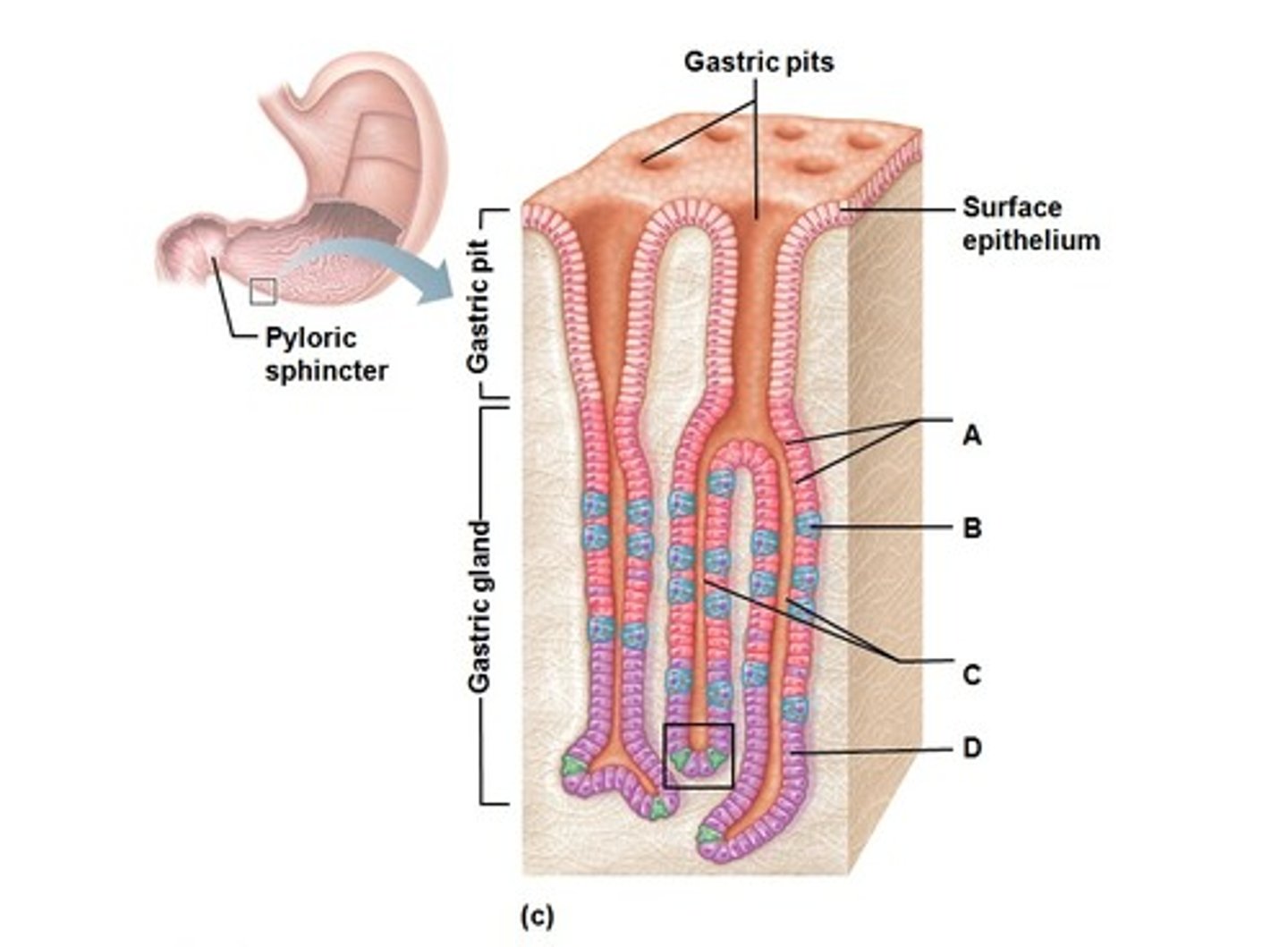
Gastric Gland
Deep to the gastric pit containing multiple cells + reaction sites
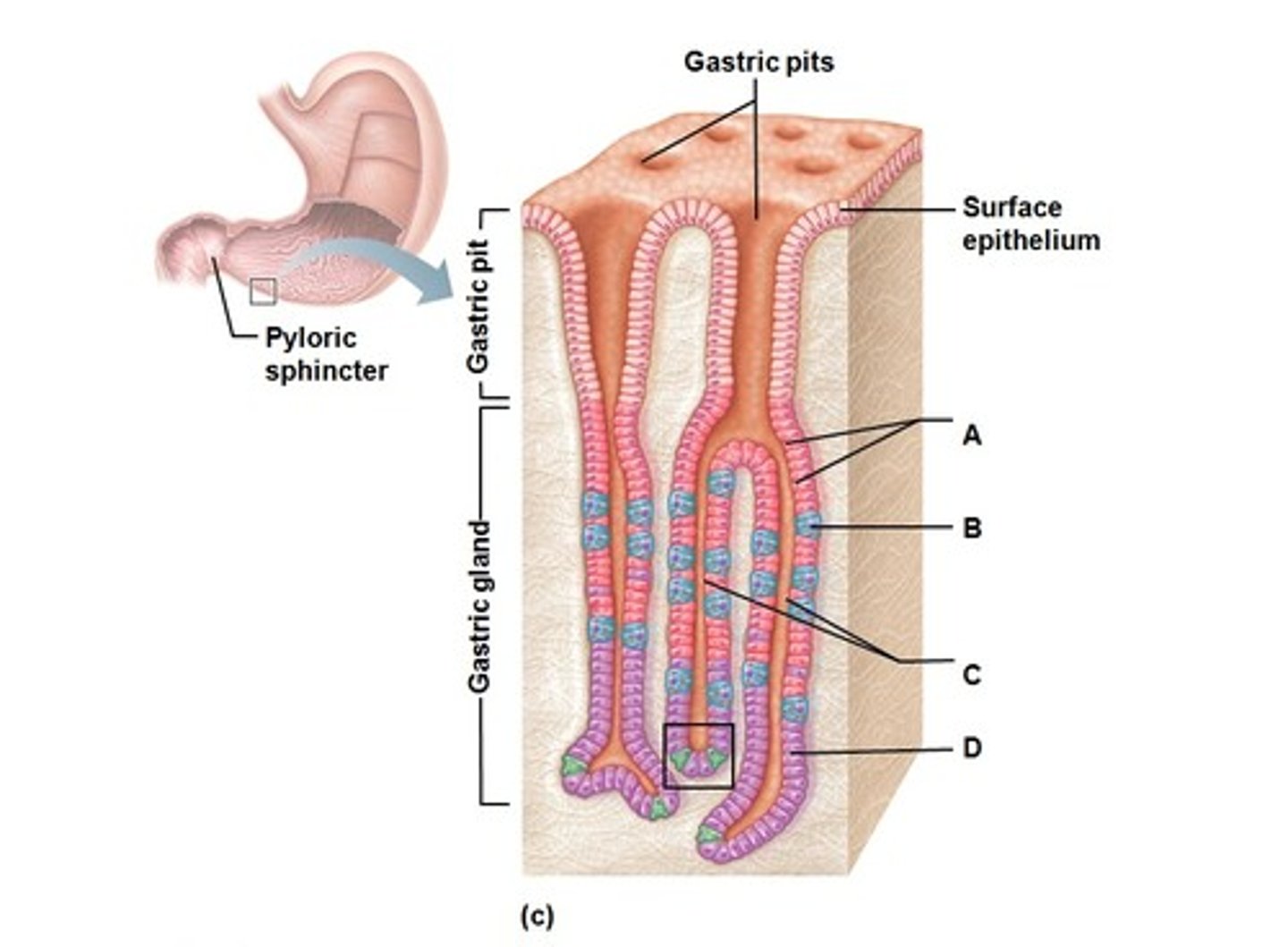
Mucous Cells of Stomach
Secretes mucous to protect stomach linings
Mucous Neck Cells
Also secretes mucous into the stomach
Parietal Cells
Produces HCl by releasing H+ and Cl- into the lumen
Chief Cells
Secretes lipase (breaks down fats/lipids) and pepsinogen (interacts with HCl to form a functional enzyme)
Pepsinogen + HCl -> Pepsin (breaks down proteins)
Enteroendocrine Cells
Releases gastrin hormones to signal release of HCl from parietal cells
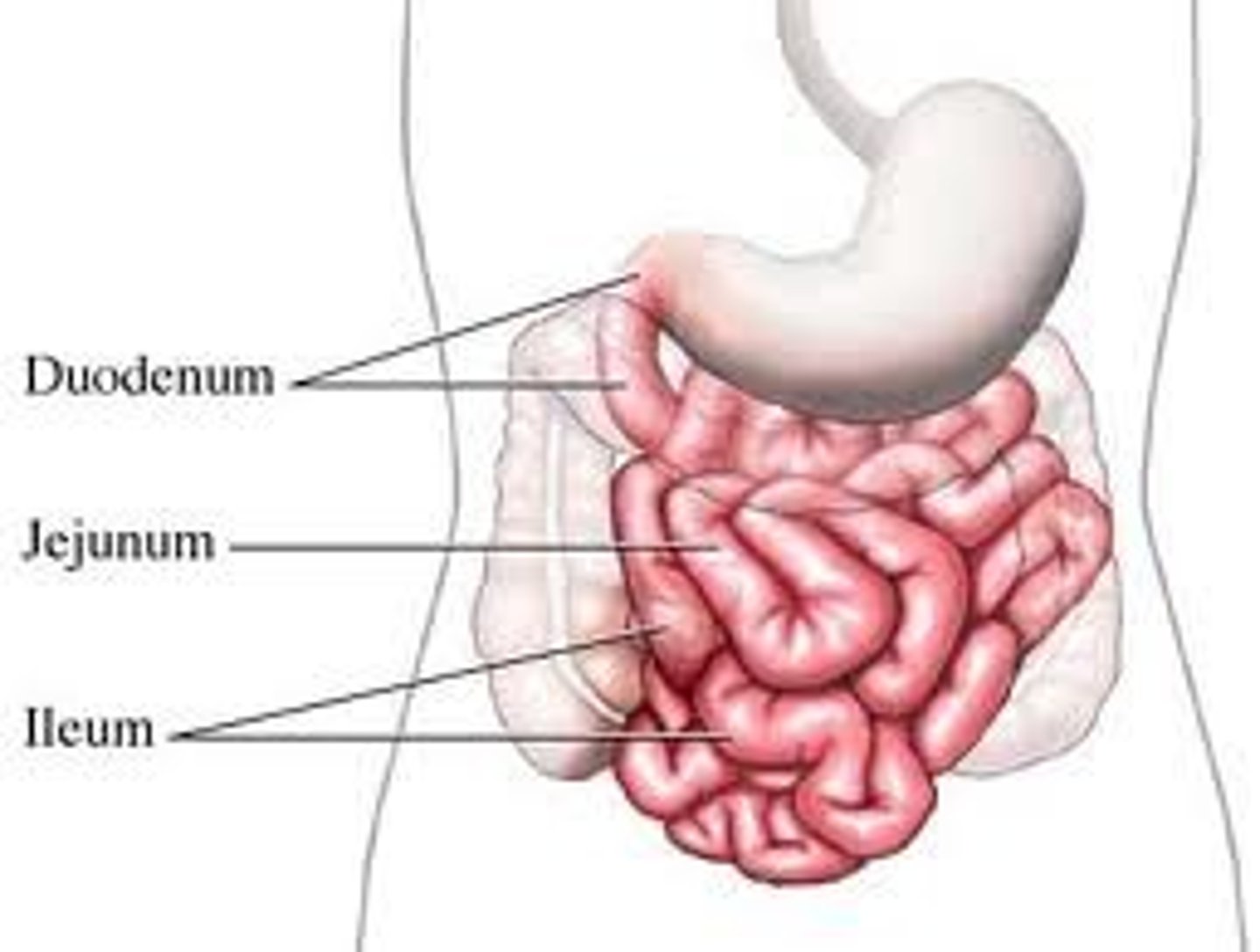
Small Intestine
- Largest part of the GI Tract
- Site of most enzymatic digestion + nutrient absorption
3 Regions of the Small Intestine
(1) Duodenum -> Area of nutrient absorption when chyme initially enters through here
(2) Jejunum
(3) Ileum
Plicae Circulares
- Circular folds that are permanent/nonexpandable (unlike rugae)
- Increases surface area for food parts to hit against the lumen for maximum absorption
Villi of Small Intestine
- Individual folds on the surface of the lumen that can be seen with the naked eye
- Made of epithelial cells and contain microvilli
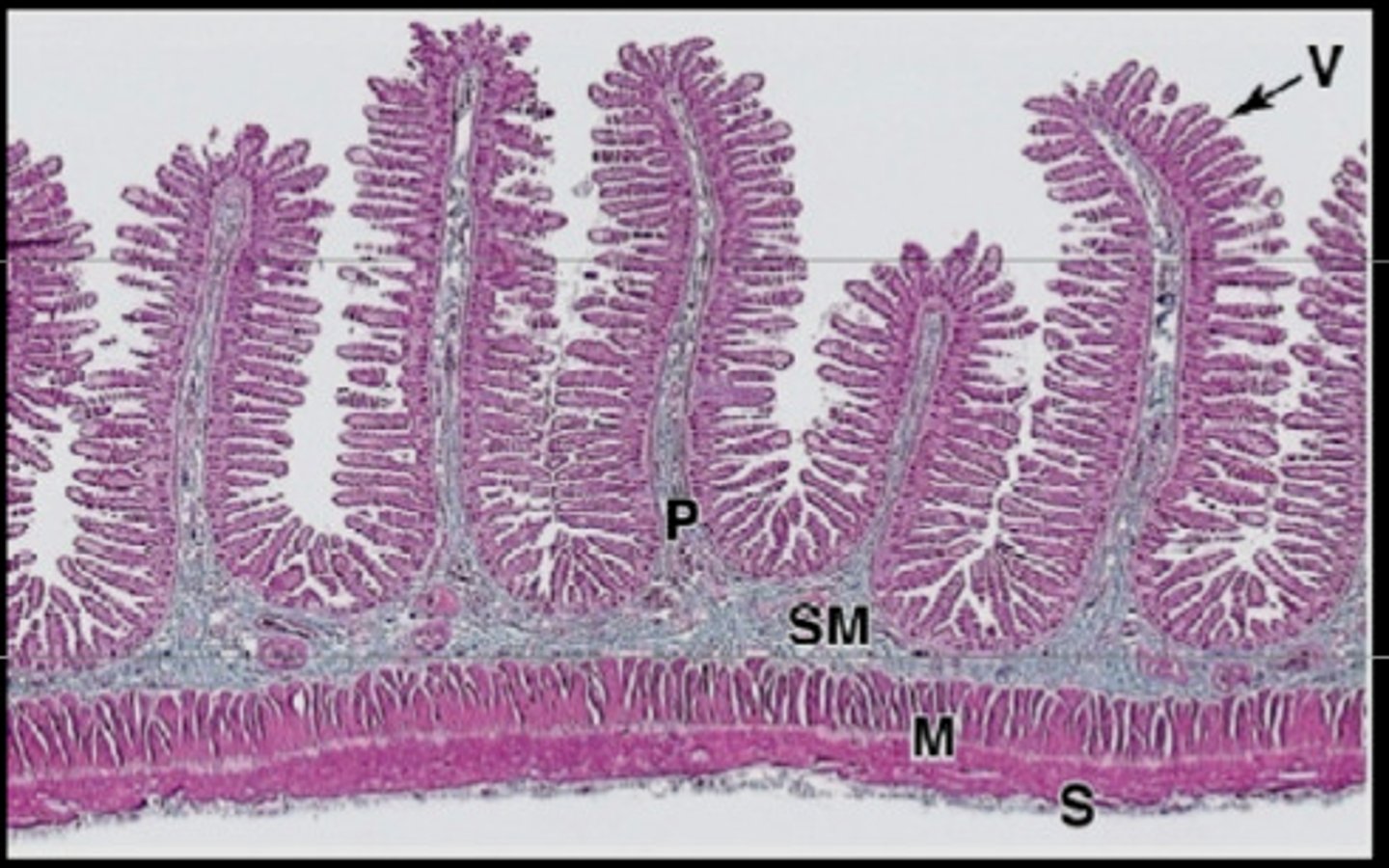
Components of the Villi w/ Description
- Lacteal -> Absorbs fat nutrients
- Blood Capillaries -> Absorbs carb/protein nutrients
- Goblet Cell -> Produces mucous for lubrication of SI
- Intestinal Crypt -> Hollow dip into the villus
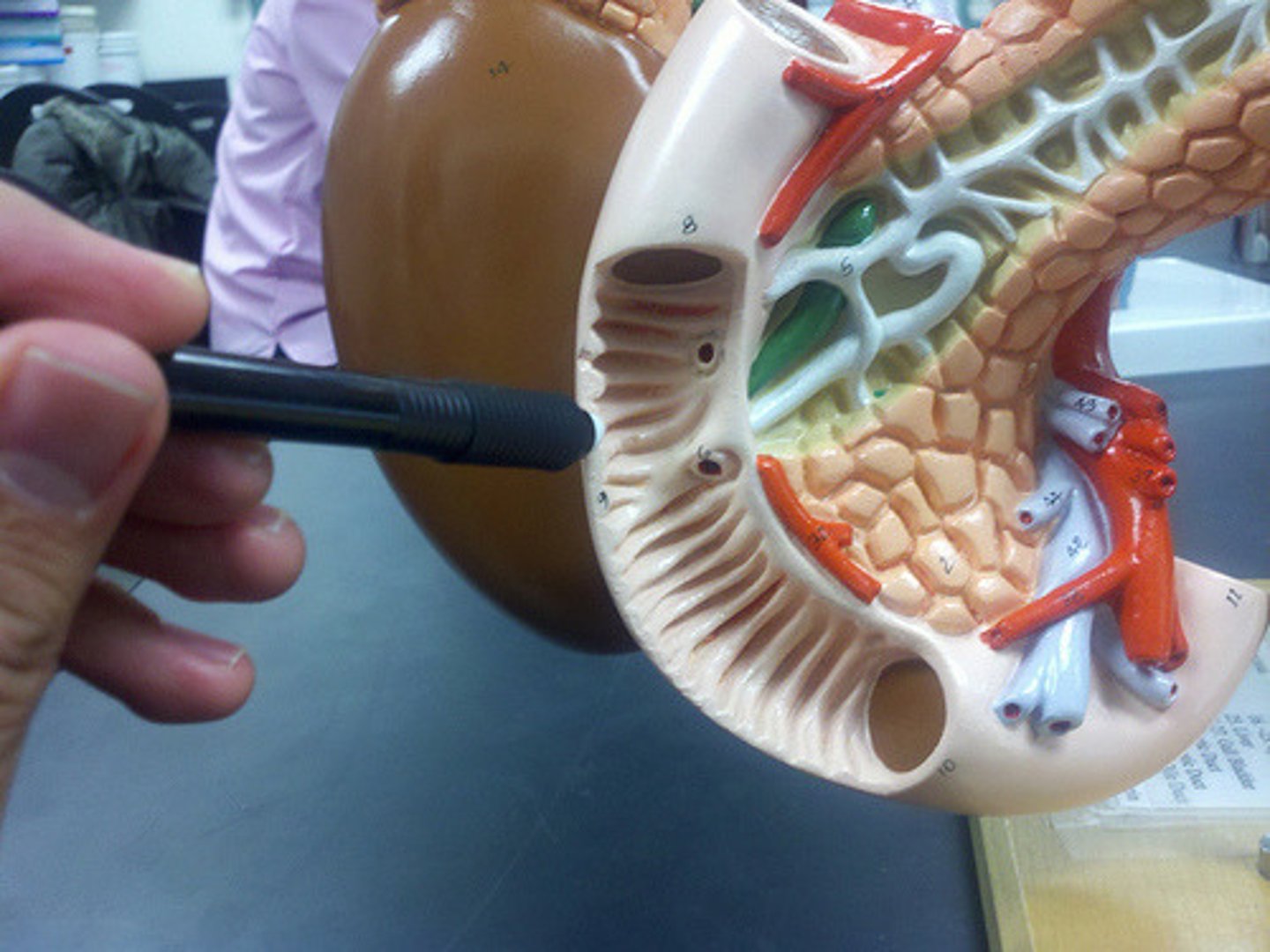
Ducts of the Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
[Liver] Right/Left Hepatic Duct -> Common Hepatic Duct -> Common Bile Duct
[Pancreas] Pancreatic Duct
[Gallbladder] Cystic Duct + Common Hepatic Duct -> Common Bile Duct
![<p>[Liver] Right/Left Hepatic Duct -> Common Hepatic Duct -> Common Bile Duct<br><br>[Pancreas] Pancreatic Duct<br><br>[Gallbladder] Cystic Duct + Common Hepatic Duct -> Common Bile Duct</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a6e93693-6093-41c6-bab4-07dd109126ce.jpg)
Major Duodenal Papilla
- Mound where ducts secrete enzymes into the duodenum
- Common Bile Duct + Pancreatic Duct join up here
Large Intestine (Colon)
- Receives undigested food from the small intestine
- Absorbs water + electrolytes
- Passes feces out of the GI tract w/ mass peristaltic movement (one big push) rather than constant peristalsis
Mucosa of Large Intestine
- Simple columnar epithelium like the SI
- Contains specialized cells called colonocytes
- Presence of many more Goblet cells than the SI for more water absorption
Ileocecal Valve
Separates the ileum from the cecum
Teniae Coli
- Ribbon-like muscular structure w/ muscular tone along the length of the large intestine
- Contractions pull on large intestines to form 'segmentations' called haustra
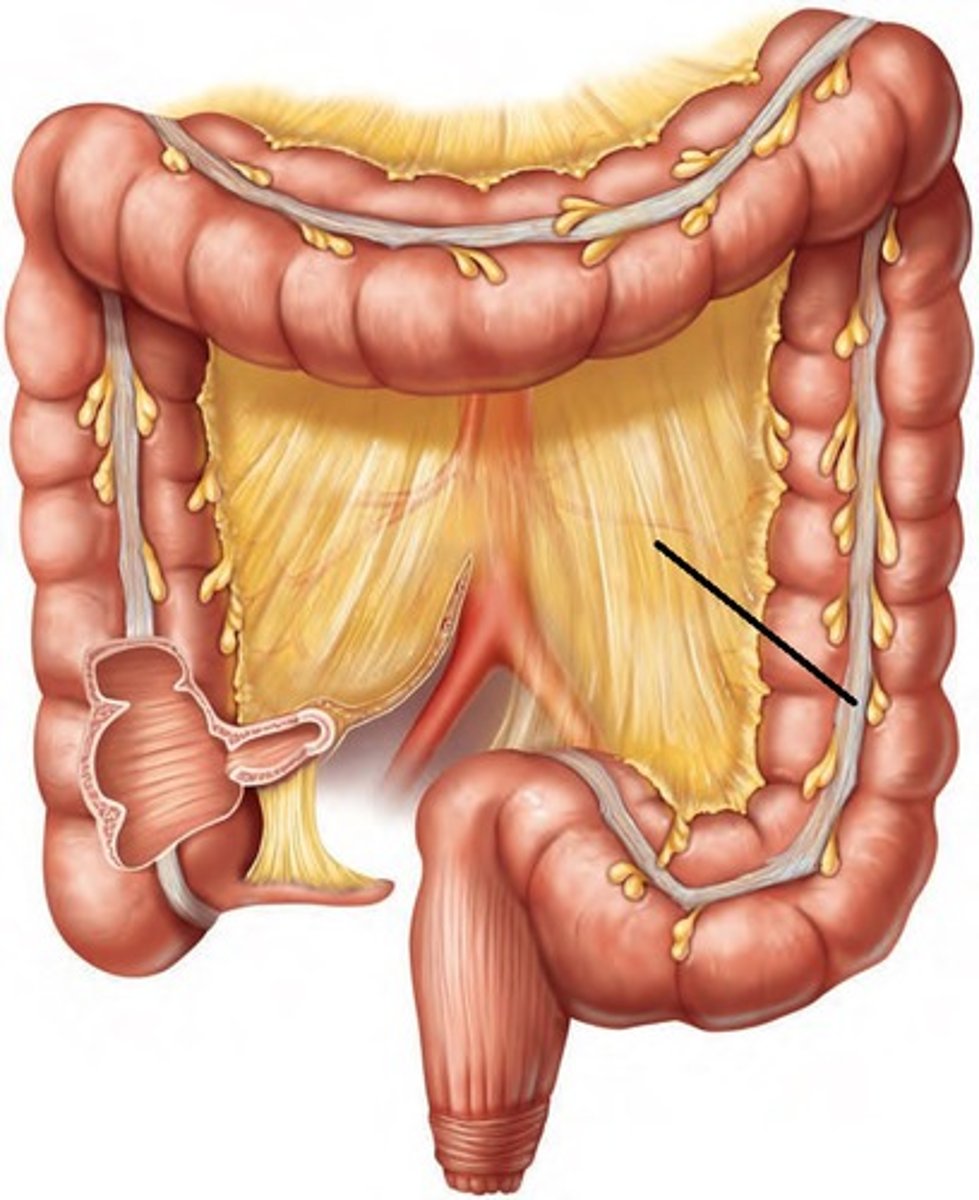
Haustra
Segments of the large intestine due to tugging from the teniae coli
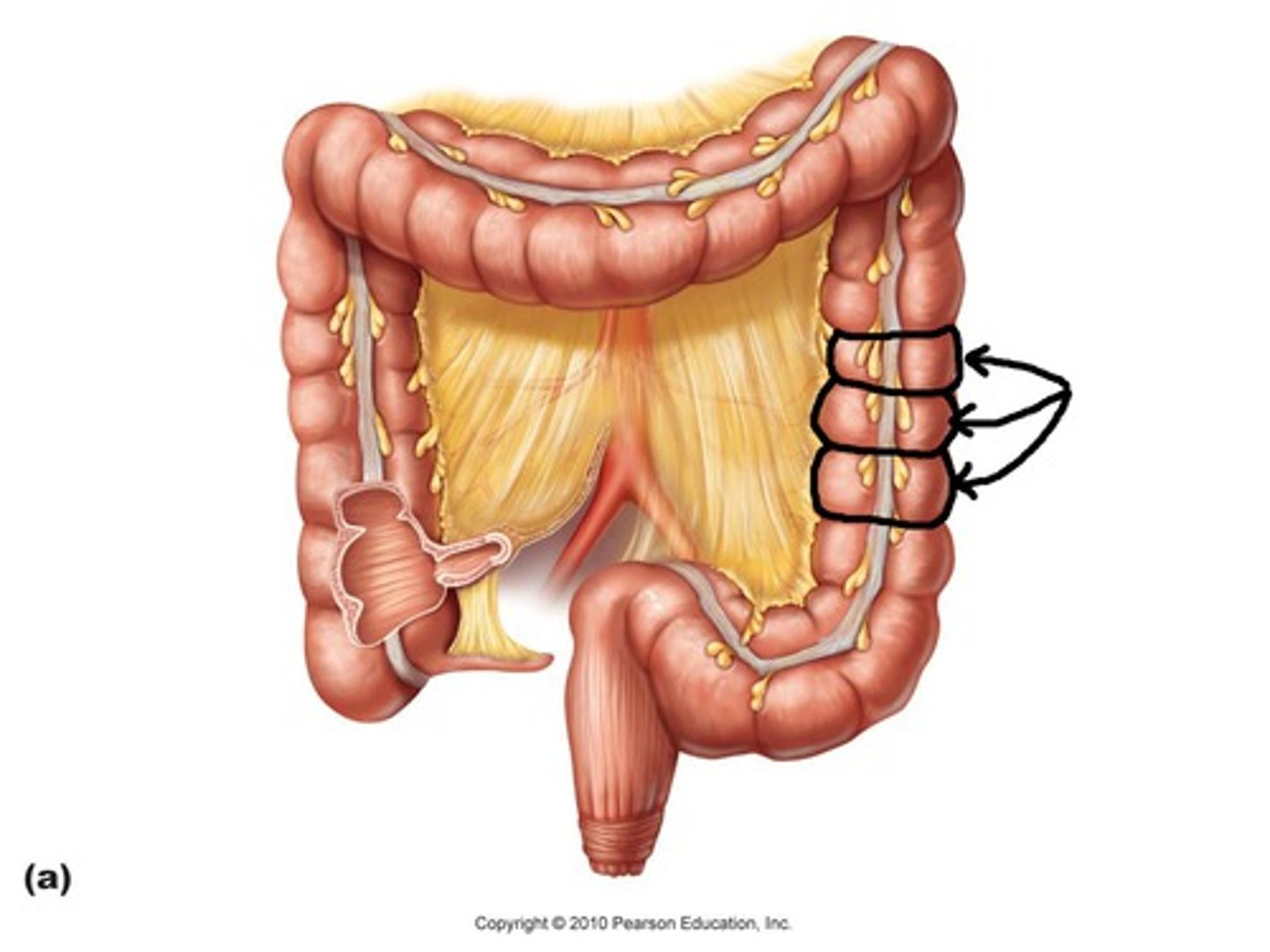
Epiploic Appendages
Sacs filled with fat hanging from the teniae coli
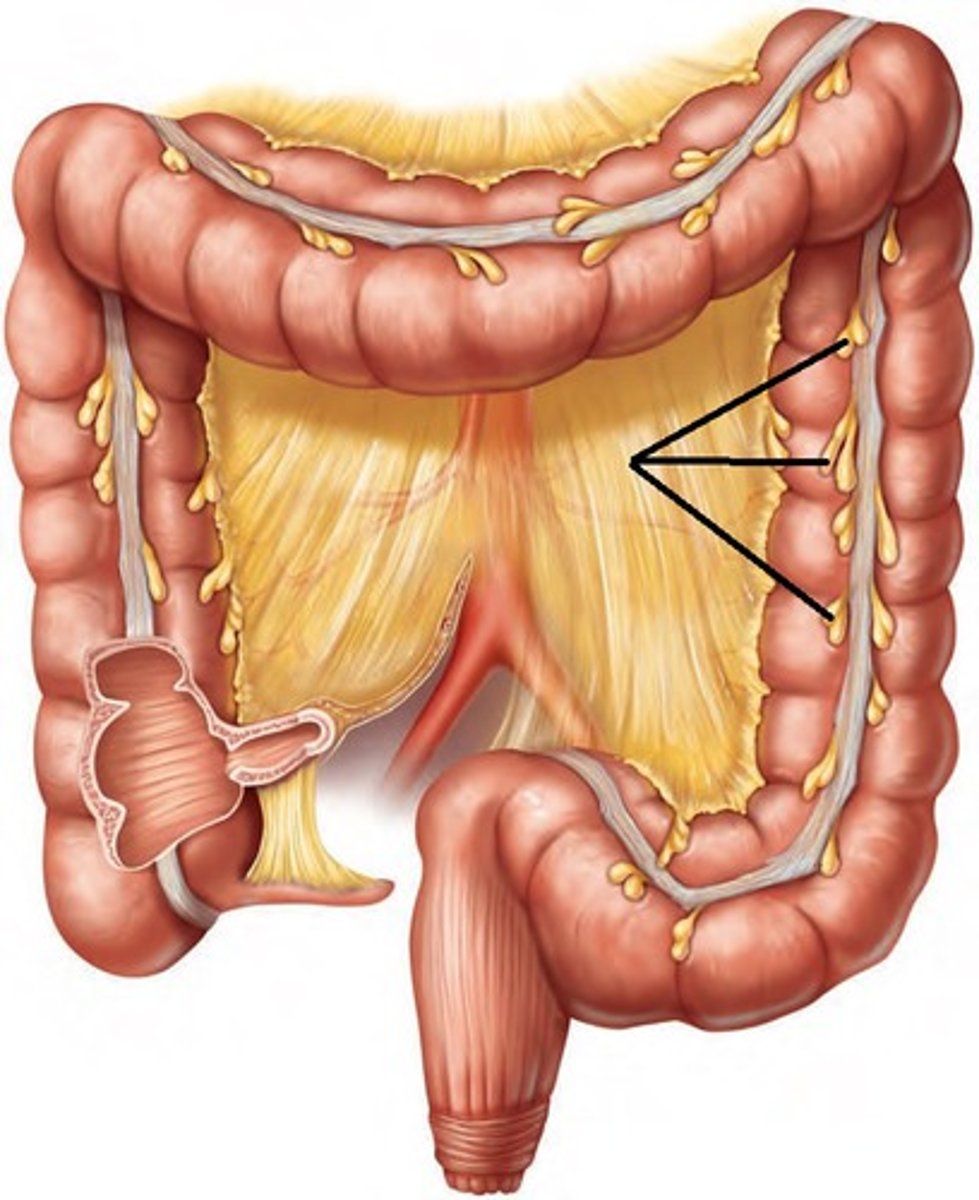
Transfer of Waste Material via Large Intestine
Cecum -> Ascending Colon -> Right Colic (Hepatic) Flexure -> Transverse Colon -> Left Colic (Hepatic) Flexure -> Descending Colon -> Sigmoid Colon -> Rectum -> Anal Canal
Rectal Valve
Transverse folds of the rectum managing the passing of gas without defecating at the same time
Levator Ani Muscle
Present in the anal cavity where it shows the transition from the rectum to the anal canal
Anal Columns
Longitudinal folds joining at anal valves
Pectinate Line
Divides the anus from the anal canal
Internal vs External Anal Sphincter
[Internal] Smooth muscle -> Involuntary
[External] Skeletal muscle -> Voluntary
Hemorrhoids
Swollen varicose veins in the rectal region due to intense stress/pressure
Internal vs External Hemorrhoids
[Internal] Located superior to the pectinate line -> Leads to bleeding
[External] Located inferior to the pectinate line -> Leads to itchiness and irritation
![<p>[Internal] Located superior to the pectinate line -> Leads to bleeding<br><br>[External] Located inferior to the pectinate line -> Leads to itchiness and irritation</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d264043f-9fb5-40c1-af9d-680fd88d9f3e.jpg)