Earthquakes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What causes an earthquake?
Rapid release of energy along a fault.
What is a fault?
A crack in bedrock where displacement has occurred.
What is elastic rebound?
When rocks snap back to their original shape after stress is released.
What are foreshocks?
Small tremors that occur before a major earthquake.
What are aftershocks?
Smaller earthquakes following the main quake as the crust adjusts.
What is fault creep?
Slow, gradual movement along a fault without major earthquakes.
What is seismology?
The study of earthquake waves.
What instrument records earthquake waves?
A seismograph.
What is the record produced by a seismograph called?
A seismogram.
What are P-waves?
Primary, compressional waves that travel fastest through all materials.
What are S-waves?
Secondary, shear waves that follow P-waves and travel only through solids.
What are surface waves?
Slowest, most destructive waves that shake or roll the ground.
What is the focus (hypocenter) of an earthquake?
The point underground where the earthquake originates.
What is the epicenter?
The point on Earth's surface directly above the focus.
How is an earthquake’s epicenter located?
By triangulating the arrival times of body waves.
Where do deep focus earthquakes usually occur?
At subduction zones (convergent boundaries).
What scale measures earthquake intensity based on damage?
Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale.
What is the Richter scale based on?
Amplitude of the largest seismic wave.
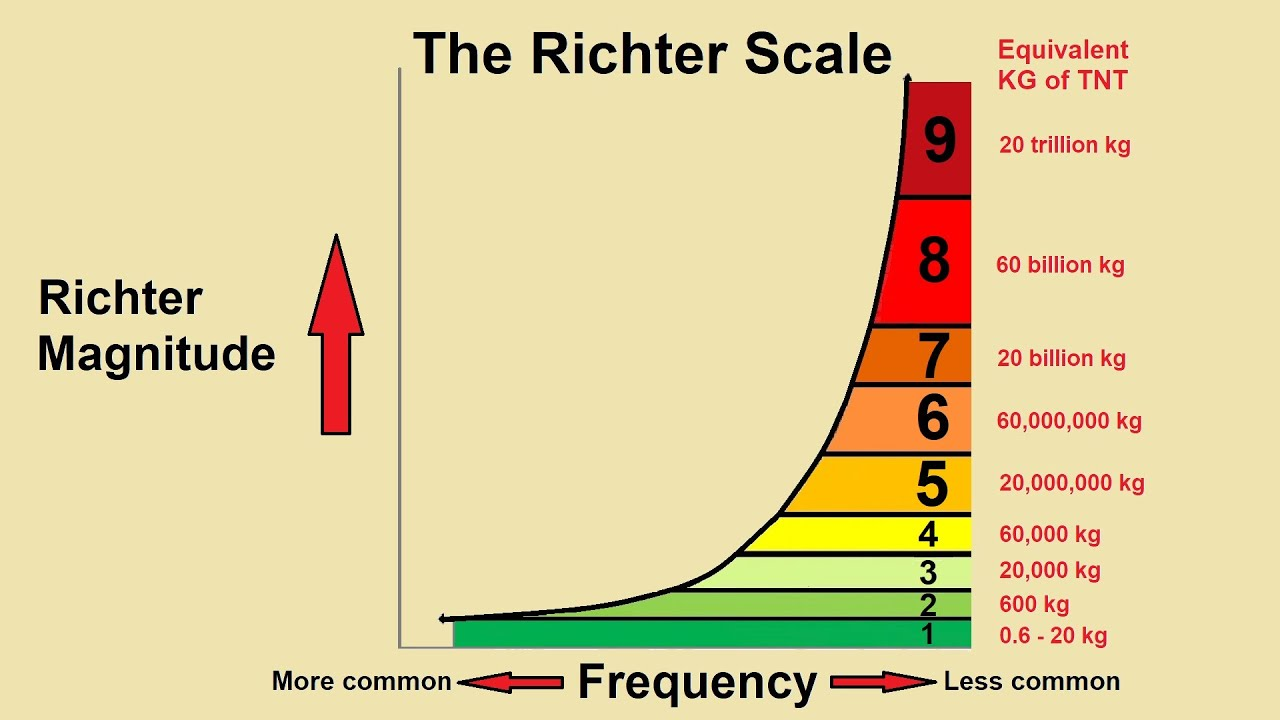
How much more energy is released with each unit increase on the Richter scale?
About 32 times more energy.
What is moment magnitude based on?
Fault displacement.
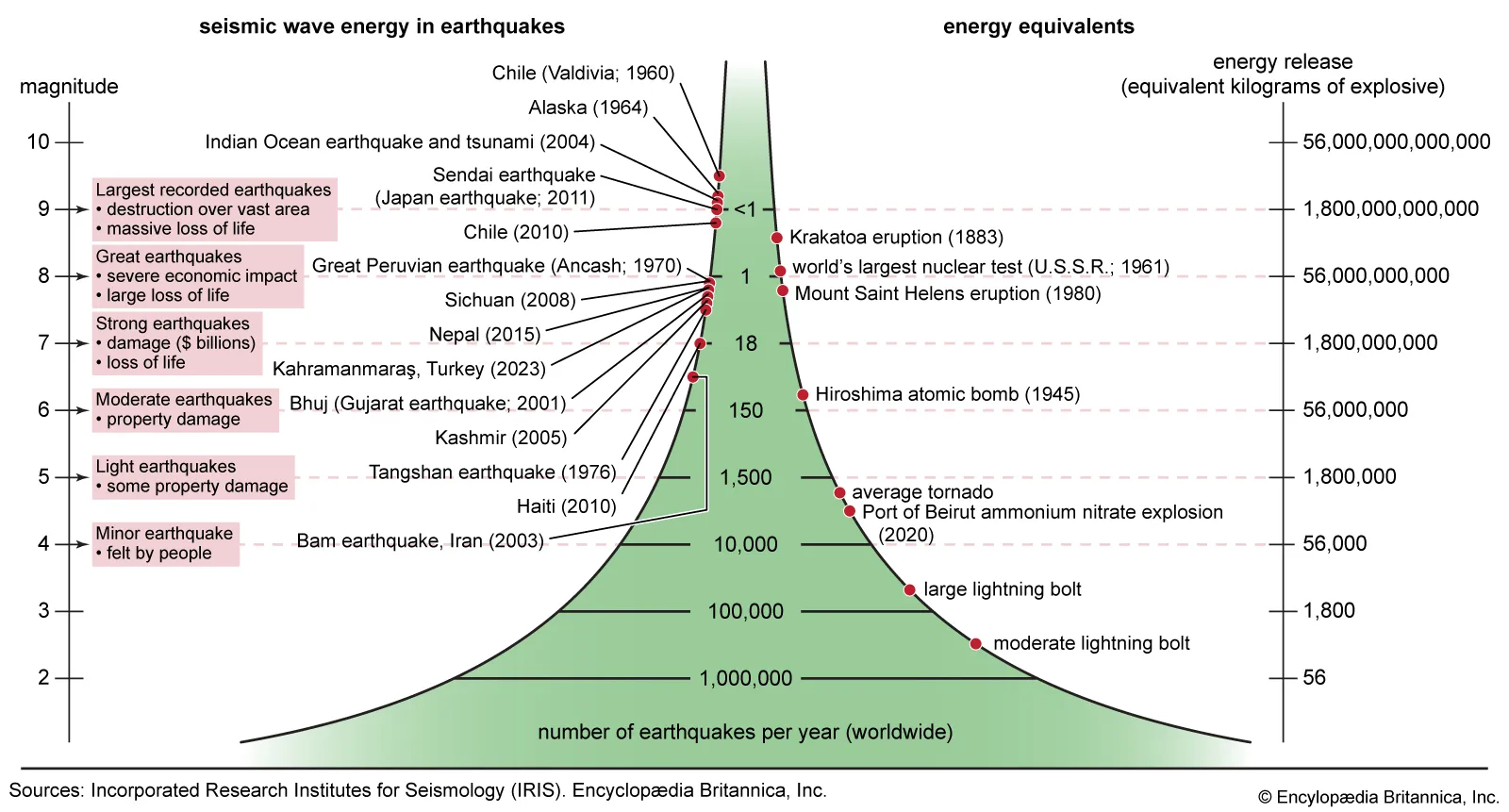
What four factors influence earthquake damage?
Intensity, duration, ground material, and structure design.
What is liquefaction?
When loose, water-saturated soil behaves like a liquid during shaking.
Can earthquakes be predicted?
No—current science cannot predict them accurately.
What do seismic waves tell us about Earth’s interior?
They reveal structure and composition by how waves travel, reflect, and change speed.
What happens to wave speed in rigid materials?
It increases.
What is the Mohorovičić Discontinuity (Moho)?
The boundary between the crust and mantle, where wave speed increases.
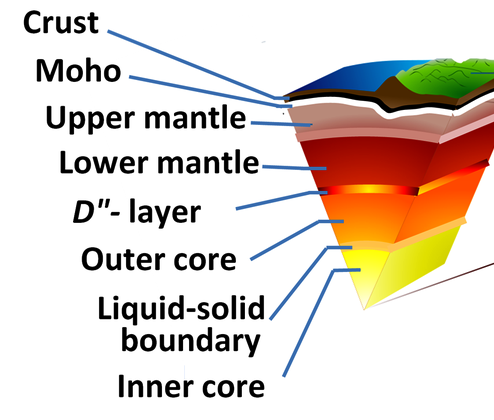
What is the shadow zone?
An area where S-waves are absent due to the liquid outer core.
What is the crust made of?
Continental: felsic rocks; Oceanic: mafic rocks.
What is the mantle mostly made of?
Peridotite; includes the soft asthenosphere and rigid lower mantle.
What is the outer core made of?
Liquid iron-nickel; generates Earth's magnetic field.
What is the inner core made of?
Solid iron.