Evolution Midterm 2
1/87
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is random genetic drift?
the fluctuation in allele frequencies due to random sampling
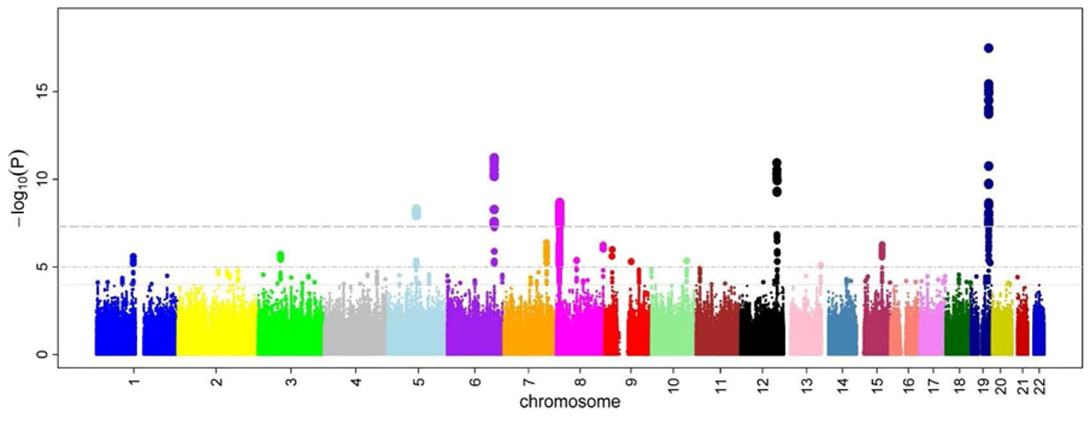
What is this type of plot called
A Manhattan plot
Why is genetic drift especially key in small populations?
Because fluctuations can result in a loss of alleles (going to fixation)
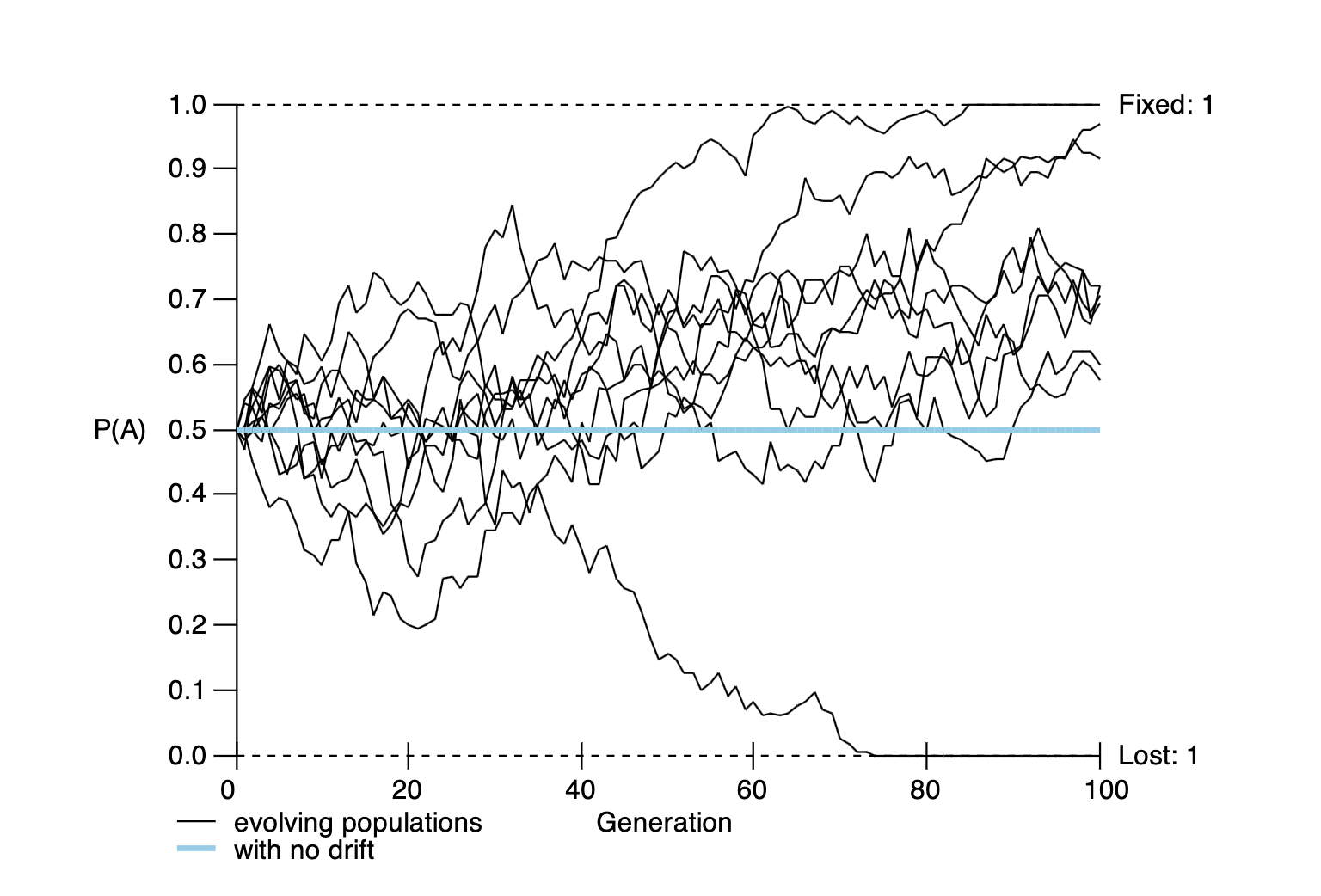
What does this figure depict?
Genetic drift, causing the populations to diverge from one another
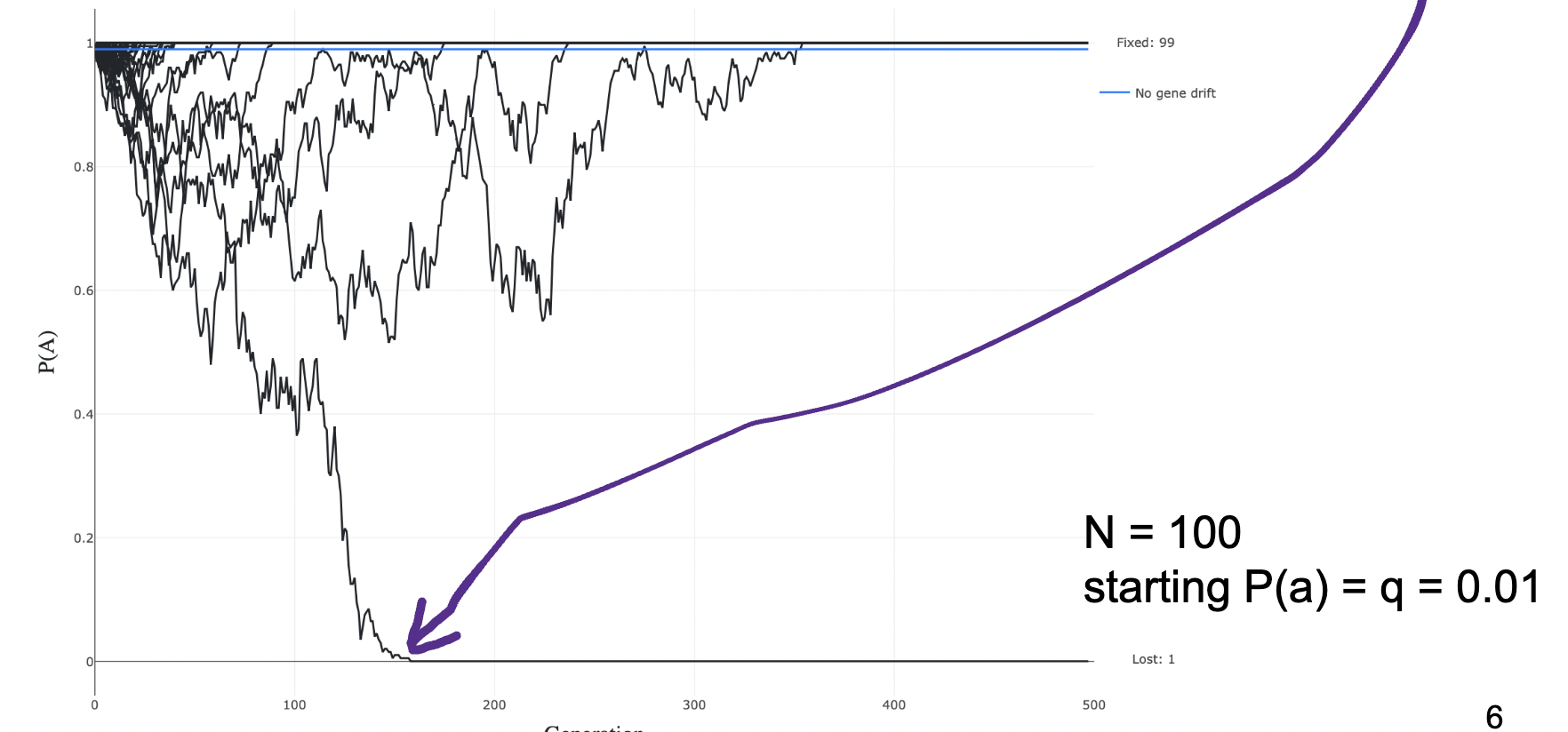
What does this figure depict?
The chance for a completely neutral new mutation to become fixed in small populations
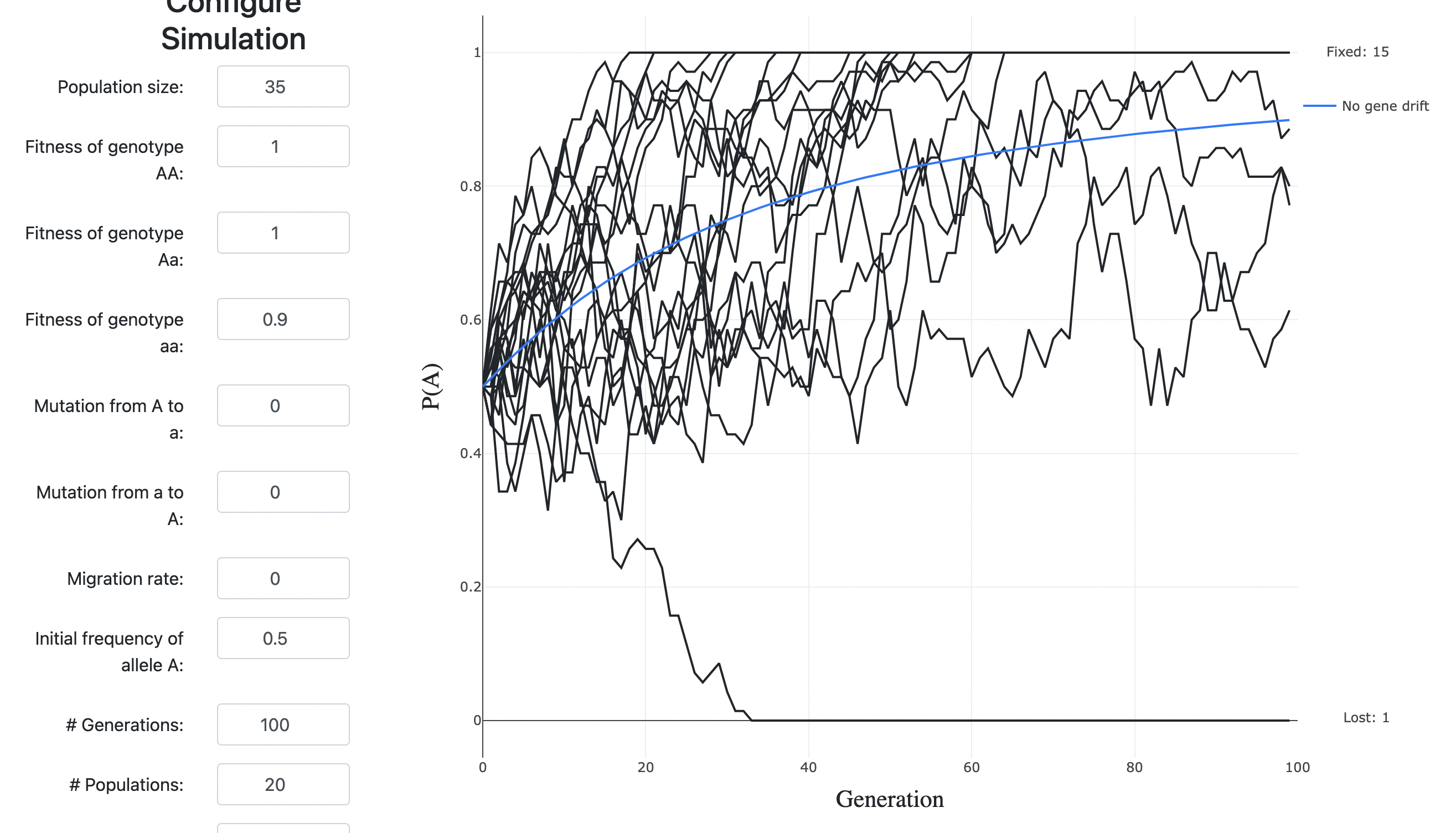
what does this figure depict?
The fixation of a slightly deleterious mutation in a small population
What is the Wright-Fischer model of genetic drift?
Based on the probability of a binomial distribution
What conditions can create a genetic bottleneck?
Reduction of a population to a small number of individuals, this can be because of…
Population crashes
Establishment of a population from a few founders
What is an example of a genetic bottleneck?
Northern elephant seal
thought to have been extinct in the 1800s
today’s population descended from approximately 20-40 individuals
Resulting in a huge reduction in heterozygosity and a decrease in fitness
Due to the presence of a premature stop codon in 5 male fertility genes (deleterious mutation)
What classic experiment demonstrated genetic drift?
A 1956 experiment by Peter Buri on genetic frequency in a small population of mutant drosophila
Followed 2 alleles in 107 populations started from only 16 flies in every generation
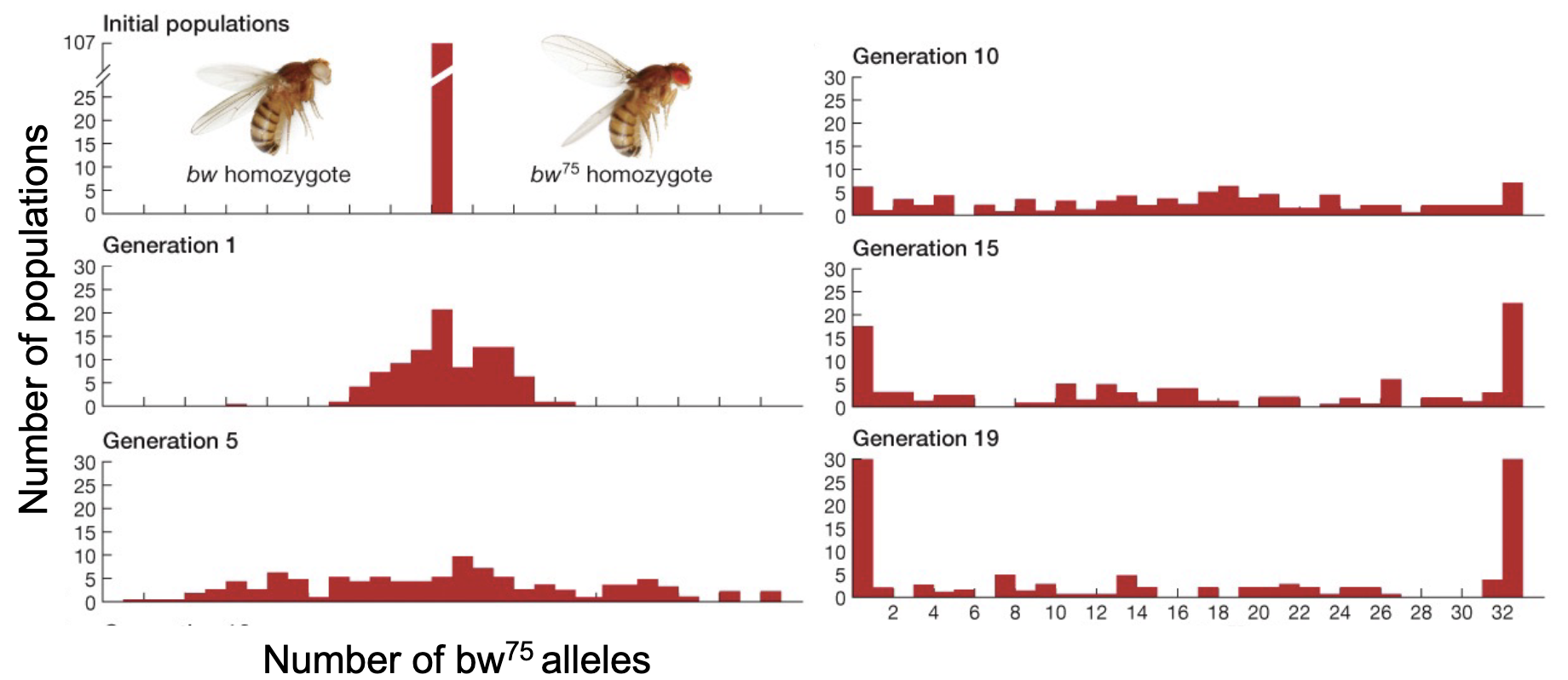
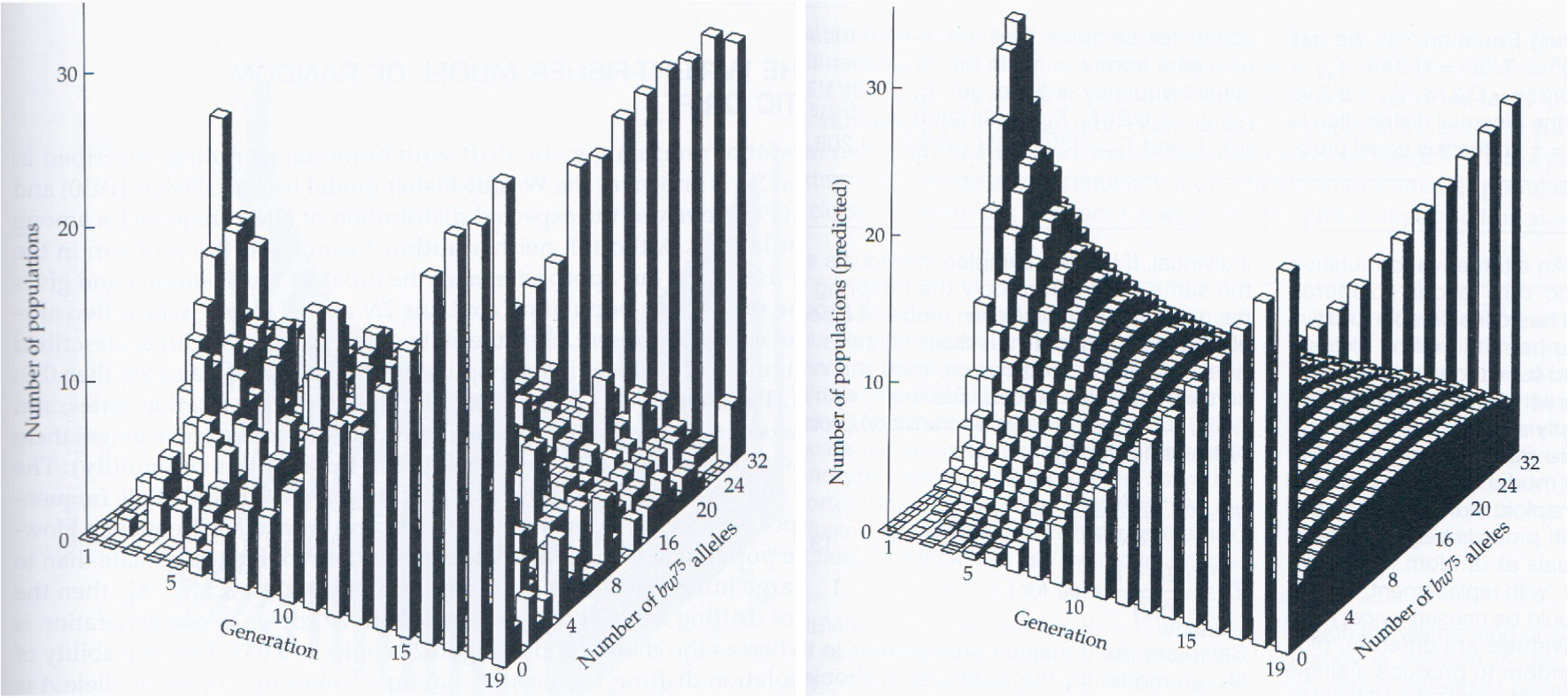
What does this figure represent?
The difference between Peter Buri’s experiment and the theoretical Wright Fisher model
the model maintains heterozygosity to a higher degree, this is because it assumes that all individuals are involved in reproduction
Define effective population size
The effective population size (Ne) refers to the number of individuals in a population which are contributing gametes to the next generation (smaller than N)
What are the effects of genetic drift on genetic diversity?
Population size has a high effect on genetic variation
Smaller population size results in higher genetic drift, lower heterozygosity and higher homozygosity
Smaller population size increases the chance that a completely neutral new mutation will become fixed
Smaller populations have an increases the chance that a deleterious mutation will become fixed
Larger populations are much more likely to have advantageous mutations go to fixation
Define the term ‘inbreeding depression’
A reduction in fitness due to the bringing together of recessive deleterious mutations, making them homozygous and exposing them to natural selection
Does genetic drift or natural selection have a larger effect on allele frequency?
Depends on the strength of each process
s= natural selection
1/Ne= genetic drift
If s»1/Ne then natural selection will have the prevailing effect
What is the longest run predator-prey experiment? What does it demonstrate?
Study of the fluctuations in population of the Isle Royale wolves (whose population was founded in the late 1940s) and the moose
population overrun with genetic defects due to inbreeding depression
studied the effects of a single individual wolf in recovering the population by facilitating gene flow
Define gene flow
The movement of an individual or gametes between populations
What are the potential effects of gene flow?
can change the genetic structure of a population
can counteract divergence among populations (greater homogeneity of populations)
How are gene flow and genetic structure measured?
Using F statistics
What is the F statistic (Fst)?
A tool used to measure the reduction of heterozygosity at different scales
tells us how much gene flow, populations structure and differentiation there is in an allele
values 0→1
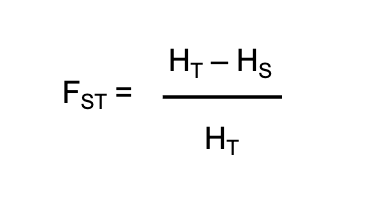
What does it mean if your Fst is very small or very large?
Very small:
there has been movement and exchange
no population structure= gene flow
Very large:
there has been little or no movement or exchange
alleles have been fixed in different populations
population structure= very little gene flow
What do genes with Fst outlier values mean?
They are strong indicators of positive selection/adaptation
What was revealed when investigating the effects of artificial selection on the dog genome?
A significant Fst deviation in shar-peis. Hylauronic synthase (HAS2) expression is elevated, associated with skin repair and stretch

What does a high degree of sequence conservation mean?
It indicates that a gene is essential and that there is high purifying selection on any deviations
What type of polymorphism occurs most frequently?
synonymous>non-synonymous
What do the variables dn + ds describe?
The variation within a species
What do the variables Ka + Ks describe?
The variation between species in their non-synonymous (amino acid) and synonymous (substitution) divergence
How do human and yeast ubiquitin proteins relate?
They are almost identical
Define systematic humanization
The replacement of an organism’s genes (for example in yeast) with human ones, reveals an extremely high degree of conservation
What genes have relatively low non-synonymous variation?
Essential genes such as those involved in transcription, translation and metabolic processes
What genes have relatively high non-synonymous variation?
Those involved in adaptation towards changing environmental conditions or against natural enemies
What are some of the fastest evolving genes in the fly genome?
Antiviral genes, have lots of non-synonymous mutations (high Ka/Ks)
Define adaptive radiation
The diversification of some lineages into many species in a short amount of time (cichlids)
What is the biological species concept?
Species are groups of interbreeding or potentially interbreeding individuals that are reproductively isolated from other such groups
Why are hybridization and introgression important in the evolution of species?
Because they act as sources of diversity and adaptation (ex. EPAS1 in Tibet)
What are the steps to speciation?
Development of a polymorphism
Reduction in gene flow
Complete or near-complete reproductive isolation
Accumulation of differences and isolating barriers independent of initial isolation
Define Allopatric speciation
Most common form of speciation, caused by complete geographic isolation, no gene flow
Define Sympatric/ecological speciation
Speciation which occurs without geographic isolation while populations are still exchanging genes
What are the major types of isolating barriers?
Premating (no mating)
Postmating (no fertilization)
Postzygotic (produce unfit offspring)
Give an example of a premating isolating barrier
Southern Cappuccino Seedeater
10 species which occur in overlapping ranges
Differ in male plumage and song
Only genetic differences occur in 3 genes associated with pigment
Males act most aggressively towards individuals with the same plumage and song
Give an example of a postmating isolating barrier
Japanese Carabid Beetles
Differences in male reproductive organs
very high mortality in cases of interspecific matings and damage of reproductive organs
Give an example of a postzygotic isolating barrier
Heliconius Butterflies
hybrids are predated upon at higher rates than their parental lines
hybrid warning patterns aren’t recognized
What is the Bateson-Dobshansky-Muller model of hybrid incompatibility?
It states that incompatibilities will accumulate over time
those that arise later may not be related to initial processes of speciation
Give an example of duplicate genes causing incompatibilities
Arabidopsis Thaliana
hybrid offspring between two strains (At1g71920 and At5g10330) are unviable
due to a premature stop codon in one and a large deletion in the other
this is the kind of incompatibility that could result in speciation
Define parthenogenesis
Asexual reproduction
What is an example of a species which reproduces parthenogenetically but requires sperm to trigger development
Amazon mollies/ ‘sperm parasites’

Why are parthenogenetic lineages not persistent?
They are short lived due to accumulation of deleterious mutations
parthenogenesis has evolved 39 times in scaled reptiles
What are the benefits of asexual reproduction
Faster growth rate
Reproductive assurance (don’t rely on finding a mate)
Don’t need to invest in expensive sexual reproductive traits
Avoid STD and other mating risks
Perseverance of successful genotypes
What is the two-fold cost of sex
Also referred to as the cost of males
if females produce 50% males then half her resources go into offspring unable to bear offspring themselves
an asexual individual will double in frequency every generation
What are the benefits of recombination?
brings beneficial mutations together
breaks associations with deleterious mutations
Define clonal interference
Competition between asexual lineages with different beneficial mutations
What is the red queen hypothesis
that because everything around you evolves so quickly you are forced to evolve simply in order to keep pace
What is the example of the New Zealand mud snail?
Snails are a mix of obligate sexual and obligate parthenogenetic individuals
Researchers found sexual snails to be more abundant when parasitism is high because asexual snails were more likely to be infected
Define linkage disequilibrium
The non-random association of alleles at different loci
What are potential causes of linkage disequilibrium?
reduced recombination due to physical linkages (most common)
inbreeding
natural selection
What is genetic hitchhiking?
when selection favours an allele at one locus nearby linked loci may also increase in frequency
Define selective sweep
A process by which a new advantageous mutation eliminates or reduces variation in linked neutral sites as it increases in frequency in the population
What is the example of genetic hitchhiking in Drosophila?
transposable element jumped into CHKov1 gene
the new variant has spread rapidly and neighbouring nucleotides have come alongside
has stronger resistance to organophosphate pesticides and viruses
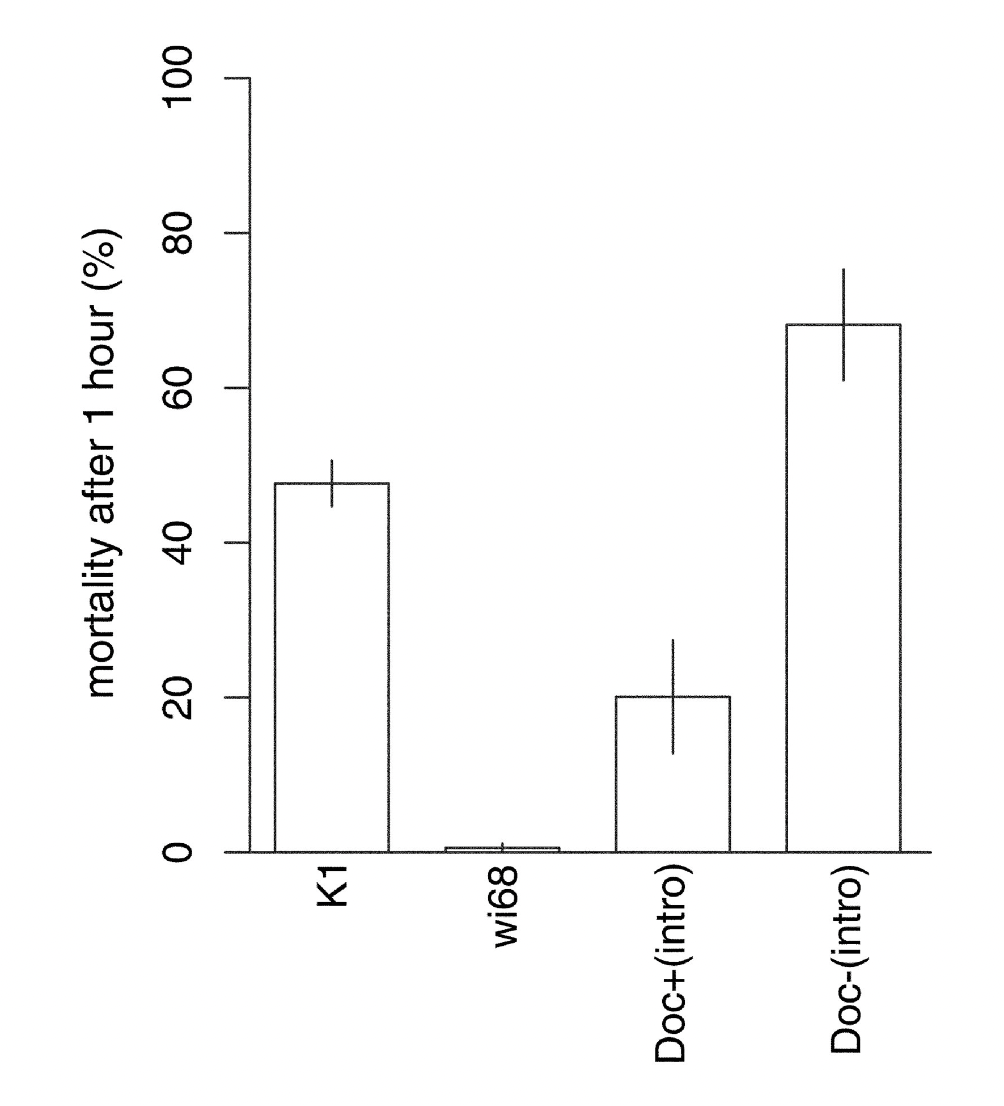
What is the ‘Ruby in the rubbish’ metaphor?
When beneficial mutation are stuck in linkage with deleterious ones
What is stated in Muller’s ratchet?
deleterious mutations will accumulate in small asexual populations
(classes of individuals with the least deleterious mutations could be lost by chance and never recovered)
Which mutations can become fixed in asexual lineages but never in sexual ones?
Deleterious
What human alleles do not undergo recombination?
Mitochondrial genomes, centromeres, telomeres and Y chromosomes
What is the PAR
pseudoautosomal region a small region of the X and Y chromosomes pair and recombine
Give an example of parthenogenesis in a eukaryote caused by bacterial infection
Encorsia hispida, an important wasp in the biocontrol of whitefly pests, parthenogenetic due to bacterial infection
female wasps fed antibiotics can produce sons
What are cases of combinations of sexual and asexual reproduction
Cyclical parthenogenesis (aphids)
Selfing (nematodes)
Anisogamy (fusion of 2 different gametes)
Dioecious (separate male and female sexes)
Androdioecy or gynodioecy (a mix of individuals that produce 1 or both types of gametes)
Protogynous or protandrous (female→male or male→female)
What is the cause of sexual selection?
Competition for mates among individuals of the same sex
What traits are selected for in individuals with small gametes? What about for in individuals with large gametes?
small gametes- increase mating opportunities
large gametes- increase in the number of eggs produced
What is Bateman’s principle?
Males have greater variance in reproductive success than females
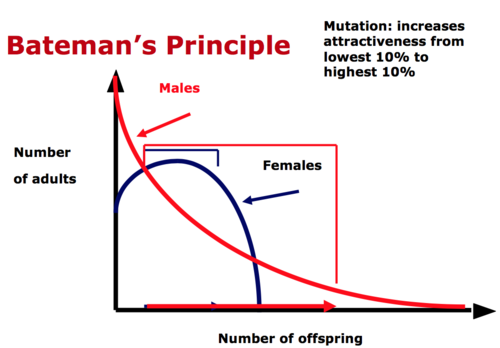
What are the two major modes of sexual selection?
male-male competition
female mate choice
What are 4 types of male-male competition in sexual selection?
scramble traits
contest and display
sperm competition
infanticide
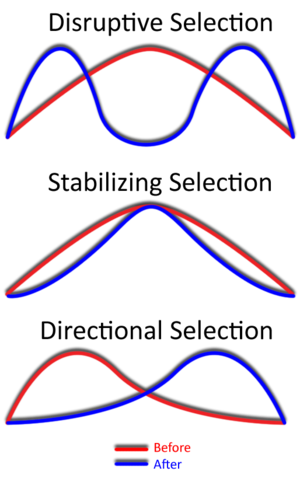
What kind of selection is horn size in dung beetles
Disruptive
How is the hornlessness phenotype determined in dung beetles?
Environmentally determined
What are examples of female mate choice?
peacock
stalk-eyed flies
sage grouse mating displays
Why are individuals chosen by females?
direct benefits
mates may offer food or other resources
indirect benefits
good genes
Give an example for mate choice for indirect benefits/good genes?
Three spined stickleback and cestode parasites
offspring of brighter males are more resistant to parasites
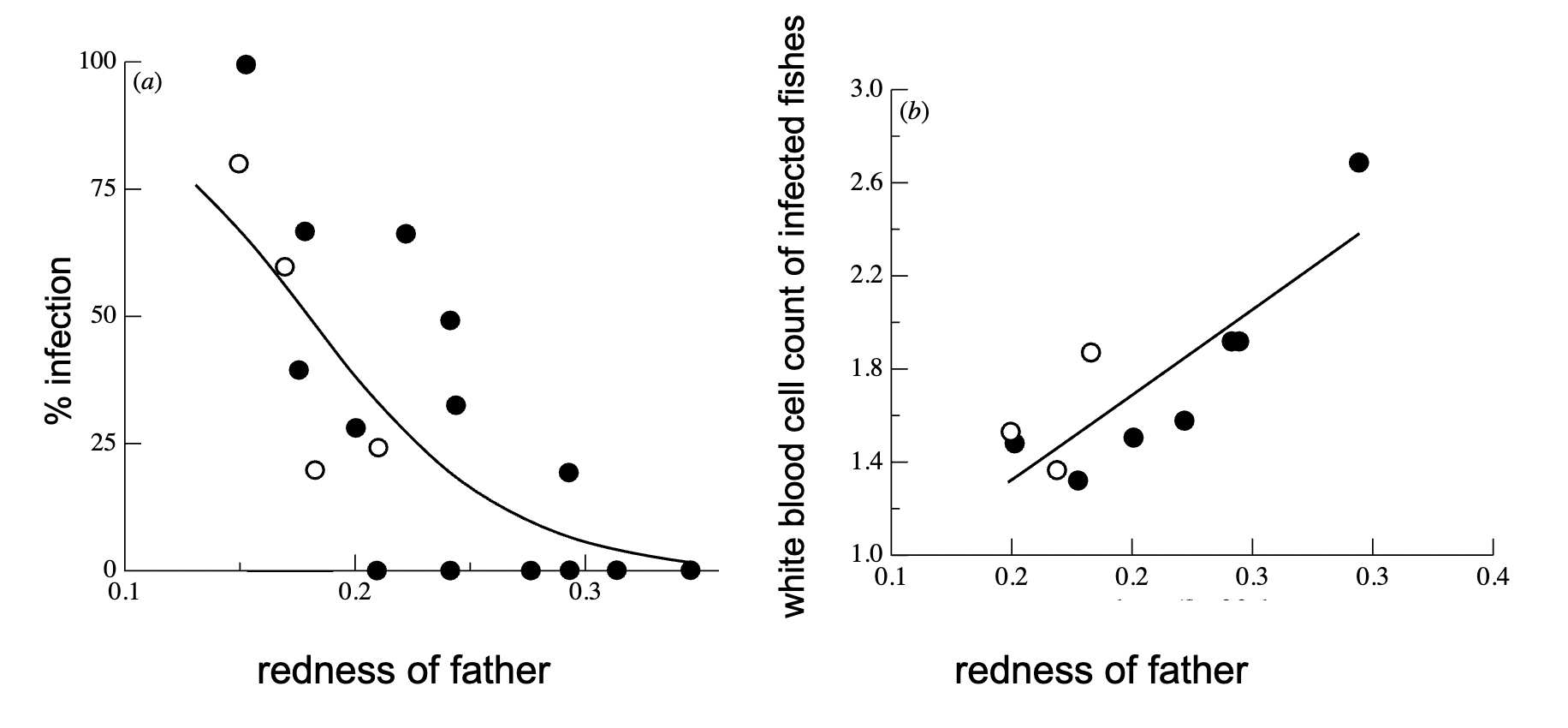
Give an example of sexual selection in plants
The swift evolution of pollen and pistil traits in Mercurialis annuas in 3 generation under conditions of high or low density
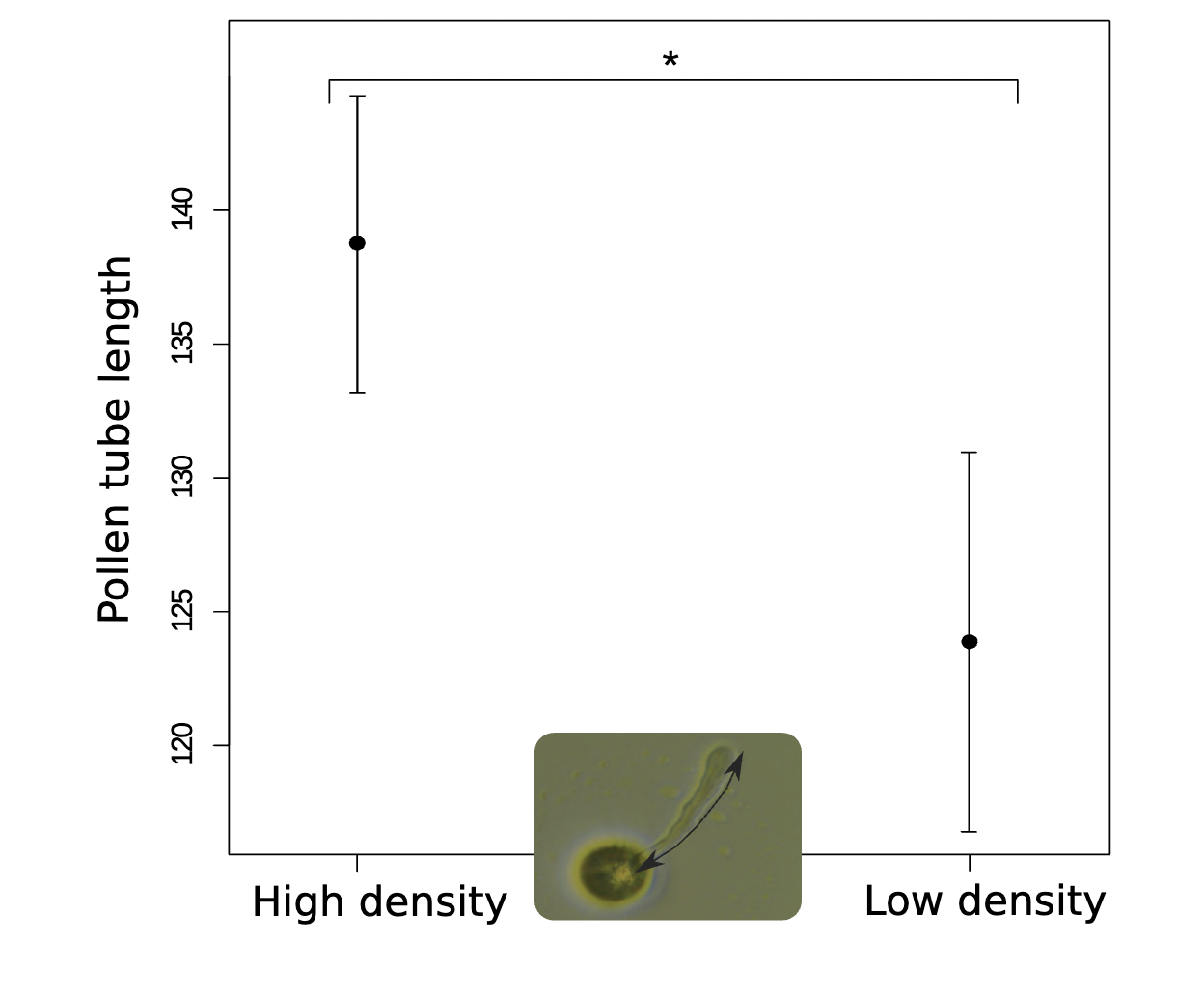
How would you perform experimental evolution to remove or reduce sexual selection?
Monogamy
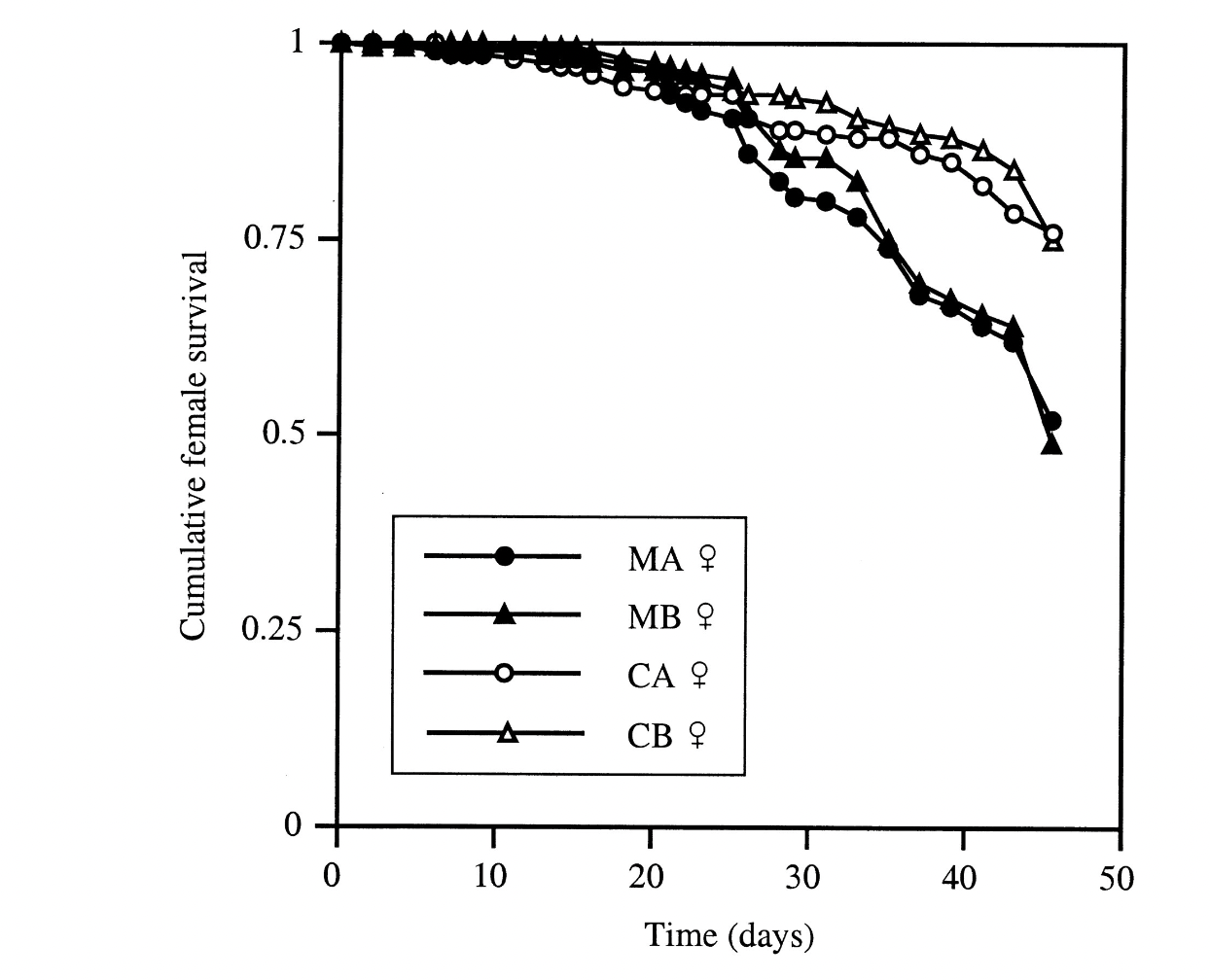
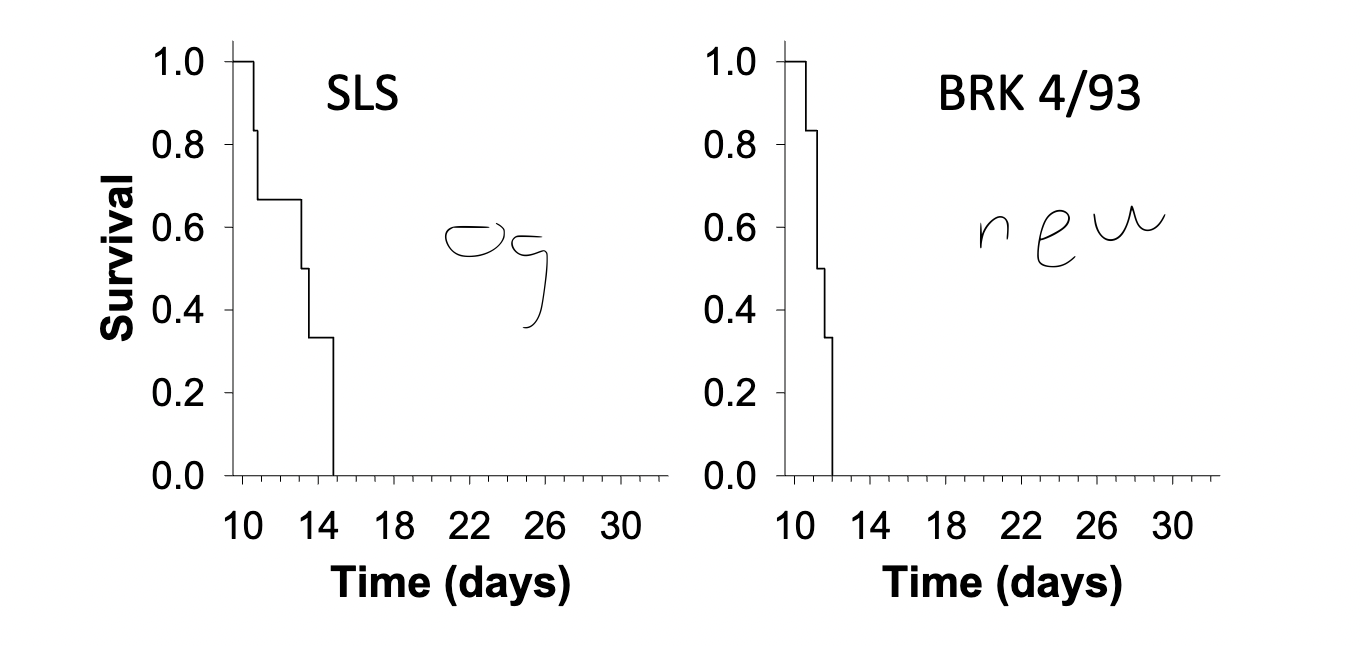
What does this figure depict?
The reduced female survivorship in Drosophila from mating between members of the monogamous treatment and the control treatment due to sexual selection for antagonistic or competitive traits
When is conflict between the sexes greatest?
When there is multiple matings and coevolution (polygamy»monogamy)
What are the phenotypes of antagonistic coevolution in riffle bugs?
Males with wider legs and spines (more successful in mating)
Females with thoracic hook (resist mating)
What does it mean for Ka«Ks? Ka=Ks? Ka»Ks?
Ka«Ks - purifying selection on the amino acid (gene is highly conserved)
Ka=Ks - gene is evolving close to neutral (natural selection doesn’t see the change)
Ka»Ks - positive selection (adaptation)
What are the fastest evolving human genes?
Reproductive proteins- for example the human fertilization protein zonadhesin whose exons (coding) evolve faster than their introns (non-coding)
Give 3 examples for coevolution between species
antagonism - host and parasite
competition
mutualism - host and beneficial endosymbiotic microbes
Give an example of coevolution between individuals within a species
sexual selection - riffle bugs
Give 3 examples of coevolution between different genes/ parts of the genome
organelles
selfish genetic element and the rest of the genome
genes that interact with each other
Define specific and diffuse coevolution
Specific- a 1:1 evolution between pairs of interacting organisms
Diffuse- reciprocal change among groups
Where does the key tension lie for parasites or pathogens?
Key tension between transmission and the effects on the host (you shouldn’t kill your host)
Describe the evolution of virulence in the myxoma virus
Infecting Australian rabbits it began with the release of a highly virulent virus
Followed by the evolution of a reduced/ intermediate virus
Evolution of host resistance
Current evolution of acute virulence through a novel disease phenotype, an immune collapse syndrome similar to septic shock