Lecture 12 - Cooperation and Conflict
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
social behavior
Cooperation and conflict are found at all levels of biological organization and range from seemingly altruistic behavior to gather food, raise offspring, and defend resources such as food or nests to conflict such as infanticide and siblicide.
In a sense, what we are talking about here is the evolution of ___________.
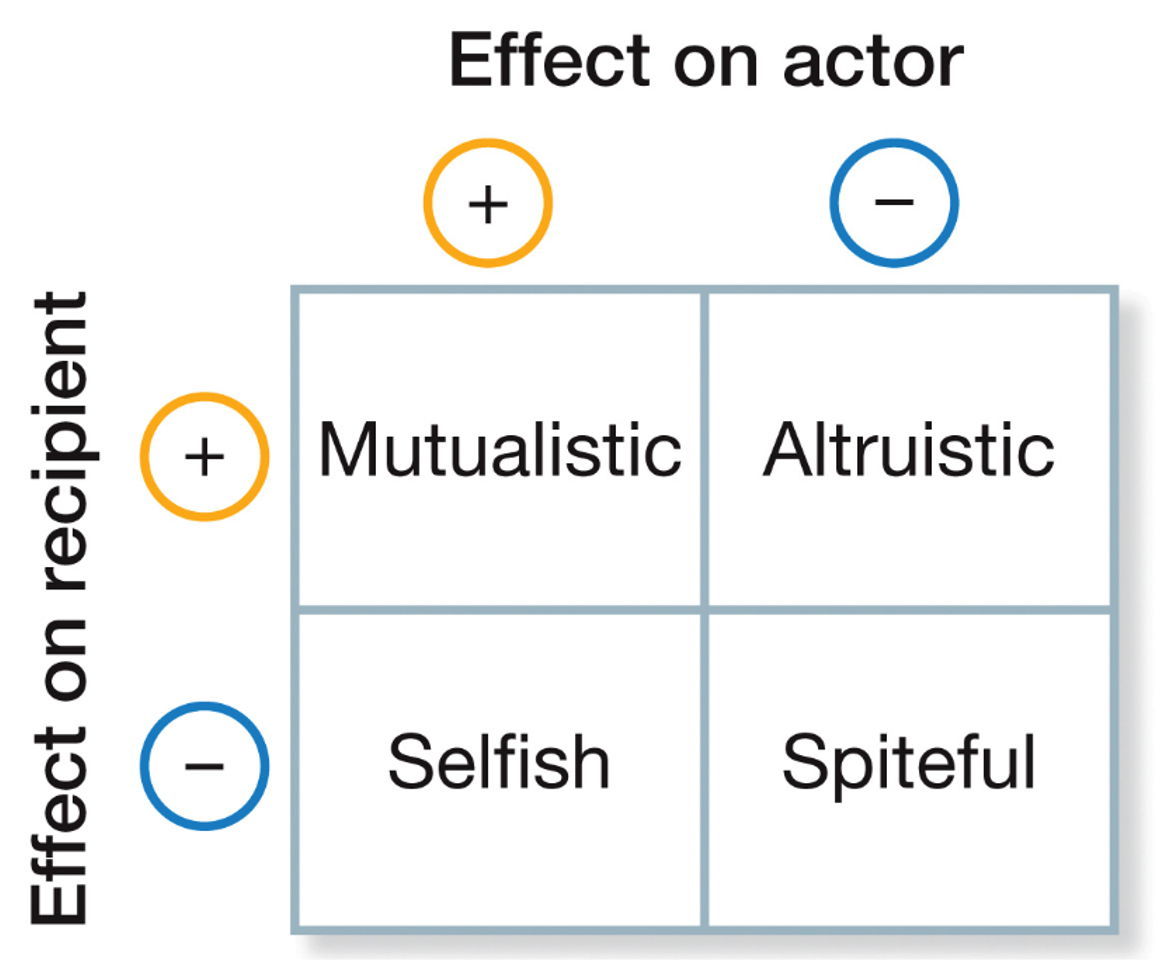
Mutualistic behavior increases fitness for both the actor and the recipient (so it’s a form of cooperation)
Altruistic behavior has a negative (or costly) effect on the actor but benefits the recipient by increasing fitness (another form of cooperation)
Selfish behavior benefits the actor by increasing fitness, but has a negative effect on the recipient by decreasing fitness (a form a conflict)
Spiteful behavior has both a negative effect on the actor and a negative effect on the recipient in terms of fitness decreases for both of them and this is another form of conflict
What does this table show?
cheating
In general, it is far from obvious how natural selection favors cooperative behavior when _________ is a possibility.
Basically, an individual can cheat if it can benefit from the actions of others without providing reciprocal benefits in return
collapse
If cheating has high fitness in a population of cooperators, then the mutation that causes cheating will spread and ultimately cooperation can _______.
It turns out that colonies that have high relatedness evolve resistance to cheaters.
Slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum example
cells with a mutation at the chtA locus are cheaters (blue spores)
Wild-type cells (yellow)
Mutants become more concentrated in the cap and have a higher probability of becoming reproductive spores
Over 11 lab growth cycles frequency of selfish mutant increases
The cheating mutation doesn’t go completely to fixation… why don’t we see the end of cooperative behavior and fixation of the cheating mutation in the population?
Colonies are able to evolve resistance against cheating. When colonies closely related, stronger resistance.
Slime mold competition experiment shows that…
benefit
What are the conditions under which cooperation can evolve?
1) Cooperation among unrelated individuals in which both the actor and the recipient ______. (mutualism)
2) Reciprocity, another form of mutualism in which individuals reciprocally increase each others fitness
3) Altruism among related individuals (kin selection – we will come back to this in a few minutes)
Reciprocity
What are the conditions under which cooperation can evolve?
1) Cooperation among unrelated individuals in which both the actor and the recipient benefit. (mutualism)
2) _________, another form of mutualism in which individuals reciprocally increase each others fitness
3) Altruism among related individuals (kin selection – we will come back to this in a few minutes)
Altruism
What are the conditions under which cooperation can evolve?
1) Cooperation among unrelated individuals in which both the actor and the recipient benefit. (mutualism)
2) Reciprocity, another form of mutualism in which individuals reciprocally increase each others fitness
3) _______ among related individuals (kin selection – we will come back to this in a few minutes)
Flocking behavior
_______ ________ is an excellent example of cooperation among unrelated individuals
selfish herd effect
In this case flocking behavior lowers the risk of predation among individuals in a group… its Less likely predator will focus on individual and there is the…
aka safety in numbers
Shared vigilance
more time can be devoted to grazing in larger herd since groups lookout for predator together
hunting large prey requires cooperative behavior
Wolves and other cooperative predators (Lions and Hyenas) hunt cooperatively in packs to take down prey that a single individual could never take down b/c…
Cooperation among non-kin – delayed benefits example
•2 unrelated Lance-tailed manakin (Chiroxiphia lanceolata) males team up to court females with an elaborate synchronized display
•Females prefer highly coordinated displays and almost always mate with dominant male
•When dominant male dies, subordinate male takes over
riendships and reciprocity
Robert Trivers suggested that cooperation can evolve when individuals provide favors to one another that both provide fitness benefits
Offspring of female yellow baboons (Papio cynocephalus) that have strong bond with females other than mom have better survival
Repeated interaction can favor cooperative behavior.
In some circumstances cooperation can be enhanced if selfish individuals are punished.
this kind of behavior is common among mammals, and is something we see in our own species
punished
In some circumstances cooperation can be enhanced if selfish individuals are…
natural selection
Mathematical models can predict the conditions under which reciprocity is favored by ___________ (we call these Evolutionary Stable Strategies – ESS)
“prisoners dilemma”
two individuals do better by active selfishly, but if both act selfishly, they do worse than if they cooperate
selfish
Game theory shows that ______ behavior is favored if individuals interact only once, but that repeated interactions favor cooperation
defect; cooperate
2 thieves commit a crime together and are caught and are isolated and cannot communicate
If they both defect each gets 2 years
If one defects, defector goes free and other serves 3 years
If both cooperate then both serve 1 year
Best strategy is to ______.
If individuals interact repeatedly strategy changes to ________
Cooperation
activity that provides a benefit to other individuals and to the actor.
Altruism
activity that enhances the fitness of other individuals but lowers the fitness of the actor. Can be explained in terms of kin selection.
Hamilton’s Rule is: rB > C
r = relatedness; B = fitness benefit to recipient; C = fitness cost to actor.
What does rB > C mean?
kin; non-kin
Kin selection can favor altruism only if individuals are more likely to help ___ than ____. Many species use cues to recognize kin, for example distinctive calls or odors.
altruistic
Hamilton’s rule is an equation that can be written as relatedness time fitness benefit to the recipient must be greater than the fitness cost to the actor and when this is met then _______ behavior can evolve
Relatedness; You share 50% of your genes with your siblings and 25% with your cousins… saving two siblings or eight cousins is better than reproducing yourself because your offspring are only related to you by 50%.
Haldane was referring to what we call Inclusive Fitness
When asked if he would give his life to save a drowning brother, JBS Haldane said “No, but I would to save two brothers or eight cousins”
Why is this? What was he referring to?
50%; 25%
Parents and offspring share ___ of their genes and cousins share ___ of their genes with each other.
direct and indirect fitness
The relative number of an individual’s alleles that are passed on to future generations, both…
direct fitness
a results of an individuals own reproductive success
indirect fitness
a results of an individual helping relatives whom with they share a proportion of their alleles
Kin Selection
The component due to indirect fitness is called _________
favors
W. D. Hamilton’s Rule (1964) indicates that selection _____ genes for altruism if:
relatedness of the actor to the beneficiary time the benefit minus the cost to the actor from helping is greater than zero.
r is relatedness to beneficiary
B is benefit in fraction of additional
offspring resulting from helping
C is cost to altruistic individuals from
helping (cost of loss of offspring)
What does Hamilton’s r B - C > 0 mean?
there’s a genetic basis for behavior
r > C/B means gene(s) for altruism more likely to spread when:
benefits to recipient are great
cost to actor is low
participants are closely related
benefits to recipient are great
r > C/B means gene(s) for altruism more likely to spread when:
there’s a genetic basis for behavior
cost to actor is low
participants are closely related
cost to actor is low
r > C/B means gene(s) for altruism more likely to spread when:
there’s a genetic basis for behavior
benefits to recipient are great
participants are closely related
participants are closely related
r > C/B means gene(s) for altruism more likely to spread when:
there’s a genetic basis for behavior
benefits to recipient are great
cost to actor is low
high for a primary helper and also very high for a secondary helper, but is low for a delayer, so it actually pays for secondary helpers to assist their non-relatives
Hamilton’s Rule for the Pied Kingfisher
We can add the fitness from years 1 and 2 and also look across different behavioral tactics (primary and secondary helpers and delayers).
What you can see is that inclusive fitness is…
Example - Altruism in Wild Turkeys
Dominant male has higher fitness than subordinates and solo displaying males. Presence of subordinate increases reproductive success from 0.9 to 7 so benefit is 6.1. [7 - 0.9 = 6.1]
Subordinate doesn’t mate, so cost of helping brother is cost of not displaying solo (0.9).
Pairs were either brothers or half brothers, average relatedness 0.42.
For brothers, rB = 0.42 * 6.1 = 2.6 and this is greater than the cost C = 0.9; this 2.6 – 0.9 = 1.7 so altruistic behavior increases the allele’s inclusive fitness by rB – C = 1.7 offspring
so there is an inclusive fitness advantage relative to going solo
Eusociality
________ is the most extremely case of altruism, in all four of these cases we have colonies of individuals where most colony members do not reproduce and a few do.
eusociality
Ants, bees, wasps and termites are famous examples of ________ in insects.
0.25; 0.75
•Males are haploid and have no father
•They inherit all genes from mom (half of her genes)
•Males are related to diploid female workers by ____
•Workers and the new queen are related by _____
conflict
Social interactions often involve _____ in the natural world
Sexual antagonistic selection
conflict between mates (ESS models)
Although males and females must cooperate to produce offspring, conflict between mates is also pervasive!
Although males and females must cooperate to produce offspring, conflict between mates is also…
siblicide and infanticide
Conflict can also include… (2 things)
siblicide happens
The image on the left shows a Brown Booby (Sula leucogaster) with a dead baby outside nest that was killed by its siblings. This also happens in owls, hawks, herons, and Pelicans (among others) and in years where food is plentiful young do not compete and parents raise a full nest of young, but when food is limiting…
Infanticide
Commonly occurs among social cooperative mammals where males take over a harem or group of females. In Lions and Hyenas when a new male or males take over a group of females they kill off all of the young because this is the only way that the females more quickly come back into estrus and can reproduce.
eliminates
Infanticide ________ alleles of competitors and females become fertile and sexually receptive sooner.
Some species kill their own offspring — in situations where offspring survival would decrease even more if all offspring were allowed to compete with each other.
infanticide
This mostly occurs in species with social groups with more females than males.
cannibalisms
One last major form of conflict is __________
In this example, the tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) becomes _________ when at high population density – in this case some larvae develop into _________ morphs
cooperation; conflict
A balance between ________ and ______ occurs in many biological systems.
aligned; conflicting
Males and females and parents and offspring can have ______ or ________ interests.
optimal
Evolutionary stable strategies can predict which phenotype or balance of phenotypes is ______.
Altruism; cooperative behavior
_______ benefits other individuals and reduces individual fitness of the actor, whereas _________ can increase individual fitness of both donor and recipient.
altruism
Inclusive fitness can explain evolution of _______.
kin selection
Usually individual selection explains situations but _________ can explain the evolution of altruistic behaviors.
Altruistic behavior
characterized by selflessness and a genuine concern for the well-being of others, without expecting any personal gain or reward.