unit #4e: general and special senses
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
describe sensory vs. perception.
* sensation: sensory info arriving at CNS
* perception: conscious awareness of a sensation
* perception: conscious awareness of a sensation
2
New cards
list and describe/give examples of the 2 groups of senses. where are their respective receptors located?
* general senses: refers to temp., pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception
* receptors located across body
* special senses: smell, taste, equilibrium, hearing, vision
* receptors localized in complex sense organs
* receptors located across body
* special senses: smell, taste, equilibrium, hearing, vision
* receptors localized in complex sense organs
3
New cards
define receptor specificity. define receptive field.
* receptor specificity: defines type of stimuli responded to; can be very general (ex. pressure, temp. chance) or very specific (ex. eye receptors response to light only)
* receptive field: area monitored by receptor
* large receptive fields → lower accuracy in localizing stimulus
* small receptive fields → higher accuracy in localizing stimulus
* receptive field: area monitored by receptor
* large receptive fields → lower accuracy in localizing stimulus
* small receptive fields → higher accuracy in localizing stimulus
4
New cards
describe 3 receptors and sensory limitations.
* must have receptor to detect stimulus
* receptors have limited range of sensitivity
* CNS interpretation of stimulus may not always reflect reality
* receptors have limited range of sensitivity
* CNS interpretation of stimulus may not always reflect reality
5
New cards
describe sensory coding. what are the two types of receptor types under this coding category? define them and give 2 examples.
* sensory coding: gives info about strength/duration of stimuli
* tonic receptors: always active; eye receptors, propriocepters
* phasic receptors: become active only when stimulated or stimulus changes; touch and pressure receptors
* tonic receptors: always active; eye receptors, propriocepters
* phasic receptors: become active only when stimulated or stimulus changes; touch and pressure receptors
6
New cards
describe sensory adaptation. what are the two types of receptor types under this coding category for PNS? what’s one type of adaptation in CNS? define them and give an example.
* adaptation: reduction insensitivity when constantly stimulated
* PNS
* fast-adapting receptors: respond strongly at first, then decline over time; characteristic of phasic receptors
* slow-adapting receptors: show little or no peripheral adaptation; characteristic of tonic receptors
* CNS
* central adaptation: restriction of stimuli by nuclei in CNS; ex. adaptation to smells
* PNS
* fast-adapting receptors: respond strongly at first, then decline over time; characteristic of phasic receptors
* slow-adapting receptors: show little or no peripheral adaptation; characteristic of tonic receptors
* CNS
* central adaptation: restriction of stimuli by nuclei in CNS; ex. adaptation to smells
7
New cards
what are 4 types of receptors under classification by type of stimulus detected?
* nocioceptors
* thermoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
* chemoreceptors
* thermoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
* chemoreceptors
8
New cards
define nocioceptors. describe the 3 types of pain.
* nocioceptors: respond to multiple stimuli types; sense pain
* fast pain: sharp stabbing pain
* slow pain: dull, throbbing
* referred pain: pain reception elsewhere than source location
* fast pain: sharp stabbing pain
* slow pain: dull, throbbing
* referred pain: pain reception elsewhere than source location
9
New cards
define thermoreceptors.
phasic receptors that respond to changes in temp.
10
New cards
define mechanoreceptors. list and describe the 3 subreceptors under this.
* mechanoreceptors: respond to stretch, compression, distortion
* tactile receptors: touch, pressure, vibration; fine vs. crude touch (skin)
* baroreceptors: pressure changes (blood vessels, urinary bladder, etc.)
* proprioceptors: joint position and tendon/ligament tension; complex
* tactile receptors: touch, pressure, vibration; fine vs. crude touch (skin)
* baroreceptors: pressure changes (blood vessels, urinary bladder, etc.)
* proprioceptors: joint position and tendon/ligament tension; complex
11
New cards
define chemoreceptors.
respond to specific chemicals dissolved in bodily fluids
12
New cards
sense of smell relies on what organs?
sense of smell relies on olfactory organs
13
New cards
describe the process in which a scent is detected.
1. target’s chemicals coming from scent enters nose
2. lands on olfactory epithelium (located on inferior surface of cribriform plate & superior nasal conchae)
3. inhaled chemicals dissolve into mucus on olfactory epithelium
4. olfactory nerve fibers that extend from olfactory bulb (thru cribriform plate) are stimulated and synapse → olfactory tract → CNS
14
New cards
what cells does sense of taste rely on? in where? what projections cover the surface of the tongue?
* sense of taste relies on gustatory epithelial cells in taste buds
* lingual papillae: epithelial projections covering surface of tongue; taste buds located in this
* taste buds sense dissolved chemicals on tongue
* lingual papillae: epithelial projections covering surface of tongue; taste buds located in this
* taste buds sense dissolved chemicals on tongue
15
New cards
what are 3 parts of ear anatomy? identify and locate the different subparts of each section.
* external ear
* auricle
* external acoustic meatus
* middle ear
* tympanic membrane
* tympanic cavity
* auditory tube
* auditory ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes
* inner ear
* bony labyrinth formed by passageways w/in temporal bone (filled with perilymph)
* semicircular canals
* cochlea
* vestibule
* membranous labyrinth makes up tubes/chambers w/in bony labyrinth (filled with endolymph)
* semicircular ducts
* cochlear duct
* saccule & utricle (sacs in vestibule)
* auricle
* external acoustic meatus
* middle ear
* tympanic membrane
* tympanic cavity
* auditory tube
* auditory ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes
* inner ear
* bony labyrinth formed by passageways w/in temporal bone (filled with perilymph)
* semicircular canals
* cochlea
* vestibule
* membranous labyrinth makes up tubes/chambers w/in bony labyrinth (filled with endolymph)
* semicircular ducts
* cochlear duct
* saccule & utricle (sacs in vestibule)
16
New cards
what sensation occurs in vestibular complex? describe the movements identified by the 3 different subparts (list these). what nerve passes this info to CNS? also, where are sensory hair cells located for each movement type?
* equilibrium sensation occurs in vestibular complex; passed to CNS in vestibular nerve
* semicircular canals/ducts (anterior/posterior, horizontal, coronal) → rotational movement
* endolymph movement thru ducts (by gravity) stimulates sensory hair cells embedded in ampullary cupula
* utricle & saccule → linear/acceleration movement (horizontal & vertical)
* sensory hair cells in otolithic membrane stimulated when moved out of level, upright position
* semicircular canals/ducts (anterior/posterior, horizontal, coronal) → rotational movement
* endolymph movement thru ducts (by gravity) stimulates sensory hair cells embedded in ampullary cupula
* utricle & saccule → linear/acceleration movement (horizontal & vertical)
* sensory hair cells in otolithic membrane stimulated when moved out of level, upright position
17
New cards
where does hearing sensation occur?
hearing sensation occurs in cochlea
18
New cards
describe the oval and round window.
thin, membranous opening between cochlear chamber and middle ear
19
New cards
what 3 ducts make up the cochlear chamber? describe them.
* (1) scala vestibuli: starts at oval window → forms (2) scala tympani → ends at round window
* two scalae filled with perilymph
* (3) cochlear duct: between scalae, filled with endolymph
* two scalae filled with perilymph
* (3) cochlear duct: between scalae, filled with endolymph
20
New cards
what is the vestibular membrane (what does it separate?)? what is the basilar membrane (what does it separate, what does it hold?)?
* vestibular membrane: separates scala vestibuli and cochlear duct
* basilar membrane: separates scala tympani and cochlear duct; holds spiral organ (sensory organ)
* basilar membrane: separates scala tympani and cochlear duct; holds spiral organ (sensory organ)
21
New cards
what is the spiral organ (what does it hold, what does it stimulate?)? what is the tectorial membrane (what is it attached to?)?
* spiral organ: holds sensory hair cells, stimulates sensory neurons of adjacent spiral ganglion
* tectorial membrane: attached to cochlear duct, overlies spiral organ
* tectorial membrane: attached to cochlear duct, overlies spiral organ
22
New cards
describe the hearing sensation process. also, where are: high pitch, low pitch, and volume intensity registered?
1. sound vibration: external acoustic meatus → tympanic membrane → auditory ossicles → oval window → vibrates perilymph in cochlea
2. vibrations move thru perilymph up scala vestibuli → scala tympani → end of round window
3. vibrations in perilymph distort basilar membrane (hair cells vibrate against tectorial membrane)
1. high pitch = register lower in cochlear spiral
2. low pitch = register higher in cochlear spiral
3. volume intensity = registered in amount of basilar membrane distortion
4. hair cells stimulate sensory neurons of spiral ganglia
5. sound info passed from spiral ganglia to cochlear nerve → fuses w/ vestibular nerve → form vestibulocochlear nerve (carries info to CNS)
23
New cards
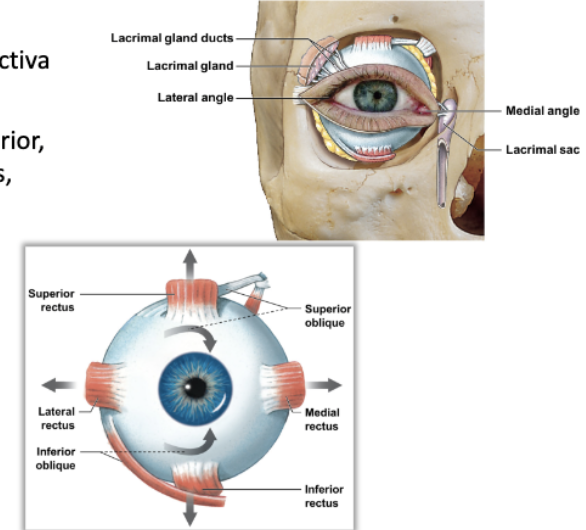
identify and locate:
* medial and lateral angles
* conjunctiva
* lacrimal gland
* lacrimal sac
* superior, inferior, medial, lateral rectus muscles
* superior and inferior oblique muscles
* medial and lateral angles
* conjunctiva
* lacrimal gland
* lacrimal sac
* superior, inferior, medial, lateral rectus muscles
* superior and inferior oblique muscles
24
New cards
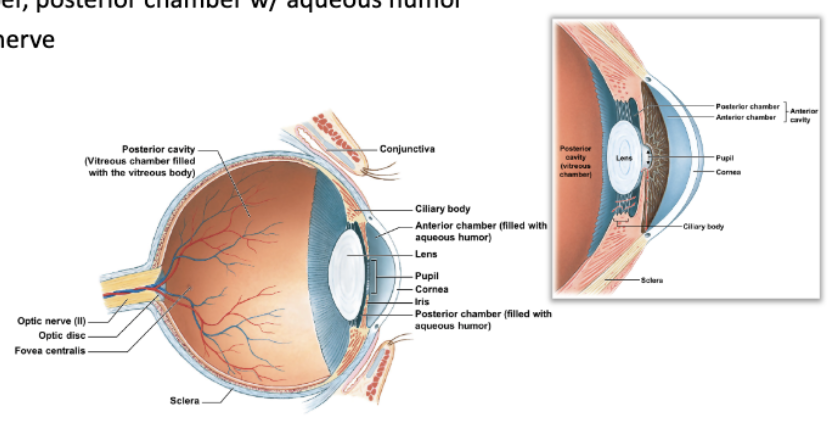
identify and locate:
* sclera
* cornea
* iris
* pupil
* ciliary body
* lens
* posterior cavity (vitreous chamber) w/ vitreous body (humor
* anterior cavity
* anterior chamber
* posterior chamber w/ aqueous humor
* optic nerve
* sclera
* cornea
* iris
* pupil
* ciliary body
* lens
* posterior cavity (vitreous chamber) w/ vitreous body (humor
* anterior cavity
* anterior chamber
* posterior chamber w/ aqueous humor
* optic nerve
25
New cards
what are the 3 layers of the eye? what parts of the eye do they include?
* fibrous layer: outermost; includes sclera, cornea
* vascular layer: middle; iris, ciliary body, choroid (has blood vessels; delivers oxygen and nutrients to retina)
* inner layer: innermost; retina
* vascular layer: middle; iris, ciliary body, choroid (has blood vessels; delivers oxygen and nutrients to retina)
* inner layer: innermost; retina
26
New cards
in the inner layer, what two sublayers does the retina have? describe their functions.
* pigmented layer: absorbs light, biochemically reacts with retina photoreceptors; under neural layer
* neural layer: has 3 sublayers
* neural layer: has 3 sublayers
27
New cards
name and describe the 3 sublayers the neural layer has.
* outer neural layer (deep): pigmented layer of retina, rods (light sensing) and cones (color sensing)
* inner neural layer (middle): bipolar neurons
* ganglion cell layer (superficial): ganglionic axons converge at optic disc, forms origination of optic cranial nerve (blind spot)
* inner neural layer (middle): bipolar neurons
* ganglion cell layer (superficial): ganglionic axons converge at optic disc, forms origination of optic cranial nerve (blind spot)
28
New cards
define and locate the macula. define and locate the fovea centralis.
* macula: region of retina with no rods
* fovea centralis: region of macula w/ highest concentration of cones
* fovea centralis: region of macula w/ highest concentration of cones