Parasitt credit 1: Trypanosomatida: Trypanosoma
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
which parasites causes NAGANA?
- Trypanosoma Brucei Brucei
- Trypanosoma vivax
- Trypanosoma vivax
- Trypanosoma congolense
- Trypanosoma suis
Which parasites causes SURRA?
Trypanosoma evansi
What is kinetoplast?
- Attached to mitochondria
- Contains circular DNA
- Mitochondrial DNA
Three functions:
1. metabolism of mitochondria
2. cyclic transmission
3. Poly-morphism (resistance to treatment)
Which trypanosoma species does not require any vector?
T. Equiperdum
What trypanosoma species can cause chronic sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis)?
T. brucei gambiense
What trypanosoma species can cause acute sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis)?
T. brucei rhodensiense
Life cycle stages in trypanosoma:
1. Amastigote: oval, no flagellum, intracellular stage
2. Promastigote: elongated, kinetoplast in front of nucleus and flagellum
3. Epimastigote: promastigote + undulating membrane
4. Trypomastigote: epimastigote but kinetoplast is behind the nucleus
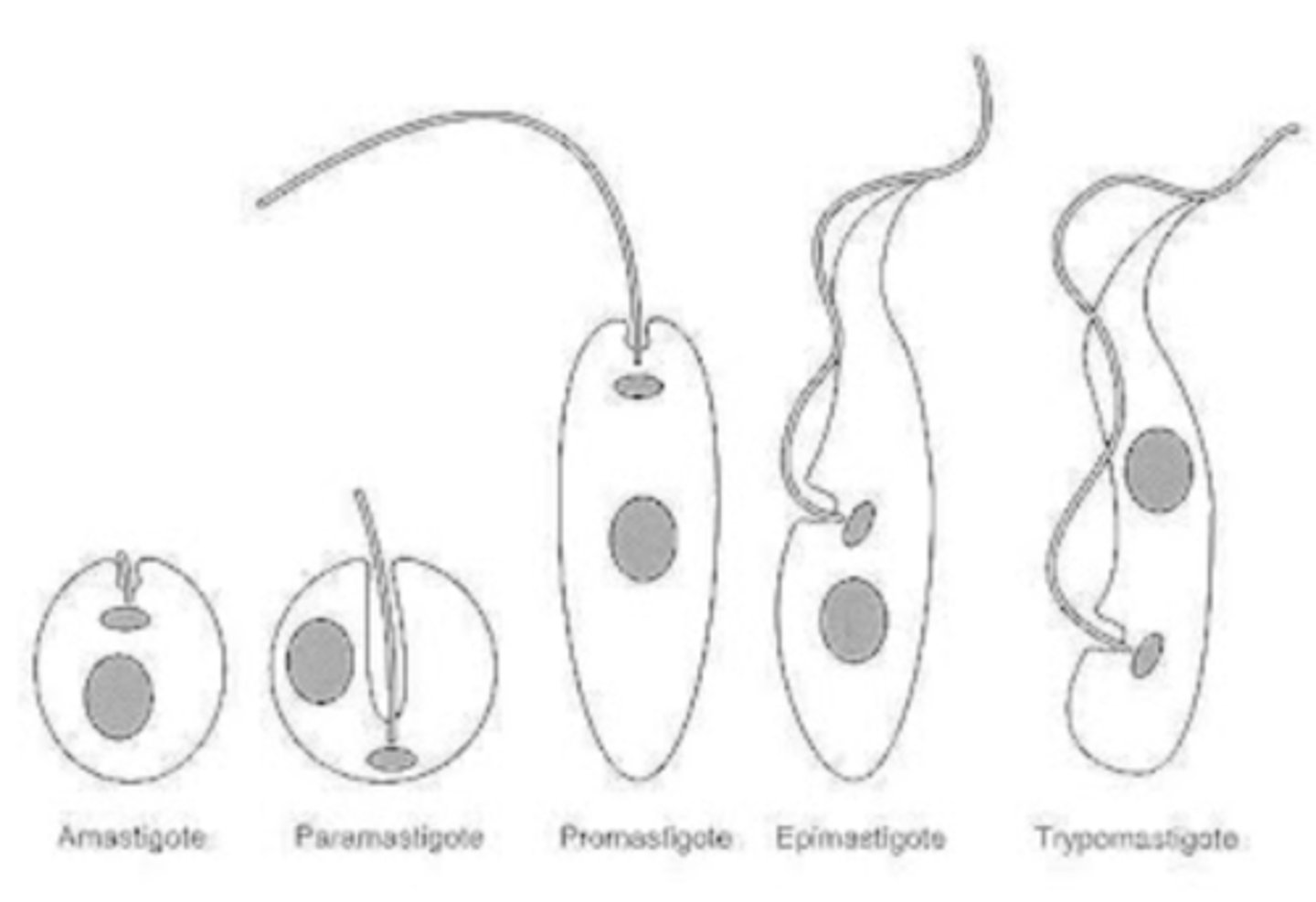
Describe the morphology of trypanosoma:
Depends on life cycle (amastigote, promastigote, epimastigote, trypomastigote)
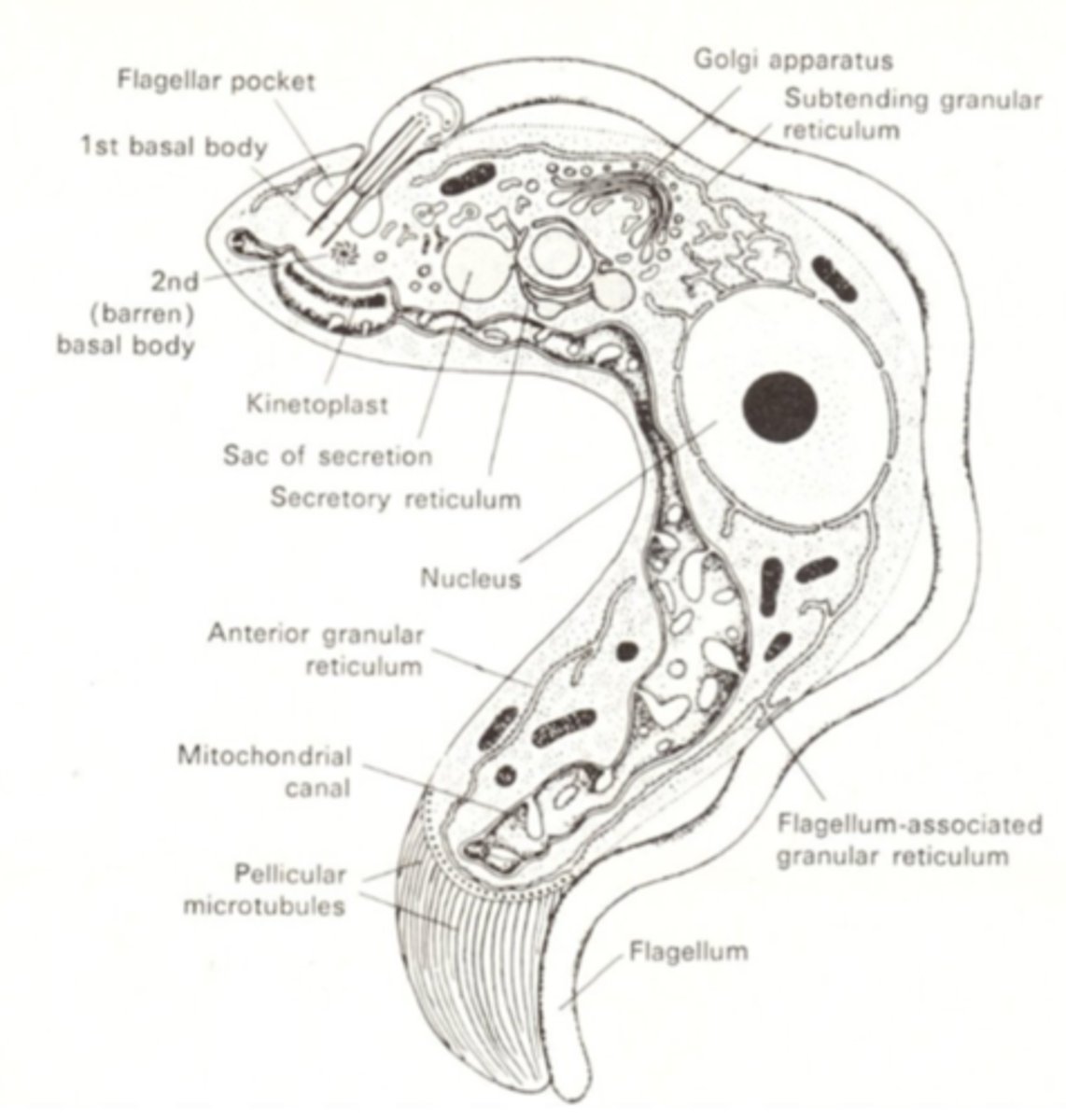
Body:
- leaf-like, round
- Elongated/spindle shape
- 1 Nucleus
- 1 Flagellum
- 1 Mitochondrium
- Basal body
- Kinetoplast
- Undulating membrane
- Axoneme
Which disease is not transmitted by the mouth part of the insect?
Chaga's disease (by Trypanosoma cruzi).
Transmitted by feces when contacting skin of host
Vector of trypanosoma cruzi?
Kissing bug (chagas disease)
Vector of trypanosoma gambiense?
tse tse fly (glossina)
How is trypanosoma equiperdum transmitted?
- Venereal transmission (intercourse)
- Mechanical transmission
- Non-cyclic
- Direct transmission
How does trypanosoma move?
- Flagellum (1)
- undulating membrane
Life cycle of Stercoraria (e.g. Trypanosoma Cruzi):
1. Vector (kissing bug) absorb tryptomastigotes from sucking blood of an infected host.
2. bug intestine: tryptomastigotes => epimastigotes
3. binary fission of epimastigote. (8-10 days), then moves to rectum.
4. In rectum epimastigote => tryptomastigote
5. kissing bug poops, infect host when feces is in contact with wound or mucous membrane.
6. penetrates macrophages: tryptomastigote => amastigote.
7. amastigote replicates by binary fission = cell ruptures.
8. amastigote => tryptomastigote. (can infect next vector or travel to new cells for replication
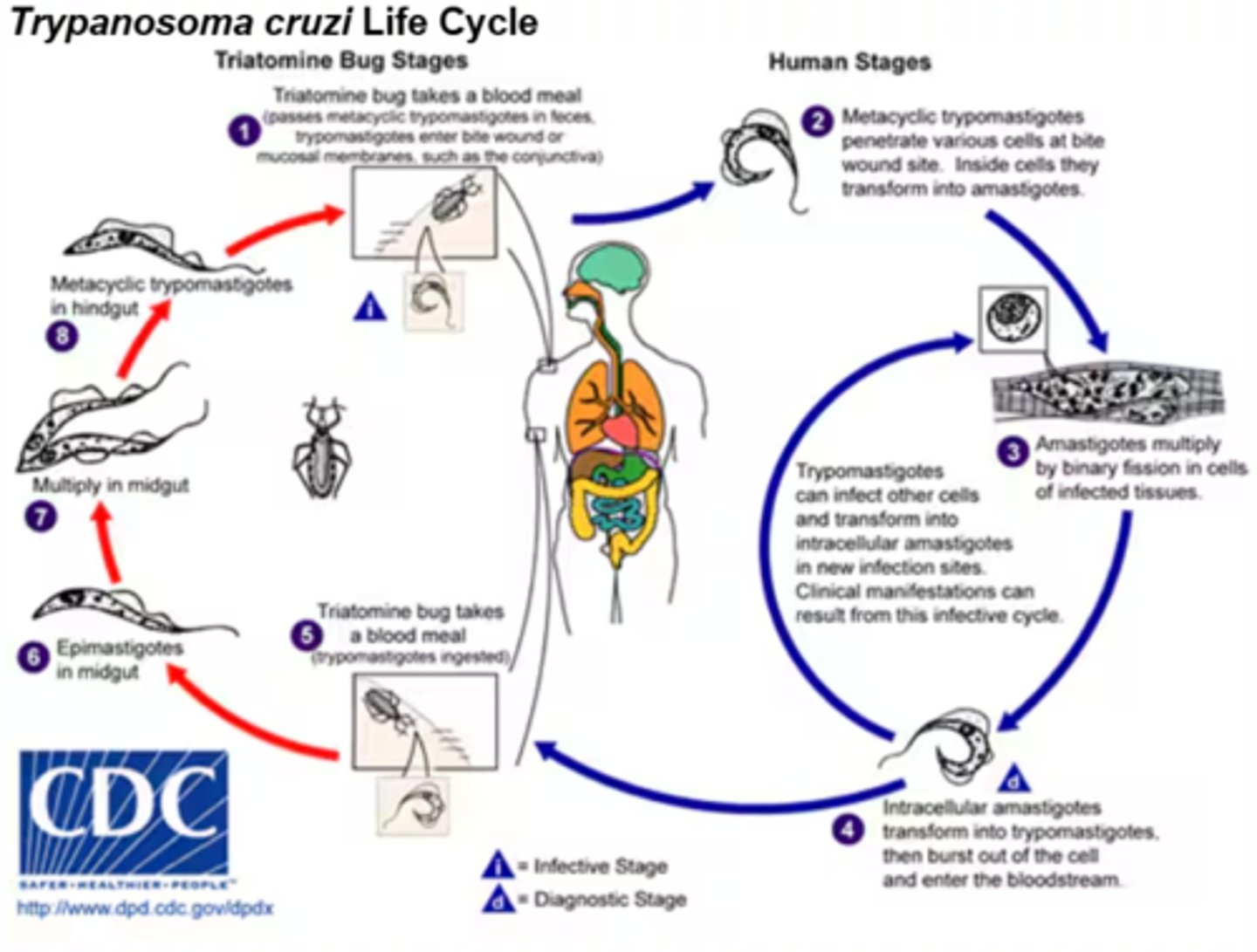
Main division of Trypanosoma?
Stercoraria and Salivaria.
Vector of T. Equiperdum
No vector
picture of pigeon
trypanosoma gallinarum
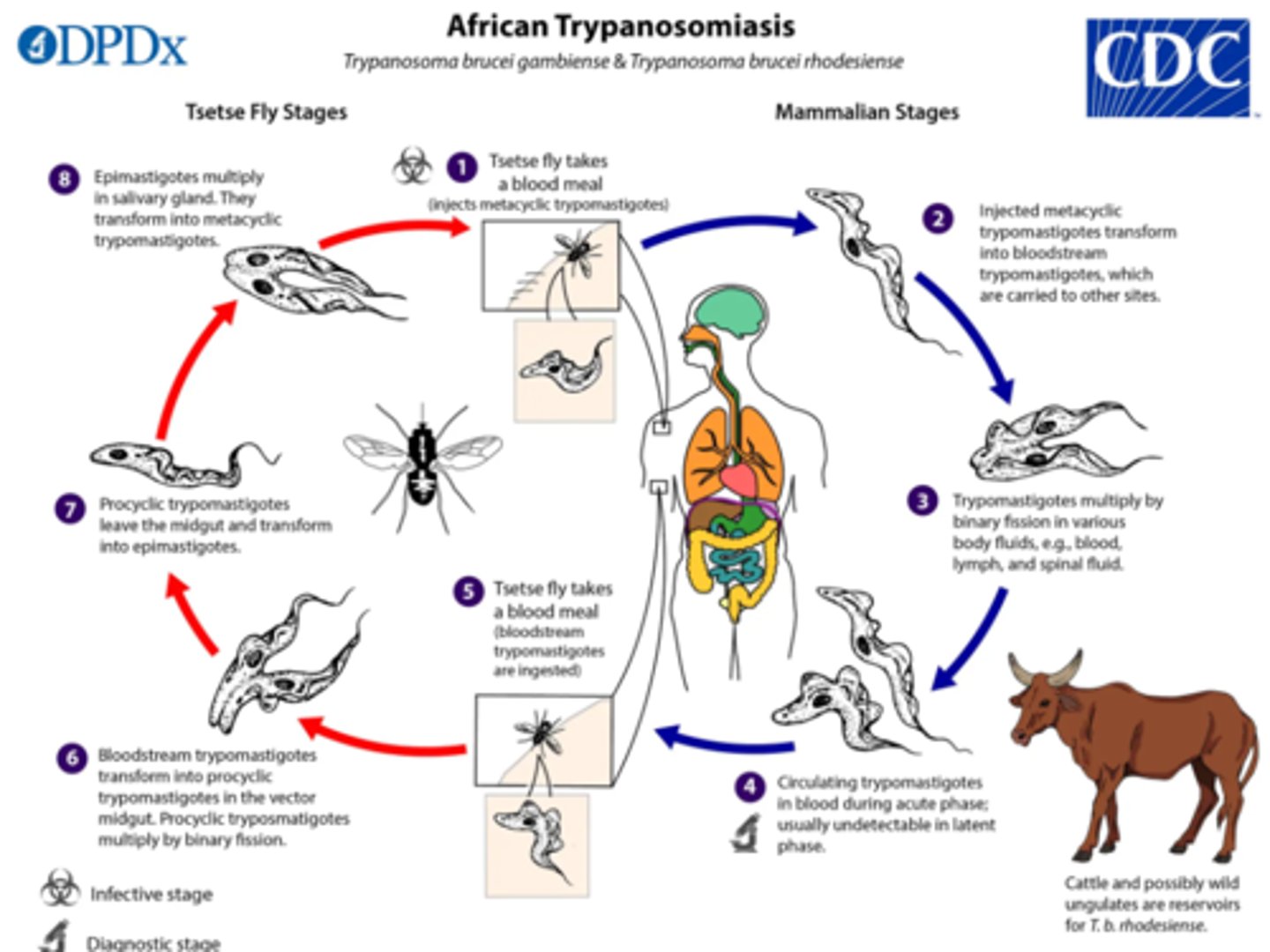
Life cycle of salivaria (eg. Trypanosmoa breucei gambiense and the others with glossina spp as vector):
1. cyclic tryptomastigote is ingested by tse tse fly.
2. In midgut: binary fission.
3. Moves to salivary gland: => epimastigote
4. Binary fission => cyclic tryptomastigote
5. Infect host during blood meal
6. binary fission. (can also enter cerevrospinal fluid)
Which trypanosoma species is transferred mechanically?
Trypanosoma equiperdum