Chemistry 1.1 and 1.2 - greenhouse gases and photochemical smog
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the main greenhouse gases
The main greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O).
What do greenhouse gases do
They trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Harmful effects of the presence of ozone in the troposphere to humans
damage the respiratory tract
damage the lung tissue
reducing the rate of diffusion
reduce how much oxygen is absorbed
Harmful effects of the presence of ozone in the troposphere to plants
gas enters stoma
cause them to close
limit gas exchange
disrupts normal functions
susceptible to extreme wealth conditions
What is photochemical smog and what are the main pollutants involved
Gaseous pollutants in environment. It forms in densely populated areas
These polutants include nitrogen oxides and ozone

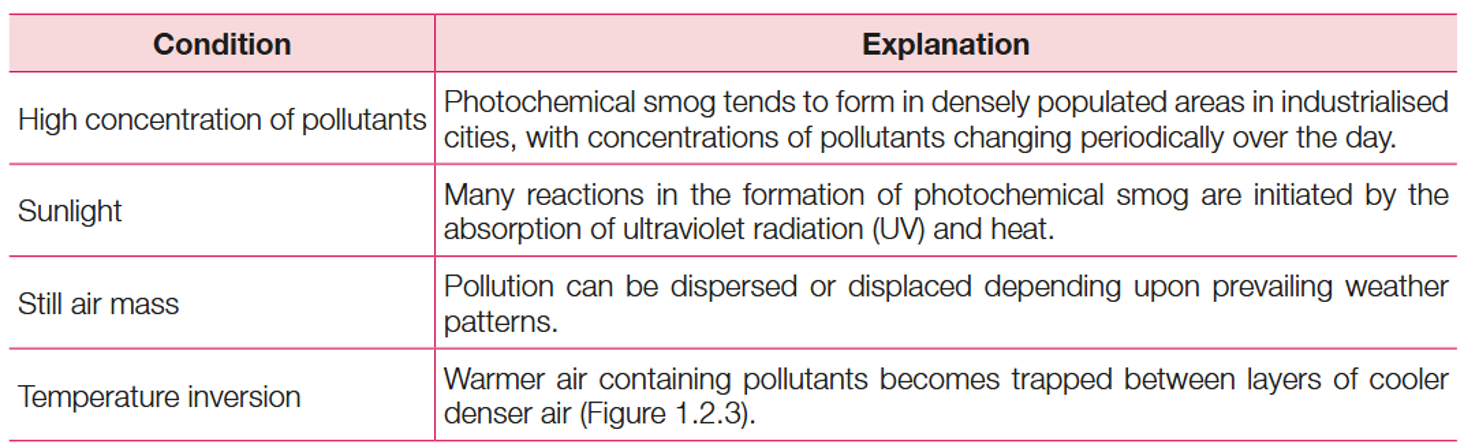
What are the conditions of photochemical smog
high concentration of pollutants
sunlight/UV
still air mass
temperature inversion
How does nitric oxide form
N2 + O2 —> 2NO
This reaction occurs at high temperatures, such as in combustion engines and lightning strikes.
How does nitrogen dioxide form
2NO + O2 —> 2NO2
This reaction occurs when nitric oxide reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere, often in the presence of sunlight.
How does the presence of NO2 lead to the formation of ozone
NO2 absorbs UV light, leading to the dissociation of nitrogen dioxide into nitric oxide (NO) and a free oxygen atom. This free oxygen atom can then react with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3).
NO2 —→ NO + O
O + O2 —→ O3
What are catalytic converters
Devices found in the exhaust of motor vehicles. They reduce the impacts of pollutants by converting them into less harmful products
How to catalytic converters work
They convert pollutants into less harmful products. They convert carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and unburnt hydrocarbons through redox reactions
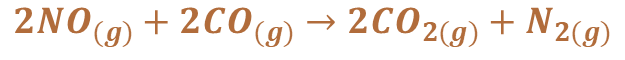
What is a radical and what is an example
Eg oxygen radical
when an element is not in its naturally occurring form so it is highly reactive
O is a radical because it wants to be O2
Why are nitrogen oxides formed in high temp engines and furnaces
For a nitrogen oxide to form, a nitrogen and oxygen needs to bond together. Nitrogen gas is bonded by a triple covalent bond, which is the strongest bond. High temps are needed to create enough energy for these bonds to break and the reaction to begin
How do you convert from mol L -1 to gL-1?
multiply by the molar mass
How do you convert from gL-1 to mol L -1 ?
divide by the molar mass
How do you convert from gL-1 to mg L -1 ?
multiply by 1000
How do you convert from mg L -1 to gL-1 ?
divide by 1000
what does ppm mean?
parts per million
What does ppb mean
parts per billion
What is the density formula
p=m/v
What is another way of saying density
The mass concentration
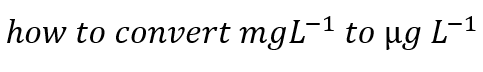
ppm to ppb
multiply by 1000
how to convert ppb to ppm
divide by 1000
What is the percentage composition formula