8. Corneal Endothelial Pump
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
How much water is in the stroma?
78%
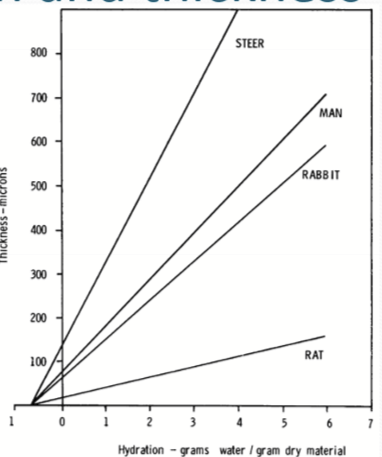
What is the relationship between the cornea hydration and its thickness
As the corneal thickness increases, there is a linear increase in water as well.
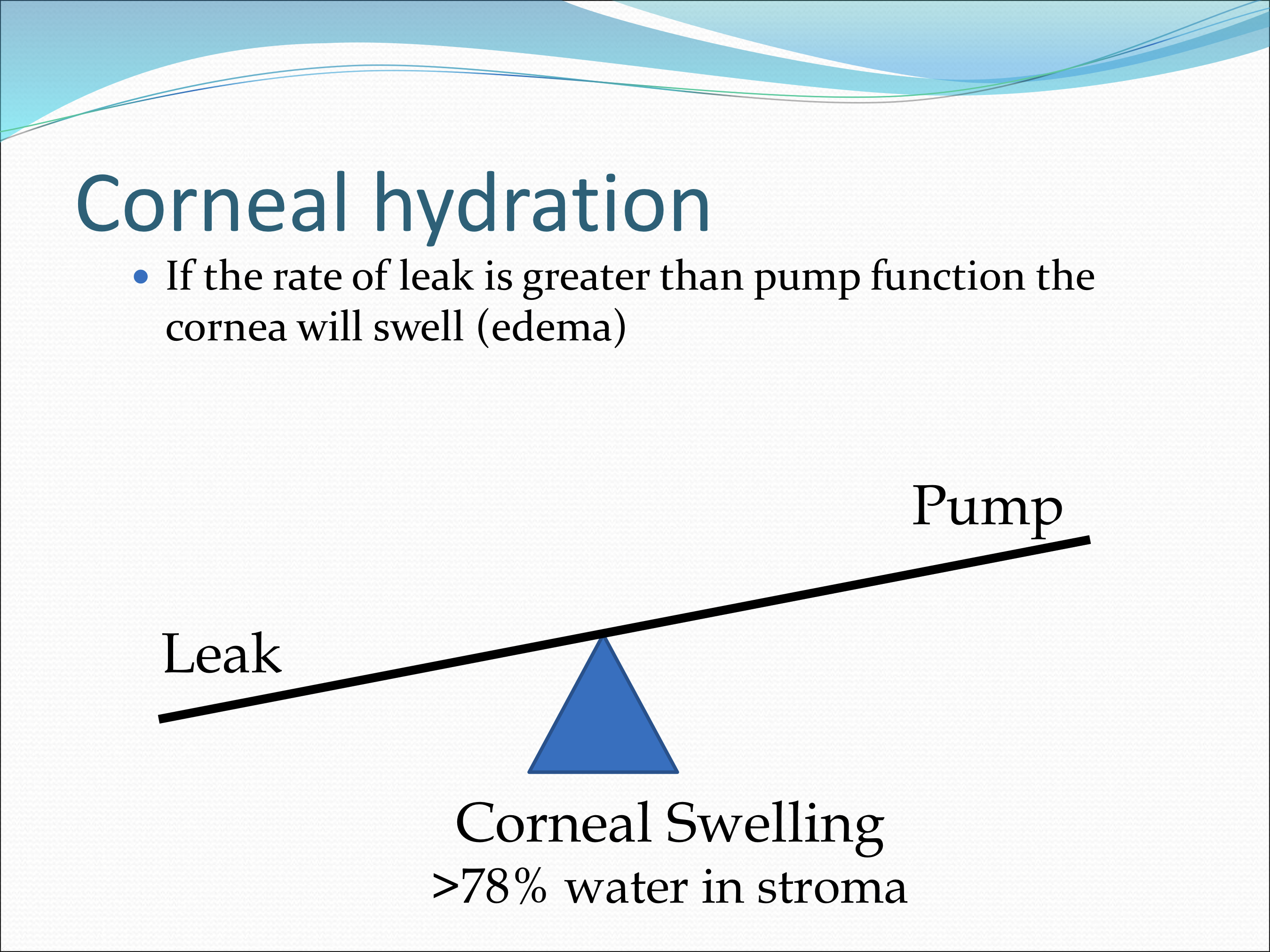
What happens of the rate of leak is greater than the pump function of the cornea?
The cornea will swell (edema)
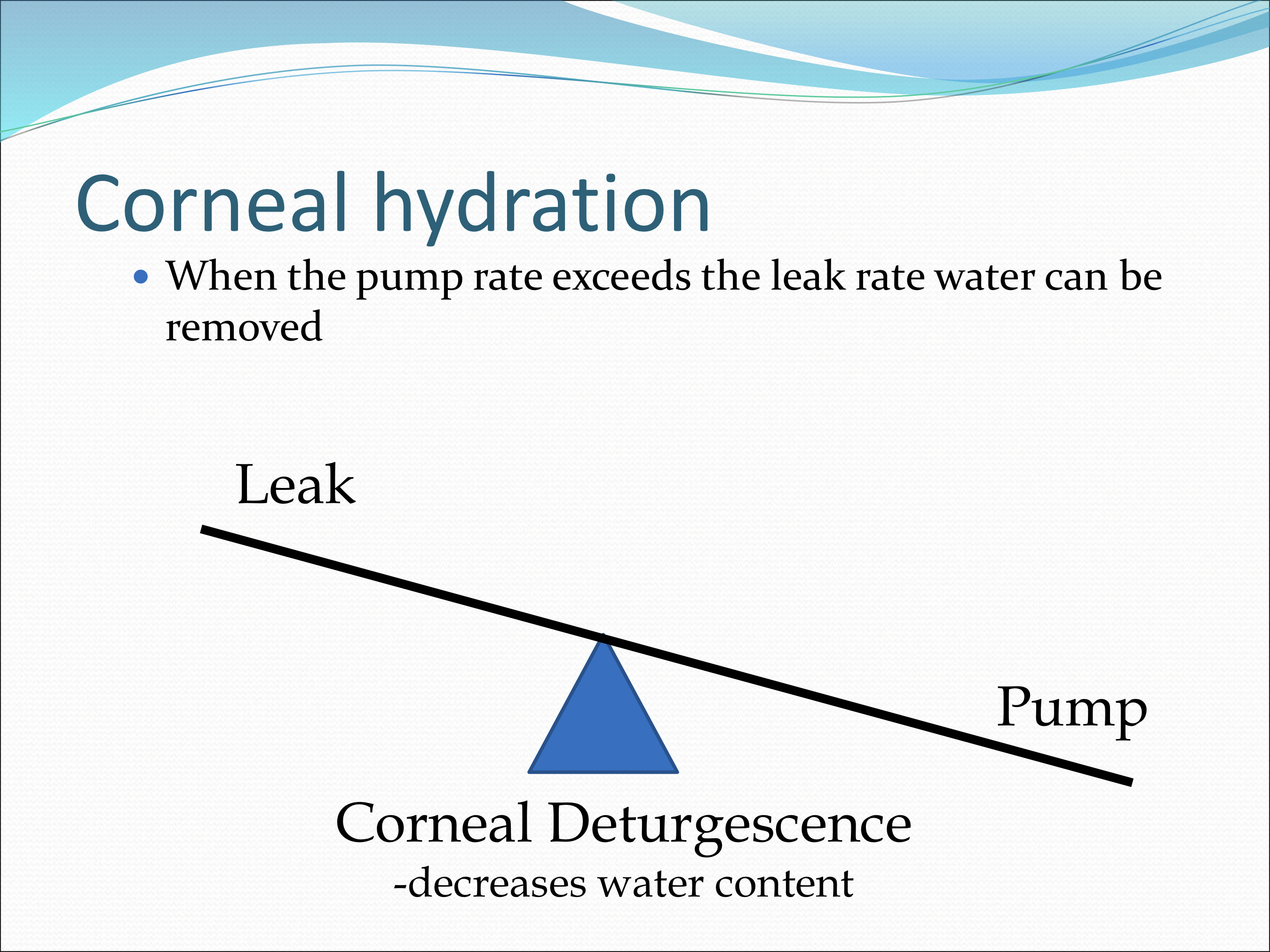
What happens when the pump rate exceeds the leak rate water can be removed?
Corneal Deturgescence (decreases water content)
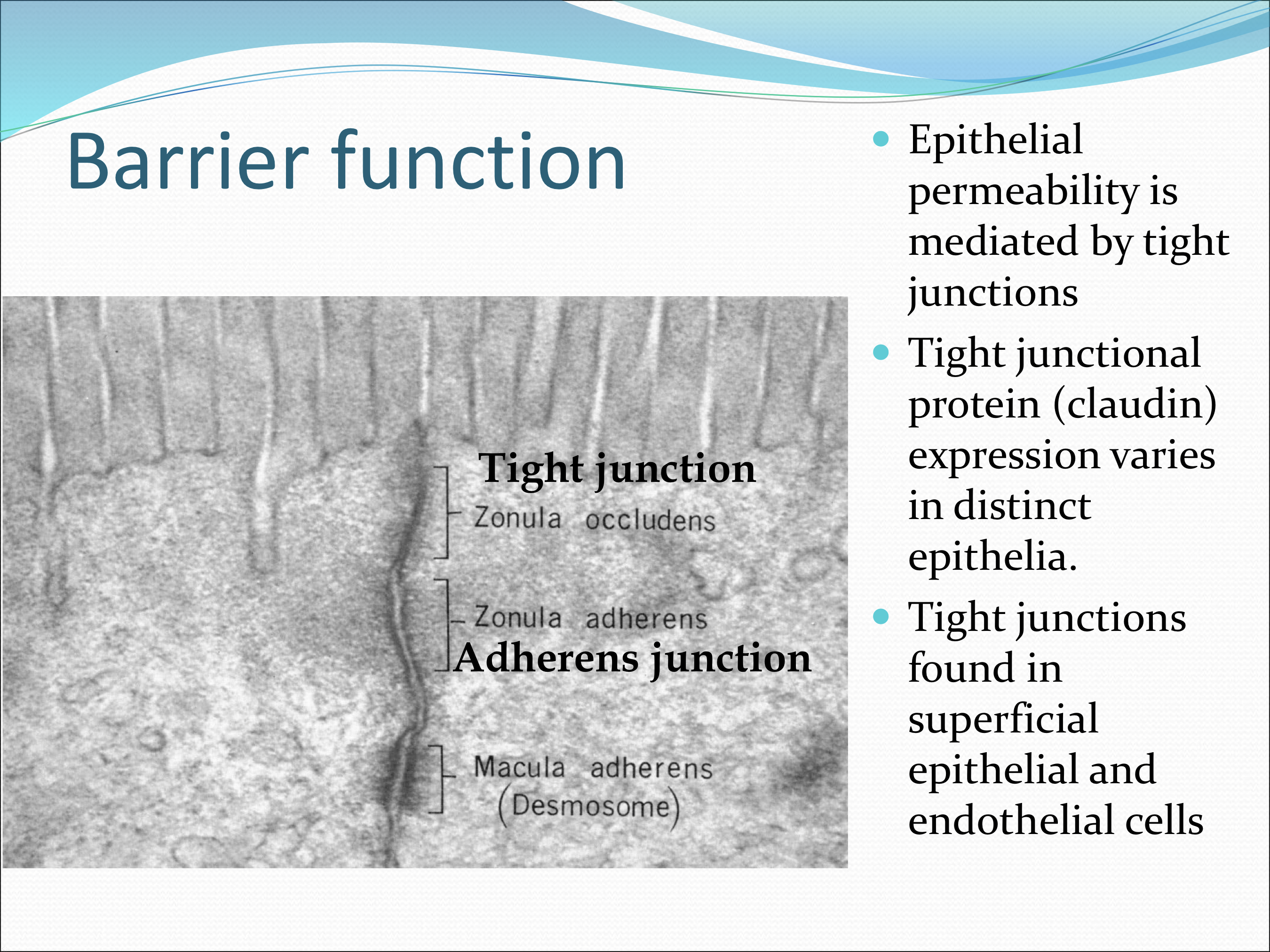
What factors contribute to the barrier function of the corneal epithelium?
Tight junctions and claudin proteins
Why is the endothelium more leaky than the epithelium?
The endothelium has a differential expression of claudin protein types
What are claudins?
A transmembrane, tight junctional proteins that form pores that allow ion and water movement, but restrict diffusion of proteins and larger molecules
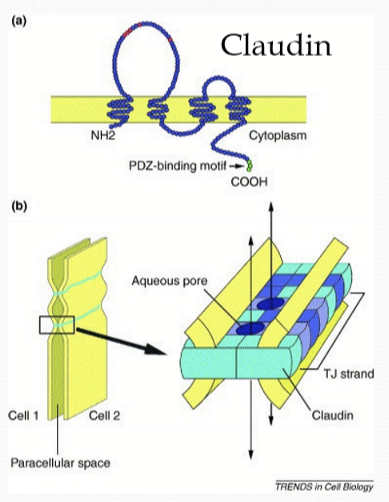
How can claudin determine leakiness of an epithelium?
Different claudin expression can affect the leakiness of an epithelium
What does Carbonic Anhydrase (CA) do?
It converts water and carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and hydrogen ion and vice versa
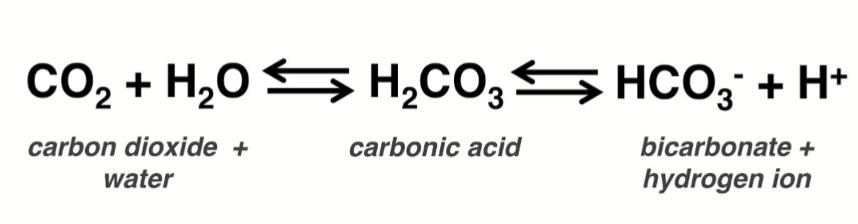
Where is CAII and CAIV found?
CAII functions within the cytoplasm of the corneal endothelial cells. CAIV functions in aqueous humor and apical membrane.
How can endothelial ion transport be stimulated?
Activating CaCC via increasing intracellular Ca2+
Activation of purinergic receptors
Triggered by secreted ATP, leading to an increase in intracellular cAMp, leading to activation of CFTR
What events can lead to increase endothelium ion transport?
Injury and cell volume alterations
What stimulates lacrimal acinar and cuts?
parasympathetic stimulation
What is Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy (CHED)?
A rare disorder affecting the corneal endothelium, causing clouding and vision impairment due to the dysfunctional endothelial cells failing to remove excess fluid from the cornea
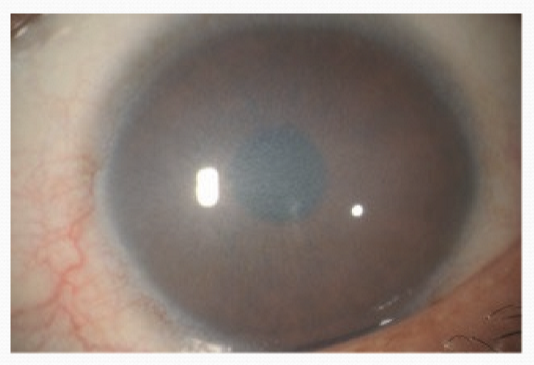
How common is CHED?
3/100,000 newborns. It can first manifest at birth or later in life depending on cause.
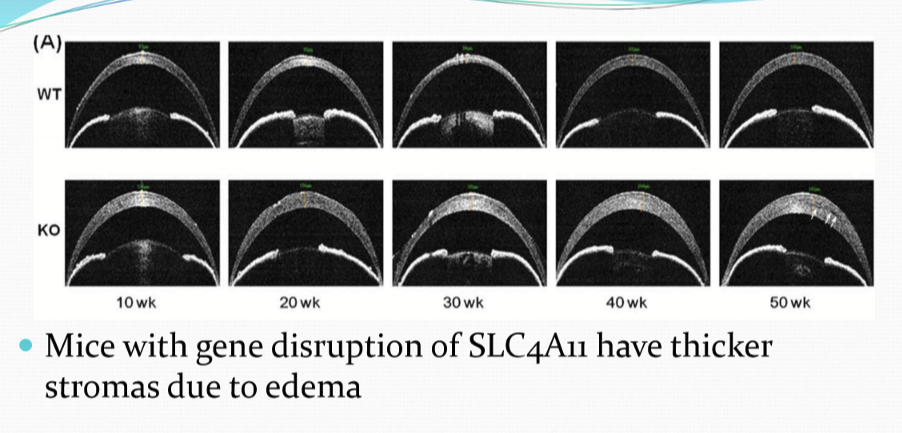
Mutation on what gene causes CHED?
An ion transport encoding gene, SLC4A11, disrupting the function of a putative NBC co-transporter
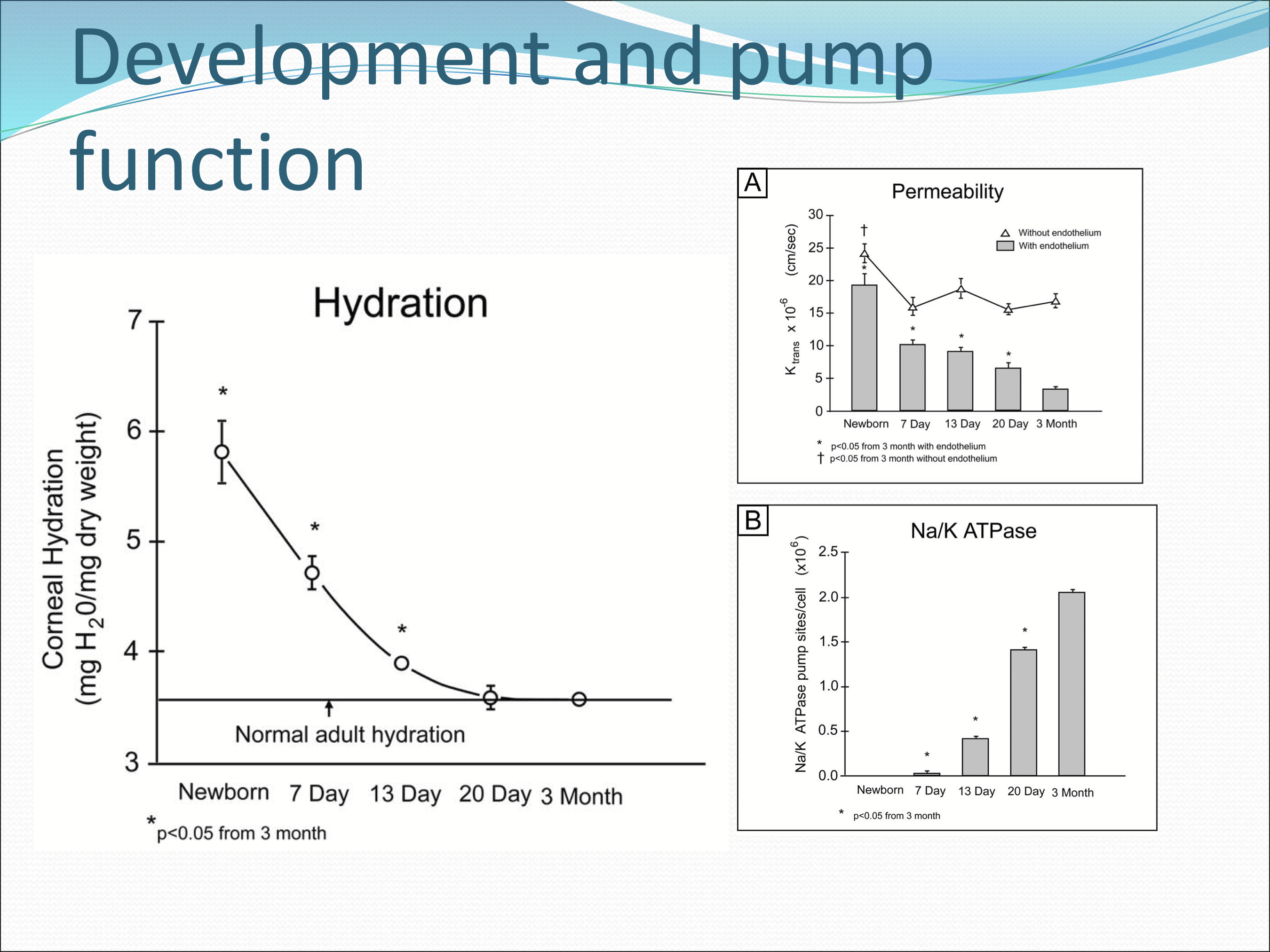
How long does it take for the endothelial pumps to fully develop, and what changes occur during the maturation?
2-3 months, with an increase in permeability and NKA activity
What happens to the endothelial density with age?
It decreases. ~4000 cells/mm2 at birth and ~2500 cells/mm2 in adults
What is the minimum endothelial cell density for normal function?
400-750 cells/mm2
What happens if the density of endothelial cells falls to far?
Reduction leads to fluid ingress > pump function
Does age typically affect normal endothelial function?
No, activity and number of NKA pumps can increase to compensate for cell loss, but there is a limit.
What can cause endothelial cell loss?
Pathological causes:
Contact lens
Crosslinking therapy
refractive surgery
cataract surgery
trauma
corneal transplants