Heart Review Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Which side of the heart is oxygenated?
Left
Which side of the heart is deoxygenated?
Right
Which artery is dexygenated?
pulmonary artery
which vein is oxygenated?
pulmonary vein
List the blood flow starting from the vena cavas
superior/inferior vena cava> right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta
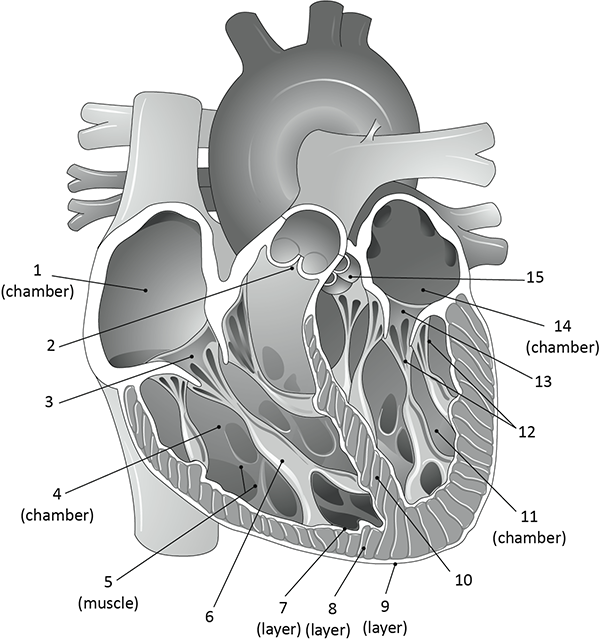
What is 2?
pulmonary valve
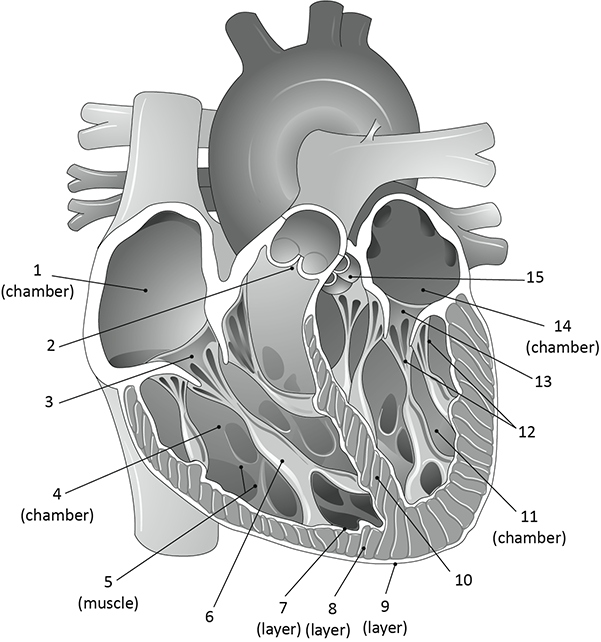
What is 5?
trabeculae carnae
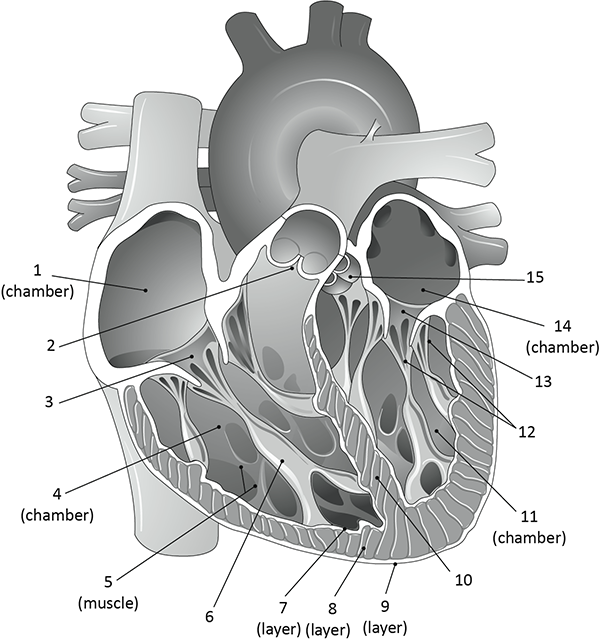
What is 6?
papillary muscle
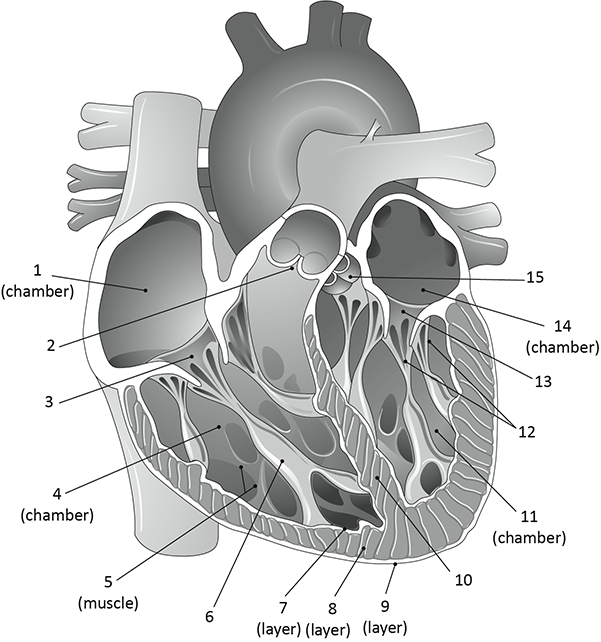
what is 7, 8, and 9?
endocardium
myocardium
epicardium
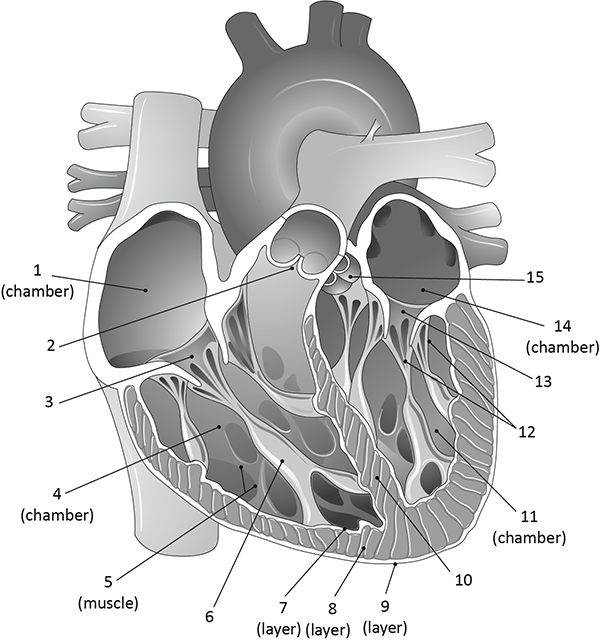
What is 12?
chordae tendinae
What type of valves are the tricuspid and mitral valve?
atrioventricular valves
How can atriventricular valves be characterized? what does it connect?
it connects the atria to the ventricles
What is another term for mitral valve?
Bicuspid valve
What types of valve is aortic and pulmonary valves?
Semilunar valve
How can semilunar valves be characterized?
located between ventricles and main arteries
Which side of the heart is responsible for the systemic circulation?
Left side
Which side of the heart is responsible for the pulmonary circulation?
Right side
What are the left and right side of the heart separated by?
cardiac septum
What node of the cardiac excitation sequence has the fastest pacemaker cells out of all the cardiomyocytes?
SA node
What node of the cardiac excitation sequence stimulates internodal pathways?
SA node
Where is the SA node located?
The point where the superior vena cava enters the right atrium
What comes after the SA node>
Internodal pathways
What conducts the action potential of the SA node through gap juncctions?
internodal pathways
What node stimulates atrial contraction and AV node?
Internodal pathways
What comes after the internodal pathways?
AV node
Which node has slower pacemaker cells to allow time for the atrial refractory period?
AV node
What happens if the SA node does not stimulate the contractile cells?
AV node may initiate stimulus
What comes after the AV node?
Atrioventricular bundle of HIS
What part of the cardiac excitation sequence conducts action potential of AV node into the interventricular septum?
Atriventricular bundle of HIS
What side of the bundle branch carries to the apex of the left ventricle?
Left bundle branch
What side of the bundle branch carries to the apex of the right ventricle?
right bundle branch
What stimulates the purkinje fibers?
the left and right bundle branches
What are purkinje fibers caused by?
a high proportion of intercalated disks
Which part of the cardiac excitation sequence carry stimulus to the ventricular cardiac muscle cells>
purkinje fibers
What is a thrombus?
is a blood clot that abnormally forms somewhere within the circulation.
What happens when it extends into the open lumen of the blood vessel, and the thrombus reduces blood flow downstream? what is it called?
occlusion
What is an ischemia?
When a coronary artery becomes occluded and the heart doesn’t receive enough blood
What is the result of ischemia?
angia pectoris
What is it called when a part of a thrombus breaks off and moves through the circulation?
embolus
Does the embolus cause an occlusion eventually?
yes