BI 220: Apoptosis and Cell Reproduction
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
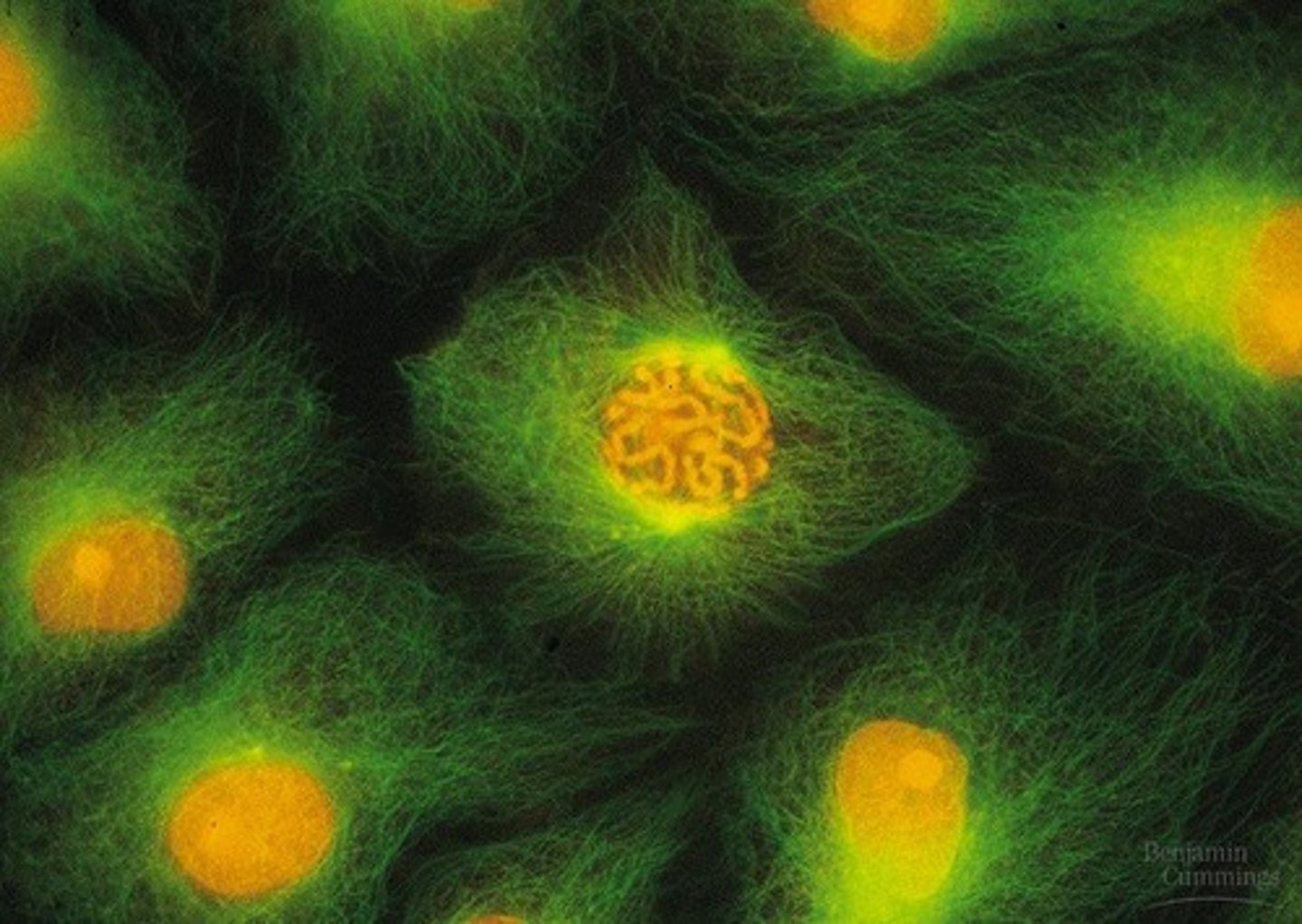
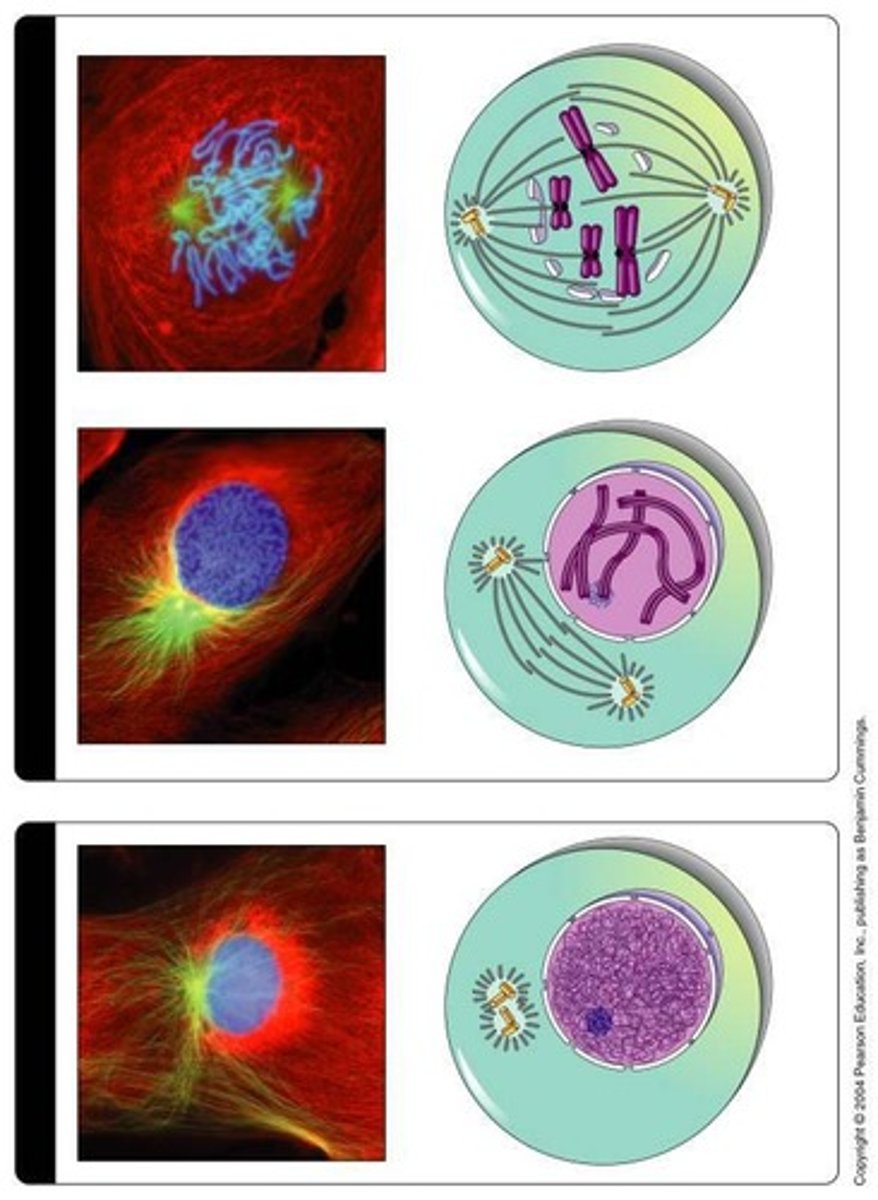
Prophase
First stage of mitosis; chromosomes condense, centrosomes begin to separate, cell starts to build the mitotic spindle
Prometaphase
Nuclear membrane breaks down, kinetechores form on the centromic DNA, microtubules begin to make attatchments to the chromosomes
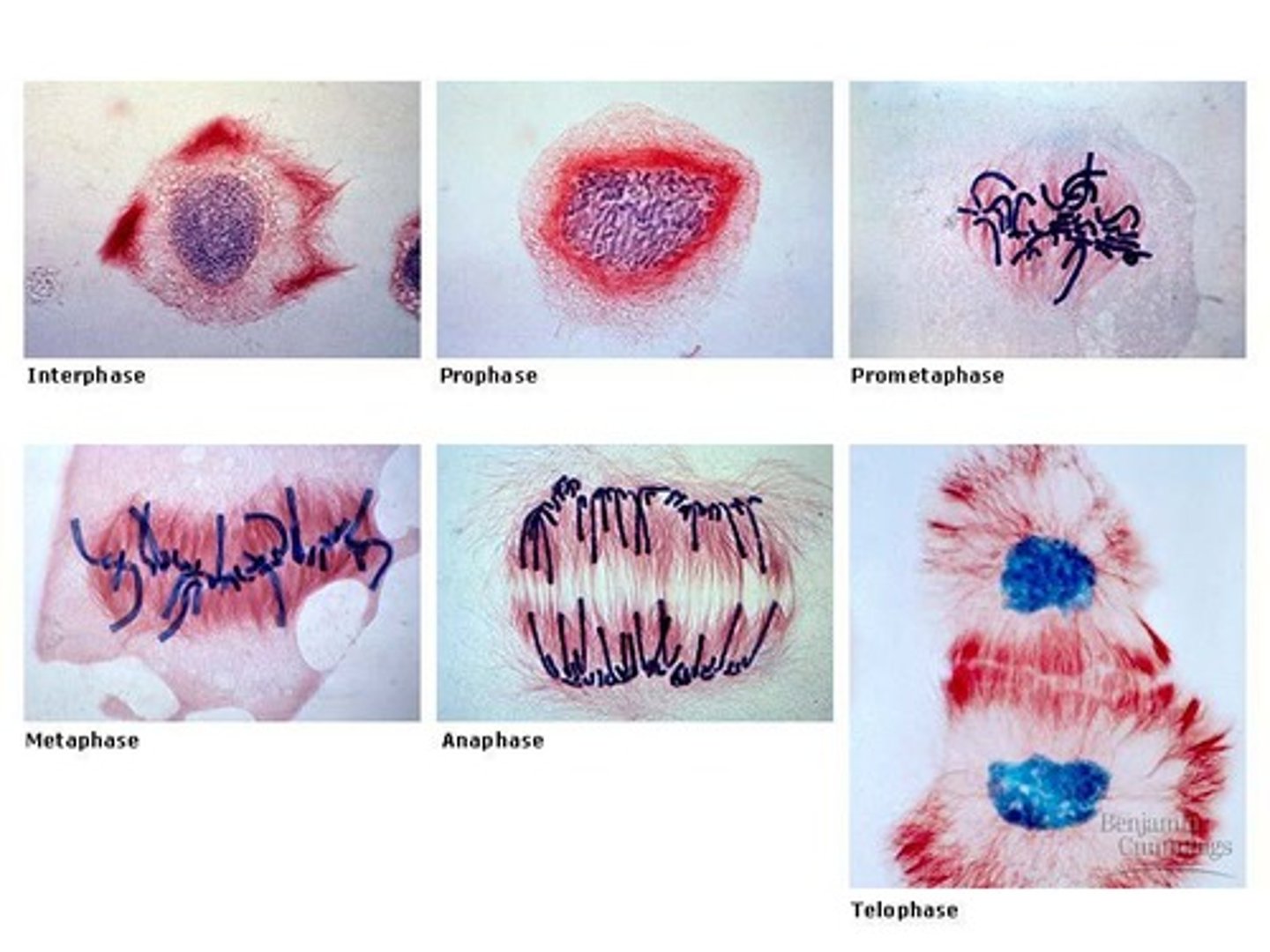
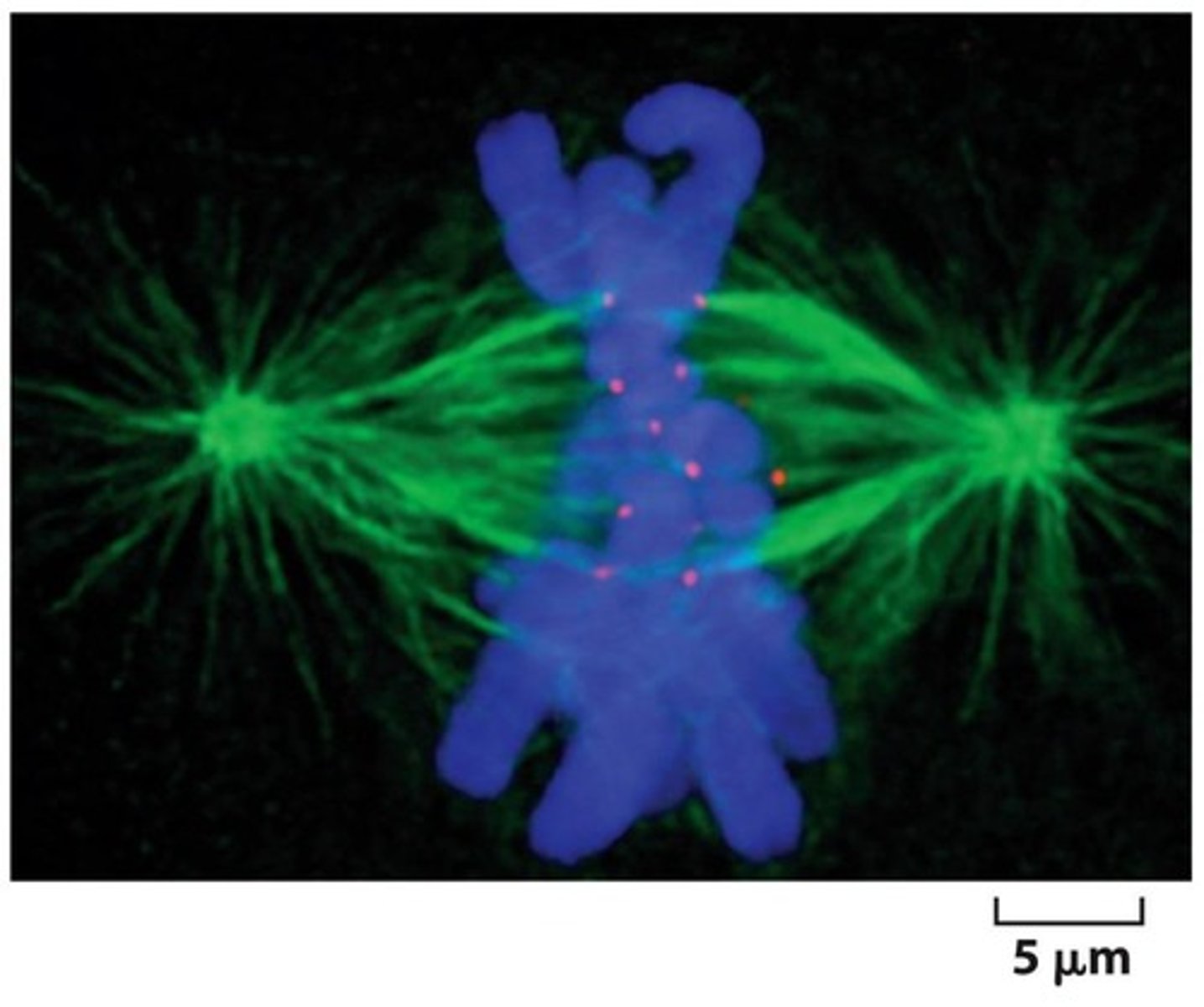
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, each chromosomes should be bioriented under tension
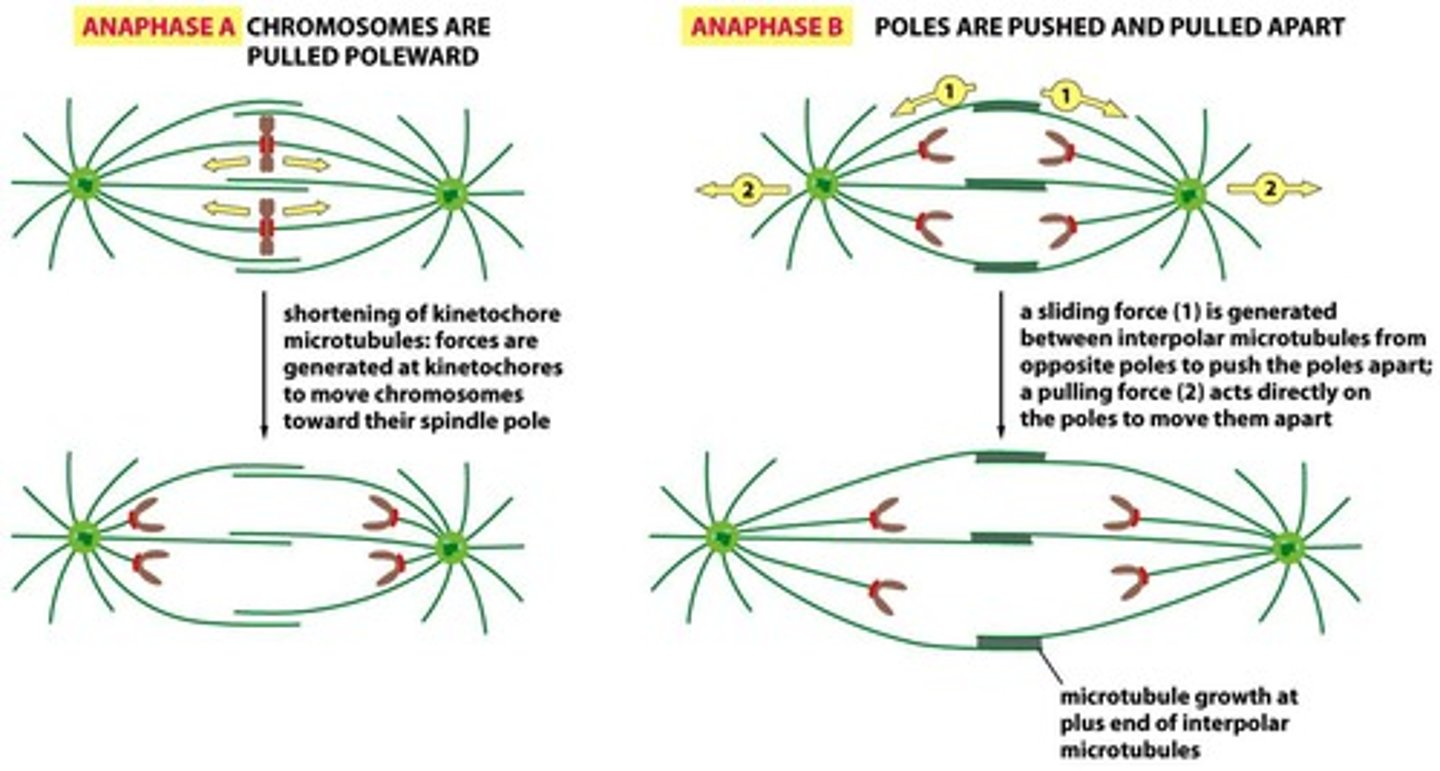
Anaphase
Cohesion is cleaved, microtubules will pull sister chromatids apart, centrosome separate
Telophase
Spindle disassemble, chromosomes decondense, reform the nuclear envelope
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm, forms two daughter cells.
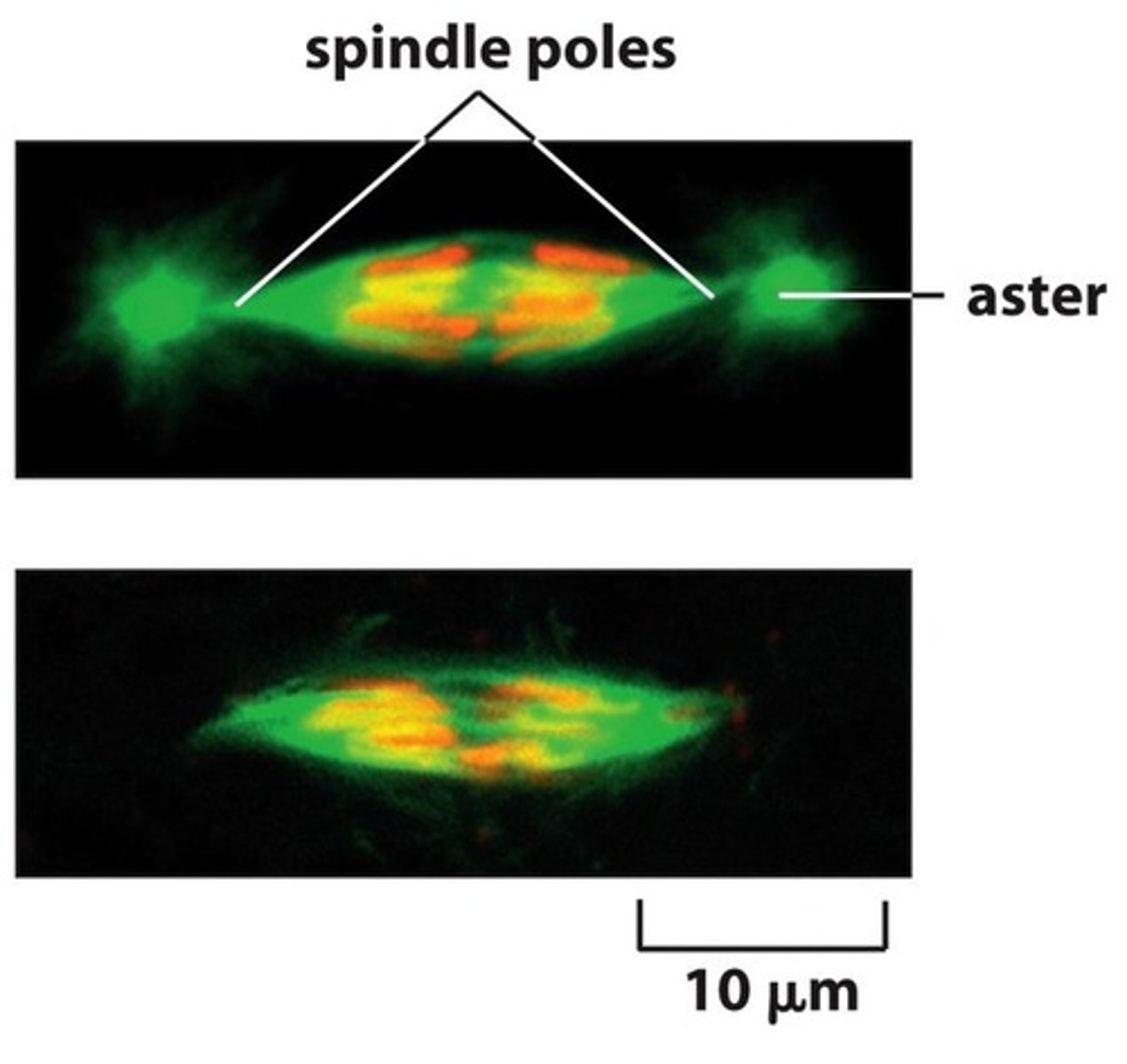
Centrosome
Organizes microtubules during cell division, the complex of tubulin proteins from which the mitotic spindle grows
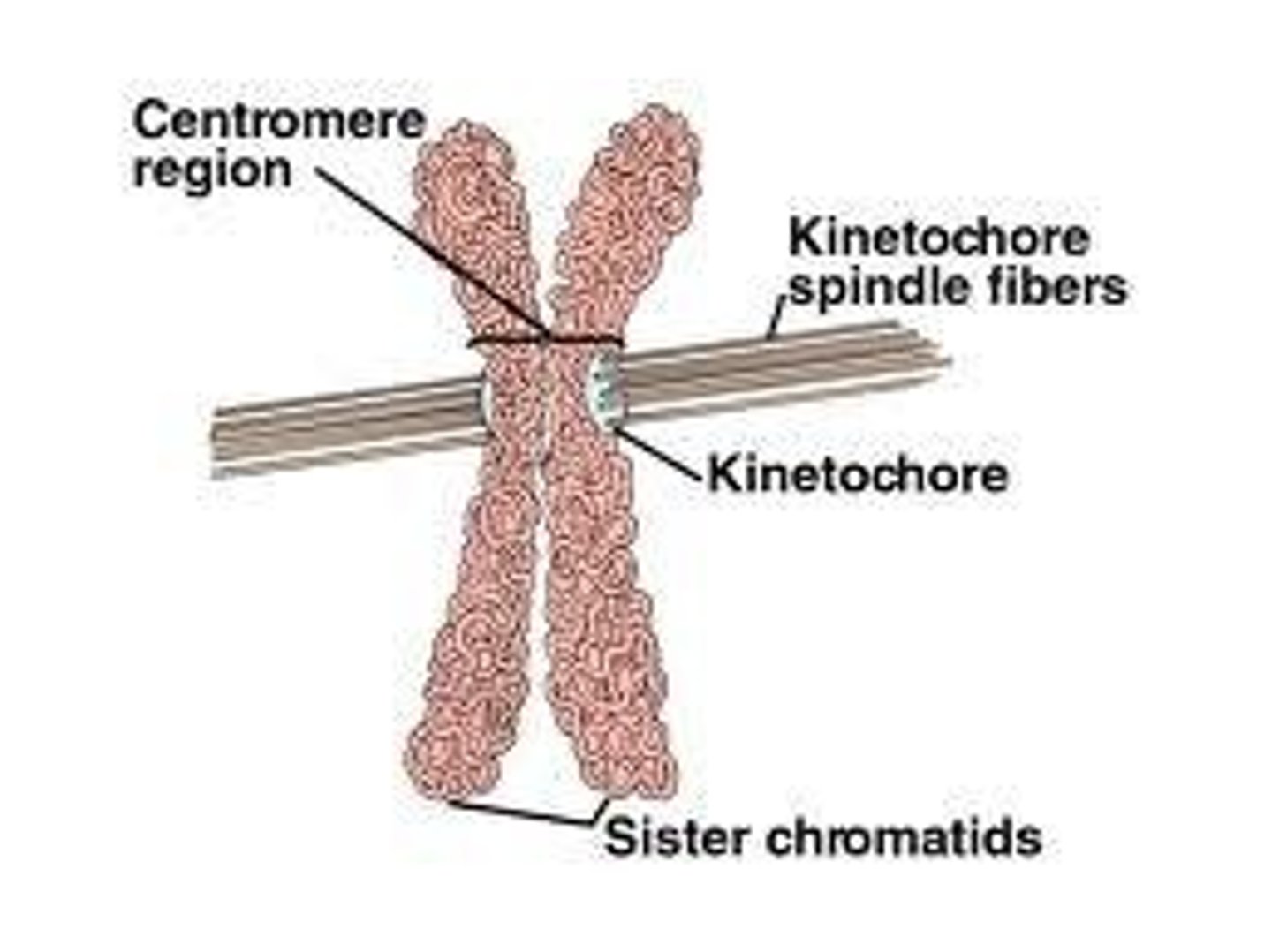
Kinetochore
Protein structure on chromosomes for spindle attachment.
Cohesin
Protein that holds sister chromatids together.
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal fibers that pull chromosomes apart.
RhoA
GTPase critical for cytokinesis and contractile ring formation.
Phragmoplast
Structure for cell plate assembly in late cytokinesis in plants.
Checkpoints
Regulatory points in the cell cycle.
G1 Checkpoint
Checks for DNA damage before S phase.
G2 Checkpoint
Ensures DNA replication is complete before mitosis.
M Phase Checkpoint
Verifies spindle attachment before anaphase, cell spends 10% of its time here
p53 Protein
Tumor suppressor protein that stop cell division at specific checkpoints if there is a problem
Cyclin
Regulatory protein that activates cyclin-dependent kinases.
Cdk
Cyclin-dependent kinase; regulates cell cycle progression.
pRb
Retinoblastoma protein; inhibits cell cycle progression.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death; eliminates damaged cells.
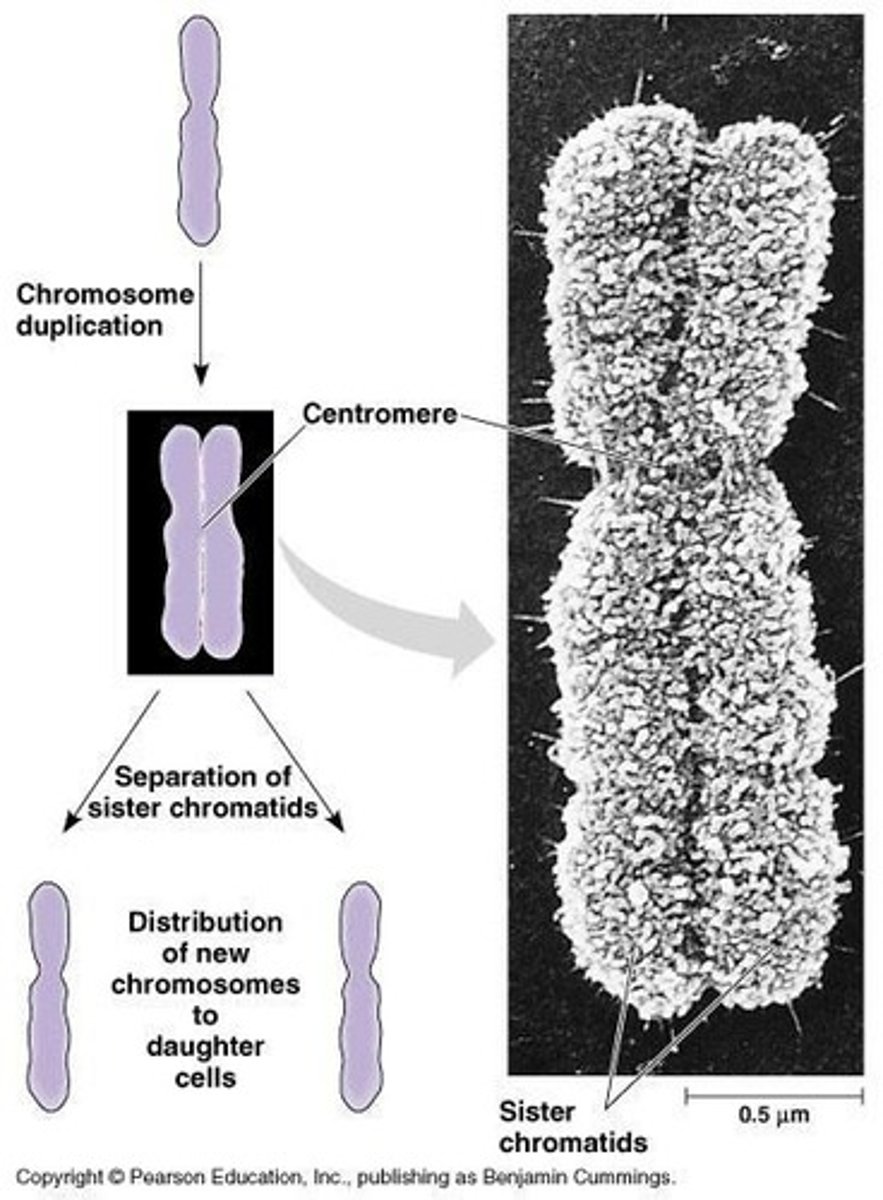
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome joined at centromere.
Chromatin
DNA and protein complex; condenses to form chromosomes.
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Nuclear Envelope
Membrane surrounding the nucleus; breaks down in mitosis.
Histones
Proteins that package and order DNA into structural units.
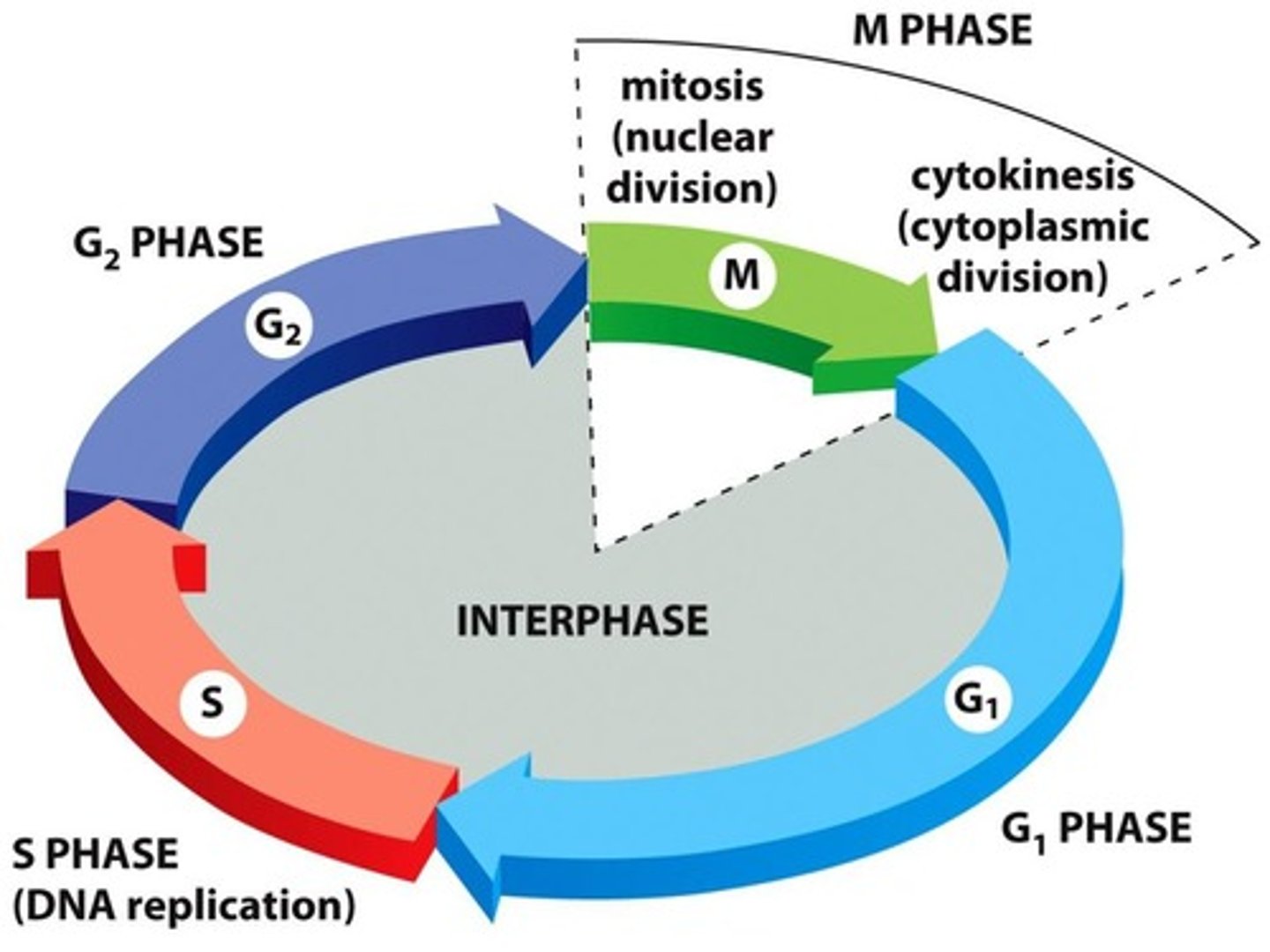
Interphase
Phase where the cell grows and DNA is replicated, cells spend most of their time here (90%)
G1 Phase
First gap phase; cell grows and synthesizes proteins.
S Phase
Synthesis phase; DNA is replicated, creating identical copies of each chromosome
G2 Phase
Second gap phase; cell prepares for mitosis.
Cell Cycle
Series of phases that cells go through for division.
Organism growth, replacement of lost or damaged cells, organism reproduction
Why do cells reproduce?
Extracellular molecules (growth factors/mitogens), GF-receptor binding triggers multistep signal transduction relay, results in molecular changes that stimulate (or inhibit) cell reproduction
What signals cell reproduction?
Ras-MAP kinase pathway
Many growth factors signal through RTKs to activate the ___.
Duplication of DNA (chromatin changes, chromosome duplication), growth of cell in size, segregation of DNA (chromosome movement, nuclear division in eukaryotes), cytoplasmic division
During reproduction, all cells must accomplish four things...
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction used by prokaryotes
Mitotic divison
Asexual reproduction used by eukaryotes
Sexual reproduction
Meiotic division (+ fertilization), often used for organism reproduction in eukaryotes
During chromosome replication
When does the cell elongate in binary fission (prokaryotes)?
Circular DNA molecule
Single bacterial chromosome
An identical complete genome
In binary fission (prokaryotes), each daughter cell inherits ___.
Nuclear membrane, genome on multiple chromosomes, growth & DNA replication as separate steps
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division: Eukaryotic cells have...
Tension, microtubules
The goal of the kinetochore attaching chromosomes to the spindle is to create ___ across the kinetochore due to pulling forces from ___ attached to the two spindle poles.
Closer to the spindle poles
Microtubules shorten at the kinetochore end to pull chromosomes ___.
Contractile ring
Cytokinesis is accomplished by constriction of a ___ - form the furrow..
GEF
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors that causes a protein to lose a GDP and replace it with a GTP
GAP
GTPase activating protein
Cytokinesis
Defects in Rho signaling lead to ___ failure.
+
Kinesine motors move Golgi vesicle to (___) ends of microtubules.
Cell plate
Fusion of Golgi vesicles forms ___ (growing wall sandwiched between two membranes)
Growing edges of cell plate
Phragmoplast expands in diameter, so microtubules lined up with ___.
Regulated
Cell reproduction is a highly ___ process.
G1
Rb inhibits TFs that promote progression into ___.
G1, G2
Kinases often give "go ahead" signal at ___ & ___ checkpoints.
Cdk/cyclin
What regulated Rb?
Rb
Regulates cell cycle progression by controlling the transition from G1 to S phase
Cdks (drive the cycle forward by phosphorylating substrates when bound to cyclins), ubiquitins (regulate cyclin degradation, which is how cells rapidly drop cyclin levels to exit a phase or reset)
What enzymes control the rapid changes in levels of the cyclins to promote cell cycle progression?
Pause & repair or apoptosis
What happens if a problem is detected at a checkpoint?
16, 16
A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. Those cells would have ___ picograms at the end of the S phase and ___ picograms at the end of G2.
20
If there are 40 chromatids in a cell at metaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
Mitogens
Promote cell division
Growth factors
Promote cell size increase
Survival factors
Surpress apoptosis
Development, tissue homeostasis, injury/disease
When do cells die?
Apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy, etc.
How do cells die?
Autophagy
A lysosome-mediated pathway for organelle degradation
Genetically programmed, starvation-induced, aids in organelle turnover, cell death (sometimes)
Autophagy is...
Cell shrinkage; chromatin condense then fragment, nuclei bleb; plasma membrane blebs to form apoptotic bodies; engulfment & destruction by phagocytes (recognize exposed phosphatidyl serine)
Apoptosis morphological hallmarks
Caspase protease
The executioner of apoptosis, which are activated by cleavage
Inactive precursors, active, irreversible
Procaspase are ___. Caspase are ___. Caspace activation is ___.
Cleave, activate
Initiator caspases ___ and ___ executioner caspases, which can further amplify the signal or directly target degradation of cellular structures.
Signal amplification
The caspase activation cascade is an example of ___.
Intrinsic, extrinsic
Apoptosis can be induced by ___ or ___ death signals.
Radiation, toxins, hypoxia, DNA damage, loss of growth factors, etc/
Intrinsic death signal triggers
Leads to mitochondrial permeability through Bax & Bcl2 can antagonize this activity
Intrinsic death signals
Death ligands and receptors
Extrinsic death signals triggers
Bcl2, mitochondrial permeability
The intrinsic apoptosis pathway is regulated by ___ family members and ___.
Prodeath, prodeath, prosurvival
Bax is ___. Bak is ___. Bcl2 is ___. (prodeath or prosurvival)
Prosurvival, prodeath → cytochrome c release from mitochondria → apoptosome formation initiates caspase activation
Intrinsic apoptosis pathway steps
Normal developmental, pathologic
Apoptosis occurs during ___ processes, whereas necrosis is ___.
Necrosis
Tissue death that causes inflammation (harmful)