LIGHTING DESIGN_LECTURE 1
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GLUCK
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Lighting
application of light to spaces
Where the light is placed, at what relative intensities, and in what direction, can have a major impact not only on vision and visual comfort, but perception.
Not just light, but the lighting equipment itself can also affect impressions of the space and its owner.
Light
creative medium, the most powerful of all.
plays a central role in the design of a visual environment: the architecture, people and objects are all made visible by it.
influence our well-being, the aesthetic effect and the mood of the room or area.
is electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye (380 or 400 nanometers to about 760 or 780 nm)
In physics, the term ___ sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not.
gets
How light is produced?
When you heat up an atom, its electrons jump to higher orbits. When the atom cools down, they go back to where they were and emit light.
“gets”
bet
WHY WE REQUIRE A LIGHT
It is the light that first enables ”what we see”.
Light defines zones and boundaries.
Light expands and accentuates rooms.
Light create links and delineates one area from another.
Has several functions (illumination, revelation of form, focus, contrast, functionality)
bet
illumination
simple ability to see what is occurring on
Revelation of form
Altering the perception of shapes on space, particularly three- dimensional elements.
Focus
Directing the public attention to an area of the region or distracting them from another.
Contrast
Lighting of an object or area so that it becomes brighter than its surroundings.
Functionality
The level of illumination required for a particular application depends greatly upon seeing the task involved and upon the surrounding conditions.
Natural Lighting
Artificial Lighting
TYPES OF LIGHTING
NATURAL LIGHTING
Daylight (using windows, skylights, or light shelves)
can be used as main light during daytime in buildings to save energy
importance of daylight
Daylight in buildings makes people happier and saves energy. Studies show it improves mood, health, and productivity, leading to benefits like increased sales and faster recovery in hospitals. So, it's worth the cost to design buildings with good daylight.
ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
Artificial light sources are created by combining specific parts of the optical spectrum. The way these parts are mixed determines the color of the light and how objects look when illuminated.
Artificial light can be created by combining red (R),green (G) and blue (B) components
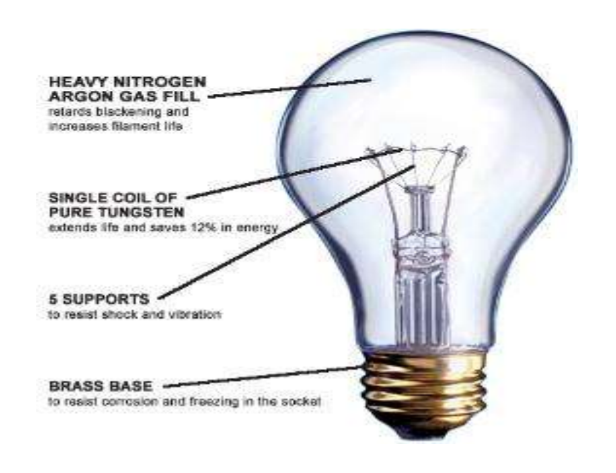
incandescent light or filament light
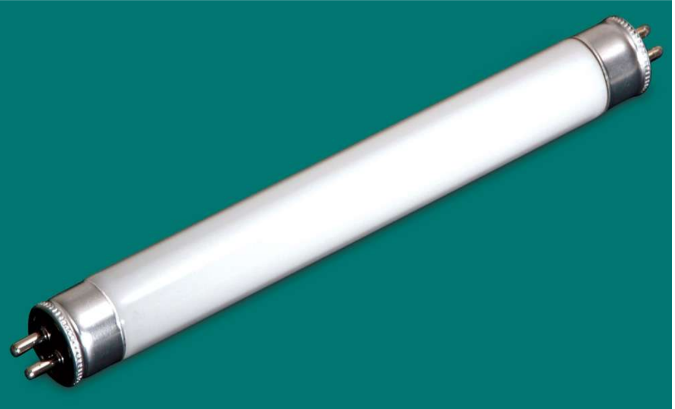
fluorescent or discharge

Low pressure lamps
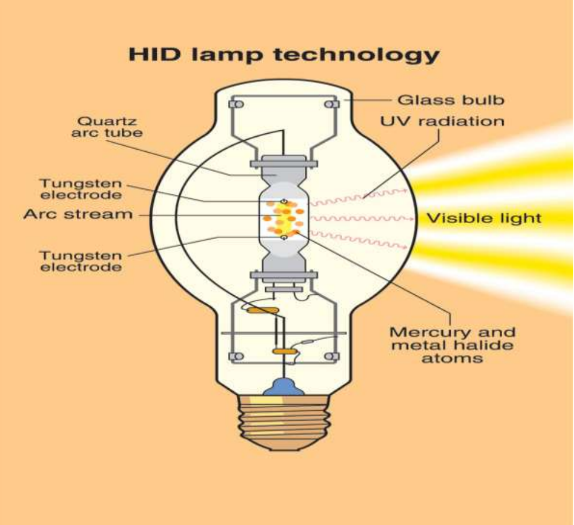
High pressure lamps
GENERAL LIGHTING
TASK LIGHTING
ACCENT LIGHTING
3 Basic Types of Artificial Lighting
Ambient/General Lighting
provides overall illumination for a room,
Task Lighting
Targeted to a particular area of a room
intended to illuminate a specific function.
Accent Lighting
also known as highlighting, is used to draw attention to specific objects such as artwork, sculptures, or plants.
It can also be used outdoors to highlight features like trees or water features.
Typically achieved with recessed or track lighting,
allows for precise focus on a particular area or object.
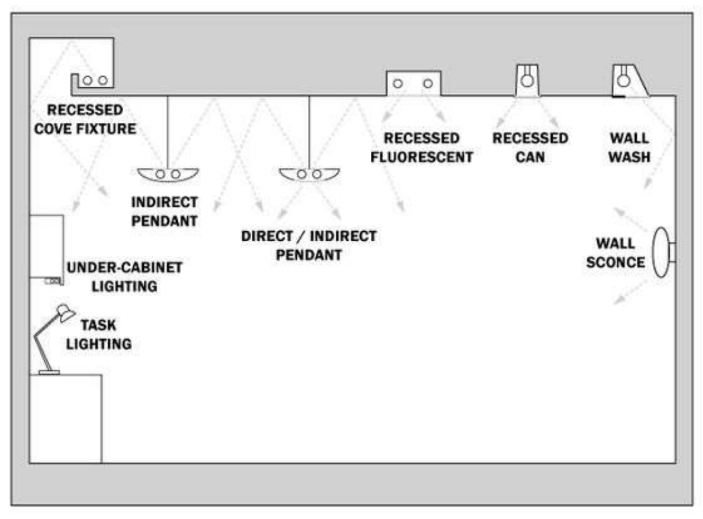
LUMINAIRE
There are basically two types of luminaries:
Stationary
Movable
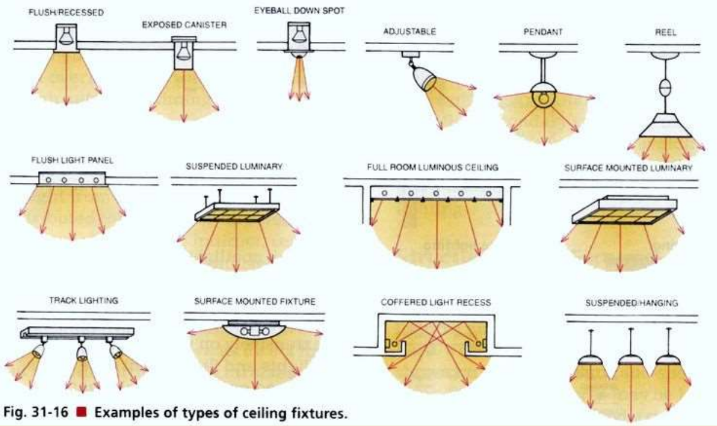
DOWNLIGHTS
most common method, where fixtures in or recessed into the ceiling cast light downwards.
While popular in both offices and homes due to its ease of design, it can lead to glare and excessive energy consumption due to the large number of fittings required.

UPLIGHTS
often employed to bounce light off the ceiling and back down into a space.
This method is commonly used in applications where minimal glare and uniform illumination are desired.
By using a diffuse surface to reflect light, up lighting can reduce glare on glossy surfaces like computer displays.
It creates a uniform presentation of light output, but its effectiveness depends on the reflectance of the surface. While it can produce a diffused and shadow-free effect, indirect lighting is sometimes seen as economically inefficient.

PENDANTS
These lights are great for dining areas, offering functionality and style. They help people see clearly and can add elegance to the space.
suspended from the ceiling

WASHERS
Most visible surfaces: Vertical walls
Asymmetric lighting fixtures
Arranged in lines of three or more
Even illumination of walls
Tool used by lighting designers to creates lighter spaces
Enhances perception of brightness and height

Wallwashing
lighting design technique for illumination of large surfaces.
It's commonly used in contemporary architecture, particularly in public cultural buildings, museums, galleries, and landscape lighting projects.
SPOTLIGHTS
Lamp projecting narrow, intense beam
Directly on place or person
Especially used for performers on stage
Strong, focused light
Highlights specific spot
Used on small area of stage or TV studio

WALL SCONCES
Wall-mounted light fixture
Relies on wall for support
Light directed upwards, but not always
No base on the ground
Installed on interior and exterior walls

TRACKLIGHTS
Versatile lighting alternative
Ideal for hard-to-illuminate areas
Consists of individual lamps or lighting heads
Fits into tracks secured to ceiling
Various shapes and lamp sizes available
Suitable for modern, contemporary, and transitional designs
Lighting fixtures attached to continuous track device
Track contains electrical conductors

Track lighting
lighting method where light fixtures can be attached to a continuous track device containing electrical conductors.
This allows for flexibility in positioning the fixtures along the track to suit various lighting needs.
FREE STAND LAMPS
Mood lighting option
Ideal for bedrooms and living room corners
Available in various sizes, shapes, and designs
Enhances ambiance and atmosphere

ok
Types of Lighting Fixtures
Architectural.
Recessed.
Track.
Undercabinet.
Pendants.
Chandeliers.
Wall Sconces.
Desk, Floor & Table Lamps.
ok
Cove lighting
Located in ledge, shelf, or recess high on wall
Light bounced toward ceiling or upper wall
Creates soft, indirect illumination
Enhances ambiance and visual interest
Soffit lighting
Located in soffit or cornice near ceiling
Light radiates downward
Washes the wall with light
Creates soft, indirect illumination
Enhances ambiance and visual interest
Valance lighting
Positioned in wood, metal, or glass valance
Mounted above window or high on wall
Light bounces both upward and downward
Provides dual-directional illumination
Enhances ambient lighting in the room
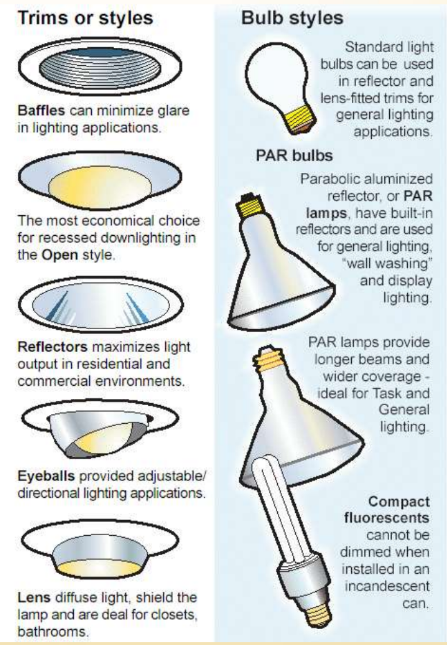
Recessed
Installed above ceiling, flush with it
Requires at least 6 inches of clearance
Insulation needed to prevent condensation
Sends narrow band of light in one direction
Can provide ambient, task, or accent lighting
gg
gg
Track
Mounted or suspended from ceiling
Linear housing with multiple heads
Heads can be positioned anywhere along track
Direction of heads is adjustable
Commonly used for task or accent lighting
Undercabinet
Mounted under kitchen cabinets
Can be linear or single puck-shaped fixture
Extremely popular as task lighting in kitchen
Pendants
Suspended from ceiling
Directs light downward
Typically over table or kitchen island
Enhances decorative style of room
Provides ambient or task lighting
Chandeliers
Suspended from ceiling
Directs light upward
Typically over a table
Enhances decorative style of room
Provides ambient lighting
Wall Sconces
Surface-mounted to wall
Can direct light upwards or downwards
Covers or shades add stylistic touch
Provide ambient or task lighting
Desk, Floor & Table Lamps
Wide range of sizes and styles
Versatile and portable
Direct light downward (except torchiere)
Torchiere directs light upward
Used as task lights, especially for reading
Can also provide ambient light
mo
mo
kk
kk