Understanding Deafness and Hearing Loss
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Deaf
Very little or no functional hearing
Hard of hearing
Milder hearing loss; better than a profound hearing loss
Audiogram
Medical picture of what you can or cannot hear
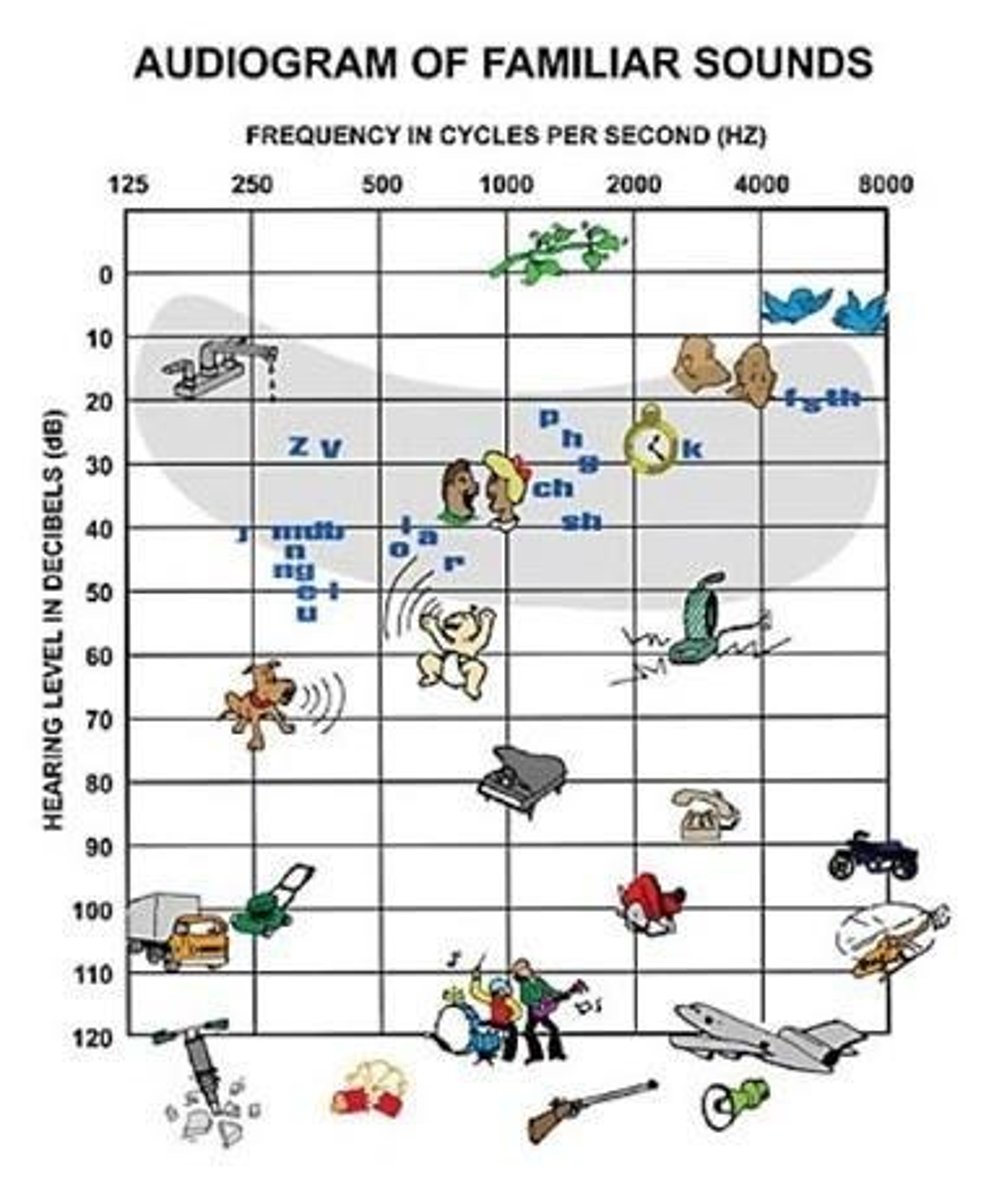
dB
Amplitude/strength of sound
hZ
Pitch of sound
Speech banana
Shaded area on an audiogram that shows the range in which speech/phonemes fall into
Big D Deaf
Culturally deaf; profound hearing loss; sign language; culture/deaf community; identity; deaf pride
Little d deaf
Medically deaf; profound hearing loss; sign language might NOT be the primary language; doesn't necessarily identify with deaf culture; medical diagnosis (loss of hearing)
CODA
Child/children of deaf adults
Hearing process
Sound → pinna → tympanic membrane → middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes) → inner ear (cochlea) → auditory nerve
Unilateral hearing loss
Hearing loss in one ear; tend to have higher rates of listening fatigue
Conductive hearing loss
Hearing loss due to problems with the ear canal, ear drum, or middle ear and its bones; being resistant to the passage of sound
Temporary conductive hearing loss
Can occur due to fluid in your ears from being sick (ear infection); can be treated with antibiotics, surgery, or hearing aids
Sensorineural hearing loss
Hearing loss due to problems of the inner ear; also known as nerve-related hearing loss; being purely nerve related
Cochlear implants
Can be a solution for those with sensorineural hearing loss
Mixed hearing loss
Combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss; may involve damage in the outer or middle ear AND in the inner ear (cochlea or auditory nerve)
Aristotle's theory
People could only learn through spoken language; deaf people were seen as being unable to learn or be educated
Geronimo Cardano
First scholar to identify that learning does NOT require hearing; used written words
Pedro Ponce de Leon
First teacher of the deaf; had huge success with his teaching methods
Juan Pablo de Bonet
Studied Ponce de Leon's successes; used methods of writing, reading, and speech reading; used his manual alphabet
Abbe de L'Epee
Established the first public deaf school in 1771 in France; created a system, not the first sign language
Laurent Clerc
Became deaf at age 1; attended deaf school; against oralism; wanted his method of communication to be sign
Samuel Heinicke
Established the first oral school for the deaf in Germany; taught pupils speech by having them feel his throat while he speaks
Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet
Had a daughter who is deaf; interested in deafness; observed and had private lessons about teaching methods for the deaf
1st deaf school in America
April 15, 1817; ranged from 10 to 51 years old; originally called the Connecticut Asylum at Hartford for the Instruction of Deaf and Dumb Persons (American School for the Deaf).
Martha's Vineyard
Significant in deaf culture and history; island had dominant and recessive genes for deafness due to inbreeding; 85% of deaf children were born to hearing parents.
Oral method
Utilizes speech reading (lipreading) and the maximal use of a child's residual hearing for the developing and production of speech; communicates effectively with hearing individuals; NO sign at all.
Cued speech method
A visual communications system that combines mouth movements of speech with 'cues' to make all sounds of spoken language look different; NOT sign language.
Pros of cued speech method
Larger understanding of how to use speech, enhanced literacy, better accessibility.
Cons of cued speech method
Hard to teach children due to distractibility; hard to speak with people who DON'T know cueing.
Manual communication methods
Utilize a child's ability to communicate through visual stimuli such as fingerspelling and sign languages.
American Sign Language (ASL)
Composed of positions and gestures made with the hands, body, and facial expressions to convey abstract concepts; ITS OWN LANGUAGE with a distinct grammatical structure that is dissimilar to English.
Manual English
Uses many of the traditional ASL signs while maintaining the English order and grammar to develop a child's ability to read and write English.
Fingerspelling
Augments most sign language systems by using hand shapes to code the letters of the alphabet as well as numbers; words are spelled out using these individual letter codes.
Total communication method (TC)
Philosophical basis that a child who is deaf or hard-of-hearing should use ANY and ALL communication methods necessary to facilitate language acquisition.
ASL is a legitimate language
Has an independent grammar including phonology, syntax, and discourse.
Five parameters of ASL
1. Handshapes (40 handshapes); 2. Location (gender, future, past, etc.); 3. Movement (direction can change a sign); 4. Palm orientation (facing front or back); 5. Facial expressions (adds context).
ASL is universal
There are different dialects of sign language, such as Chicago vs NYC.
ASL is a form of shorthand
ASL is an actual language.
All deaf people use sign language
Not all deaf individuals use ASL.
ASL is easy to learn
It is easy to forget.
Parents of deaf children learn ASL
Sadly, this is not true.
ASL is purely iconic
Most signs make sense to others, but not always.
Hearing aids restore hearing
They don't restore it, just make distortion louder.
Education considerations for parents
Not a 'one-size-fits-all' situation; research schools based on experience with deaf or hard-of-hearing children.
Classroom acoustics
Consider the acoustics of the classroom and other areas where the child will spend time, such as curtains and carpets.
Faculty accommodation
The level of accommodation made by the faculty and staff is important.
Comfort with hearing-related technology
Faculty's comfort with hearing-related technology is crucial for effective education.
Teaching style
Consider the teaching style and administration style when choosing a school.
Class size
Class size can impact the learning experience for deaf or hard-of-hearing children.
Early intervention
Birth to 3 year olds, when the adults partner with early interventionist to plan on how to best support the child and make goals.
Coaching
Hands-on, play-based, LOTS of repetition.
Preschool program
For 3 and 4 year olds.
Residential schools
An institution where students typically go and live full time while attending.
Pros of Residential schools
Accessibility for students who may not be able to afford the assistive technology; Being around other deaf and hard-of-hearing (DHH) students; Education is specifically tailored to DHH; Most have a variety of extracurricular activities that can help foster a larger Deaf community; Involved in deaf culture and community; Often have access to strong Deaf role models.
Cons of Residential schools
Parents are learning ASL at a different rate than the students; Disconnect from the family; May be expensive; Usually away from family/homes.
Day schools
Oral vs sign.
Oral schools
Focus more on oral/auditory skills and don't focus on sign language.
Sign schools
Focus more on sign language and get information in through signing and/or residual hearing.
Pros of Day schools
Balance between school and family; Lowered tuition; Lots of communication between families and teachers.
Cons of Day schools
Isolation from parents not signing, but going to a signing school; Often located in higher populated areas, like metropolitan cities; May be expenses of attending.
Mainstreaming
Student is in a gen-ed classroom with hearing students and all instruction is from the classroom teacher.
RM device
Includes FM (frequency modulation), RM (remote microphone), and DR (direct microphone).
Educational interpreter
Used for younger kids to help a little more than just interpreting.
Resource room
The student is in a regular classroom with hearing students, however, they leave the classroom for designated periods to receive special instruction.
Self-contained (public school)
The student is in a class SEPARATE from the regular classroom with a teacher for the deaf.
Pros of Mainstreaming
Exposure to hearing culture; Speech practice.
Cons of Mainstreaming
Isolation; not able to find a mainstream school with resources.
Homeschooling environment
When students are educated by parents or tutors outside of the formal setting of a public or private school.
Pros of Homeschooling
Can be tailored to the student; Easier schedule for many students.
Cons of Homeschooling
May feel isolated from peers; May be less variety in teaching methods; Possibility of decrease in income.
Hearing aids
A device worn to AMPLIFY sound.
Hearing aid evolution
Includes pre-electric (acoustic), carbon, and vacuum tube hearing aids.
Pre-electric hearing aids
These ear trumpets captured sound waves, sending them down a tube to the listener's ear.
Carbon hearing aids
These were the first electric hearing aids, included an ear mold and a cord connected to a device.
Vacuum tube hearing aids
Used to control the flow of electricity, connected to a microphone to amplify ALL sound.
Microphone
Amplifies all sound and connects to an earpiece.
Transistors
Enabled hearing aids to fit into a smaller shell; first transistor hearing aids appeared in 1952.
Digital hearing aids
Use digital technology and can connect via Bluetooth to devices.
Cochlear implants
A small complex electronic device that provides a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing.
Auditory nerve
The nerve that cochlear implants bypass to provide sound signals.
RM systems
Wireless systems designed to help identify and understand speech in noisy situations over distances of up to 15 meters/50 feet.
TTY (text telephone)
A device that allows users to type messages back and forth instead of talking and listening.
Relay system
A service where a deaf person calls an operator who relays information back and forth between parties.
Video relay service
Allows the deaf to sign to a voice interpreter through video equipment.
Open captions
Always visible captions on a screen.
Closed captions
Optional captions that are only visible when the feature is turned on.
Texting
A form of communication used today, alongside email, Skype, Facetime, Zoom, Facebook, Instagram, X, and Snapchat.
Closed captioning in the movie theater
A headset amplifies the film's audio and provides a written display of the film's dialogue.
Bluetooth listening system
Connects and streams audio from cell phones and TVs to up to five devices.
Lights for alerts
Different lights are needed for various alerts in multiple rooms.
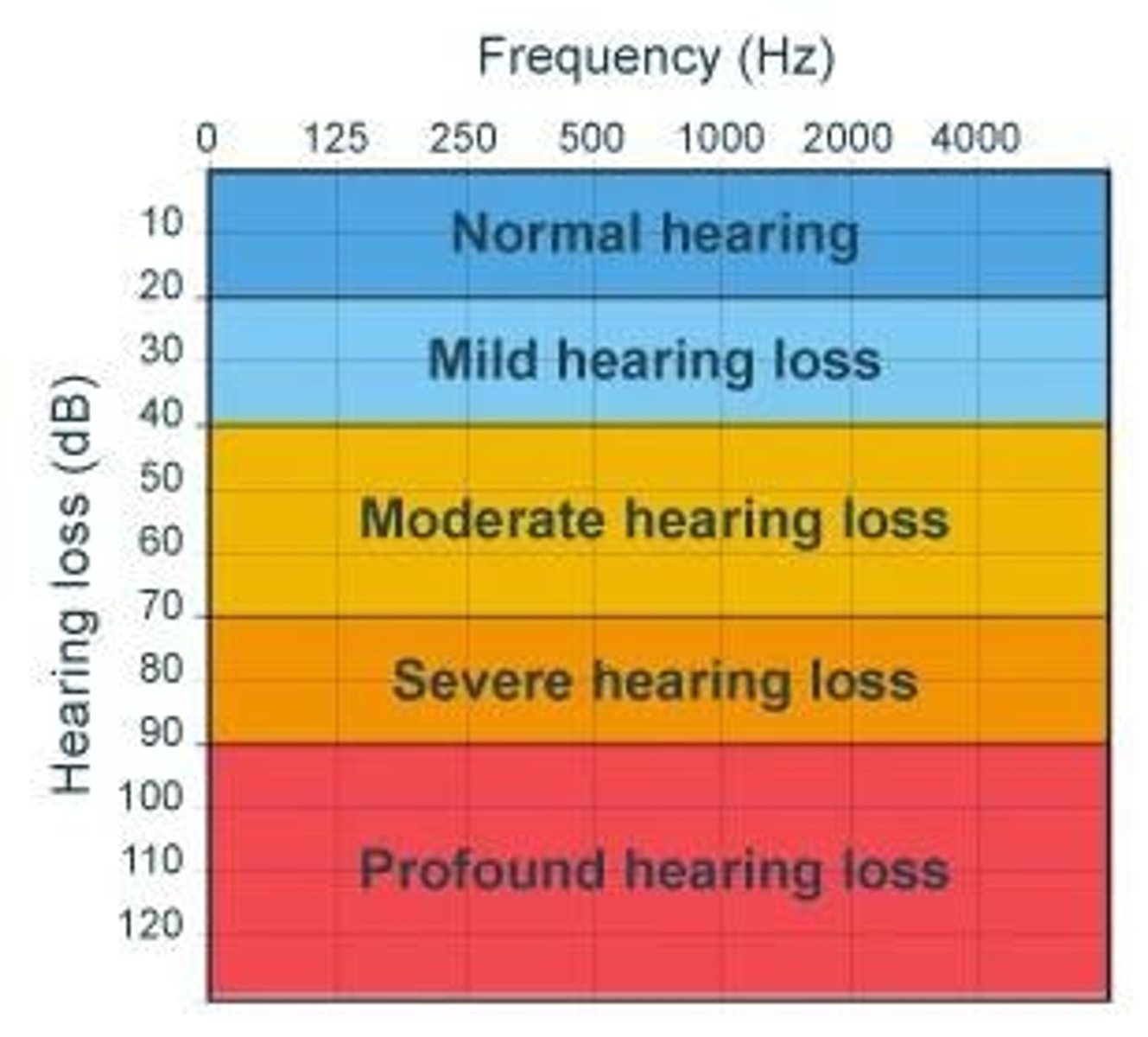
Audiogram
A chart that represents a person's hearing ability across different frequencies.
Flat audiogram
A pattern where a person's hearing is diminished in all frequencies but can still hear across all Hz.
Sloping audiogram
A pattern where a child may miss consonant sounds critical to understanding speech.
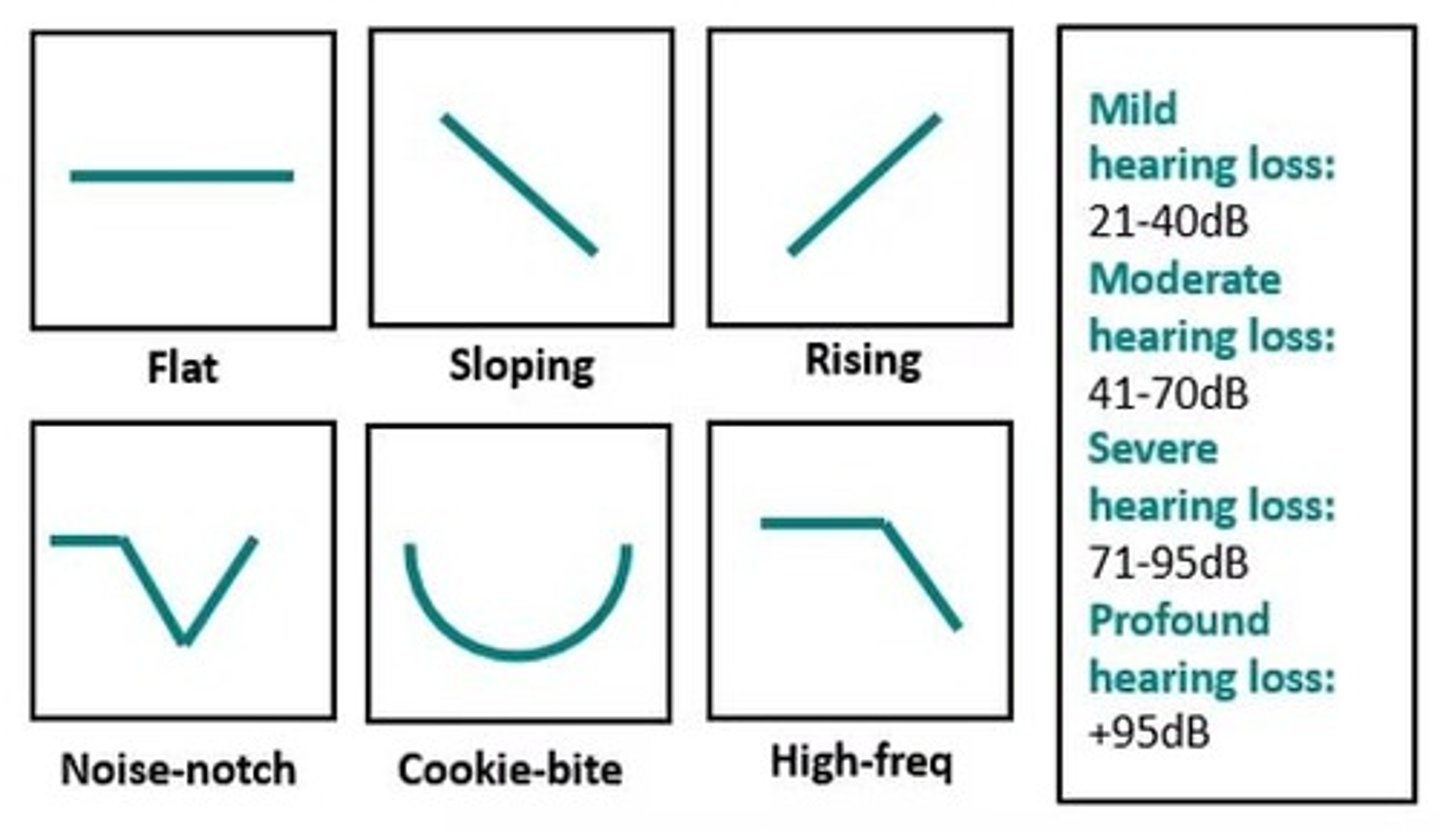
U-Shaped (cookie bite) audiogram
A pattern where a child can hear more in low and high pitches than in middle pitches.
Rising audiogram
A pattern that provides a child with consonant sounds beneficial to speech understanding.