Micro HSB - Digestive System Development and Histology
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Epithelial lining and glands
Germ layer present at 2 weeks - ENDODERM (2)
Lamina propria, muscularis mucosae, submucosa, muscular serosa and externa
Germ layer present at 2 weeks - MESODERM (5)
Enteric nervous system and posterior luminal digestive structures
Germ layer present at 2 weeks - ECTODERM (2)
3-4 weeks, yolk sac
The PRIMITIVE GUT develops at weeks _____ to _____, by incorporating _________ during the craniocaudal and lateral folding of the embryo.
Foregut
Esophagus, liver, gallbladder, stomach, bile duct, pancreas, and proximal duodenum is classified as
Midgut
Distal duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, 2/3 of transverse colon is classified as
Hindgut
1/3 of transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, upper anal canal is classified as
Cloaca
Endoderm-lined cavity covered at its ventral boundary by surface ectoderm
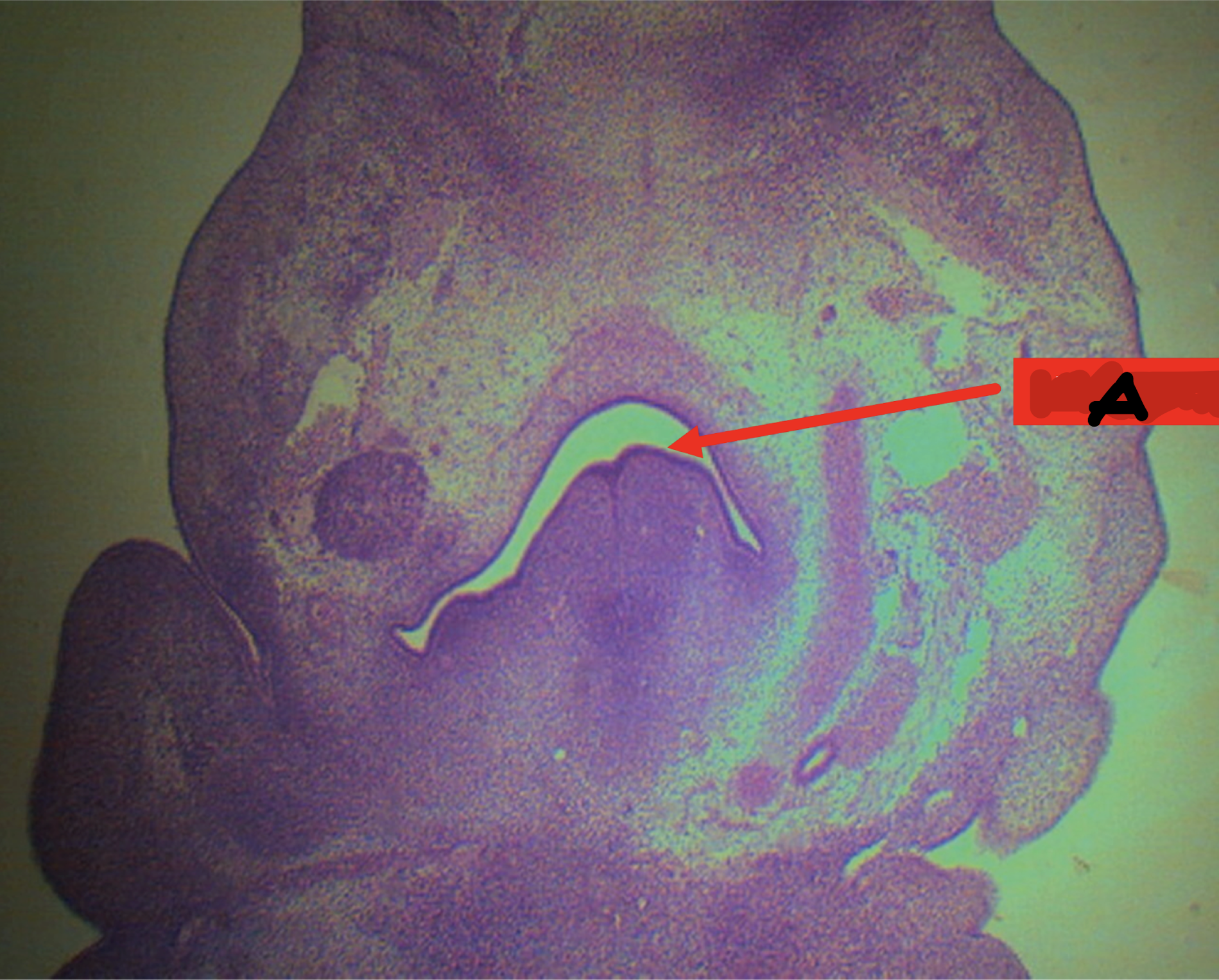
A: pharynx
Identify the structure
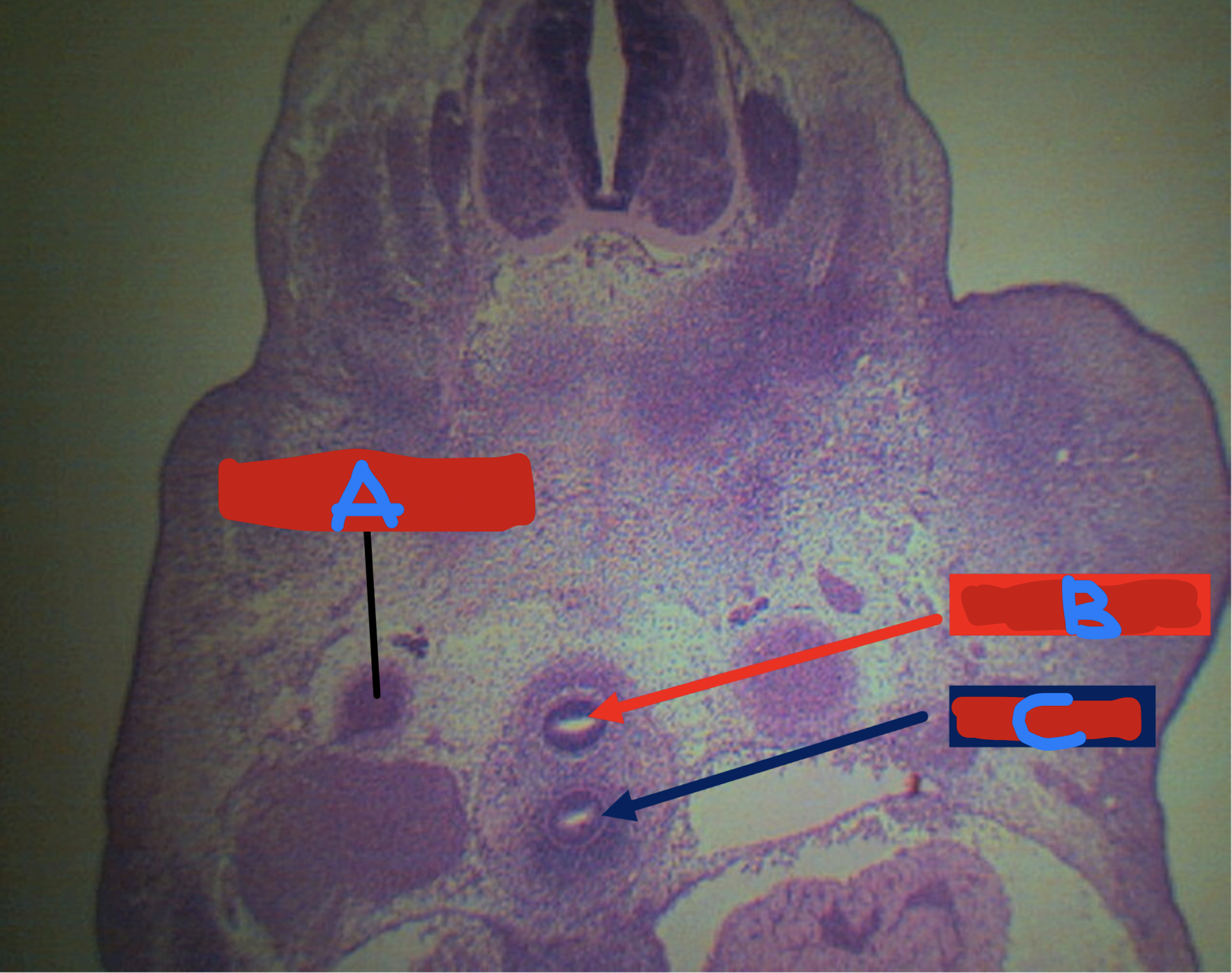
A: dorsal aorta
B: esophagus
C: trachea
Identify the structure
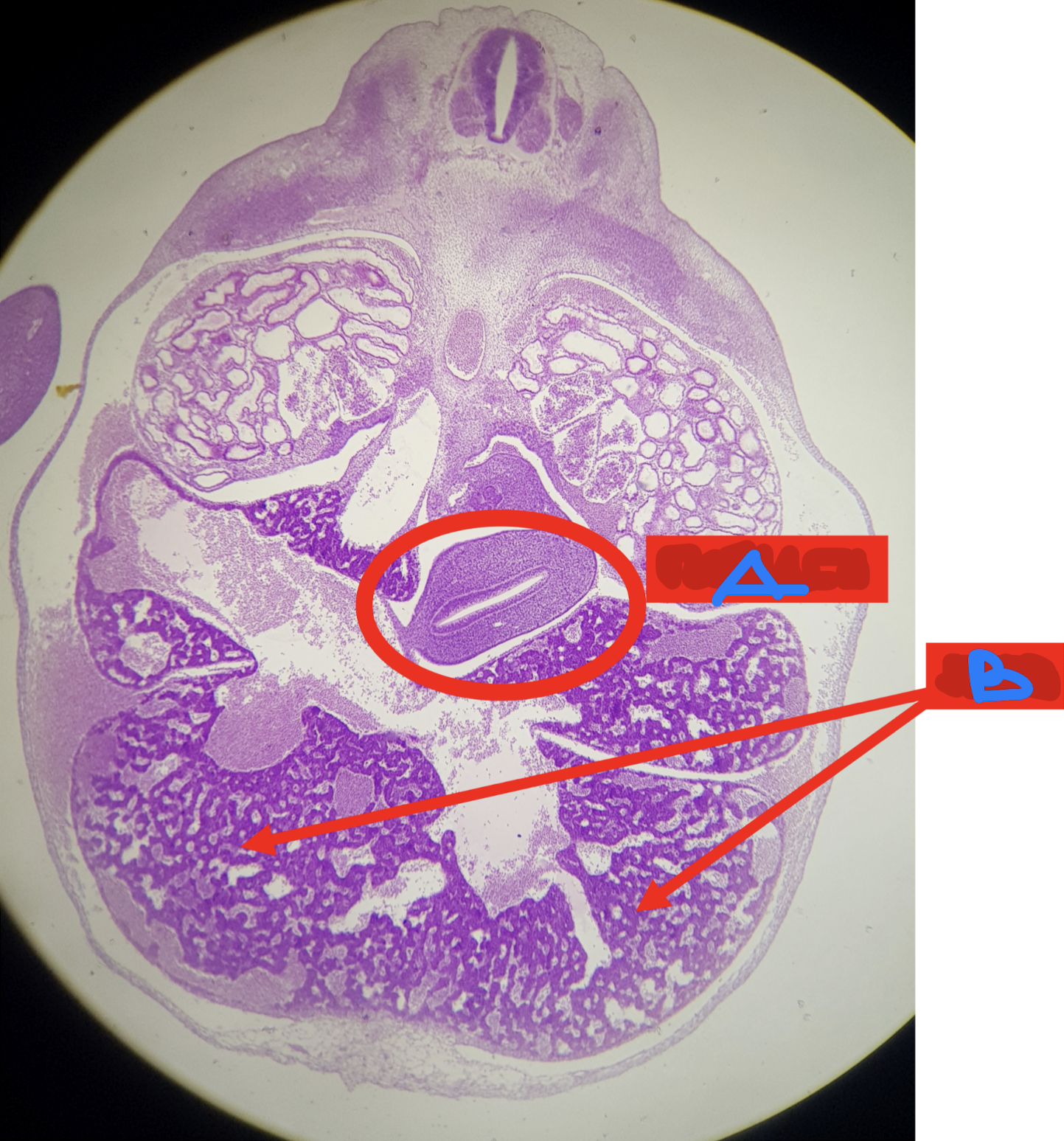
A: stomach
B: liver
Identify the structure
A: dorsal mesentery
B: dorsal pancreatic bud
C: stomach
D: liver sinusoid
Identify the structure
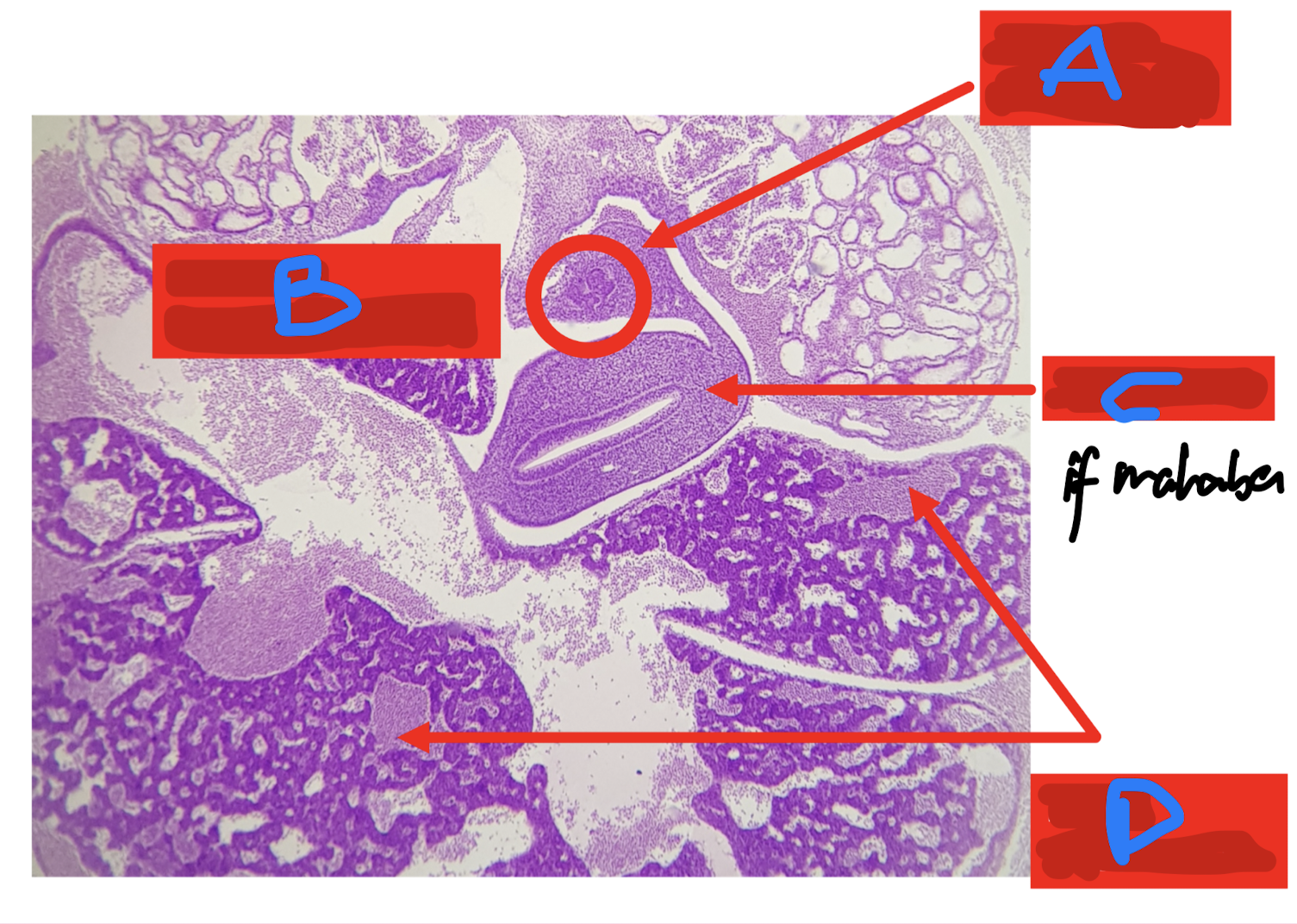
A: dorsal pancreatic bud
B: duodenum
C: liver sinusoid
Identify the structure
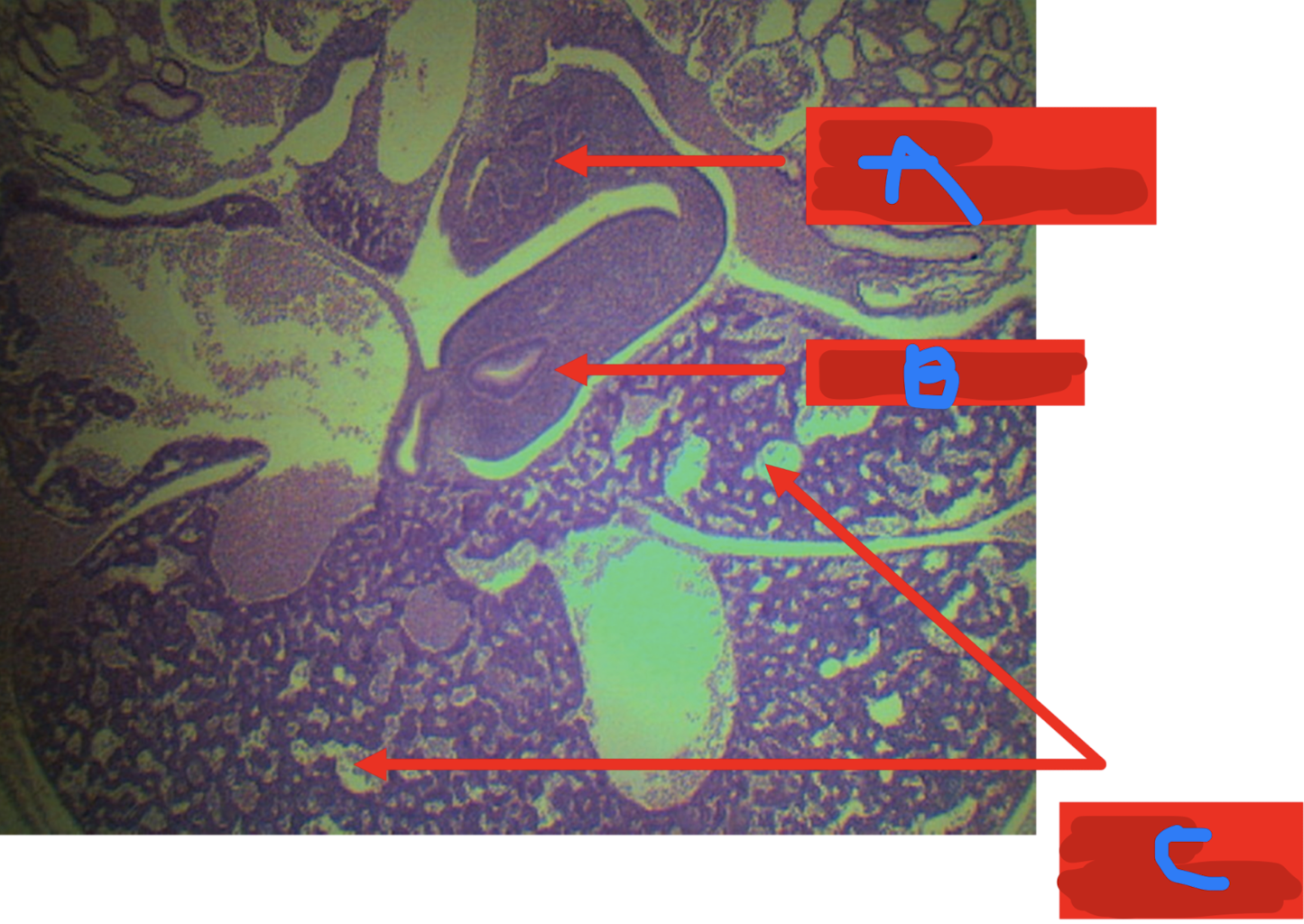
A: dorsal pancreatic bud
B: ventral pancreatic bud
C: duodenum
Identify the structure
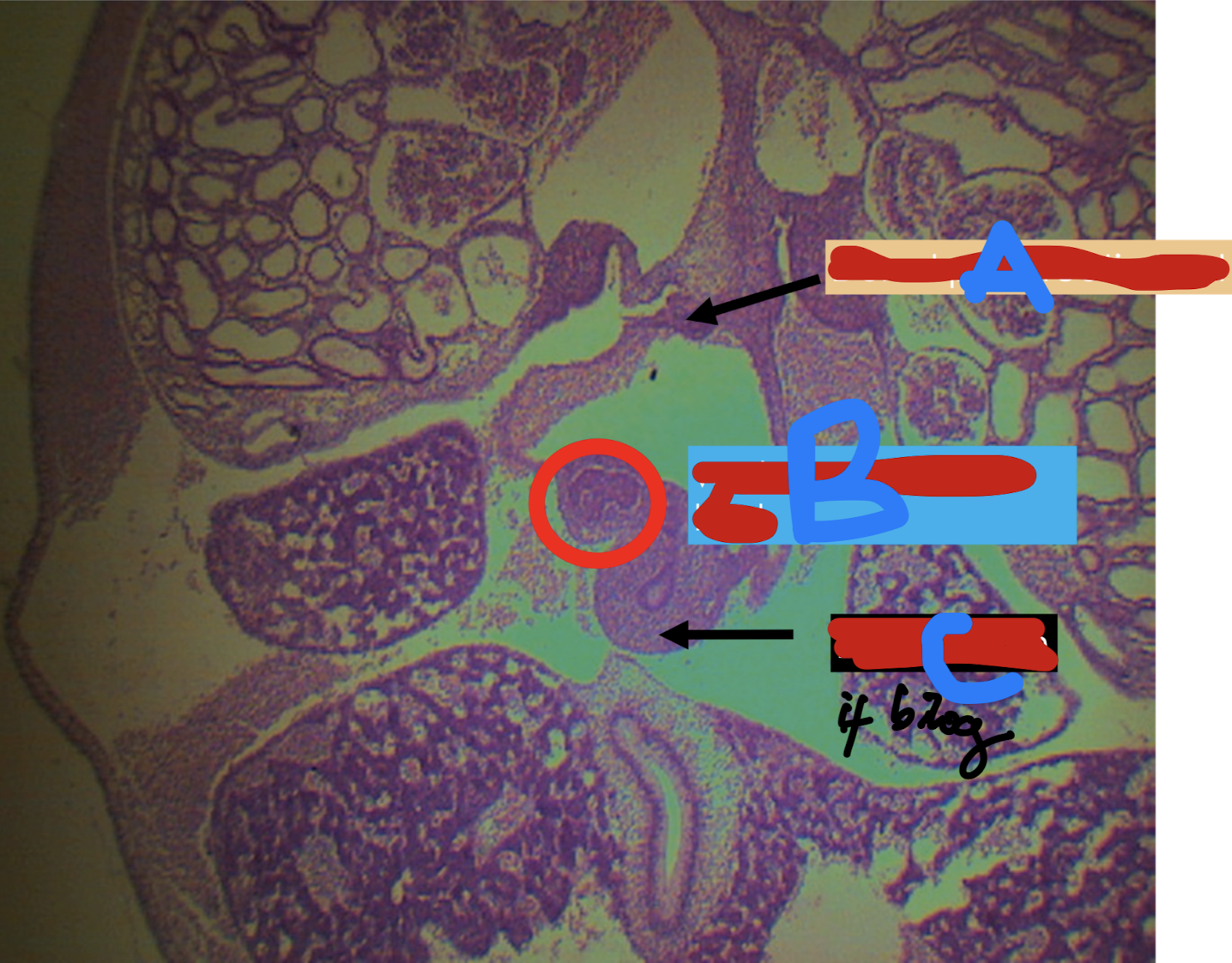
A: dorsal pancreatic bud
B: ventral pancreatic bud
C: duodenum
D: liver
Identify the structure
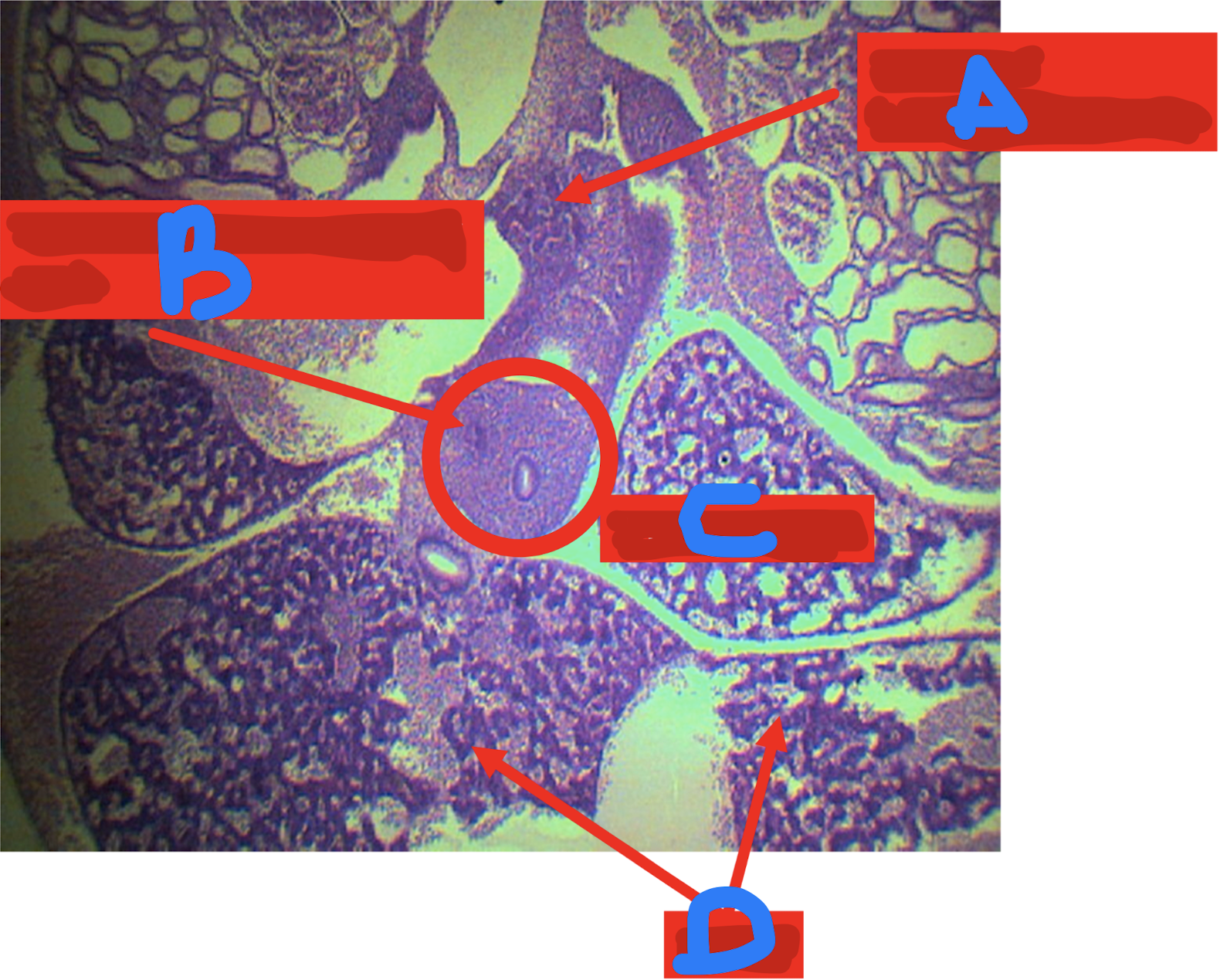
A: duodenum
B: cystic duct
C: gallbladder
D: liver
Identify the structure
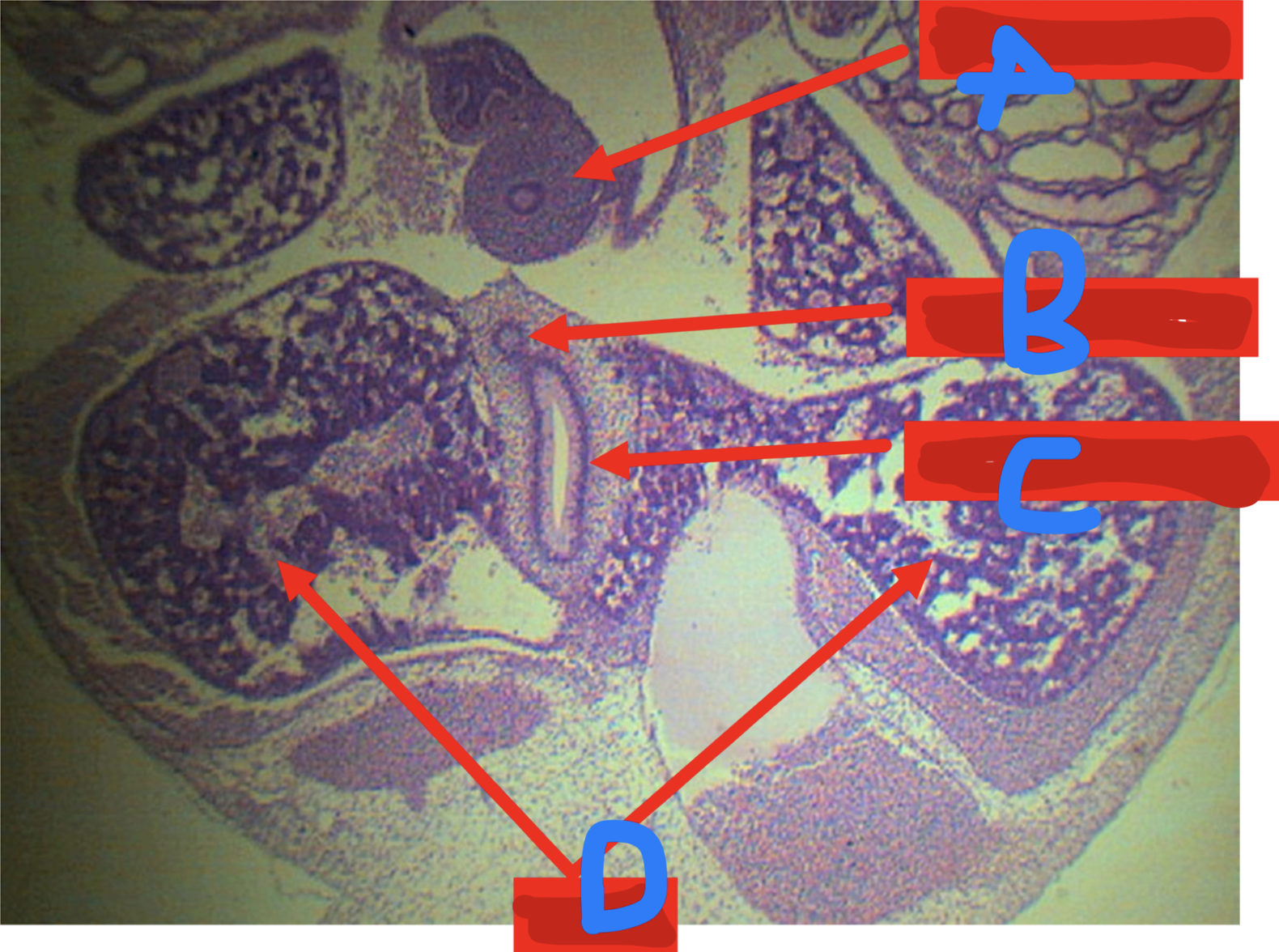
A: mesocolon
B: colon
Identify the structure
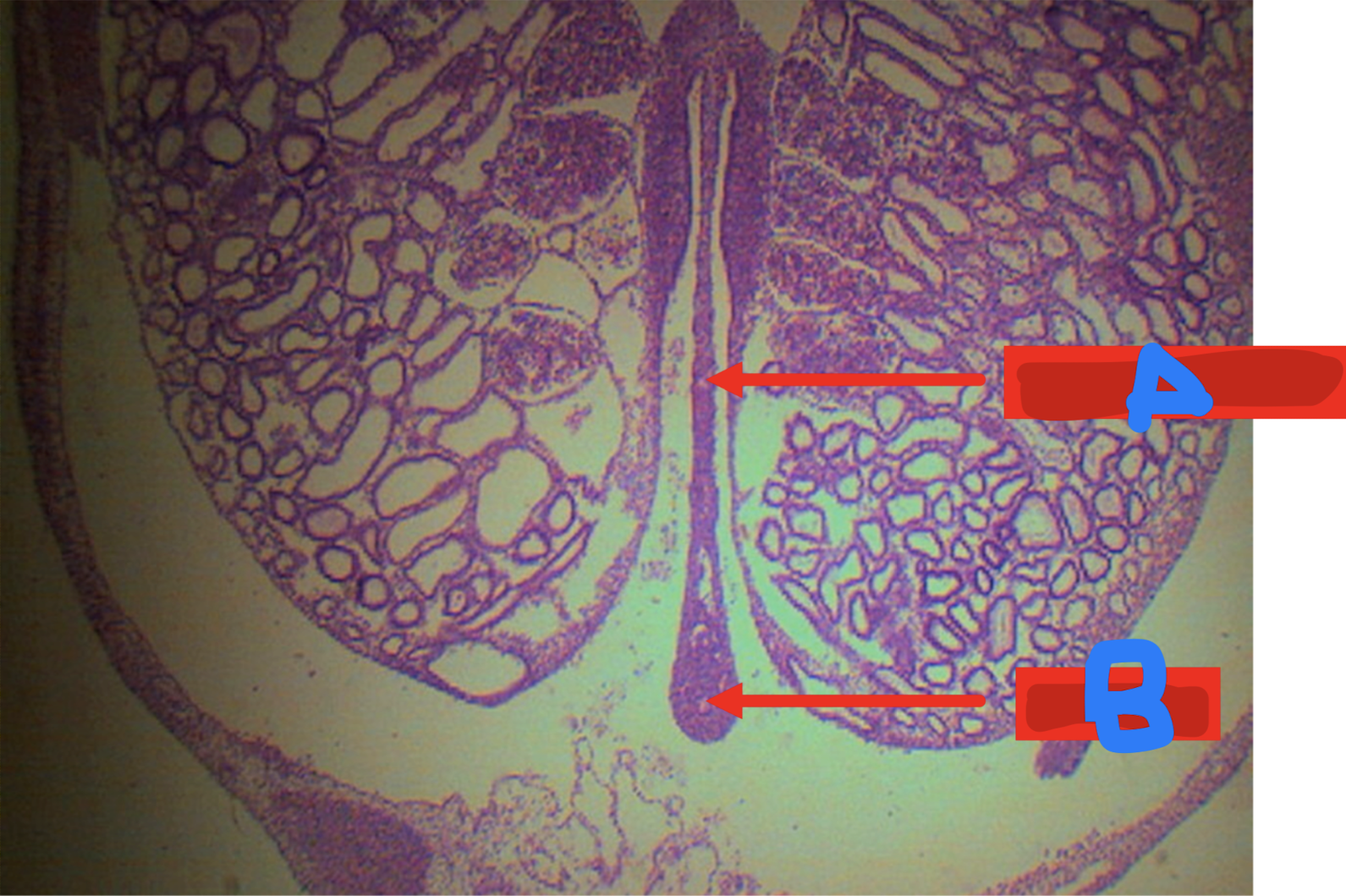
A: physiologic herniation of intestinal loop
Identify the structure
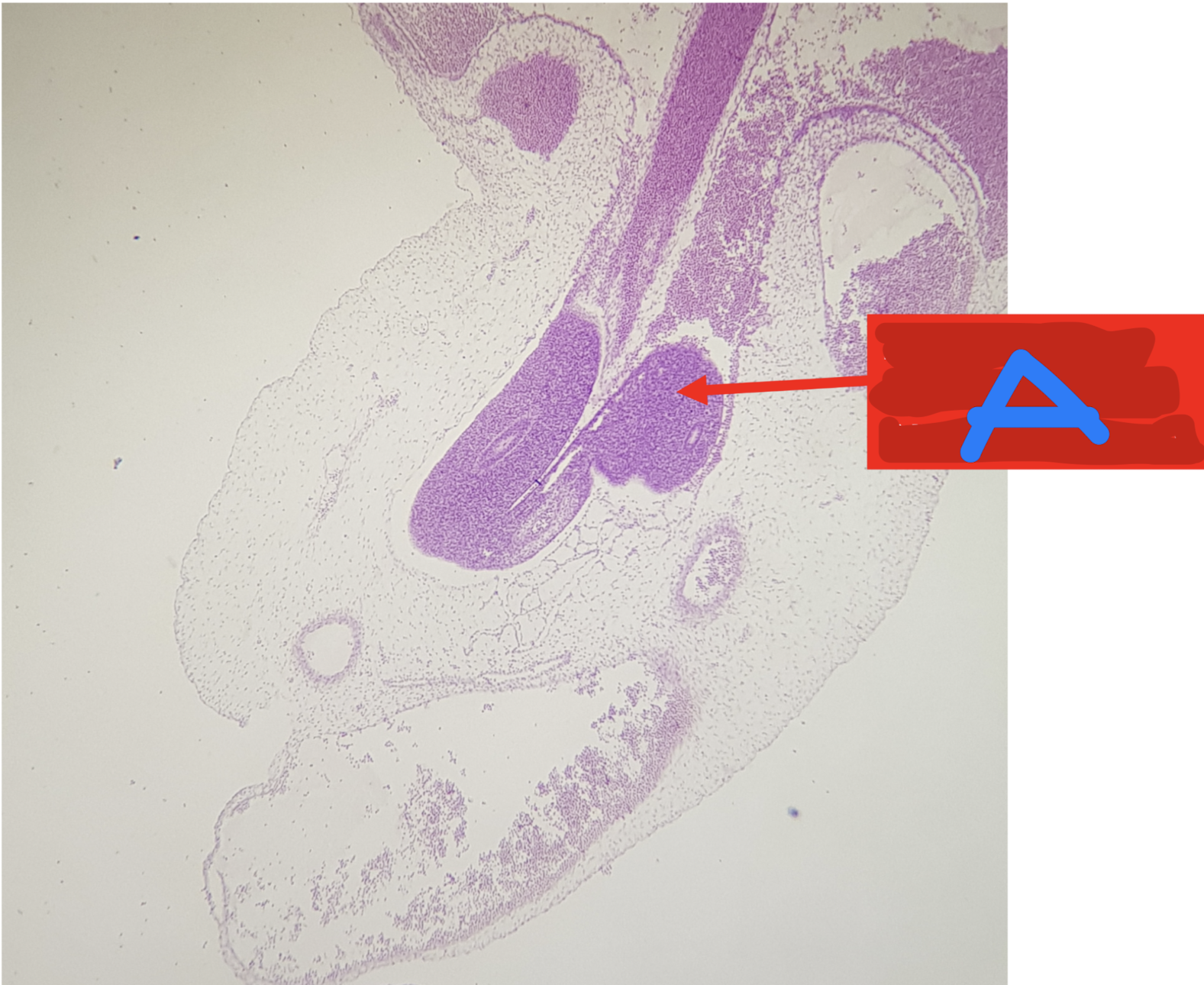
A: physiologic herniation of intestinal loop; week 10-12
Identify the structure; it returns back to the abdominal cavity at weeks _____
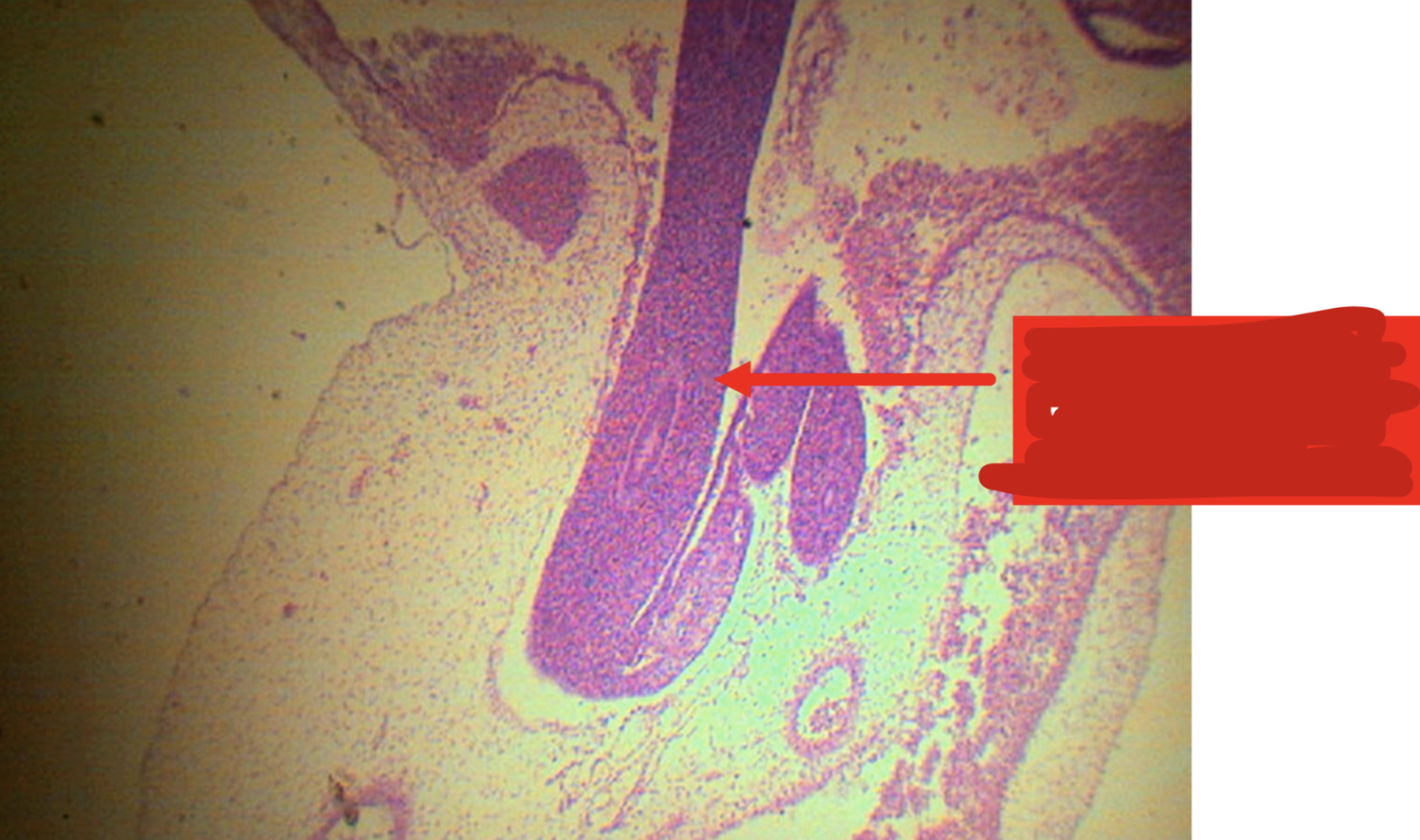
A: physiologic herniation of intestinal loop; week 10-12
Identify the structure; it returns back to the abdominal cavity at weeks _____
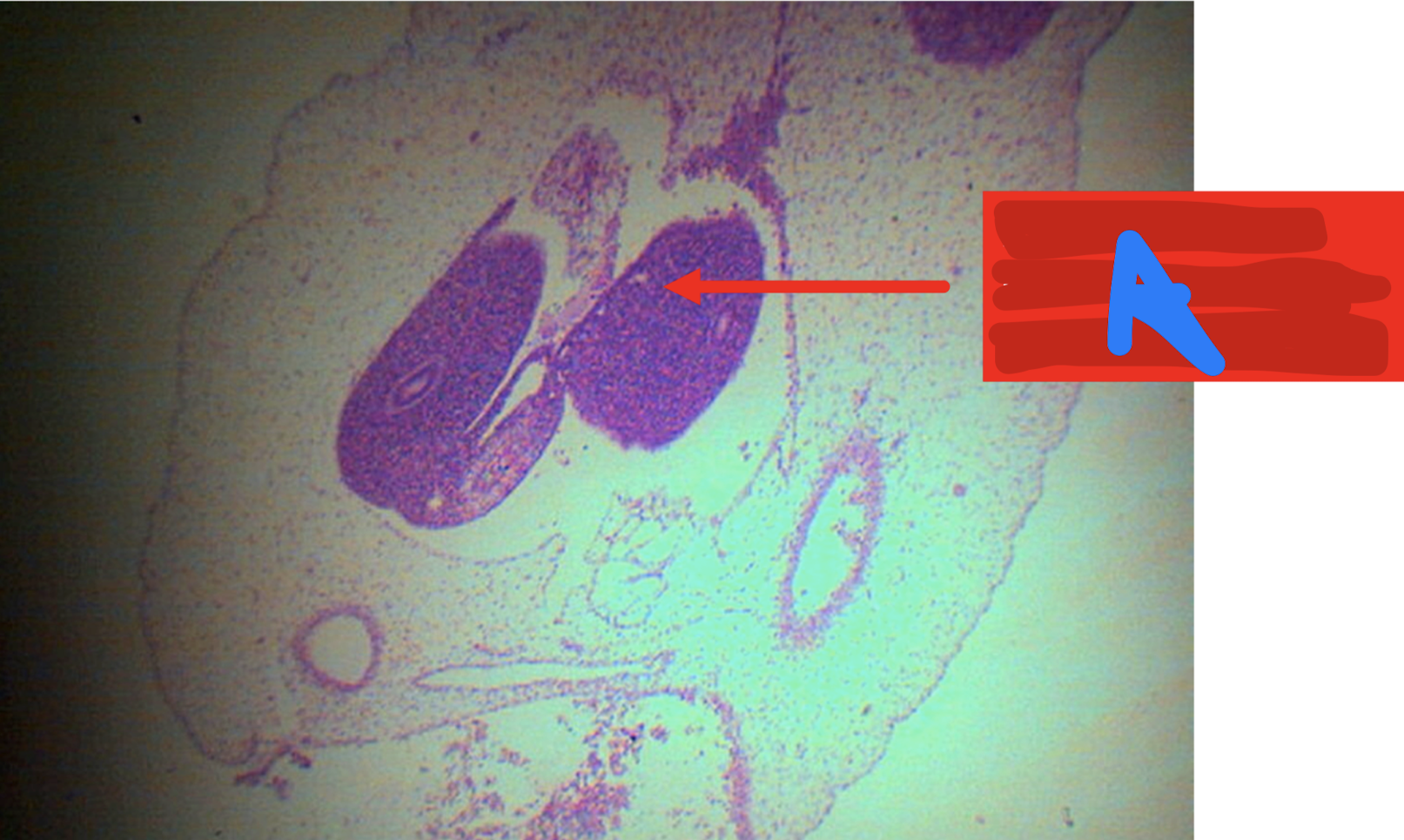
A: cloaca
B: urorectal septum
C: urogenital canal/sinus
D: anal canal (anorectal canal)
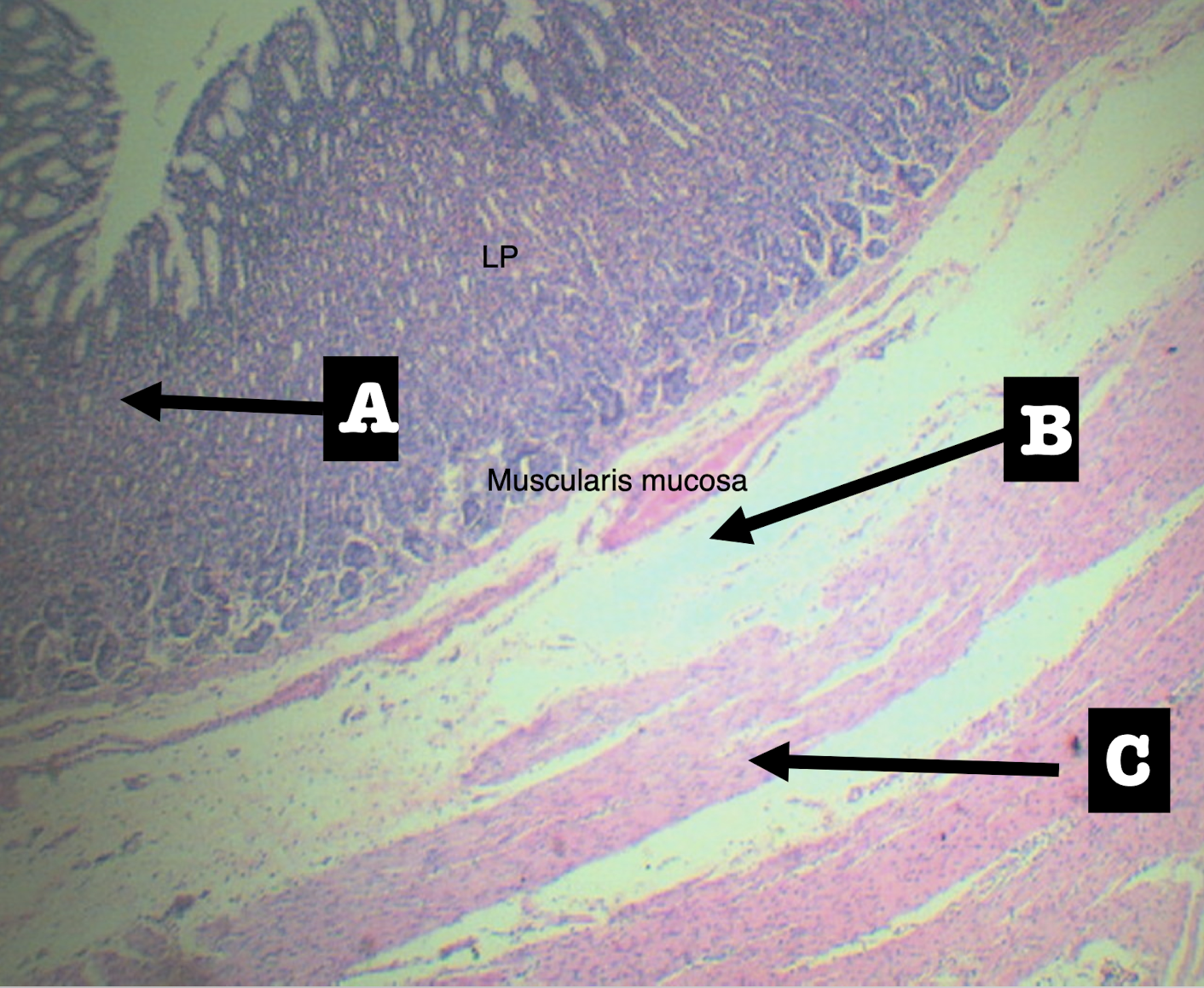
Identify the structure
mucosa
submucosa
tunica muscularis/muscularis propria
tunica adventitia/tunica serosa
4 layers of the digestive tract
lining epithelium
lamina propria
muscularis mucosa
3 layers of the mucosa of the digestive tract
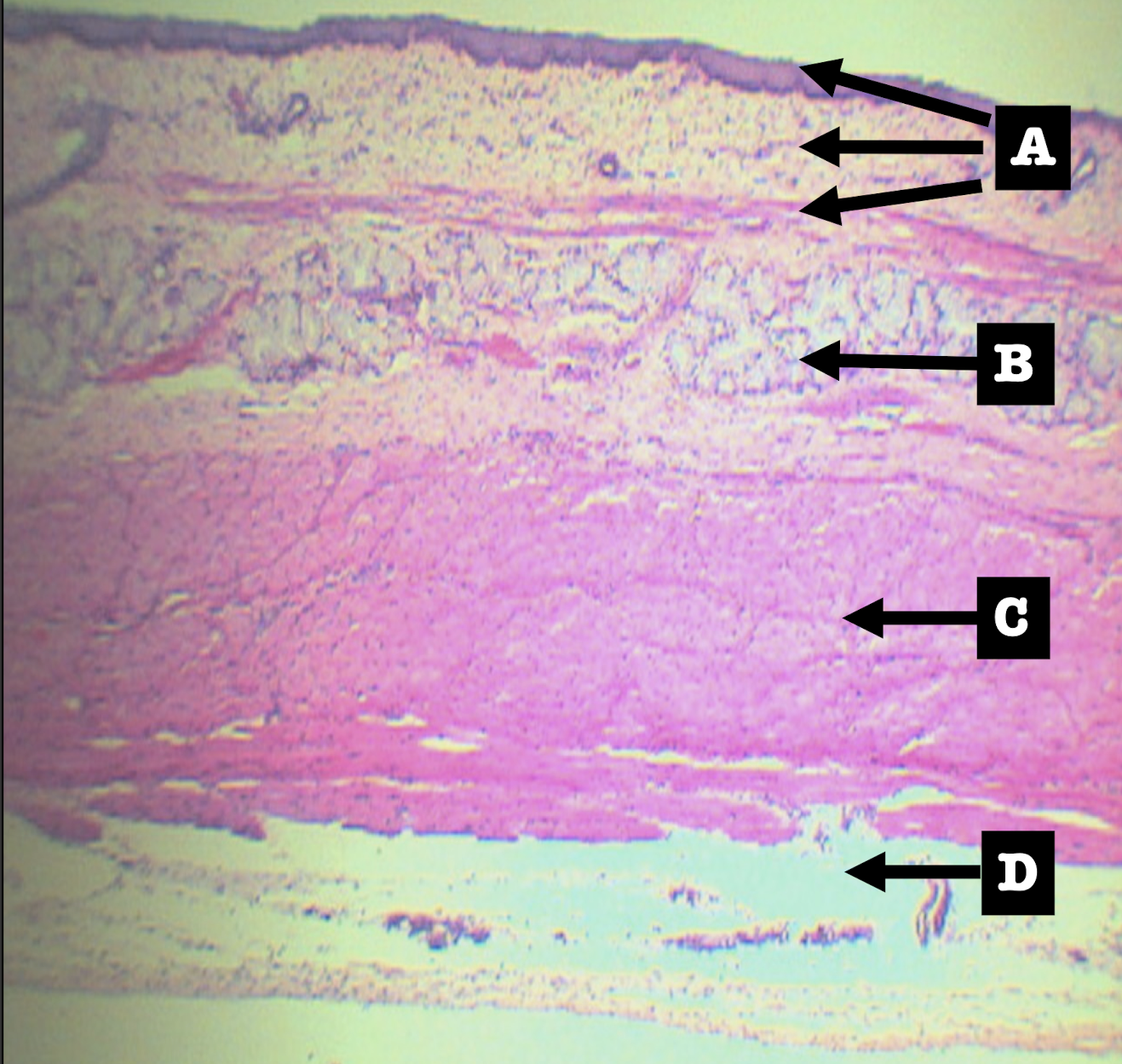
Scanner View of ESOPHAGUS
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
D: tunica adventitia/serosa
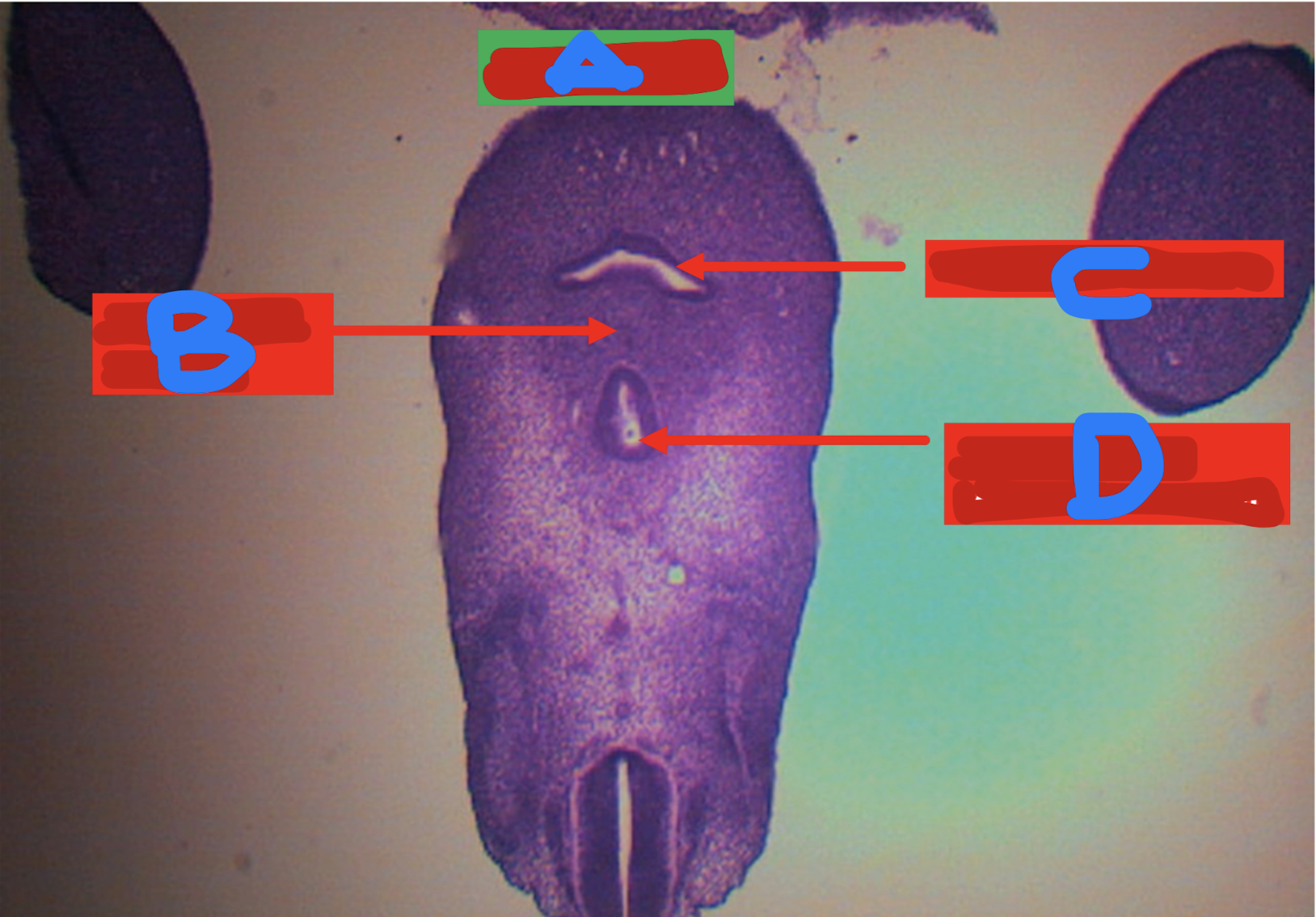
Identify the structure
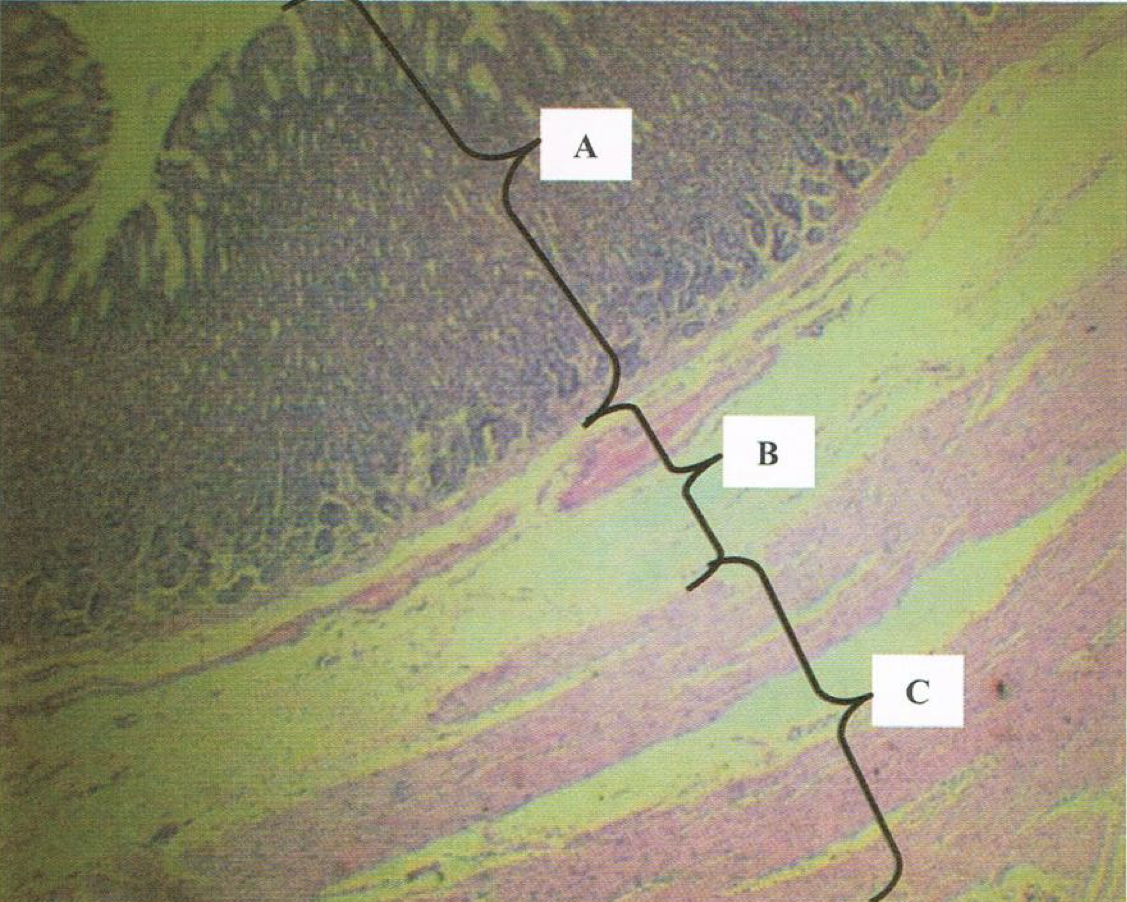
LPO - MUCOSA OF ESOPHAGUS
A: lining epithelium
B: lamina propria
C: muscularis mucosa
Identify the structure
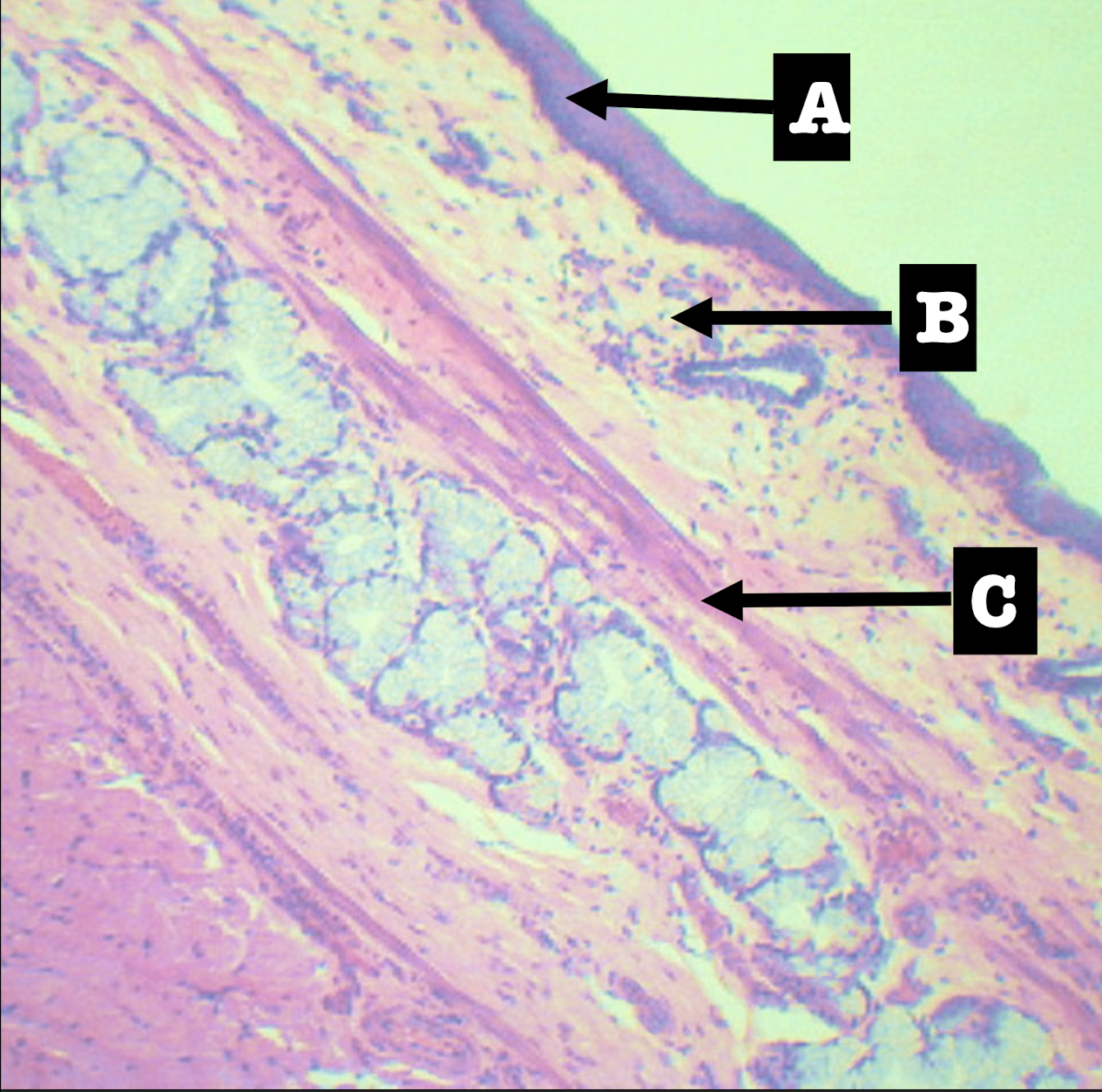
Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
Lining epithelium of the structure
Loose connective tissue with scattered lymphocytes; (+) superficial esophageal glands
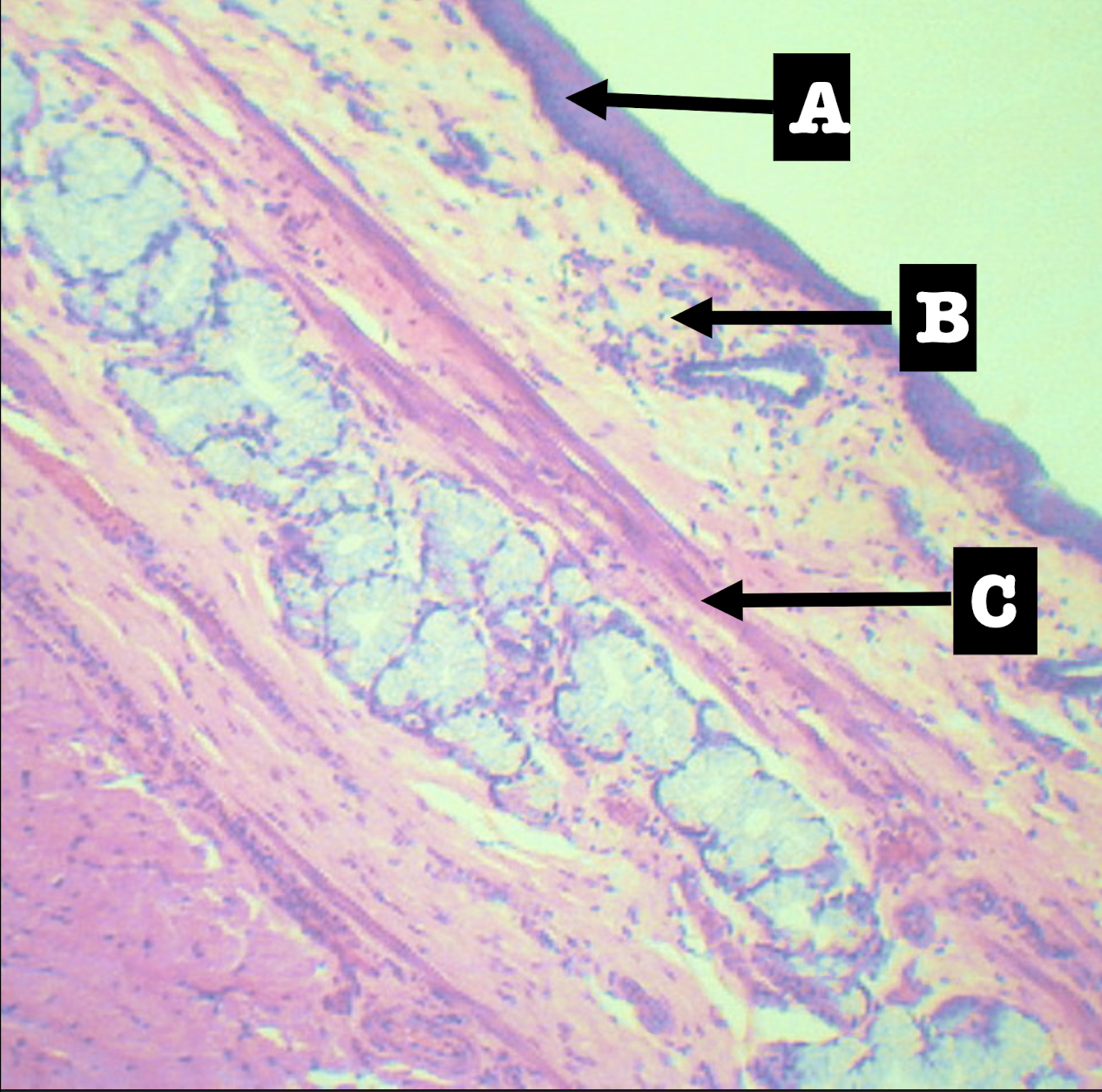
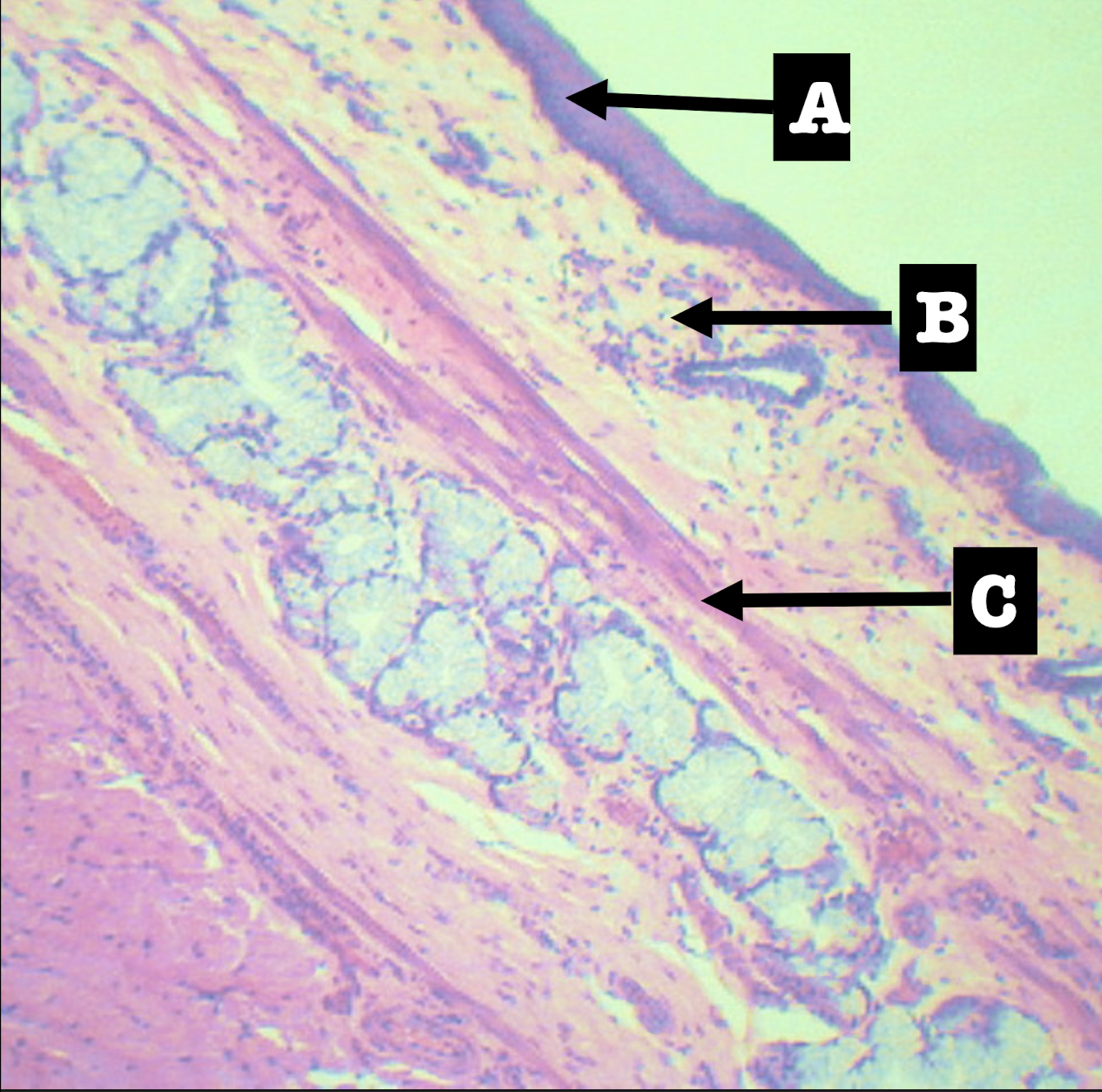
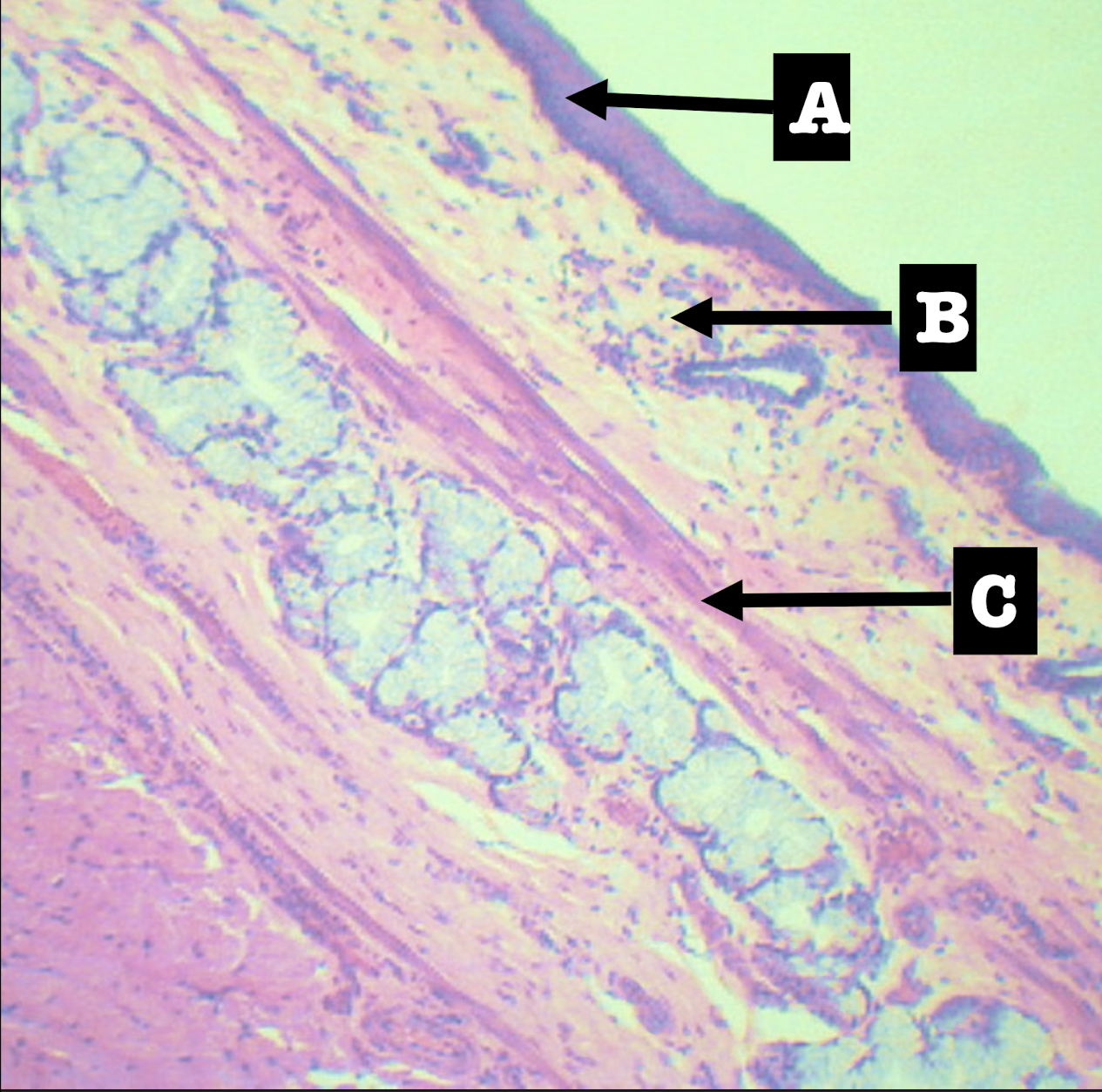
Lamina propria of the structure
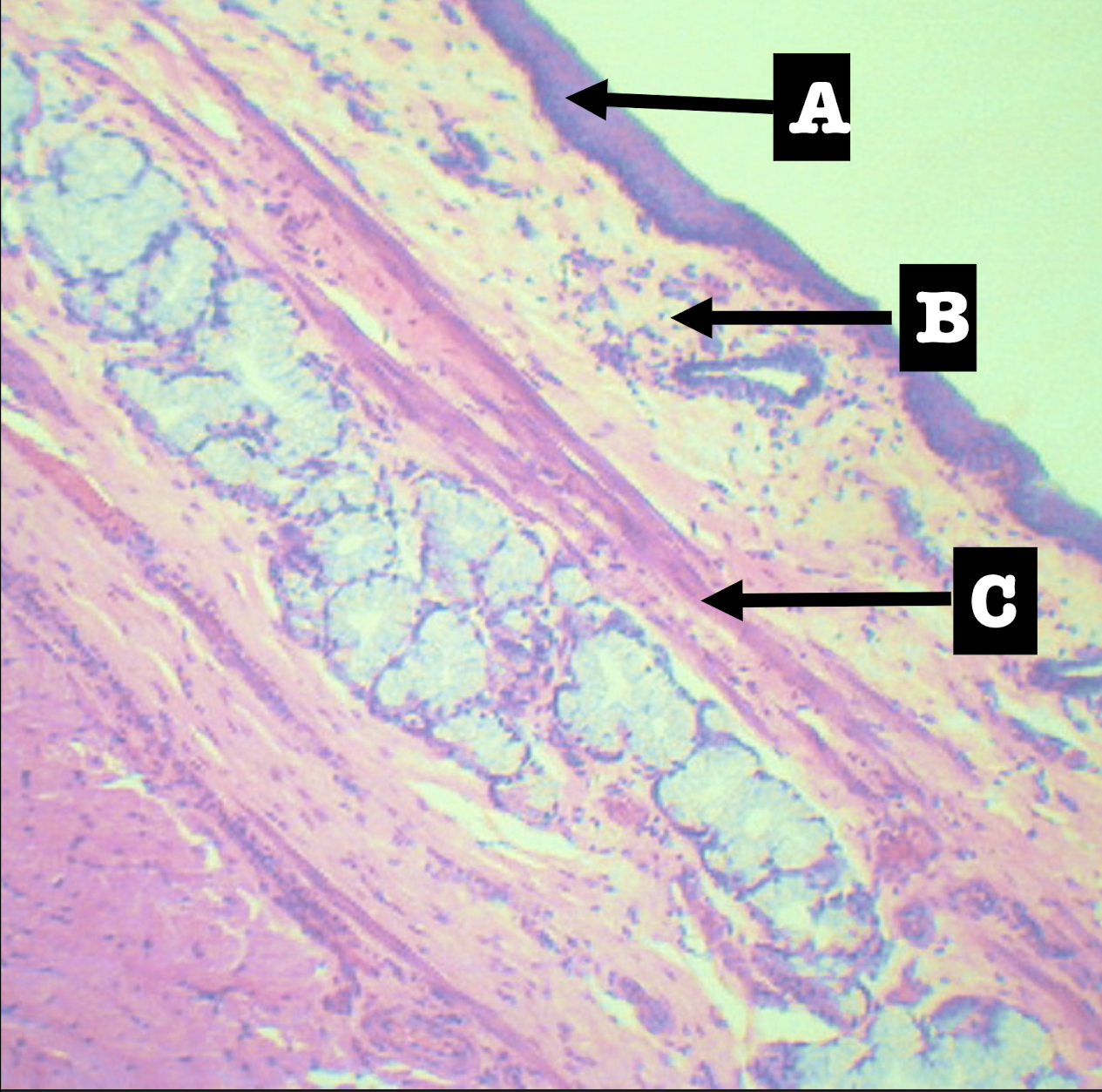
Morphology: branched coiled glands
Location: lower end of esophagus
MORPHOLOGY and location of lamina propria of structure
Single layer of smooth muscle
Muscularis mucosa of the structure
Submucosa of esophagus
Dense irregular connective tissue
Meissner’s plexus
Deep esophageal glands
Identify the structure, its arrangement, and contents found in it (2)
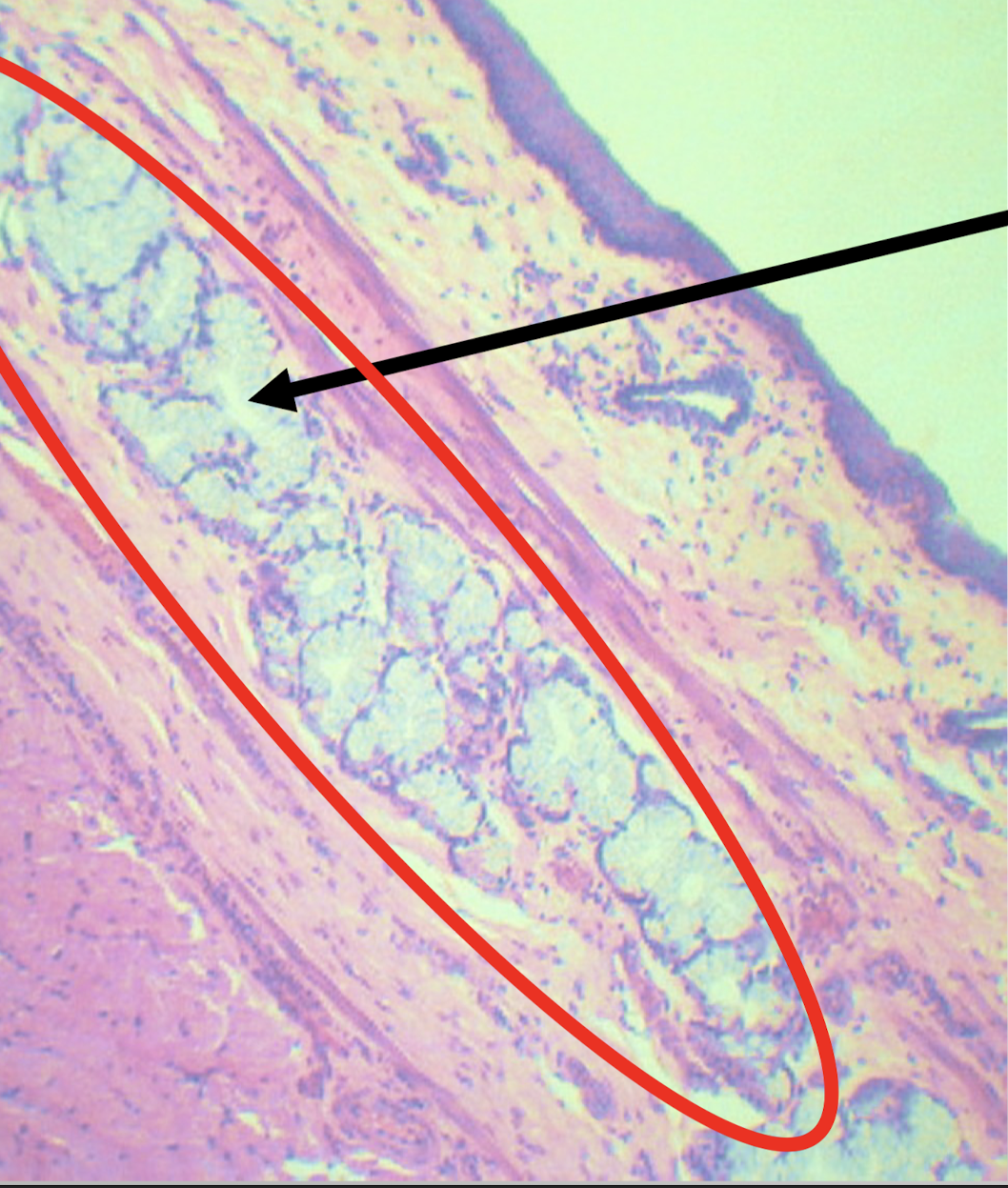
Meissner’s plexus and deep esophageal glands
Structures found in the submucosa of esophagus with mucus secretion function (2)
tunica muscularis of esophagus
inner circular, outer longitudinal
myenteric/auerbach’s plexus
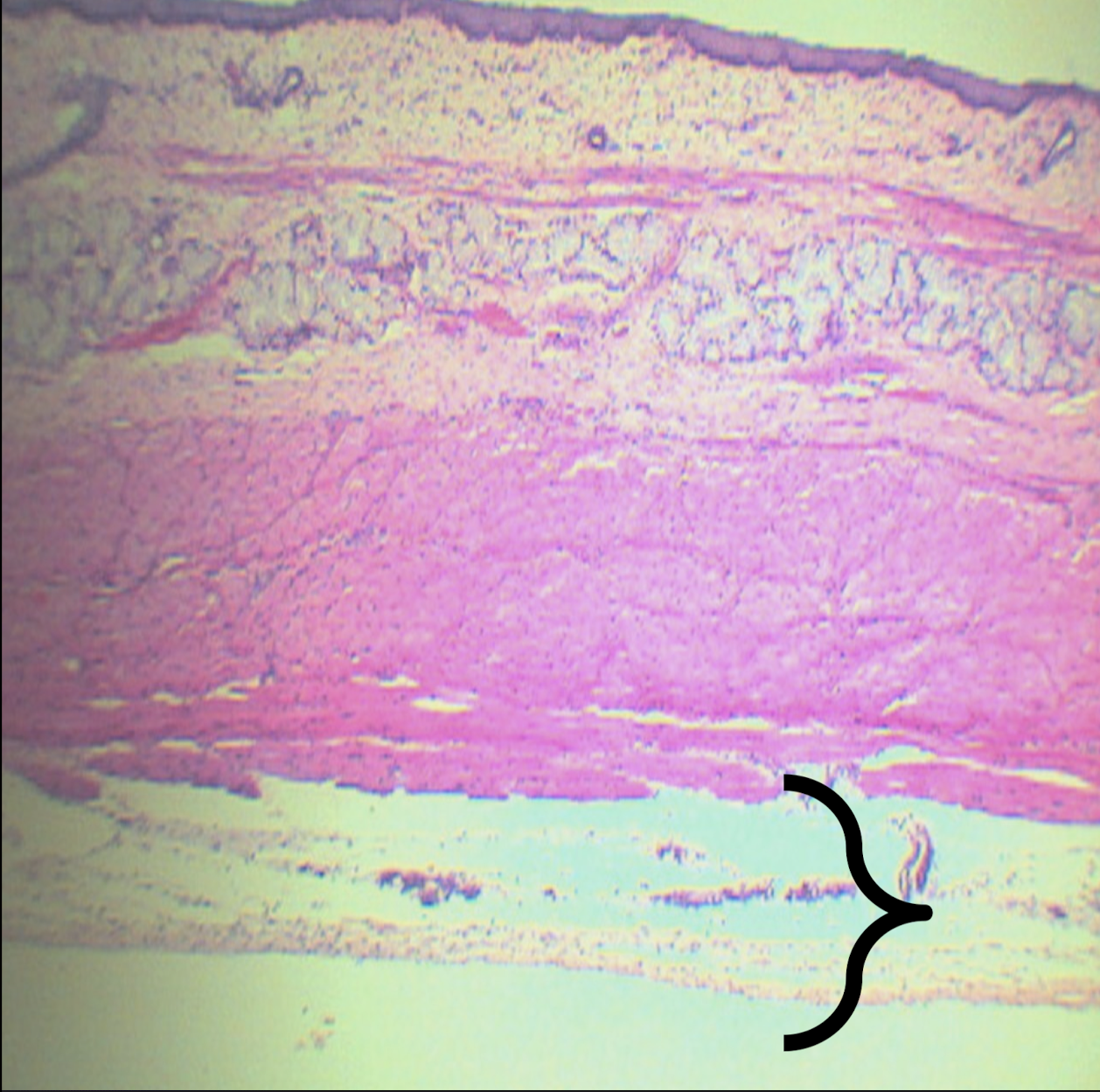
Identify the structure, its arrangement, and contents found in it (1)
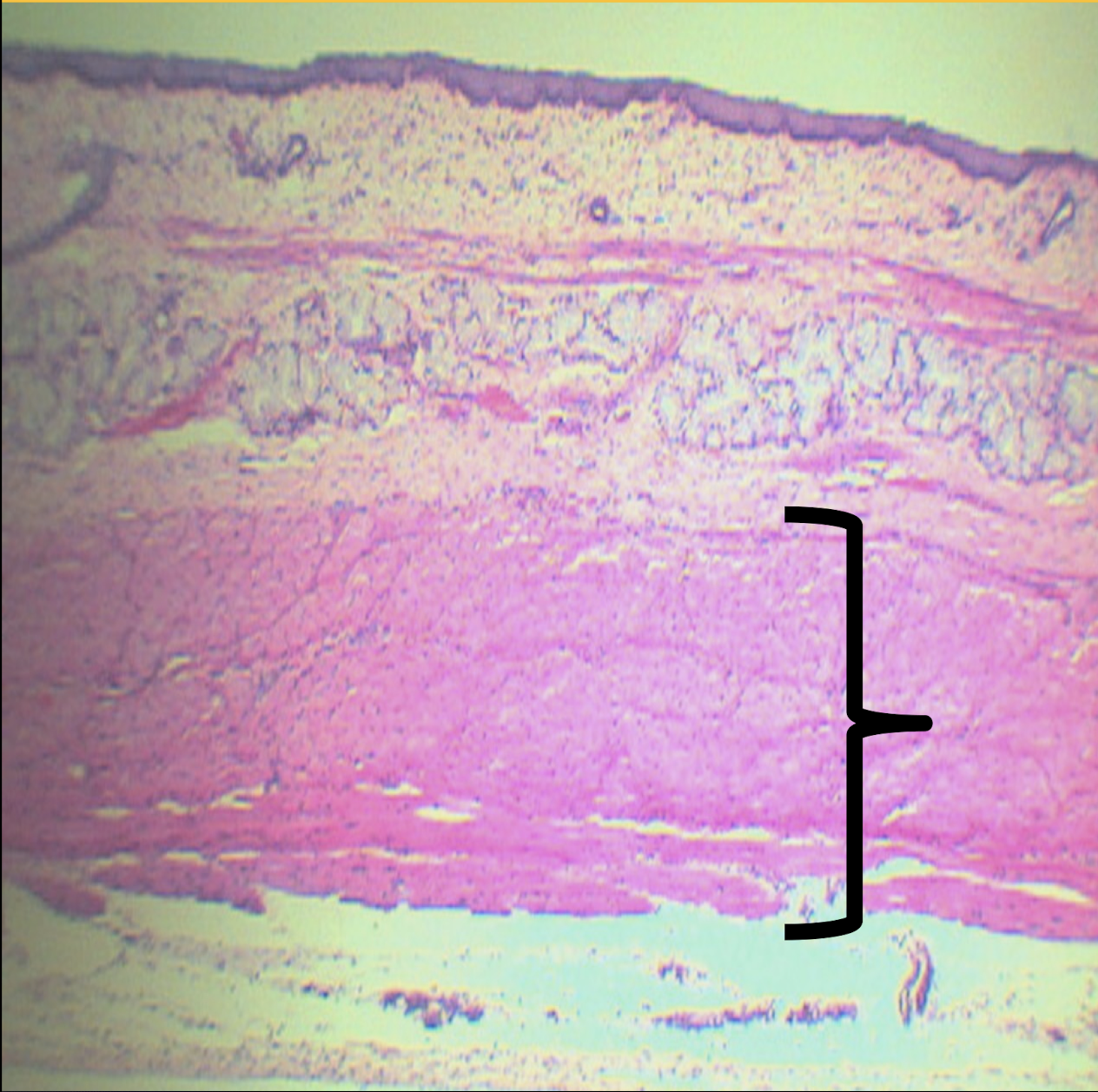
For peristalsis and motor movement; tunica muscularis of esophagus
Function of Auerbach’s/myenteric plexus and its location
upper: skeletal muscle
middle: skeletal and smooth muscle
lower: smooth muscle
Tunica muscularis of the upper 1/3, middle 1/3, and lower 1/3
tunica adventitia of the esophagus
loose CT
blood and lymph vessels
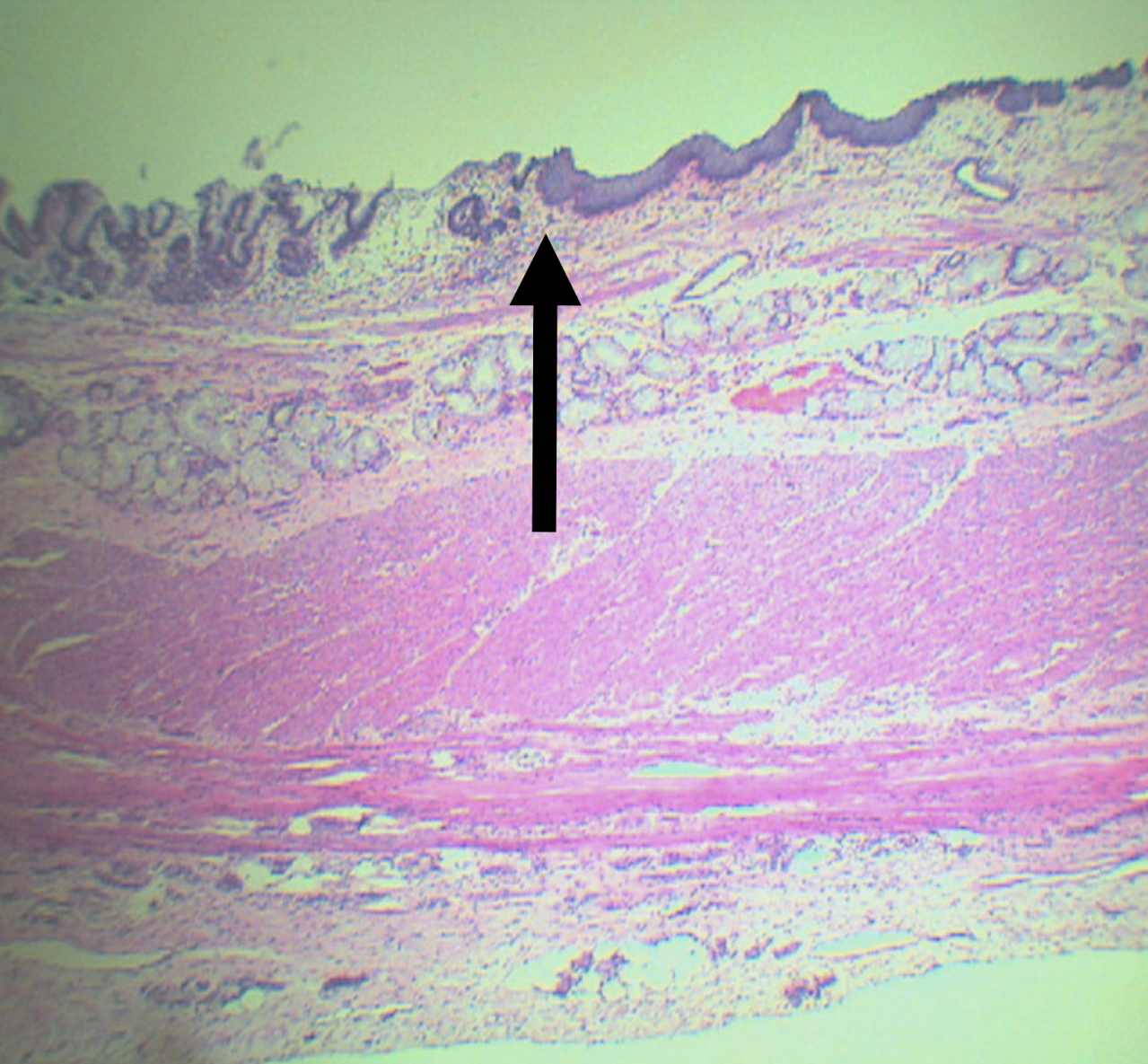
Identify the structure, its arrangement, and contents found in it (2)
Gastroesophageal junction or squamocolumnar junction
Identify the structure
SC: simple columnar (stomach)
SSNK: stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
D: tunica adventitia/serosa
Identify the structure
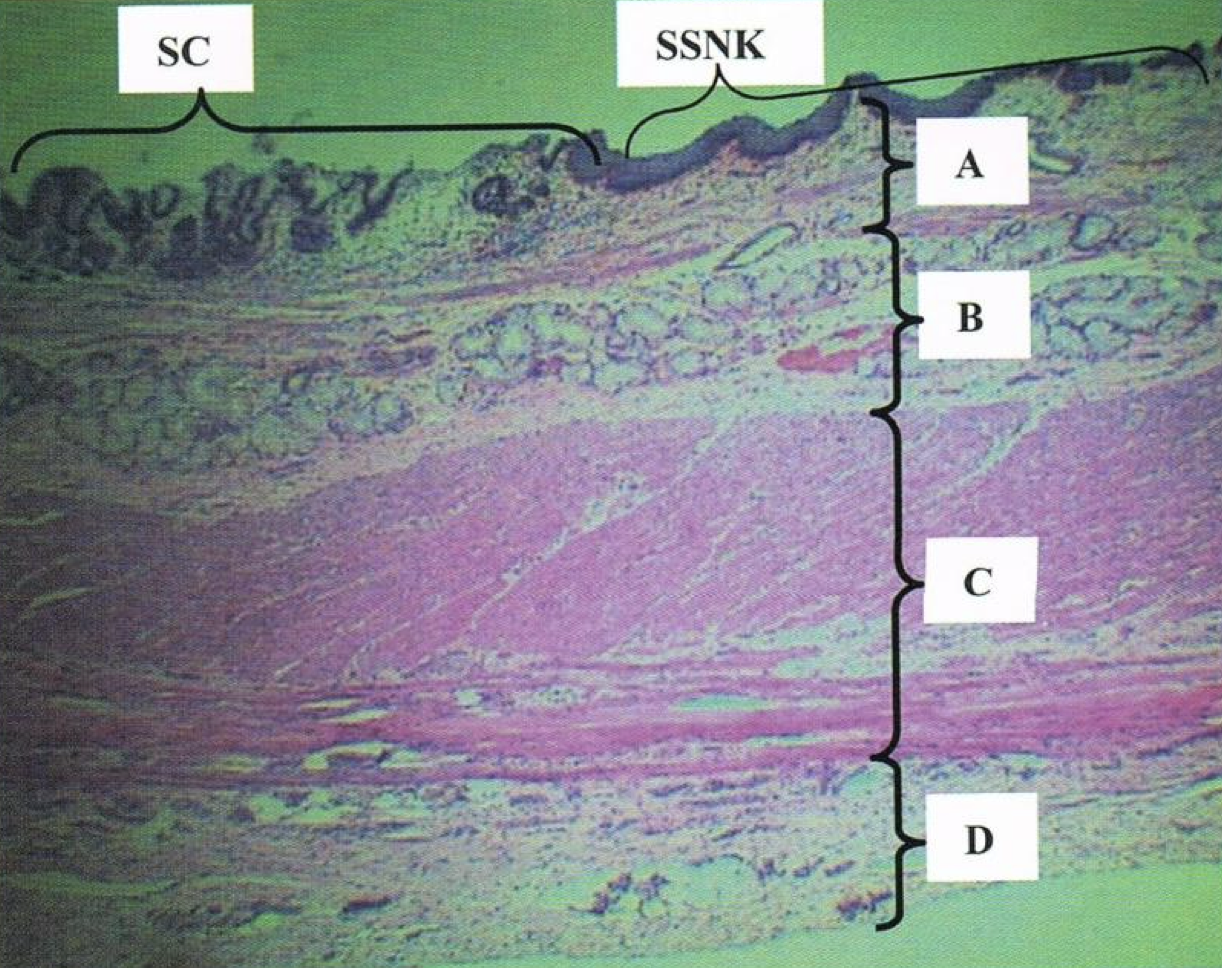

Scanner view of STOMACH
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
Identify the structure
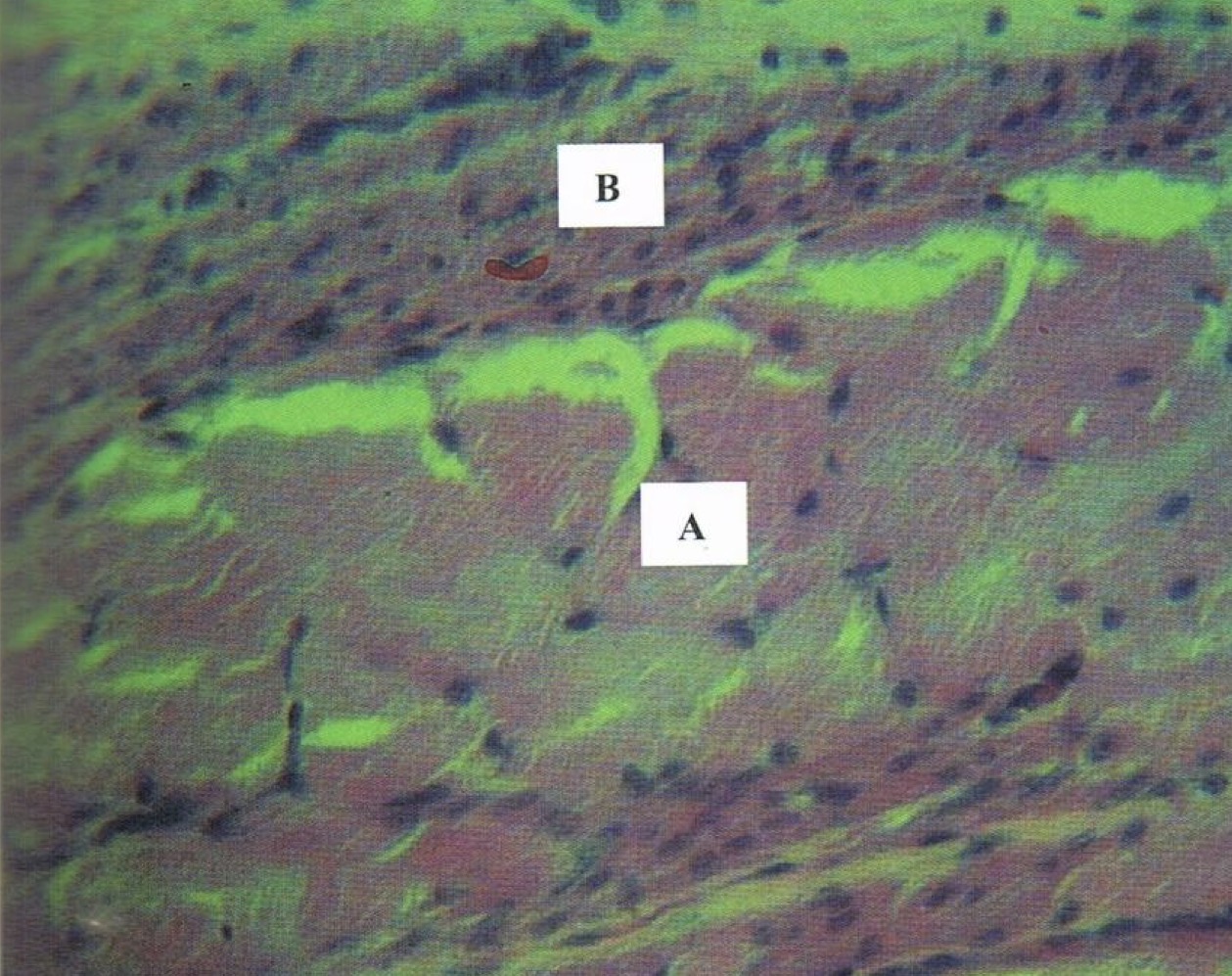
A: smooth muscle (peripheral nuclei)
B: skeletal muscle (central nuclei)
Identify the structure
Scanner view of STOMACH
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
Identify the structure
LPO view of STOMACH
E: submucosa
A: internal oblique
B: middle circular
C: outer longitudinal
D: tunica serosa/adventitia
Identify the structure
STOMACH
A: rugae
B: surface mucus and mucus neck cells
C: parietal or oxyntic cells
D: chief/principal/zymogenic cells
E: mucosal folds
F: submucosa
Identify the structure
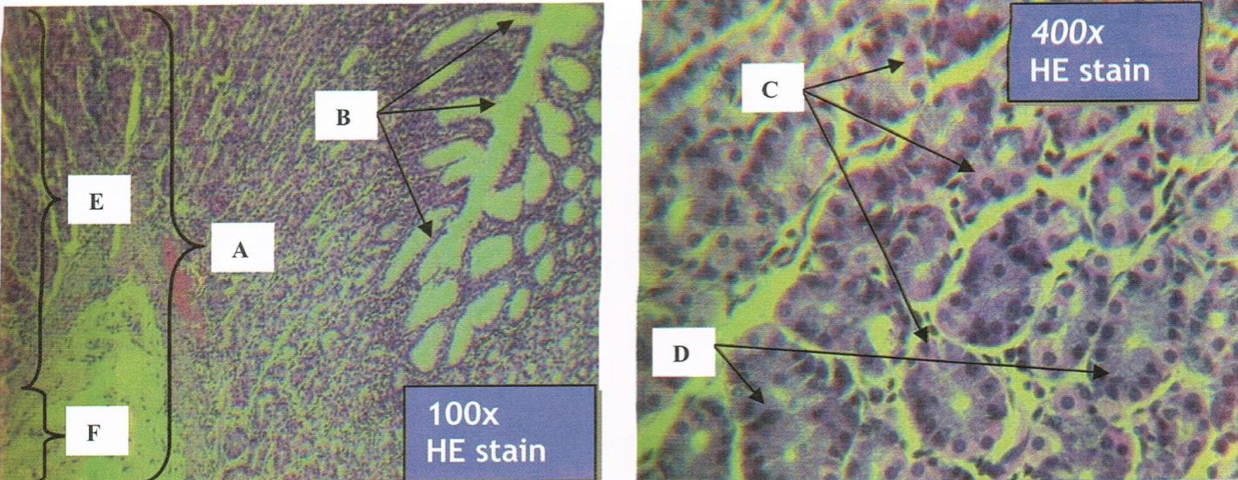
STOMACH
A: mucosa
B: gastric pits
C: gastric glands
D: muscularis mucosa
E: submucosa
Identify the structure
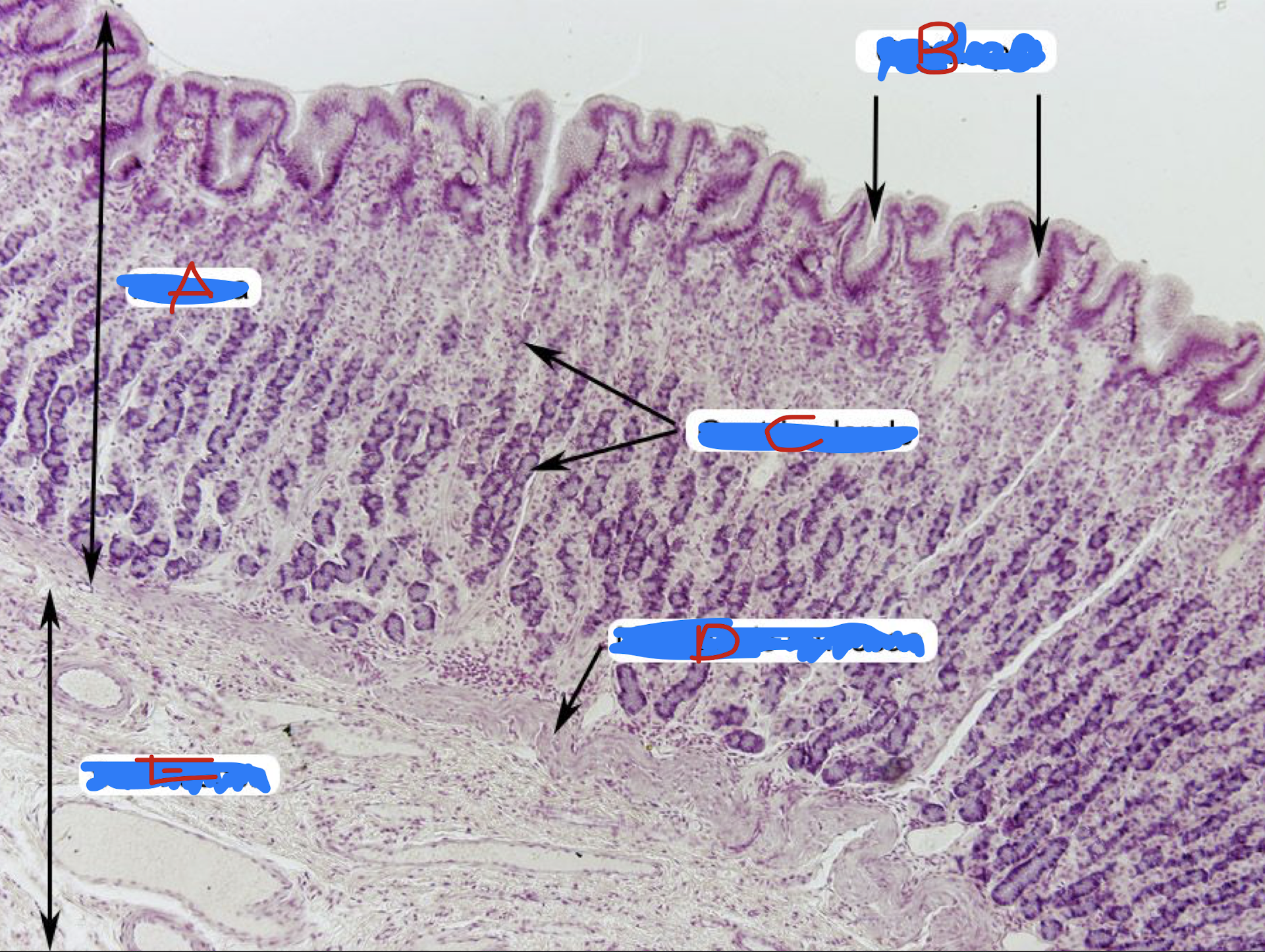
LPO - STOMACH MUCOSA
A: LE (simple columnar epithelium without goblet cells)
B: Mucous neck (columnar) cells
Identify the structure, its arrangement, and cell found in it (1)
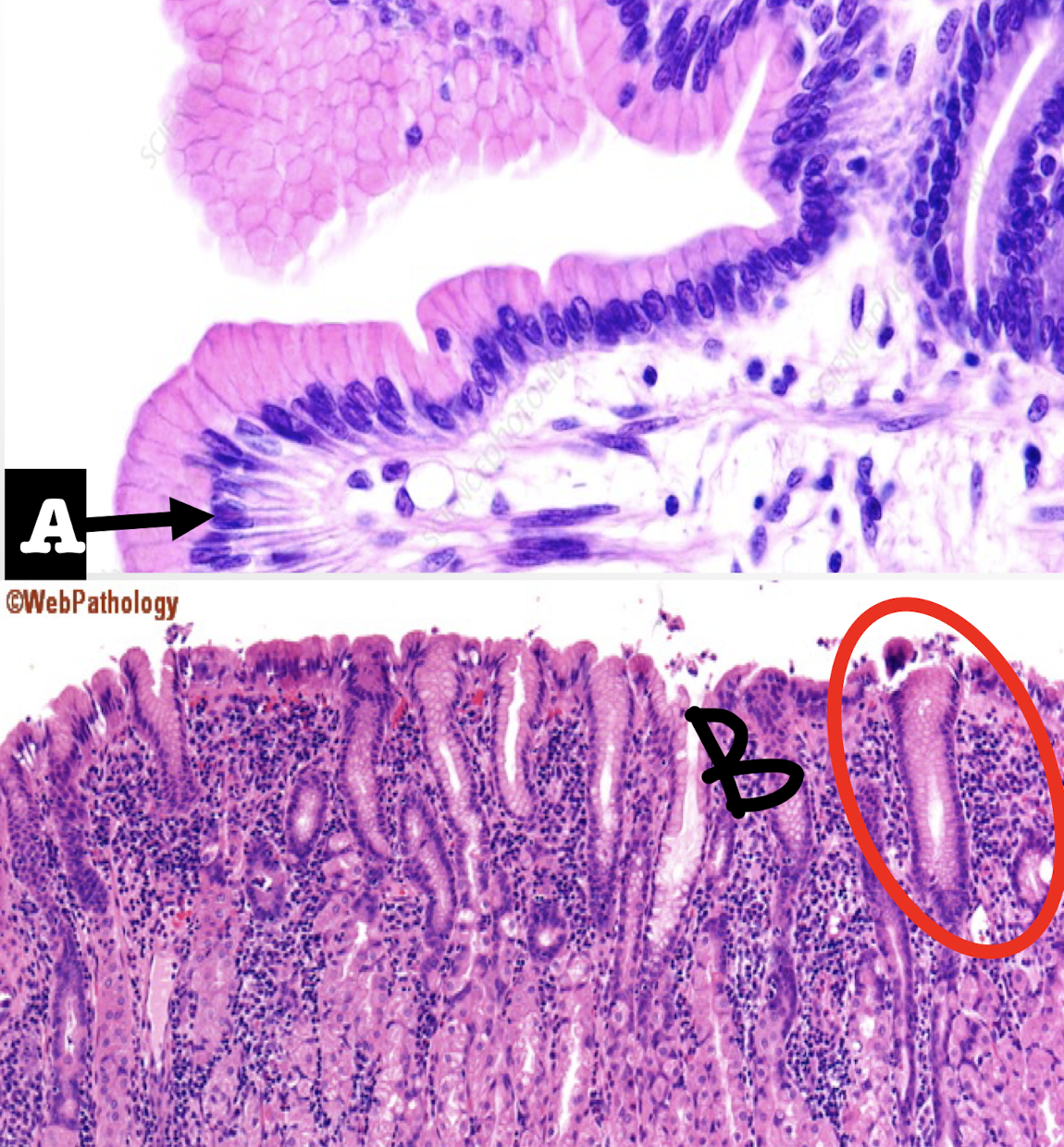
Gastric Mucosa of STOMACH
A: mucus cells
B: parietal/oxyntic cells
Identify the structure
Mucous neck (columnar) cells
Cell in the stomach that produces a thick coating of mucus, that protects the gastric mucosa from acid and enzyme secretion
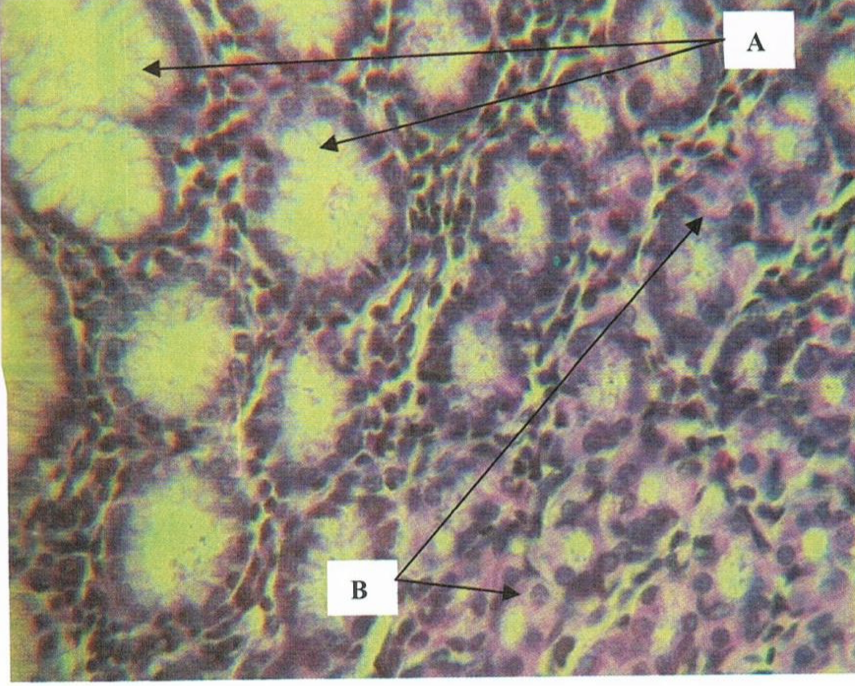
LPO - LAMINA PROPRIA OF STOMACH
gastric glands - synthesis and secretion of gastric juice
Identify the structure and content found in it (1)
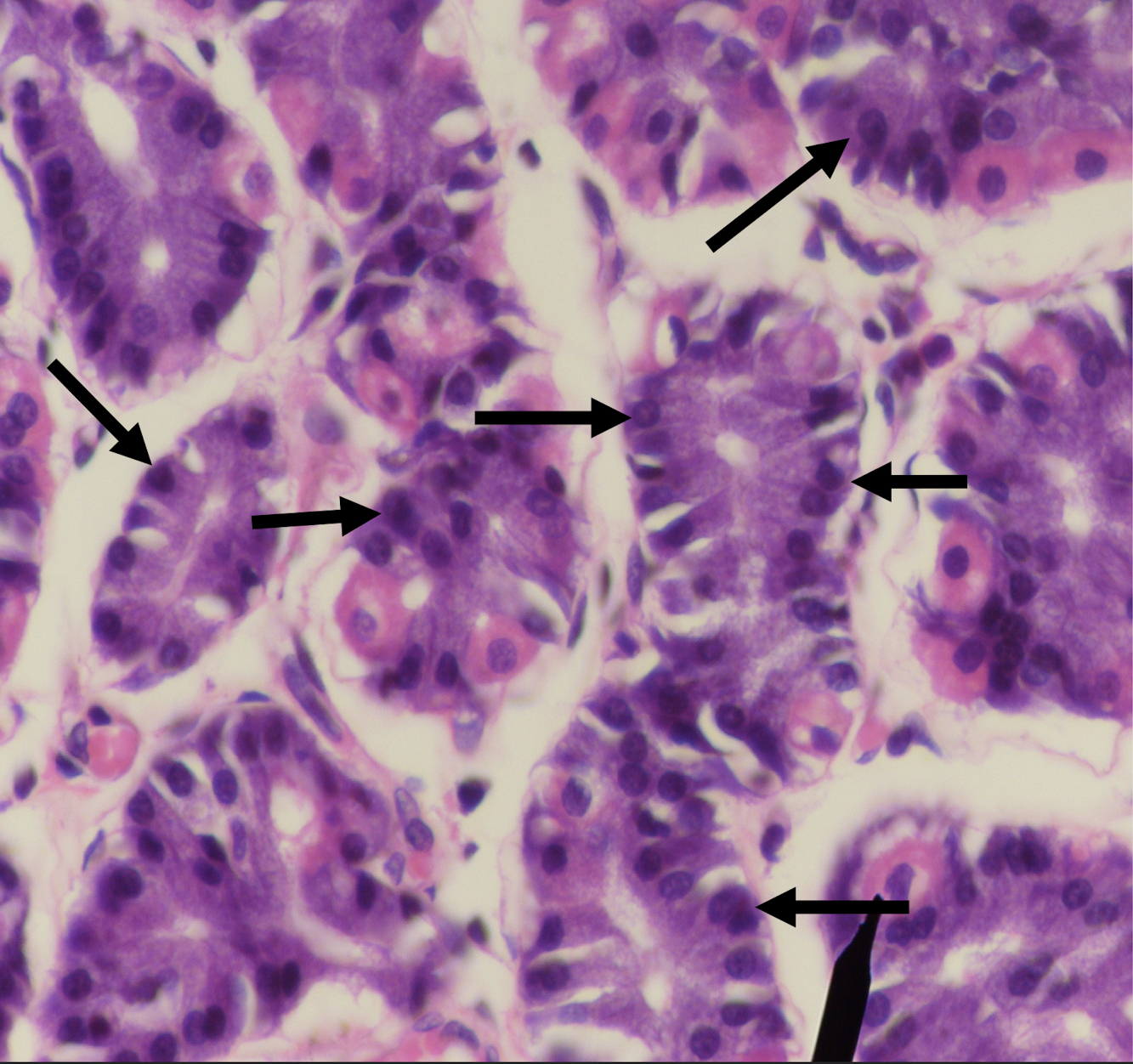
LPO - Gastric glands in the lamina propria
Parietal or Oxyntic Cells - secretes HCL and intrinsic factor; eosinophilic
Identify the structure
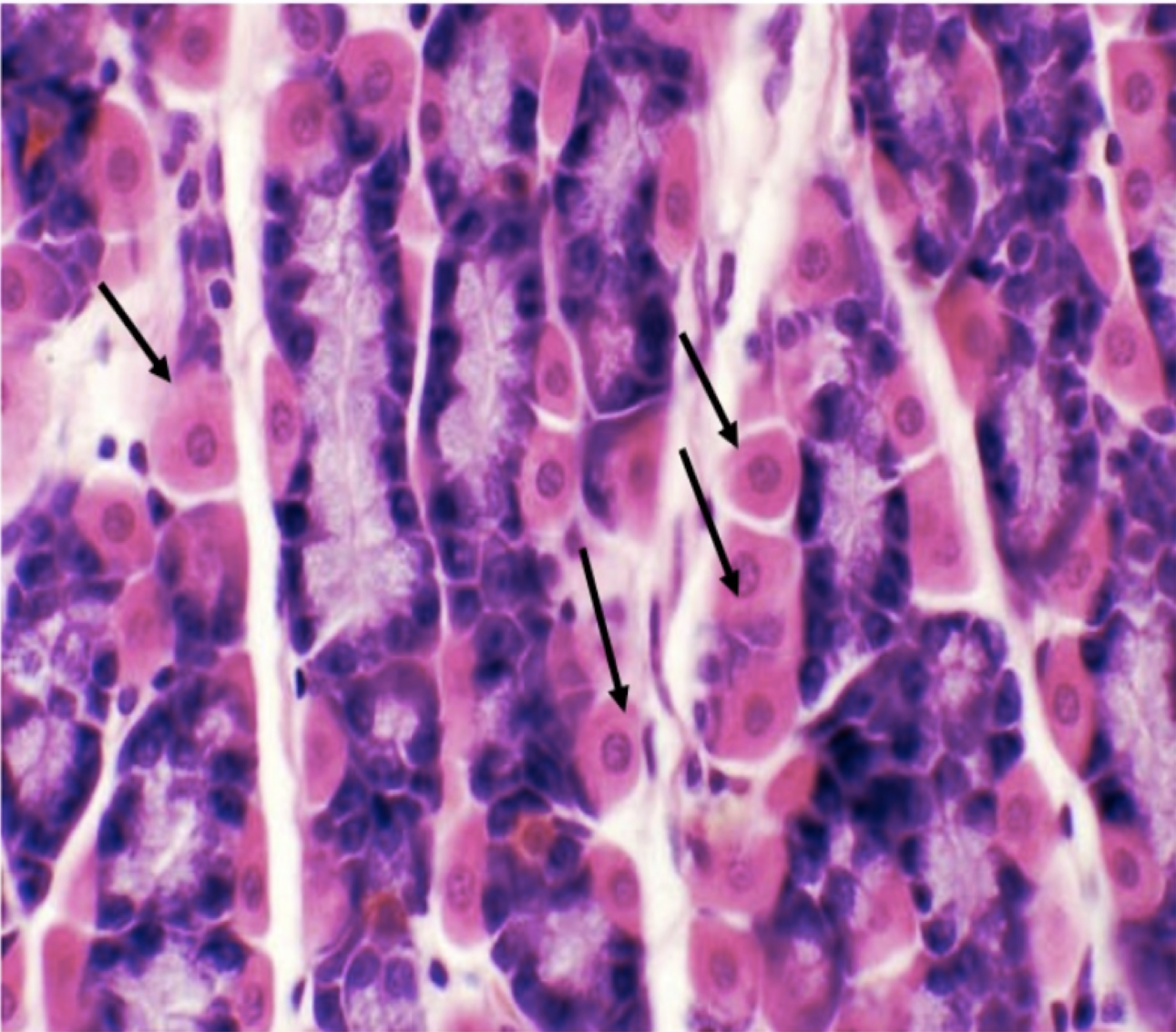
LPO - Gastric glands in the lamina propria
chief/peptic/zymogenic cells - most numerous, basophilic, and secretes pepsinogen and gastric lipase
Identify the structure
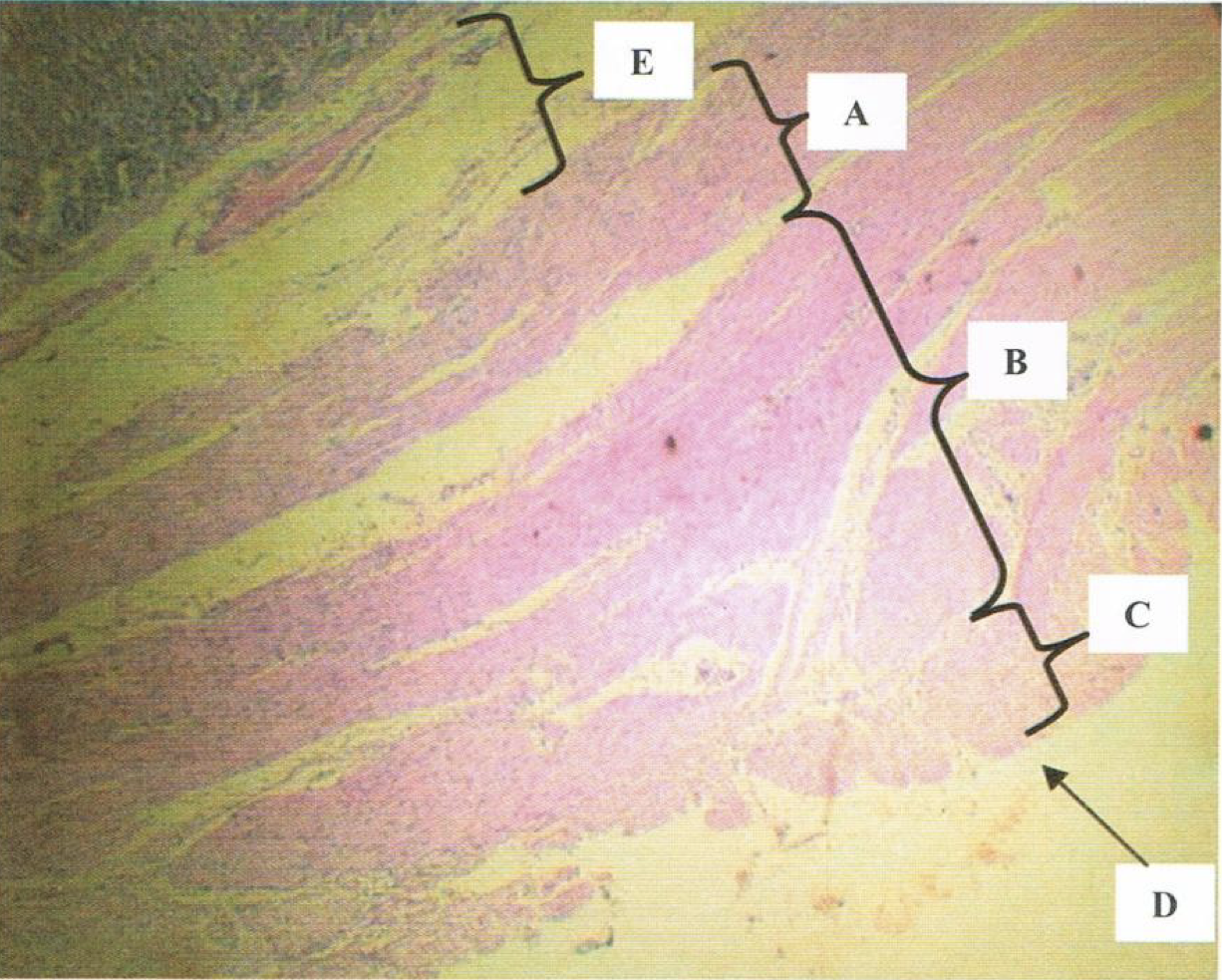
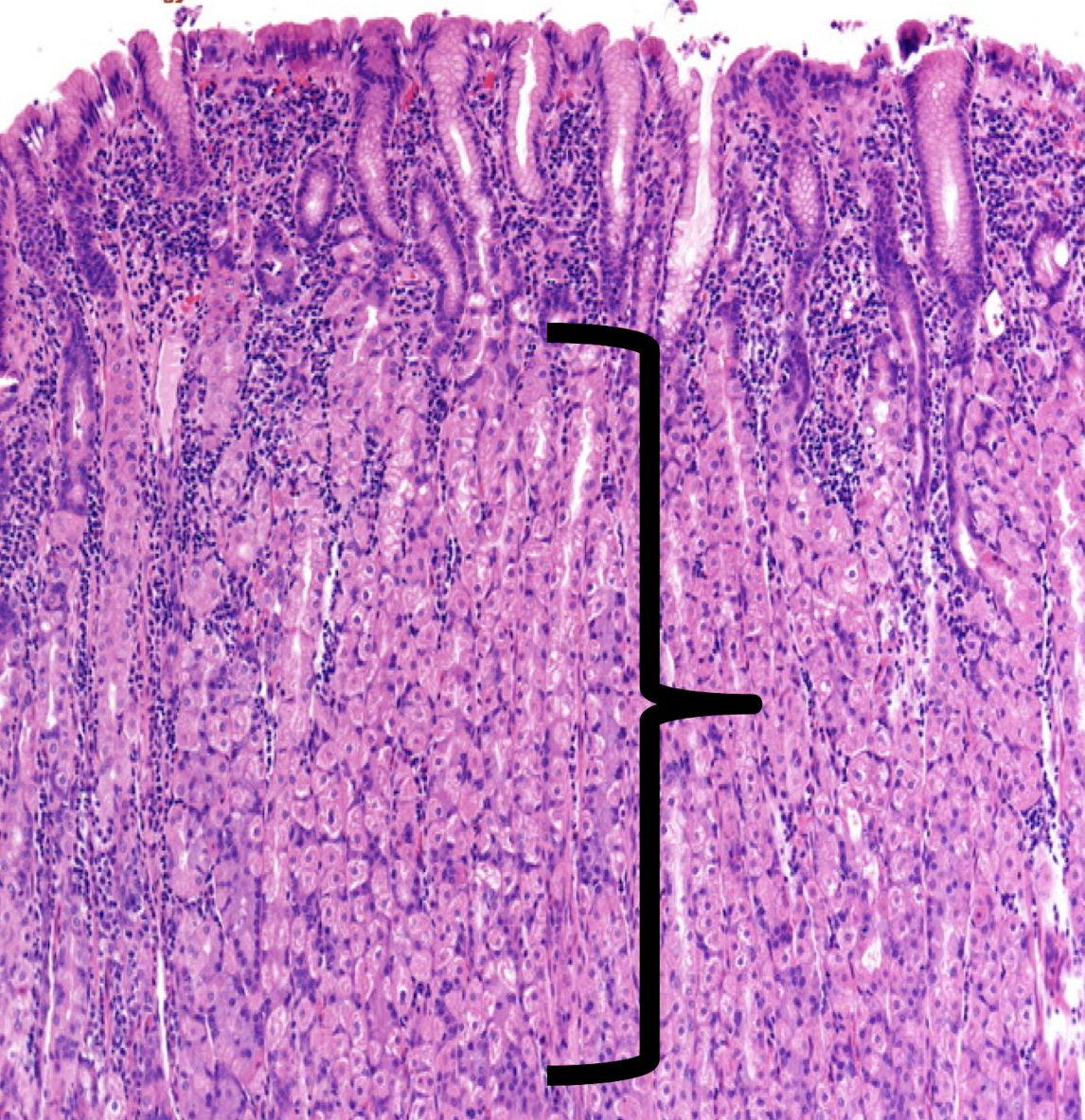
E: submucosa of stomach
LE: dense connective tissue
Has: Meissner’s corpuscles, blood and lymphatic vessels
No: gastric glands
Identify the structure E, its lining epithelium, and content found in it (3)
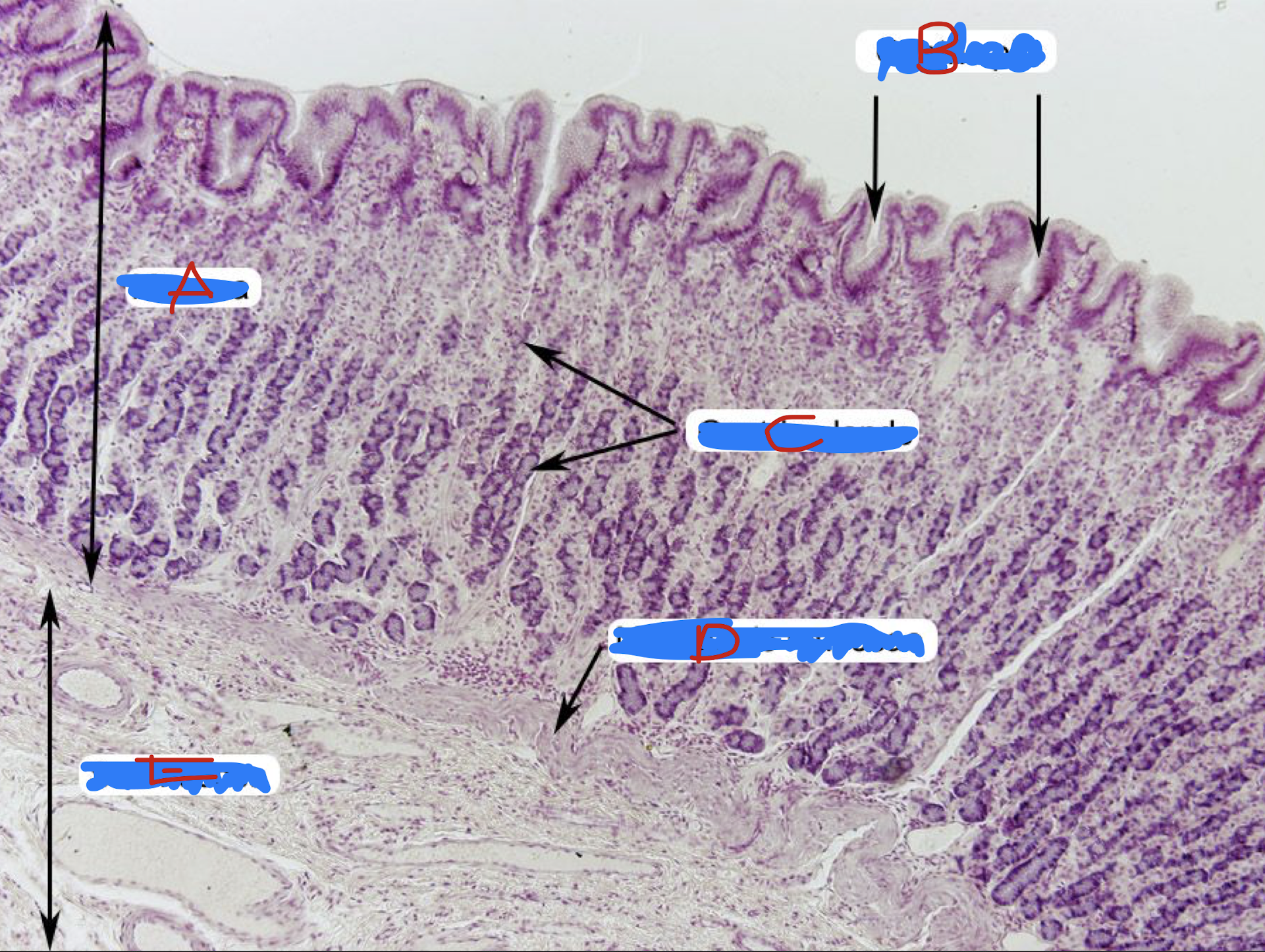
Tunica muscularis of stomach
inner oblique
middle circular
outer longitudinal
Identify the structure and muscle arrangement
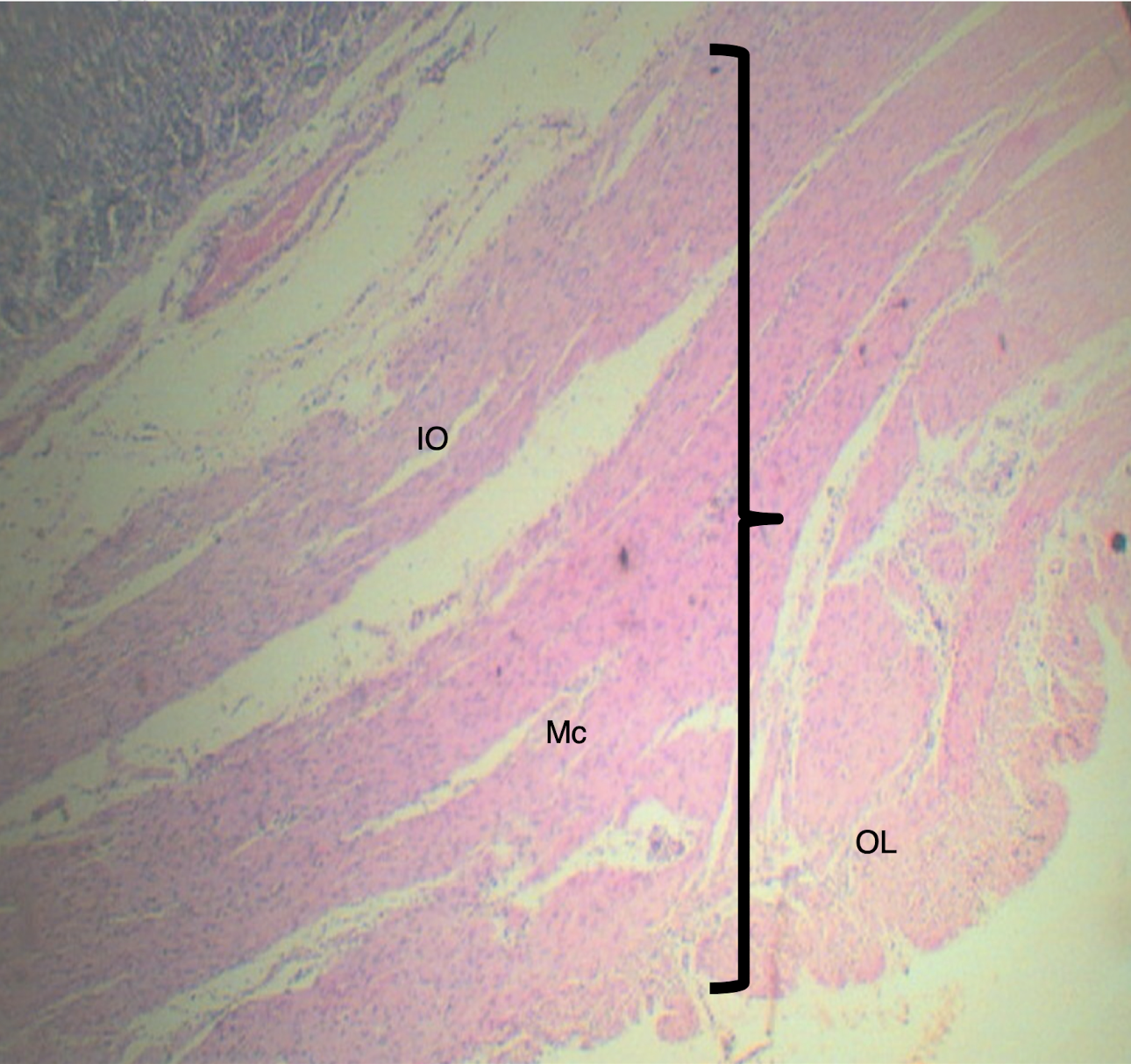
Small Intestine
LE: simple columnar with goblet cells
LP: loose CT
MM: 2 thin layers of smooth muscle
Lining epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa of the small intestine
SMALL INTESTINE
dense ct with bv, ln, and meissner’s plexus
Describe the submucosa of the small intestine
A: intestinal gland
B: columnar cells/enterocytes
C: goblet cells
D: paneth cells
Identify the structures found in the small intestine
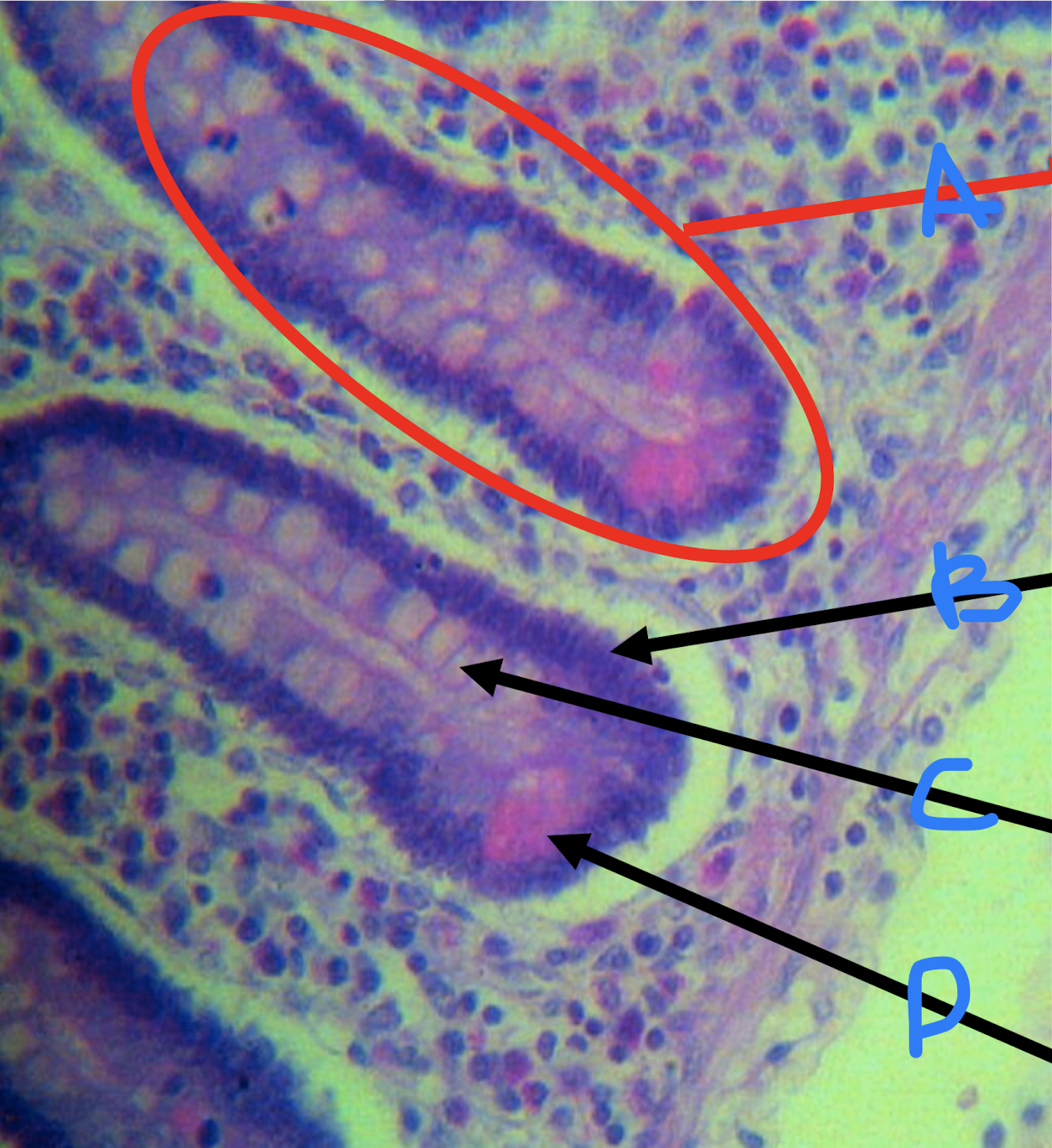
Paneth cells
Identify the structure
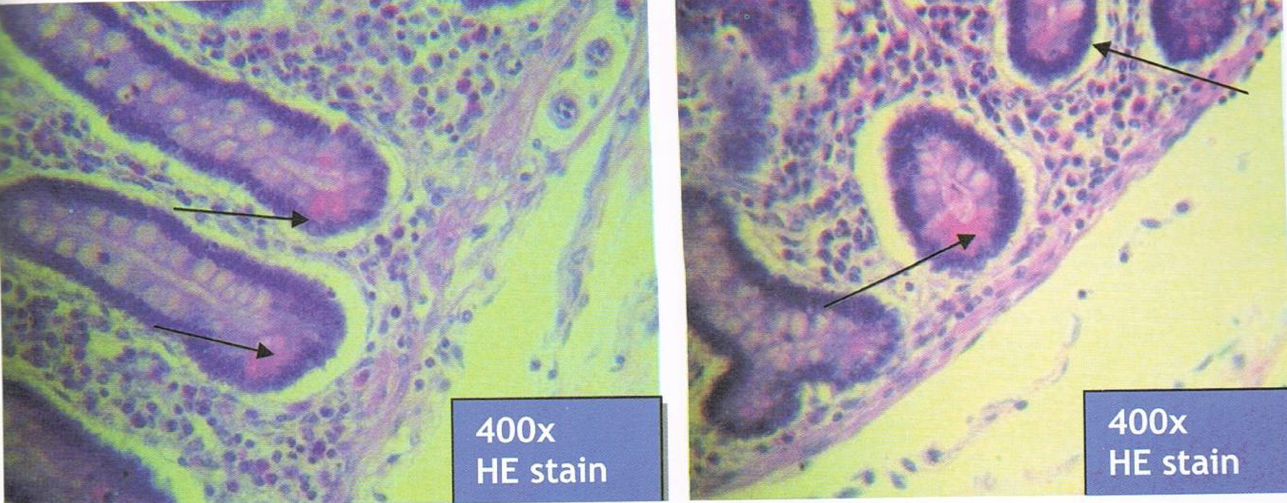
SMALL INTESTINE
Left: meissner’s plexus
Right: myenteric/auerbach’s plexus
Identify the structure
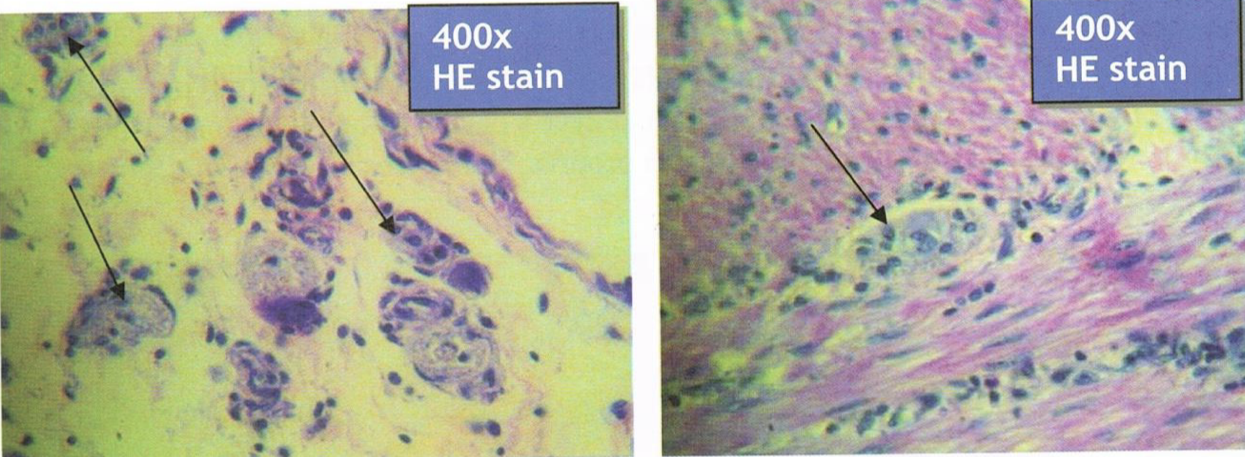
DUODENUM
Brunner’s gland or duodenal glands
secrete alkaline fluid composed of mucin as protection for acidic chyme from stomach
Identify the structure
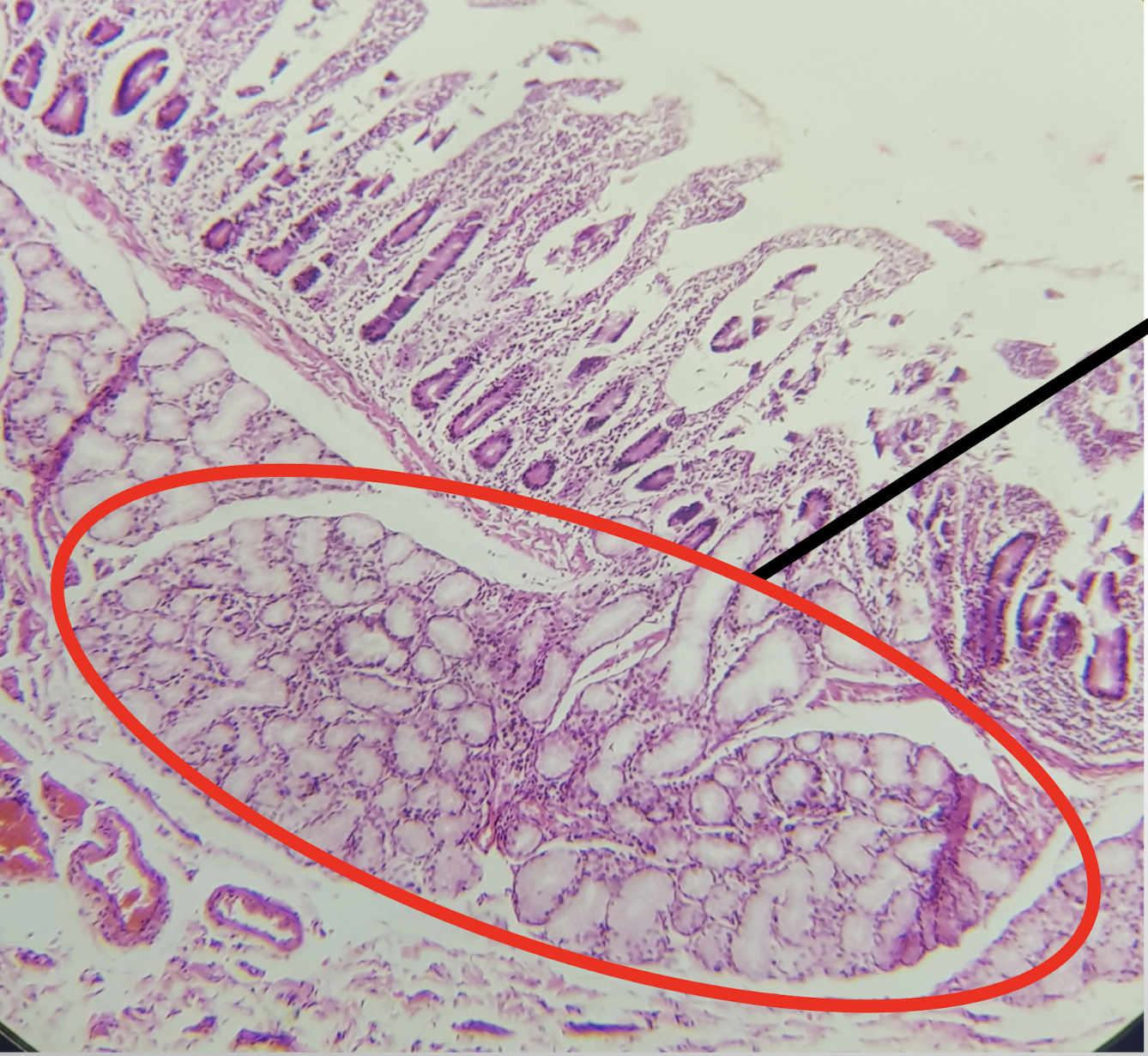
DUODENUM
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
D: tunica serosa/adventitia
E: intestinal glands
Arrow: Brunner’s gland
identify the structure
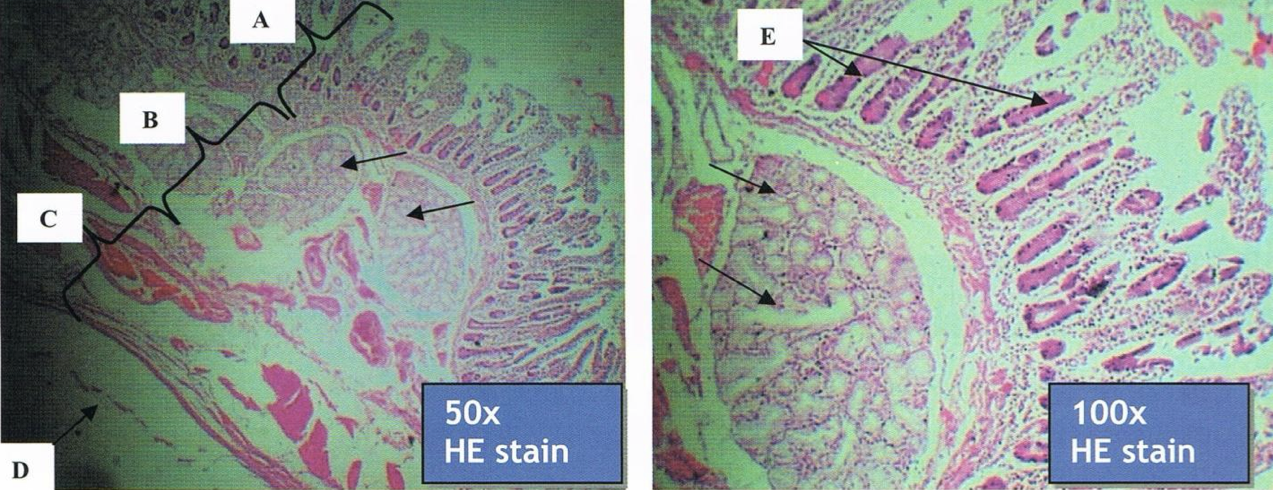
JEJUNUM
prominent plicae circularis
increase surface area = increase absorption
Identify the structure and its characteristic feature
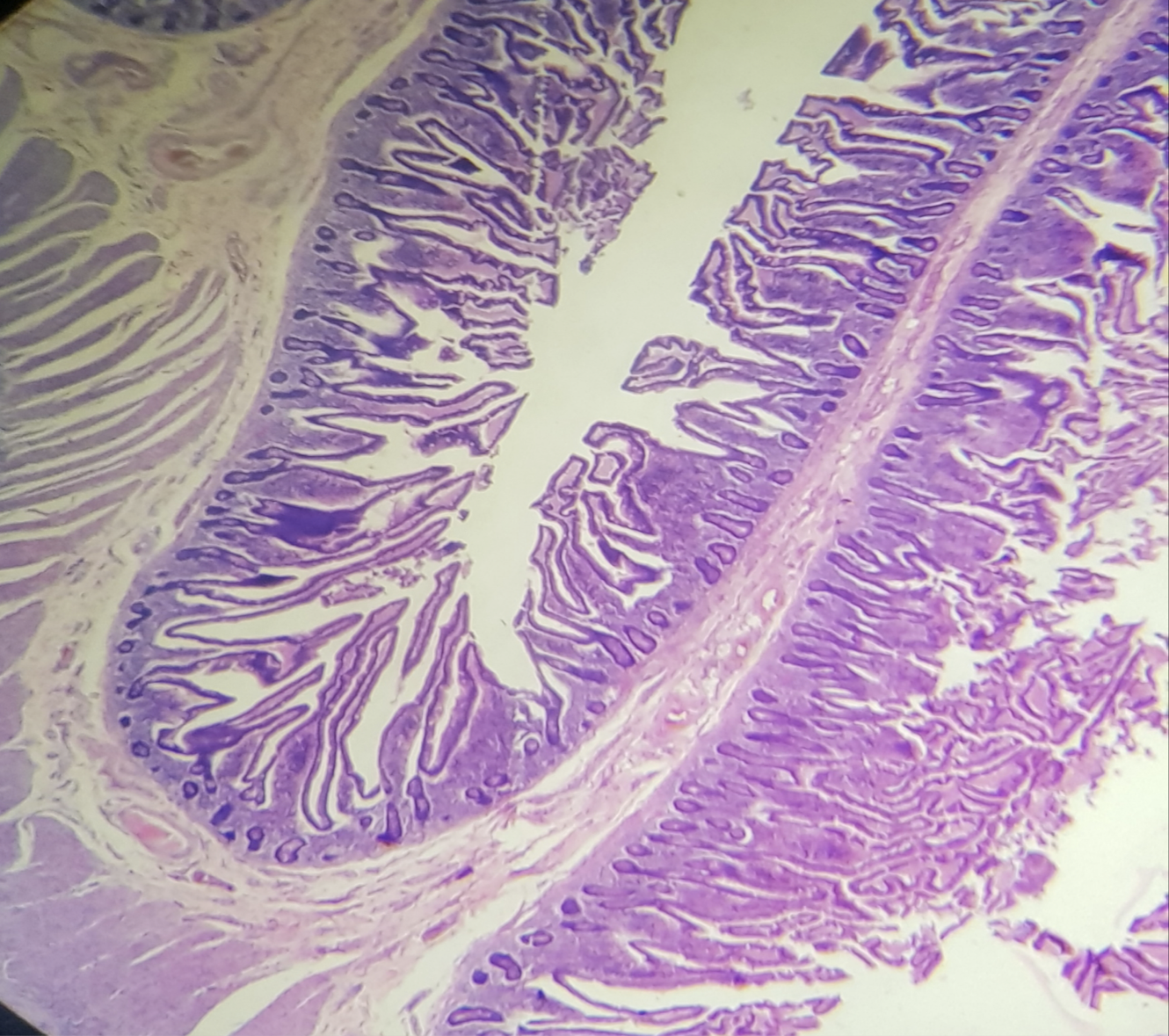
JEJUNUM
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: tunica muscularis
D: tunica serosa
Identify the structure
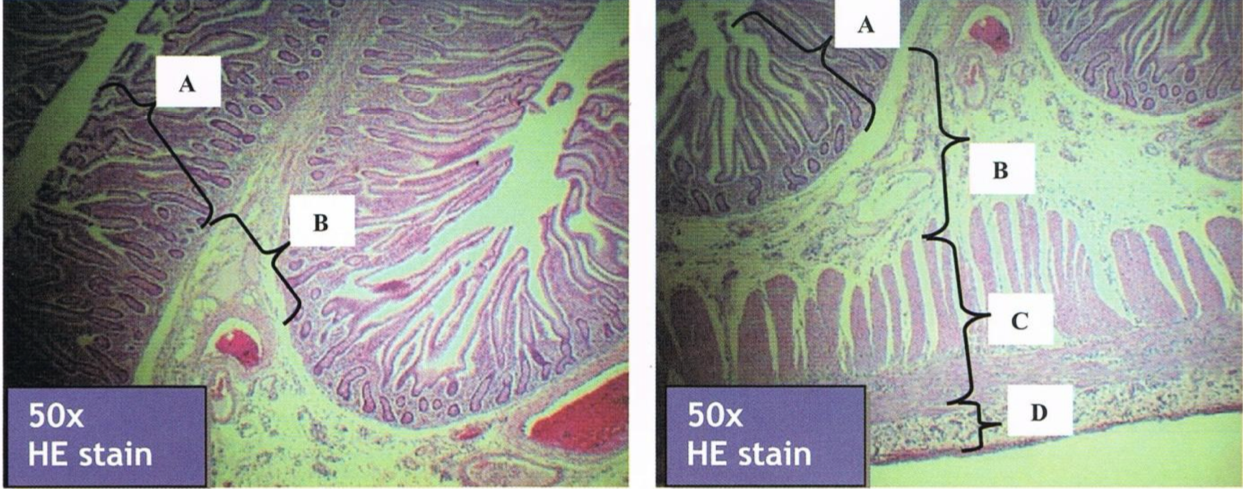
ILEUM
peyer’s patches
lymphoid nodular aggregates
Identify the structure and its characteristic feature
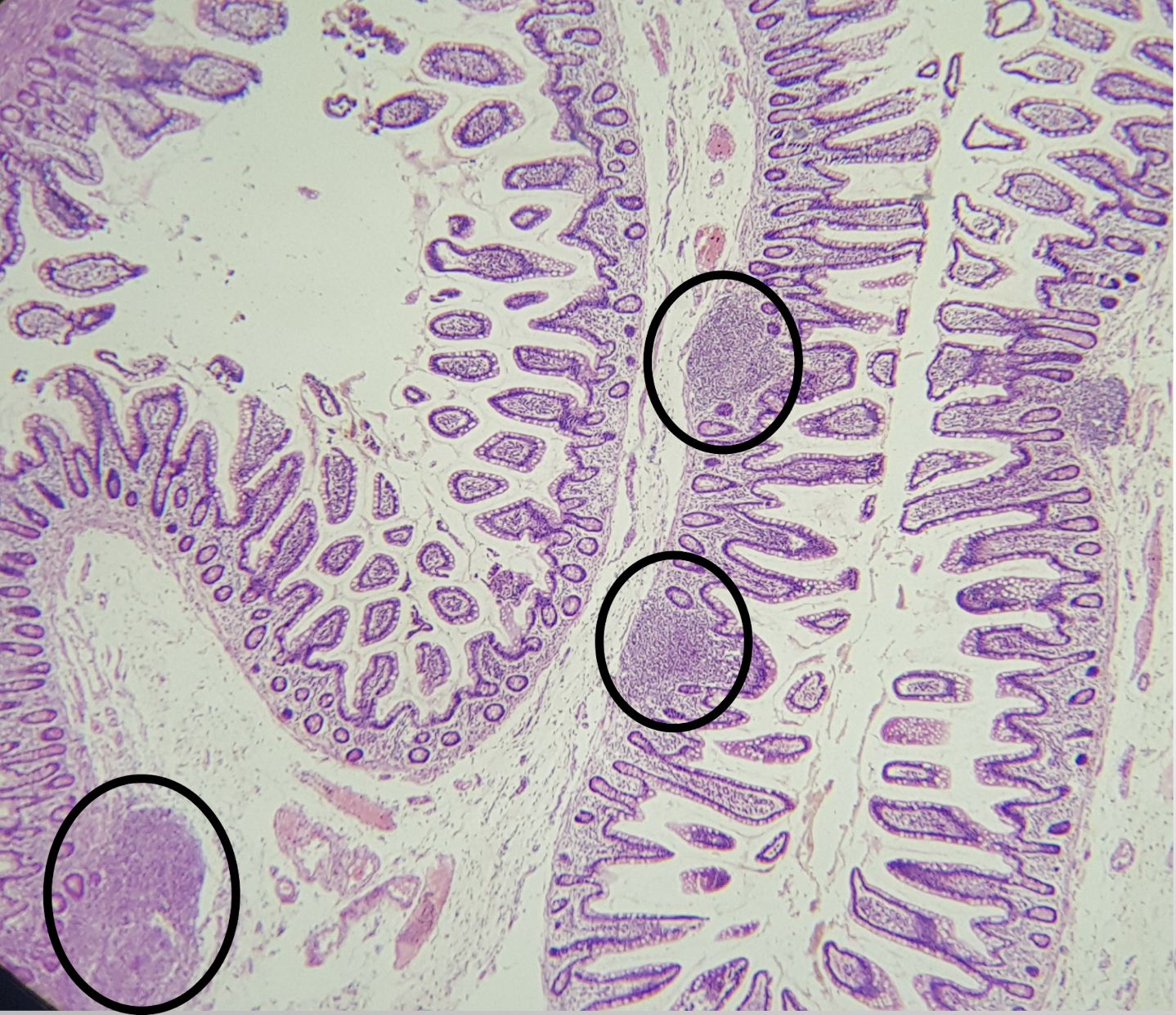
ILEUM
peyer’s patches
lymphoid nodular aggregates
Identify the structure and its characteristic feature
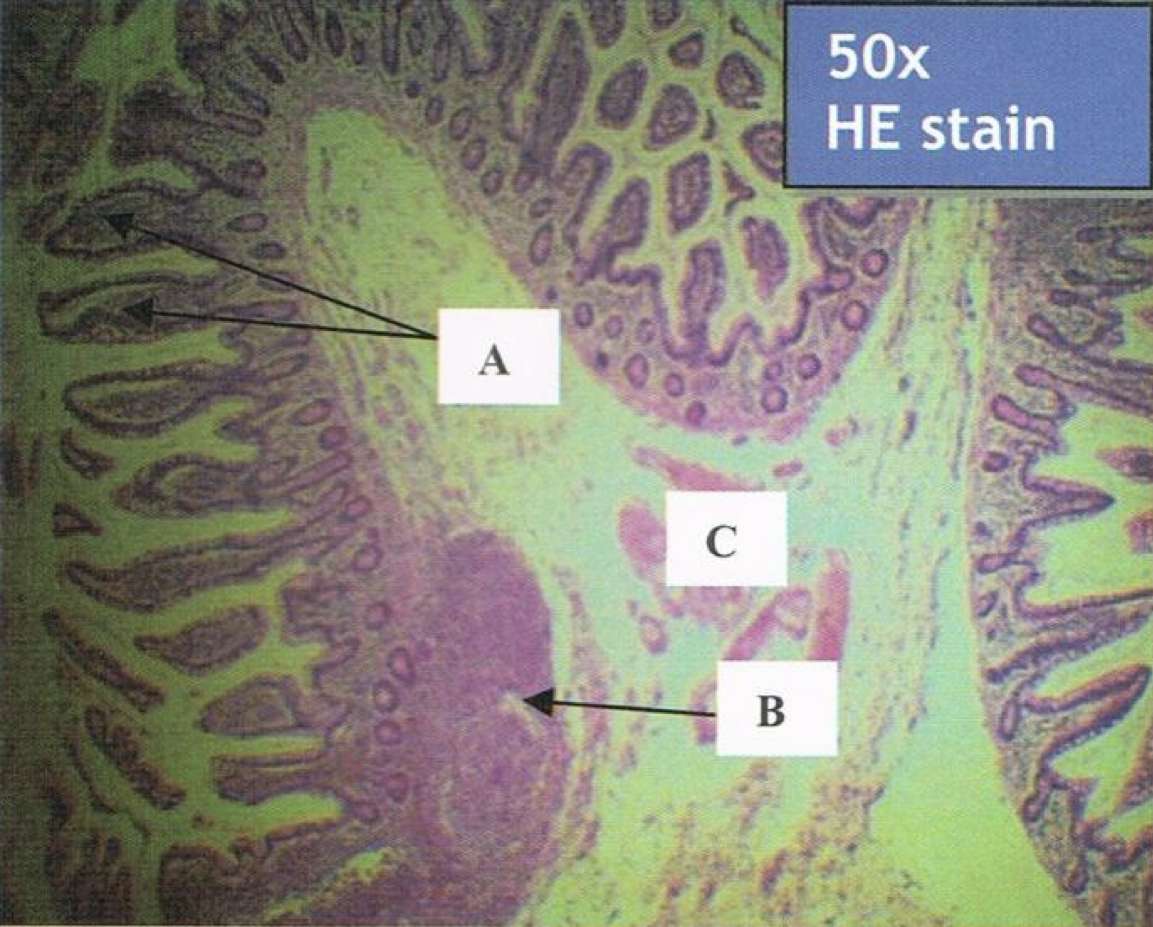
ILEUM
A: villi
B: peyer’s patch
C: submucosa
Identify the structure
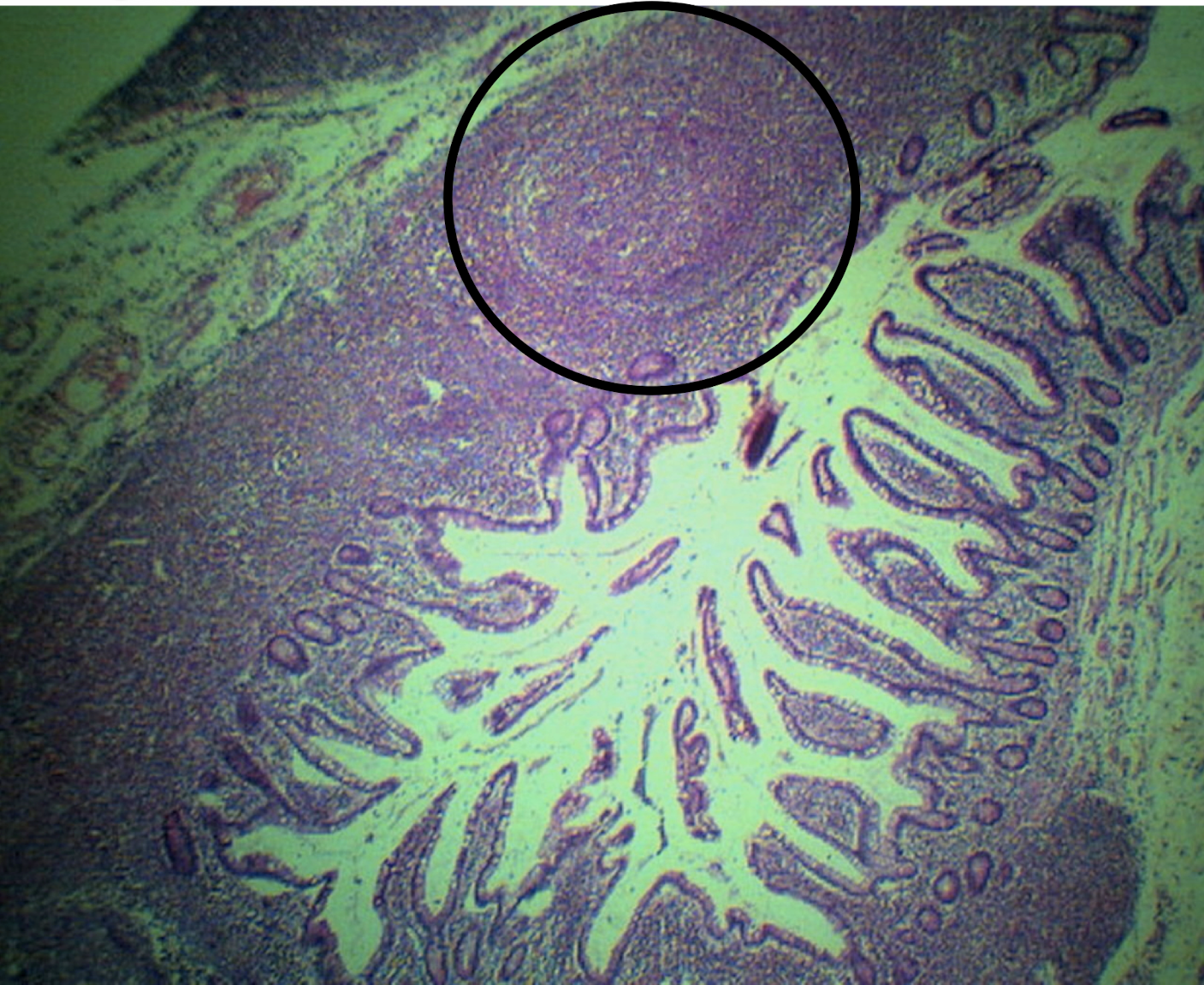
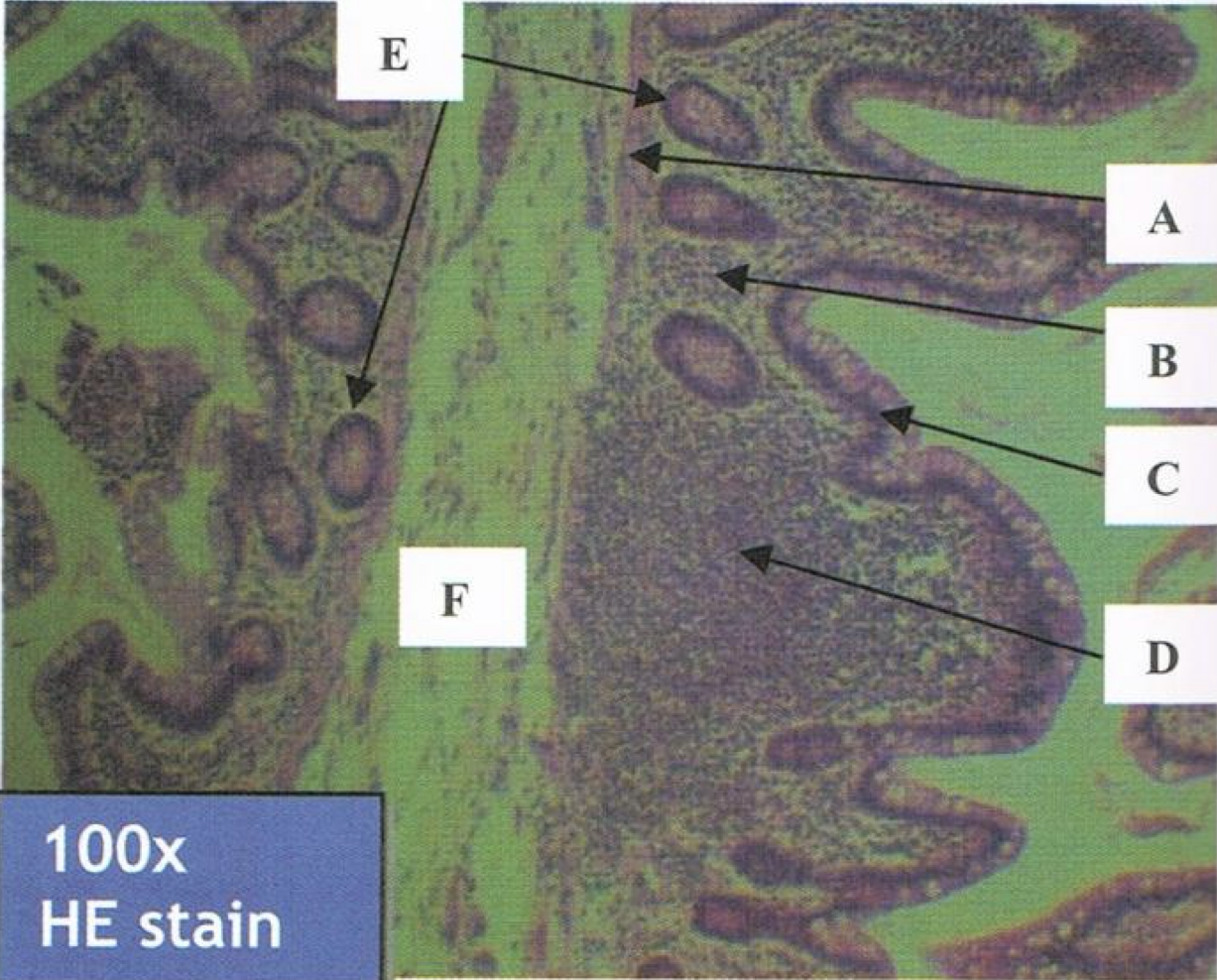
ILEUM
A: muscularis mucosa
B: lamina propria
C: lining epithelium
D: peyer’s patch
E: crypts or lieberkuhn (intestinal glands)
F: submucosa
Identify the structure
Appendix
A: mucosa
B: submucosa
C: muscularis mucosa
D: tunica adventitia
E: intestinal glands in lamina propria
Arrow: lymphatic nodules
Identify the structure
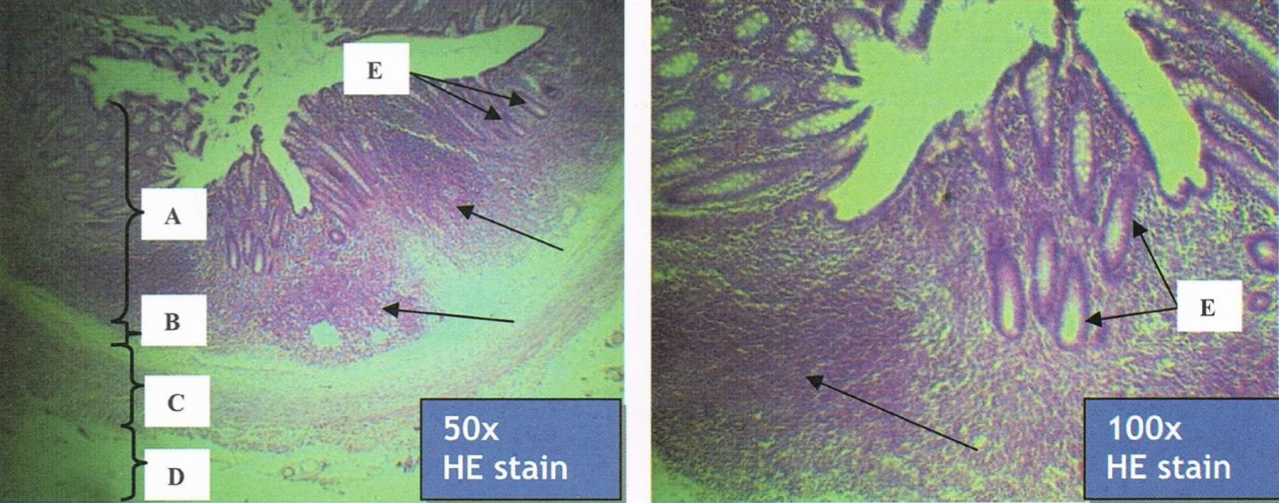
COLON
goblet cells
plenty of goblet cells in the intestinal gland
Identify the structure and its parenchyma

F: no more intestinal villi
T/F: The structure has intestinal villi
T
T/F: Crypts of Lieberkuhn are still present and usually longer and straighter than that of small intestine
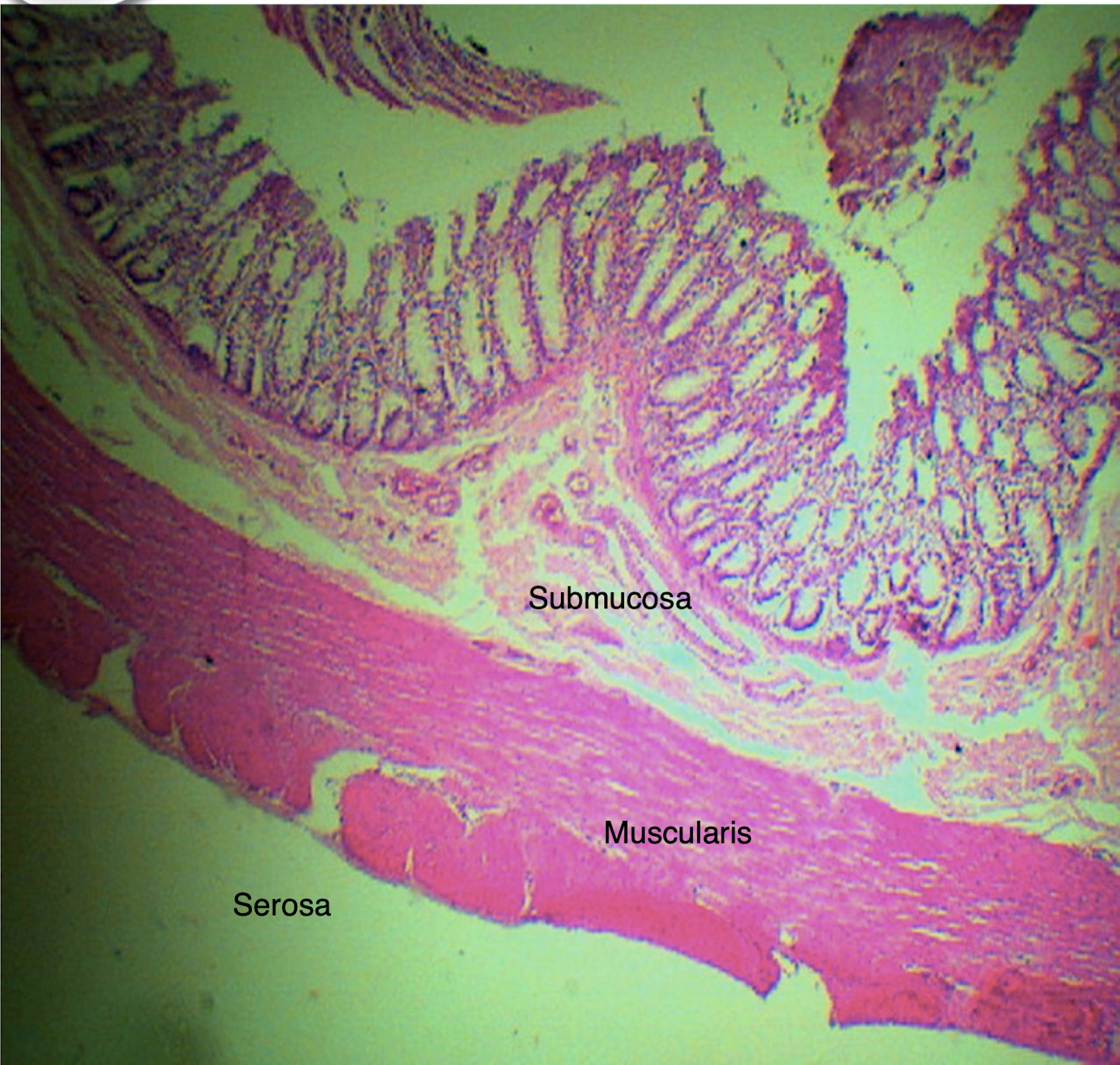
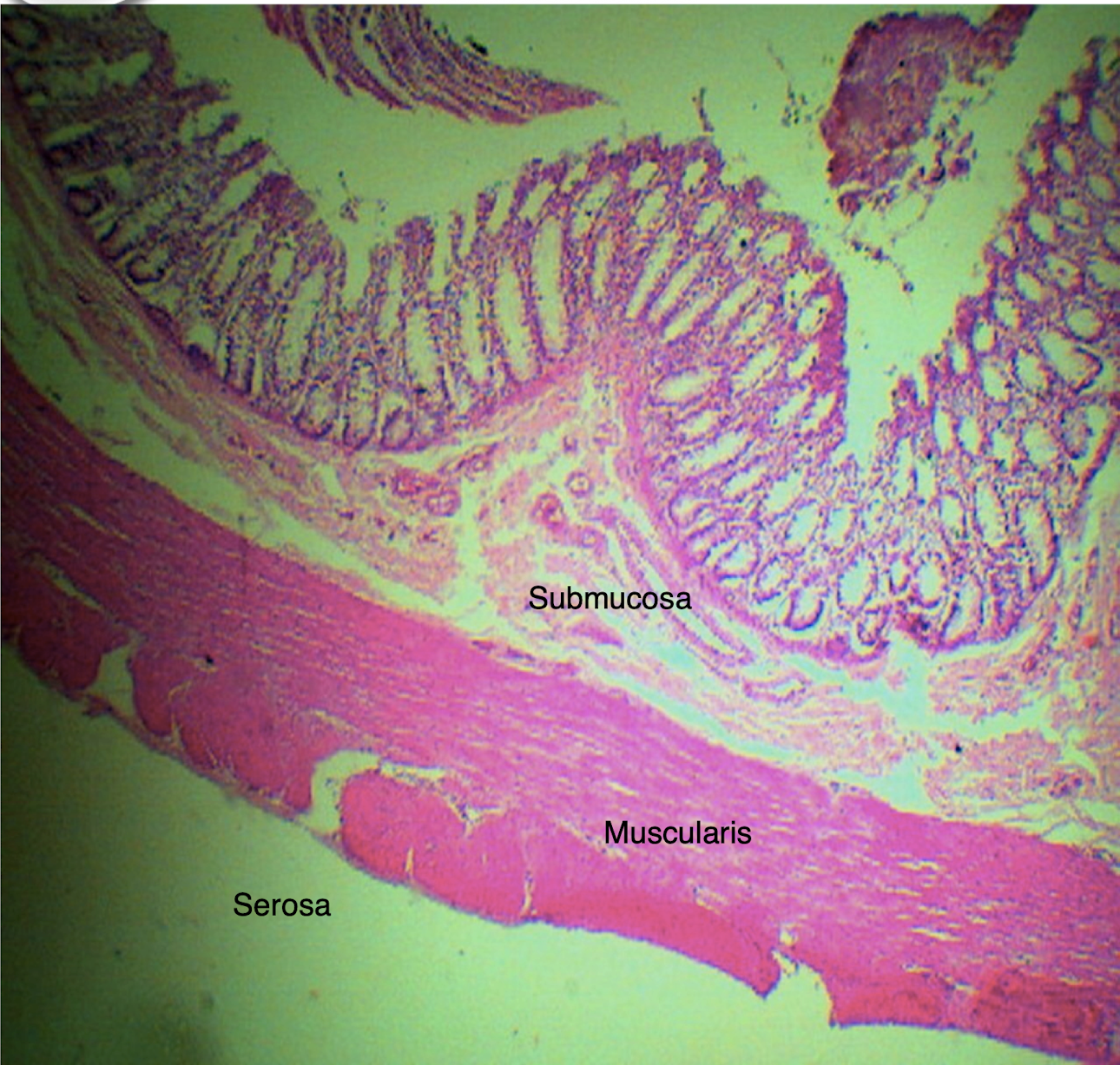
COLON
intestinal glands with plenty of goblet cells
Identify the structure
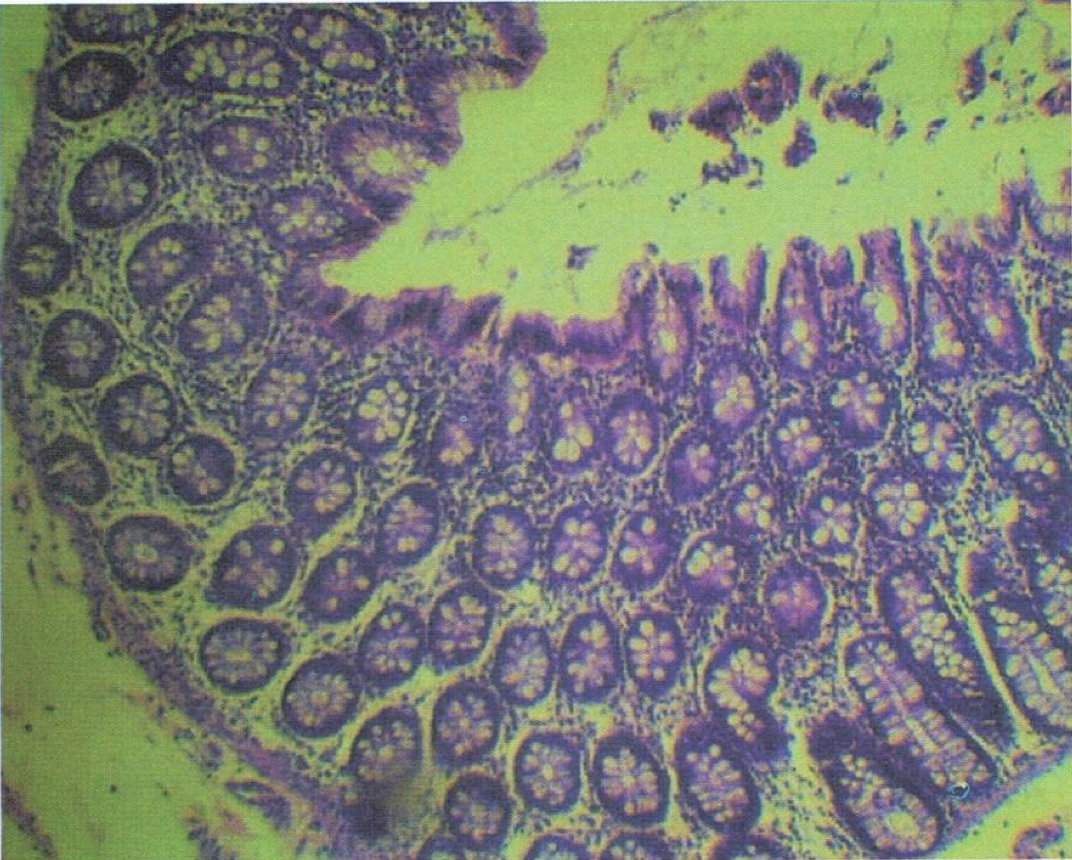
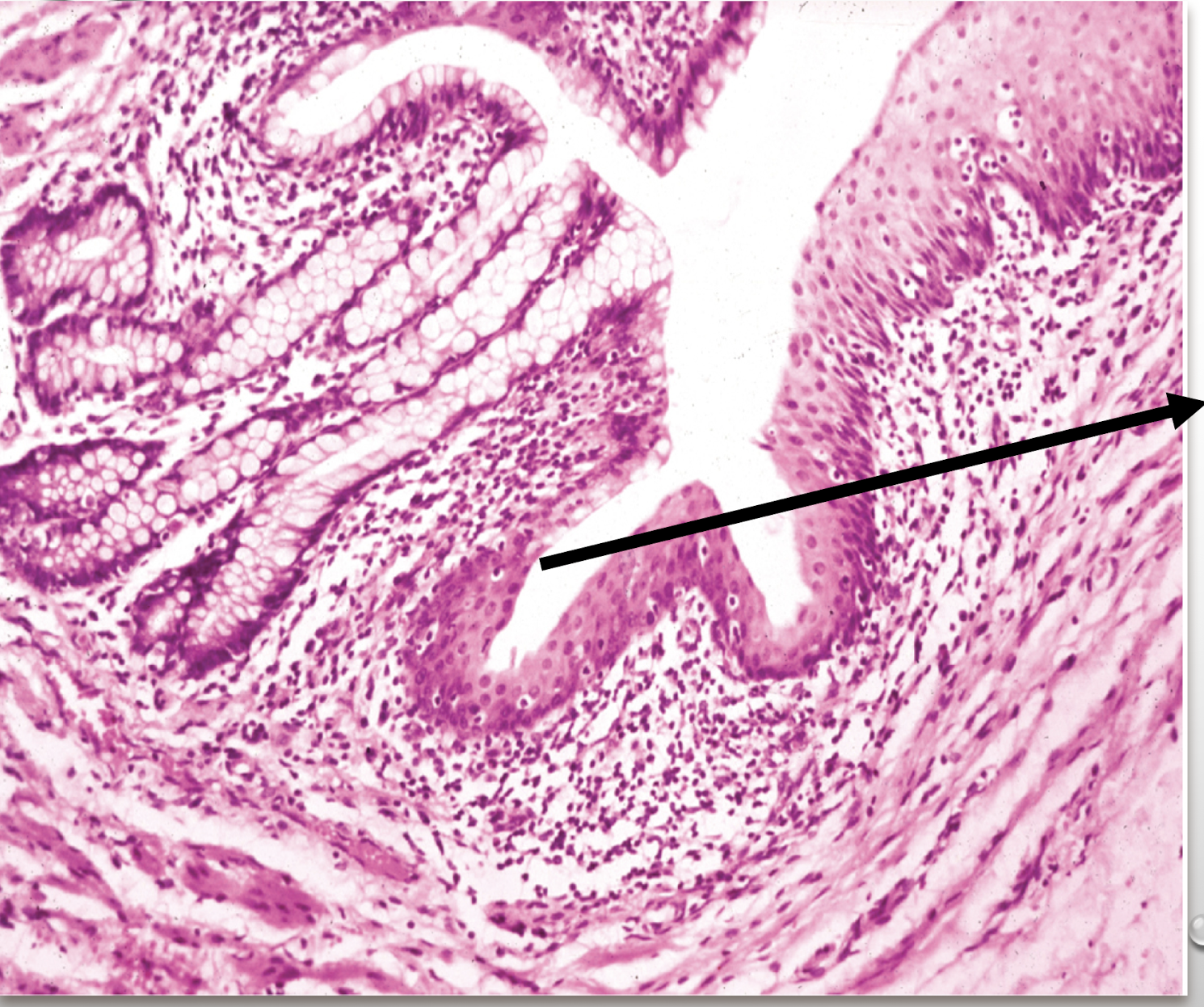
Recto-anal junction
A: rectum (simple columnar with goblet cells)
B: anus (stratified squamous non-cornified epithelium)
Identify the structure
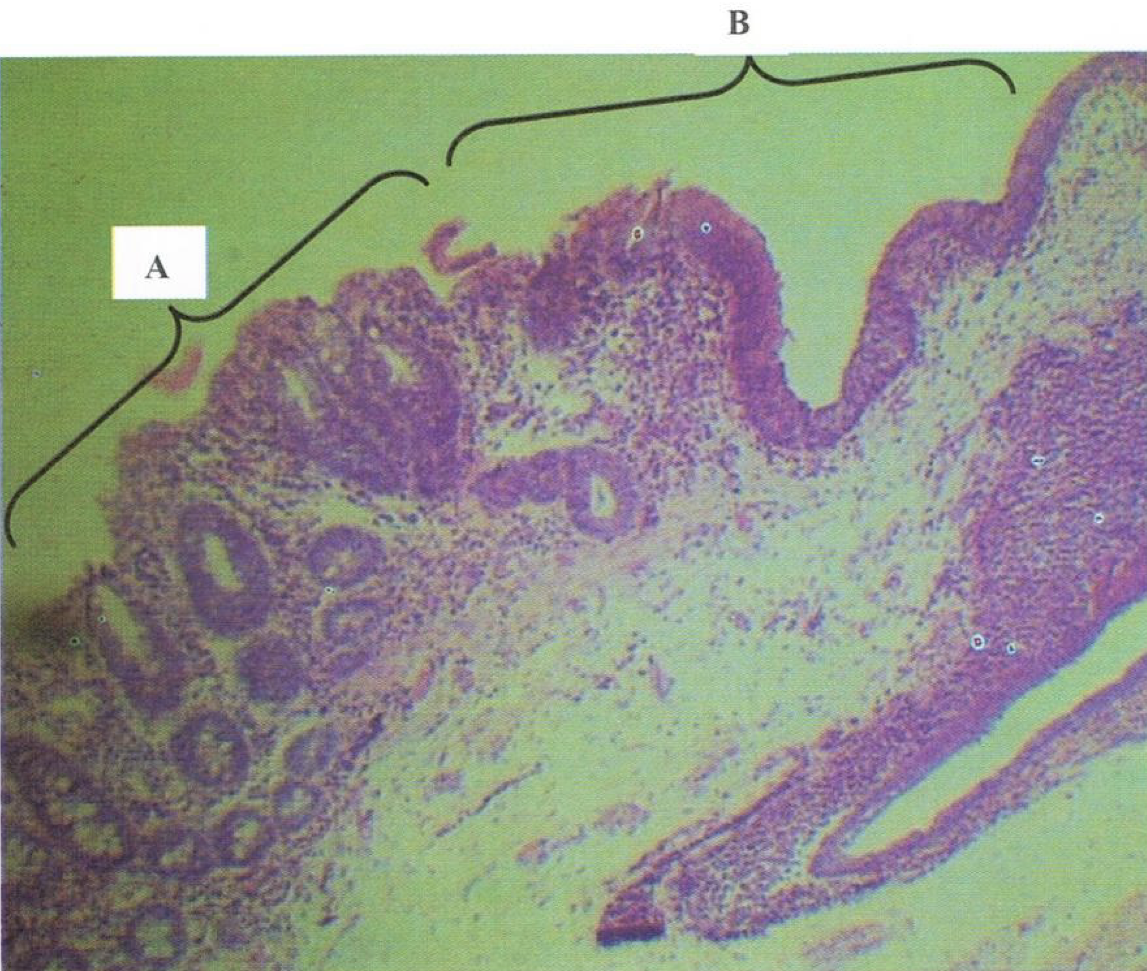
rectum
Goblet cells are most numerous in this segment of the large intestine
rectoanal junction
simple columnar rectum to stratified squamous non-cornified anus
identify the structure