DAT alkene reactions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
hydrohalogenation
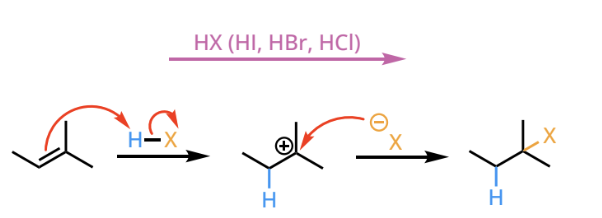
hydrohalogenation reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
halide bonded to H
hydrohalogenation products
markovnikov addition of a hydrogen halide across a carbon-carbon double bond. Due to a carboncation intermediate, carbon rearrangement is possible
radical addition(antimarkovnikov hyrdrohalogenation)
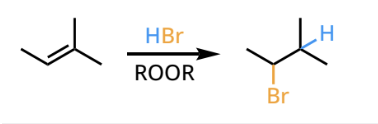
radical addition reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
halide bonded to H
ROOR
radical addition products
anti- markovnikov addition of a hydrogen halide across a carbon-carbon double bond.
acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes
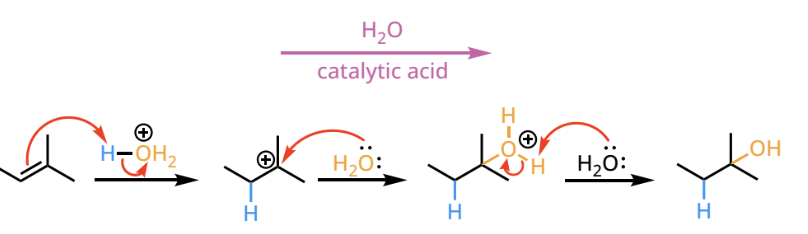
acid catalyzed hydration reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
H2O or alcohol
catalytic acid
acid catalyzed hydration products
an alkene is replaced by the markovnikov addition of H and OH(now alkane)
oxymercuration-demurcuration
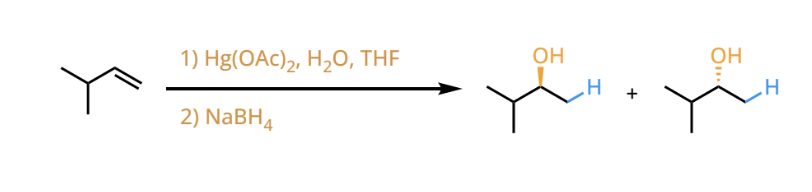
oxymercuration-demurcuration reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O, THF
2. NaBH4
oxymercuration-demurcuration products
converts and alkene to a markovnikc alcohol without the possibility of carbocation rearramgements. stereorandom products
what is special about oxymercuration-demurcuration?
it is used to convert an alkene into an alcohol without the possibility of carbocation rearrangements
hydroboration-oxidation
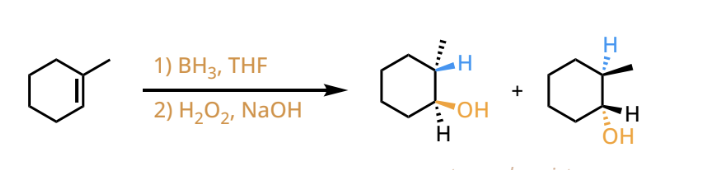
markovnikov hydroboration-oxidation reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. BH3, THF
2. H2O2, NaOH
hydroboration-oxidation products
anti-markovnikov addition of a H and OH across the carbons of the alkene
dihalogenation
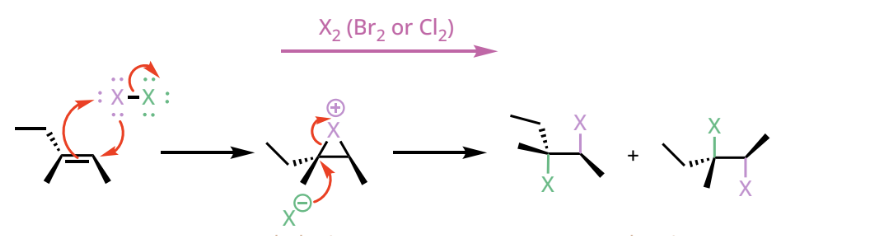
dihalogenation reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
X2(Br2 or Cl2)
neutral, non-nucleophilic solvent(CCl4)
dihalogenation products
an alkane with a stereospecific anti-addition of two halides
vicinal dihalide
contains two halogen atoms bonded to neighboring carbons
halohydrin formation
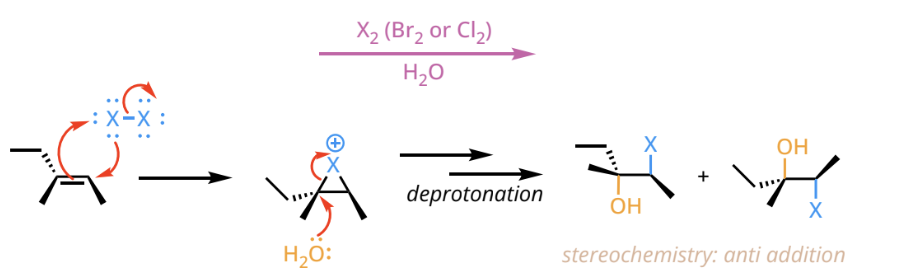
halohydrin mechanism reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
dihalide
water molecule
halohydrin mechanism products
an alkane with a the anti-additon of a halogen and then hydroxyl group(OH) on an adjacent, more substituted carbon.
epoxidation
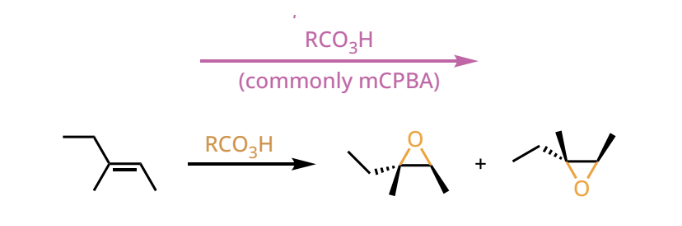
epoxidation reactant and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
RCO3H( commonly mCPBA)
epoxidation products
an epoxide forms on either face of the alkene(now alkane). If the product is chiral, both enantiomers will be formed.
epoxide
a three memebred ring consisting of oxygen and two carbon atoms
anti dihydroxylation of alkenes
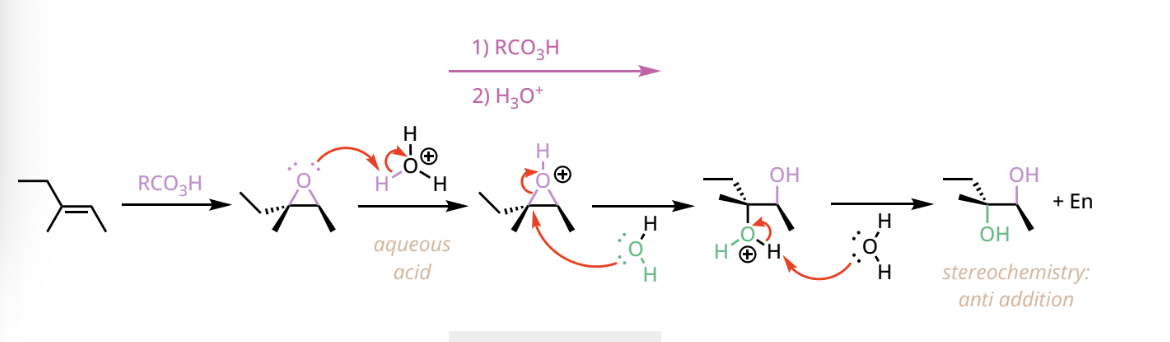
anti dihydroxylation reactant and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. RCO3H( commonly mCPBA)
ex. CH3CO3H
2. H3O+
anti dihydroxylation products
first forms and epoxide, and then a vicinal diol with two hydroxyl groups ortiented anti to one another + EN
syn dihydroxylation
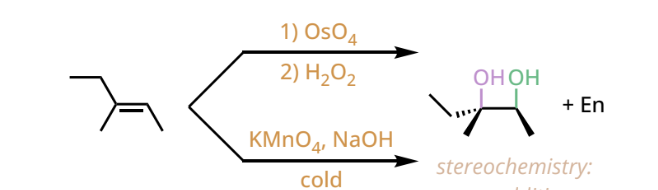
syn dihydroxylation reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. OsO4
2. H2O2
OR
1. KMnO4,NaOH/ H2O, H2O2
cold
syn dihydroxylation products
a vicinal diol(with two hydroxyl groups on neighboring carbons). The two hydroxyl groups attach in the syn fashion
reductive ozonolysis
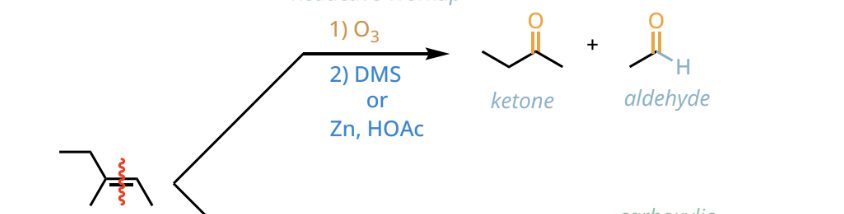
reductive ozonolysis reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. O3
2. DMS or Zn, HOAc
reductive ozonolysis products
ketones and aldehydes
oxidative ozonolysis
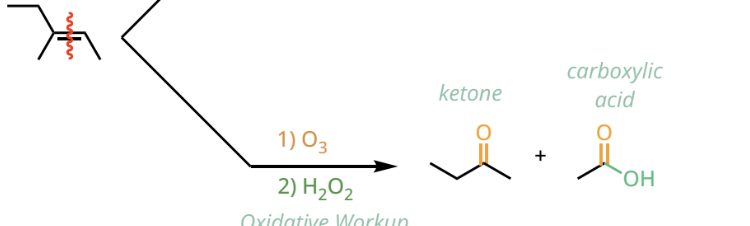
oxidative ozonolysis reactants and reagents
reactants:
alkene
reagents:
1. O3
2. H2O2
oxidative ozonolysis products
ketones and carboxylic acid
catalytic hydrogenation
alkene reacts with hydrogen atoms on the surface of a solid metal catalyst and the alkene is reduced to an alkane
catalytic hydrogenation reactants and reagents
reactant:
alkene
reagent:
H2
a metal catalysts such as Pd, Pd/C, or Pt