EVR 1001 FINAL FSU
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Please explain the four main types of climate change mitigation?
1. reduce emissions
2. remove CO2 from atmosphere
3. Block sunlight
4. Protect against change in agriculture
please explain the difference between a positive and negative feedback related to the arctic?
positive feedback: colder temps will lead to growth of the polar ice caps
neg. feedback: warmer temps cause ice to melt over the tundra
draw a diagram of the carbon cycle
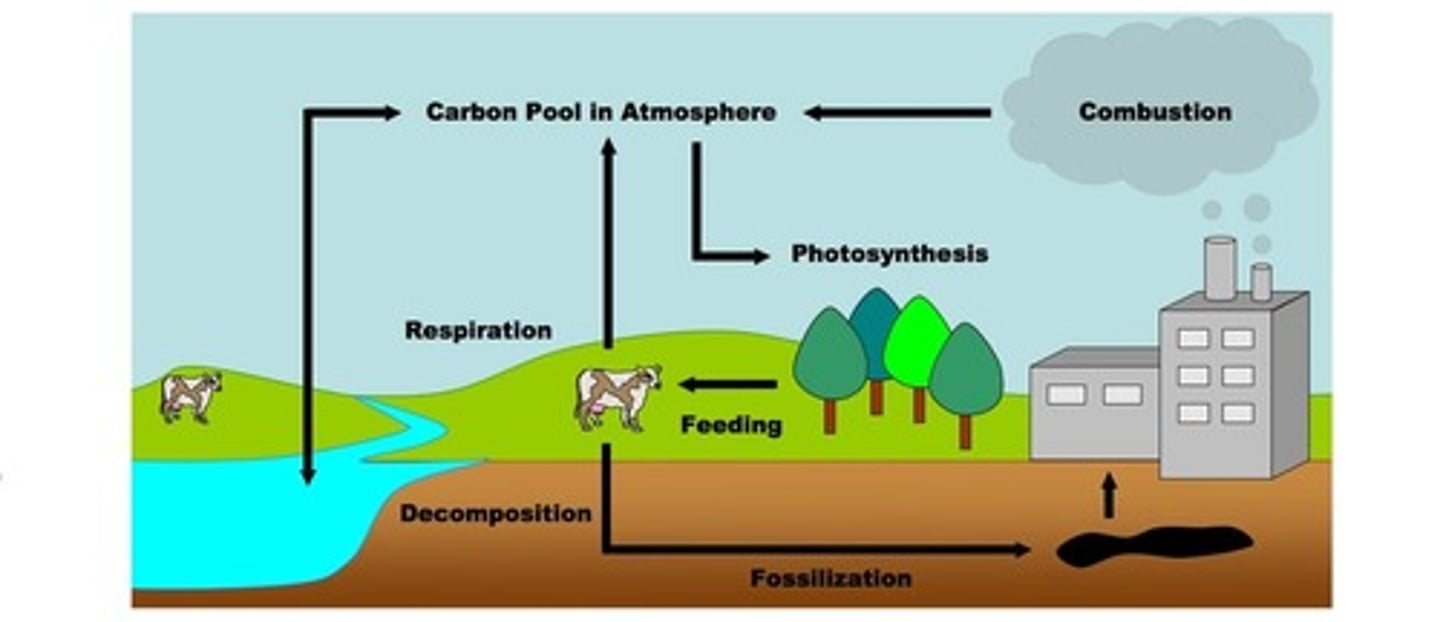
please explain three major ways in which climate change is likely to impact the state of FL
increased temp, sea level rise, increased respiratory issues
describe four negative impacts agriculture may have on the environment
land conversion & habitat loss, wasteful water consumption, and soil erosion, degradation
describe five major categories of pollutants and provide an example of a source for each one
air
-ozone
-carbon monoxide
water
-heavy metals
-chemical waste
soil
-pesticides
-hydrocarbons
outline what determines the impact of mineral exploitation on the environment and describe direct and indirect and social impacts of mineral development
ore quality, mining procedures, climate rock type, size of operation.
-direct impact: plants and animals killed by mining activity or contact w/ toxic or water
-indirect:changes in nutrient cycling total biomass, species diversity and ecosystem stability
social impacts: rapid influx of workers into areas unprepared for growth
define ecological restoration and describe how human activities have impacted the Everglades providing examples
restoring an ecosystem to its historical rage of variation and to an ability to sustain itself and its crucial function. Human activities have impacted the Everglades include: draining wetlands, channelizing rivers, installing water control structures
Select three sources of energy--one conventional (e.g. coal, petroleum, etc.) and two alternative-and list two advantages and two disadvantages of each in terms of cost, jobs lost or gained, environmental impact, or potential for supplying energy. Of the three, which energy source do you believe is the most desirable?
solar, wind, and coal.
The "tragedy of the commons" provides explanations for why individuals don't always act in ways that promote the long-term health and sustainability of the environment. Describe the concept behind the "tragedy of the commons", the problems associated with public use of "a commons" and name three different national or international examples of "a commons?"
when a resource is shared, an individuals personal share of profit from exploitation of the resource is usually greater than that individuals share of the resulting loss. Problems with public use are they don't seek sustainability, and profit motive does not always lead a persona to act in the best interest of the environment.
Examples of "a commons": pastureland, forest, ocean fisheries away from coastline, the atmosphere.
biodiversity
the variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem
threats to biodiversity
habitat loss, habitat fragmentation(humans divide habitat), overharvesting, climate change
strategies for conserving biodiversity
preserves and protected areas, managing populations of individual species, national parks and wilderness areas
US and international polices on convervation
US:
creation of national parks (1916 Woodrow Wilson), 1914 Wilderness Act, 1900 Lacey Act., 1972 Marine Mammal protection act, 1973 Endangered Species Act
INTERNATIONAL:
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, Regulation of whaling
climate
vs
weather
C: long-term averages, patterns, or trends in the weather
w: meteorological condition in a given place on a given day
what do scientists agree on?
instrumental and historical records of climate change
historical record journals note precipitation, frost etc.
climate proxies
tree rings, ice cores, marine sediments
Milankovitch cycles
ice age climate, related to orbital changes affecting the amount of heat reaching the Earth.
green house gases
transparent to visible light, but absorb long wave radiation given off by the earth. co2 has a long life-time in the atmosphere
climate change feedback
positive feedbacks:
-water vapor
-forest fire
-reduce Ice
-cloud cover in polar regions
negative feedback:
-cloud cover
-cloud cover in tropics
-vegetation regrowth
-ocean absorption of CO2
climate models
global circulation models (GCMs) uses math equations to explain how a system will change in time
fossil fuels
forms of stored solar energy. oils, natural gas and coal, 87% of energy consumed worldwide
oil
derived from organic matter( mostly plants and phytoplanton) primarily found along plate boundaries
natural gas
recently utilized, recoverable gas, clean fuel
shale gas/ oil
fine grained sedimentary rock containing organic matter (kerogen) recovered from surface and subsurface
coal
partially decomposesd vegetation, most abundant fossil fuel
mining impacts
environmental effects of fossil fuels
-air & water pollution
-acid rain
-climate change
-health impacts
can we feed the world
in order to feed the entire population agriculture must grow, some places in the world food is already inadequate.
what we grow on the land
crops, for livetock, range land and pasture
soils and its layers
key to life on land
-o horizon- organic layer, top of the soil
-A&E horizon: upper horizon
-B horizon: zone of accumulation
-C horizon: most similar to parent material
controlling pests
4 stages
1: broad spectrum inorganic toxins
2: petroleum based sprays and natural plant chemicals
3: artificial organic compounds
4: return to biological and ecological knowledge
genetically modified foods-concers
-risks for people
-can transgenes escape, pollute ecosystems and harm organisms
-can pests evolve resistance to GM crops like pesticides
-can weeds become superweeds
-negative impacts on traditional native crops
aquaculture
farming food in aquatic habitats
marine an freshwater food obtained from fishing
main sources of water
1: surface water: renewable resource but can be variable over time (droughts)
2: Groundwater: largely non-renewable but high quality and reliable
water resources
surface water (movement of water into the oceans)
ground water (US uses as drinking water)
desalination
treated wastewater
conservation of water
water conservaion
careful use and protection of water resources quality and quantity of water
3 components
-agricultural use
-public supply and domestic use
-industrial and manufacturing use
water management
use of water w/o degrading the various components of the hydrologic cycle or the ecological systems depend on it
complex issue, more difficult when demand increases
wetlands
land forms such as salt marshes, swamps, bogs, prairie potholes and vernal pools
-seasonally hold water
-freshwater wetlands are a natural sponge for water: reduce flooding
dams and the environment
dams are multi functional structures:
-ensure a more stable water supply
-generate electricity
-provide flood control
-recreational activities
environmental effects of dams:
-loss of land
-potential flood hazard
-downstream changes in hydrology
-fragmentation of ecosystem
water pollution
degradation of water quality
water pollutants include:
-heavy metals
-sediments
-certain radioactive isotopes
-heat
-excess nutrients
wastewater treatment
-septic tank disposal systems
-treatment plants:
primary treatments
secondary treatment(required by law)
advanced wastewater treatment
-Chlorine treatment: kills pathogens, hazard to fish and cancer to humans
water resuse
water is withdrawn, treated, used, treated and returned to the environment
water pollution and environmental law
law dealing w/ conservation and use of natural resources and control of pollution
-federal laws to protect water go back to Refuse Act 1899
water sustainability will require modification of the clean water act
importance of waste management to resources of society
modern society depends on:
Renewable:
-air
-surface water
-plants and animals
-some fuel sources
Nonrenewable resources:
-soil
-fossil fuels(oil,coal)
-groundwater
-most minerals
mineral resources
nonrenewable resource
new deposits forming but too slowly to use today
impacts of mineral development
releasing of harmful elements, water degradation, water toxins could cause diesase
materials management and waste
-Reduce, recycle, reuse
goals of restoration? timeline
1. preindustrial- maintain ecosystem as they were in AD 1500
2. Presettlement (e.g. of N. Amer.) maintain ecosystem as they were in AD 1494
3. Agricultural- 5000 BC
4.before any significant impact of human beings-10,000 BC
5. Maximum production- independent of specific time
6. maximum diversity- independent of a specific time
7. Maximum biomass- independent of old growth
8. Preserve a specific endangered species- whenever stage it is adopted to
9. historical range of variation-create the future like the known pas
define restoration
restoring an ecosystem to its historical range of variation and to an ability to sustain itself and its crucial functions
how have humans impact the Everglades
-disturbed hydrology
-increased demands for land and freshwater
-oxidation of peat soils in wetlands
-introduction of invasive species
what is usually restored
wetlands, rives and streams
restoring heavily damaged lands
judging the success of restoration
• General structure and process of the target ecosystem
• Appropriate integration with the larger landscape • Adaptations to withstand disturbances such as fire • Ability to be nearly as self-sustaining as the target ecosystem
alternative energy- solar
RENEWABLE
-passive solar energy:
Cooling in hot weather and retaining heat in cold weather
-Active solar energy
requires mechanical power circulates fluids or air/water from solar collectors to a location where heat is stored
-solar collector: space heating or hot water (flat plate/evacuated tube collector)
A.E. OCEAN
high energy in motion of waves, currents and tides in the ocean
-tidal power most successful, 7 current station currently worldwide
A.E.-WIND
wind produced when differential heating of Earth's surface created air masses w/ differing heat contents ad densities
-cheapest form of Alt. energy
-issues:
highly variable in time place and intensity
-kills birds, esp. large birds
-uses lard areas of lanf
A.E. BIOFUELS
energy recovered from biomass (organic matter)
-oldest fuel used by humans
-1 billion people in the world still use wood as a primary source of energy for heat and cooking
-can pollute the air and degrade the land
A.E. GEOTHERMAL
energy from the interior of the Earth
-most grroundwater can be a source of geothermal energy
A.E.- the future
-use of renewable is growing rapidly
-do not cause air pollution, health problems, climate change
public services of nature
services ecosystems provide to humans and the environment
-system that provide these functions as natural capital
-natural capital and economic activity are highly linked
-pollinating animals pollinate $15 billion worth of crops grown on 2 million acres in the US
tragedy of the commons
when a resource is shared , an individuals personal share of profit from exploitation of the resource is usually greater than that of individuals share of the resulting loss
-a common is any resource owed publicly, with public asses for private uses
low growth rate/ low profit- exploitation
2 approaches:
-resource sustainability
-maximum profit
externalities
indirect cost
value the beauty of nature
landscape aesthetics
problem: personal preference
risk-benefit analysis
the riskiness of a present action in terms of its possible outcomes is weighed against the benefit or value of the action