Other labs
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Endocrine
- thyroid
- diabetes
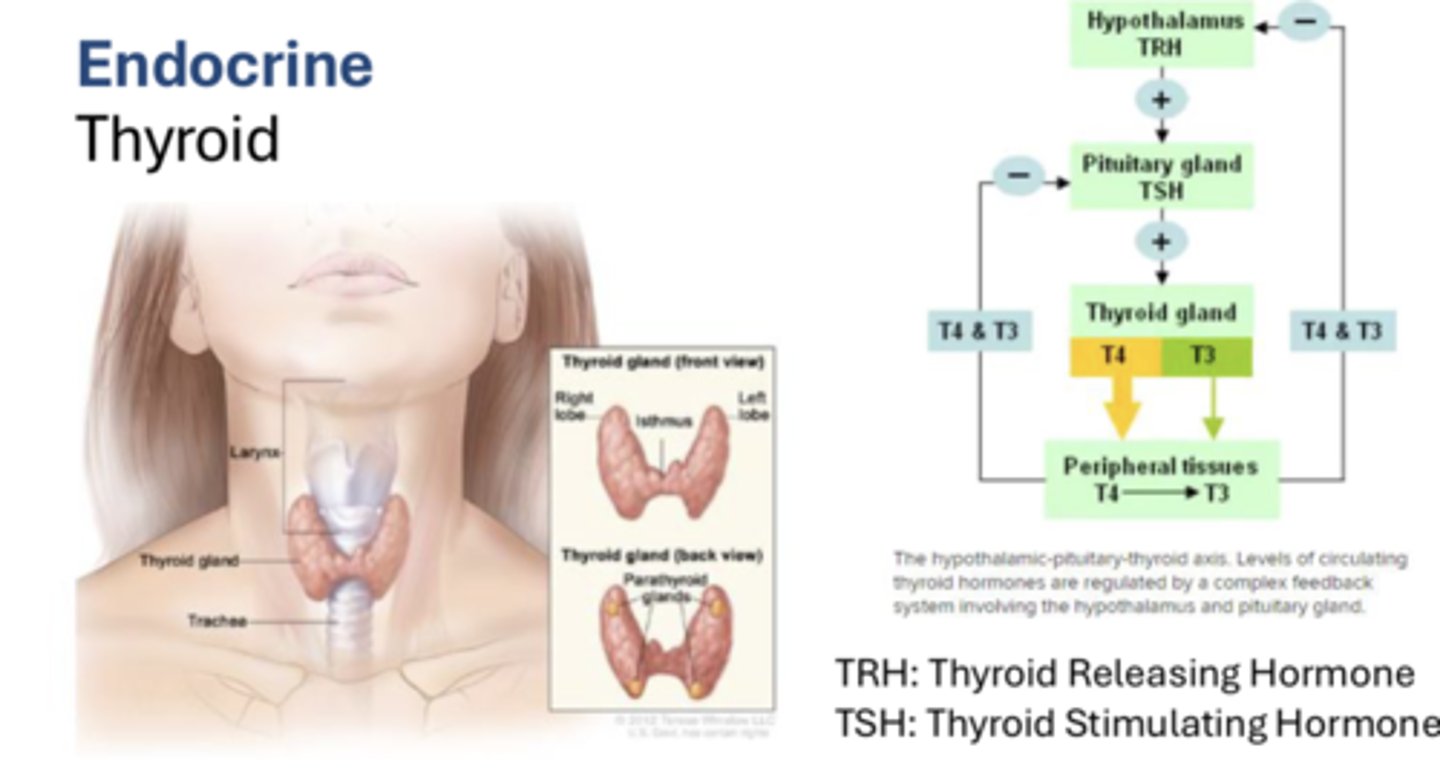
Thyroid hormones:
Hypothalamus:
Pituitary gland:
Thyroid:
Hypothalamus: TRH
Pituitary gland: TSH
Thyroid: T3 and T4
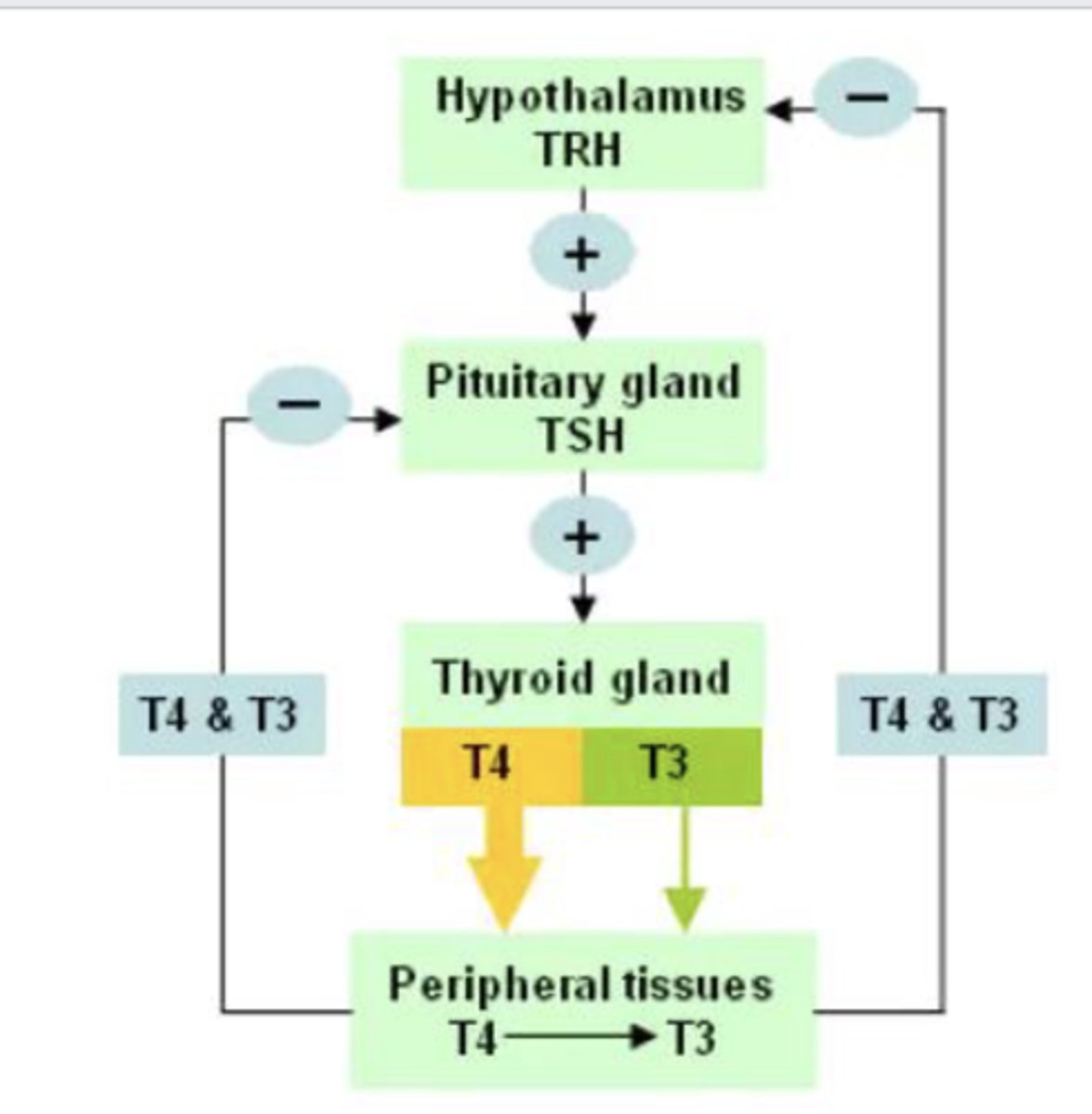
TRH
thyroid releasing hormone
TSH
thyroid stimulating hormone
As T4 and T3 are released....
they serve as a negative feedback loop, inhibiting more release from hypothalamus and pituitary
Endocrine thyroid symptoms
- cold/heat intolerance
- slow/rapid heart rate
- weight gain/loss
- goiter
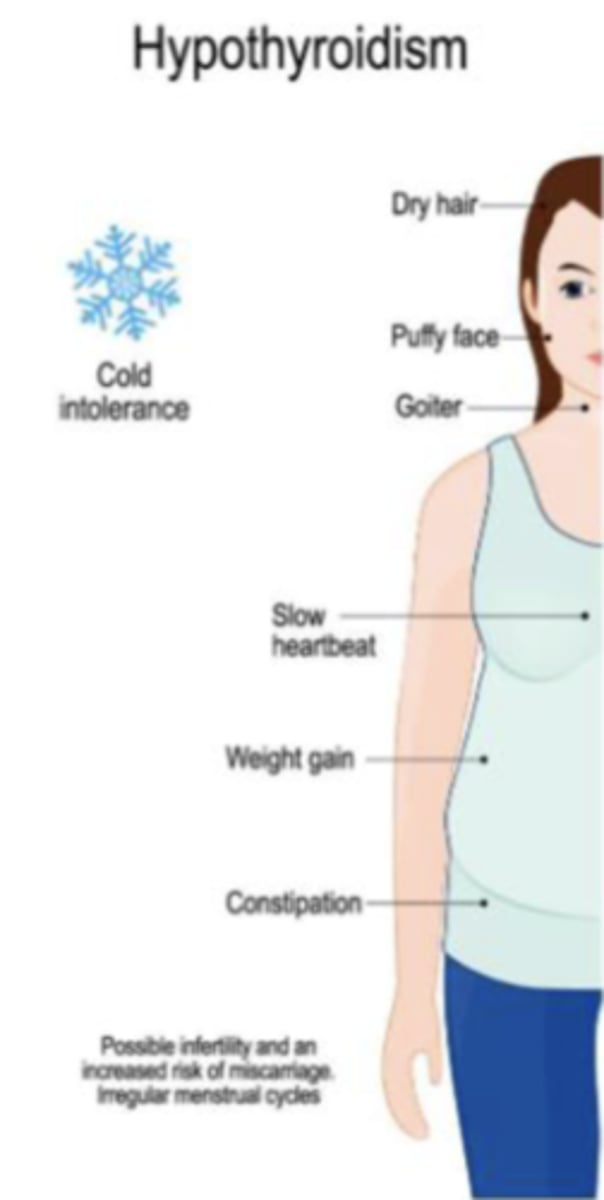
Hypothyroidism
- dry hair
- puffy face
- goiter
- slow heat beat
- weight gain
- constipation
- cold intolerance
- possible infertility and an increased risk of miscarriage, irregular menstrual cycles
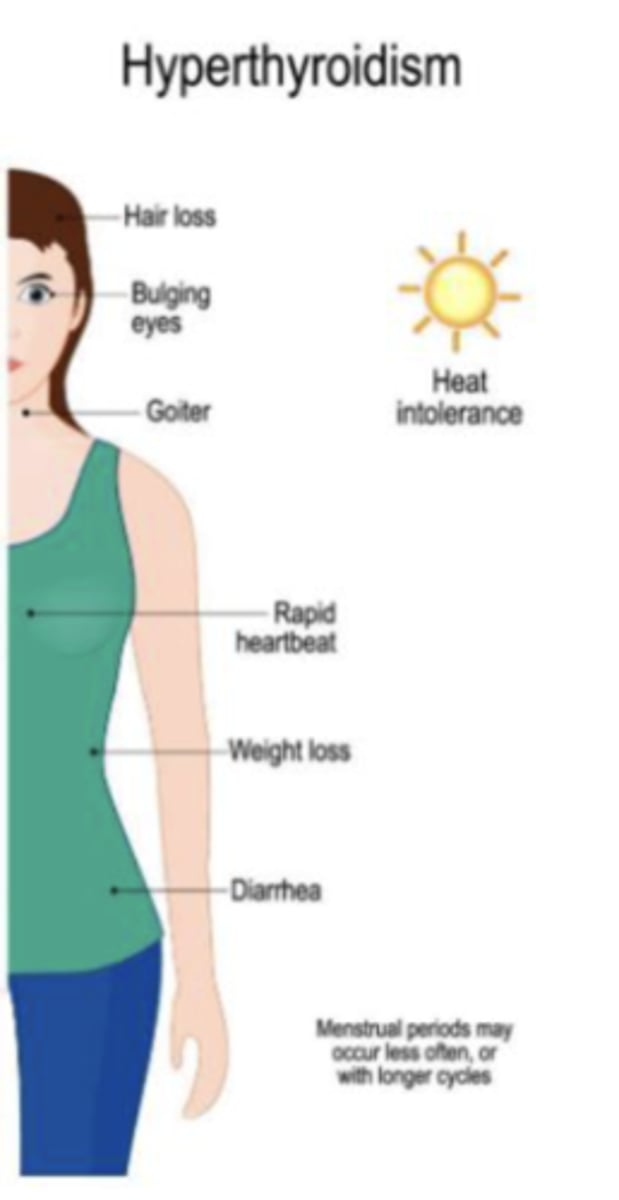
Hyperthyroidism
- hair loss
- bulging eyes
- goiter
- rapid heart beat
- weight loss
- diarrhea
- heat intolerance
- menstrual periods may occur less often, or with longer cycles
TSH normal range
0.5-5 milliunits/L
Is TSH active?
yes, it stimulates thyroid to secrete hormone
TSH HIGH value:
Do you have hypo or hyperthyroidism?
- >5 milliunits/L
- HYPOthyroid
- high TSH means the body is trying to compensate for low thyroid hormone, which is the hallmark of hypothyroidism
TSH LOW value
Is it hypo or hyeprthyroid?
- <0.5 millinuits/L
- HYPERthyroid
- thyroid is overactive, too much T3 and T4. produces less TSH
Is Free T4 thyroid gland active?
What is measured?
- probably active
- measure UNBOUND T4 in serum
High value Free T4 thyroid: Is it hyper or hypo?
high value: HYPERthyroid
Low value Free T4: is it hyper or hypo?
low value: HYPOthyroid
Is total serum T3 active?
free portion is the active form (PROTEIN BOUND)
High value total serum T3: Is it hyper or hypo?
HYPERthyroid
Low value total serum T3: Is it hyper or hypo?
HYPOthyroid
Total serum T4 thyroid gland: Is it active?
free portion
High value total serum T4: is it hyper or hypo?
HYPERthyroid
Low value total serum T4: is it hyper or hypo?
HYPOthyroid
Normal range for A1c (Glycated or glycosylated hemoglobin)
4-5.6%
How is A1c taken?
• VENOUS Blood draw or fingerstick
• NOT require fasting
Glucose is ____________ bound to hemoglobin proportionally to the _________ in serum
- irreversibly
- glucose
A1c provides a _______________ measurement of glucose
3-month measurement
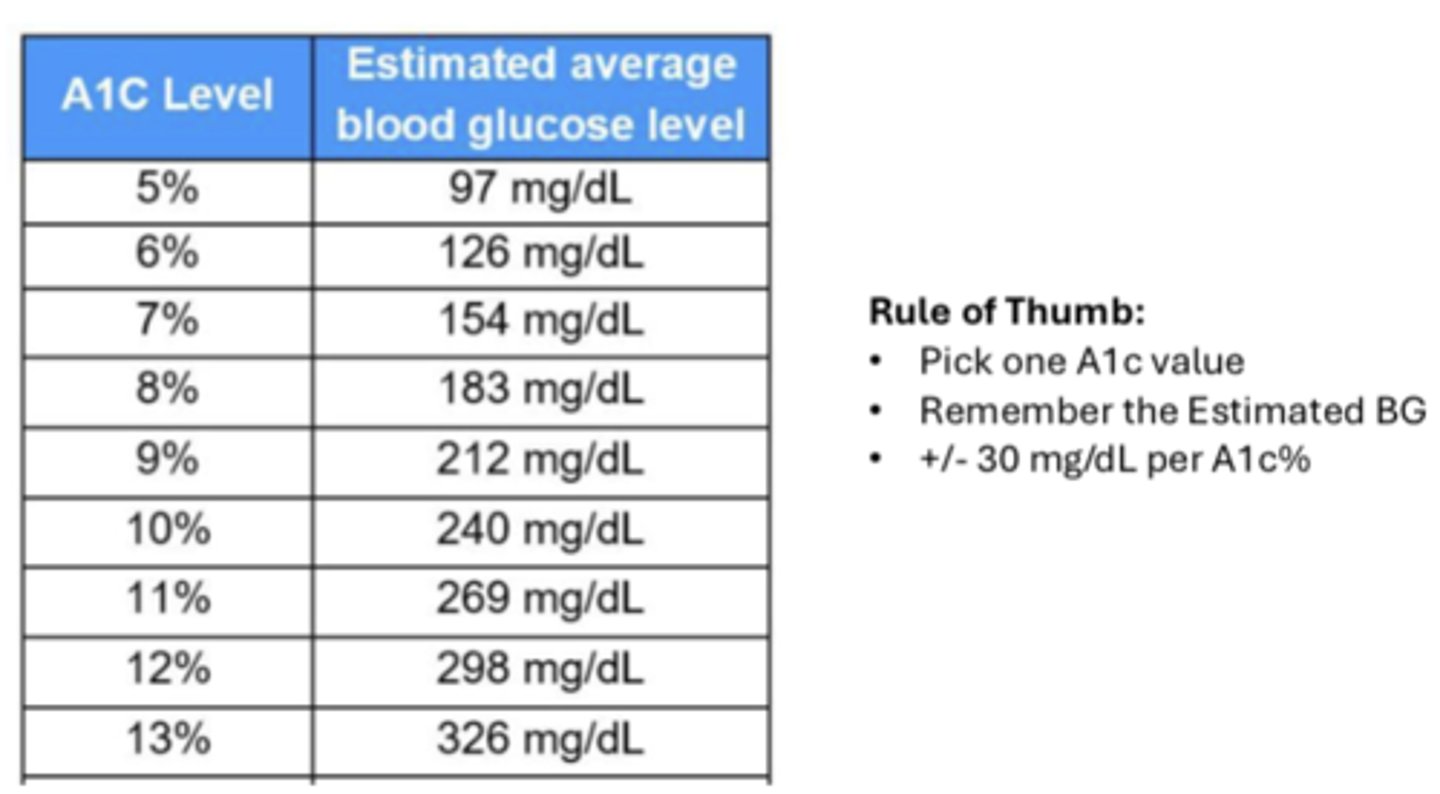
Diabetes - Conversion A1c to estimated BG
A1c conversion to estimated BG
7% = 154 mg/dL
for each 1% increase = + 30 mg/dL
How are lipids measured?
venous blood draw
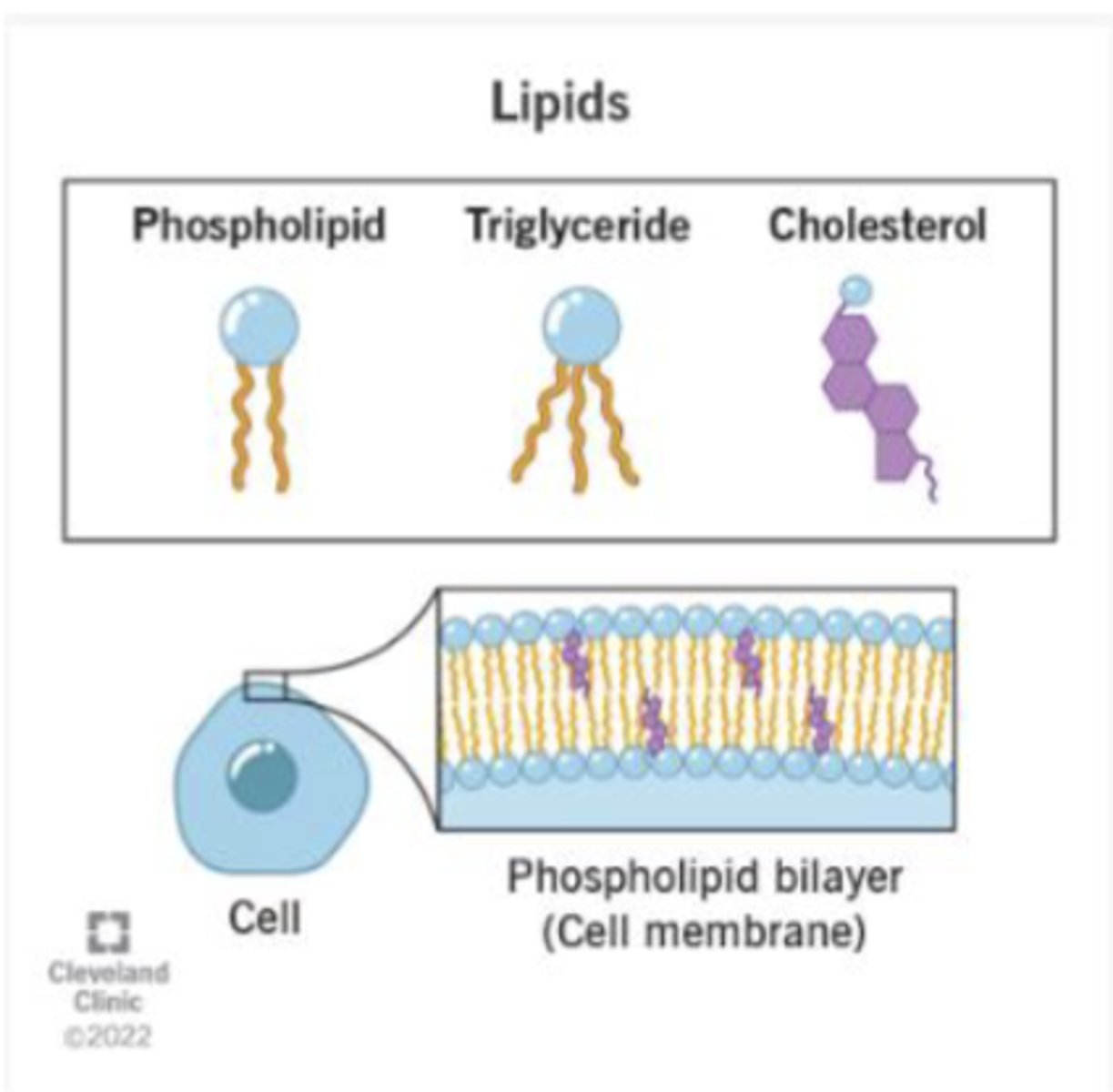
Total cholesterol (TC)
amount og blood cholesterol
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
- "bad" cholesterol
- plaque build up
- cuts off blood flow
High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL)
- "good" cholesterol
- carries LDL away from the arteries
Triglycerides (TG)
- "fat" (VLDL x5 -very low density lp)
- goes up when you eat
T/F: Triglycerides need to be tested after eating
NEED to check labs FASTING
Formula for TC
TC = HDL + LDL + (TG / 5)
Example problem for TC
TC = HDL + LDL + (TG / 5)
• HDL = 42 mg/dl
• LDL = 144 mg/dl
• TG = 148 mg /d
216 mg/dL
Another example problem for TC
TC = 225
HDL = 38
TG = 215
225 = 38 + LDL + (215 / 5)
225 = 38 + LDL +. 43
225 = 81 + LDL
225 - 81 = 144 mg/dL
Total cholesterol normal range
< 200 mg/dL
LDL normal range:
Desirable:
For higher risk:
• <130 mg/dL
• Desirable: <100 mg/dL
• For Higher risk: < 70 mg/d
HDL normal range for men
≥40 mg/dL men
HDL normal range for women
≥50 mg/dL women
Triglycerides normal range
<150 mg/dL
CRP is produced by liver in response to....
injury or infection which causes swelling (inflammation)
CRP role in inflammation
atherosclerosis (build up of plaque in arteries)
What are increased hs-CRP levels linked to?
linked to an increased risk for heart attack, stroke, and heart disease
CRP test usually _________, _______ weeks apart
- twice
- two weeks apart
High hs-CRP range >____________ can lead to ___________
- >2.0 mg/L
- increased risk of heart disease
Cardiology Natriuretic peptides
- B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
- N-terminal-pro BNP (NT-proBNP)
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
hormone/protein released by heart and blood vessels when responding to an increase in pressure or volume
N-terminal-pro BNP (NT-proBNP
more stable BNP form that is elevated in the elderly
What do natriuretic peptides help indicate?
severity of HEART FAILURE
Physiology: Nature defense to relieve stress on the heart
• Blood vessels:
• Blood pressure:
• Heart:
• Kidneys:
• REDUCE hormones that cause...
• Blood vessels: Dilate or relaxes blood vessels
• Blood pressure: Decreases
• Heart: Decreases workload
• Kidneys: Get rid of salt and water (fluids) - cause urination
• REDUCE hormones that cause narrowing of blood vessels, increase the heart rate, or retain fluids (adrenaline, angiotensin, aldosterone)
- Normal adult range for BNP
- Is heart failure likely?
- <100 pg/ml
- heart failure NOT likely
With what range in BNP is heart failure likely?
>500 pg/ml
Troponin
protein in the heart muscle
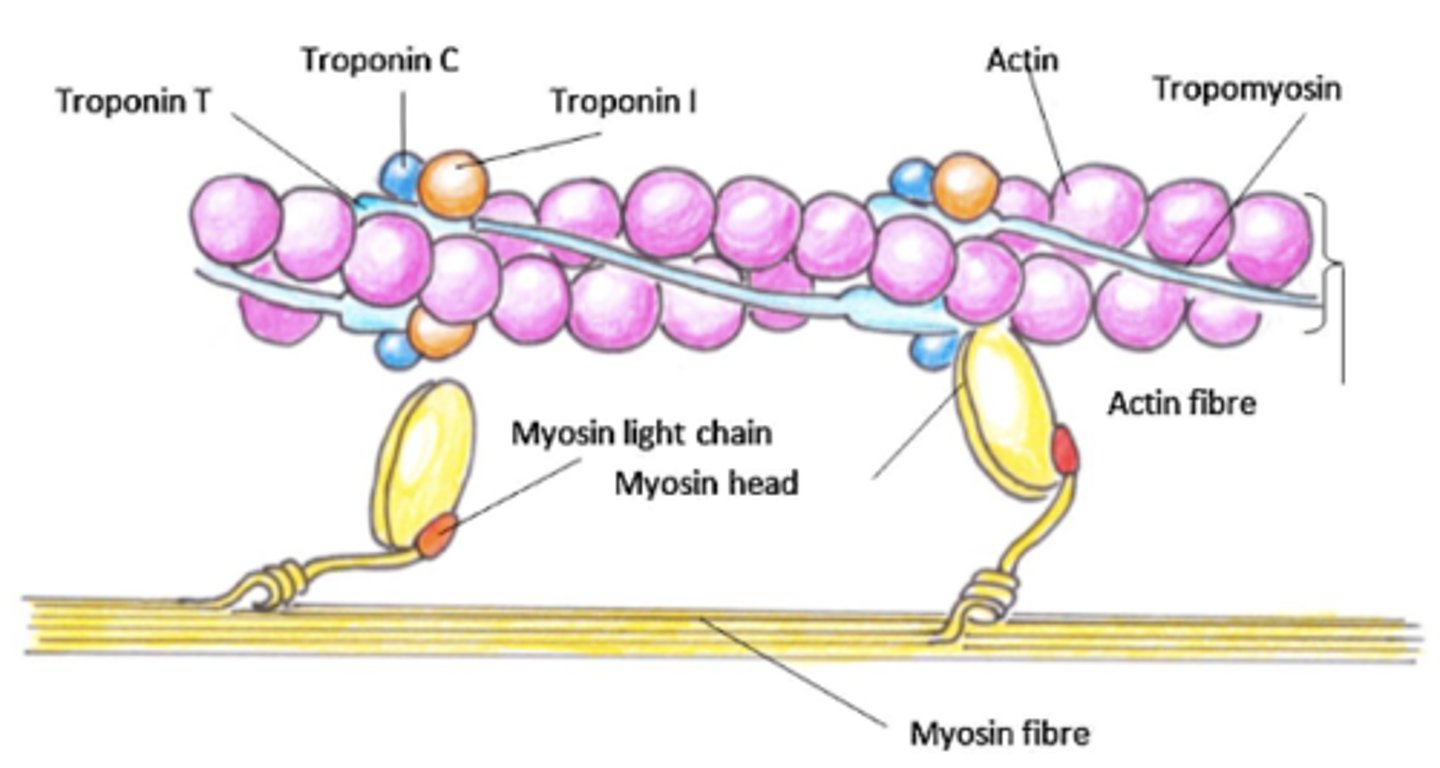
Purpose of troponin (3)
• Detects myocardial injury
• Diagnose heart attack
• Identify risk for heart disease
Troponin's 3 subunits
- Troponin C (TnC)
- Troponin I (hsTNI)
- Troponin T(hsTnT)
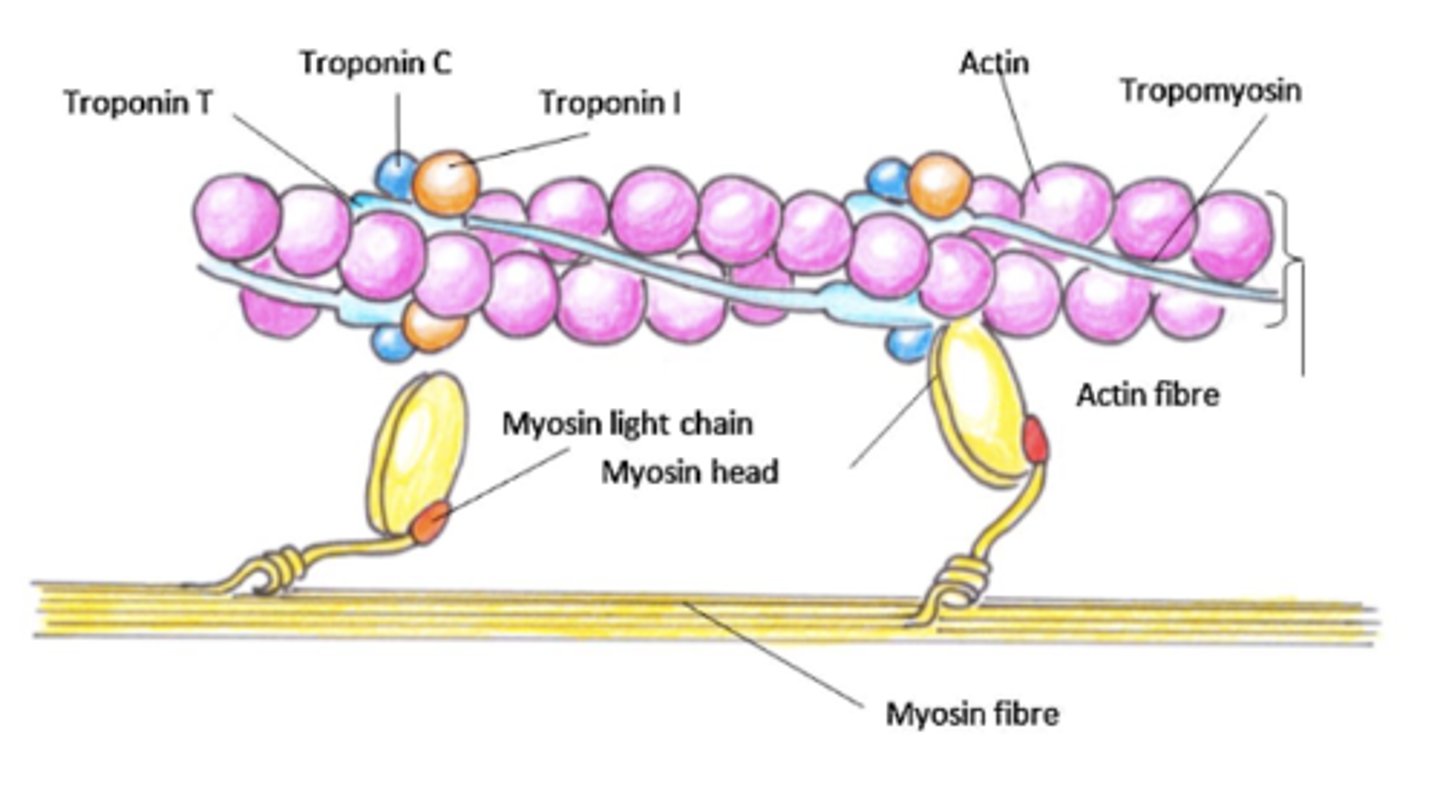
Tropmyosin is a contractile protein that works with _________ and __________ proteins to cause ______________
- actin and myosin
- contractions
Troponin regulates interplay ______________ with actin and myosin needed for _________________ of the heart
- calcium
- muscle contraction
Troponin activation
Troponin C (red) binds Ca2+, which stabilizes the activated state, where troponin I (green) is no longer bound to actin. Troponin T(blue) anchors the complex on tropomyosin
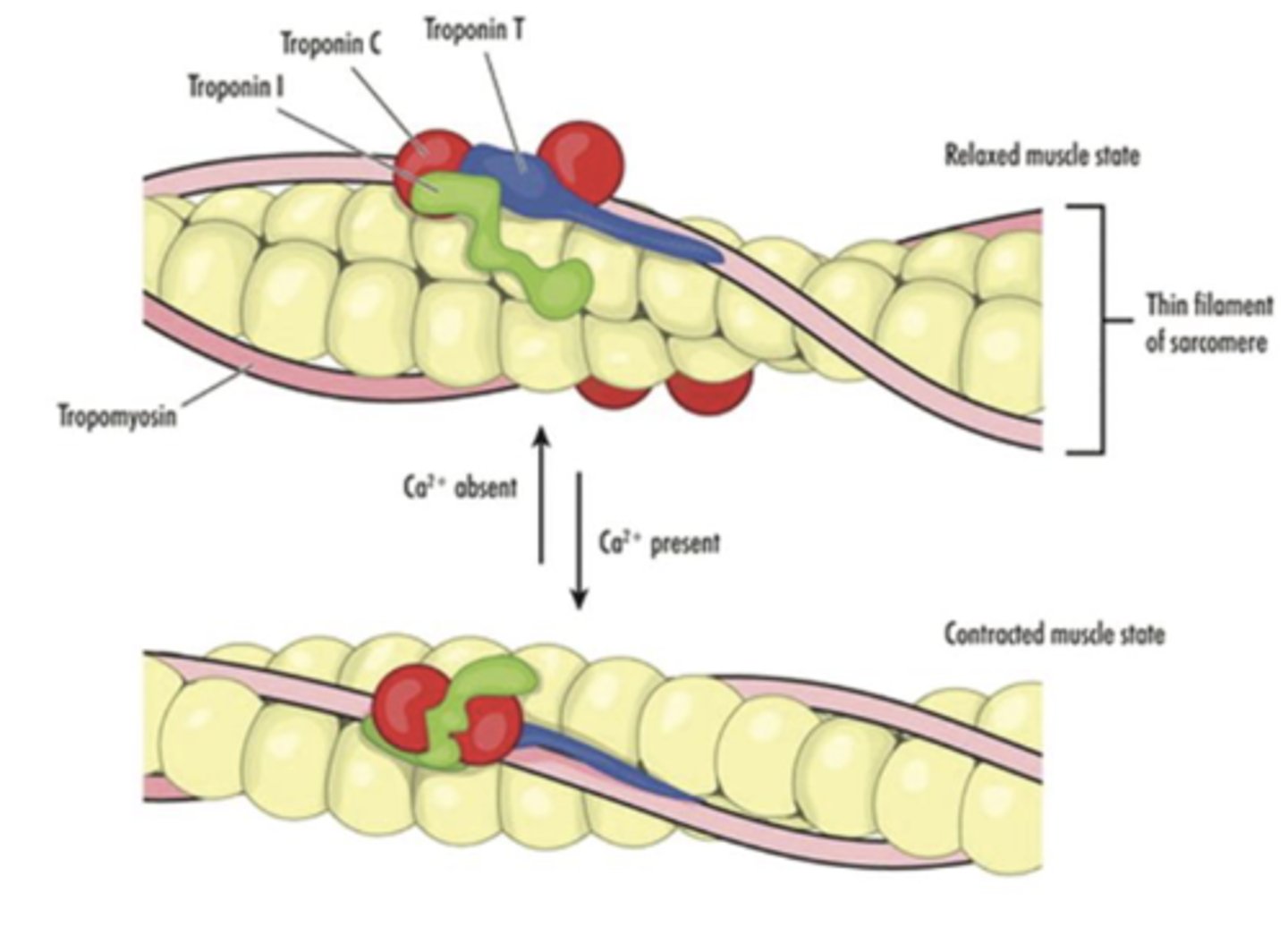
How is troponin tested?
venous blood draw
What are biomarkers of troponin?
• high-sensitivity Troponin I (hsTnI)
• high-sensitivity Troponin T (hsTnT)
• These troponins are very specific to myocardial injury
cTnI
Time to increase:
Time to PEAK:
Time BACK to NORMAL RANGE:
Time to increase: 3-12 hours
Time to PEAK: 24 hours
Time BACK to NORMAL RANGE: 5-10 days
cTnT
Time to increase:
Time to PEAK:
Time BACK to NORMAL RANGE:
Time to increase: 3-12 hours
Time to PEAK: 12-48 hours
Time BACK to NORMAL RANGE: 5-14 days