Diagnostic Imaging of the Heart
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Imaging the heart, why use radiography?
Visualization of overall size
Visualization of shape
Location
Evidence of congestive heart failure (pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, etc.)
Imaging the heart, why use ultrasound?
Visualize chamber size
Myocardial function
Blood flow and leakage through valves
Disease of internal cardiac structures
Less useful for evidence of congestive heart failure
Full assessment of the heart requires
Both radiography and echocardiography
What cannot be visualized on radiography in regards to the heart?
Internal structures
Myocardial function
Valve incompetence
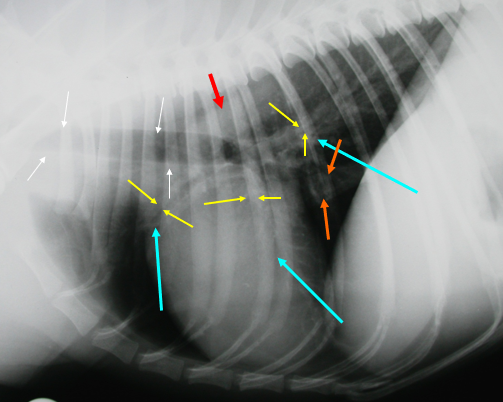
What is indicated by the red arrow?
The aorta (image, lateral)
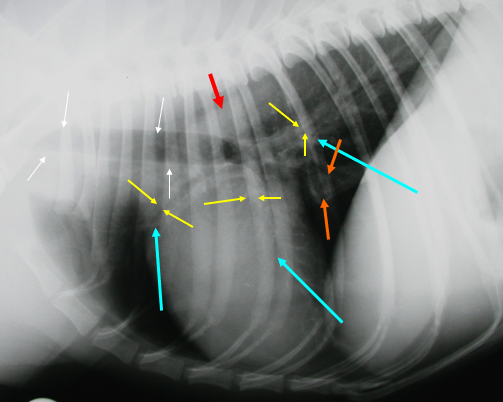
What is indicated by the white arrows?
Trachea (image, lateral)
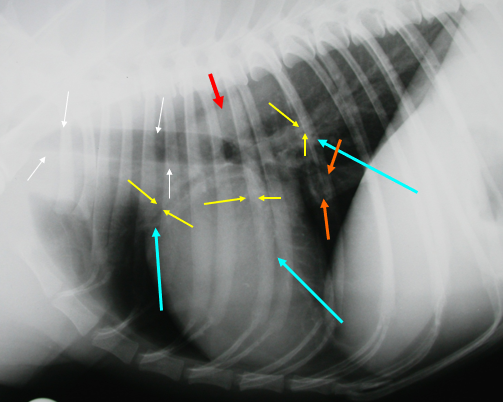
What is indicated by the yellow arrows?
Large bronchi (image, lateral)
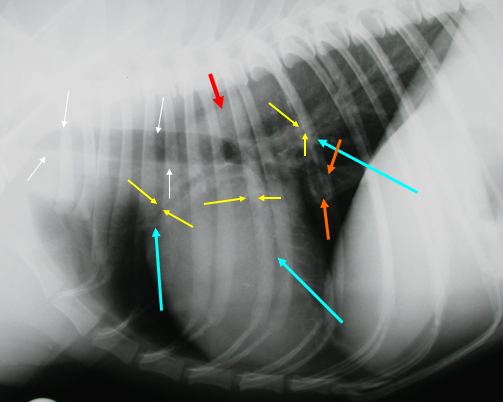
What is indicated by the blue arrows?
Pulmonary vessels (image, lateral)
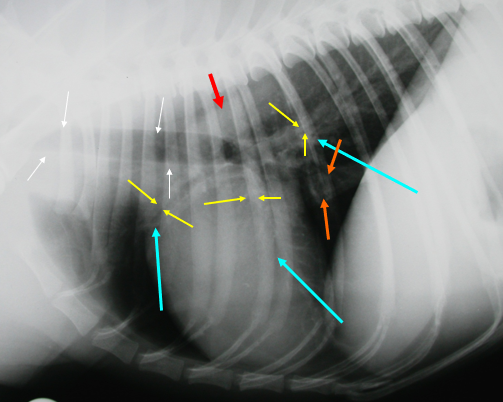
What is indicated by the orange arrows?
Caudal vena cava (image, lateral)
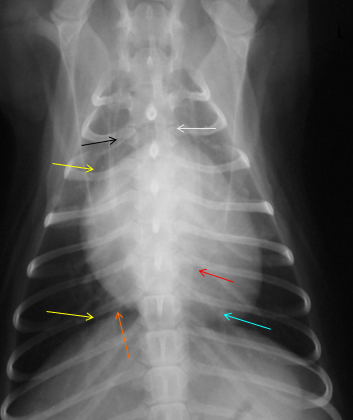
What is indicated by the red arrow?
Aorta (image, dorsoventral)
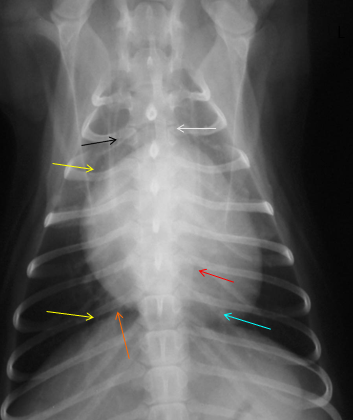
What is indicated by the black arrow?
Trachea, usually deviates to the right of midline (image, dorsoventral)
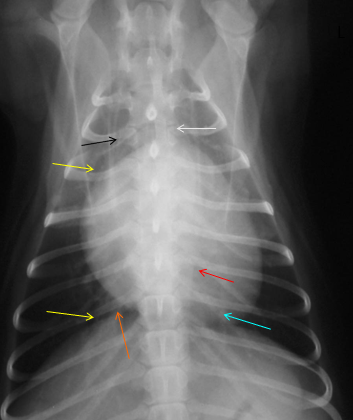
What is indicated by the yellow arrows?
Large bronchi (image, dorsoventral)
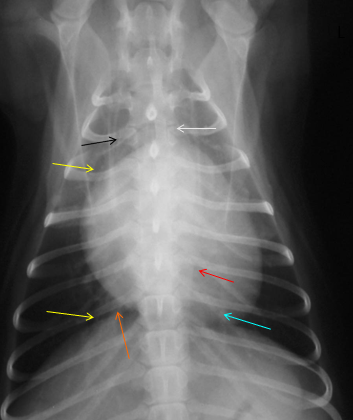
What is indicated by the blue arrow?
Pulmonary vessels (image, dorsoventral)
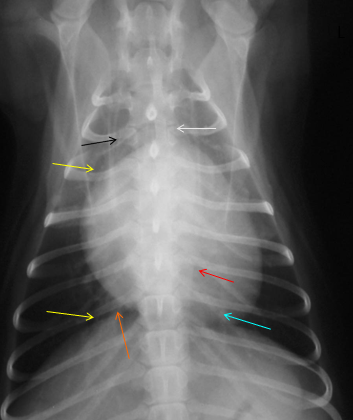
What is indicated by the orange arrow?
Caudal vena cava
What is indicated by the white arrow?
Mediastinum (image, dorsoventral)
What structure(s) are not typically seen on a lateral radiograph?
Esophagus
Mediastinum
What should you note while assessing normal and abnormal findings called Roentgen signs?
Size
Shape
Opacity
Margins
Location
Number
What position is best to assess the heart?
Right lateral recumbency and Dorsoventral radiographs
How many intercostal spaces should the heart cover in a dog?
3-3.5
How many intercostal spaces should the heart cover in a cat?
2-3
The height of the heart relative to the height of the thorax should be about ____ in dogs and cats
2/3
The width of the heart relative to the width of the thorax should be about ____ in dogs and cats
1/2-2/3
Position of the heart should be within/near the
Middle mediastinum, 4th-6th intercostal space
Degree of sternal contact of the heart depends on
Breed
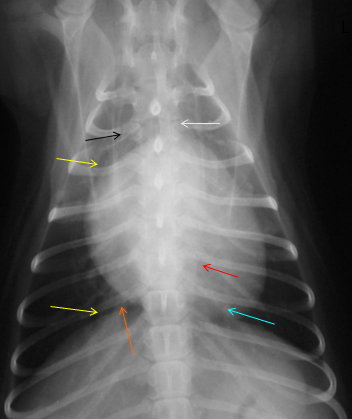
What condition is visualized here?
Cardiomegaly
How would you quantify a canine heart being enlarged? (ie cardiomegaly)?
Heart with >2-3 height of thorax
Heart >3.5 intercostal spaces covered
Heart shape: RLR view: What is seen at 12-3?
Left Atrium (lateral view)
Heart shape: RLR view: What is seen at 3-5?
Left Ventricle (lateral view)
Heart shape: RLR view: What is seen at 5-8?
Right ventricle (lateral view)
Heart shape: RLR view: What is seen at 8-10?
Right Atrium (lateral view)
Heart shape: RLR view: What is seen at 10-12?
Great Vessels (lateral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 11-1?
Aortic arch (Ventral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 1-2?
Pulmonary artery (ventral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 2-3?
Left auricle (ventral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 3-5?
Left Ventricle (ventral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 5-9?
Right ventricle (ventral view)
Heart shape: DV view: What is seen at 9-11?
Right Atrium (ventral view)
Complete assessment via echocardiography requires the following
B-Mode
M-Mode
Doppler
Integrated ECG
What does B-mode show?
“Slice” of anatomy
What does M-mode show?
Functional measurements
Shows movement or contraction of structures over time
Measurements of myocardial contractility
What does Doppler show?
Quantitative and qualitative assessment of blood flow
How does M-mode ultrasound work?
Echoes from a single line of ultrasound are plotted against time
What is the benefit of having integrated ECG?
Allows synchronization of ultrasound images with known heart beat patterns at a given time
How does Doppler imaging work?
Reflection of sound from moving object → change in frequency
If doppler imaging has color flow, what color means flow is away from transducer?
Blue
If doppler imaging has color flow, what color means flow is towards transducer?
Red
What type of measurement is color flow doppler imaging considered?
Qualitative blood flow
What type of measurement is pulsed-wave or continuous wave doppler imaging considered?
Quantitative blood flow
When scanning the heart, how should the patient be positioned?
In R and L lateral recumbency
Where is the best position to place the transducer when scanning the heart?
Beneath the patient, nearest the dependent wall of thorax (ideally via a hole in ultrasound table), between the ribs
Why should sedation be avoided when scanning the heart?
It can affect myocardial contraction
Right parasternal approach is the
most widely used scanning approach
What does the Right parasternal approach give you information on?
Chamber sizes
Myocardiac function
Valve function
What is a limitation of the right parasternal approach?
Difficult to image all chambers together
What direction are the planes of view when doing the right parasternal approach?
Ventral to dorsal, labelled A-F
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice A on a right parasternal short axis scan?
LV and a little of RV
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice B on a right parasternal short axis scan?
LV, more of RV, and papillary muscles
Mushroom slice is a view to visualize which structures?
Left ventricle is the characteristic shape, some of Right ventricle
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice C on a right parasternal short axis scan?
LV, RV, and CH?
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice D on a right parasternal short axis scan?
LVO, RVO, PM, PMV, AMV
“Fish mouth” appearing structure is what structure within the heart?
Mitral valve
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice E on a right parasternal short axis scan?
LA, RV, pulmonary valve, TV, Aorta and aortic valve
What structure(s) are visible when looking at slice F on a right parasternal short axis scan?
RA, R auricle, Caudal vena cava, R and L pulmonary artery, aorta
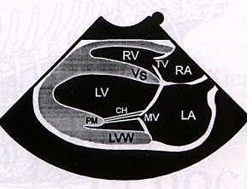
What view is being shown in this image?
Right parasternal long axis - LA/MV
What view is best for viewing vegetative growth on the mitral valve?
Right parasternal long axis L atrium view
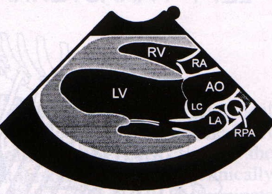
What view is being shown in this image?
Right parasternal long axis - Aorta
How should the patient and transducer be oriented for left apical views of the heart?
Patient: L lateral recumbency
Scan from dependent left thoracic wall
Why are L apical views beneficial?
Good “end-on” views through the mitral and tricuspid valves (four chamber) and aortic outflow (five chamber)
Good for accurate measurements of blood flow velocities
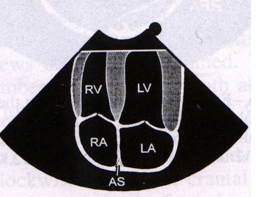
What view is being shown in this image?
Left apical Four-Chamber view
What are common classes of cardiac diseases?
Myocardial disease
Valvular disease
Pericardial disease
Describe Myocardial disease: Dilated cardiomyopathy
Reduced myocardial contractility
Decreased cardiac output and dilation of chambers
Describe Myocardial disease: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Decreased capacity of ventricles
Reduced cardiac output
Describe Valvular disease aetiologies
Dysplasia, infection, etc.
Leakage of valves and chamber dilation
Ex endocardiosis
Describe Pericardial disease
Prevents proper fulling of heart chambers (esp. RV) and reduces cardiac output
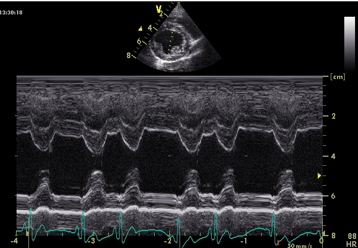
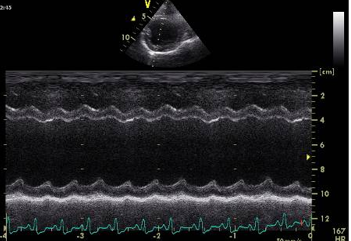
M Mode ultrasound, is this normal or an example of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Normal
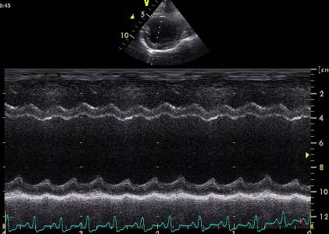
M Mode ultrasound, is this normal or an example of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
What is shown in this image?
M mode ultrasound of a dog with DCM
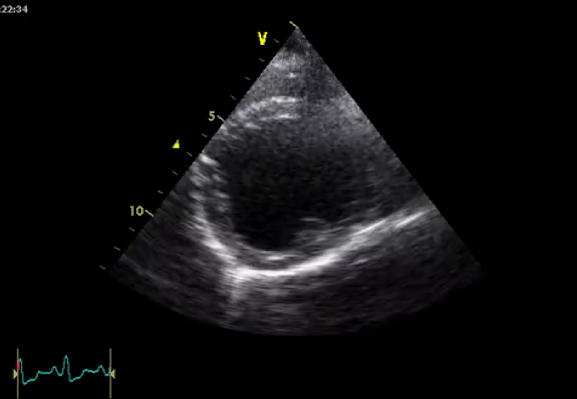
What is shown in this image?
B mode ultrasound of a dog with DCM
How can you identify a cat having hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
“Valentine’s heart” or atrial enlargement on DV view
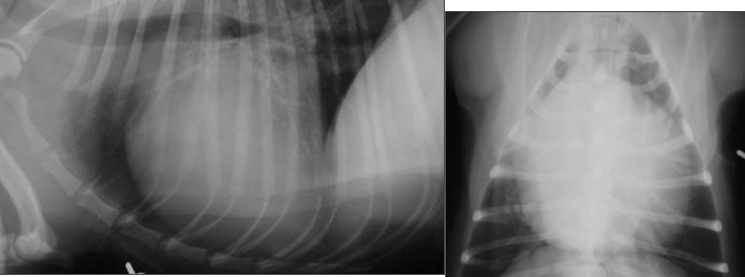
What is shown in this image?
Cardiomegaly with LA enlargement
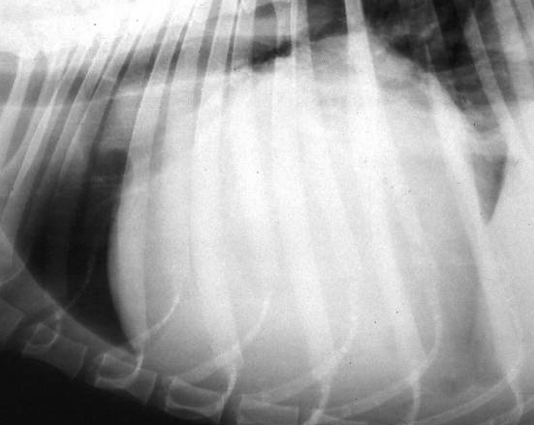
What is shown in this image?
Pericardial effusion