Species Diversity: the 6 kingdoms of life
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) - "The amazing kingdom adventure" + review [also see bacteria and virus quizlet]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
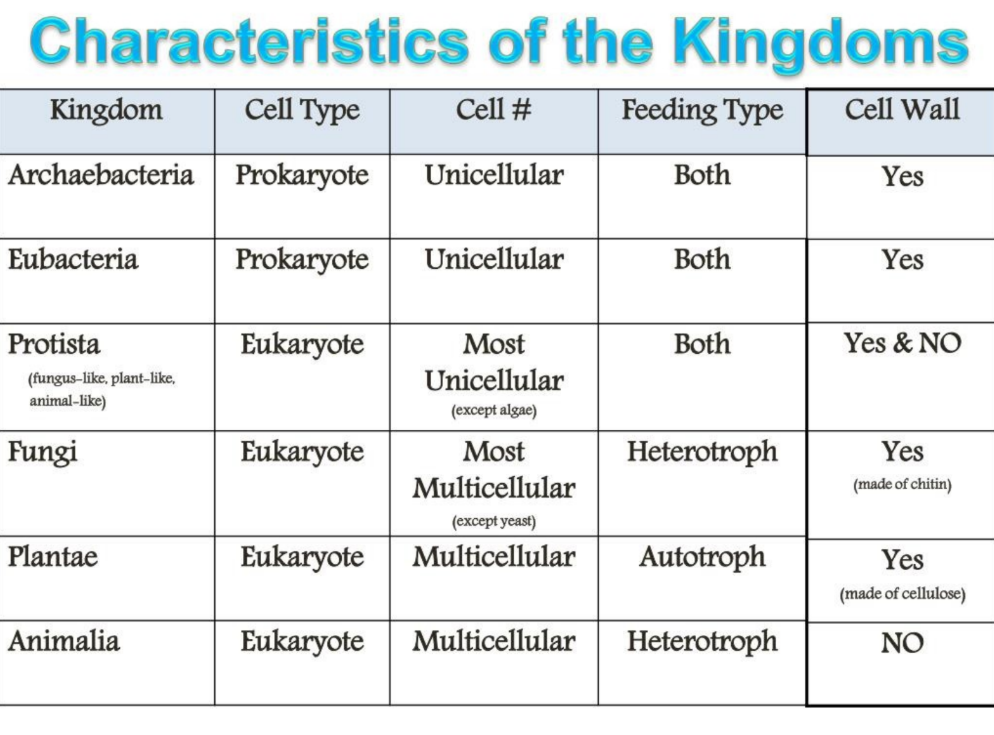
3 factors used to group kingdoms
Cell Type: eukaryote vs prokaryote
Cell Number: multicellular vs unicellular
Feeding Type: autotroph vs heterotroph
Protists
⇨ the “junk drawer”
mostly unicellular, with the exception of some algae and seaweeds
eukaryotes
can be both heterotrophs and autotrophs
Some have cell walls and some don’t
What diseases are caused by protists? (give 4 examples)
Malaria
Amebic Dysentry
Toxoplasmosis
Beaver fever
Many protists are ______ , so contaminated water causes many diseases
aquatic
3 groups of protist classification
Animal-like (protozoans)
Fungi-like
Plant-like (algae)
subgroups/phyla of protozoans
Sarcodina
Ciliates
Zooflagellates
Sporozoans
Sarcodina
move by false feet called pseudopods
ex: amoeba
Ciliates
move by cilia
ex: paramecium
Zooflagellates
move by flagella, live in other organisms
ex: Giardia, a parasite that causes beaver fever
Sporozoans
cannot move, they are carried from host to host
ex: Plasmodium, which causes malaria
subgroups/phyla of plant-like protists (algae)
Diatoms
Dinoflagellates
Euglenoids
Green Algae
Red Algae
Brown Algae
Diatoms
move by oozing, have glassy cell walls
ex: ground up for use in toothpaste and diatomaceous earth
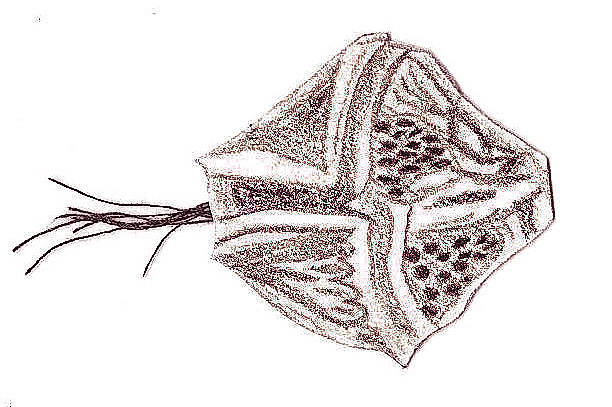
Dinoflagellates
armour-like cell walls, have 2 flagella
ex: red tides
Euglenoids
both autotrophic and heterotrophic
ex: Euglena
Green Algae
green colour, most are unicellular, but some are multicellular like seaweed
Red Algae
red colour, multicellular
ex: dried to make nori, used in hair products

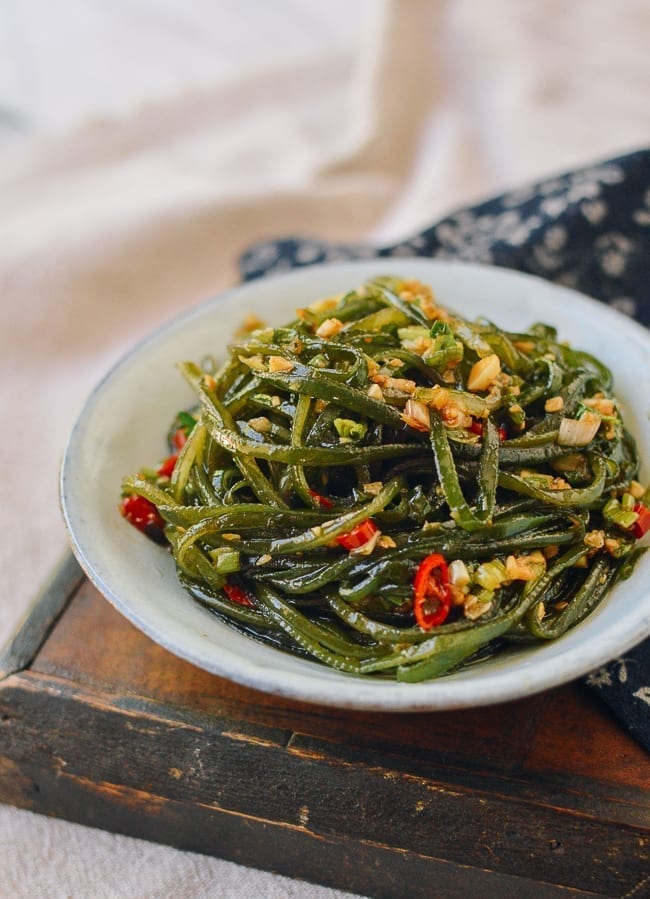
Brown Algae
many colours, multicellular, forms plant-like structures (kelp)
ex: kelp can be eaten as food or used as thickener

subgroups/phyla of fungi-like protists
Water Molds
Slime Molds
Water Molds
grow as tiny threads, looks fuzzy
ex: caused the Irish Potato Famine
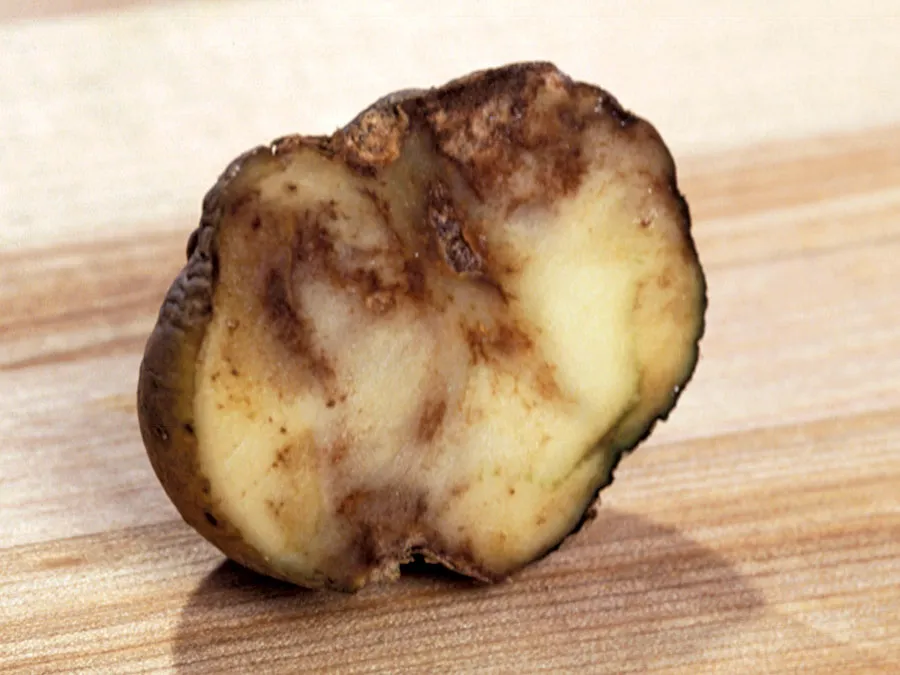

Slime Molds
lives in moist soil or decaying plants, yellow/orange colour, pulses and oozes like an amoeba

Although sometimes confused with one another, algae are NOT plants, they are ______
plant-like protists
Fungi
multicellular except for yeast
eukaryotes
heterotrophs
cell walls made of chitin
Ideal conditions for fungus
warm, moist, and dark
How do fungi affect our lives? (advantages and disadvantages)
Many are edible such as mushrooms or blue cheese
Yeast is used to make bread and alcohol
Can produce antibiotics like penicillin
Cause diseases like athlete’s foot and ringworm
Fungi are _____ , meaning they are stationary
sessile
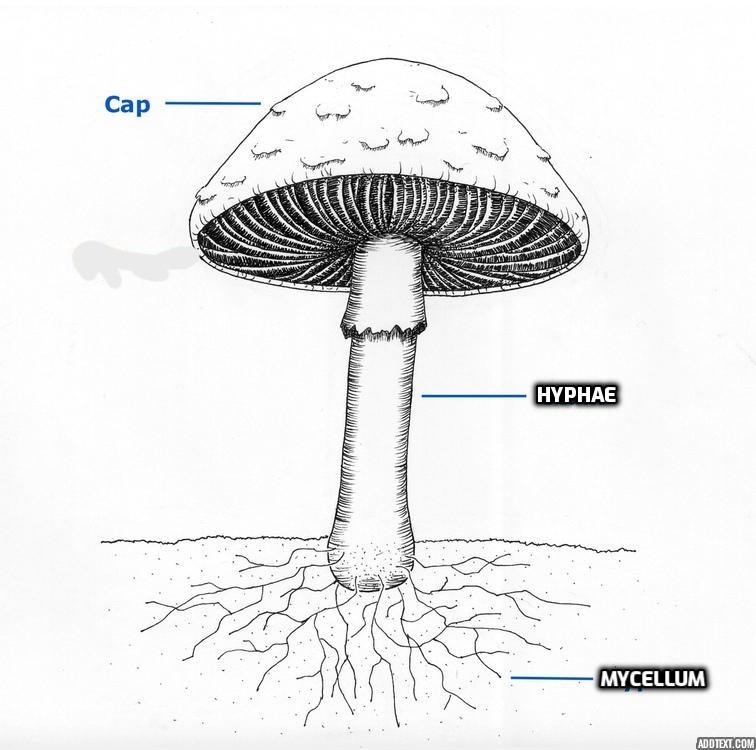
3 main structures of a fungus
Cap
Hyphae
Mycelium
3 types of fungi diets
Saprophytes: get nutrients from dead organic matter
Mutualist: live symbiotically
Parasites: absorb from their host, harmful to the host
All fungi are multicellular, except for ______, which is a unicellular fungi
yeast
The general structure of a fungi includes filaments called ______. A mass of hyphae make up the fungi’s body, which is called a ______.
hyphae, mycelium
In most fungi, hyphae are separated into cell-like compartments by _____ , which usually contain ______.
septa, pores
Common types of fungi (3)
Mushrooms, Yeast, and Moulds
How do fungi reproduce?
spores are released from the gills
budding (yeast)
some also reproduce by fragmentation
Plantae
multicellular
eukaryotes
autotrophs
cell walls made of cellulose
Plants are different from fungi because unlike heterotrophic fungi, they are _______.
autotrophs
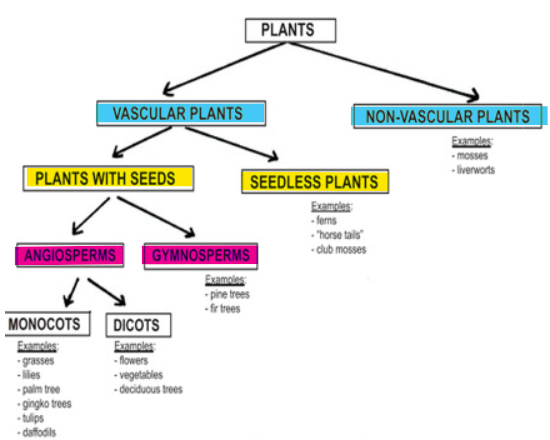
3 classifications that divide plants into groups
Vascular vs Non-Vascular
With Seeds vs Seedless
Angiosperms vs Gymnosperms
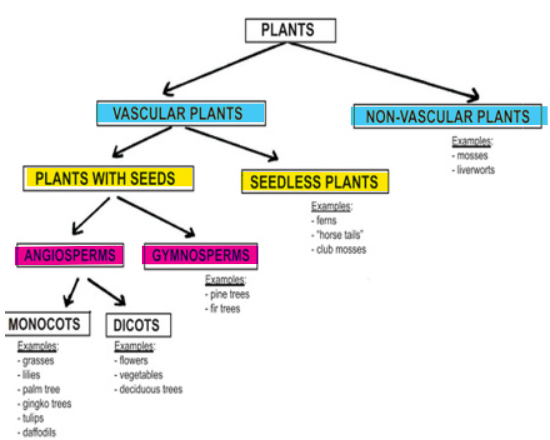
Vascular plants
contain internal transportation system, two kinds of tissues called xylem (water-carrying) and phloem (nutrient-carrying)
Non-vascular plants
simplest of all land plants
lack a vascular system to transport water = fertilization depends on water!
no woody tissue necessary for support = low to the ground
⇨ ex: mosses and liverworts
Plants with seeds
produce seeds, which protect and nourish the embryo and can be dispersed by wind or animals, without water
reproduce sexually using pollen grains (male gametophytes) that fertilize the ovule (female gametophyte)
Seedless plants
do not produce seeds (use spores to reproduce)
⇨ ex: ferns, horse tails
Angiosperms
flowering plants, produce fruit which disperse the seeds
nectar attracts pollinators, which carry the pollen to other plants
Gymnosperms
do not produce flowers or fruits
produces seeds in special structures called cones
male cones produce and release pollen, female cones produce eggs
⇨ ex: coniferous trees like pines and cedars
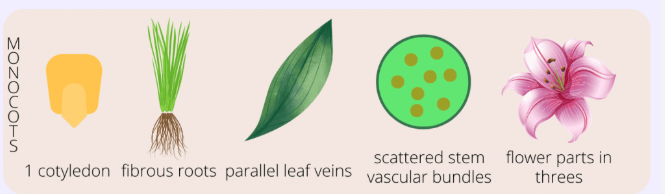
Monocots
petals in multiples of 3
parallel veins
fibrous roots
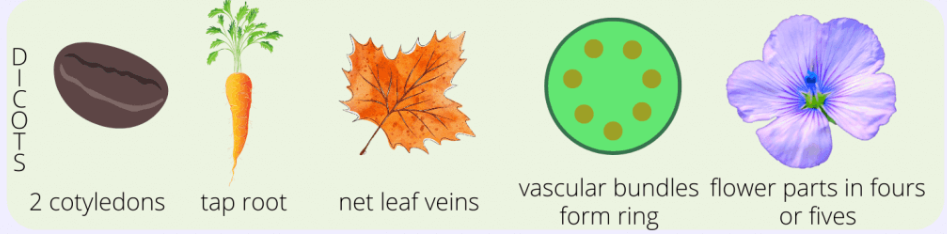
Dicots
petals in multiples of 4-5
net-like/branched veins
tap roots
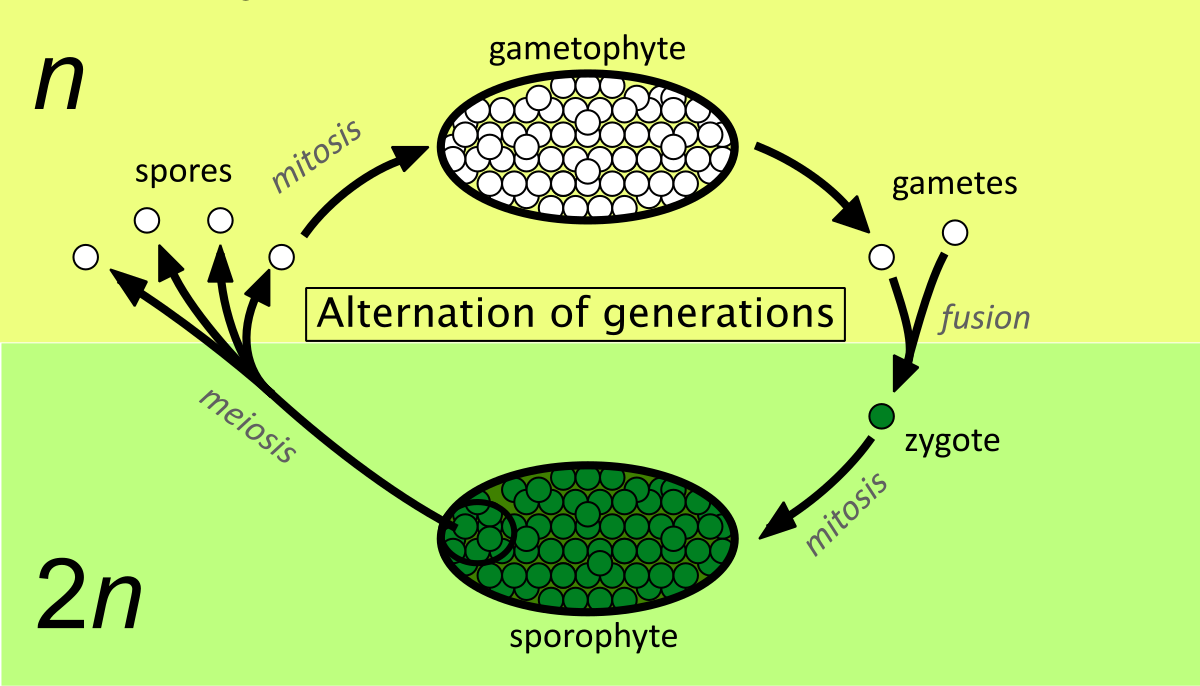
Alternation of generations
a life cycle that alternates between haploid and diploid generations
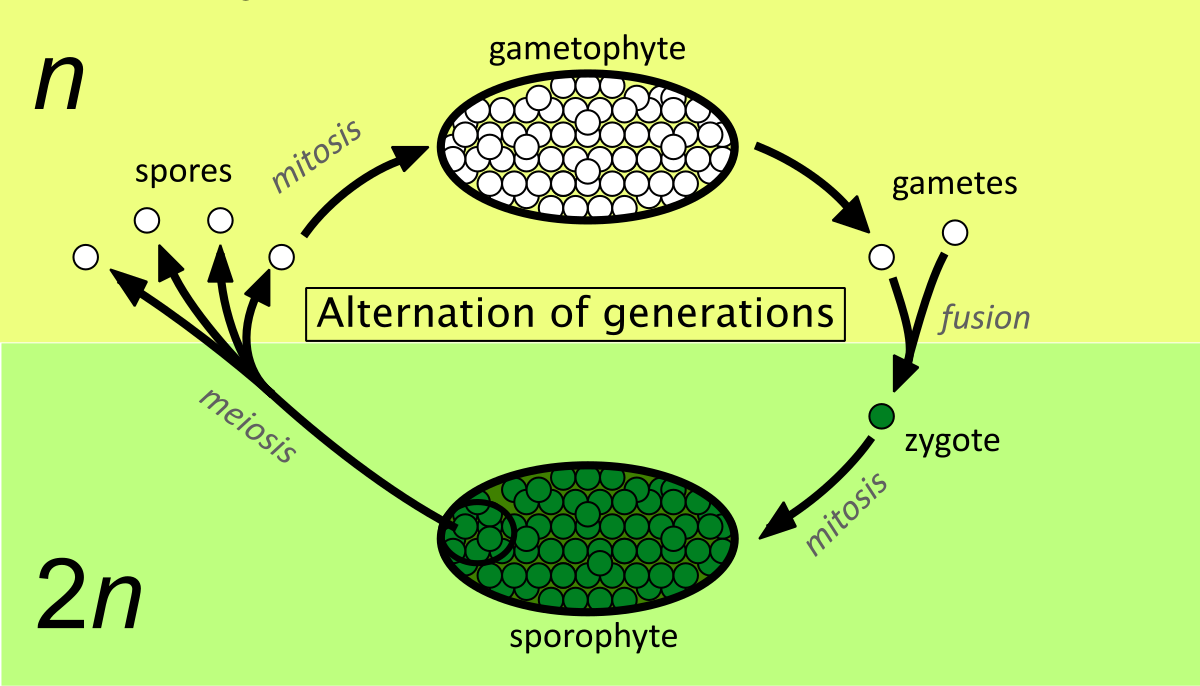
In an alternation of generations, the diploid generation produces _____, and the haploid generation produces ______.
spores, gametes
A plant in the diploid generation is called a _________, and a plant in the haploid generation is called a ________
sporophyte, gametophyte
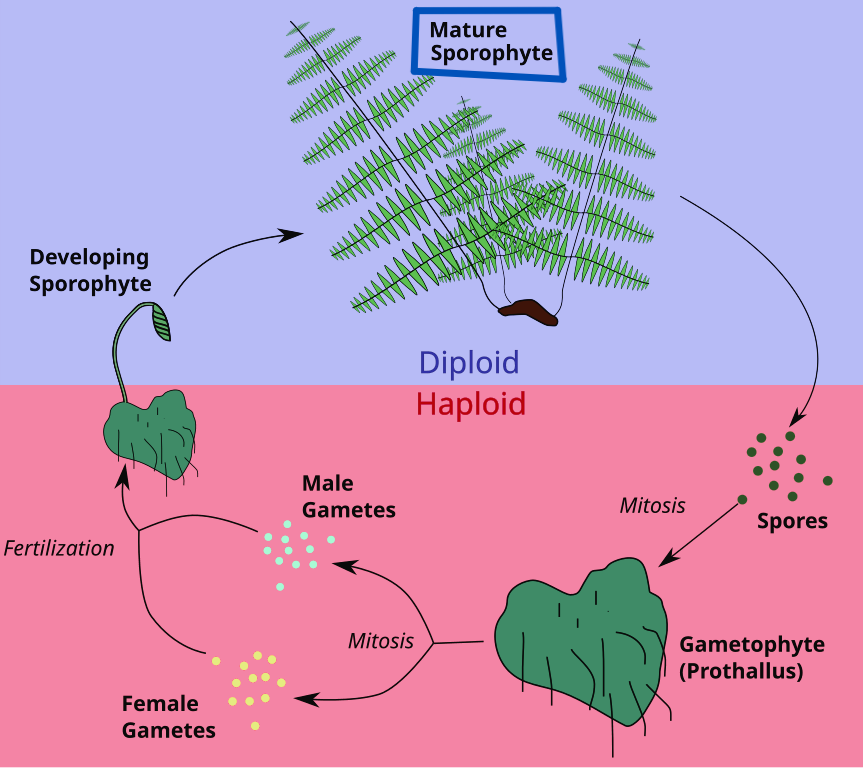
Sporophytes (2n)
divide by meiosis to produce haploid asexual spores
these spores then grow into gametophytes
Gametophytes (n)
produce gametes, the haploid sex cells
the gametes are then fertilized and become zygotes that grow into diploid sporophytes, continuing the cycle
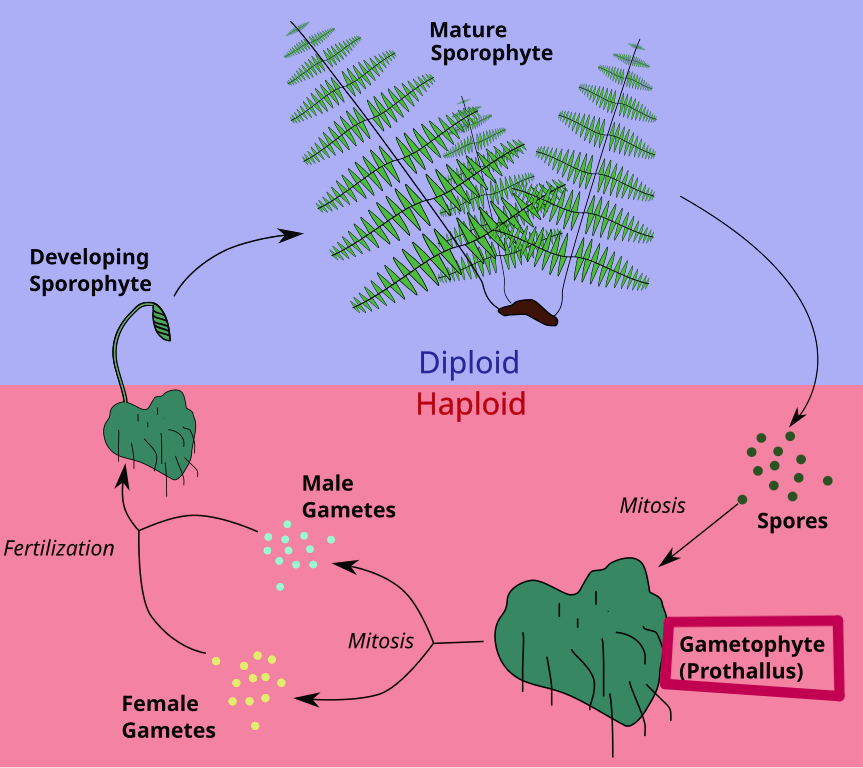
The alternation of generations life cycle is used mainly by __________ and __________ plants
non-vascular, seedless
Animalia
multicellular
eukaryotes
heterotrophs
do not have cell walls
motile at some stage
the simplest type of animals are the _______
sponges
Protostome vs Deuterostome
during embryonic development…
Protostomes: mouth forms before the anus (mollusks, annelids, arthropods)
Deuterostomes: anus forms before mouth (echinoderms, chordates)
6 criteria used for classifying animals
Body Symmetry
Skeletal Characteristics
Body Layers
Body Cavity
Movement
Reproduction
Body Symmetry types
Asymmetrical: no general body plan (ex: sponges)
Radial Symmetry: body parts organized about central axis (ex: jellyfish)
Bilateral Symmetry: have a single plane of symmetry that creates mirror halves (ex: humans)
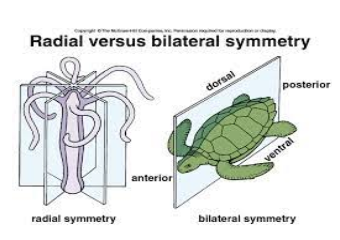
Skeletal Characteristics types
Invertebrates (95%): have a hard external skeleton, made of chitin and called exoskeleton (ex: crabs)
Vertebrates: have a hard internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage (ex: fish)
also have a dorsal backbone or notochord

Notochord
a flexible rod that runs along the dorsal surface and beneath the nerve chord
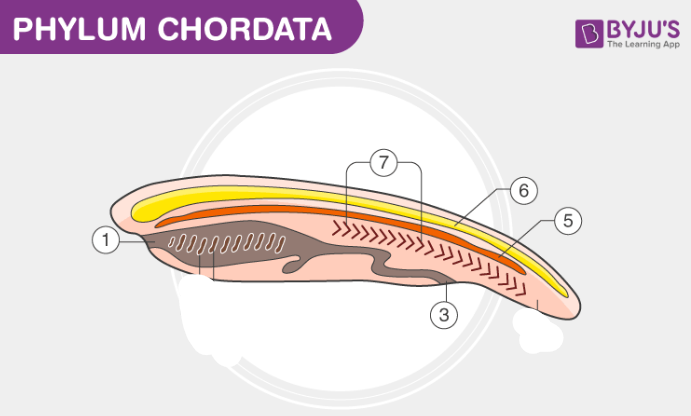
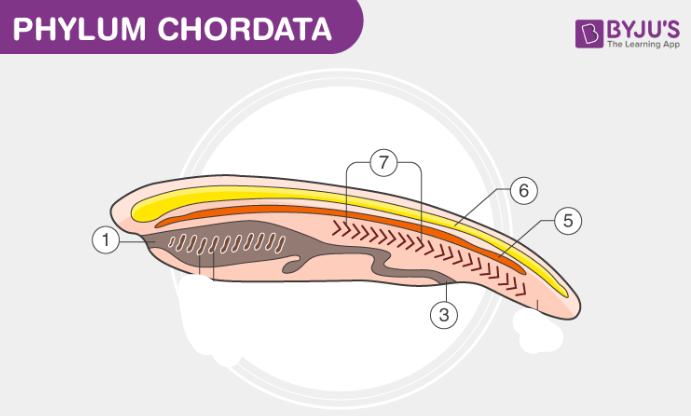
Label this chordate
Mouth
Segmented body wall muscles
Anus
Notochord
Dorsal nerve chord
3 kinds of body layers
Ectoderm: outer layer (skin, scales, nerves)
Mesoderm: middle layer (muscle, bone)
Endoderm: inner layer (digestive and pulmonary systems)
Body Cavity
Acoelomates: no true cavity (platyhelminthes)
Pseudocoelomates: partial cavity (cnidarians, nematodes)
Coelomates: full cavity (all other phyla)
Reproduction
Sexual (majority) vs Asexual
Internal vs External fertilization (ex: fish)
The 10 animal phyla
Porifera
Cnidarians
Platyhelminthes
Nematodes
Annelids
Mollusks
Arthropods
Echinoderms
Chordata
Rotifera (original animal)
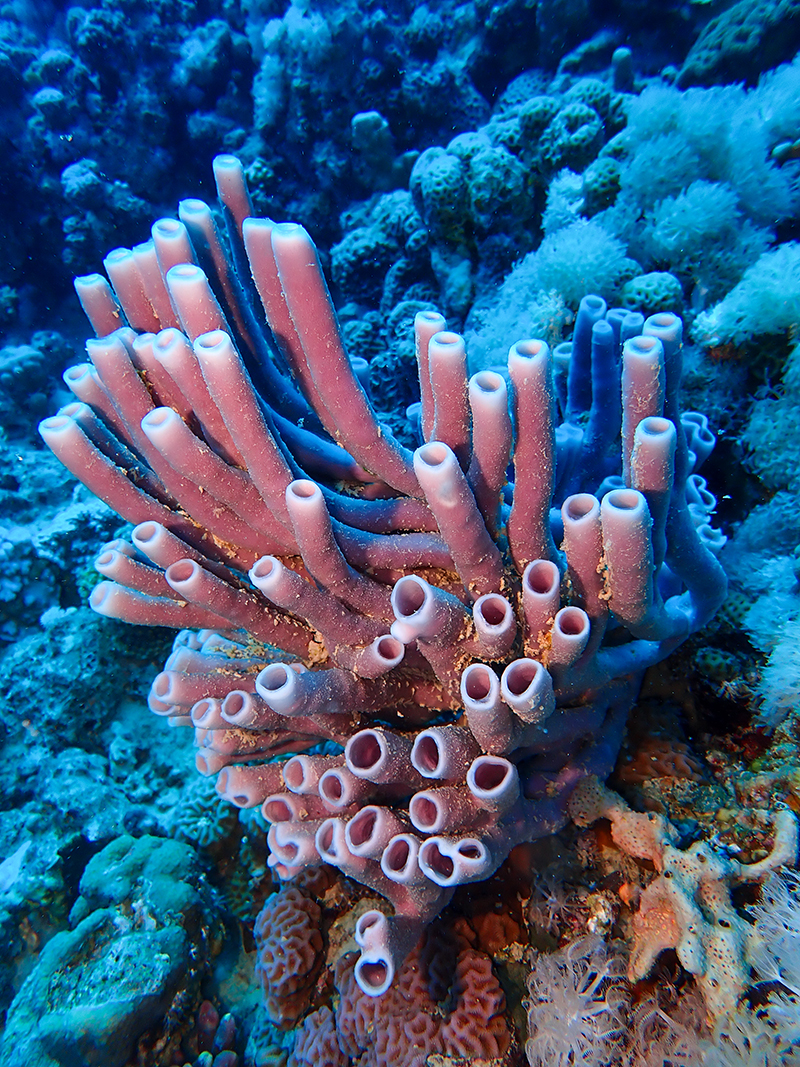
Porifera
asymmetrical
no nerves
have pores and get their nutrients from diffusion
ex: sponges

Cnidarians
radial symmetry
have stinging tentacles whose cells contain nematocysts
2 body layers
ex: anemones, jellyfish

Platyheminthes
bilateral symmetry
flat, unsegmented worms
many are parasites (like tapeworms)
ex: planaria, who are capable of regeneration and fertilize their own sex cells
Nematodes
bilateral symmetry
round, unsegmented worms
many are parasites
ex: hookworms
Annelids
bilateral symmetry
segmented worms
gas is exchanged through specialized parts
ex: earthworms, leeches

Mollusks
mostly bilateral symmetry
most have radula, a structure used for scraping
ex: squid, oysters

Arthropods
bilateral symmetry
segmented bodies
jointed appendages
ex: lobsters, spiders

Echinoderms
radial symmetry (technically pentaradial bc 5)
spiny skin
ex: sea urchins, sea cucumber, starfish

Chordata
bilateral symmetry
spinal chord
notochord
ex: mammals, fish

5 classes within the chordata phylum
Mammals
Fish
Amphibians
Reptiles
Birds
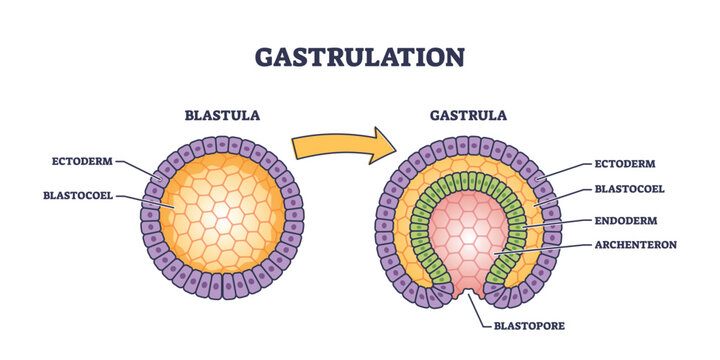
Blastula
Hollow ball of cells formed after the zygote undergoes mitosis
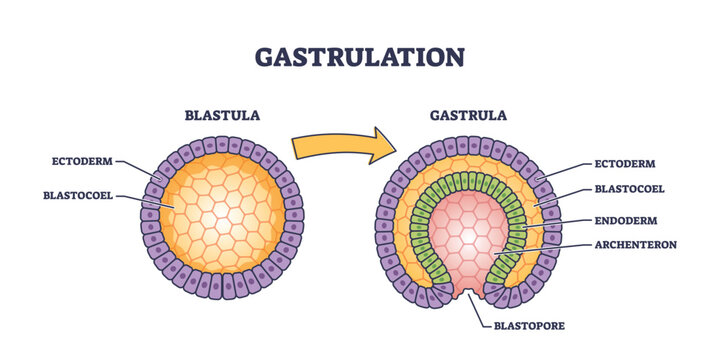
Gastrula
developed from the blastula, now has 3 layers of cells