603: Oral Cavity and Pharynx
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
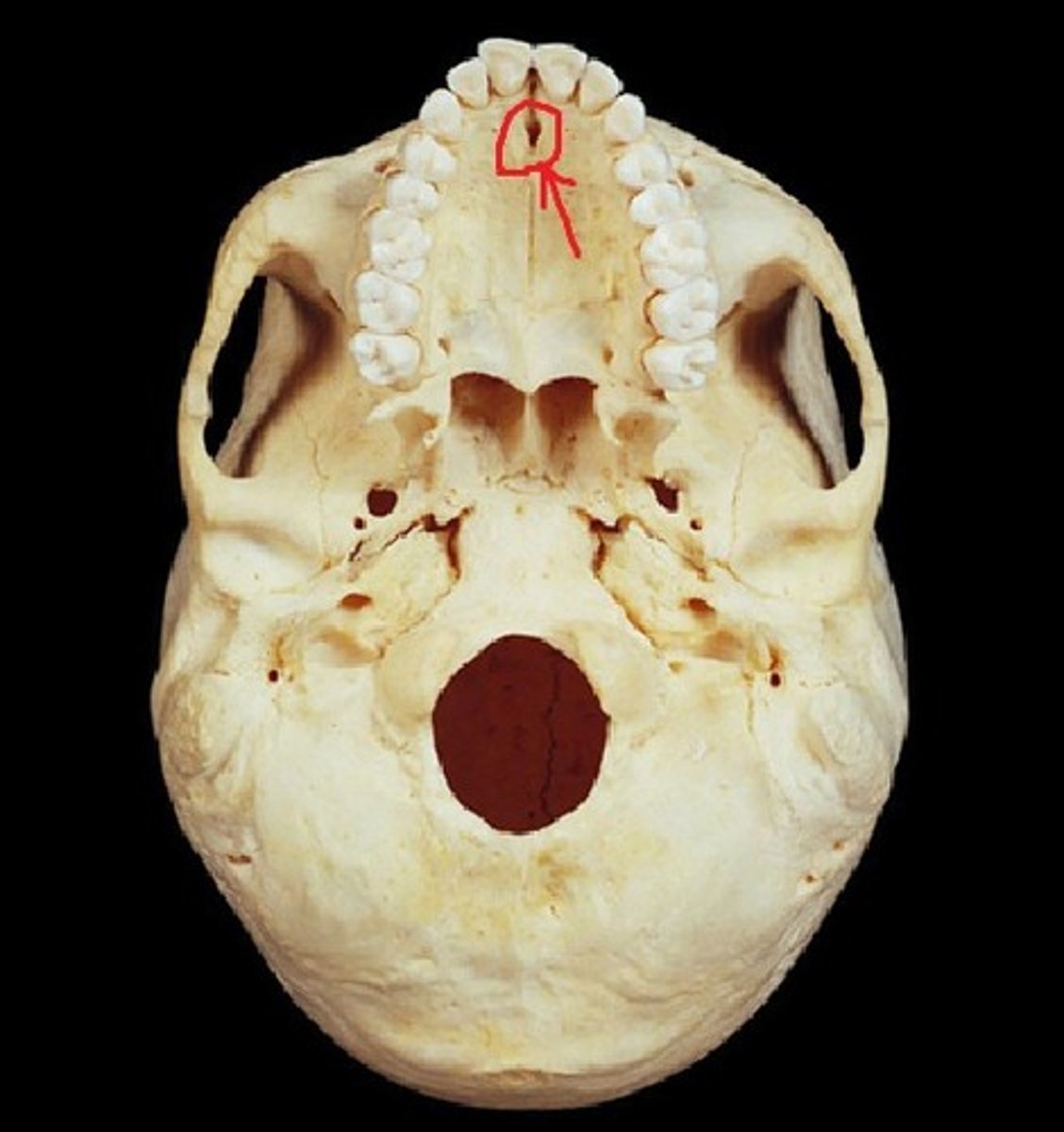
incisive canal
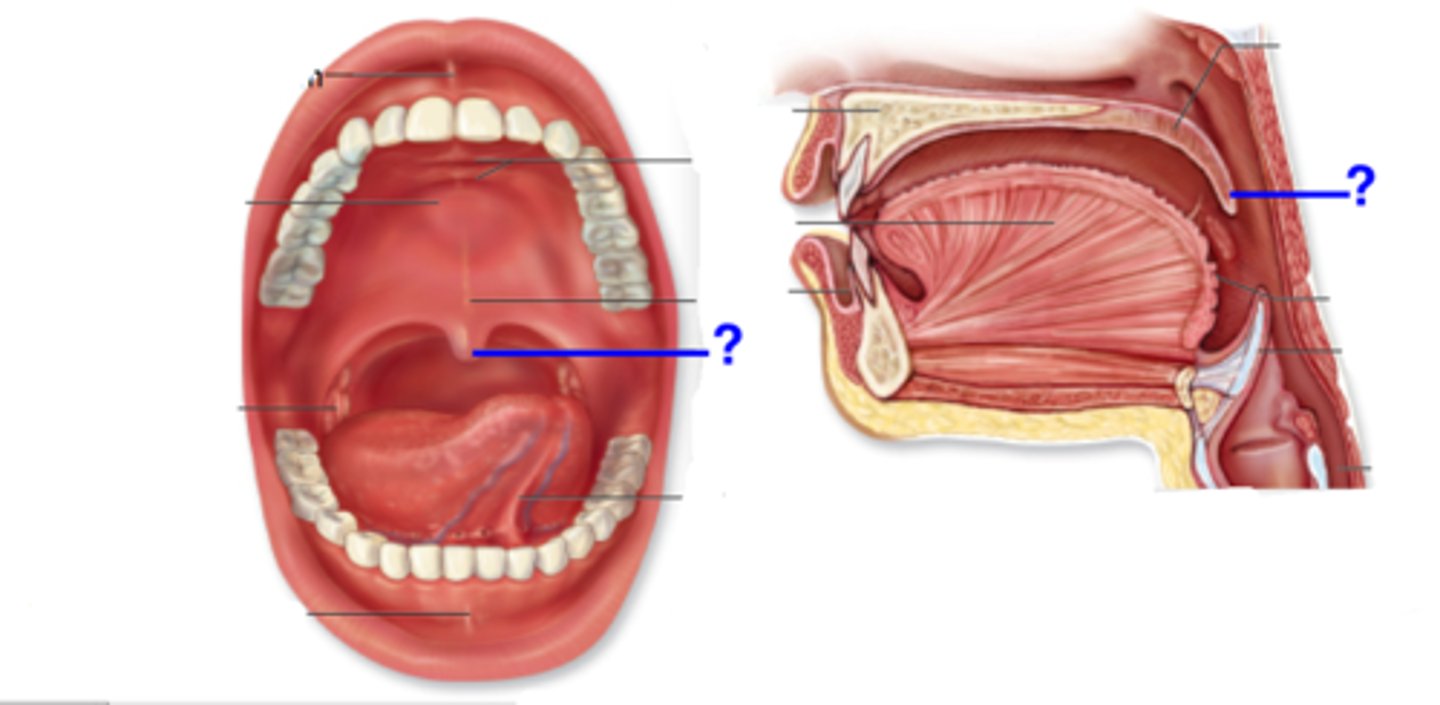
identify the structure:
alveolar bone
the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth. It forms the bony sockets that support and protect the roots of the teeth
horizontal plate of palatine bone
identify the structure:
medial pterygoid plate
identify the structure:
lateral pterygoid plate
identify the structure:
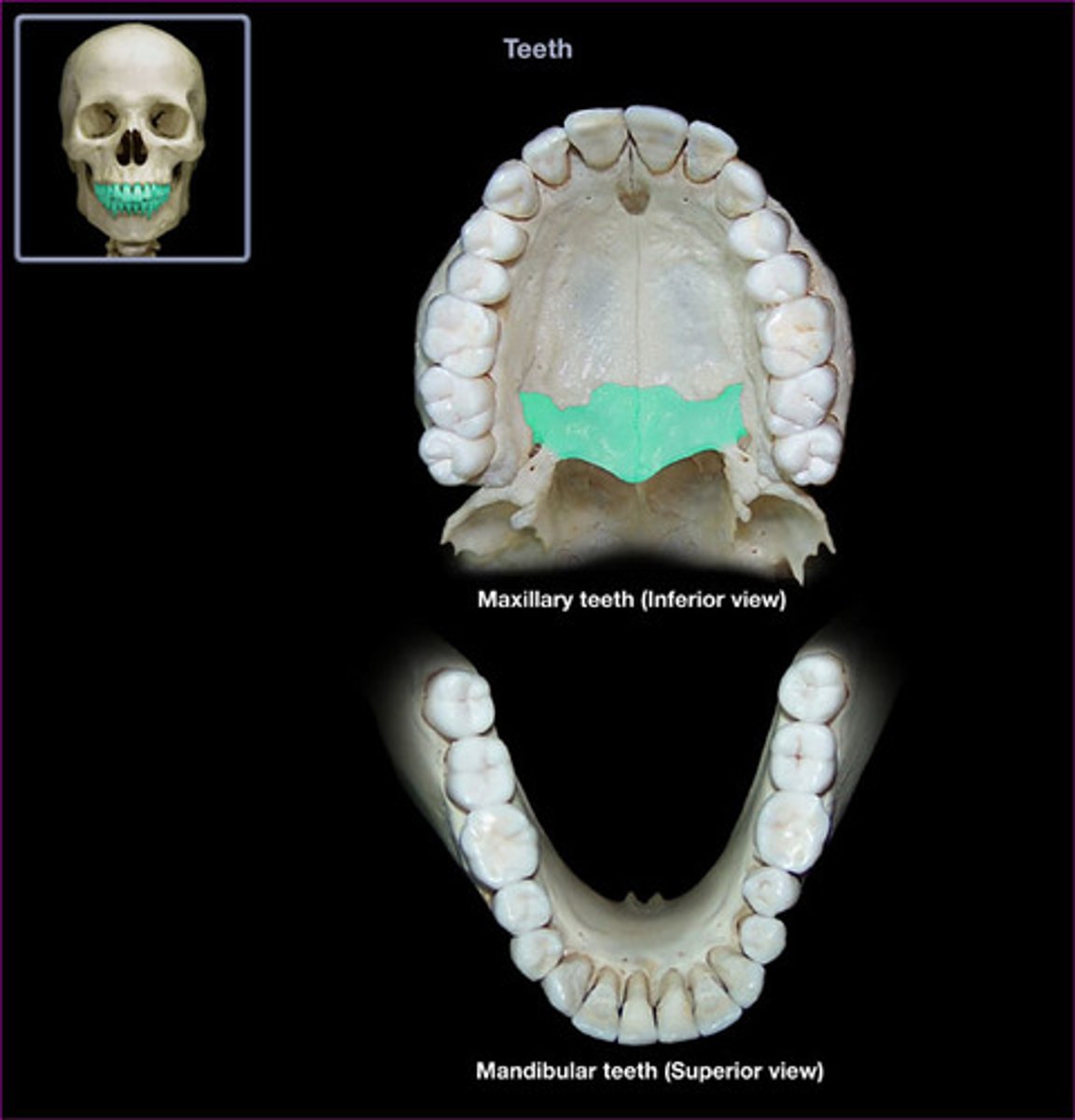
palatine process of maxilla
identify the structure:
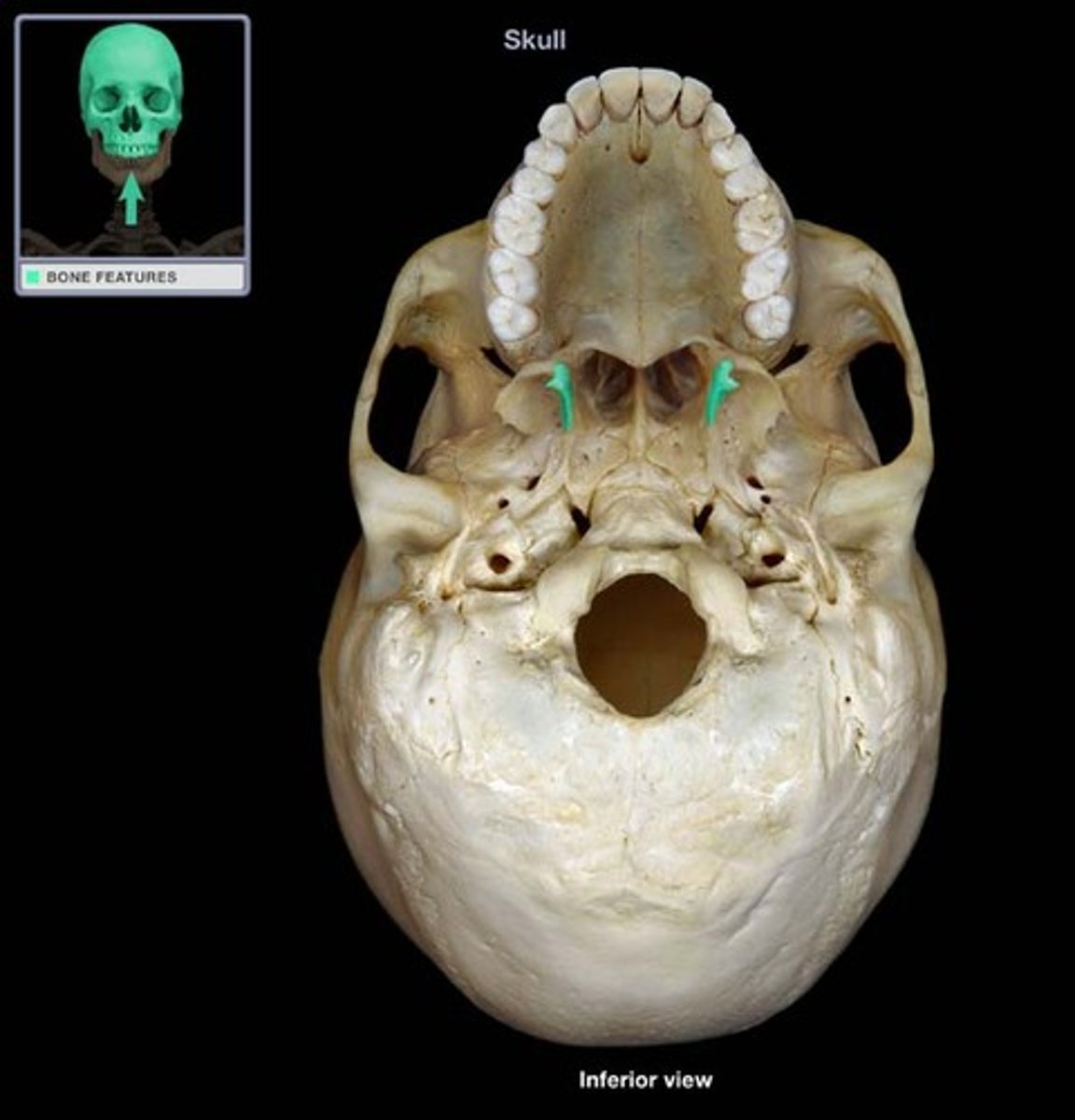
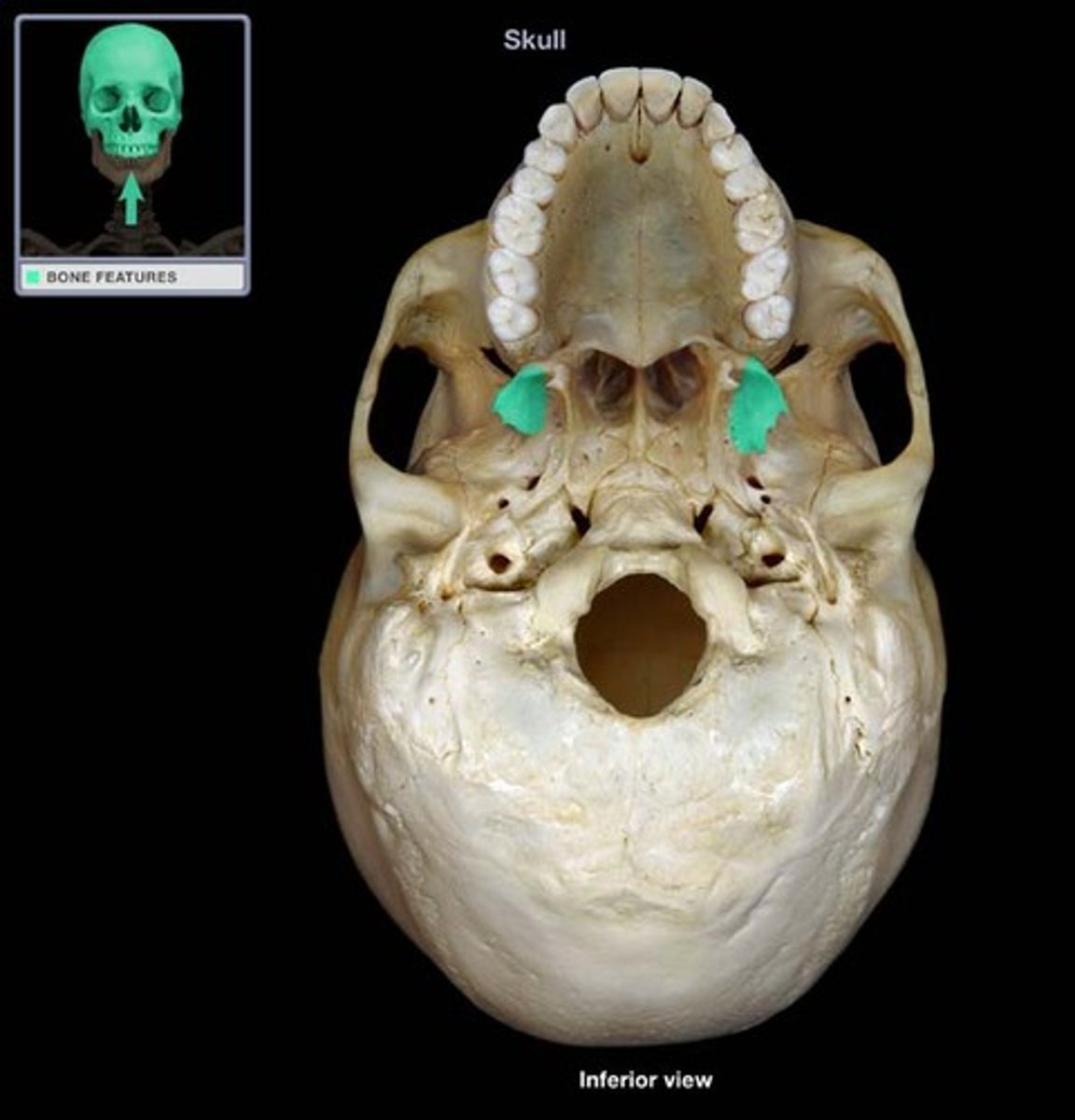
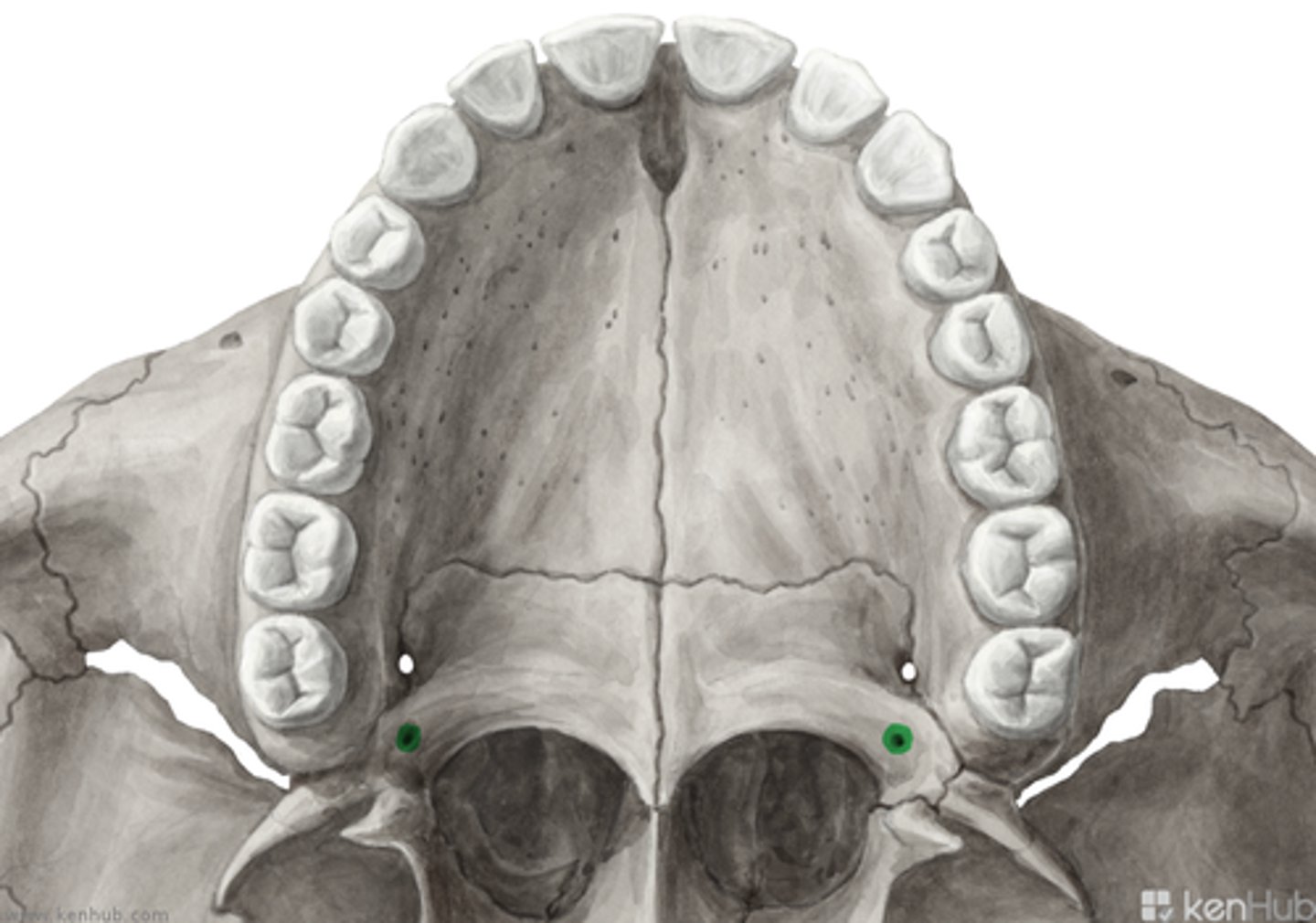
greater palatine foramen
identify the structure:
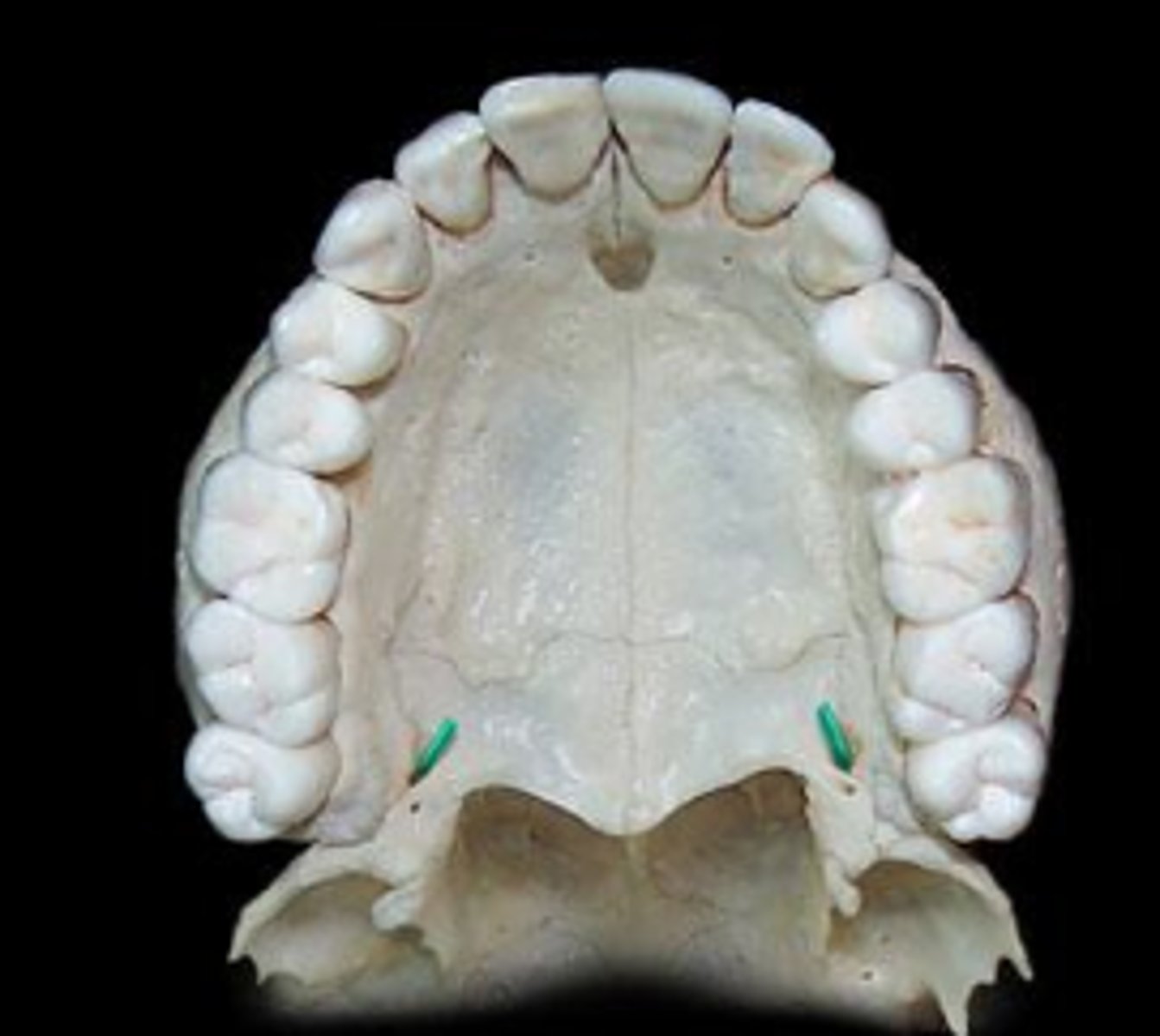
lesser palatine foramen
identify the structure:
hamulus
identify the structure:
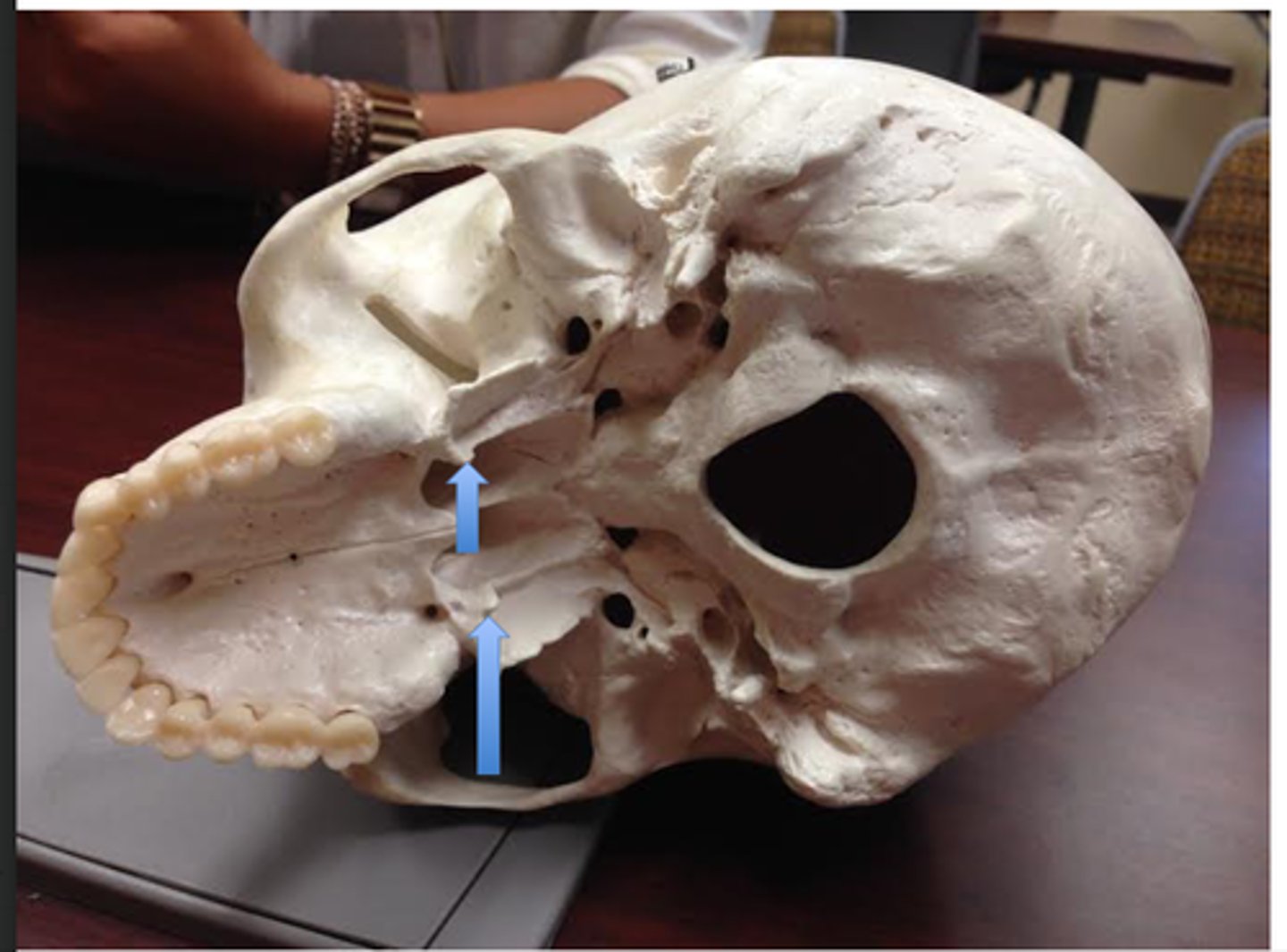
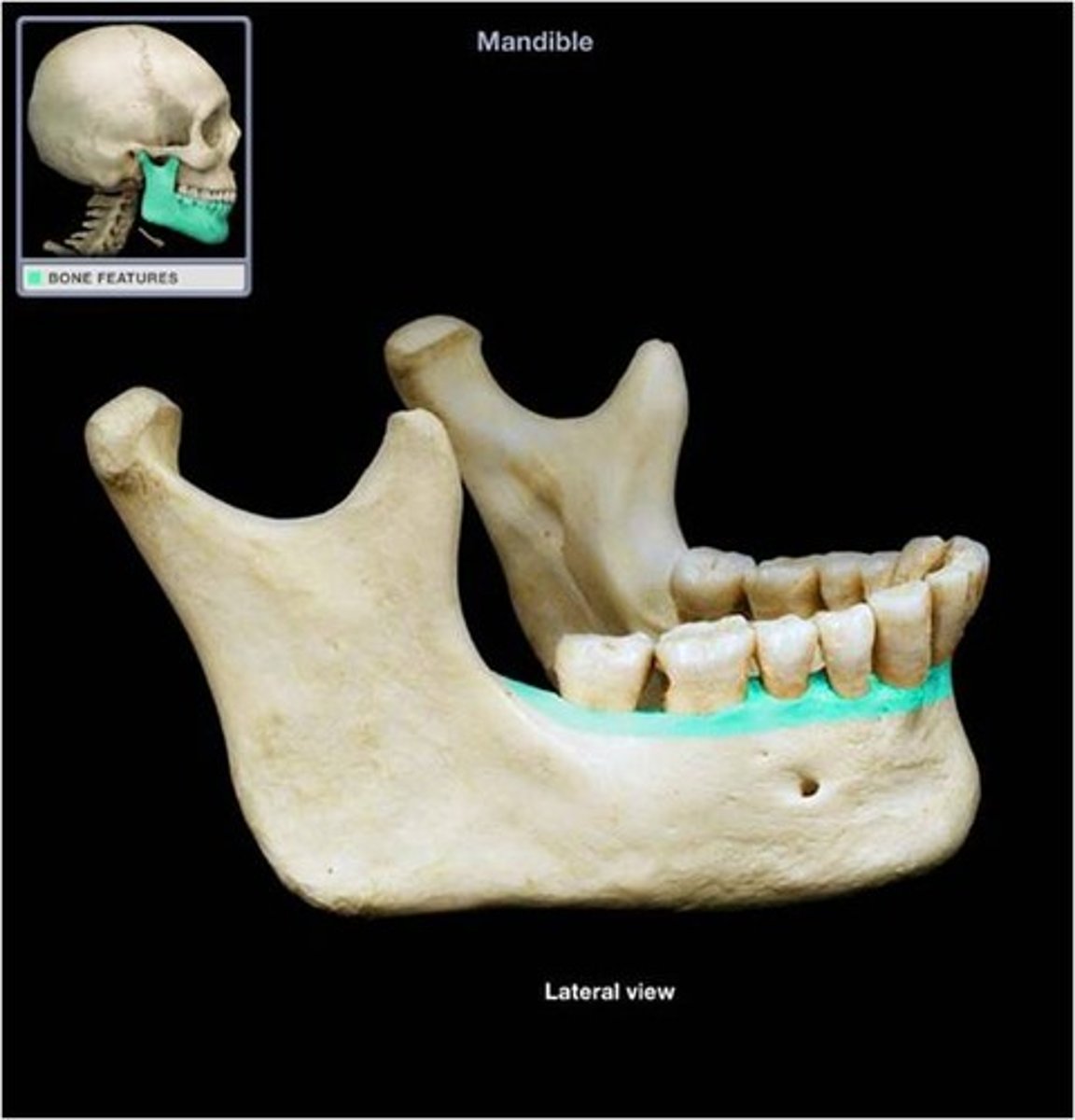
mandibular foramen
identify the structure:
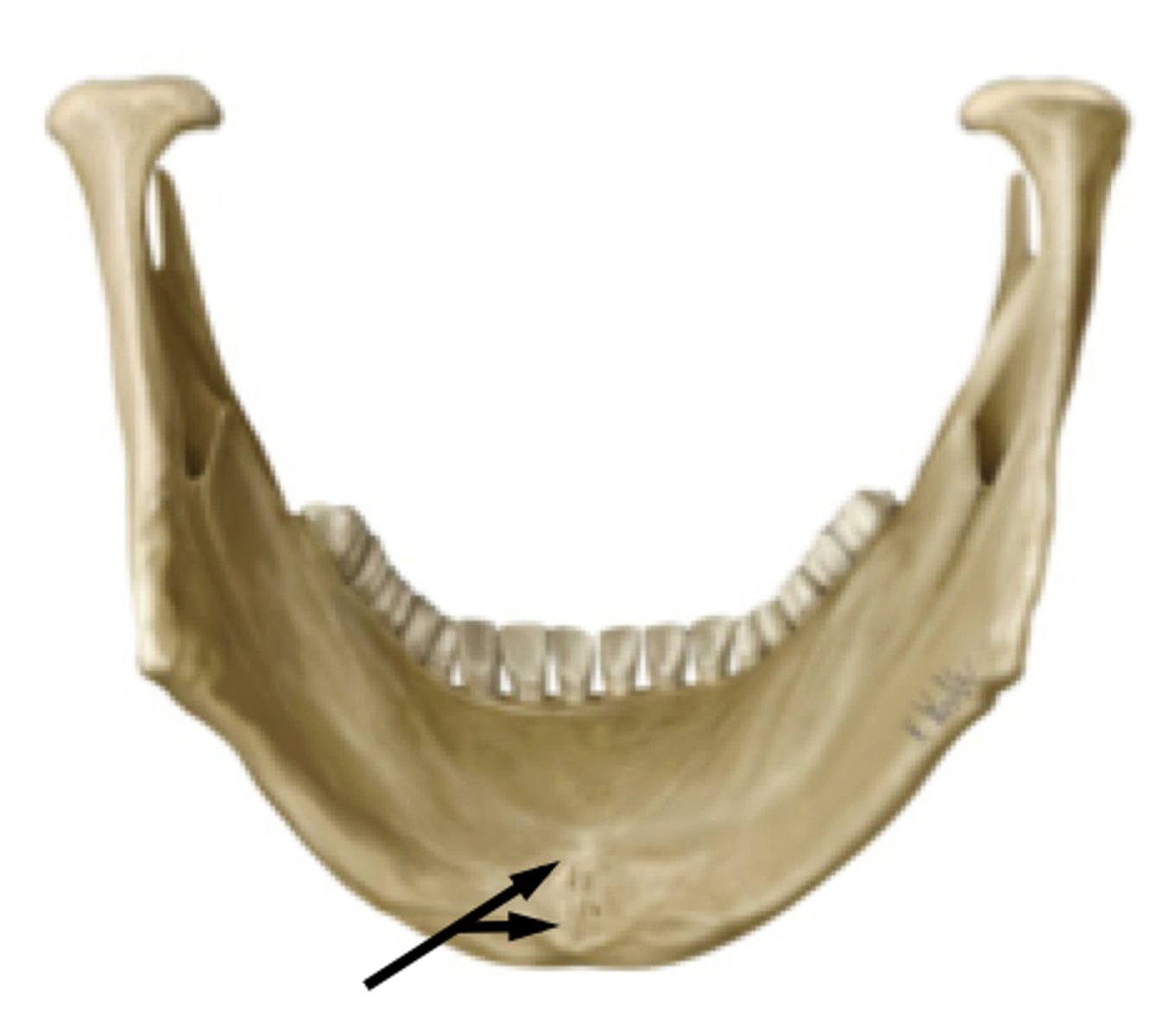
genial spines
identify the structure:
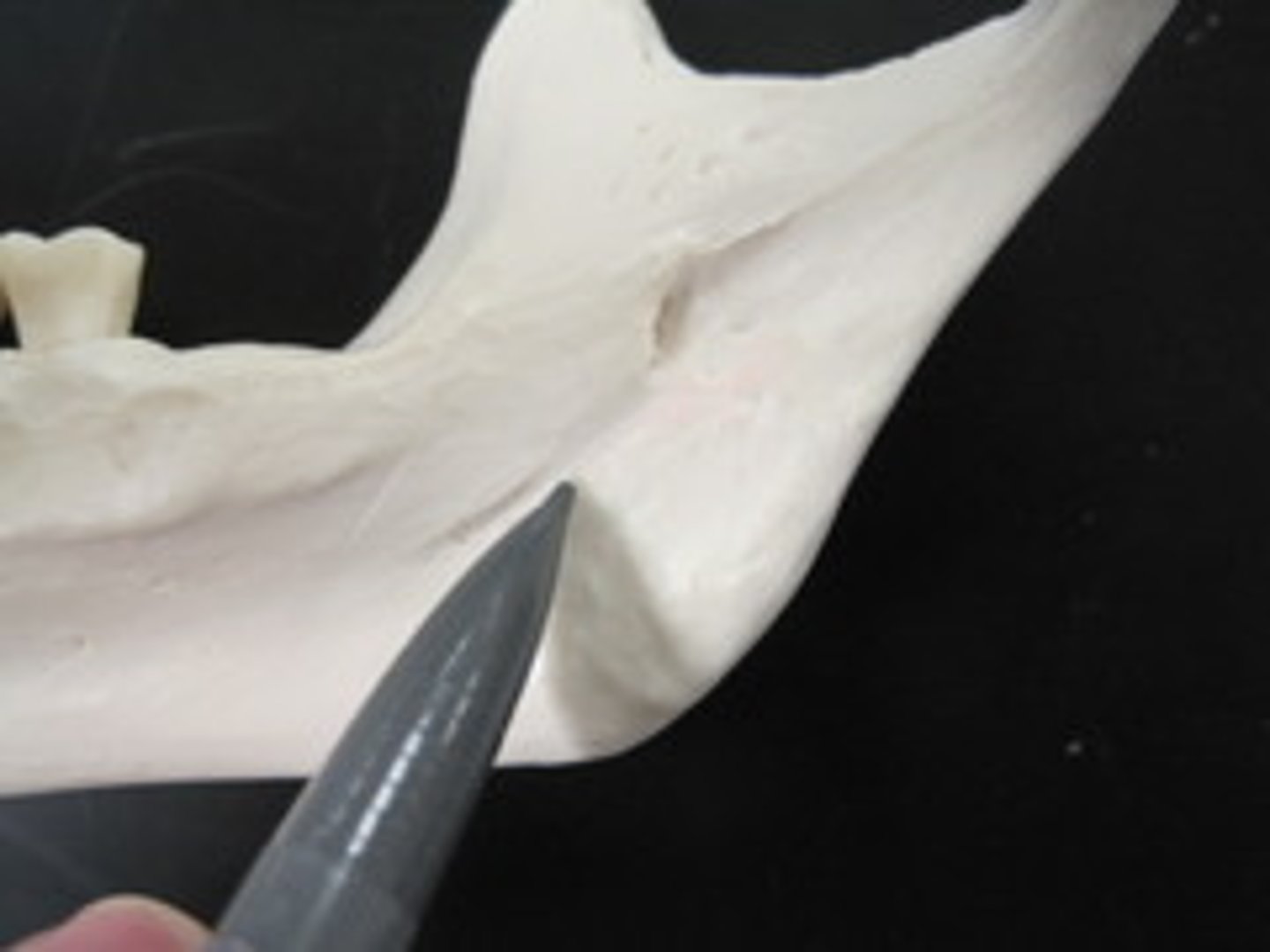
mylohyoid groove
identify the structure:
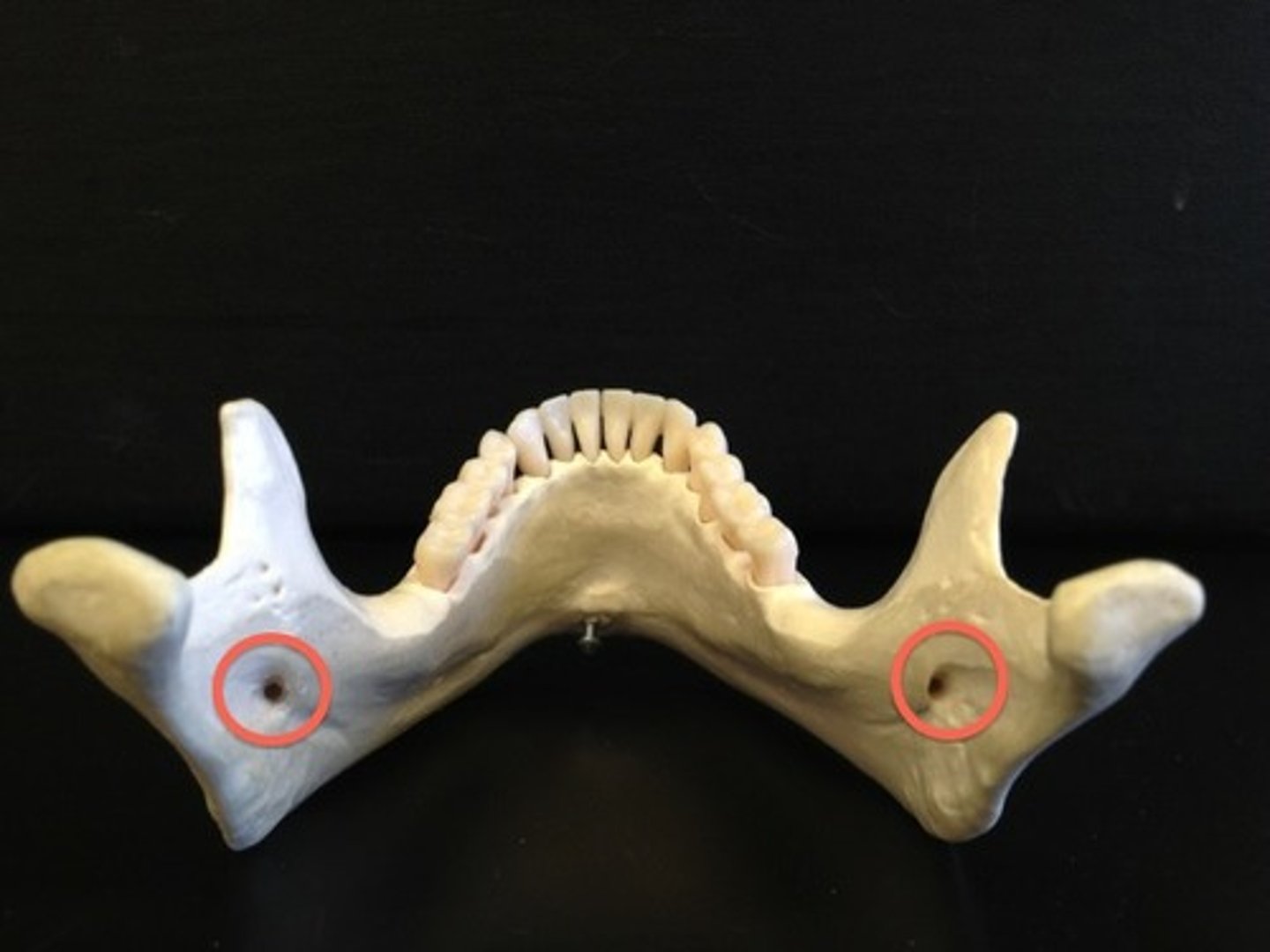
mental foramen
identify the structure:
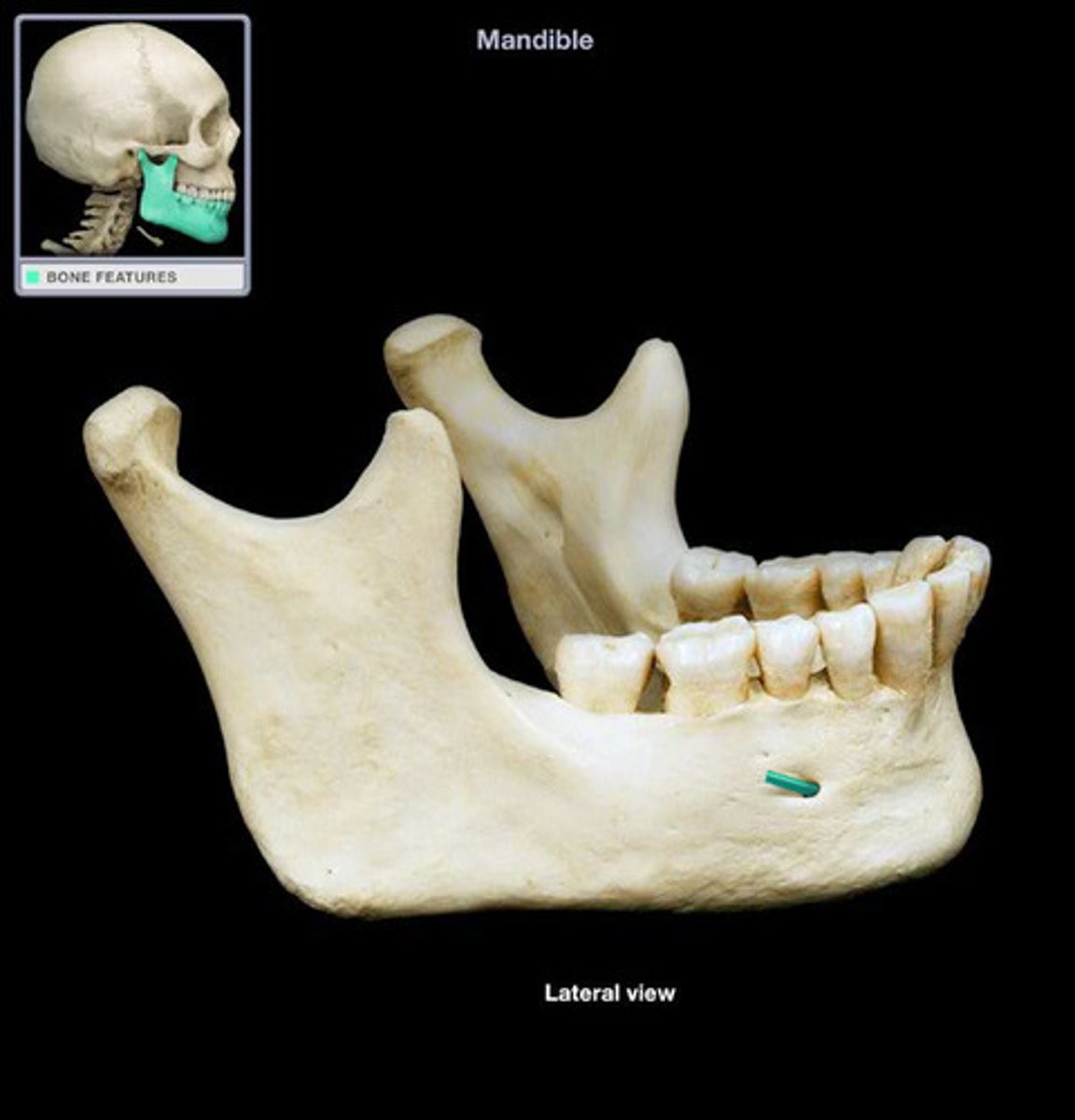
mandibular tori
identify the structure:
mandibular tori
which osseous bony growth is associated with bruxism?
torus palatinus
identify the structure:
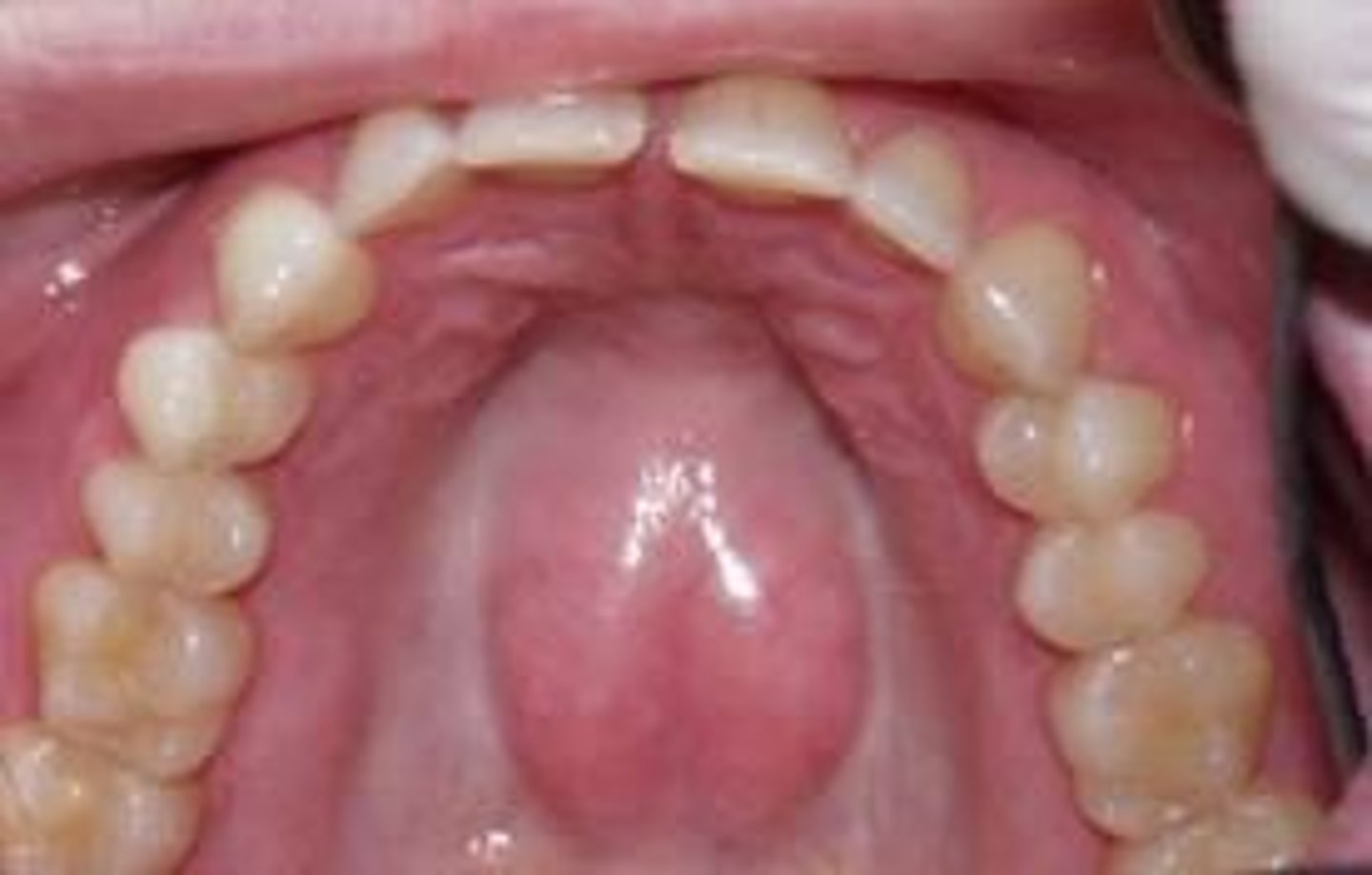
torus palatinus
which osseous bony growth is associated with hereditary and maybe trauma and diet?
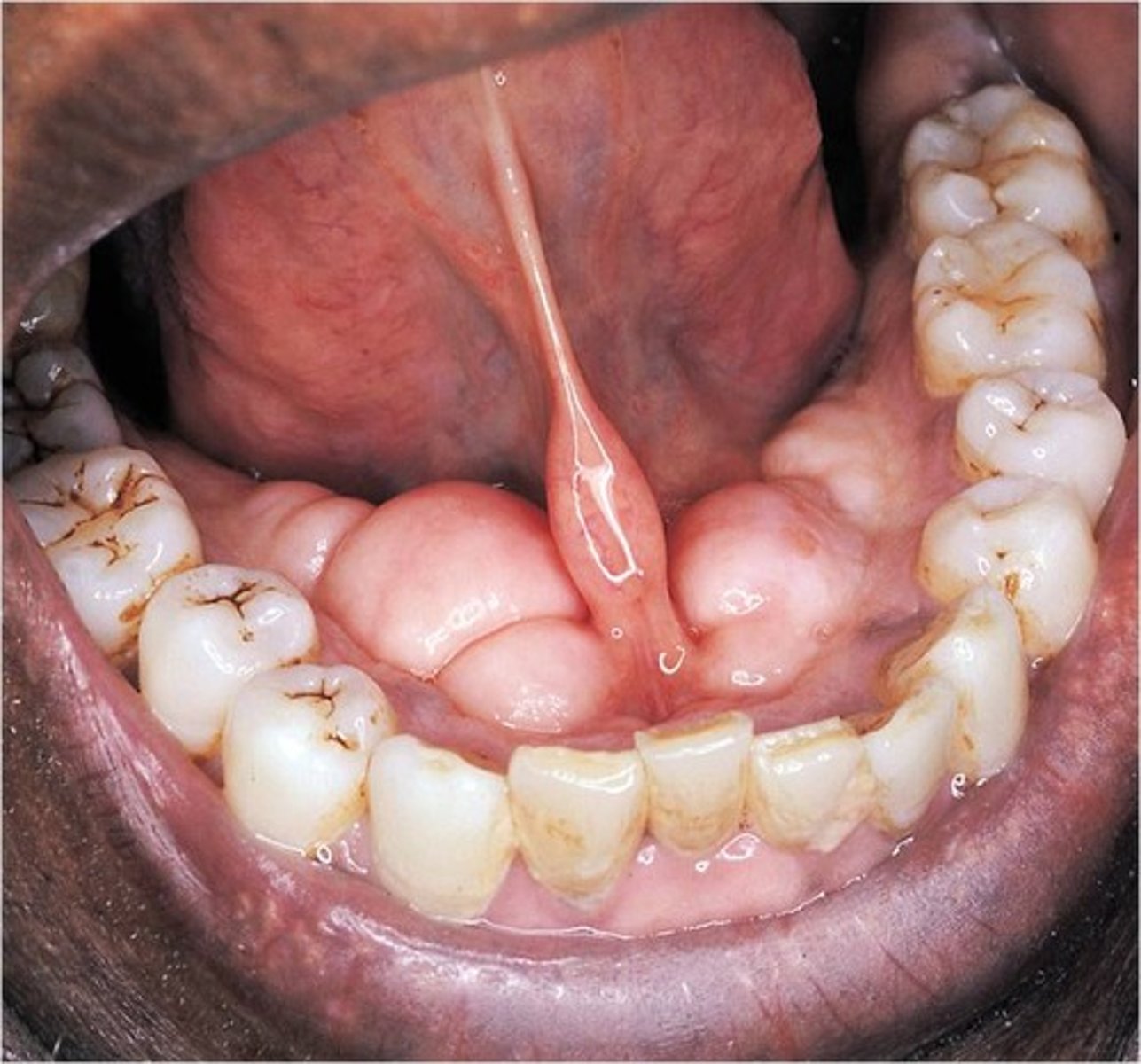
incisive papilla
identify the structure:
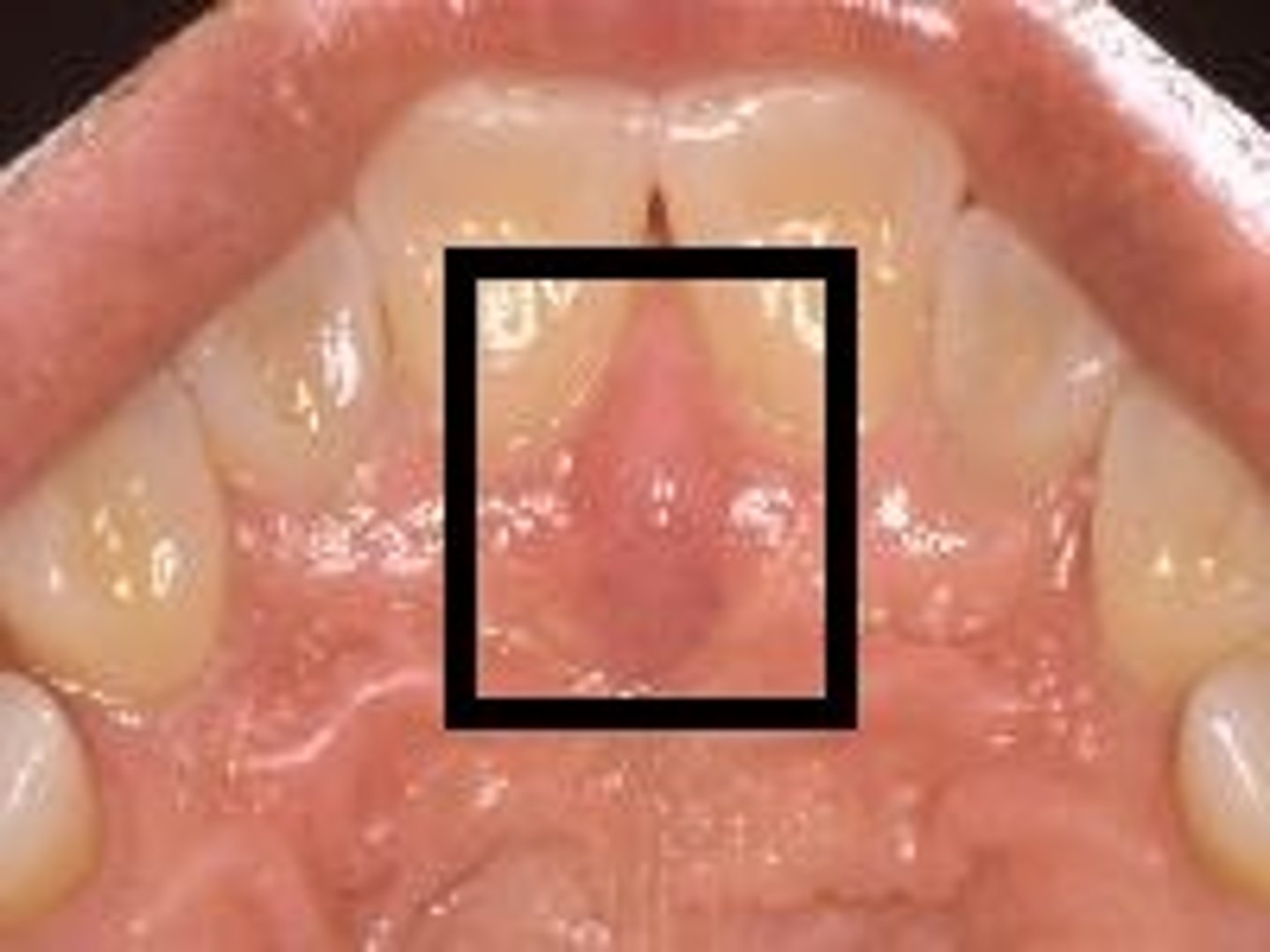
palatine raphe
identify the structure:
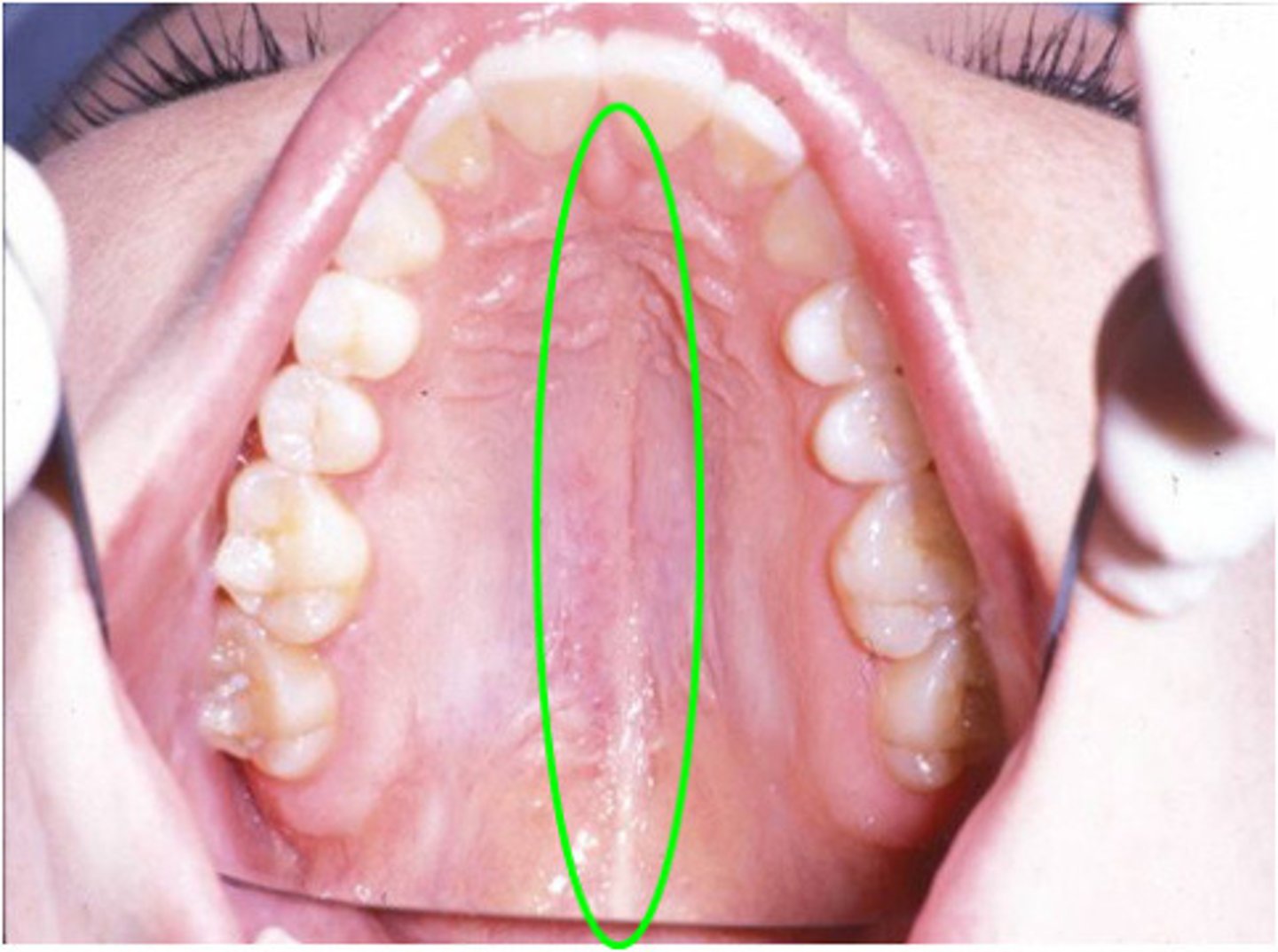
transverse palatine folds (palatine rugae)
identify the structure:
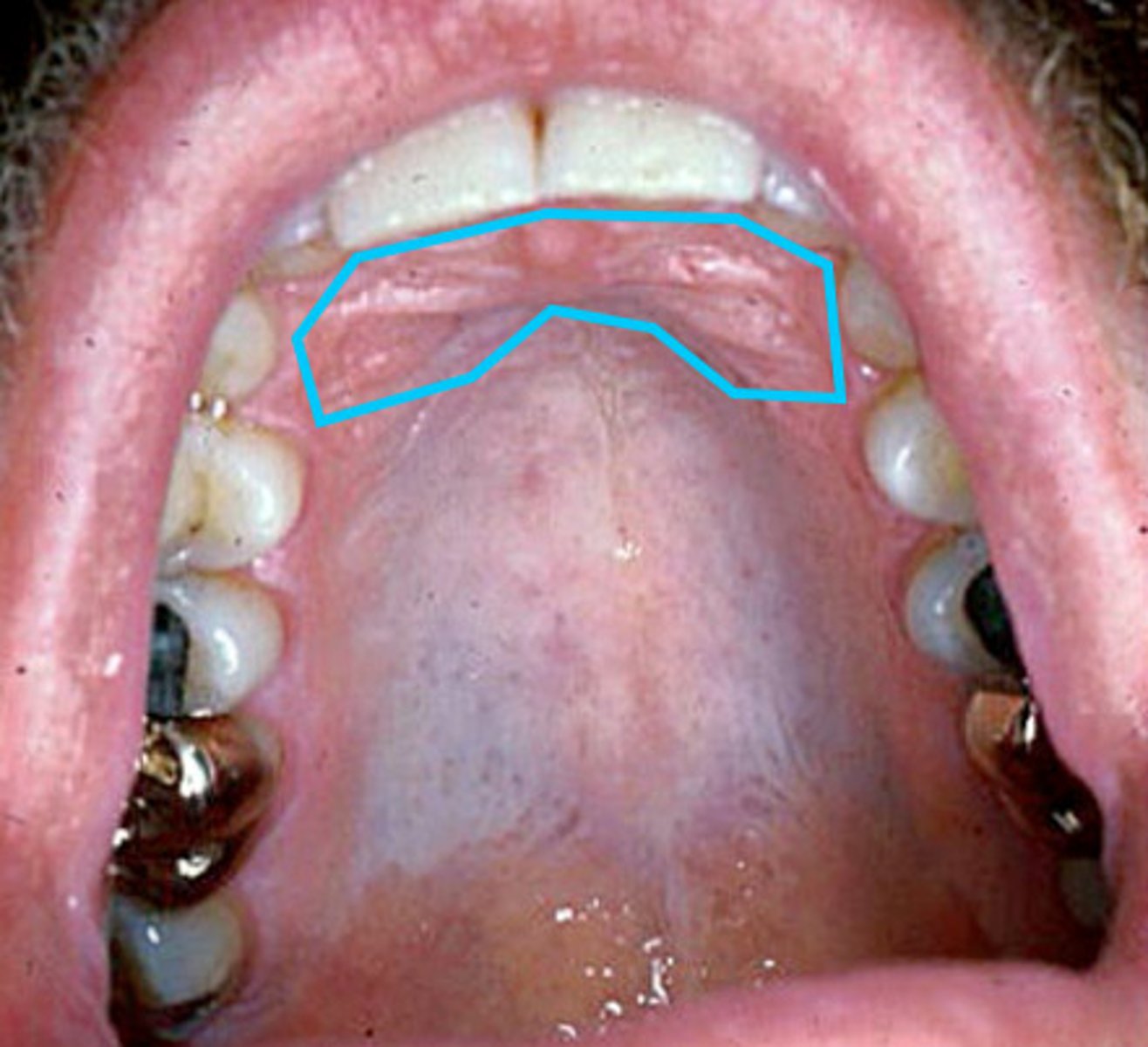
palatine tonsils
identify the structure:
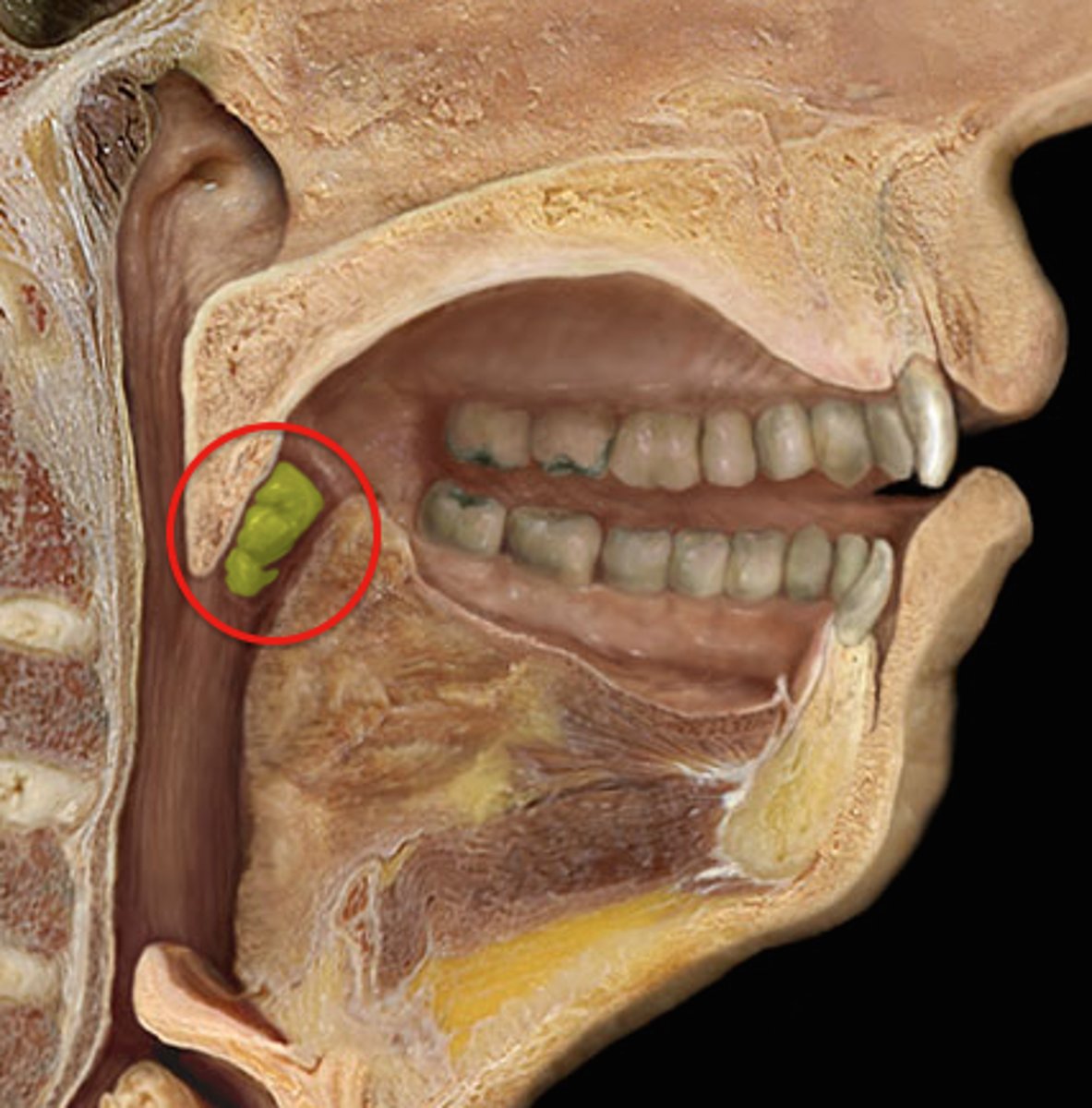
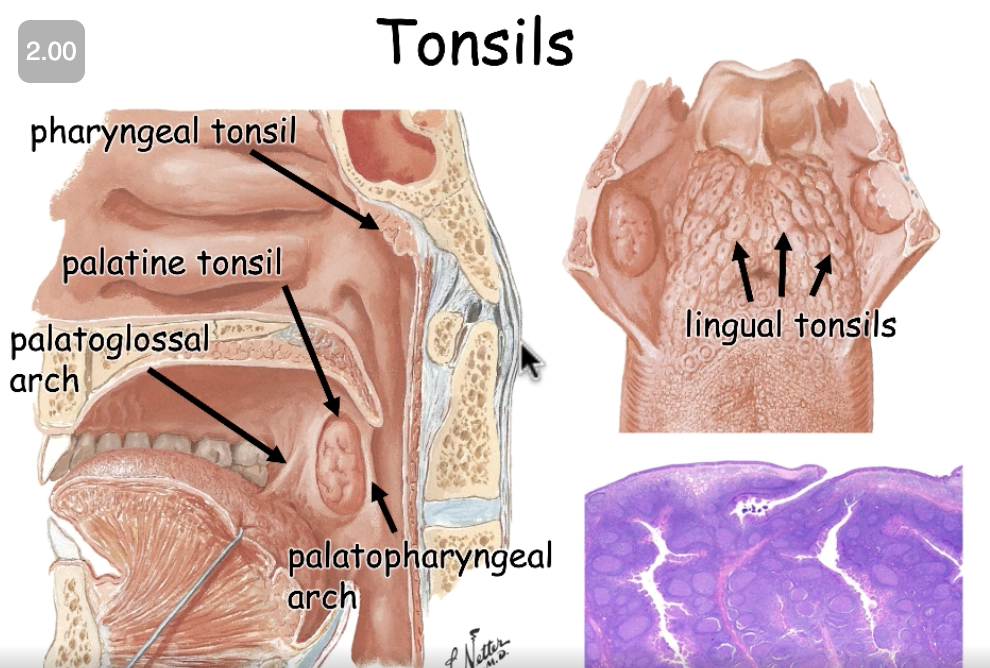
palatine tonsils, lingual tonsils, pharyngeal tonsils
surface (oral = stratified squamous, non-keratinized vs nasal = respiratory epitheleum)
what are the different types of tonsils? what are the differences?
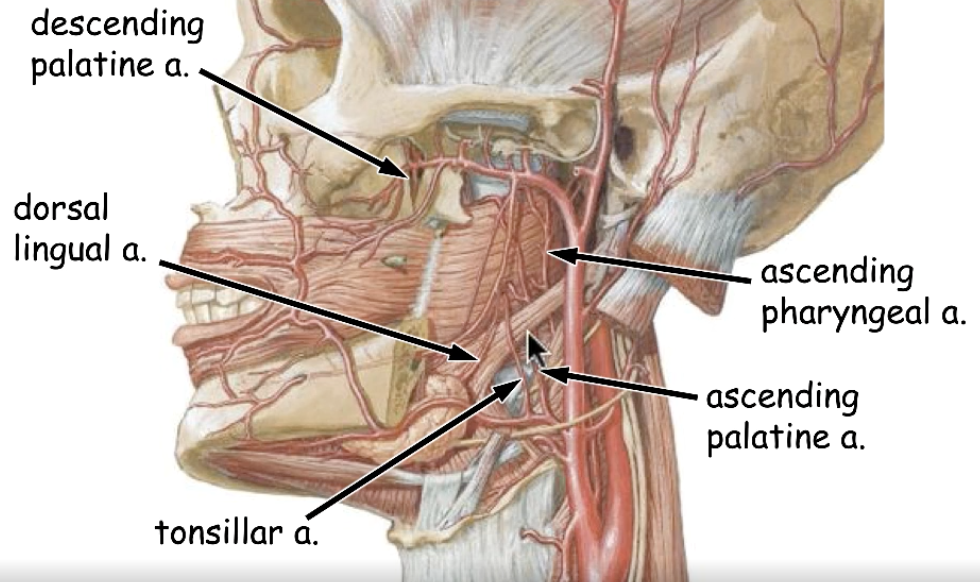
Hemorrhage is a common concern with tonsillectomy
the vascular supply of tonsils are robust. therefore, what medical complication is a common concern?
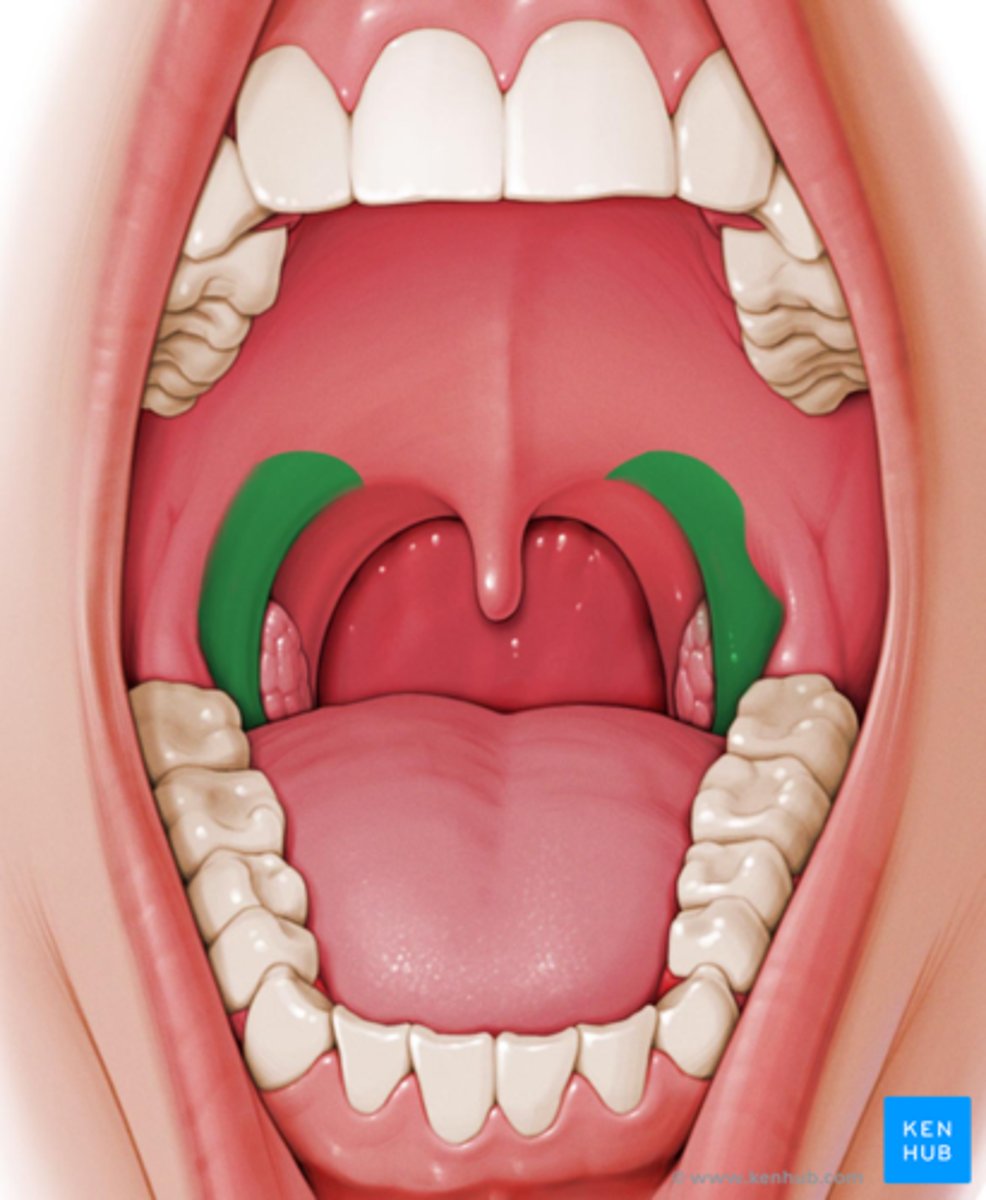
palatoglossal arch
identify the structure:
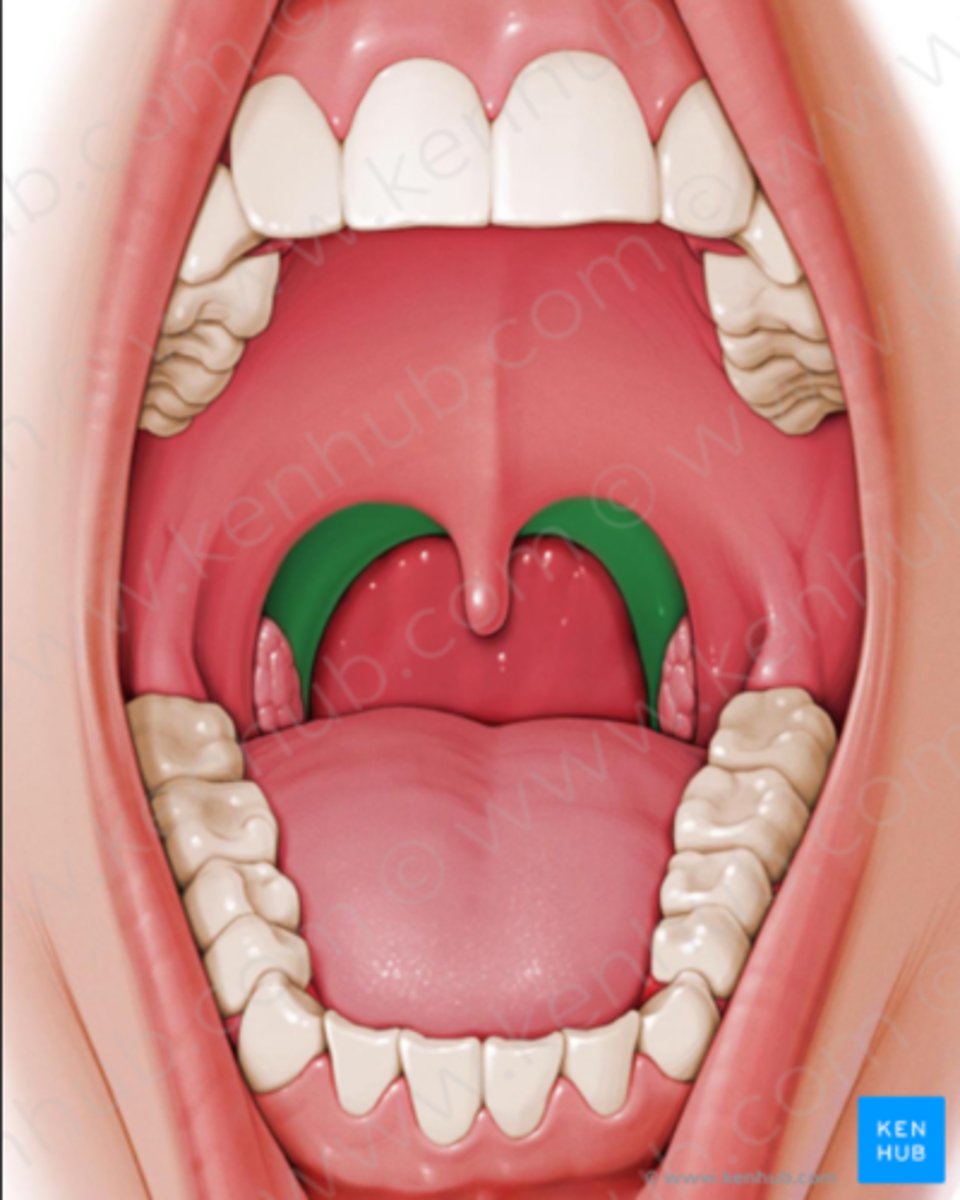
palatopharyngeal arch
identify the structure:
CN V
CN VII
CN IX
CN X
CN XII
what cranial nerves are relevant to the oral cavity/pharynx?
CN X
innervation for levator veli palatini
CN X
innervation for palatopharyngeus
CN X
innervation for palatoglossus
CN X
innervation for uvula
CN V (only soft palate muscle NOT innervated by CN X)
innervation for tensor veli palatini
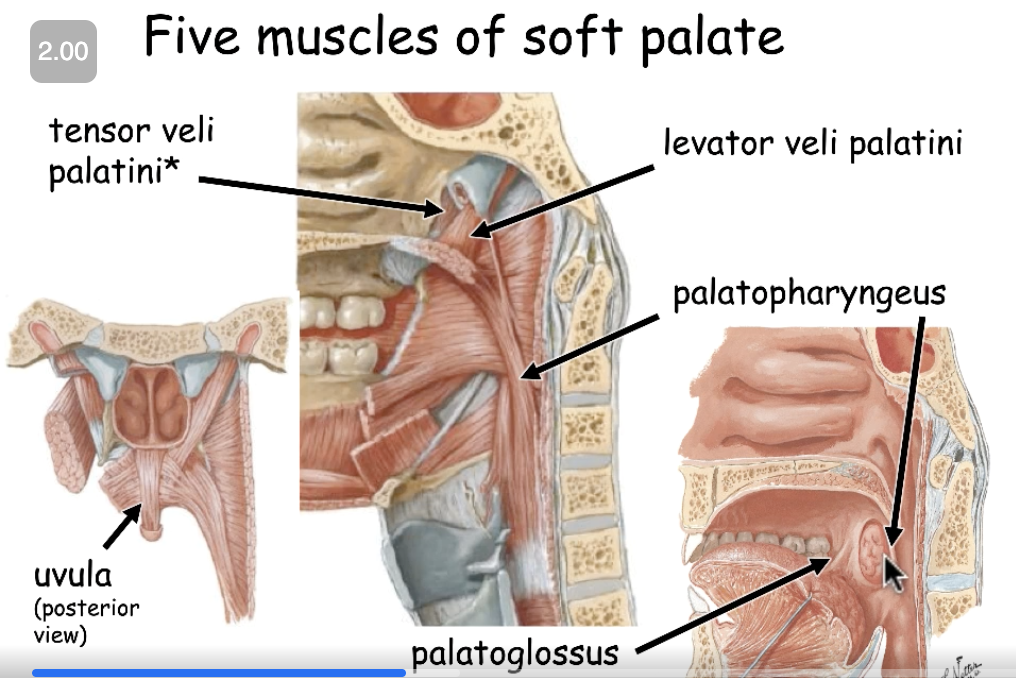
levator veli palatini
tensor veli palatini
palatopharyngeus
palatoglossus
uvula
list the 5 muscles of the soft palate:
palatoglossus m.
identify the structure:
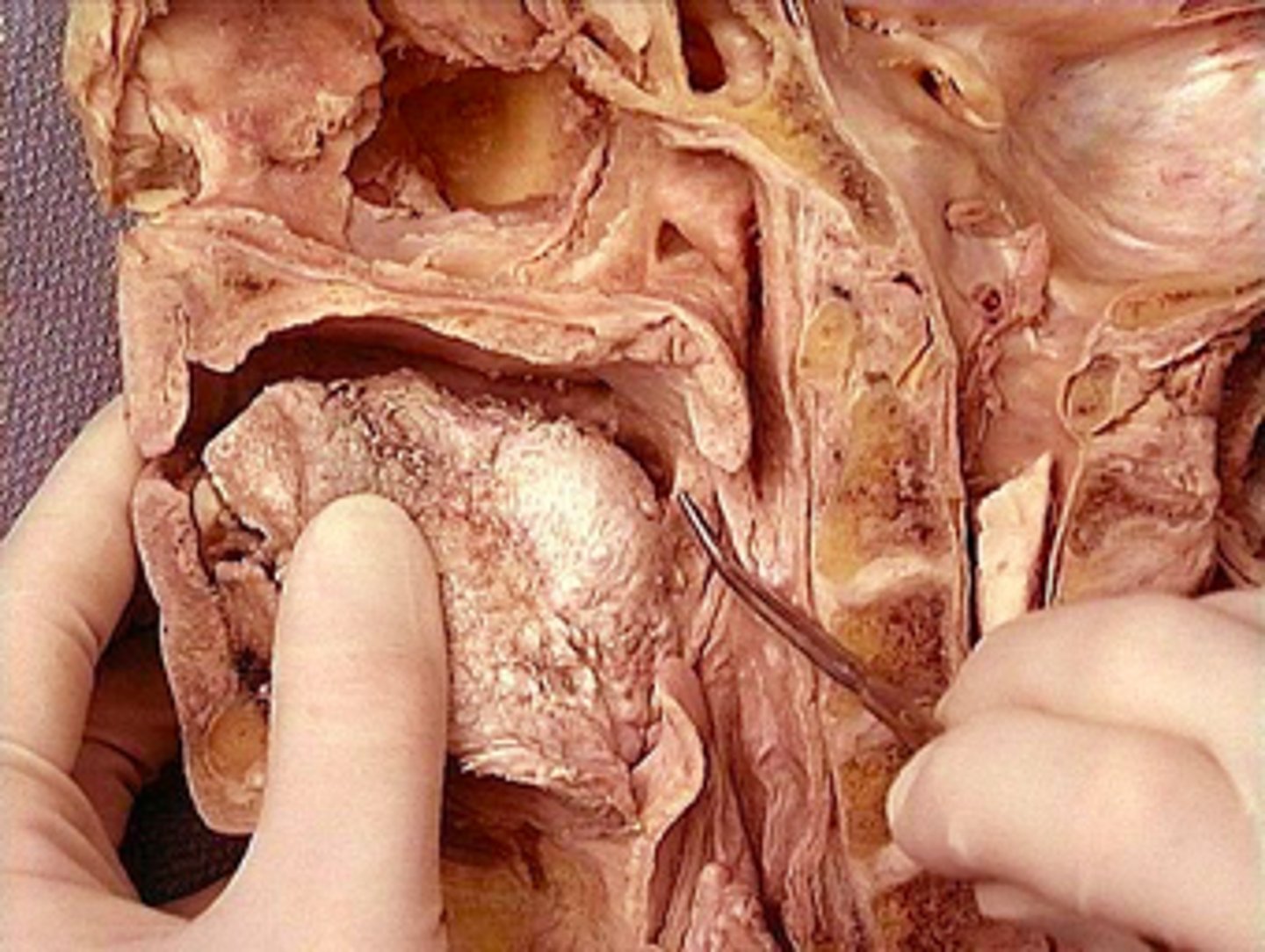
palatoglossus m.
muscle actions:
-elevates tongue, pulls down soft palate
- sealing oropharynx
-velar consonants (e.g. "K" sound)
-isolates vestibule saliva
-assists in swallowing
uvula m.
muscle actions:
- uvular consonants (none exist in English language)
-sealing nasopharynx during swallowing
_ can present elongated, shortened or bifid
uvula m.
identify the structure:
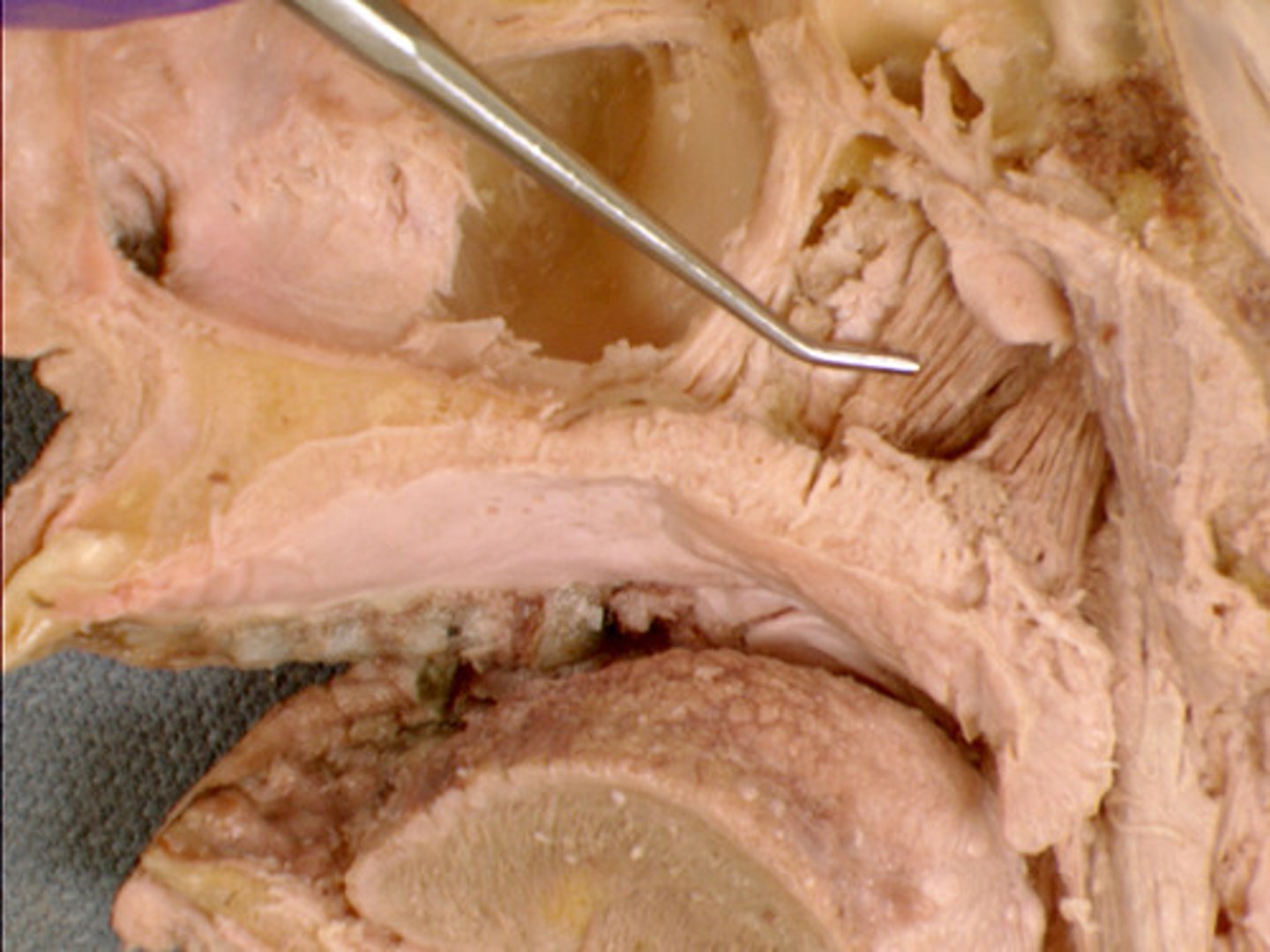
tensor veli palatini m.
muscle action: tenses soft palate
tensor veli palatini m.
identify the structure:
levator veli palatini m.
muscle action: elevates soft palate
levator veli palatini m.
identify the structure:
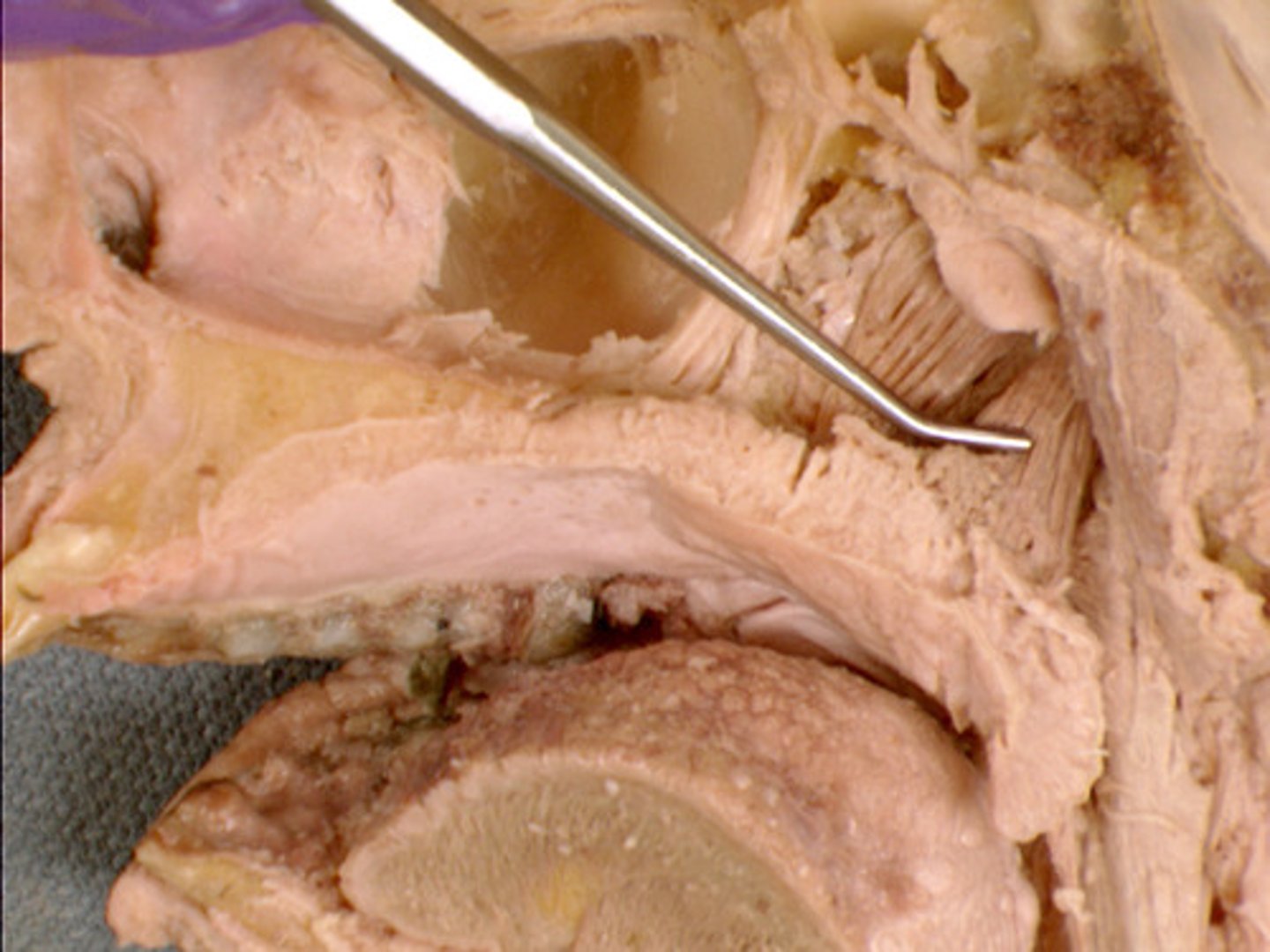
scaphoid fossa
what space does the tensor veli palatini m. and the levator veli palatini m. sit in?
tensor veli palatini m.
what muscles hooks around the hamulus of the pterygoid?
medial pterygoid plate
which pterygoid plate is the hamulus located on?
styloglossus m.
hyoglossus m.
genioglossus m.
palatoglossus m.
list the 4 extrinsic tongue muscles:
styloglossus m.
muscle action: retracts and cups the tongue
CN XII
innervation for styloglossus m.:
styloglossus m.
identify the structure:
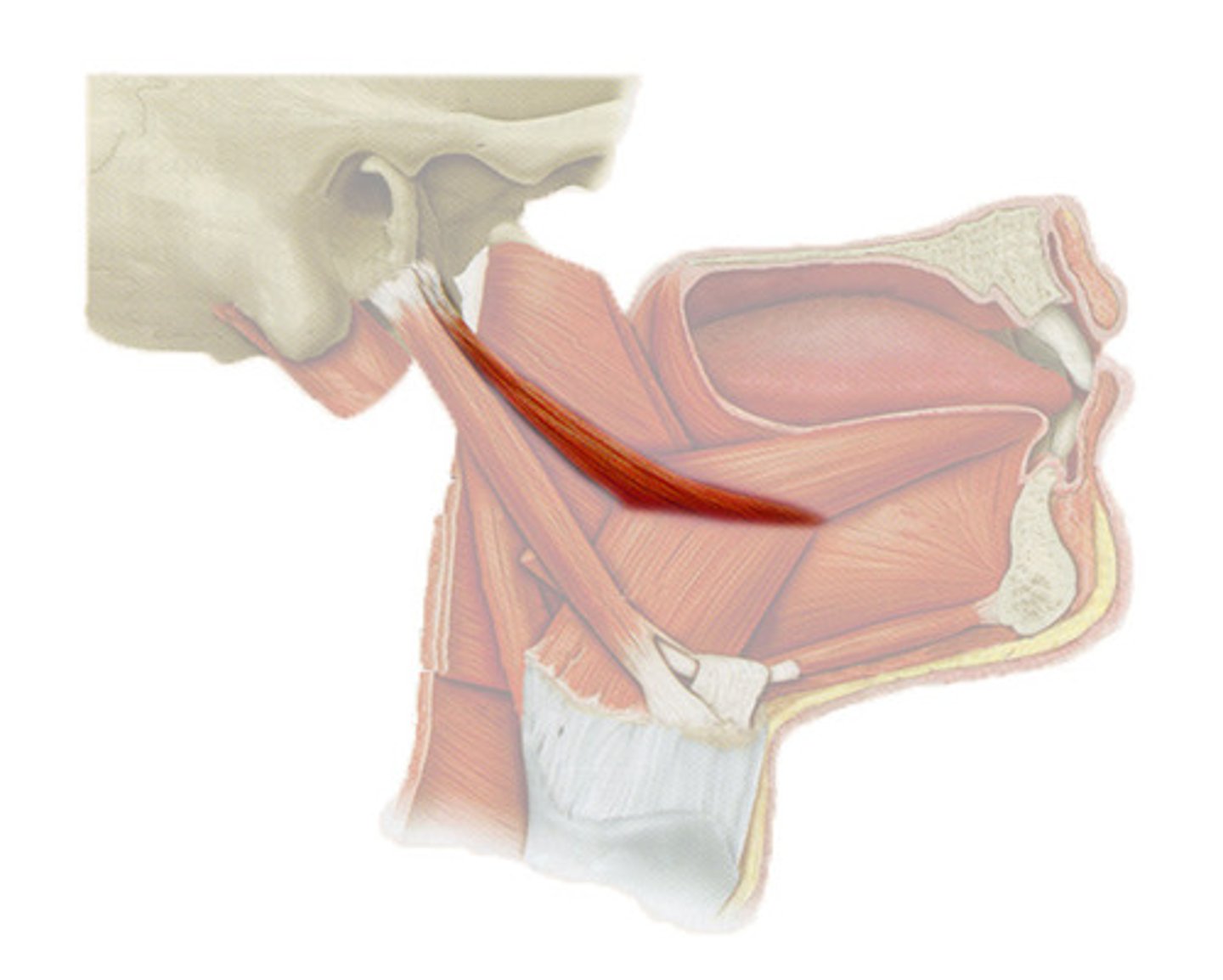
hyoglossus m.
identify the structure:
CN XII
innervation for hyloglossus m.:
hyoglossus m.
action: depresses tongue
genioglossus m.
muscle action:protrudes tongue
CN XII
innervation for genioglossus m.:
genioglossus m.
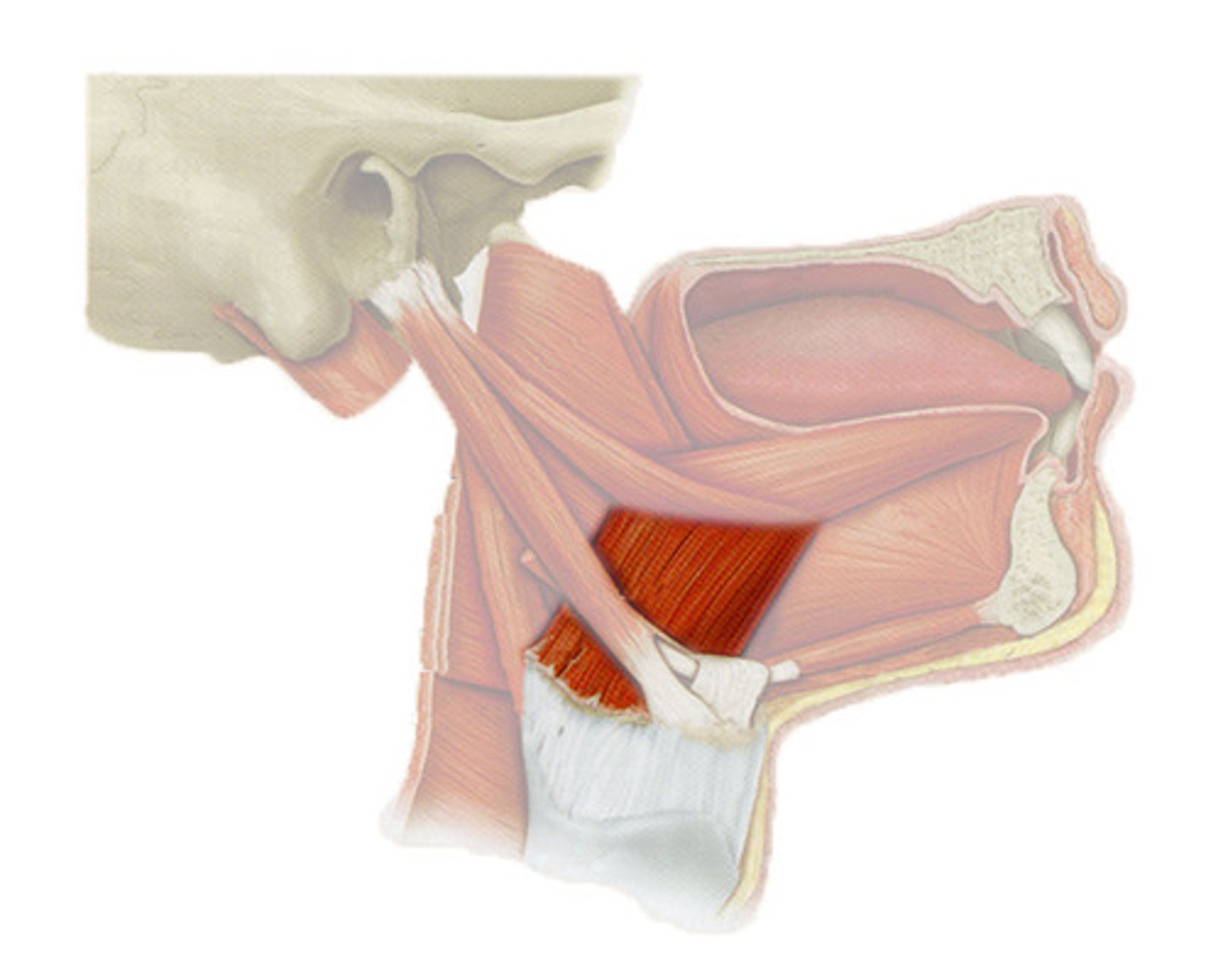
identify the structure:
palatoglossus m.
which of the tongue muscles does not have a bony attachment?
palatoglossus m. (CN X)
which of the tongue muscles is not innervated by CN XII? instead it is innervated by?
CN XII
motor innervation for the tongue is done by:
CN XII
identify the structure:
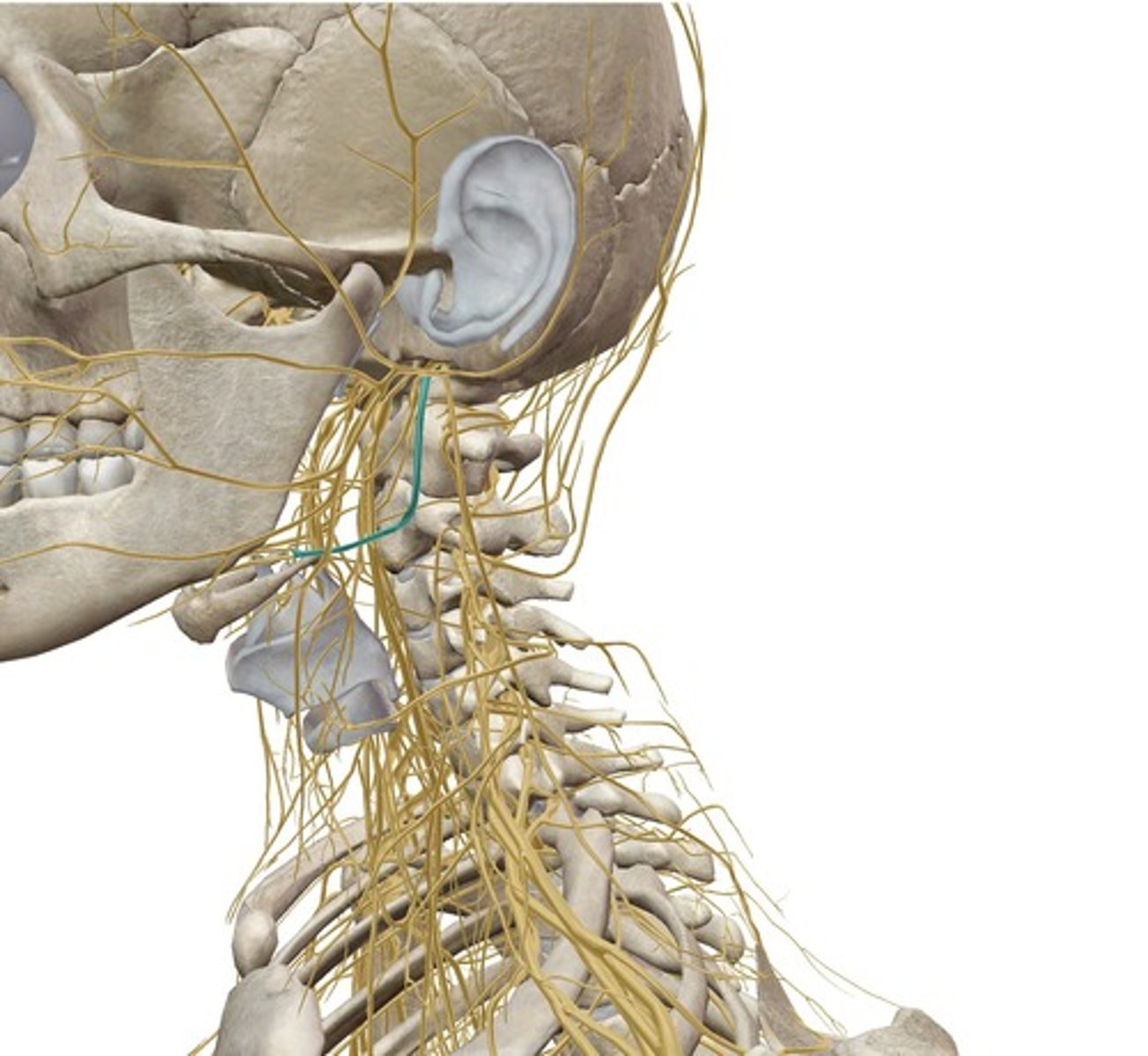
CN VII
motor innervation for the buccinator m.:
CN VII
motor innervation for obicularis oris m.:
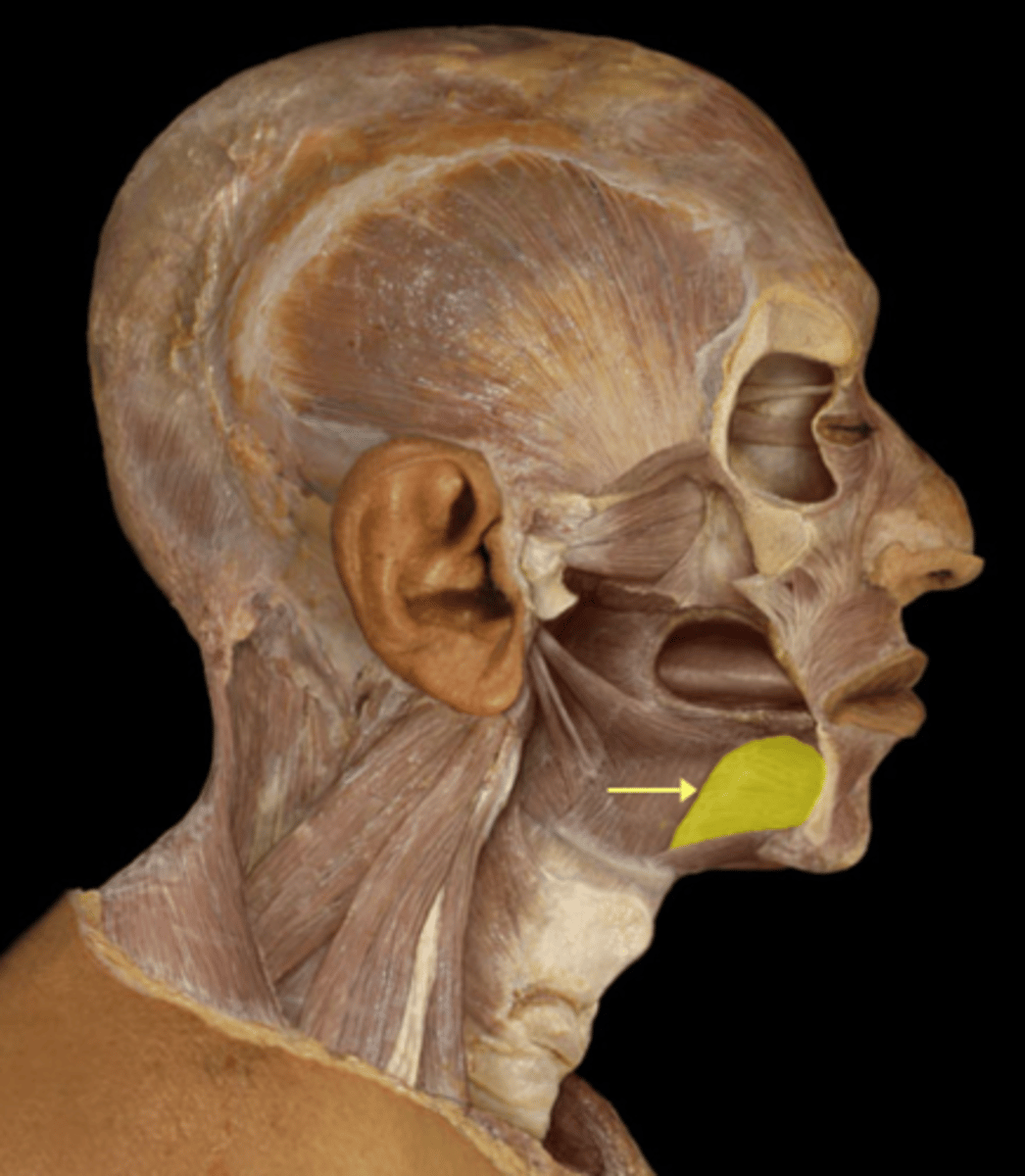
buccinator m.
obicularis oris m.
what two muscles is the musician using?
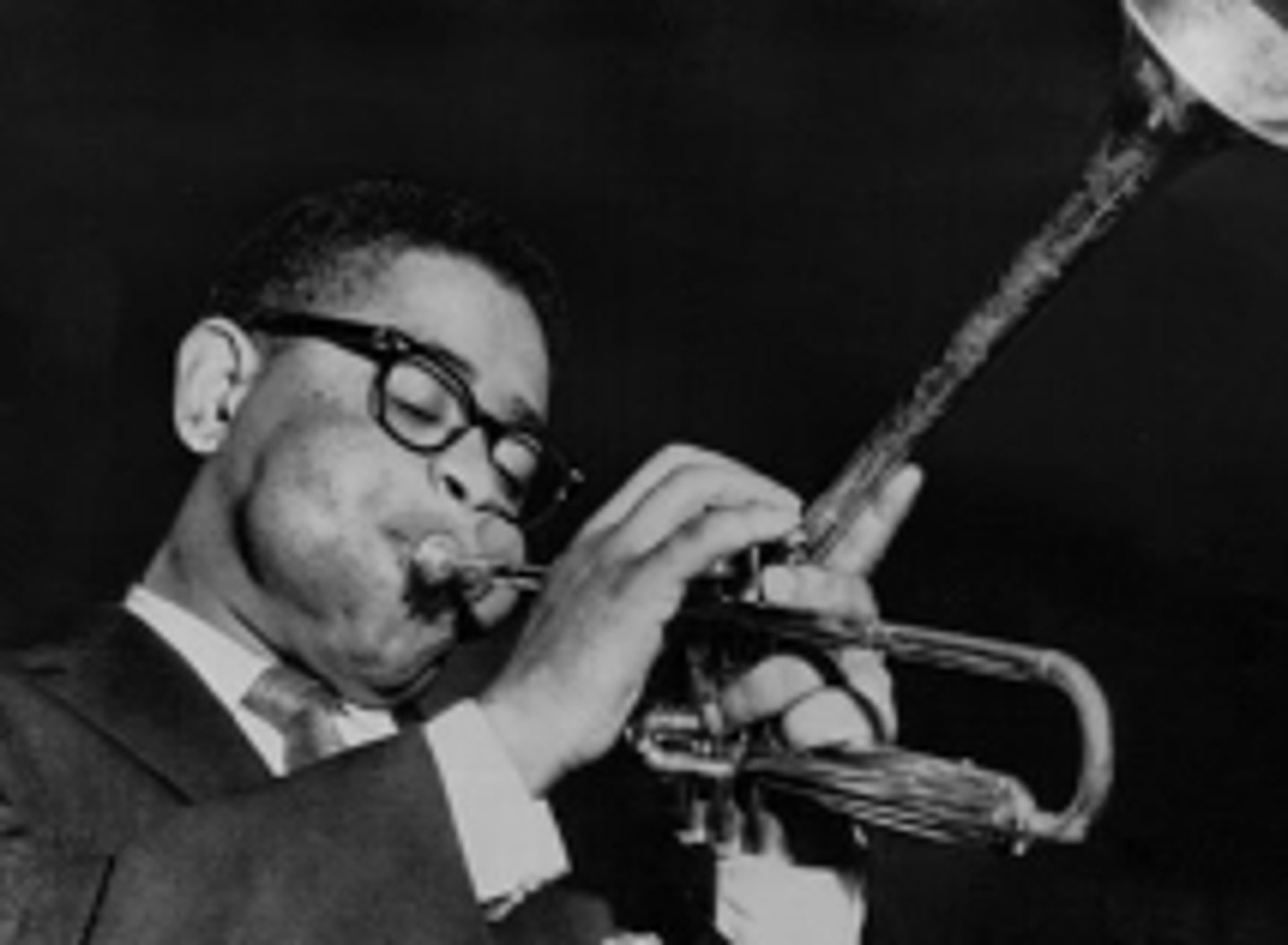

CN V3
the muscles of mastication are innervated by:
temporalis m.
masseter m.
medial pterygoid m.
lateral pterygoid m.
list the 4 muscles of mastication:
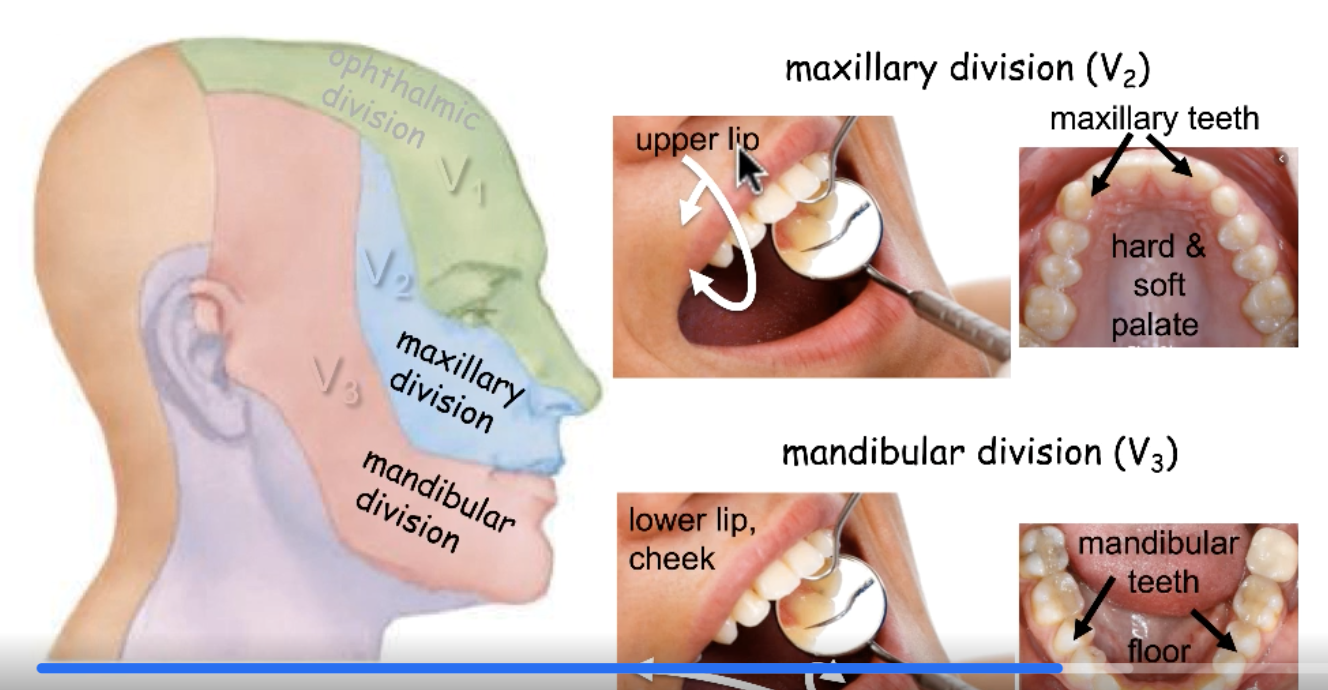
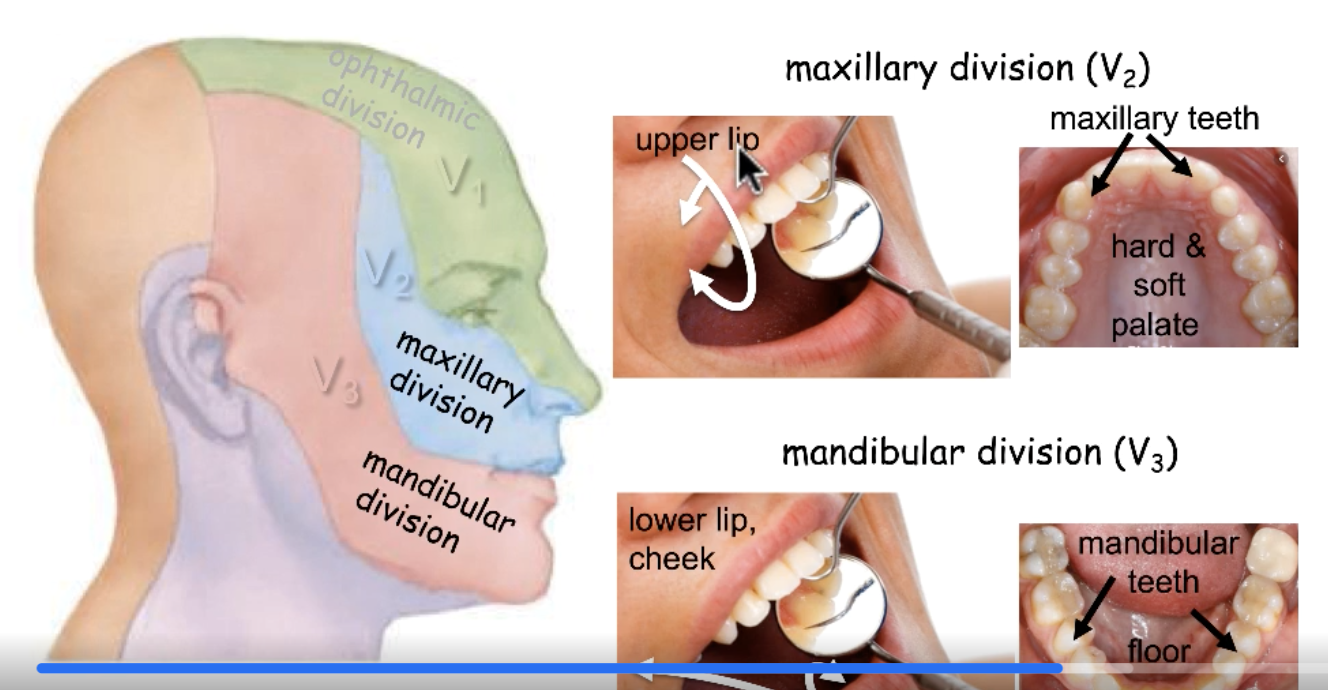
CN V2
sensory innervation for upper lip:
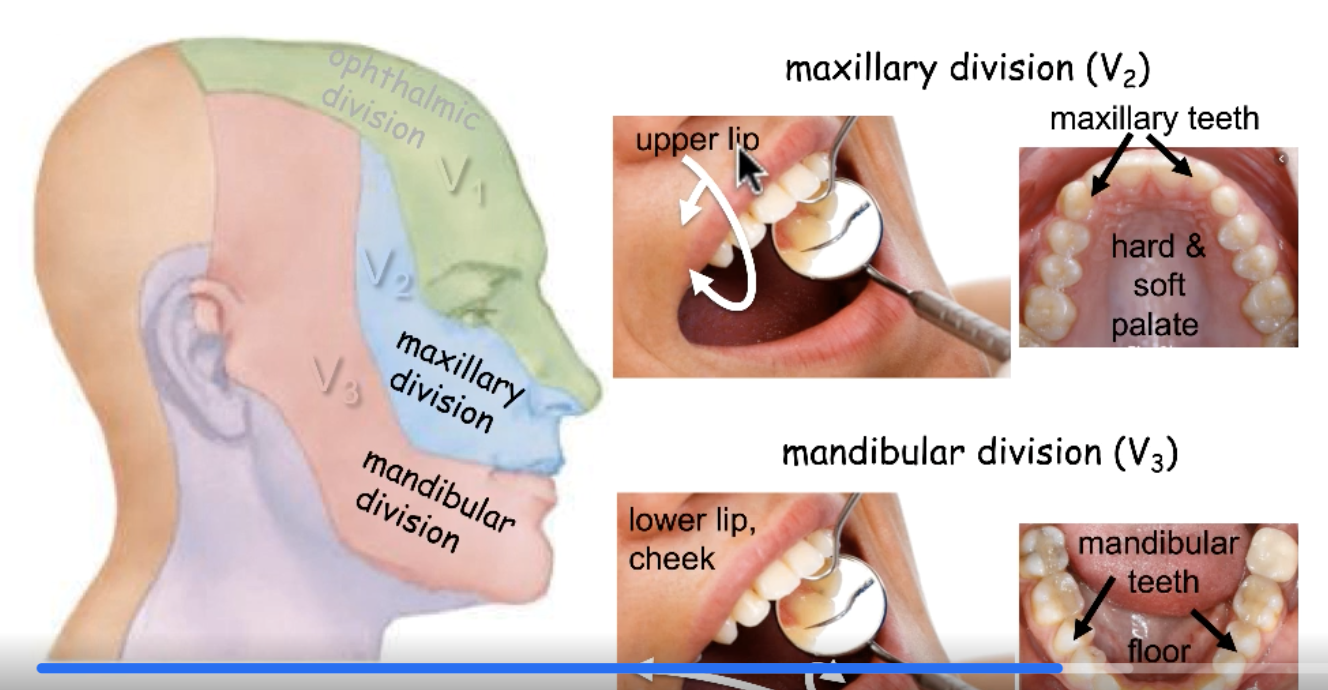
CN V2
sensory innervation for hard and soft palate:
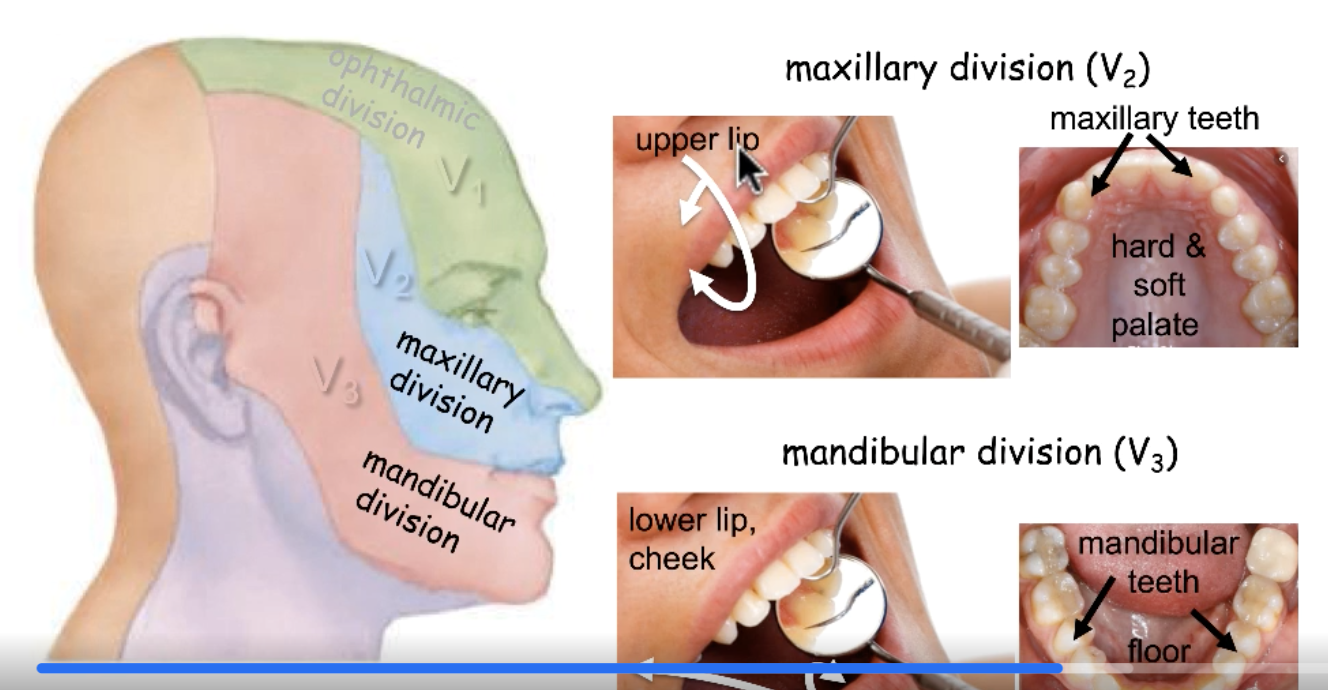
CN V2
sensory innervation for maxillary teeth:
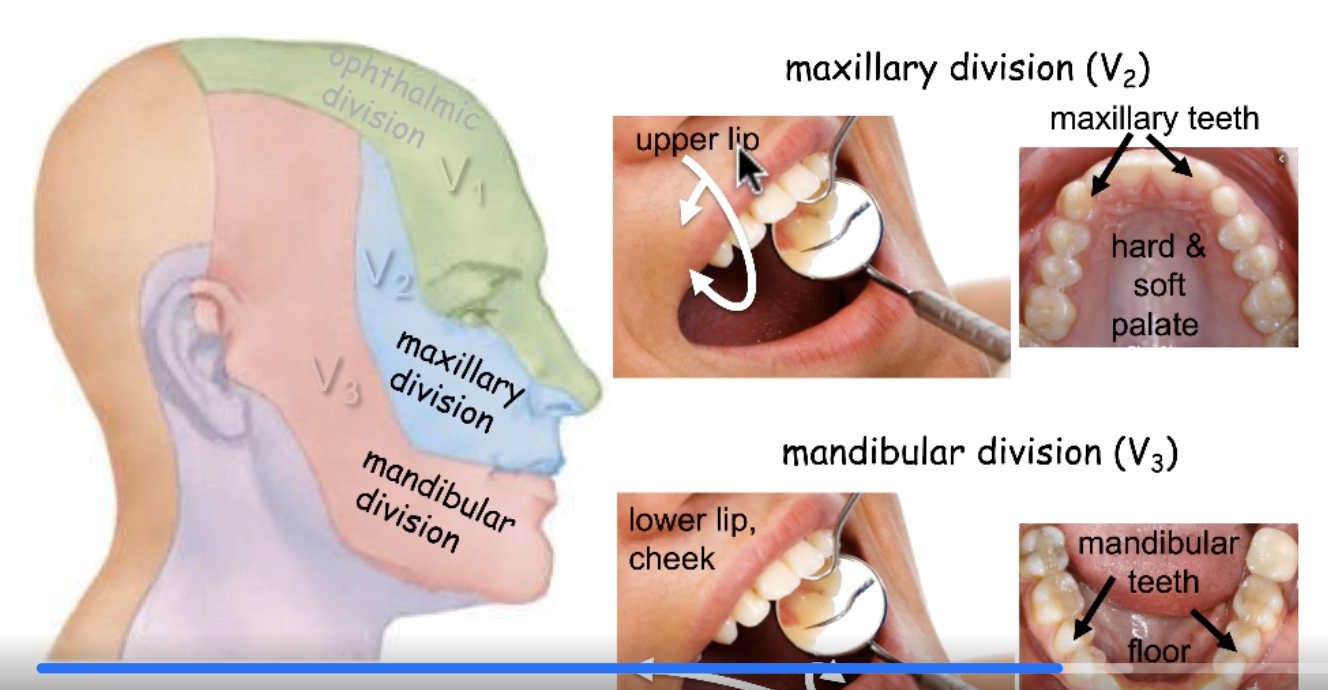
CN V3
sensory innervation for mandibular teeth:
CN V3
sensory innervation for cheeks:
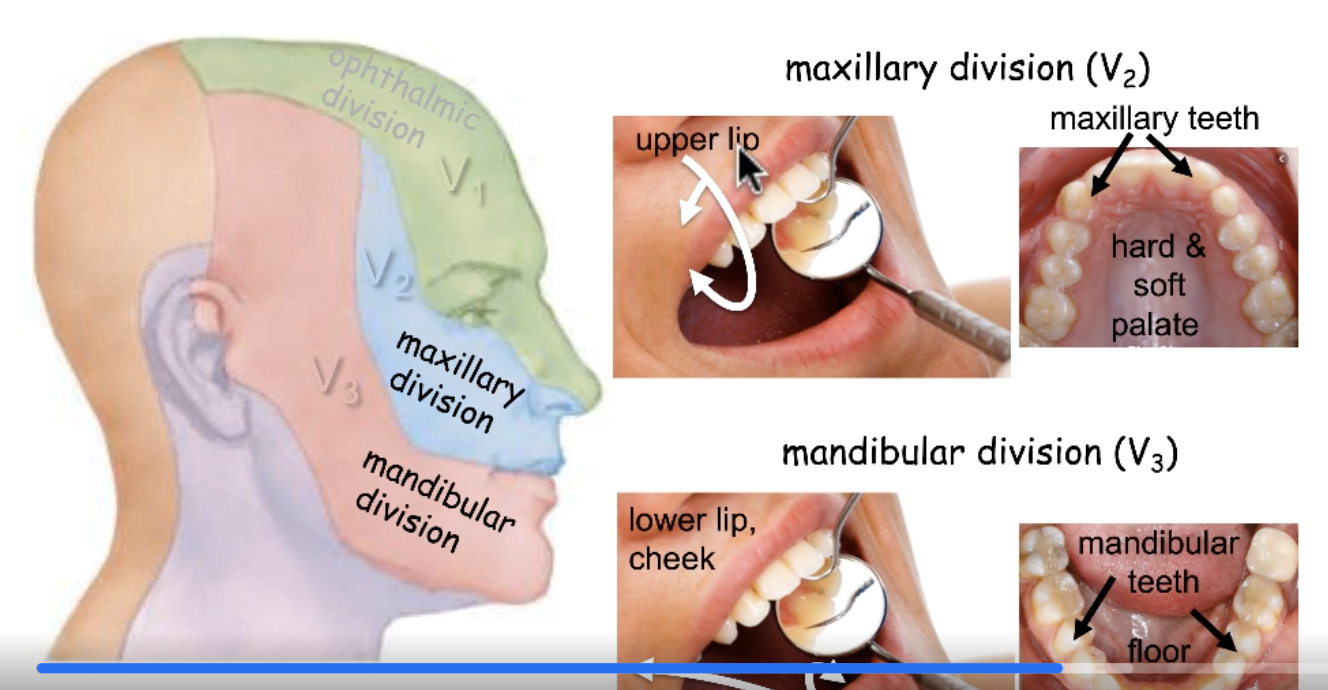
CN V3
sensory innervation for lower lip:
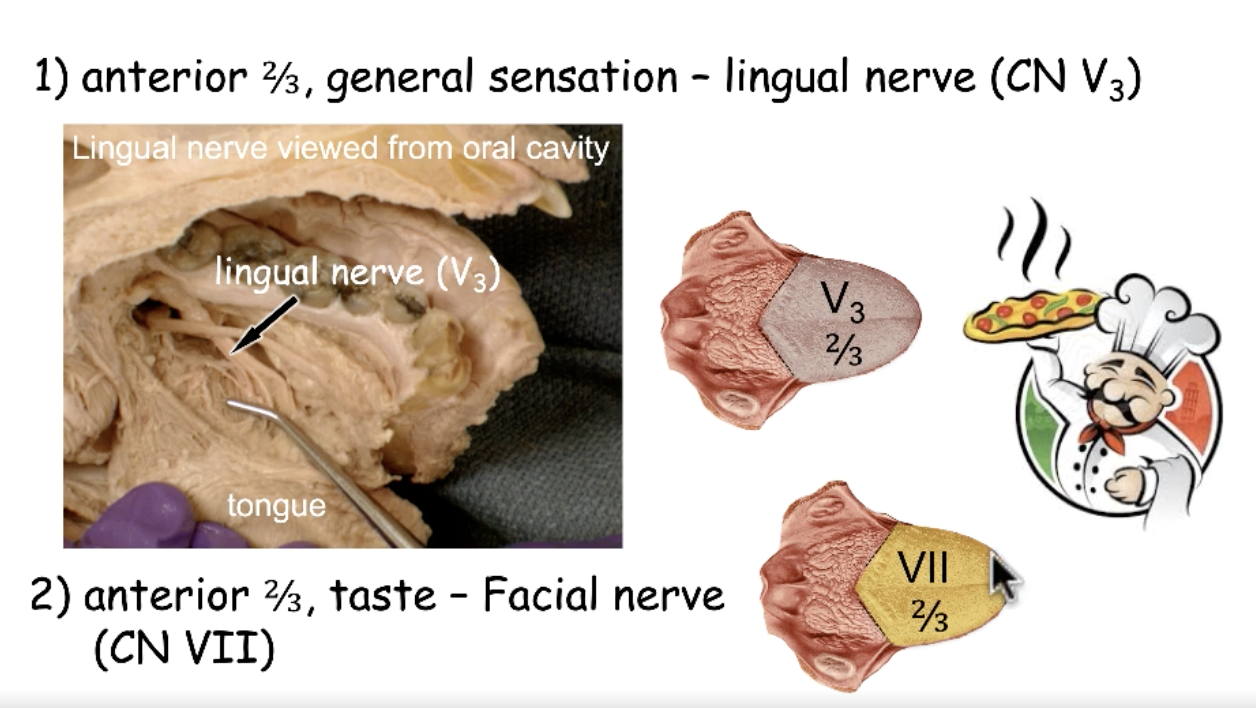
CN V3 (lingual nerve)
what nerve provides general sensation to the anterior 2/3 tongue?
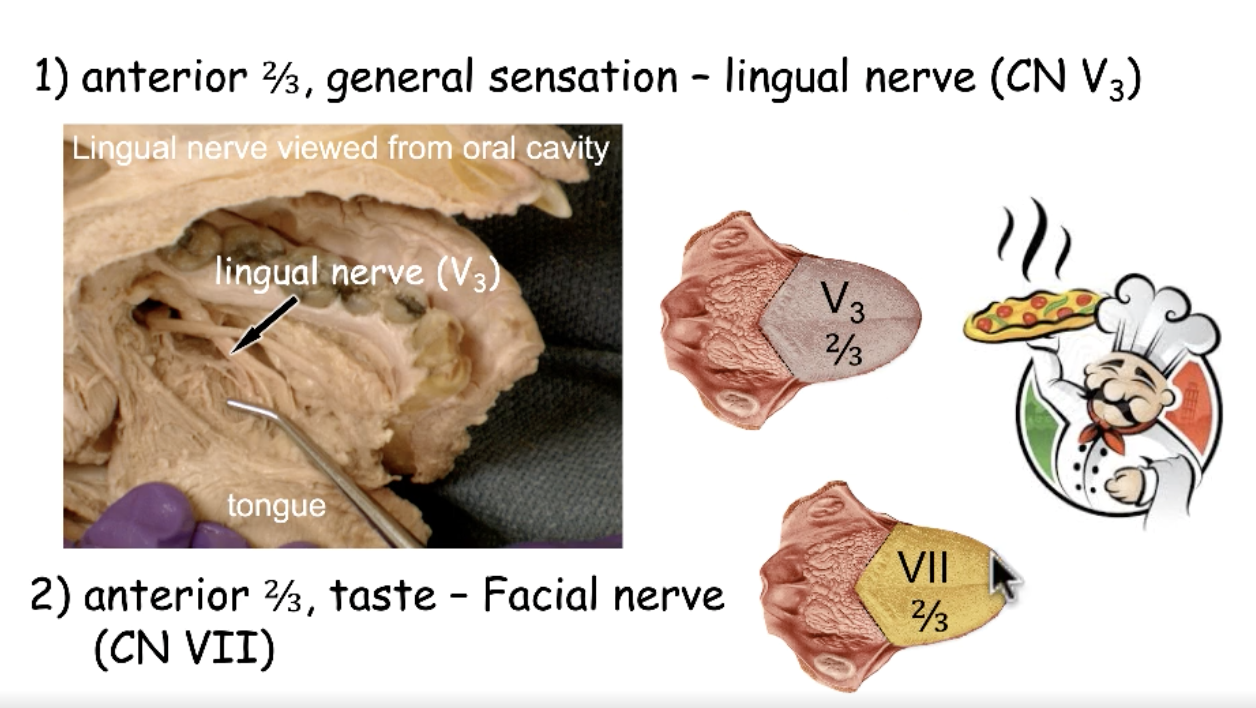
CN VII
what nerve provides taste to the anterior 2/3 tongue?
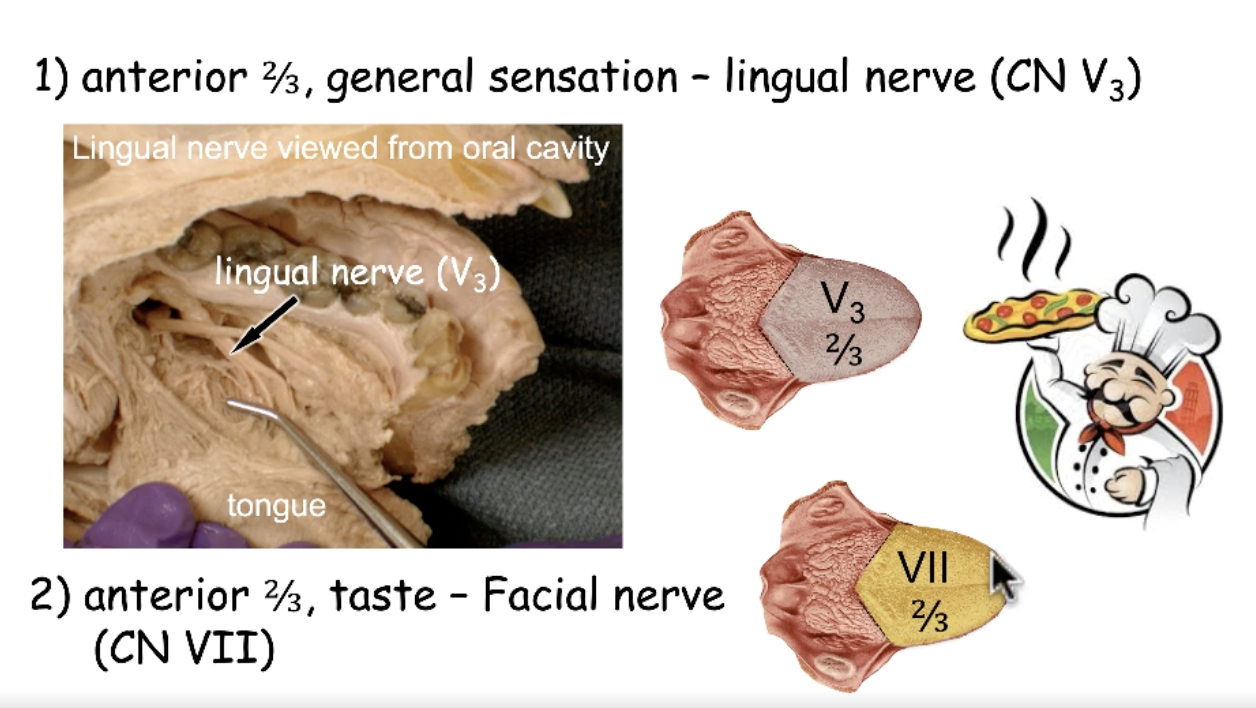
CN V3
the lingual n. is a branch of:
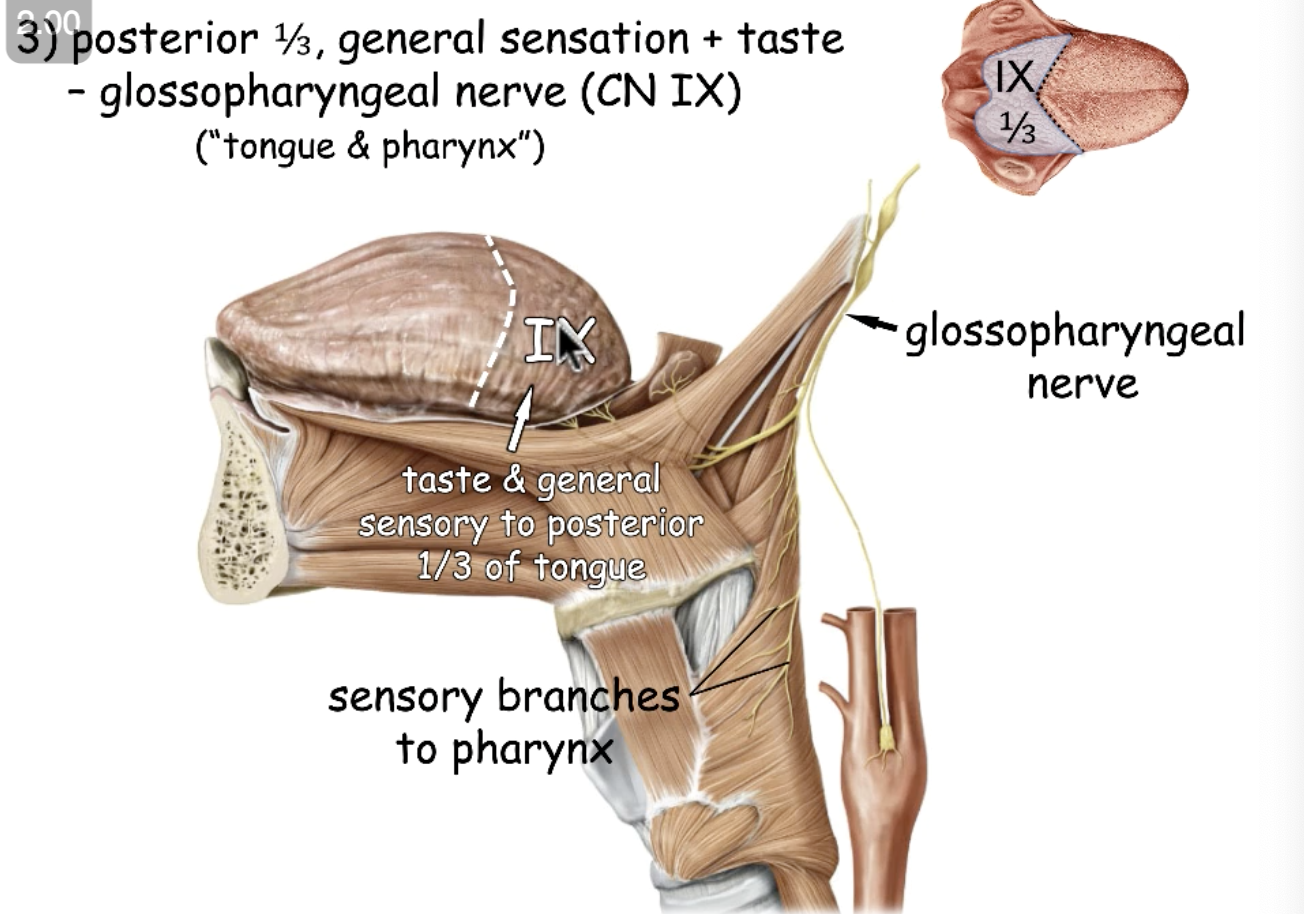
CN IX
what nerve provides general sensation and taste to the posterior 1/3 tongue?
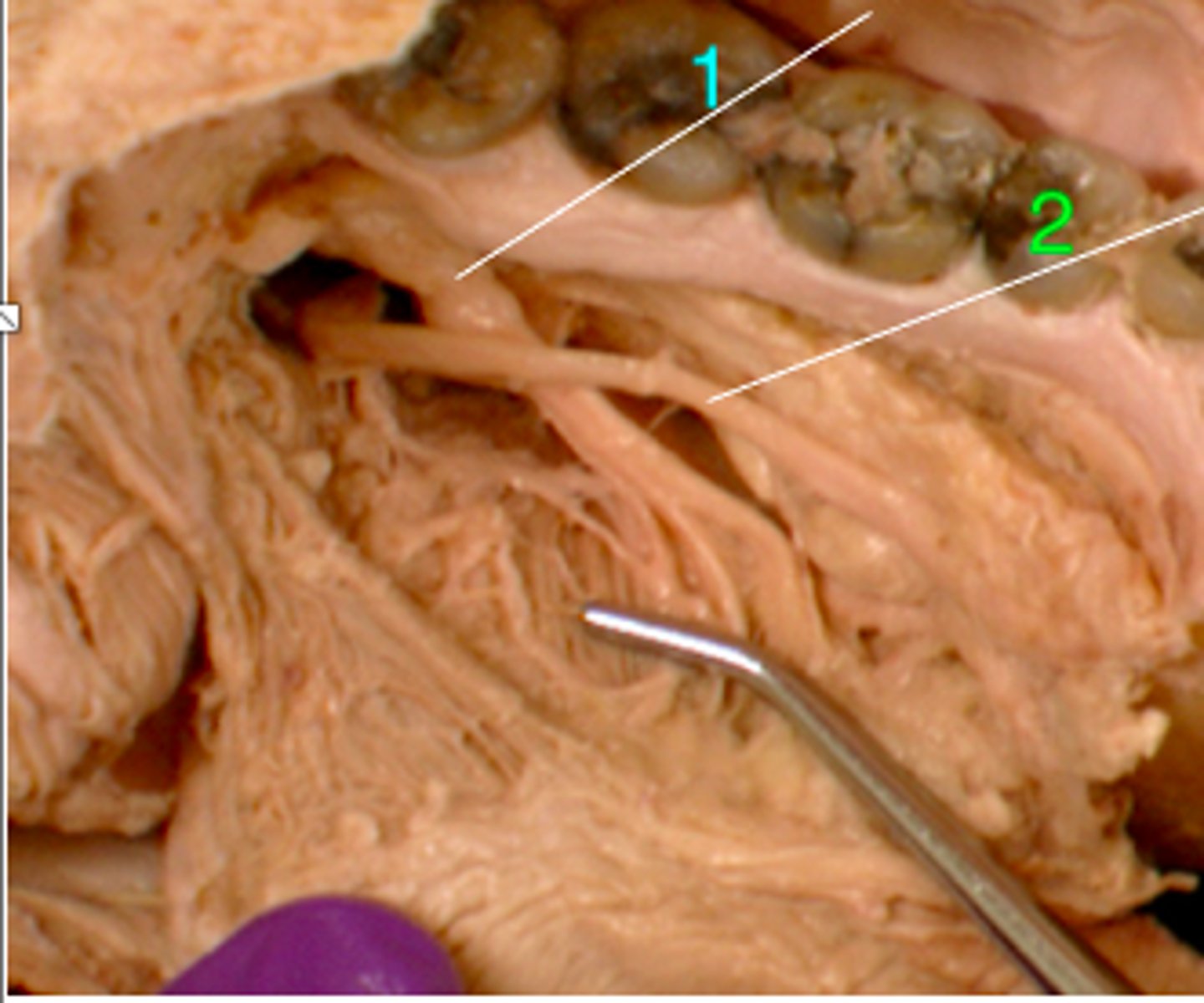
submandibular duct
what structure crosses over the lingual n.?
lingual n.
identify structure #1
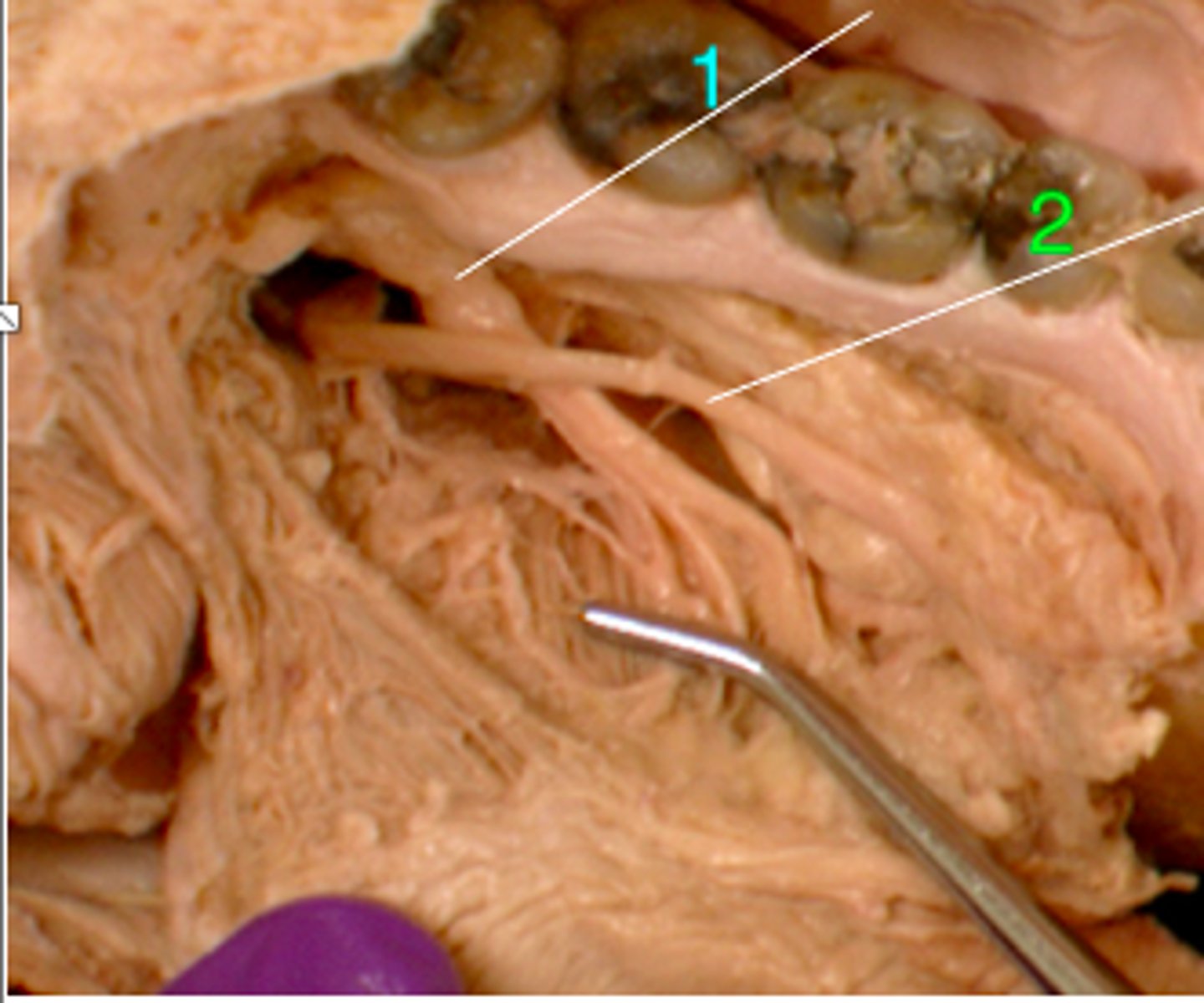
submandibular duct
identify structure #2
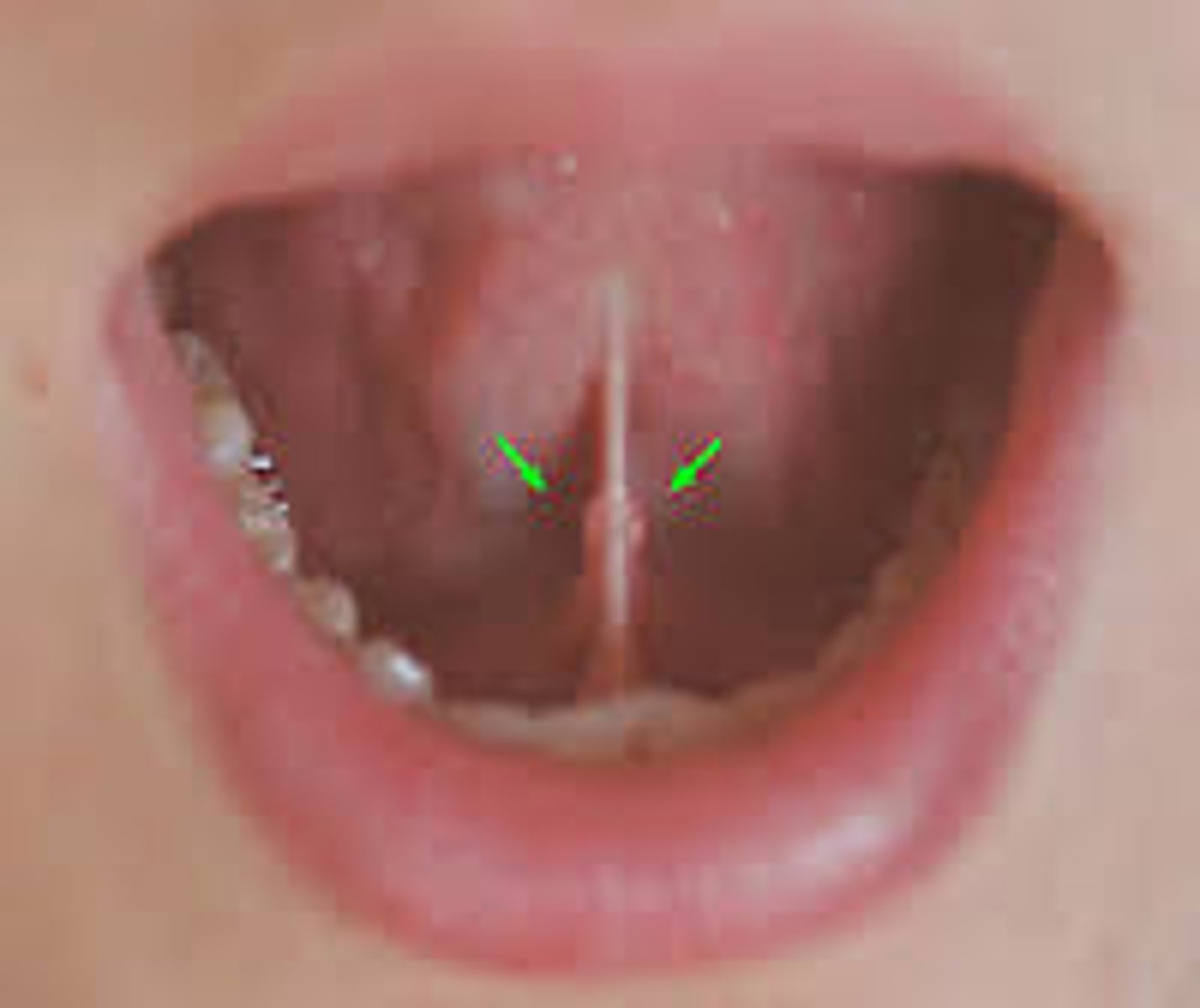
sublingual caruncle (opening to submandibular duct)
identify the structure:
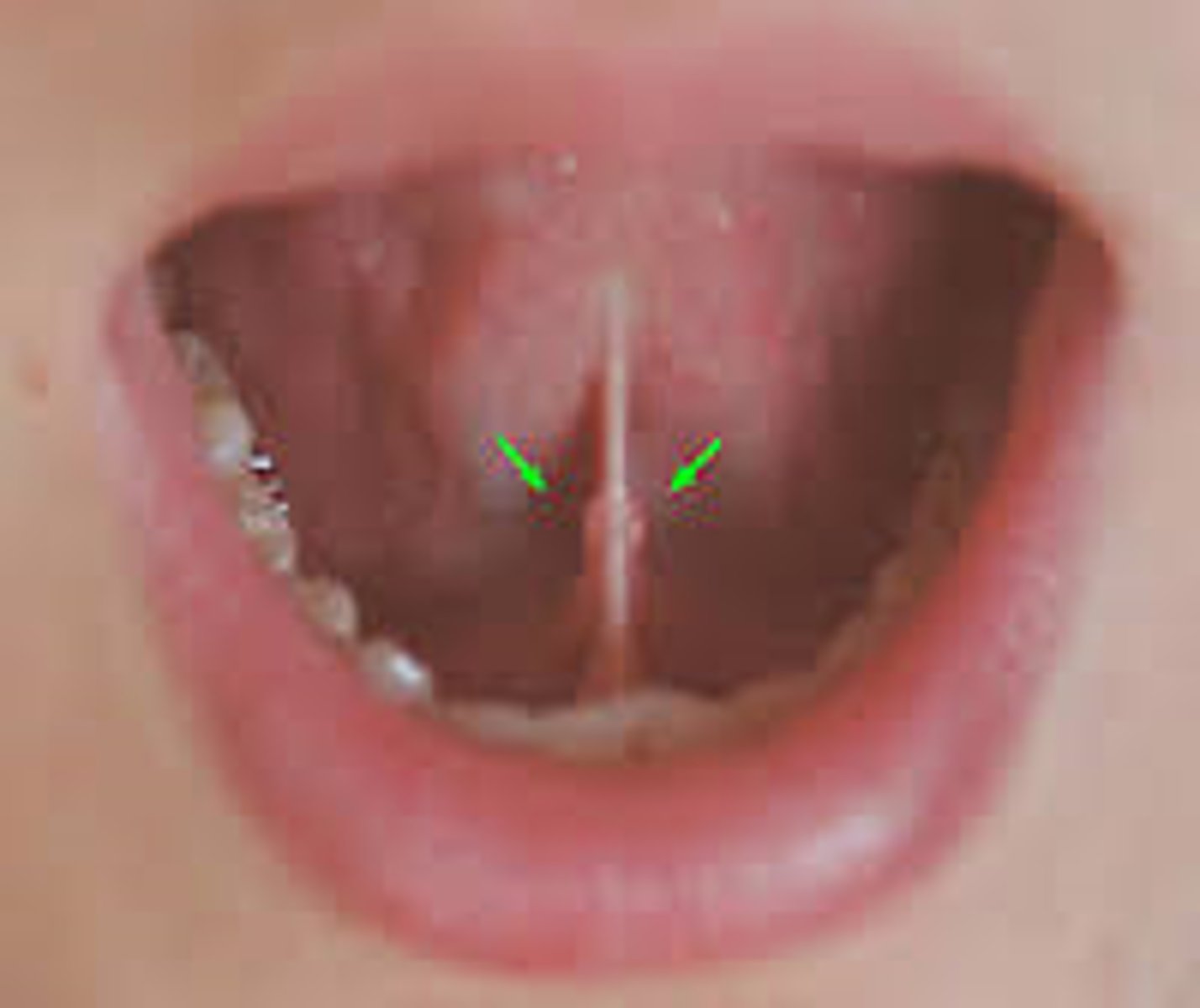
submandibular duct
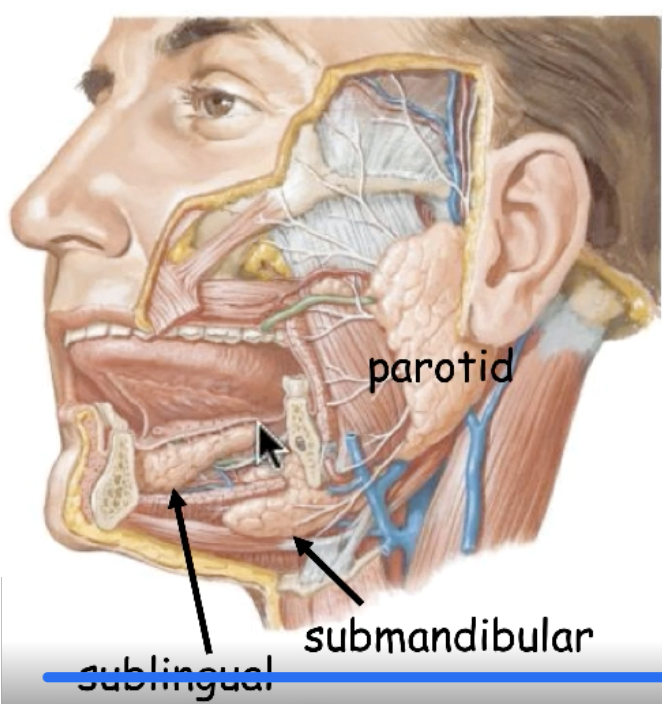
the saliva secreted from this location is from what gland?
parasympathetic
salivary secretion is what type of autonomic function?
CN IX
parasympathetic salivary stimulation of the parotid gland is done by:
CN VII
parasympathetic salivary stimulation of the submandibular, sublingual and all minor salivary glands is done by:
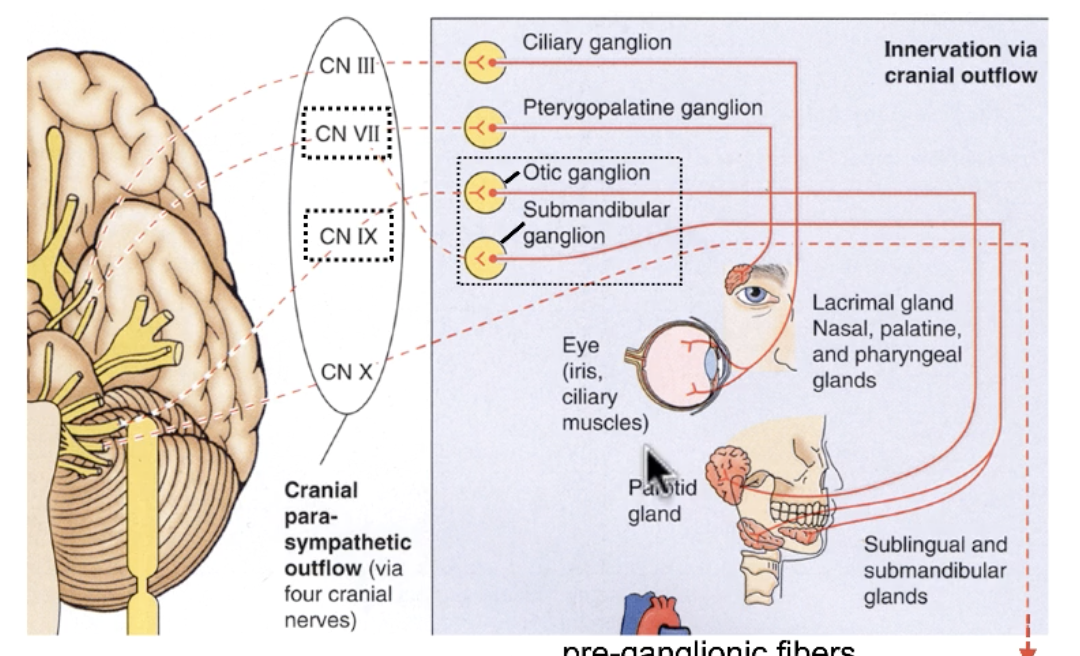
otic ganglion
the cell bodies for postsynaptic parasympathetic fibers for parotid gland salivary secretion are found in the:
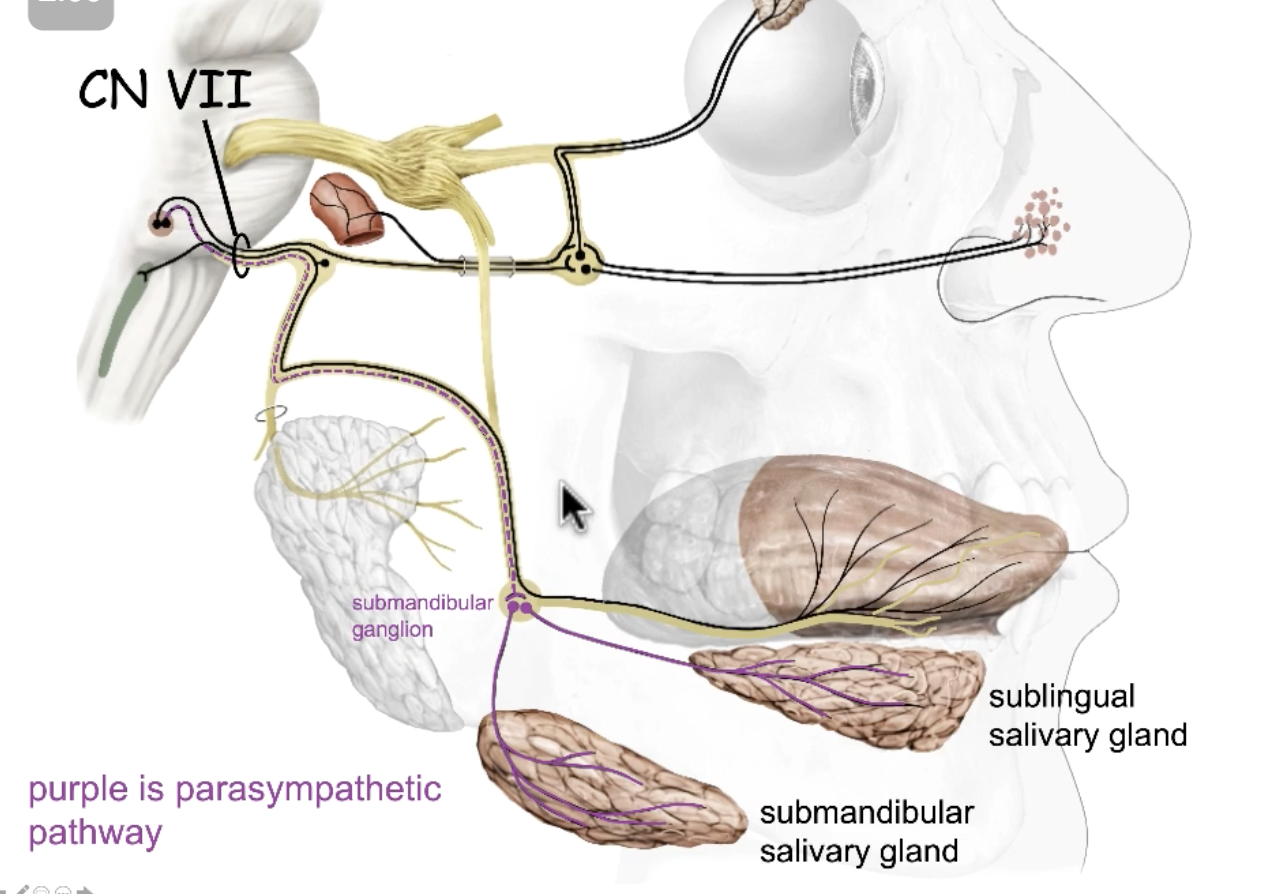
submandibular ganglion
the cell bodies for postsynaptic parasympathetic fibers for submandibular/ sublingual gland salivary secretion are found in the:
oropharynx
identify the structure:
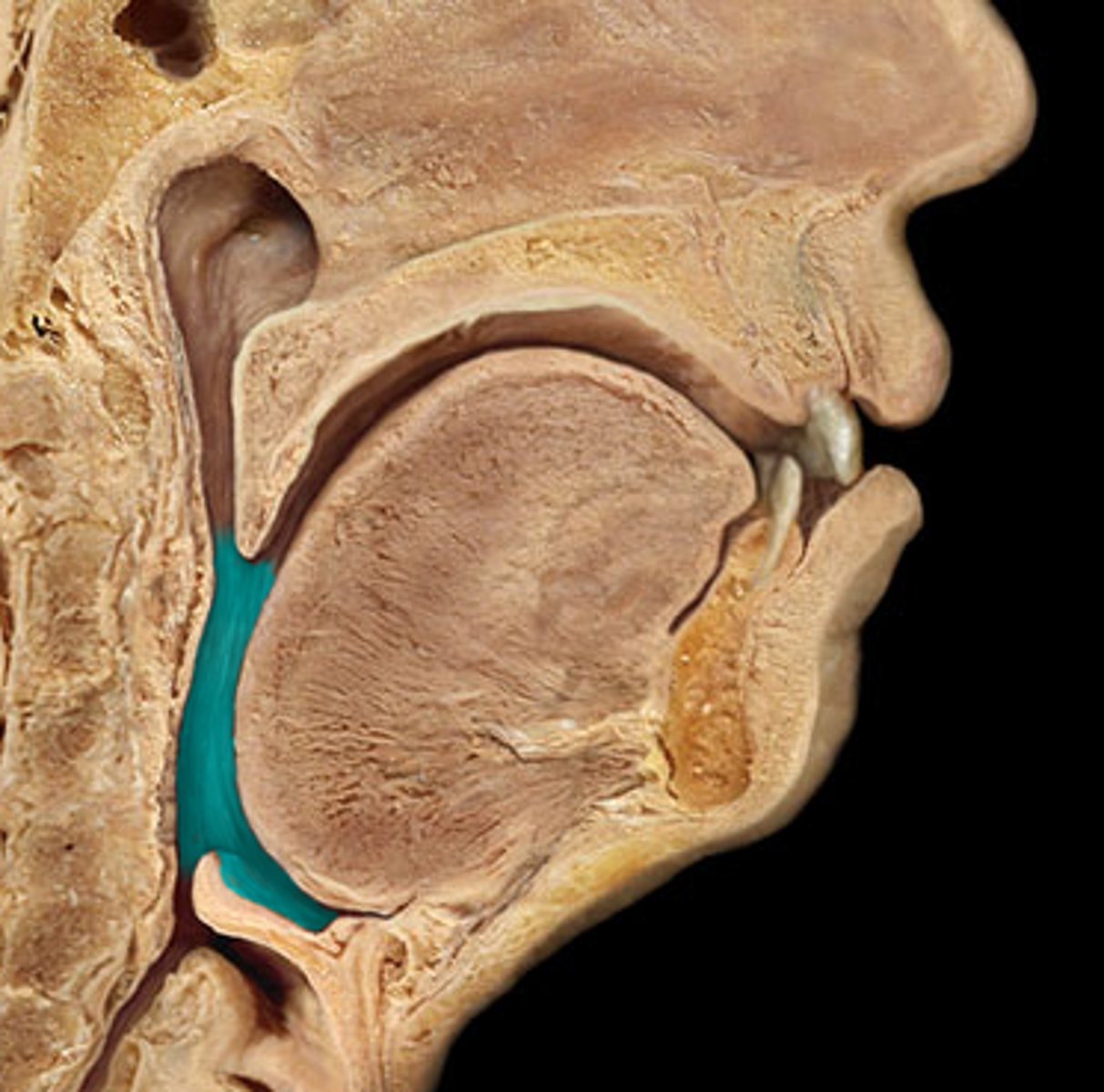
soft palate to epiglottis
palatine tonsil
palatopharyngeus m.
superior constrictor m.
middle constrictor m.
what does the oropharynx consist of?
superior pharyngeal constrictor
middle pharyngeal constrictor
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
what are the outer circular layer muscles of the pharynx?
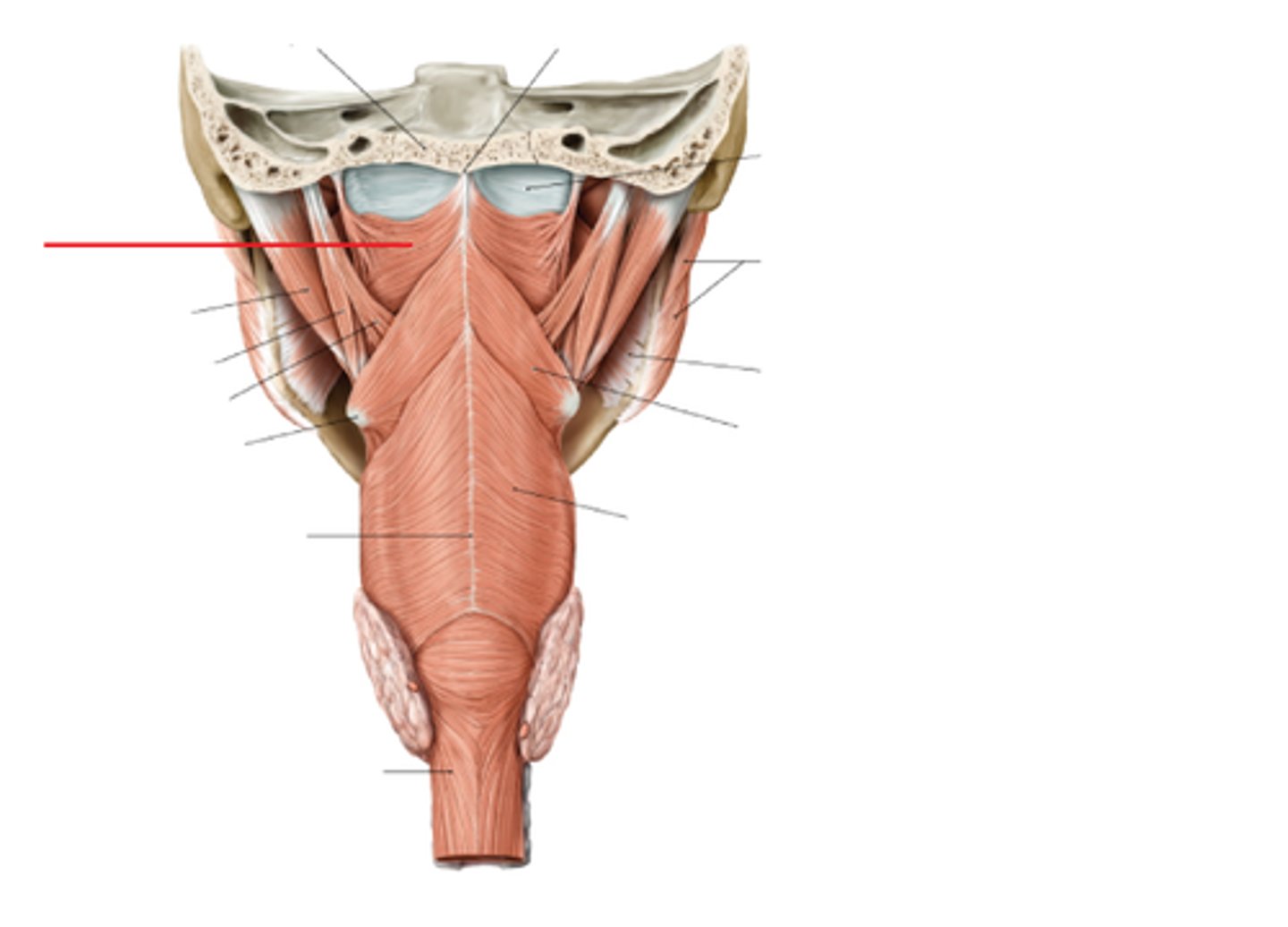
superior pharyngeal constrictor m.
identify the structure:
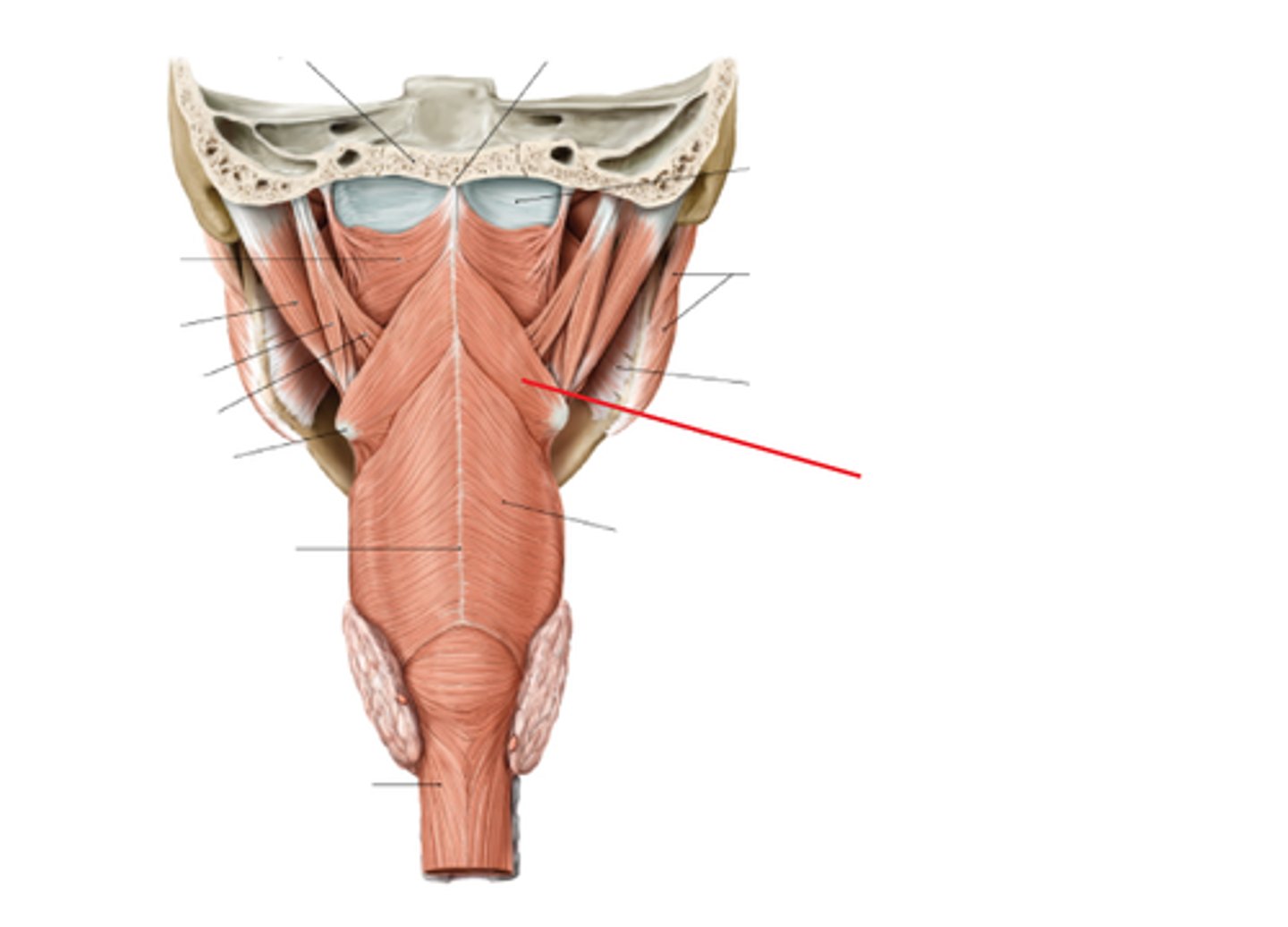
middle pharyngeal constrictor m.
identify the structure:
inferior pharyngeal constrictor m.
identify the structure:
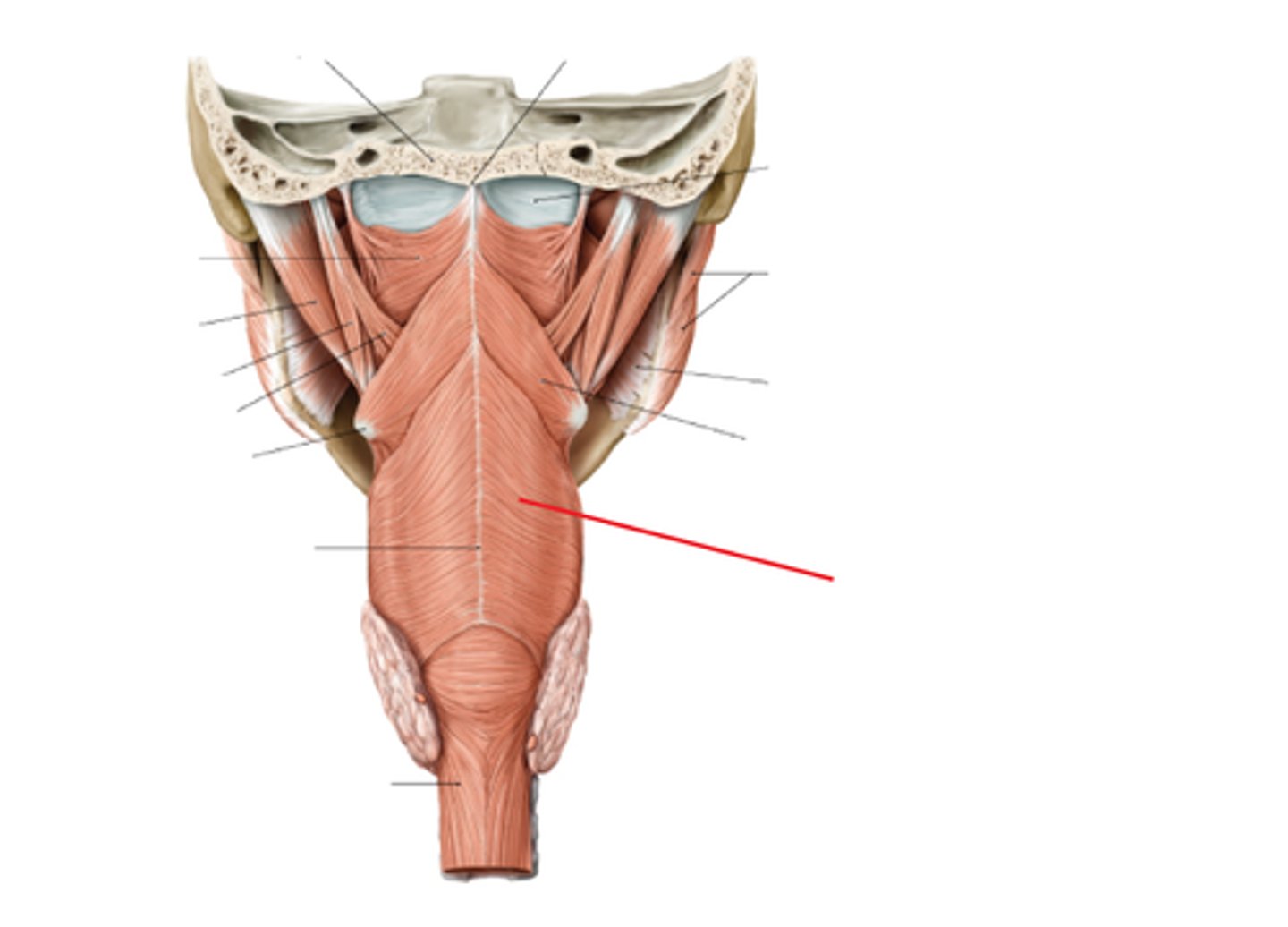
middle pharyngeal constrictor m.
what muscle wraps into the deep surface of the hyoid bone?
pharyngeal raphe
identify the structure:
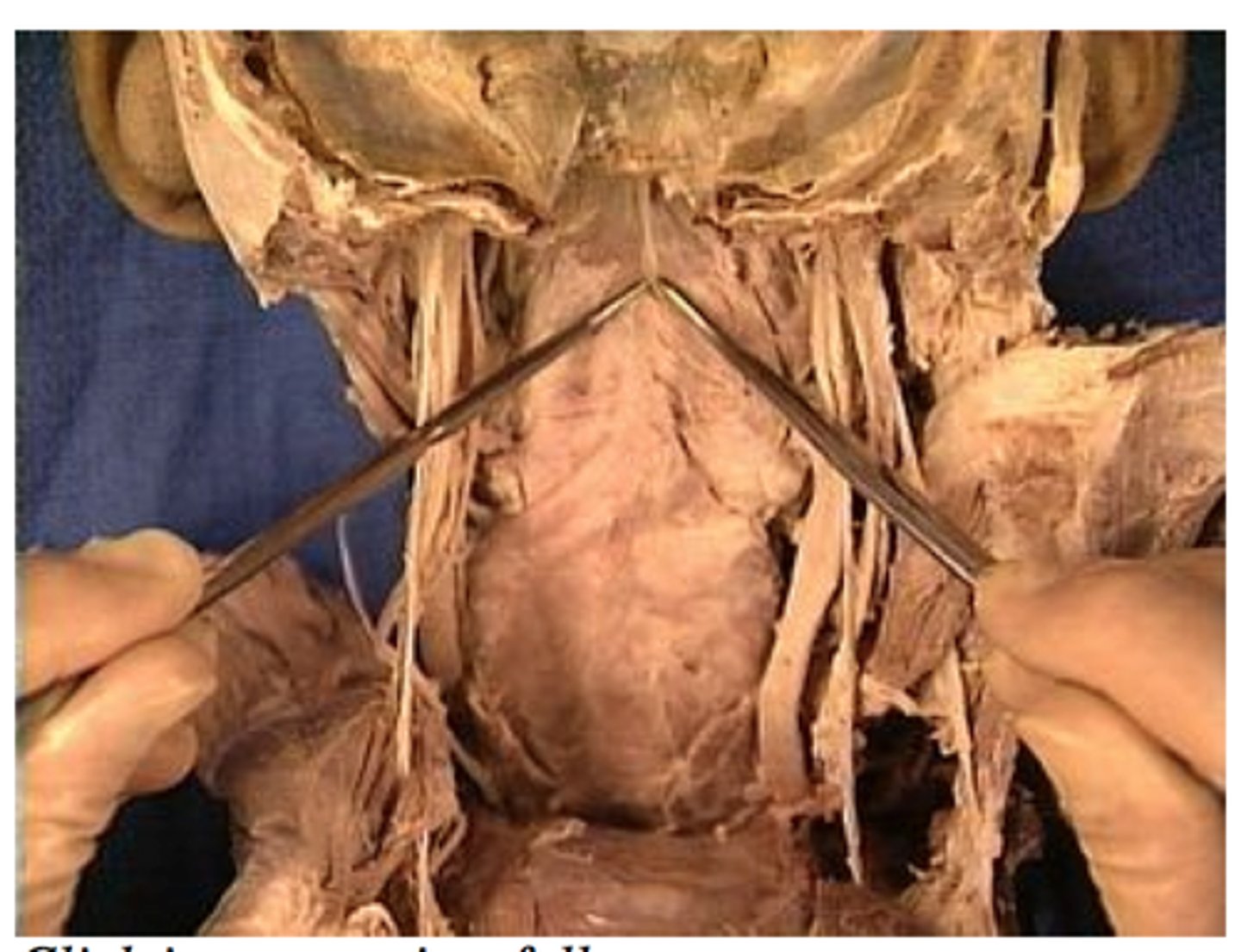
pharyngeal tubercle
the pharyngeal raphe suspends from the base of the skull from the:
salpingopharyngeus m.
identify the structure:
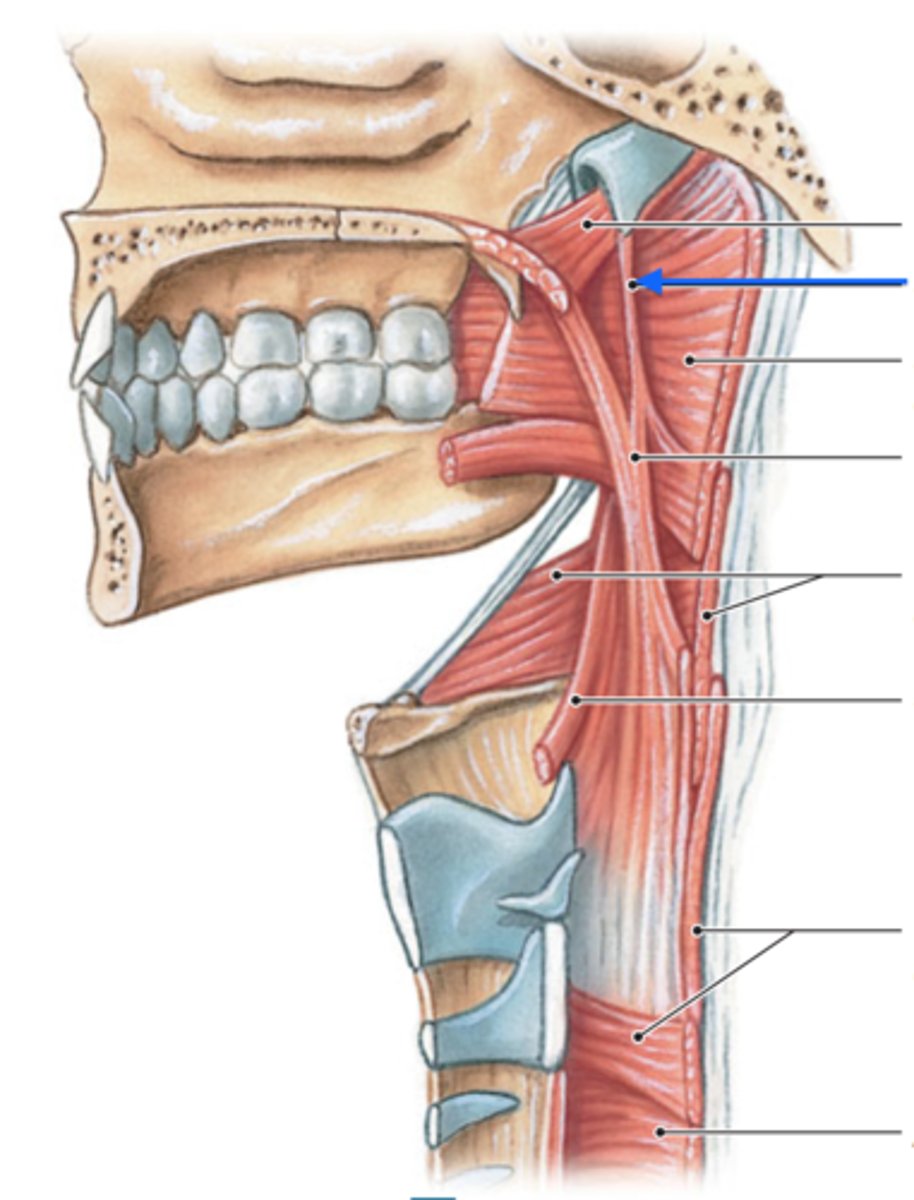
CN X
innervation for salpingopharyngeus m.:
palatopharyngeus m.
identify the structure:
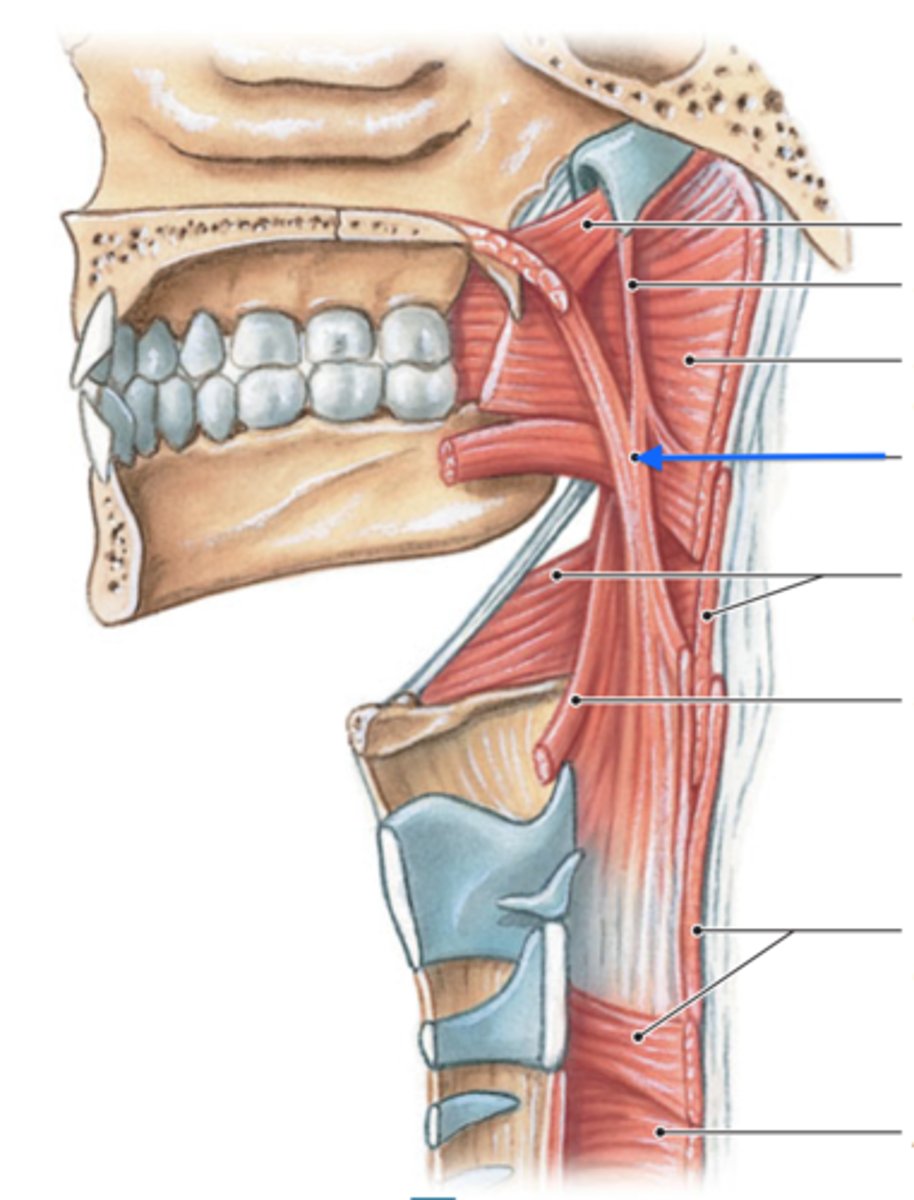
CN X
innervation for palatopharyngeus m.:
stylopharyngeus m.
identify the structure:
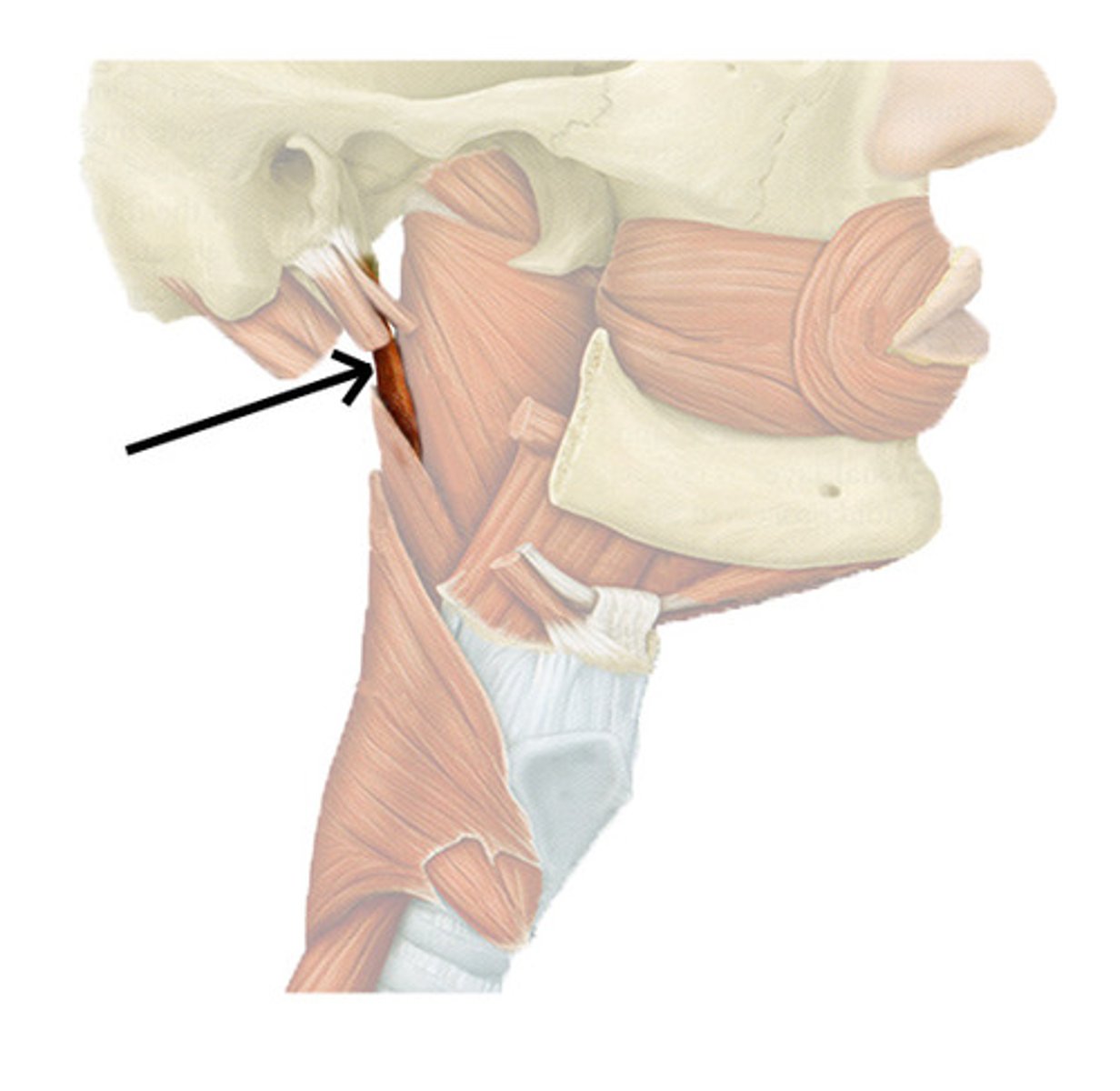
CN IX
innervation for stylopharyngeus m.
CN IX
CN X
sensory fiber that trigger the gag reflex is done by:
salpingopharyngeus
palatopharyngeus
stylopharyngeus
what are the inner longitudinal muscles of the pharynx?
contract sequentially to move food into esophagus
what is the action of the outer circular layer of pharyngeal muscles?