Ch. 1: Orientation to the Human Body
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is Anatomy?
Study of structure (shape of the body and its parts)
What is Physiology?
Study of function (how the body and its parts work or function)
How are Anatomy and Physiology related?
Structure determines function
What is Pathology?
Study of structural changes that lead to disease
What are the levels of study in Anatomy?
Macroscopic (Gross) Anatomy, Microscopic Anatomy, Developmental Anatomy
What is Macroscopic (Gross) Anatomy?
Study of large structures that are easily visible to the naked eye
What are the subdivisions of Macroscopic (Gross) Anatomy?
Regional, Systemic, and Surface Anatomy
What is Microscopic Anatomy?
Study of very small structures that can only be viewed with a microscope
What are the subdivisions of Microscopic Anatomy?
Cytology (study of cells) and Histology (study of tissues)
What is Developmental Anatomy?
Study of structural changes that occur in the body throughout the lifespan
What is a subdivision of Developmental Anatomy?
Embryology
What are some subdivisions of Physiology?
Renal physiology, neurophysiology, cardiovascular physiology, etc.
What are the levels of structural organization?
Chemicals → Organelles → Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Organism
What happens at the Chemical Level?
Atoms and molecules form the basis of life
What happens at the Cellular Level?
Cells are formed from organelles
What happens at the Tissue Level?
Tissues are formed from similar cells
What happens at the Organ Level?
Organs are formed from different tissues
What happens at the Organ System Level?
11 organ systems work together
What happens at the Organism Level?
Complete human body functions as a unit
What are the necessary life functions?
Maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth
What does maintaining boundaries mean?
Keeping the internal environment separate from the external environment
What does movement include?
Locomotion and transport of substances throughout the body
What is responsiveness?
Ability to sense changes (stimuli) and respond to them
What is digestion?
Breakdown and absorption of nutrients
What is metabolism?
All chemical reactions within the body
What are the two types of metabolism?
Catabolism (breaking things down) and Anabolism (building things up)
Why is ATP important?
It provides energy for body functions
What is excretion?
Elimination of wastes from metabolic reactions
What is reproduction?
Production of offspring
What is growth?
Increase in cell size and number
What are the survival needs?
Nutrients, oxygen, water, normal body temperature, and appropriate atmospheric pressure
Why are nutrients important?
They provide chemicals for energy and cell building
What are the major types of nutrients?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals
Why is oxygen important?
Required for chemical reactions
Why is water important?
Makes up 60-80% of body weight and is involved in metabolic reactions
Why is normal body temperature important?
Necessary for proper metabolic function
Why is appropriate atmospheric pressure important?
Needed for proper breathing and gas exchange
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining a stable internal environment within narrow limits, regardless of environmental changes
Why is homeostasis important?
It must be maintained for normal body functioning and survival
How does the body maintain homeostasis?
Through neuronal & hormonal control systems
What are the three components of homeostatic control?
Receptor, Control Center, Effector
What does the receptor do?
Responds to changes (stimuli) and sends information to the control center
What does the control center do?
Determines the set point, analyzes information, and determines the response
What does the effector do?
Executes the response (only in muscles or glands)
What are feedback mechanisms?
Systems that regulate homeostasis
What is negative feedback?
A mechanism that shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity, moving the variable back to its set point
What are examples of negative feedback?
Heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, blood glucose levels, etc.
How does negative feedback work?
Moves the variable back toward the set point, like a thermostat
What is positive feedback?
A mechanism that amplifies the original stimulus, pushing the variable further from the set point
What are normal examples of positive feedback?
Blood clotting, childbirth, and sexual response
Why is positive feedback often harmful?
It can lead to excessive responses, such as in heart attacks
What is homeostatic imbalance?
A disturbance in homeostasis that results in disease
What are causes of homeostatic imbalance?
Infection, injury, or genetic abnormality
Why is the language of anatomy important?
To prevent misunderstanding and provide exact terms for position, direction, regions, and structures
What are anatomical directional terms used for?
To describe locations and relationships of body parts
What is the proper anatomical position?
Standing upright, facing forward, arms at sides with palms facing forward
What do superior and inferior mean?
Above; Below
What do anterior and posterior mean?
Front; Back
What do medial and lateral mean?
Toward the midline; Away from the midline
What do proximal and distal mean?
Closer to point of attachment; Further from point of attachment
What do superficial and deep mean?
Near body surface; Further from body surface
What are body planes and sections?
Ways to divide the body for study
What does the frontal plane divide?
Anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections
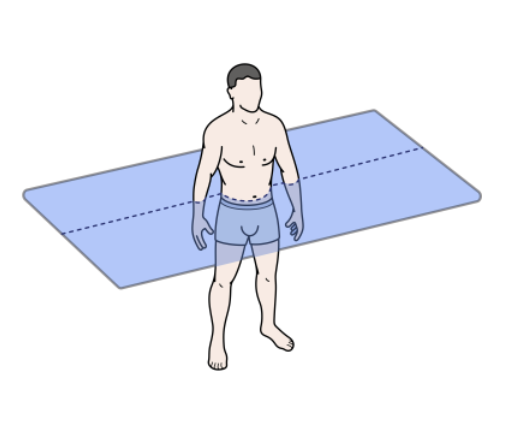
What does the transverse plane divide?
Superior (top) and inferior (bottom) sections
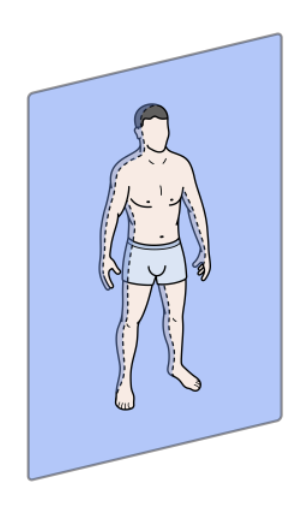
What does the sagittal plane divide?
Left and right sections
What is a midsagittal plane?
A perfect left/right division
What is an oblique plane?
A diagonal cut
What are the two major body cavities?
Dorsal cavity and Ventral cavity
What does the dorsal cavity contain?
Cranial cavity (brain) and vertebral (spinal) cavity
What does the ventral cavity contain?
Thoracic cavity, mediastinum (pericardial), and abdominopelvic cavity
What are body cavity membranes?
They line cavities and cover organs
Which membrane lines the cavity walls?
Parietal membrane
Which membrane covers the organ?
Visceral membrane
What are the thoracic cavity membranes?
Parietal pleura (lining cavity), Visceral pleura (covering organs)
What are the abdominopelvic cavity membranes?
Parietal peritoneum (lining cavity), Visceral peritoneum (covering organs)
What are the pericardial cavity membranes?
Parietal pericardium (lining cavity), Visceral pericardium (covering the heart)
What are abdominal regions and quadrants?
Ways to divide the abdomen for study and clinical use
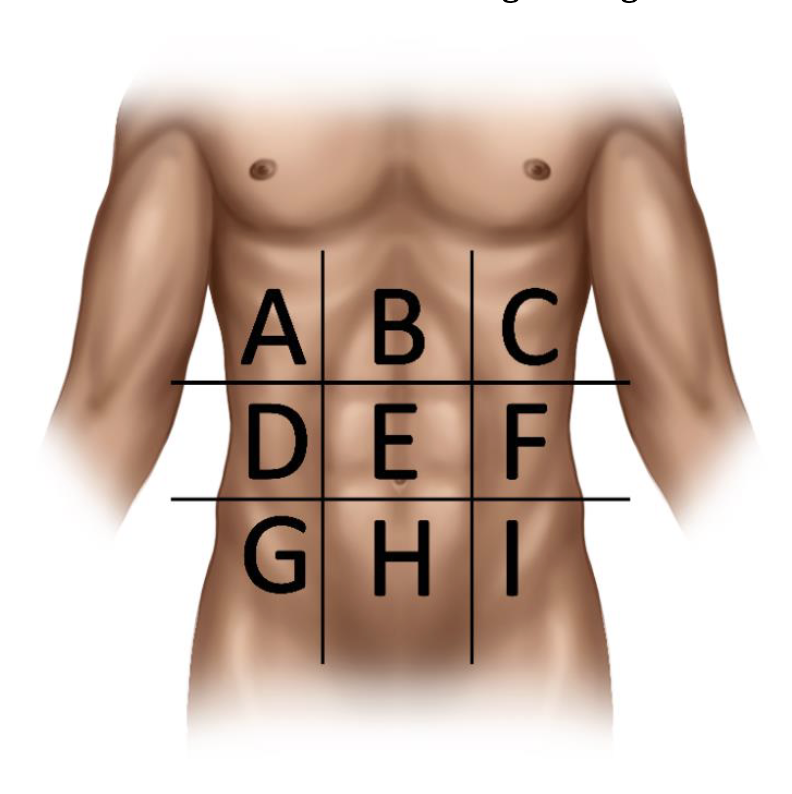
What are the 9 abdominal regions?
(A) Right hypochondriac
(B) Epigastric
(C) Left hypochondriac
(D) Right lumbar
(E) Umbilical
(F) Left lumbar
(G) Right iliac
(H) Hypogastric
(I) Left iliac
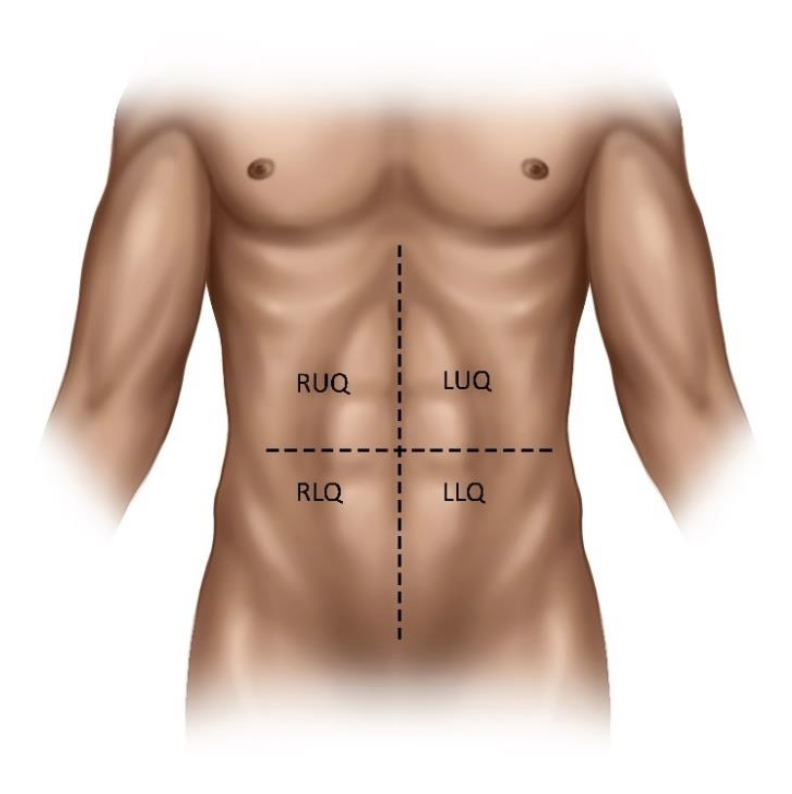
What are the 4 abdominal quadrants?
(RUQ) Right upper quadrant
(LUQ) Left upper quadrant
(RLQ) Right lower quadrant
(LLQ) Left lower quadrant