Inorganic 1 Topic 6
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
s and p block
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
… bonds are typically stronger than corresponding … bonds
heteronuclear, homonuclear
Amphoteric defjnition
can act as both an acid and a base
Effective nuclear charge definition
the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom, accounting for both the nucleus and electron shielding effects
The … force between the nucleus and the electron in question is offset by … between the electron in question and all electrons …
attractive, repulsion, between
Electronegativity definition
the ability of an atom to attract electron density towards itself in a molecule
Electronegativity can lead to the … of a covalent bond
polarisation
A … bond with partial charges due to … is sometimes described as having … character
covalent, polarisation, ionic
Is electronegativity affected by oxidation state?
yes: a greater oxidation state results in greater Zeff due to fewer electrons and less shielding
How does the electronegativity differ with respect to different hybridisation states?
sp > sp2 > sp3 due to increased s character
Electronegativity depends on which four properties?
effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
principal quantum number (n)
oxidation state
hybridisation
It is possible for a … to polarise an … in an ionic bond
cation, anion
An ionic bond in which the cation … the anion is described as having some … character
polarises, covalent
Definition of polarizability of an atom
its ability to be distorted by an electric field, such as that of a neighbouring atom
Atoms are … if their … can be distorted easily
polarisable, electron cloud
What type of cations have polarising ability
small and highly-charged
General properties of metals:
electric and thermal conductors
ductile
malleable
lustrous
often form alloys
What type of oxides do metals form?
basic
General properties of non-metals:
poor conductors of heat and electricity
dull
brittle
lower density than metals
What type of oxides to non-metals form?
acidic
Electronegativity values of metals, metalloids, and non-metals:
Metal < 1.9
Metalloid = 1.9 - 2.2
Non-metal > 2.2
What are the requirements for something to be a metal?
must have a partially filled band (band theory)
electrons must be delocalised
Elements with … electronegativity have more … bound electrons in more … orbitals
lower, loosely, diffuse
In a metal, the … orbitals can easily … and therefore … can move easily
diffuse, overlap, electrons
Non-metals in the lower half of the periodic table are … in high oxidation states and … in low oxidation states
acidic, amphoteric
How does electronegativity relate to an element forming a basic or acidic oxide?
basic oxides: low electronegativity
acidic oxides: high electronegativity
amphoteric oxides: intermediate electronegativity
For the s- and p-block, the most important factor determining oxidations state is …
closed shell electronic configuration
Closed shell electronic configuration definition
a state in which all the atomic or molecular orbitals within a specific energy level (e.g. both 2s and 2p) are fully occupied with electrons
Atoms prefer to follow the … and have a …configuration
octet rule, noble gas
Groups in the p-block tend to have favoured …
oxidation states
The favoured oxidation state values in each group tend to vary by …
±2
For the common oxidation states in the p-block, the atoms tend to contain no …
unpaired electrons
The favoured oxidation state of an element in the p-block can … down the group
change
Inert pair effect definition
the tendency of the two outermost s-electrons being excluded from bonding (i.e. the element only uses its p-electrons in bonding), resulting in higher oxidation states becoming inaccessible
In hybridisation of carbon, an … is promoted to a …
s-electron, p-orbital
The energy required to promote an electron to a higher-energy orbital is called the …
promotion energy
For certain compounds, the energy … to … the s-electron is compensated for by the energy … in the formation of more … bonds
required, promote, gained, stronger
How do the electron promotion energies (s → p) change down the groups?
electron promotion energy increases down the group as the energy gap between s- and p-orbitals increase
How does the energy gain from more bond formation change going down a group?
the energy gain decreases as the atoms get larger and the bonds they form are weaker (so release less energy when they form)
Species with … positive oxidation states tend to be good … agents
high, oxidising
What are the effects of the high electronegativity of fluorine and oxygen in terms of being oxidised?
they are sufficiently electronegative to withstand the oxidising effect of species with a high oxidation state, such as in SO3
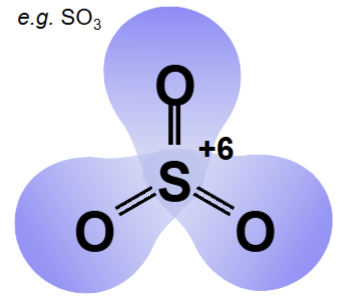
High “formal charge” centres are good at … electrons
attracting
Bond energy definition
the amount of energy required to break a bond into neutral atoms, defined for all gaseous species
Mean bond enthalpy definition
the amount of energy required to break a given bond, averaged over a range of different compounds which contain that bond
Mean bond enthalpies allow us to … trends in typical bond energies across …
compare, multiple compounds
What is the general trend in the strength of homonuclear single bonds?
bonds get weaker as you go down the group
Why does the strength of a homonuclear single bond decrease down a group?
atomic radii increase
orbitals become larger and more diffuse
there is poorer overlap between orbitals, resulting in a weaker interaction
Why are homonuclear single bonds between nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine atoms particularly weak?
N, O, and F are very small atoms
the atoms sit very close together in a single bond
the adjacent lone pairs experience significant repulsion
Why do carbon and boron not experience the same bond-weakening interaction as N, O, and F?
because they don’t have any lone pairs
Why are heteronuclear bonds stronger than homonuclear bonds?
there is a bigger difference in electronegativity in heteronuclear bonds, so there is a degree of strengthening ionic character
As the … difference between atoms in a … bond increases, the strength of the bond … due to … overlap between orbitals
size, heteronuclear, decreases, poorer
Why is the F-F bond weak?
very short bond, repulsion of the positive nuclei
lone pairs in close proximity to each other increases repulsion
MO theory suggests highly-populated anti-bonding orbitals
Why is multiple bonding common in the first row of the p-block but not in other rows?
2p orbitals are small, so lateral overlap to form π orbitals is stronger
Catenation definition
when elements preferentially form lots of single bonds, generating polymer-like structures, rather than form multiple bonds
If sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds, … bonds are more likely to form, and the species will be …
catenated, polymeric
If pi bonds are stronger than sigma bonds, … bonds are more likely to form, and the species will be …
multiple, molecular
Compounds in the second row of the p-block may display …
octet expansion
… involves attack by the … on the oxygen in water
hydrolysis, lone pair
Attack during hydrolysis requires an increase in … of the central atom
coordination atom
CCl4 and SiCl4 are … saturated and obey the …
coordinatively, octet rule
Explanation for the hydrolysis of SiCl4
silicon has empty 3d-orbitals, which are readily available and similar in energy
these allow attack by oxygen lone pair
silicon is a larger atom and there is more space around it for a water molecule to attack
silicon is less sterically hindered
silicon can expand its octet