4. large animal med- equine large/small colon diseases
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what is the most common cause of equine colic?
spasmodic/gas colic
what is the difference between spasmodic and gas colic?
spasmodic: motility alteration (disorganized motility)
gas: accumulation of gas in large colon
clinically, we cannot differentiate between the 2
what is the etiology of spasmodic/gas colic?
unknown- likely multifactorial due to rapid change in routine and diet, parasites
what are clinical signs of spasmodic/gas colic?
-mild to moderate pain
-pain responsive to analgesics (xylazine, banamine)
-short duration (<1 hour)
-systemically stable
-with gas colic: abdominal distention and large colon distention on rectal
what is the treatment for spasmodic/gas colic?
-analgesics
-for spasmodic colic, can use buscopan
what are risk factors for large colon impactions?
-decreased water intake
-poor dentition
-poor quality feed
what are clinical signs of large colon impactions?
-mild-moderate colic
-inappetence
-dull
-laying down more
-usually normal TPR
-may have abdominal distention
how are large colon impactions diagnosed?
1. rectal exam (firm ingesta in pelvic flexure)
2. no reflux
3. normal abdominocentesis (since no compromised blood supply)

what is the treatment for large colon impactions?
-enteral fluid/laxative is preferred
-may use IVFs for supportive care or if fluids via NGT not tolerated
-pain meds (banamine)
-may need surgery if fails to respond, severe pain, or abnormal ab-tap
what is the prognosis for large colon impactions?
good
what medications/fluids can be given thru the NG tube to help resolve large colon impactions?
1. plain water
2. isotonic electrolyte solution
3. magnesium sulfate (epsom salts)
4. mineral oil
5. DSS (dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate)
what are limitations of giving plain water thru the NGT for large colon impactions?
does not increase the water content of ingesta in right dorsal colon
may also cause hyponatremia if food is being restricted
what are the benefits of giving isotonic electrolyte solutions thru the NGT for large colon impactions?
-does not change blood electrolytes
-increases water content of ingesta in right dorsal colon and fecal matter
what are the pros/cons of giving magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts) via NGT for large colon impactions?
- unlikely to cause hypermagnesemia when given at recommended dose 1g/kg or 1lb/1000lb to P with normal kidney funciton
- increase water content of the feces but had no effect in the right dorsal colon
what are pros/cons of giving mineral oil thru the NGT for large colon impactions?
pros: lubricating agent for fecal matter, and used as a marker of transit
cons: does not penetrate into impaction
-aspiration or accidental administration into lungs results in severe/fatal pneumonia
what is DSS and what are the pros/cons of giving DSS (dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate) via the NGT for large colon impactions?
- surfactant acts by decreasing surface tension of ingesta to allow water o penetrate fecal mass to soften it
- limited margin of safety, doses > 65 mg/kg may cause death
- stimulate secretory activities of the small intestine and inhibit absorption of fluids from the distal SI - contraindicated in any horse with systemic fluid or electrolyte abnormalities
- DO NOT ADMINISTER CONCURRENTLY WITH MINERAL OIL - may allow for absorption of mineral oil
what are large colon displacements?
luminal obstruction with little or no vascular compromise (simple obstructions)
how are large colon displacements characterized?
based on configurations of the displacement relative to where the left colon has moved:
-nephrosplenic entrapment (left dorsal displacement)
-right dorsal displacement
-cranial displacement of left colon
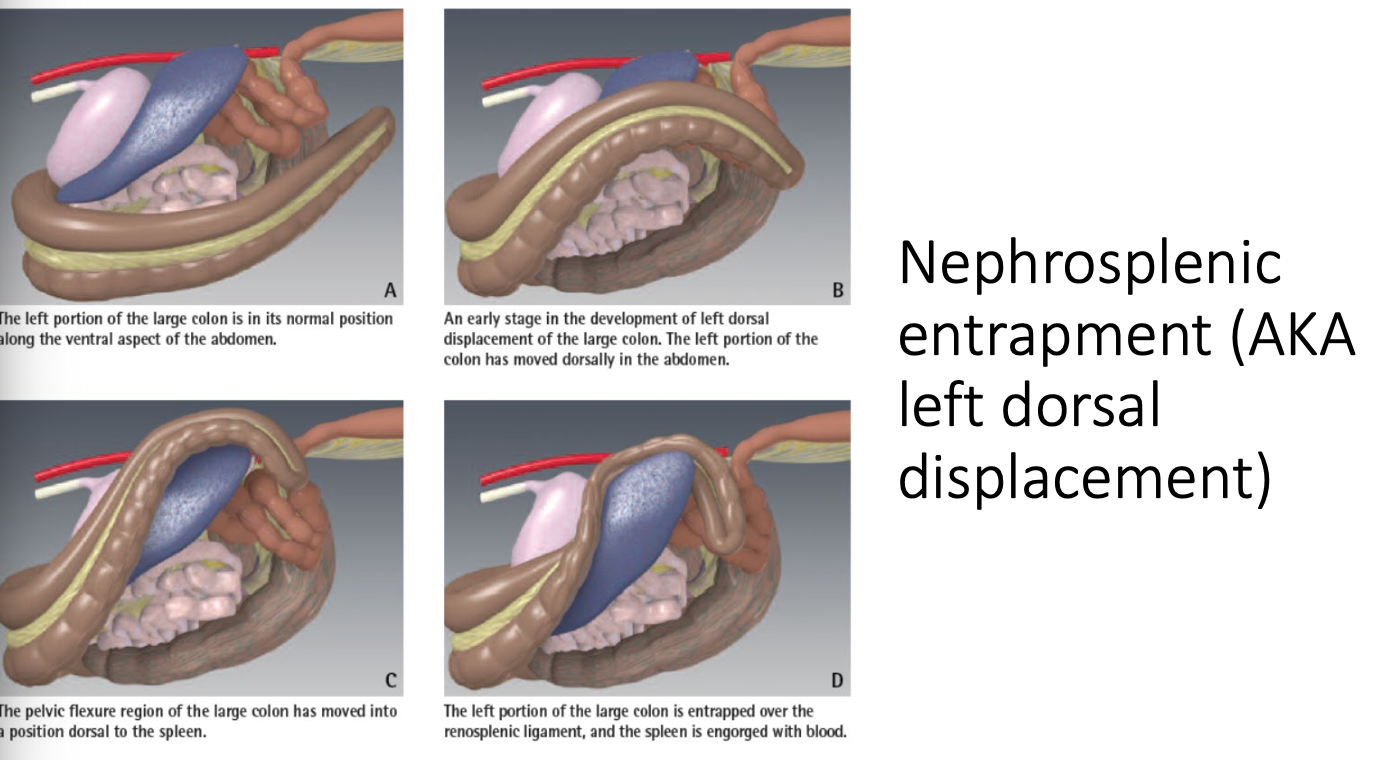
what are clinical signs of large colon displacement?
persistent mild-moderate colic, abdominal distention
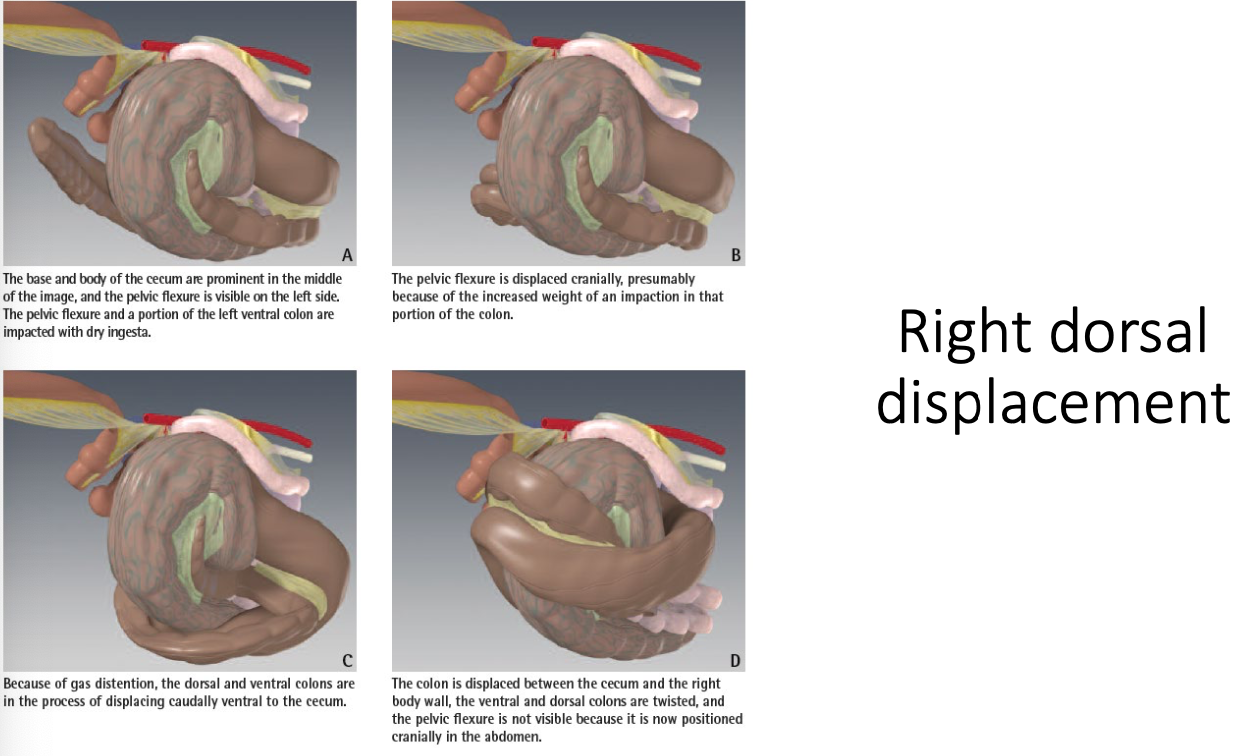
how are large colon displacements diagnosed?
-ultrasound
-rectal palpation
-NGT (usually no reflux)
-ab-tap (normal but becomes abnormal with increased duration)
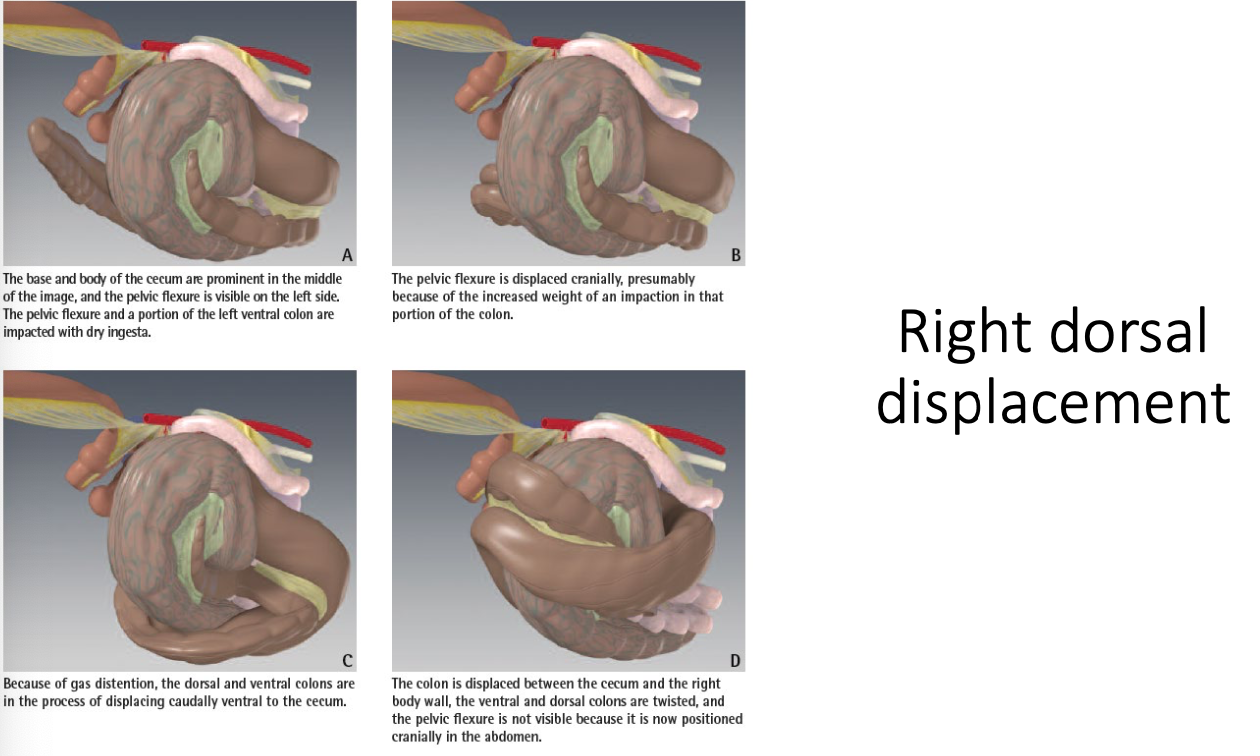
what is the treatment for large colon displacements?
medical: fasting, supportive care (IVFs), pain management
surgery: if dont respond to medical treatment
what is the medical treatment for nephrosplenic (left dorsal displacement) entrapment?
exercise horse +/- phenylephrine
rolling horse to reposition colon (start in right lateral and make complete 360 degree rotation)
what is the prognosis for large colon displacements?
good (if surgery is an option)
what is the most painful and severe form of colic?
large colon torsion/volvulus
can be non-strangulating if less than 360 degree rotation
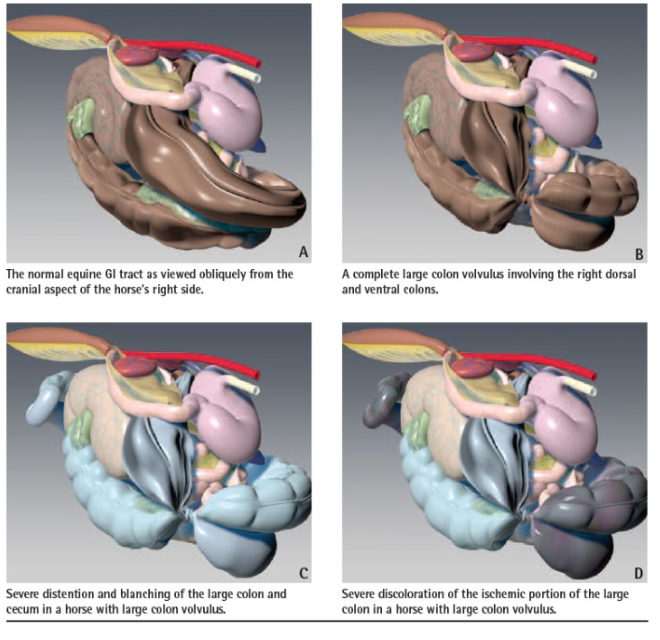
what are risk factors for large colon torsion/volvulus?
more common in postparturient brood mares
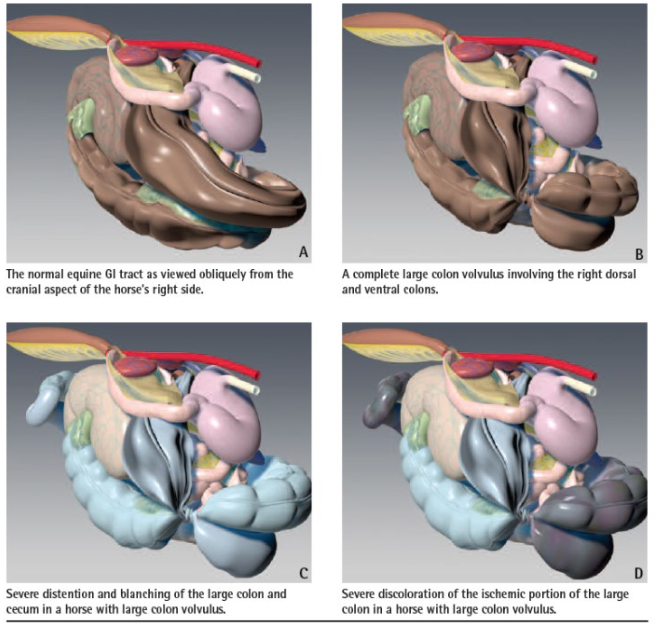
what are clinical signs of large colon torsion/volvulus?
-severe, violent pain
-rapid deterioration
-high heart rate
-endotoxemia (bc high amount of bacteria in colon)
-abdominal distention
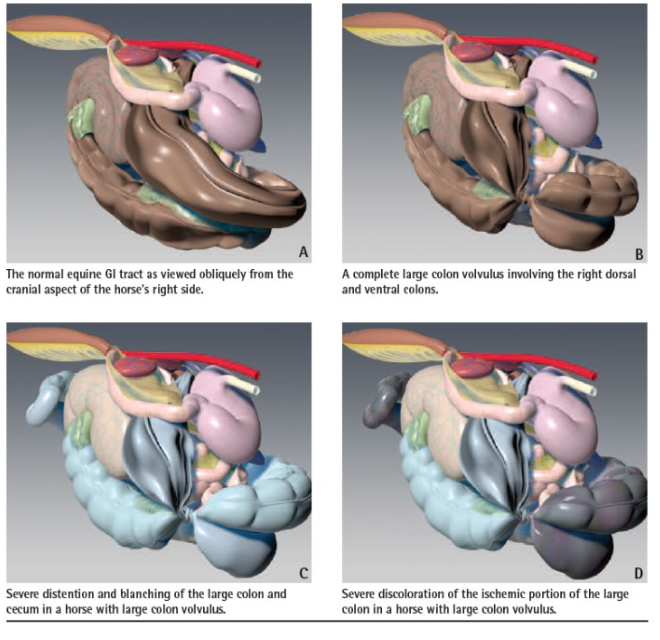
how is large colon torsion/volvulus diagnosed?
-rectal exam (severe gas distention)
-ultrasound (thickened large colon walls)
-ab-tap: evidence of strangulation (serosanguinous w/ high lactate)
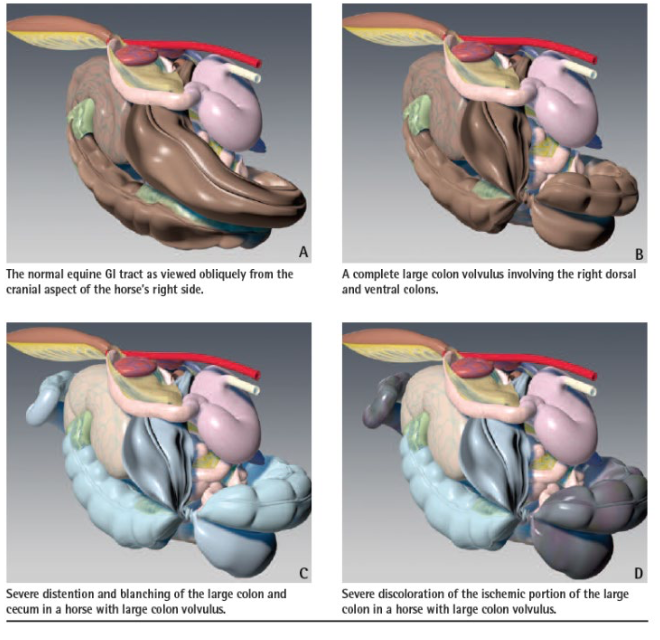
what is the treatment for large colon torsion/volvulus?
-surgery
-irreversible tissue damage in 3-4 hours
-reperfusion injury post-op
-colon resection if the cecum and base of colon are viable

what is the prognosis for large colon torsion/volvulus?
poor to grave
what are enteroliths?
stone like concentrations in large colon
due to mineral deposition in concentric rings around a nidus (typically ammonium magnesium phosphate- struvite)

what location do enteroliths most commonly obstruct?
transverse colon

what does it mean if an enterolith has a flat side?
indicates that there are other enteroliths present

what are risk factors of horses developing enteroliths?
-mature horses (over 4 years)
-feeding alfalfa
-geographic location (california)

what are clinical signs of enteroliths?
-acute colic: obstruction leading to gas distention
-chronic/intermittent colic: can act like ball-valve
-some horses may pass enteroliths with feces

how are enteroliths diagnosed?
rectal: gas distention, may palpate enterolith
radiographs

what is the treatment/prognosis of enteroliths?
tx: surgery
prognosis: good with surgery

what are risk factors of cecal impactions?
-hospitalization
-pain (ortho, ocular)
-stress
-anesthesia
PASH

what are clinical signs of cecal impactions?
-slow onset of clinical signs (but can lead to death quickly)
-mild intermittent colic initially
-may persist for days before rupture
-decreased manure production

how are cecal impactions diagnosed?
rectal exam: cecum feels heavy, may feel impaction later
what is the treatment for cecal impactions?
-fasting
-aggressive fluid therapy (oral and IV fluids)
-analgesics
-surgery may be needed

what is the prognosis of cecal impactions?
guarded
which animals are small colon impactions common in?
mini horses, also arabians and ponies
likely due to fecaliths

what are clinical signs of small colon impactions?
-lethargy and inappetence initially
-progresses to colic, diarrhea, decreased fecal production, abdominal distention

how are small colon impactions diagnosed?
rectal:
-solid tube of ingesta with loss of normal sacculation
-may also see gas distention of large intestine and cecum and loose manure
-if fecalith--> large fecal ball in small colon
ab-tap: WNL initially

what is the medical treatment for small colon impactions?
-enteral fluids
-laxatives (epsom salts)
-pain control
-enema
-may need to trocharize cecum if too much abdominal distention

when is surgery indicated for treatment of small colon impactions?
if medical tx fails or evidence of intestinal compromise
