SQL - Joins & Indexes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are Joins in SQL?
A join clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
What are the types of Joins in SQL Server?
Left outer join
Right outer join
Full outer join
Inner Join
Left join
A left join returns all the rows from the left table, along with any matching rows from the right table.
All left with matching right
-- LEFT JOIN: All rows from Table A, matched rows from Table B
SELECT [list]
FROM [Table A] A
LEFT JOIN [Table B] B
ON A.Value = B.Value;
Right join
A right join returns all the rows from the right table, along with any matching rows from the left table.
All right with matching left
-- RIGHT JOIN: All rows from Table B, matched rows from Table A
SELECT [list]
FROM [Table A] A
RIGHT JOIN [Table B] B
ON A.Value = B.Value;
Full join
A full outer join returns all the rows from both the left and right tables in the join.
Both
-- FULL OUTER JOIN: All rows from both tables, matched where possible
SELECT [list]
FROM [Table A] A
FULL OUTER JOIN [Table B] B
ON A.Value = B.Value;
Inner join
An inner join returns only the common rows from both tables that meet the join condition.
Same
-- INNER JOIN: Only rows with matching values in both tables
SELECT [list]
FROM [Table A] A
INNER JOIN [Table B] B
ON A.Value = B.Value;What is Self-Join and when to use?
A self join is a join of a table to itself.
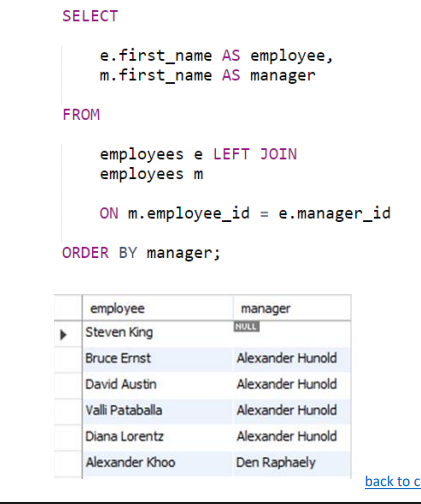
What are Indexes in SQL Server?
Indexes in SQL Server are data structures that improve the speed of data retrieval operations on tables and views.
They are similar to indexes at the start of the BOOKS, which purpose is to find a topic quickly.
What is Clustered index?
A clustered index is a type of index that determines the physical order of data in a table.
physical order
Table data can be sorted in only way, therefore, there can be only one clustered index per table.
only one
In SQL Server, if you set a primary key on a column, then it will automatically create a clustered index on that particular column.
primary key automatically create
What is Non-Clustered index?
A non-clustered index is stored at one place and table data is stored in another place.
A table can have multiple non-clustered index in a table.
EX: Card Catalog (Non-Clustered Index): A separate system that lists books by author name and points to their location on the shelf.
What is the difference between Clustered and Non-Clustered index?
Feature | Clustered Index | Non-Clustered Index |
|---|---|---|
Data Storage | Determines physical order of data in the table | Stored separately from table data; points to row locations |
Quantity per Table | Only one clustered index allowed | Multiple non-clustered indexes allowed |
Performance | Generally faster for range queries and sorting | Slightly slower due to indirect access |
Real-Life Analogy | Books arranged by ISBN on shelves | Card catalog organized by author pointing to book location |
How to create Clustered and Non-Clustered index in a table?
-- Clustered Index
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_name ASC/DESC);
-- Non-clustered Index
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_name ASC/DESC);When you create a PRIMARY KEY constraint, a clustered index on the column is automatically created.
In which column you will apply the indexing to optimize this query. “select id, class from student where name=”happy””?
The column after WHERE condition, which is “NAME” here.