Unit 3 chemistry
1/36
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Democritus
Came up with the idea of the atom
John Dalton
Father of the atom
First atomic theory:
Dalton- Father of Modern Atomic Theory - has four components
1. All matter is made of indivisible atoms- PROVEN WRONG BECAUSE ATOMS ARE DIVISIBLE
2. All atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different
from those of any other element— PROVEN WRONG BECAUSE SUBATOMIC PARTICLES OF THE SAME ELEMENT CAN HAVE DIFFERENT ISOTOPES
3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with
one another in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds (Law of Definite
Proportions)
-applies when 2 or more elements combine to make more than one type of compound
(Law of Multiple Proportions)
4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of
one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical
reaction

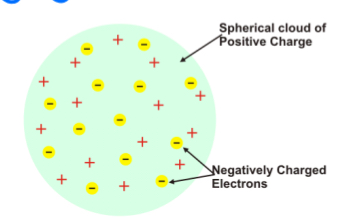
Thomson
Used a Cathode ray tube (discovered by Sir. William Crookes) and magnetics discover the electron.
Found atoms are divisible
Plum pudding model
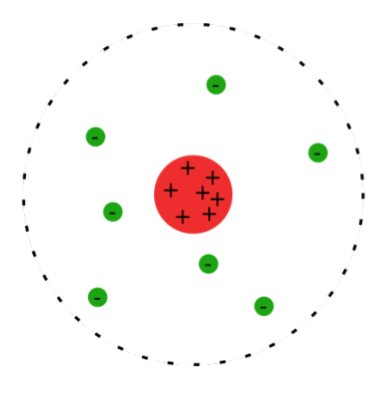
Rutherford
Used gold foil and alpha radiation to discover the proton and nucleus
Protons inside nucleus and electrons are around
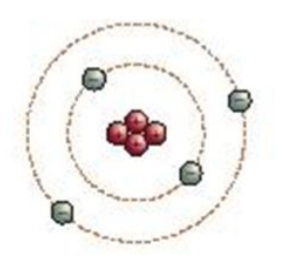
Bohr
Bohr model
Electrons move in orbits that have a set amount of energy levels
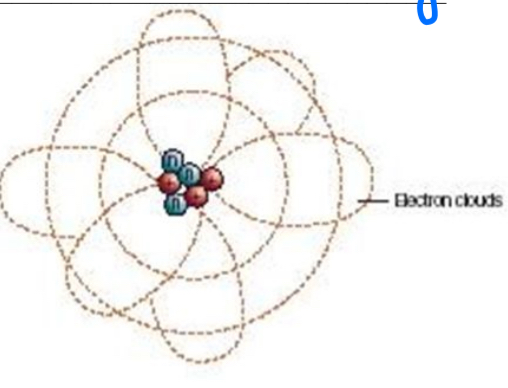
Schrödinger
Quantum Mechanic model
Electron clouds- wave function
Chadwick
Discovered neutron
Found that different masses of the same element
Becquerel
Discovered radioactivity
Alpha Radiation- positive-can be stopped by paper
Beta Radiation- fast moving electrons-can be stopped aluminum foil
Gamma Radiation-no mass, no charge- can be stopped by lead or concrete
Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom
Identifies the element
Mass number
Number of protons AND neutrons
Atom Mass
the weighted average of the mass of different isotopes of the same element based on their abundance in nature
Nucleus
contains protons and neutrons, takes up very little space, contains the mass of the atom
Electron Cloud
contains electrons, takes up all the volume of the atom
Nuclear Notation

Hyphen Notation
Name of element - mass number (Ex. Carbon-13)
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutons.
Same atomic #, different mass #
Netural atoms
Number of electrons equals to number of protons
Ions
Atoms that have gained or lost electrons
Cation- positive, lost electrons
Anion- negative, gained electrons
Chemical reactions:
1. Definition
2. What happens to the atoms during reactions?
3. The subatomic particles involved during reactions.
4. Energy change (heat) during reactions
5. Factors that influence the speed of reactions
Chemical reactions occur when bonds are broken and/or formed
No new elements
Valence electrons are the only subatomic particles involved during the reaction
Small energy change
Temperature and catalyst affect speed of chemical reactions
Nuclear reactions
1.Definition
2. What happens to the atoms during reactions?
3. The subatomic particles involved during reactions.
4. Energy change (heat) during reactions
5. Factors that influence the speed of reactions
Nuclear reactions Occur when a nucleus emits particles and/or rays
New elements are made
Protons and neutrons are involved in reaction
Large energy change
Temperature and catalyst DO NOT influence speed of nuclear reactions
Alpha radiation
Helium nucleus
+2 charge, 4 mass,
slowest
can be blocked by paper

Beta
fast moving electrons
Charge= -1
Mass= 0
Medium speed
Can be blocked by Al foil

Gamma
High energy electromagnetic radiation
Light
Charge=0
Mass=0
Fastest
Can be blocked by lead(Pb) or concrete
Balancing Nuclear Reactions
Balance the mass number (the total of mass numbers on the left is equal to the right)
2. Balance the atomic number (the total of atomic numbers on the left is equal to the right)
3. Take into account the coefficient when applicable.
4. Identify the missing element by using the atomic number
5. Possible missing particles involved in nuclear reactions are:
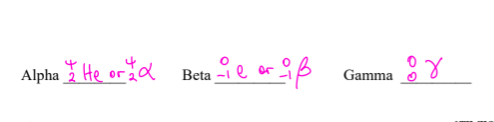
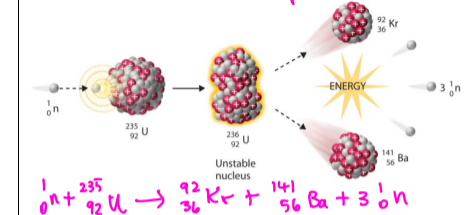
Fission
A nucleus splits into multiple nuclei
Happens in nuclear reaction/ weapon
Fussion
Two nuclei combine into one nucleus
Only happens on the star or sun
More energy produced than fission
Waste is safer
Dmitri Mendeleev
arranged elements by increasing atomic mass
Mendeleev’s periodic table was in error because as atomic masses became calculated more accurately; it was evident that some elements were placed into groups with differing properties
Henry Moseley
organized the elements by increasing atomic number instead of atomic mass. This arrangement resulted in a clear periodic pattern of properties
Periods
Horizontal rows
Increasing energy levels
Groups
Aka families
Same # of V.E
Most reactive nonmetals
Halogens
Most active metals.
Alki metals
Most active metal
Francium
Most active nonmetal
Fluorine
As you go down metals…
Become more active
As you go down nonmetals become..
Less active