Proteins (+ Electrophoresis Notes)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Proteins
Large biomolecules composed of amino acids linked through peptide bonds, essential for various biological functions including structure, enzymes, and signaling.
Functions of Proteins
Carrier molecules
Maintenance of osmotic pressure
Immune response agents
Enzymes
Acts as a marker for nutrition
Albumin, Transferrin, Transthyretin or thyroxine binding prealbumin
Acts as a marker for liver function
important in assessment of renal function
Essential Components of Proteins
Essential Components:
• Carbon - Forms the backbone of amino acids
• Hydrogen - Contributes to protein folding and stability
• Oxygen - Essential for peptide bonds and functional groups
• Sulfur - Forms disulfide bridges crucial for protein structure
• Nitrogen (16%) - Distinguishing feature from carbohydrates and lipids
Amino Acid Structure:
Each amino acid contains:
• An amino group (-NH₂)
• A carboxyl group (-COOH)
• A unique side chain (R group)
• A central carbon atom (α-carbon)
Amino Acid Analysis
Draw blood after a 6-8 hour fast in a heparin tube, removing plasma promptly. Avoid aspiration of platelet and white cell layers to prevent protein interference and hemolysis.
Protein Structure Hierarchy
1. Primary Structure:
The linear sequence of amino acids is joined by peptide bonds.
2. Secondary Structure:
Regular folding patterns stabilized by hydrogen bonds
3. Tertiary Structure:
Three-dimensional arrangement of the entire polypeptide chain.
4. Quaternary Structure:
Assembly of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) into a functional protein complex.
Quaternary Structure of Protein Examples
• Hemoglobin (4 subunits: 2 α and 2 β chains)
• Immunoglobulins (4 chains: 2 heavy & 2 light)
Ampholyte (Zwitterion):
Amino acids at physiologic pH (7.4) exist as dipolar ions (both positive and negative charges on the same molecule) with
Protonated amino group (-NH₃⁺)
Deprotonated carboxyl group (- COO⁻)
Isoelectric Point (pI):
The pH at which a protein has no net electrical charge, important for
Protein separation techniques
Understanding protein behavior in solution
Optimizing laboratory procedures
Protein Analysis
Sample: Serum, Plasma, CSF & Urine
Refractometry: measure of refractive index due to solutes in a serum
rapid and simple
Albumin
Major Serum Proteins: (3.5-5.0 g/dL)
Maintains 80% plasma oncotic pressure
Antioxidant activity
pH buffering
Transport protein for:
Fatty acids
Drugs
Bilirubin
Metals
Hormones
Vitamins
Albumin Methods: Dye: BCG and BCP
BCG (bromcresol green): Albumin binds to dyes; causes shift in absorption maximum
More common
Sensitive - overestimates low albumin levels
BCP (bromcresol purple): Albumin binds to dyes; causes shift in absorption maximum
Clinical Conditions Affecting Albumin:
Hyperalbuminemia
Hypoalbuminemia
Analbuminemia
Bisalbuminemia
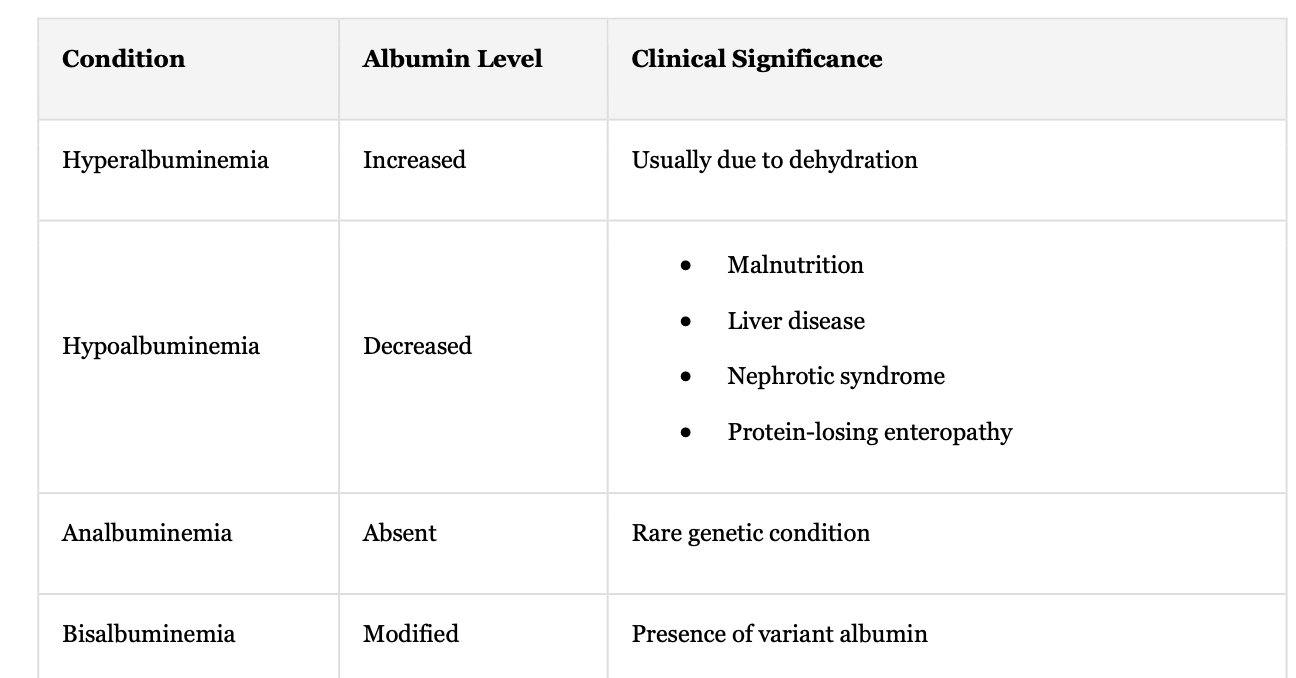
Conditions + Albumin Level + Clinical Significance
Hyperalbuminemia + Increase + Usually due to dehydration
Hypoalbuminemia + Decrease + malnutrition, liver disease, nephrotic syndrome, protein losing enteropathy
Analbuminemia + absent + rare genetic condition
Bisalbuminemia + modified + presence of variant albumin
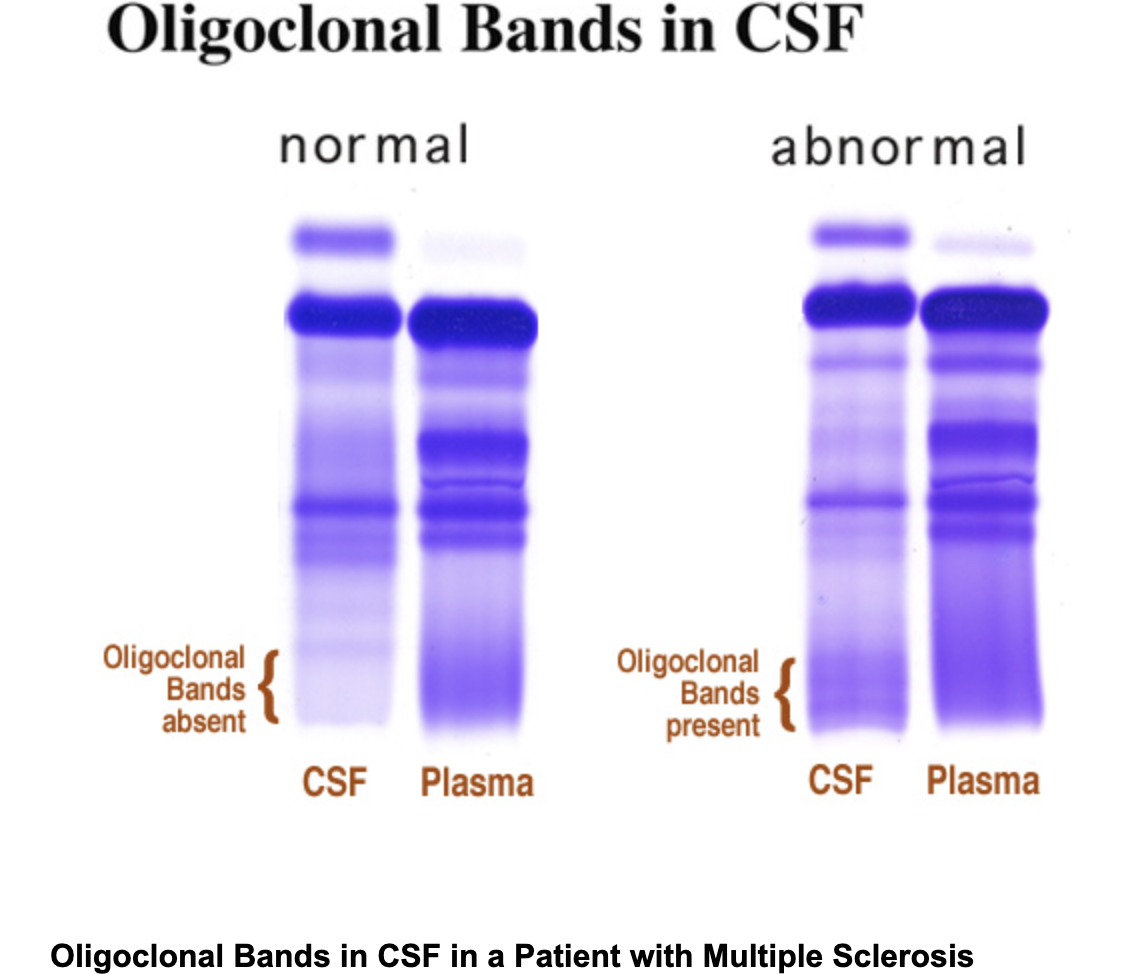
Oligoclonal Bands
Oligoclonal bands are distinct bands observed on electrophoresis, indicating the presence of immunoglobulins
Darker band = higher conc,
Protein Fractions
Prealbumin
Albumin
Alpha1 proteins
Alpha 2 proteins
Beta Proteins (Beta1 and Beta2)
Gamma proteins
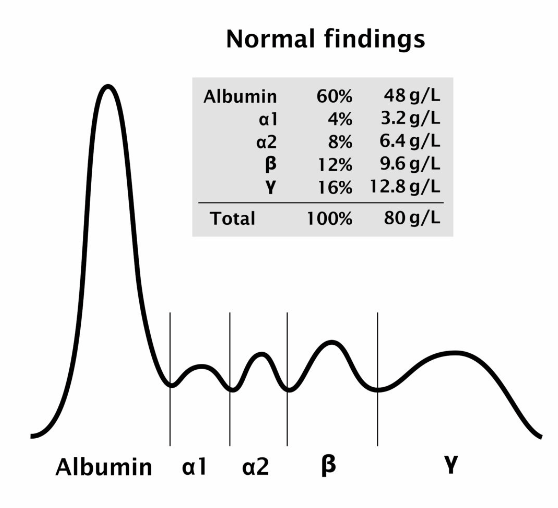
Acute Phase Proteins
Positive APPs like C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen = increase rapidly
Negative APPs such as albumin and transferrin decrease
changes occur simultaneously
Acute Phase Proteins: Negative and Positive
APP’s play a role in host defense, balane occurs due to compensation
Ex: Fibrinogen CRP, AAT, C3, AAG, a2-Macroglobulin, haptoglobin and ceruloplasmin
APPs proteins increase, levels of negative APR proteins decrease
Ex: albumin, prealbumin and transferrin.
CRP: C-reactive proteins (beta)
first acute phase reactant to rise in response to inflammation and it is an independent cardiovascular risk factor, assessed using the hsCRP assay.
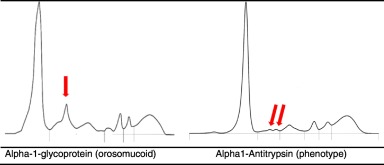
Alpha-1 Proteins
a class of serum proteins based on their electrophoretic mobility. Major examples include:
α1-Antitrypsin (AAT): A protein that protects tissues from enzymes of inflammatory cells, particularly elastase
α1-Fetoprotein (AFP): A protein produced by the fetal liver that has a function in binding and transporting nutrients.
α1-Antitrypsin (AAT)
Key protease inhibitor synthesized in the liver:
protects tissues from neutrophil elastase
Decreased in:
Emphysema
Liver cirrhosis
Increased in:
Acute inflammation
Pregnancy
Oral contraceptive use
α1-Fetoprotein (AFP)
Important diagnostic marker: synthesized by fetal liver
Major fetal protein in 2nd trimester
Maternal serum screening for:
Neural tube defects (ONTD) - increased levels
Down syndrome - decreased levels
Tumor marker for liver cancers:
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Germ cell tumors
Alpha-2 Proteins
a2-Macroglobulin: Inhibits proteolytic enzymes, regulating proteolysis and protecting tissues.
a2-Haptoglobin: Binds free hemoglobin, preventing kidney damage and aiding in immune response.
a2-Ceruloplasmin: Carries copper, oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+ for iron transport, and provides antioxidant protection.
α2-Macroglobulin
Large alpha protein with multiple functions:
Protease inhibition
trypsin, pepsin, and plasmin
Hormone binding - insulin
Increased in nephrotic syndrome - excessive protein loss in urine
How does a2-macroglobulin act as a hemoglobin binding protein?
prevents hemoglobin loss in urine
Decreased in hemolytic conditions
increased in inflammatory states
Haptoglobin
Binds free hemoglobin and transports it to the RE system for degradation, preventing renal loss of hemoglobin and iron.
Levels decrease in hemolytic diseases (HDN and transfusion rxns)
Increase in inflammation, burns, and nephrotic syndrome.
Ceruloplasmin
Copper-carrying protein:
Decreased in Wilson's disease
Increased in inflammation
Important in iron metabolism
Beta Proteins: Transferrin and B2-Microglobulin
Transferrin: Iron transport protein
Increased in iron deficiency
Decreased in inflammation
Negative acute phase reactant
B2-microglobulin: Important in renal function assessment:
Filtered by glomerulus
Reabsorbed by tubules
Marker for tubular function
Fibrinogen
analyzed in a green top tube (heparinized) while Fibrin clot formation observed in a red top tube (serum)
Decreased levels: extensive coagulation (e.g., DIC), liver disease, or major blood loss
Positive acute phase reactant
Peaks between beta (β) and gamma (γ)
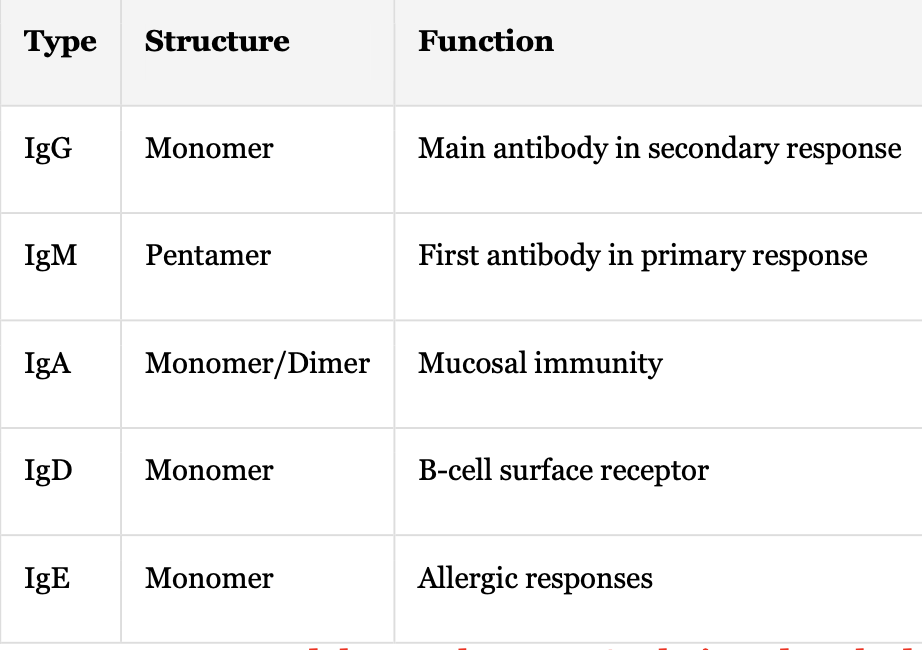
Immunoglobulins: Types + Structure + Function
IgG + Monomer + Main antibody in secondary response
IgM + Pentamer + First antibody in primary response
IgA + Monomer/Dimer + Mucosal immunity
IgD + Monomer + B-cell surface receptor
IgE + Monomer + Allergic responses
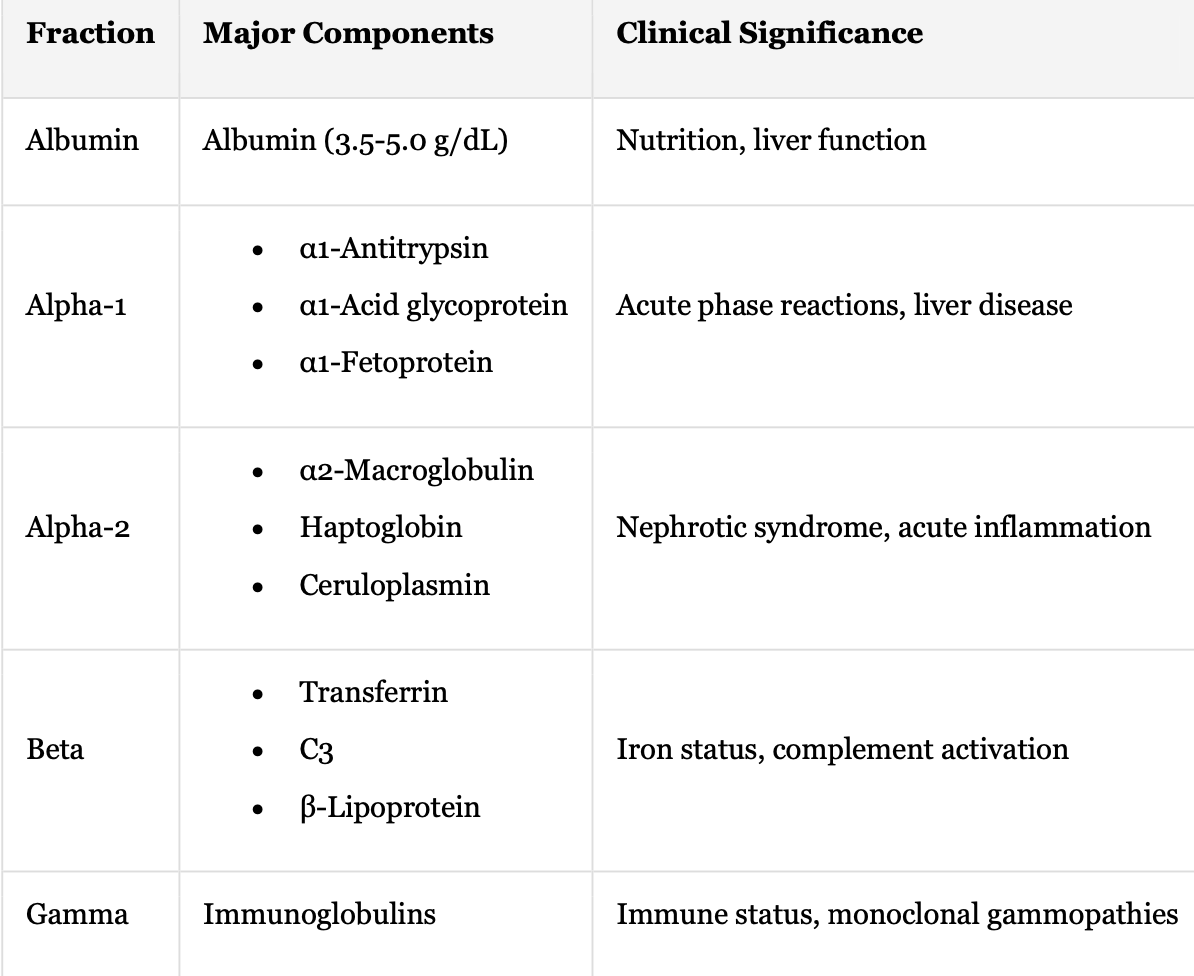
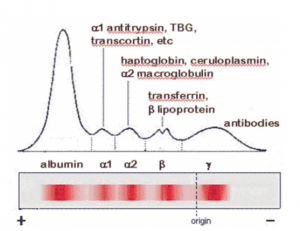
Protein Electrophoresis: Fraction + Major Components + Clinical Significance
Albumin + Albumin (3.5-5.0 g/dL) + Nutrition, liver function
Alpha-1 + Acute phase reactions, liver disease
α1-Antitrypsin
α1-Acid glycoprotein
α1-Fetoprotein
Alpha-2 + Nephrotic syndrome, acute inflammation
α2-Macroglobulin
Haptoglobin
Ceruloplasmin
Beta + Iron status, complement activation
Transferrin
C3
β-Lipoprotein
Gamma Immunoglobulins + Immune status + monoclonal gammopathies
Gamma globulins
IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE
composed of 2 identical heavy and 2 identical light (kappa and lambda) chains
Single sharp peak in gamma region indicates monoclonal (coming from one cell line) gammopathy
Increased in plasma cell malignancy (multiple myeloma), infection etc
Hypoproteinemia vs Hyperproteinemia
Low protein levels due to renal loss, GI leakage, bleeding, and decreased intake from malnutrition or malabsorption
vs
High protein levels caused by dehydration from vomiting/diarrhea and excessive production, such as Bence Jones protein in multiple myeloma.
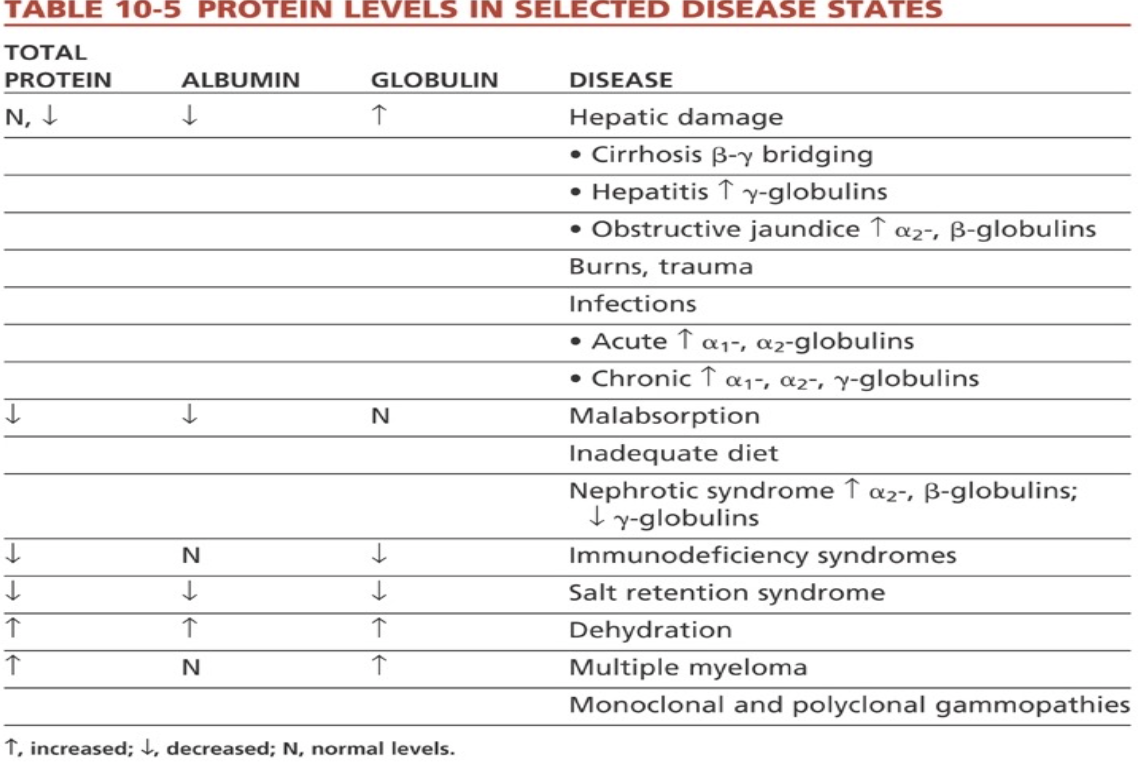
Acute Phase Response:
Decreased albumin
Increased α1 and α2 globulins
Elevated C-reactive protein
Multiple Myeloma:
M-protein spike
Sharp, narrow peak in gamma region
Possible hypogammaglobulinemia
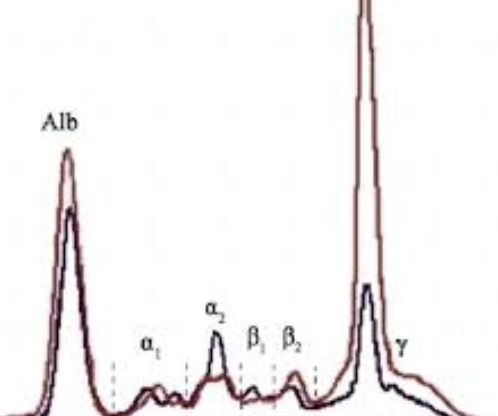
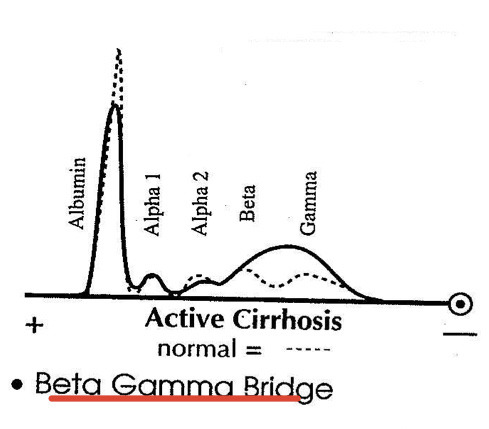
Chronic Liver Disease:
Decreased albumin
β-γ bridging
Polyclonal gamma increase
Nephrotic Syndrome:
Severe hypoalbuminemia
Increased α2-macroglobulin
Decreased gamma globulins
Advanced techniques/Testing Methods for specific protein analysis:
Method + Applications + Advantages
Immunofixation + High specificity for paraprotein characterization
Monoclonal protein typing
Light chain identification
Capillary Electrophoresis + High resolution, automation capability
Serum protein separation
Hemoglobin variants
Mass Spectrometry + Precise molecular characterization
Protein identification
Post-translational modifications
Positive Acute Phase Reactants
Protein + (Response Time) + Clinical Applications
C-Reactive Protein: (6-8 hrs)
Bacterial infections
Inflammatory conditions
Cardiovascular risk
Fribrinogen: (24-48 hrs)
Coagulation status
Inflammation marker
Negative Acute Phase Reactants
Protein + Response + Clinical Significance
Albumin + Decreased + Long-term nutritional status
Transferrin + Decreased + Iron status assessment
Prealbumin + Decreased + Short-term nutritional status
Electrophoresis example: Serum Proteins
When serum proteins are placed in a buffer of pH 8.6, they become (-) charged and migrate to an anode, while the buffer particles migrate to a cathode
What 2 properties affects the charge of Ampholytes in Buffer?
pH and Ionic Strength
Neutral proteins do not migrate when pH = pI.
If pH > pI, proteins carry a net negative charge and migrate to the anode (+ pole);
if pH < pI, they carry a net positive charge and migrate to the cathode (-) pole.
For example, at pH 8.6, albumin (pI 4.7) has a net negative charge and migrates to the anode.
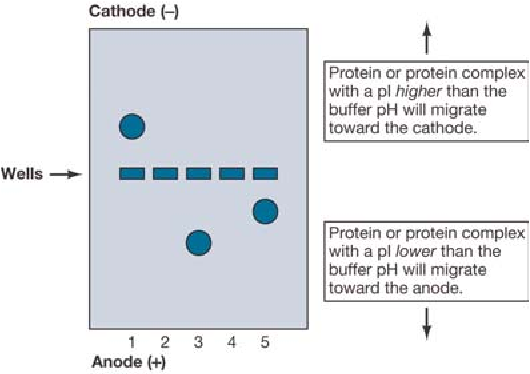
Electrophoresis vs Electroendoosmosis
Electrophoresis involves the movement of charged particles in a fluid under the influence of an electric field, while electroendoosmosis refers to the movement of liquid in a porous medium due to an electric field, affecting the migration of particles.
Electroendoosmosis
the flow of buffer solution in contact with a negatively charged stationary surface, caused by an applied electric field, which attracts positive ions that drag surrounding water molecules towards the cathode.
Electroendoosmosis Results and Effects on Proteins
Weakly negatively charged proteins, such as gamma globulins, may be pushed toward the cathode due to buffer flow overriding the electrical pull, resulting in slower-than-expected migration. This tension can help achieve better separation of protein bands.
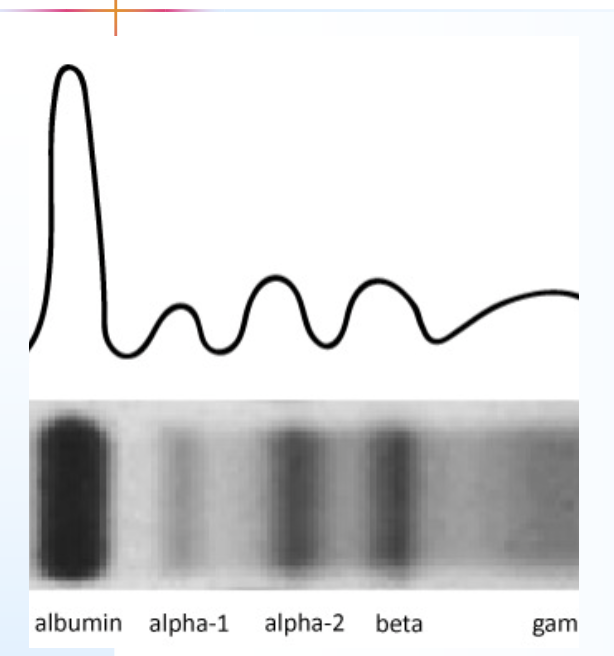
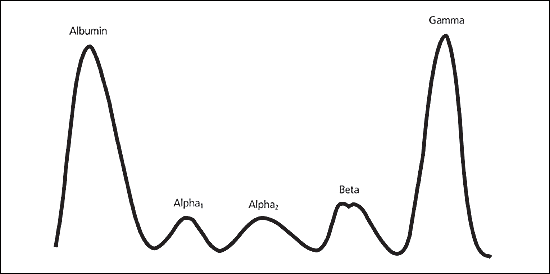
serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) Patterns
separates serum proteins into five main fractions: albumin, alpha-1 globulin, alpha-2 globulin, beta globulin, and gamma globulin
Patterns include: (A) Reference; (B) Monoclonal increase in γ area; (C) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency; (D) Nephrotic syndrome; (E) Inflammation; (F) Cirrhosis .
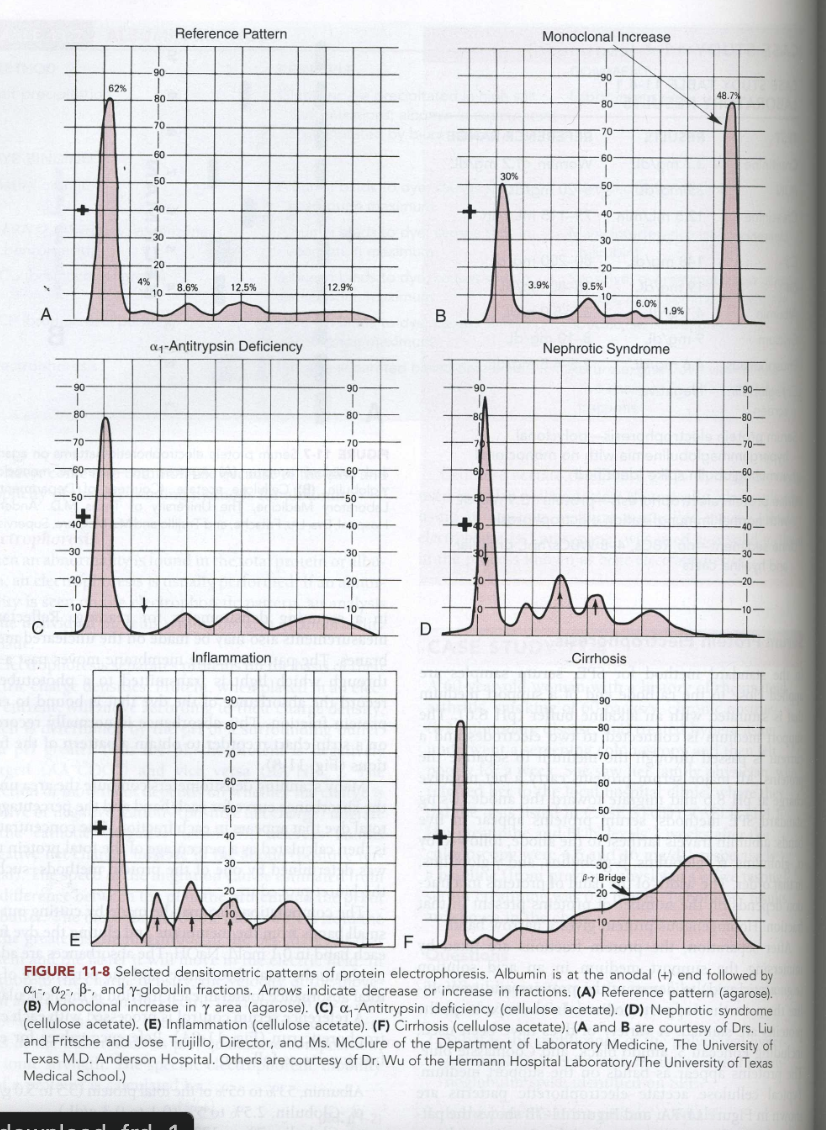
SPE: Reference Pattern
The normal densitometric pattern of serum protein electrophoresis, characterized by distinct albumin and globulin fractions, used as a baseline for comparison with other patterns.
SPE: Monoclonal Increase
A monoclonal spike in the gamma-globulin zone indicates a monoclonal gammopathy
SPE: a1-antitrypsin defiency
reduced or absent alpha-1 globulin peak may indicate low AAT levels.
Low alpha-1 globulin levels may indicate AAT deficiency, which can lead to lung or liver disorders.
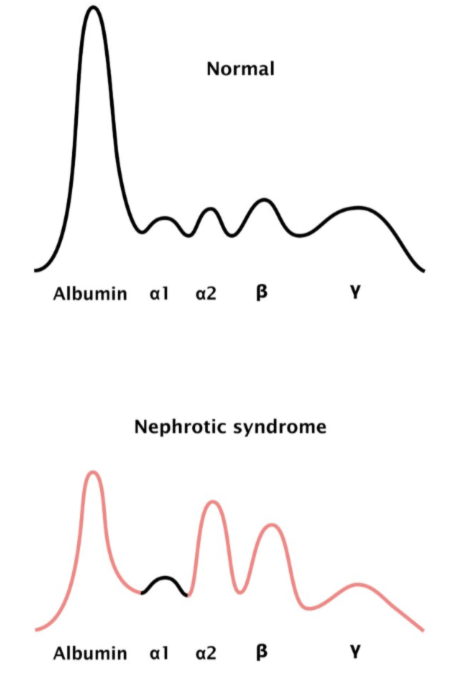
SPE: Nephrotic Syndrome
Decreased albumin and gamma globulins
Increased alpha-2-globulins and beta-globulins
Decreased total protein
SPE: Inflammation
Increased levels of alpha-1 and alpha-2 globulins, with possible elevation of immunoglobulins.
SPE: Cirrhosis
Decreased albumin levels and increased gamma globulins, often indicating liver dysfunction. Beta Bridge to gamma globulins present
SPEP: Hemolyzed Sample
Free hemoglobin will peak b/w a2 and b region while Hemoglobin-haptoglobin complexes will cause a peak in the a2 region
Proteins in Urine
Elevated urine protein is an early indicator of renal impairment
Bence Jones protein (Ig light chains) is present in multiple myeloma
Protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Elevated gamma (IgG) levels produced in the CNS cause oligoclonal banding on high-resolution CSF electrophoresis, a marker for Multiple sclerosis
CSF IgG also increases in bacterial, viral, and fungal meningitis.
oligoclonal bandings
are distinct bands of immunoglobulins seen in cerebrospinal fluid, indicating an autoimmune response or central nervous system pathology.
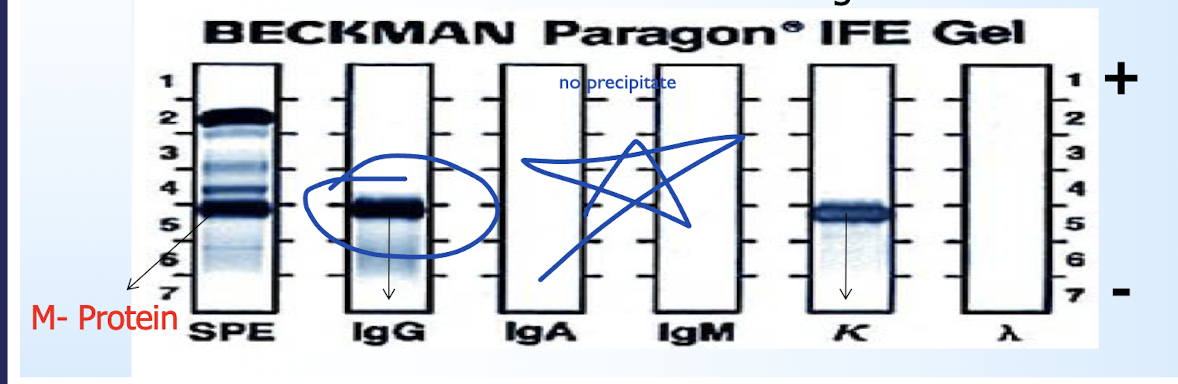
Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE)
identifying and characterizing monoclonal proteins (M-proteins) by separating them in a gel based on hevy and light chains.
Forms dark visible bands that indicate monoclonal gammopathies
Ex: multiple myeloma (dark band)
IgG vs IgM
IgG providing long-term immunity and is the main antibody in secondary response + most abundant while IgM is the first antibody produced during an immune response providing short-term immunity