Ch. 6: Unemployment
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Unemployment
The difference between the quantity of labour supplied and the quantity of labour demanded
Unemployment Rate
Percentage of the labour force that is unemployed
Labour force survey
Must be actively looking and available for work within the past four weeks
=(number of unemployed/ labour force) x 100
UR= Incidence of unemployment/year X Average Duration of unemployment in the year
Problems with Official Unemployment Figures: Inactive Job Seekers
Could overstate the unemployment rate
Problems with Official Unemployment Figures: Discouraged Workers
Persons who want a jobs but have given up looking
Understate the rate
Problems with Official Unemployment Figures: Underemployed Workers
Involuntary part-time work
Under state the rate
Problems with Official Unemployment Figures: Marginal Workers
Weak attachment to the labour force
Come and go regarding status
To What Extend Does the Unemployment Rate Measure Economic Hardship?
Measures the amount of unused labour and the amount of economic hardship
Associated with unemployment is not as severe when families have more than one breadwinner
Unemployment insurance reduces this
Depends on the duration of the unemployment
Long term vs short term
Utilization of Labour
AKA Employment Rate
=(total number of employed/population) x 100
Easier to determine
Three Main Characteristics of Unemployment in Canada
The unemployment rate has gradually increased since WW2
There have been large fluctuations in the unemployment rate
From 2% to 12% due to Recessions and Expansions
Unemployment rates tend to remain high for some period
Flow Amoung Three Labour Market
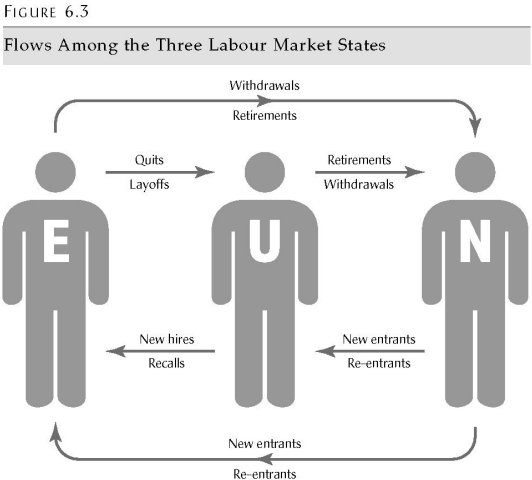
Frictional Unemployment
Normal turnover of labour
Inevitable in a well-functioning labour market
Recent grads
Workers between jobs
Seasonal Unemployment
Resulting from the decline in the number of jobs at certain times of the year
UR seasonally adjusted
Structural Unemployment
Resulting from a mismatching of workers and job opportunities based on either skills or geography
Caused by Industrial restructuring and technological change
Globalization is contributing to sectoral shifts
Cyclical Unemployment
Arises because the economy does not generate enough jobs for those seeking one
Natural: The unemployment rate that exists when the economy is functioning at full capacity
The difference between the actual rate of unemployment and the natural rate
Why the Natural Unemployment Rate has Increased
Natural UR = Frictional + Structural
Demographic Shifts
Employment Insurance
Industrial Restructuring
Technological Change