Lesson 2.1: The Law of Demand
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on the Law of Demand.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms

Market
Any institution or mechanism which brings together buyers and sellers for voluntary exchanges, at local to international scopes and personal to impersonal relationships
Supply and demand model
A model of how a competitive market works, where sellers compete for the dollars of buyers through product differences

Competitive market
A market where many buyers and sellers offer the same good or service, such as in the market for blue jeans
Quantity demanded (QD)
The amount of a good or service consumers are willing to buy at any given price
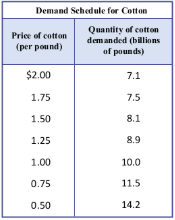
Demand schedule
A table that displays the quantity demanded at different prices for a good or service
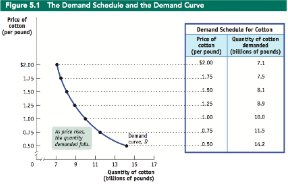
Demand curve
The graphical representation of the demand schedule, showing the quantity demanded of a good or service at any given price
Is downward-sloping due to the law of demand
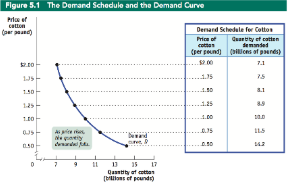
Law of demand
Law that states that all other things being equal, people demand less of a good or service at higher prices
Affected by the substitution effect (prices can affect preferences) and the income effect (people will not buy as much with less income)

Substitution effect
Effect and factor in the law of demand that states that rising prices will encourage consumers to buy alternative goods that are cheaper

Income effect
Effect and factor in the law of demand that states that rising prices and the same amount of purchasing power will lead to consumers not buying as much with less disposable income