Reproductive 3 - Female Intro, Folliculogenesis, Oogenesis
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What are three general characteristics of the female reproductive system?
- Cyclic changes in activity (menstrual cycle)
- Restricted periods of fertility (ovulation)
- Limited gamete production (pool established at birth)
What is menarche
the first menstrual period
What are the cyclic changes of the female reproduction?
Menstrual cycle - uterus changes during menstruation (uterine lining)
What is the time period of menstrual cycles?
From menarche in the teenage years to menopuase around age 45-50
Is menopause instantenous
No - various hormonal changes
How does obesity affect the hormonal reproductive axis?
Obesity can cause early puberty
What are the female gonads
Ovaries
What composes the female reproductive tract
Uterus, uterine (fallopian) tubes, vagina
What is the composition of the ovaries
Connective tissue with follicles
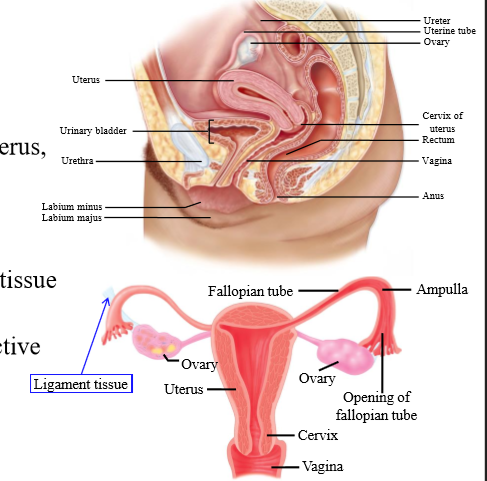
Location of the ovaries
Suspended by ligament tissue in the peritoneal cavity
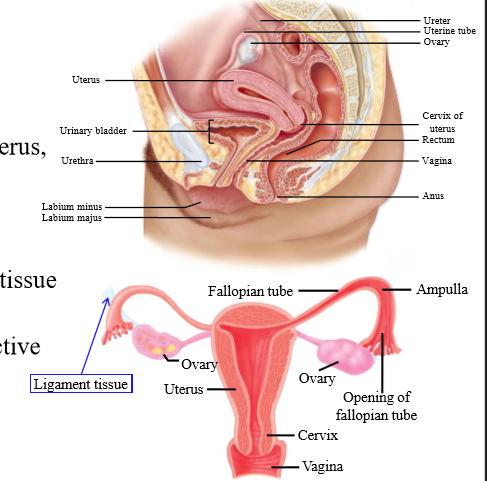
Do the fallopian tubes connect to the ovaries?
No. There is a gap
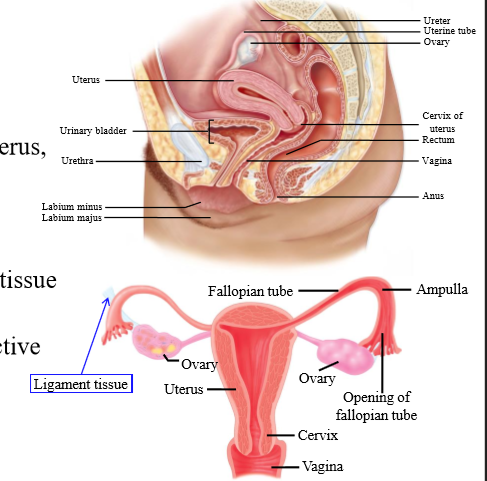
Function of the ovaries
Site of ova maturation
Role of the fallopian tubes
Transport ova from ovaries to the uterus
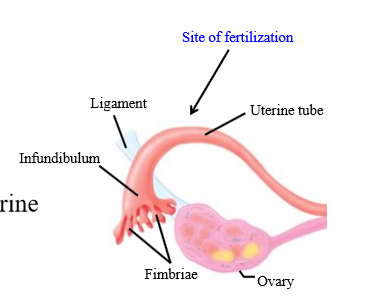
Role of fallopian tube fimbriae + infundibulum
Pick up the ovum released by the ovary
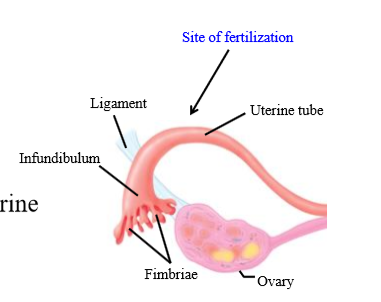
What is the site of fertilization in females
In the fallopian tube (ampulla)
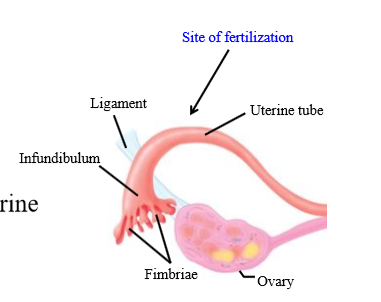
How does the ovum move through the fallopian tube
- Initially, peristaltic contractions of smooth muscle
- Mostly caused by ciliary actions of fallopian tube epithelial cells
How long does it take for ova to get to the uterus
4 days
Layers of the uterus (outer to inner)
perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
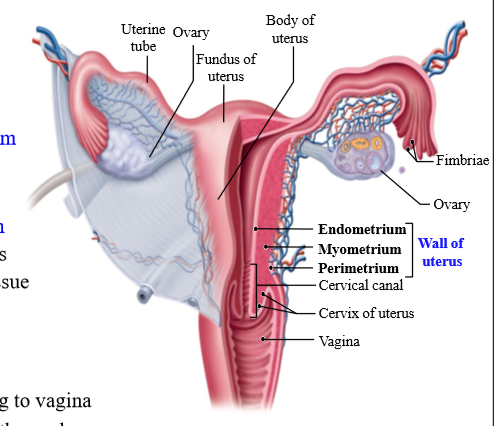
Perimetrium composition
Epithelial cells and connective tissue
Myometrium composition
smooth muscle
Role of myometrium
involved in contraction during childbirth
Endometrium composition
Epithelial cells, connective tissue, glanfd
What do the endometrium glands contain
Glycogen
What is the cervix
Canal leading to vagina
What is the birth canal
Cervix + Vagina
What is an ovarian follicle
Fluid filled sac on the ovary containing the oocyte. Dense cells surround
What is the ovary covered by
Capsule
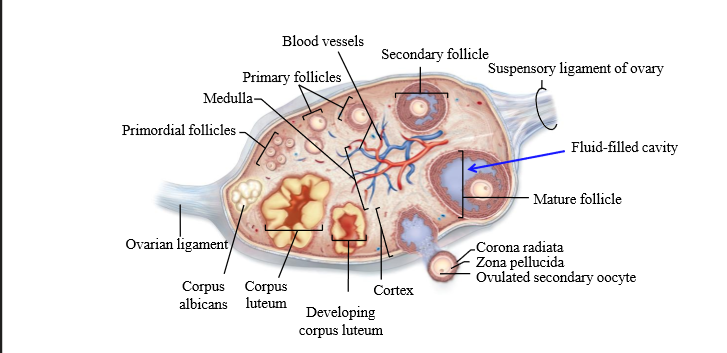
What is the corpus luteum
a hormone-secreting structure that develops in an ovary after an ovum has been discharged but degenerates after a few days unless pregnancy has begun.
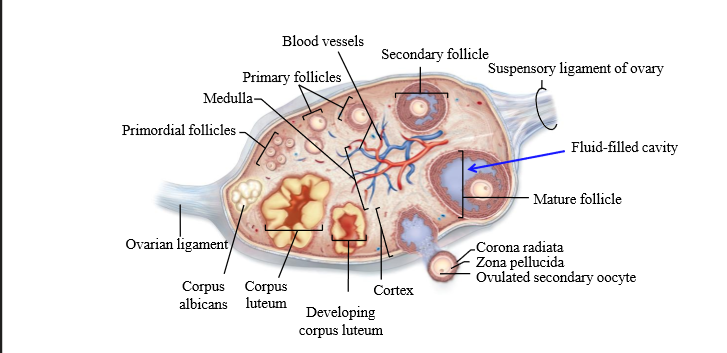
What is the corpus albicans
degenerated corpus luteum
What causes the change in structure and function of the ovary
Hormones from the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
Role of corpus luteum
Endocrine gland - produces progesterone
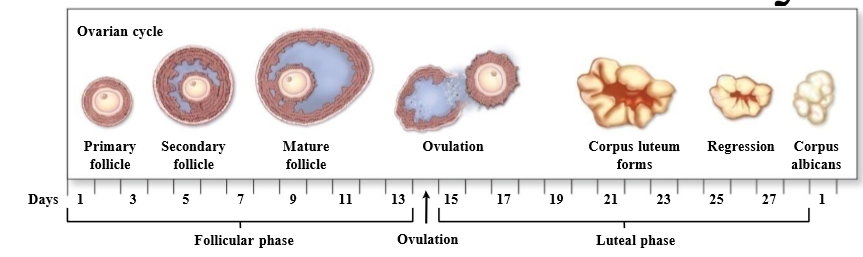
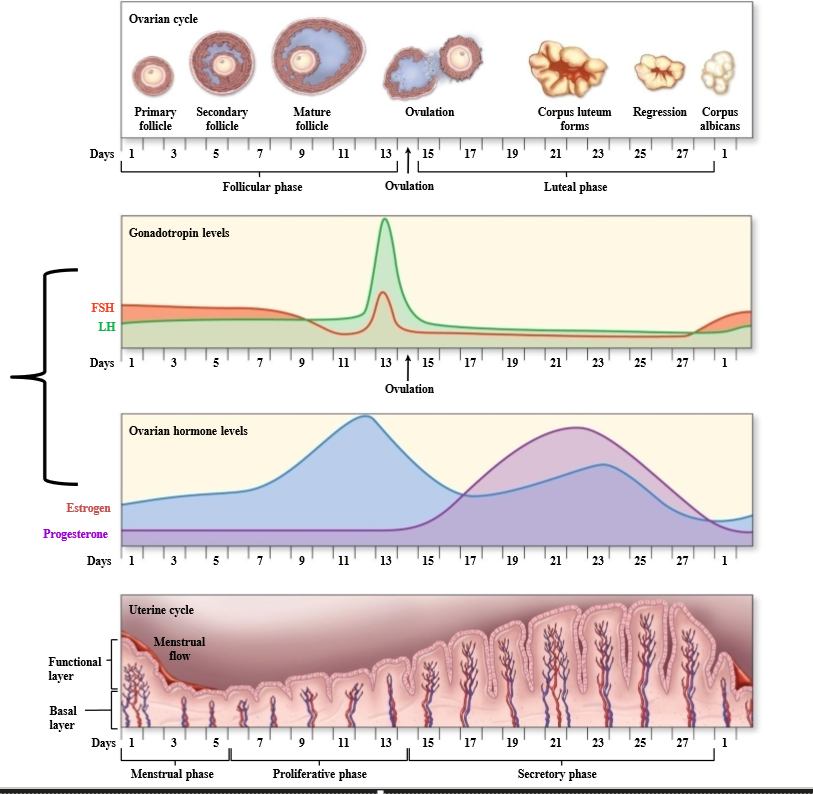
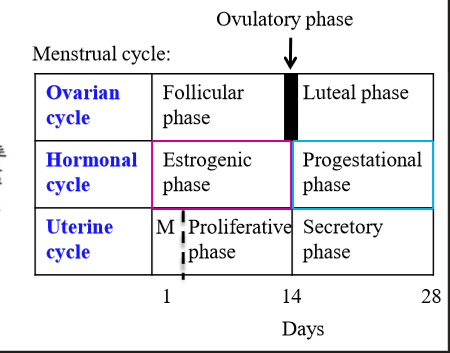
What is the ovarian cycle
Cycle that looks at the development of the follicle, discharge, and formation of the corpus luteum
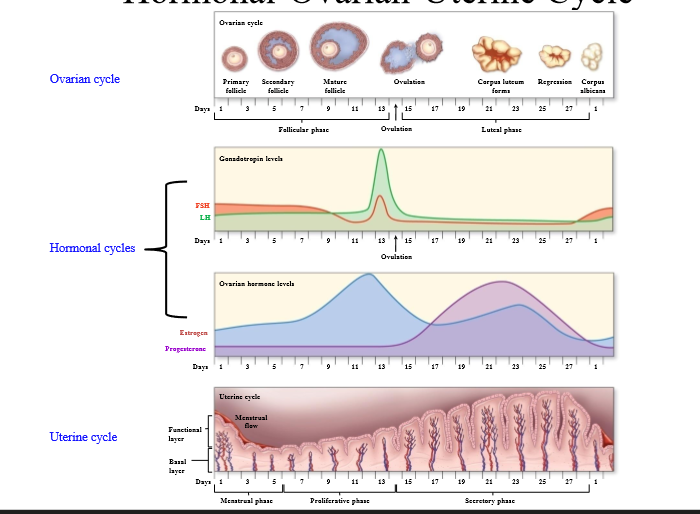
What hormones cause changes in the ovary, and what does this cause?
LH and FSH cause ovarian changes. These ovarian changes accompany changes in estrogen and progesterone, which cause changes in endometrium
How long is the menstrual cycle
28 days on average
What are the 2 phases of the ovarian cycle
follicular phase and luteal phase
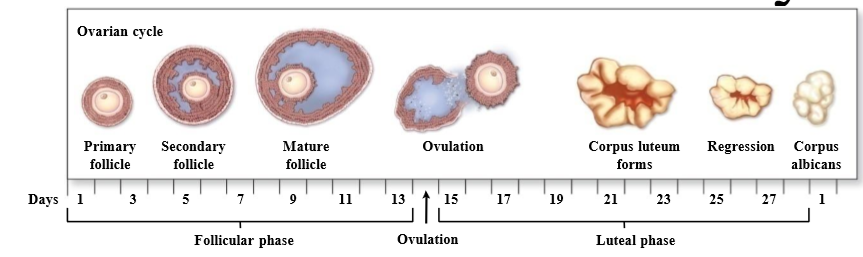
What is follicular phase
Ovarian phase associated with development of follicles (around first 14 days)
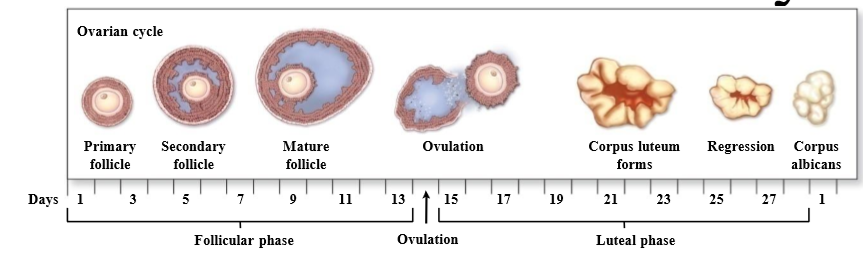
What is the luteal phase
Ovarian phase associated with the corpus luteum
What is day 1 of the uterine cycle
First day of menstrual bleeding
What is the uterine cycle
Cycle associated with changes in the endometrium due to ovarian and hormonal changes
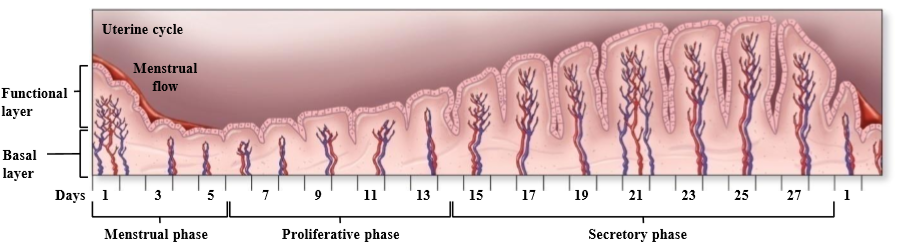
What are the phases of the uterine cycle
menstrual phase, proliferative phase, secretory phase
Menstrual phase
Uterine cycle phase associated with shedding of the endometrial layer
Proliferative phase
Uterine cycle phase associated with endometrium + blood vessel growth, and development of a functional layer
Secretory phase
Uterine cycle phase associated with further endometrial vascularization + uterine gland development
What ovarian phase coincides with the menstrual + proliferative phase?
Follicular phase
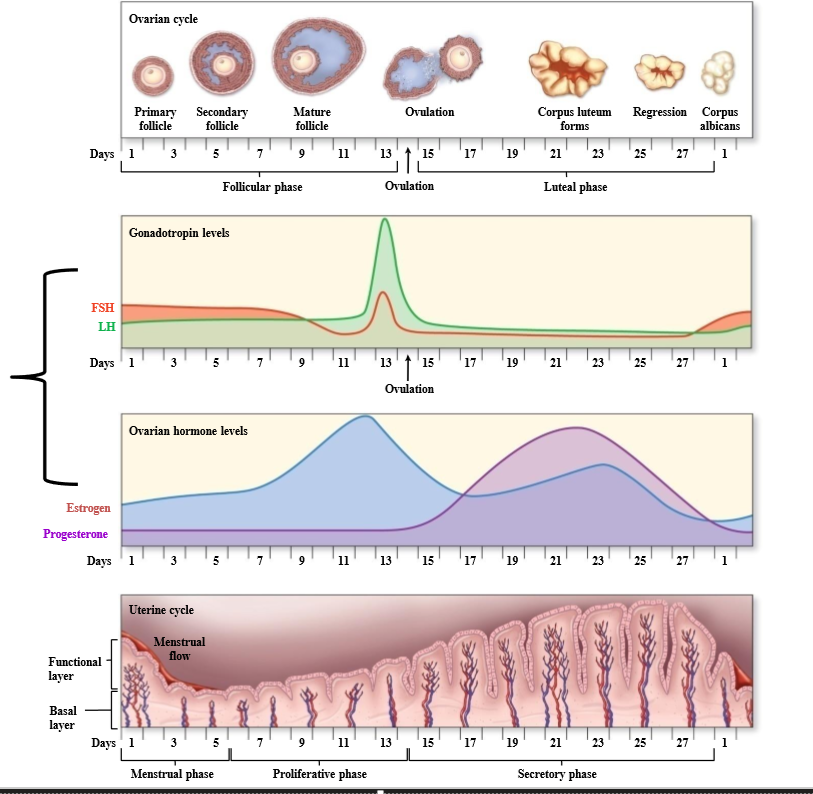
What ovarian phase coincides with the secretory phase?
Luteal phase
What is the difference between oogenesis and folliculogenesis?
Oogenesis is the development of the oocyte (female gamete)
Folliculogenesis is the development of the ovarian follicle (that the oocytes sit in)
How many oocytes are in a follicle
1 - primary oocyte stage
What is primordial follicle
A primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of follicle cells
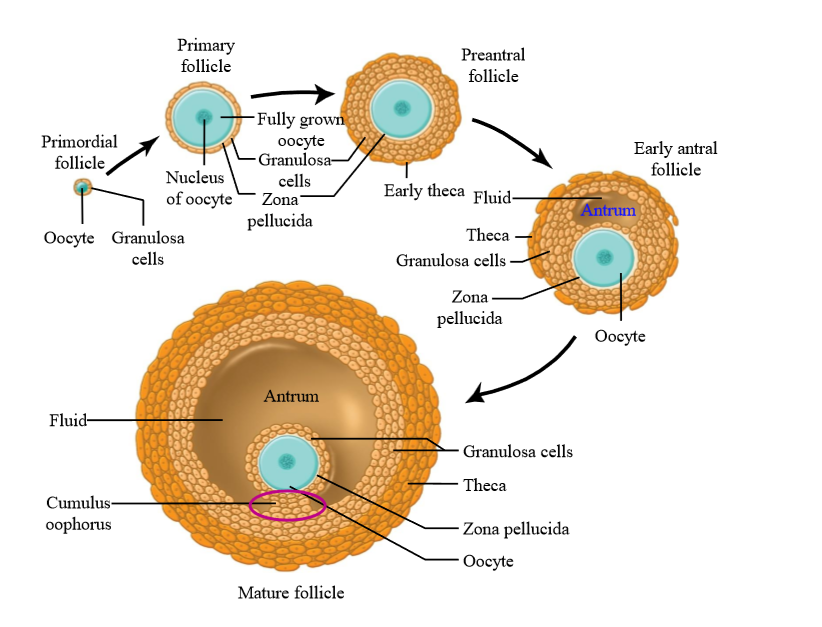
Granulosa cells
the majority of the cells surrounding an oocyte in a follicle. They can multiply, divide, undergo mitosis, and they develop as the oocyte develops
What do granulosa cells secrete
Granulosa cells secrete estrogen during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle (before ovulation).
Theca cells
Ovarian connective tissue layer that has developed and differentiated
Layers of theca cells
Theca interna, theca externa
What is the earliest stage of follicle growth
Primordial follicle
What is a primary follicle
Fully grown oocyte surrounded by several layers of epithelial cells
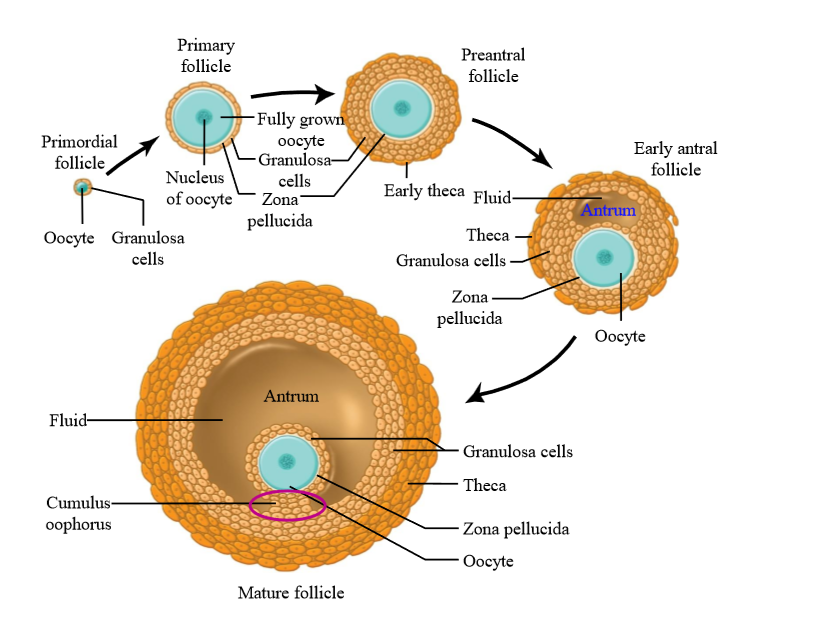
Role of granulosa cells in primary follicle
Secrete proteins and glycoproteins around the oocyte = zona pellucida
Preantral follicle
large oocyte, multiple layers of granulosa cells, thin layer of theca cells (connective tissue has divided)
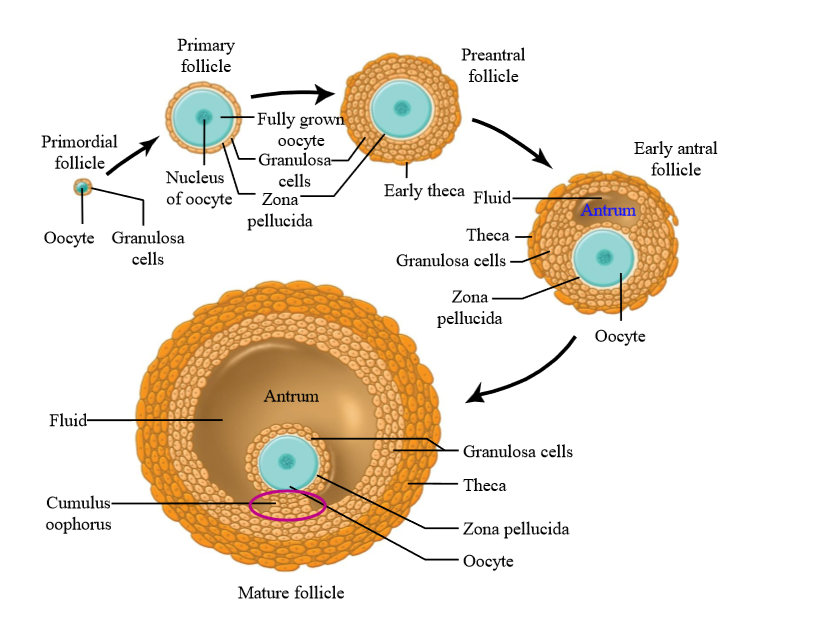
Early antral folicle
Follicle contains an Antrum (follicle structure with fluid filled space)
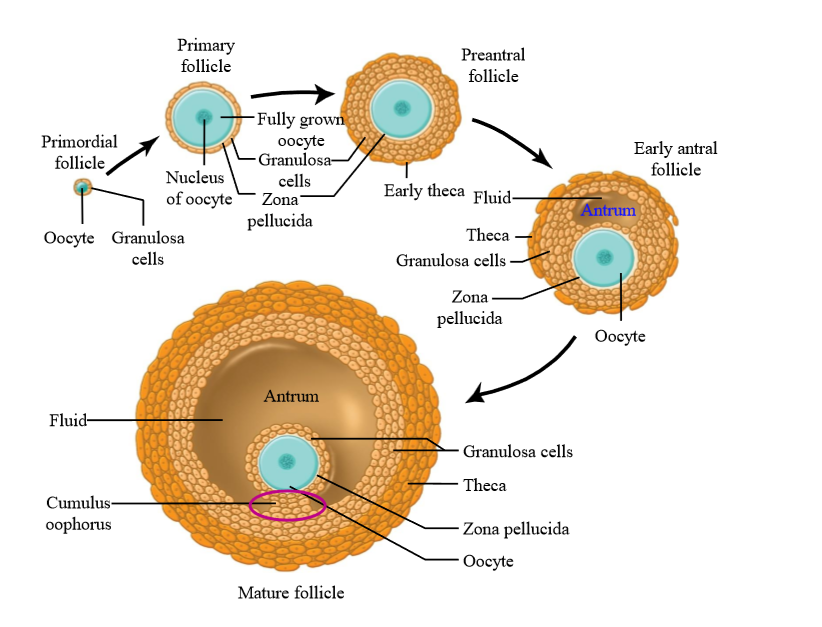
Mature follicle characteristics
very large, multiple layers of granulosa and theca cells, large antrum - ready to ovulate. Contains cumulus oophorus
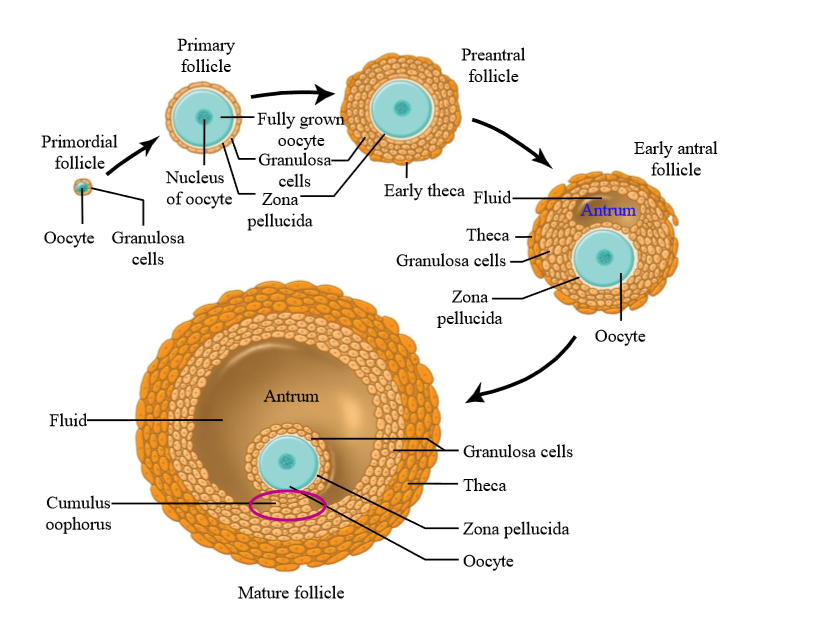
Cumulus oophorus
a mound of granulosa cells on one side of the antrum that covers the oocyte and secures it to the follicular wall
If you take a cross section of an ovary, what follicles will you see
Several follicle in several stages of growth
In each menstrual cycle, how many follicles mature to pre-antral and early antral stage?
10-25
Of the 10-25 follicles that begin to grow at the beginning of of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, the dominant follicle is selected by...
The follicle that secretes the most estrogen
Once the dominant follicle is chosen, what happens to the rest of the follicles?
Undergo atresia (programmed cell death)
What hormone dominates the first 14 days of menstrual cycle
Estrogen - known as the estrogenic phase. Occurs during the ovarian follicular phase and the uterine menstruation + proliferative phase
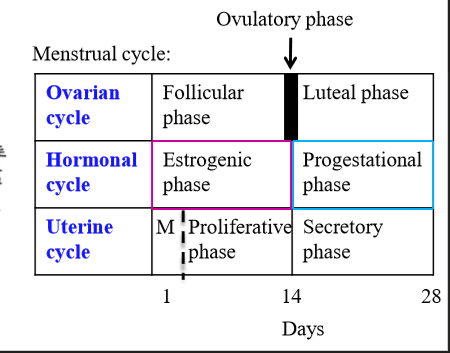
What hormone dominates the last 14 days of the menstrual cycle
Progesterone - known as the progestational phase. Occurs during the ovarian luteal phase and the uterine secretory phase
What hormone causes granulosa cell differentiation + mitosis
FSH
How does the oocyte get nutrients and paracrine factors
Granulosa cells send out cytoplasmic processes through the zona pellucida and form gap junctions. Nutrients and paracrine factors are send through these junctions to aid in growth
How many oocytes are available at ovulation at birth?
2-4 million - come from initial pool in gestation
At puberty, how many oocytes are available for ovulation?
100-200 thousand
How many oocytes go through ovulation during a female lifetime?
Around 400 - the rest go through atresia