Intro to personality, Freud, Alder, Jung, Klein, Horney (ch 1-6) (Intro, psychoanalysis, individual psych, analytic psych, object relations theory, psychoanalytic social theory) | Quizlet
1/339
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
340 Terms
Psychoanalytic Social Theory
personality development is influenced by social and cultural factors, particularly the need for security and love in childhood, and how anxiety from unmet needs leads to behaviors like neurotic patterns and the search for validation
3rd aspect Neurotic pride
pride based on an idealized view of self, they are glorious, wonderful, perfect, avoid ppl who won't agree with this view as it would hurt their pride
ego
starts to form at first feeding
all experiences are evaluated by the ego and related to the good and bad breast
Freud combined what to create his theory
philosophical speculations and scientific method
Freud created a Grand Theory which..
attempts to explain all personalities of all people
to him, ________ to his clients was the method that began his road to knowledge
LISTENING
personality comes from latin word persona, meaning a theoretical mask (persona) to project a role or false appearance--NOT GOOD
What is Personality
no single definition, but it is a pattern of relatively permanent traits and unique characteristics that give both consistency and individuality to a person's behavior
Psychology of personality
the scientific study of the psychological forces that make people uniquely themselves
traits
contribute to individual differences in behavior, consistency of behavior overtime, and stability of behavior across situations
may be unique, common to a group, or shared w/whole species
they may be common in a species but_____is different
the pattern for each individual
characteristics
unique qualities of an individual that include such attributes as temperament, physique, and intelligence
temperament
emotional reactivity and intensity
we know theory doesnt = facts or truth, just to generate research and organize observations
theory --accepted as IF it were true
a SET (not one) of RELATED assumptions that allows scientists to use logical deductive reasoning to formulate TESTABLE hypothesis
IF-THEN statements: IF child brought up in isolation, THEN child will not learn language
logical deductive reasoning
used to formulate hypothesis--start with theory and use LDR to get to the hypothesis --bridge
going from the general to the specific
inductive reasoning
going from specific to general
altering theory--as theory grows and changes, other hypotheses can be drawn from it--alters theory to reflect results
taxonomy
classification of things according to their natural relationships --can evolve into theory
what relates closely to theory
philosophy because its abt the pursuit of knowledge
Epistomology
the nature of knowledge
theories rely on what relative
speculation --tied to empirical (conducted with the 5 senses or instruments that use the 5 senses to gather data that is rigorous, systematic, and unbiased) research and data
corner stones of theory
speculation and empirical observations
hypothesis
an educated guess or prediction specific enough for its validity to be tested using the scientific method
theory=too general
theory=give birth to hypo, more specific
Why different theories?
built on assumptions that are subject to individual interpretation --theories depend on ability to generating research and data rather than agreeability
Perspective in theories of personality:
psychodynamic theories
freud
focuses on early childhood experiences and relationships with parents as guiding forces that shape personality development
unconscious mind and motives more powerful than conscious awareness
psychoanalysis--dream interpretation to uncover unconscious thoughts, feelings, impulses: to treat neurosis and mental illness
key ppl in psycho
freud
alder
jung
klein
horney
Erickson
humanistic-existential theories
positive psych
ppl strive toward meaning, growth, well-being, happiness, and psych health--pos emotions and happiness foster better psyche
driven by a search for meaning but also negative experiences like failure, death, anxiety-can foster growth
key ppl in human
maslow
rodgers
may
dispositional theories
unique and long-term tendencies to behave in certain ways
traits like extraversion or anxiety are called traits--traits serve the function of making behaviors more likely in some ppl
key ppl
allport
McCrae and Costa
biological-evolutionary theories
Behavior, thought, feelings, and personality are influenced by differences in basic genetic, epigenetic, and neurological systems between individuals
these differences stem from genotype and CNS
shaped by evolution --always an interaction between nature and nurture --based on evolved brain systems

key ppl in bio
Eysenck
Buss
Learning (social) cog theories
only focus on behavior not hypothetical or unobservable states like thoughts
all behavior learned through association and consequences (reinforcement or punished)
what personality we have is shaped by how we think and perceive the world
KEY POINTS: What is personality?
What is a theory?
Theory and its relatives:
Why different theories?
Perspective in theories of personality:
Theorists' personalities and their theories on personality:
What makes a theory useful?
dimensions for a concept of humanity:
research in personality theory:
key ppl in social
skinner
bandura
rotter
mischel
kelly
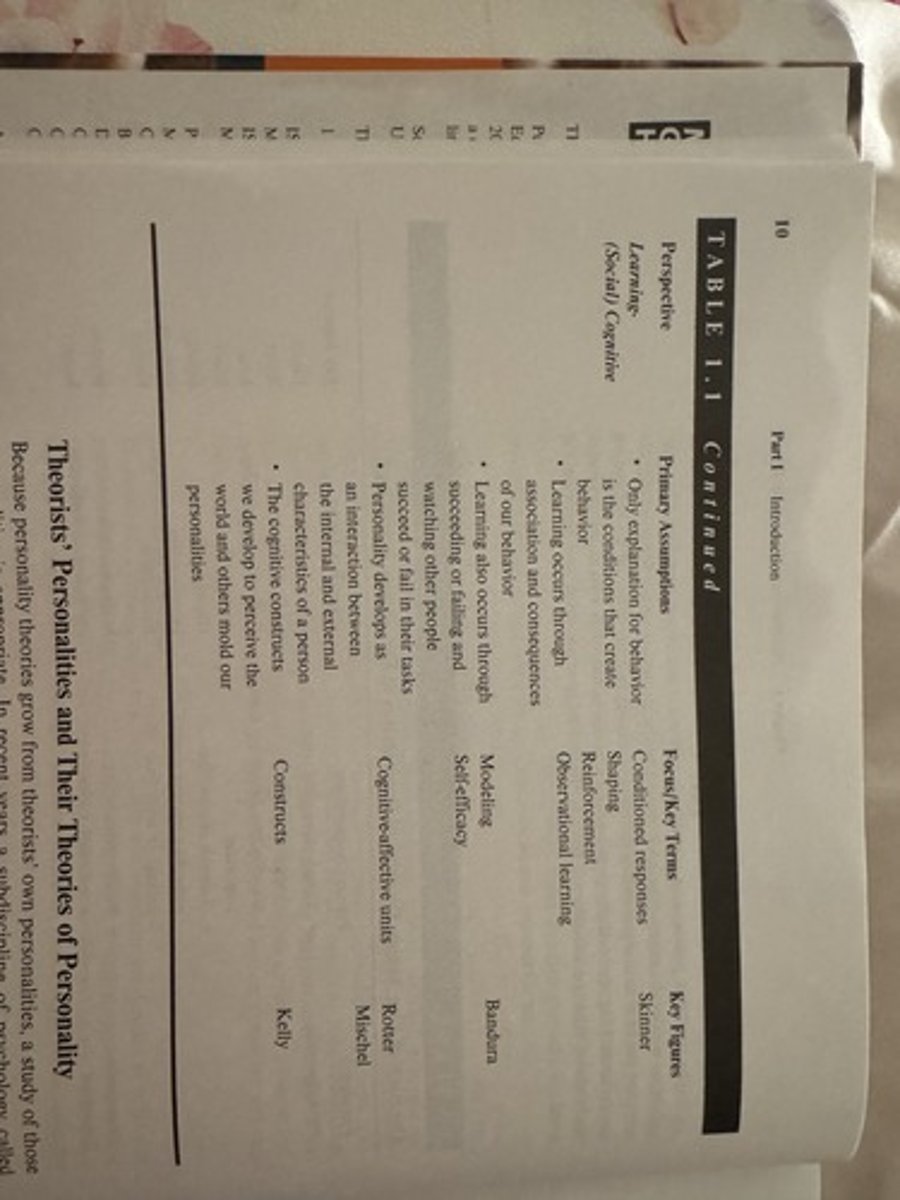
Theorists' personalities and their theories on personality:
psychology of science
personal traits of scientists --studying personality since personality theory grows from theorists own personalities
What makes a theory useful?
generates research, is falsifiable, organizes data, guides action, is internally consistent, is parsimonious
parsimonious
simple and straightforward theories
internally consistent
must be consistent with itself --good construct validity, good operationalization
guides action,
provides a structure for finding answers --the if-then framework, like a freudian vs rogerian counselor answering the same question
organizes data
organize and classify into a framework
a personality theory must offer a reasonable explanation of at least some kinds of behaviors
falsifiable
precise enough that research may support or fail to support --cannot be vague enough to the point where pos and neg results both support the theory
u think because u can't prove its false then it must be true--this is not falsifiable
dimensions for a concept of humanity: these diff dimensions cause diff personality theories
determinism vs free choice
are people's behaviors determined by forces over which they have no control, or can people choose to be what they wish to be?
Pessimism vs Optimism
are people doomed to live miserable, conflicted, and troubled lives, or can they change and grow into psychologically healthy, happy, fully functioning human beings?
Causality--behavior is function of past experiences vs. Teleology--c of behavior in terms of future goals
do people act as they do because of what has happened to them in the past, or do they act as they do because they have certain expectations of what will happen in the future?
chapter 2-Freud
conscious vs unconscious determinants of behavior
Are people ordinarily aware of what they are doing and why they are doing it, or do unconscious forces impinge on them and drive them to act without awareness of these underlying forces?
Biological vs. Social Influences on Personality
Are people mostly creatures of biology, or are their personalities shaped largely by their social relationships?
nature vs nurture
Uniqueness vs. Similarities
is the salient feature of people their individuality or is it their common characteristics?
should studying personality focus more on traits that make us alike or different
personality inventories must be reliable and valid
reliability
consistency of measurement and results
validity
the degree to which a test/instrument actually measures what it's supposed to measure
1. type of validity:
construct validity: how well the constructs are operationalized
Convergent validity: The degree to which a test correlates strongly with other tests that measure the same or similar constructs.
Divergent validity: The degree to which a test does not correlate strongly with tests measuring different or unrelated constructs.
Discriminant validity: A form of validity that shows a test is distinct from unrelated constructs, confirming it measures what it is supposed to measure.
2. predictive validity
extent to which a test can predict future behavior
High Predictive Validity:
People who score high on your extroversion test are more likely to perform well in sales jobs (e.g., making more sales or receiving higher performance reviews).
This supports that the test predicts future outcomes related to extroversion.
Low Predictive Validity:
People’s extroversion test scores do not correlate with their success in sales jobs.
This suggests the test does not accurately predict the outcome it was intended to measure.
Predictive validity evaluates how well the personality test predicts a specific future behavior or outcome (e.g., job performance in sales).
generates research
generates descriptive research--measurement, labeling, categorizing units, and hypothesis testings--verifies the usefulness of a theory
useful theory=many hypos
purpose of psychoanalysis
To strengthen the ego, to make it more independent of the super ego, to widen its field of perception and enlarge its organization, so that it can appropriate fresh portions of the ID. Where the ID was, the ego shall be.
Cornerstones of Psychoanalysis
sex and aggression
--small sample sizes
--not objective
--upper to middle class
--no observing under controlled conditions
--always in case study
--HARking
Freuds issues with his "experiments"
free association--this is his main technique that he replaced hypnosis with
uncover repressed memories, transforming what is UC into what is C
verbalize every thought that comes to mind, no matter how irrelevant or unacceptable it may appear
following a C idea to the UC through a train of accosiations wherever it leads
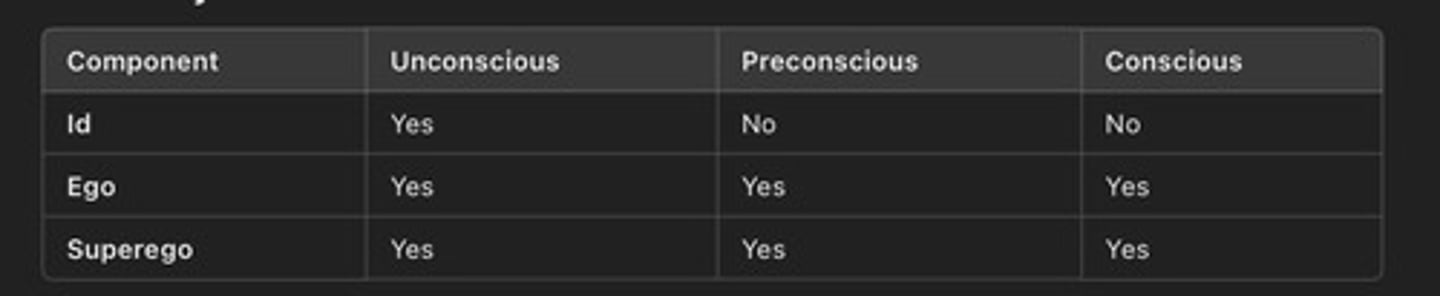
freud identified 3 levels of mental life
unconscious, preconscious, and conscious
unconscious,
contains all the drives, urges, and instincts that are beyond our awareness yet motivate most of our words, feelings, and actions
drives may appear in the C from the UC but only after certain transformations____
like through teasing or joking, the original sex/agression is hidden from both persons C mind but each gain satisfaction of sexual or aggressive urges without being conscious abt it --there can be communication between the UC minds of people without them knowing. many forces in the UC strive to become C but just dont appear in original form
because the unconscious is not available to the conscious how can we truly know it exists?
can only be proved indirectly Freud believed, it explains the meaning behind dreams, freudian slips, and forgetting (repression)
repression
the forcing of unwanted, anxiety-ridden experiences into the unconscious as a defense against the pain of that anxiety
phylogenetic endowment
a portion of our UC comes from our early ancestors experiences that have been passed on to us through hundreds of generations of repetition (similar to Jungs collective UC)
preconscious
contains all the elements that are not C but can become C easily or through difficulty
Example: If someone asks for your address, you weren’t thinking about it a moment ago, but you can quickly recall it.
Role: It’s like a storage area where information is accessible but not immediately active.
the contents of the precocious come from 2 sources...
conscious perception:
UC:
conscious
plays a minor role in psychoanalytic theory
mental elements in awareness ataxy given point in timee--only level of mental life directly available to us
how can ideas reach C
perceptual C system: what we preceive through our sense organs, if not too threatening
within the mental strict: nonthreatening ideas from the PC and menacing but well-disguised images from the UC: these images escaped into the PC by disguise and evading the primary sensory, then when in the PC, they avoid the final censor and go to the C--by this time they are darted and often seen in dreams and behaviors
early childhood experiences that create high levels of anxiety are _____where they may influence behavior, emotions, and attitudes for years
repressed into the unconscious
events that aren't associated with high anxiety but just forgotten make up the contents of ________
preconscious
____images are those in awareness at any given time
conscious
final censor
primary censor
Here’s a summary of each part in one sentence:
Unconscious processes entering consciousness: Thoughts from the unconscious can only become conscious if they are disguised enough to avoid triggering anxiety.
Primary censor: A mental "guard" blocks anxiety-producing memories from moving from the unconscious to the preconscious.
Final censor: Another "guard" ensures only non-threatening, disguised thoughts pass from the preconscious to the conscious mind.
Disguised thoughts: By the time these thoughts reach consciousness, they appear pleasant and unrecognizable from their original form.
Source of these thoughts: Many of these thoughts stem from suppressed childhood experiences involving sexuality or aggression, which were punished and caused anxiety.
Repression: As a defense against anxiety, the mind forces painful memories into the unconscious to avoid dealing with them.
3 provinces of the mind
id, ego, superego
id
unconscious, chaotic, out of contacts with reality and in service of the pleasure principle
completely unconscious in the physical region, no contact with reality, but strives to reduce tension by satisfying basic desires--cannot be accessed by the C
sole function is to seek pleasure--no moralitty
TO SEEK PLEASURE WITHOUT REGARD FOR WHAT IS PROPER OR JUST
primary process (ID and UC) vs secondary process (ego and C)
Primary Process
The primary process is how the unconscious mind works.
It’s driven by instincts and desires (like hunger or pleasure) and seeks immediate satisfaction.
It doesn't care about logic, reality, or long-term consequences—its only goal is to reduce tension and get what it wants as quickly as possible.
For example, if you’re hungry, your mind might imagine eating food to feel better, even if food isn’t actually available.
Secondary Process
The secondary process is how the conscious mind operates, guided by logic and reality.
It’s responsible for planning, thinking, and considering consequences to meet desires in a realistic way.
Instead of imagining food when you’re hungry, the secondary process helps you figure out how to get actual food, like going to the kitchen or a restaurant.
In summary, the primary process is about immediate, fantasy-based satisfaction, while the secondary process is about practical, reality-based problem-solving.
pleasure principle
tendency of the id to strive for immediate gratification
ego
the executive of personalty, in contact with the real world, and is service of the reality principle
only region in contact with reality--grows out of the ID during infancy and becomes the source of communication with the external world, governed by reality principle
in constant fight with the ID, superego, and eternal world: creates anxiety and thus uses repression and other defense mechanisms
continues to develop strategies to meet needs of ID while id stays unchanged
at the mercy of the more powerful id
can make decisions on all 3 levels
reality principle
tendency of the ego to postpone gratification until it can find an appropriate outlet
superego
serves the moral and idealists principles and begins to form after the Oedipus complex is resolved
grows from the ego
no contact with outside world and has unrealistic demands for perfection
tries to control sexual and agressive impulses through repression--it can order the ego to produce these repressions
watches over and judges the ego
guilt is a function of
the conscious
inferiority feels stem from
ego-ideal
superego subsystems
The Conscious - tells us what you should not do
The Ego Ideal -tells us what you should do
all motivation is traced to what?
sexual and aggressive drives
childhood behaviors related to sex and aggression are usually punished and leads to
repression or anxiety
to protect itself against anxiety, the ____initates various ____the most basic is repression
ego
defense
infantile stages has three substages
oral, anal, phallic
1. repression
when the ego is threatened by underseriable id impulses it represses those impulses by forcing them into the UC
dreams, slips of the tongue, get into the C and make more anxiety
during this Oedipal stage the child wants_____
sexual unity with one parent while harboring hostility for the other
dreams and Freudian slips are disguised means of expressing ______ ________
unconscious impulses
Levels of mental life and provinces of the mind refer to the____of personality, but personality also does something
structure
drive
operates as a constant motivational force
internal stimuli
drives grouped under 2 major headings
sex and aggression
every drive is characterized by an....
impetus
impetus
the amount of force it exerts
what's the drives source
the region of the body in a state of excitement or tension