Economic methodology and the economic problem
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How do scientists form a theory?
Postulate a theory - scientist puts forward a hypothesis capable of refutation
Gather evidence to support or reject the theory e.g. through experimentation
Accept, modify or refute the theory
Theories that gain universal acceptance known as laws
What is a social science?
Study of human society - economist has to gather information in the ordinary everyday world where many variables are changing over a given time period. However, economists are studying behaviour of groups of individuals which is often far more predictable than the behaviour of single individuals
Positive Statement definition
A statement of fact that can be scientifically tested to see if its correct or incorrect. Contains no value judgements
Normative Statement definition
Describes what should/ought/must happen. Will contain a value judgement
3 parts of the economic problem
What is to produce in the UK or world economy
How is it to be produced?
Who is to benefit from the goods and services produced?
Basic economic problem
Resources are scarce but wants are infinite
Opportunity cost definition
The cost/benefit of giving up the next best alternative whenever an economic decision is made. Can be shown using a PPF
4 Factors of Production
Labour - the workforce in the economy
Land - Raw materials (renewable and non-renewable)
Capital - The manufactured stock of tools, machines and factories used in the production of goods and services
Entrepreneurship - Individuals who organise production
What does a PPF diagram show?
PPF (Production Possibility Frontier) shows the combinations of goods or services which can be produced with an economy's resources
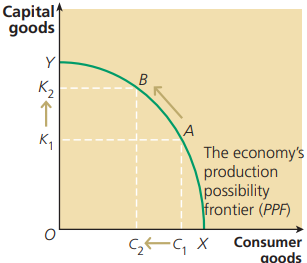
Productive Efficiency definition
This occurs when it is impossible for an economy to produce more of one good without producing less of another. The economy would be operating somewhere on its PPF.
X Inefficiency definition
Inefficiency in production that occurs when a firm does not minimise its costs and is usually present in monopolies or oligopolies where there is less competitive pressure to operate efficiently.
2 main causes of X Inefficiency
Overstaffing or employing machines that are underutilised
Paying its staff unnecessarily high wages or buying raw materials or capital at unnecessarily high prices
Allocative Efficiency definition
This occurs when the available economic resources are used to produce the combination of goods and services that best matches peoples' tastes and preferences. Also known as the Pareto Optimality
Dynamic Efficiency definition
Measures improvements in technical and productive efficiency that occur over time. Can result from an introduction of better methods of producing existing products
Value Judgement definition
Subjective opinion based on principles and beliefs rather than facts
Capital/producer good definition
A good which is used to produce other goods (e.g. tractors, factories)
Consumer good definition
A good which is consumed by individuals or households to satisfy their needs or wants
Technical progress definition
New and better ways of making goods and techniques for producing more output from scarce resources
Full employment definition and how is it shown on a PPF
When all who are able and willing to work are employed
All points on the PPF
Unemployment definition and how is it shown on a PPF
When not all of those who are able and willing to work are employed
Points inside the PPF indicate idle resources