REGENTS PHYSICS STAMPS
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
In freefall acceleration is always
constant (-9.8 m/s²) near the Earth's surface.
Friction / (air resistance)
the resistance that one surface or object encounters when in motion
In freefall when an object reaches it maximum height
The finalpoint at which the object's velocity becomes zero before descending due to gravity.
Scalar
A physical quantity that has only magnitude and no direction, such as mass or temperature. * cant be negative
Vector
A physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as force or velocity. *can be negative
When an object moves downward in projectile motion
Acceleration is positive as gravity is helping the object increase it’s speed as it falls.
Projectile Motion
An object moves along a curved path under the influence of gravity and has both horizontal and vertical components of motion.
In projectile motion when an object is thrown downward, it’s vertical velocity
Increase in the negative direction because it going down the y-axis
Gravity is constantly accelerating the rock in the y-direction.
In projectile motion the horizontal velocity
is constant if air resistance is neglected
When the angle in projectile motion increases
The total horizontal distance of the projectile traveled increases & maximum altitude also increases.
Newtons 1st Law
An object in motion will stay in motion and an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by unbalanced a force.
Newtons 2nd Law
Fnet = m x a
When a force acts on a object without friction / air resistance object begins to accelerate towards the direction in which the force of motion moves (usually to the right).
Inertia
An objects tendency to resist change depending on mass
Greater mass = Greater inertia
objects with heavier mass have a higher tendency to resist change
Equilibrium
When balanced forces are acting on an object causing it to stay still or move at a constant velocity
What causes an object in motion to stop moving
When an unbalanced force acts upon it
What causes an object at rest to begin moving
When an unbalanced force acts upon it
When an object is at rest in equilibrium
Fnet = 0 N
V = 0 m/s
A = 0 m/s2
When an object moves at constant velocity at equilibrium
Fnet = 0N
a = 0 m/s2 → No change in magnitude of velocity = 0 acceleration
How does frictional force move?
It works against the force of motion making it harder to move things
Kinetic Force
Is a resistive force → meaning it acts to resist your force of motion no matter what.
- Kinetic friction generates heat & sound or both
Normal force
the force a surface exerts on a object
Fn / Fw = m x g → mass x gravity
g = 9.8 m/s2
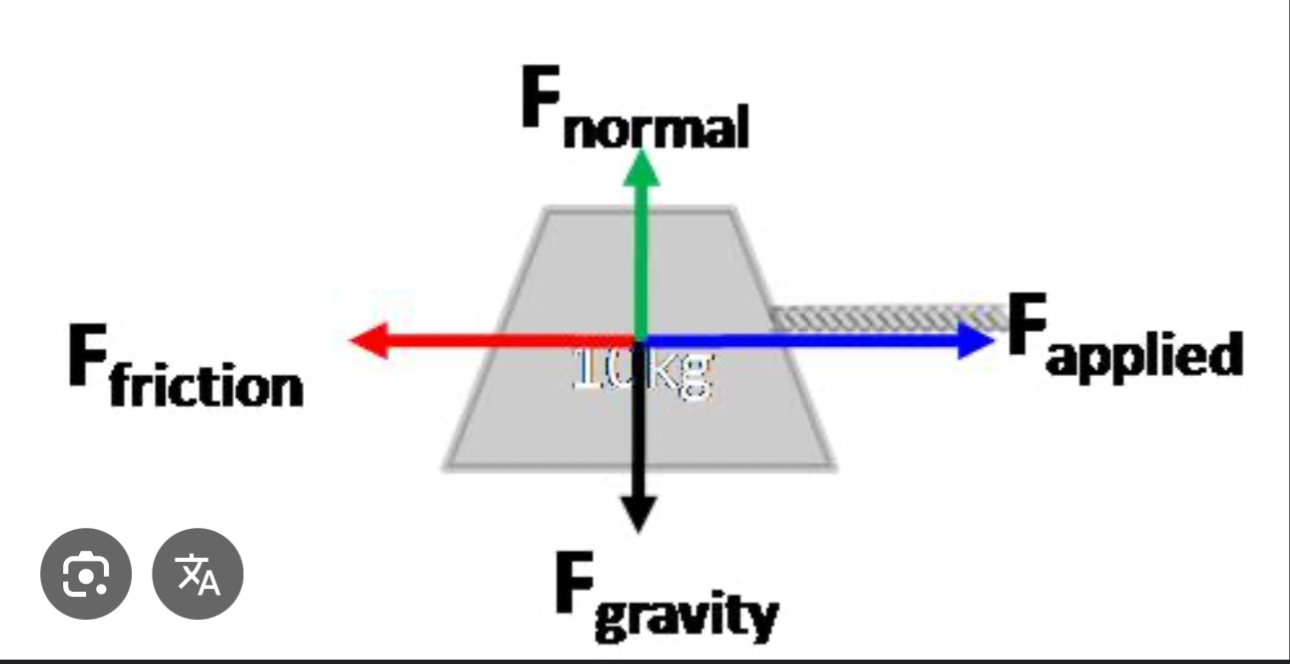
How do you get an object at rest to begin moving?
You have to apply a force greater than the static friction that’s keeping the object in place
Momentum & Impulse
P = m x v → units = kgm/s
J / impulse = F x Δt → F x tfinal - tinitial
F = force
Δt = change in time
J = F x Δt = Δp / momentum → J = mvfinal- mvinitial
If you apply force on an object it will gain some momentum
Momentum in all collisions are always conserved never lost.
Units for Impulse = n x s ****NOT n/s
Conservation of momentum equations
(M1i)(V1i) + (M2i)(V2i) = (M1f)(V1f) + (M2f)(V2f) → Used for elastic collisons
(M1)(V1) = (M2)(V2)
(M1i)(V1i) + (M2i)(V2i) = (M1+M2) Vf → Used for inelastic collisions
Pbefore = Pafter
Collisions
When an object in motion comes into contact w/ another object
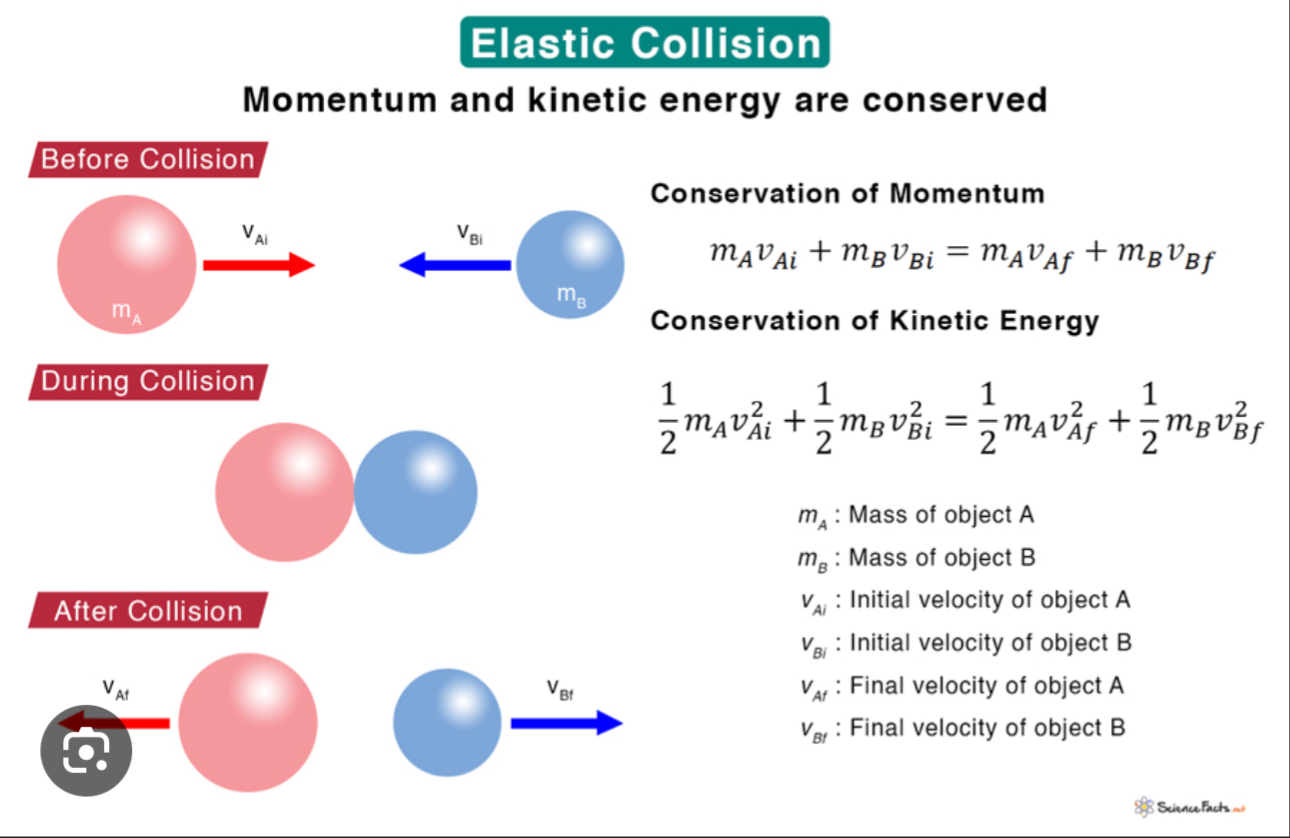
Elastic Collisions
Kinetic energy & momentum is conserved
* NO ENERGY IS LOST
Equation: (M1i)(V1i) + (M2i)(V2i) = (M1f)(V1f) + (M2f)(V2f) → Used for elastic collisons
When objects collide / bounce off of eachother and seperate after collision.
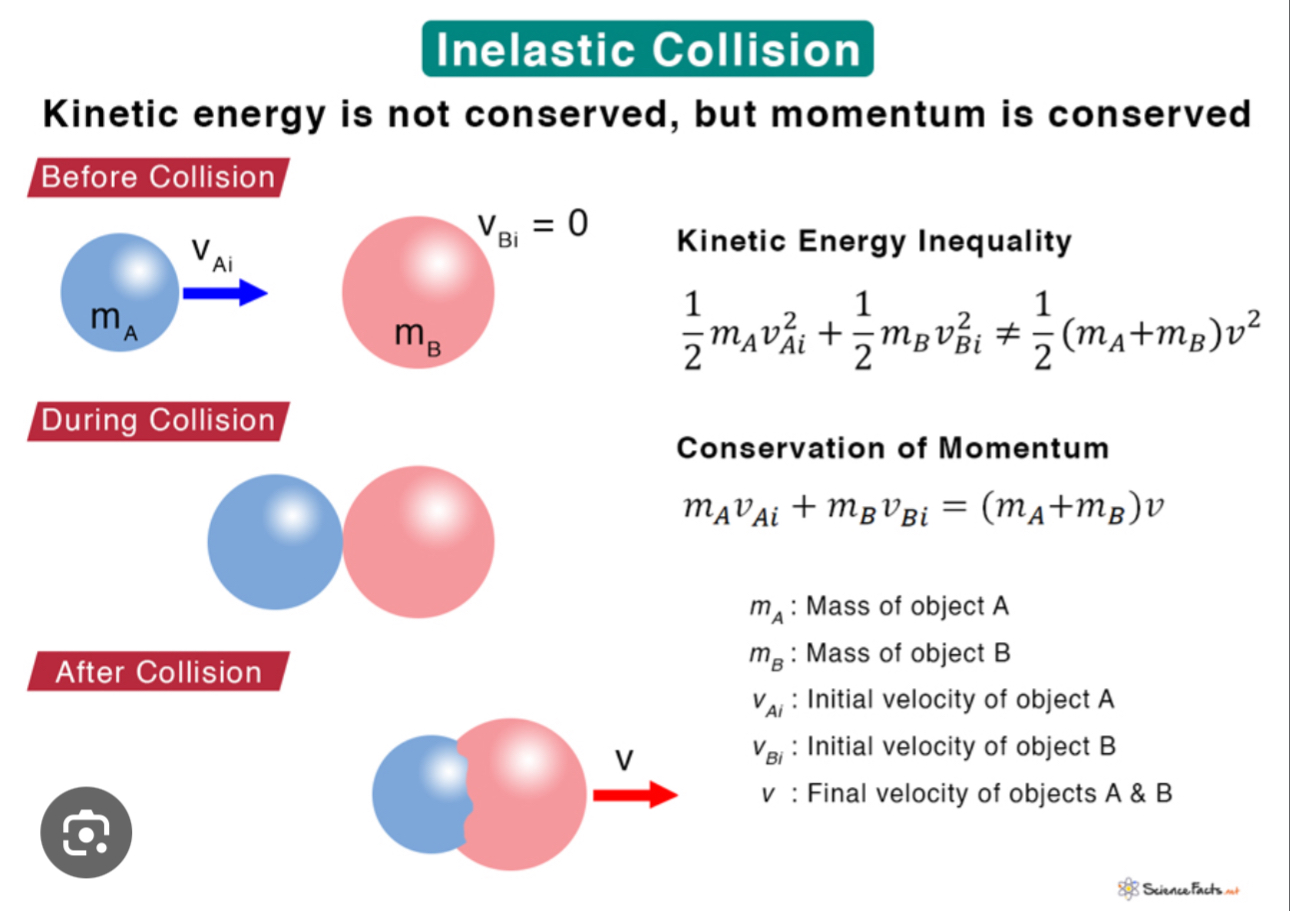
Inelastic Collisions
Kinetic energy IS NOT conserved, but momentum is conserved
* ENERGY IS LOST in the form of sound, heat or internal energy of the new system
When an object in motion collides with another object at rest, and after the collision the objects stick together becoming one combined mass that travels at the same velocity
Equation = (M1i)(V1i) + (M2i)(V2i) = (M1+M2) Vf → Used for inelastic collisions
When a force is applied over a longer interval of time
Amount of impulse / change momentum increases
if time is doubled, impulse is also doubled
When a force is applied over a shorter interval of time
Amount of impulse / change in momentum decreases
If time is havled, impulse is also halved
Power
units = watts
Equations = fd /t or w/t → force x distance / time
Remember to gain power you have to put in a lot of work over time!!
Power is the net force applied to an object w/ a particular average velocity
Work
W = fd = Δ ET → force x distance
ΔET = PE + KE + Q
PE = potential energy, m x g x Δh
KE = ½ mv2
Q = heat / internal energy
units = joules
Work is a change in energy
Potential Energy
Is energy stored in an object that could be used to do work.
ΔPE = m x g x Δh
Hooke’s Law
Fs = kx
Fs = force of spring
k = spring constant
x = change in distance of the spring (streched or compressed)
PEs = ½ kx2
Energy
* ENERGY IS ALWAYS CONSERVED NEVER CREATED NOR DESTROYED
Energy can also be converted into different forms
Ex: turning on a light bulb, electrical energy → light / heat energy
Ex 2: Eating food and riding a bike later in the day
chemical energy → mechanical energy
This means that PE = KE = W in certain circumstances
Ex 3: Holding a ball over a 10 foot building in let it fall to hit the ground potential energy → kinetic energy
Units = Joules
When an object is at the peak / greatest height
PE = highest magnitude / non zero
KE = 0 J
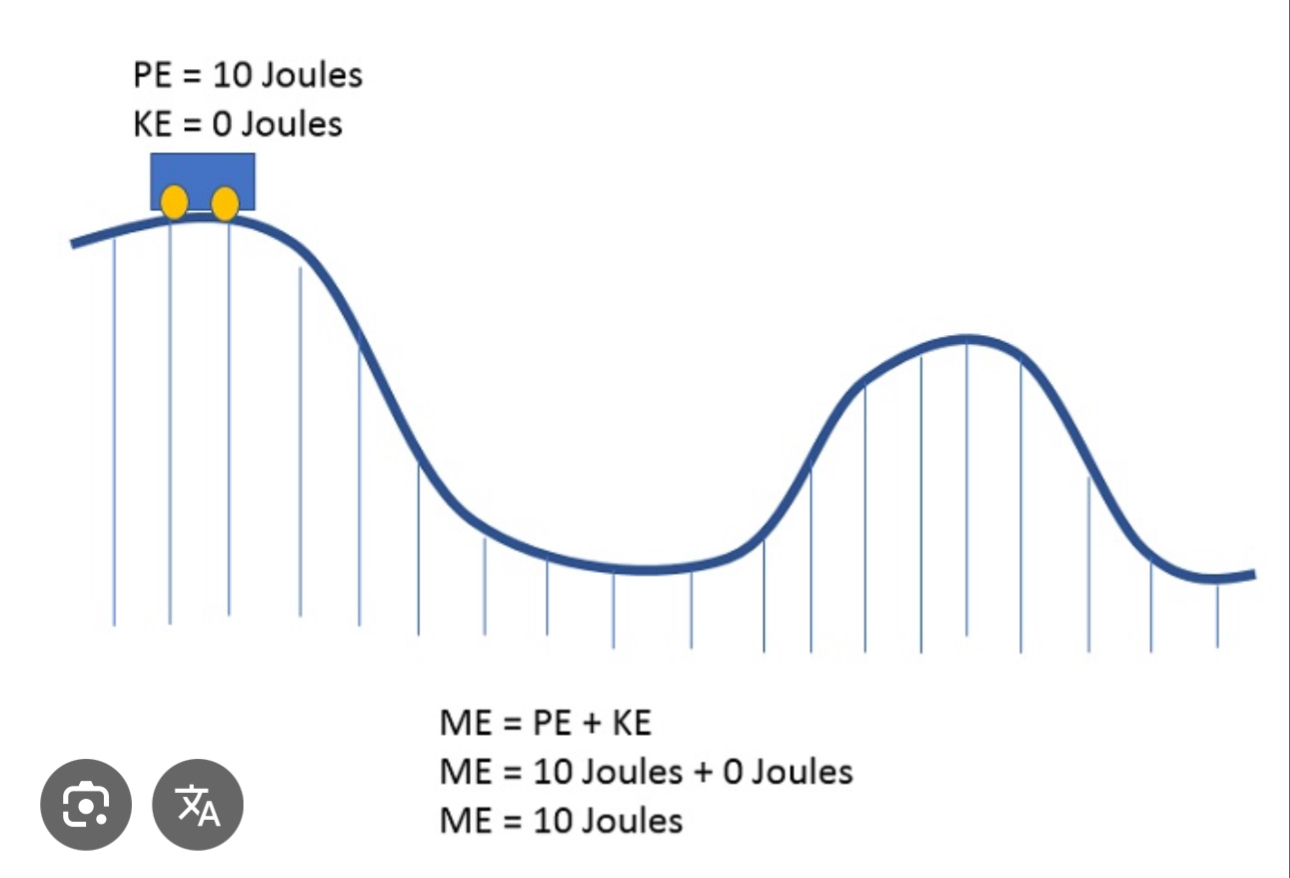
When an object is at its lowest point / no height
PE = 0 J
KE = non-zero J
Static Electricity
Occurs when an object obtains a total amount of positive or negative charge, creating an imbalance that wants to be returned to equilibrium
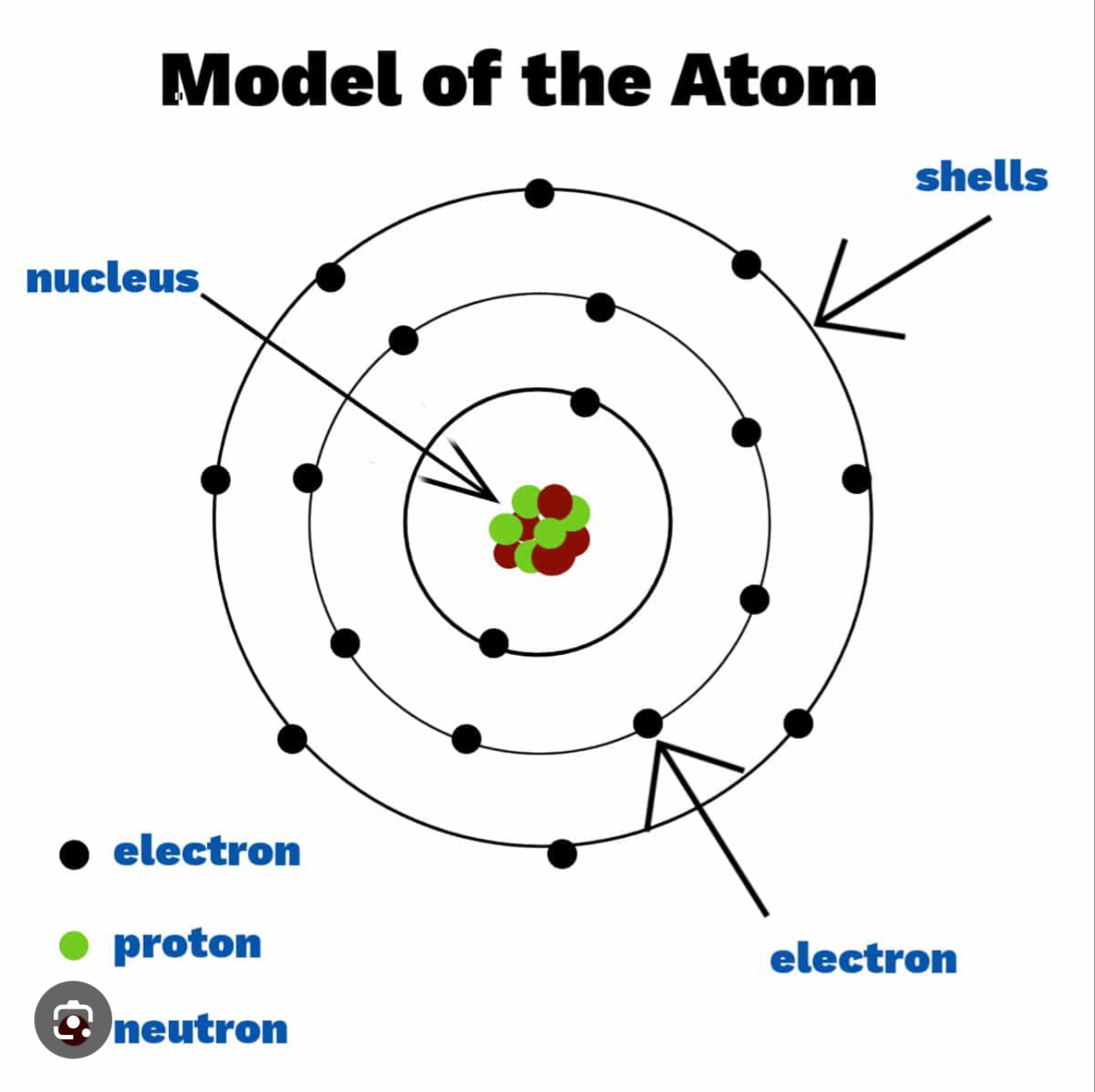
Atoms
Contains charged particles, positive protons and negative electrons
Law of Conservation of Electric Charge
You can never create a total electric charge. Instead, charge can only move from one place to another.
Coulombs Law
Symbol for charge = q | Units for charge = C / coulombs
One single electron = -1.60 × 10^-19 C
One single proton = 1.60 × 10^-19 C
* sign changes depending on the particle
K = 8.99×10^9 n x m² / c²
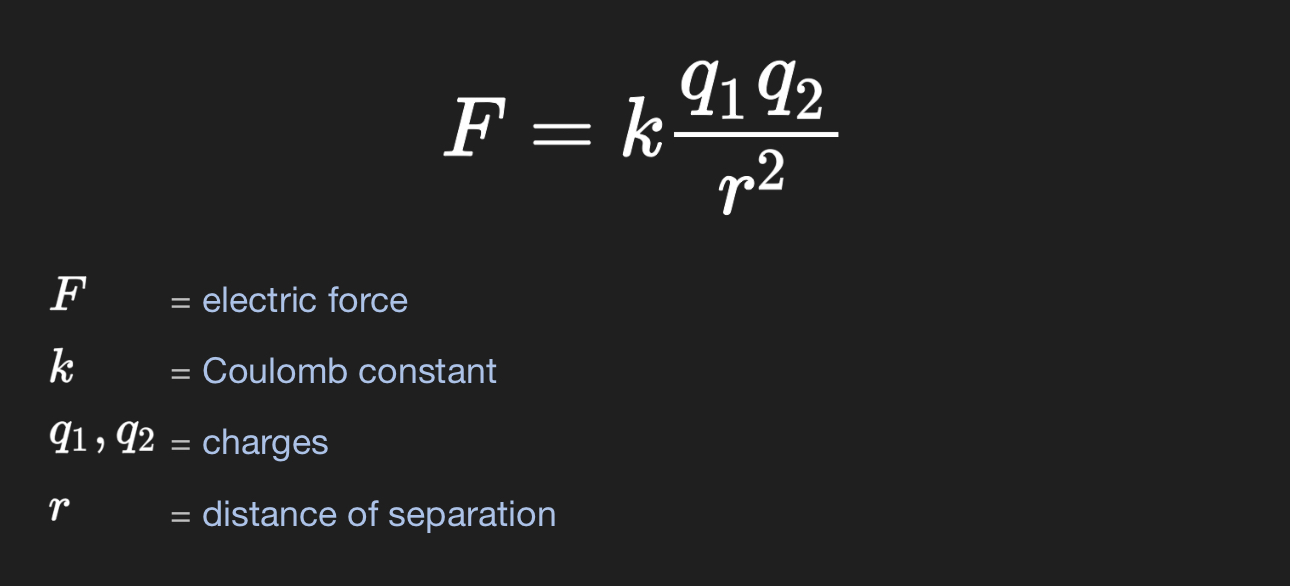
Electrostatic force
when radius increases, electrostatic force increases, Direct relationship.
Electrostatic forces can be attractive or repulsive, depending on the signs of the charges.
Electrostatic force is a vector.
Electric field
An electric field is a measurable effect generated by any charged object.
An electric field carries energy and passes it onto another charge object by exerting electric forces.
E = f / q
q = charge
f = force
E = electric field
E = K x q / r²
r = radius
k = electrostatic constant → 8.99×10^9
Electric field line show the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on any nearby positive test charge.
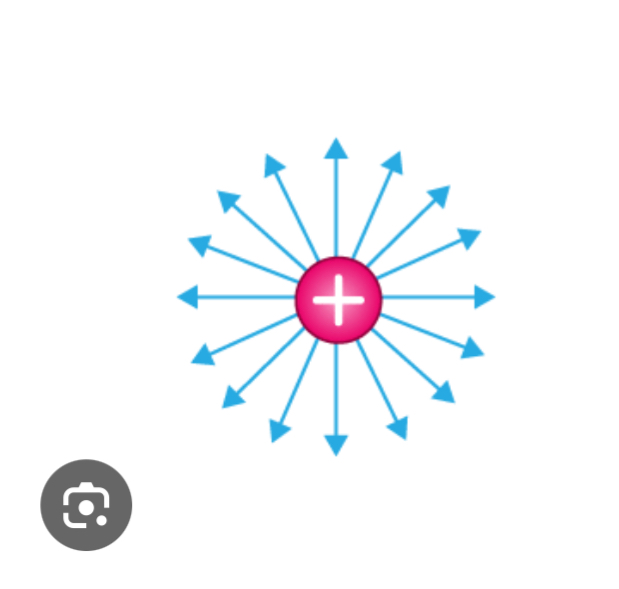
Positive charge
Electric field lines point outwards to signify that positive test charge is a repulsed by +Q
Negative charge
Electric field lines point inwards to signify that positive test charges attracted to -Q
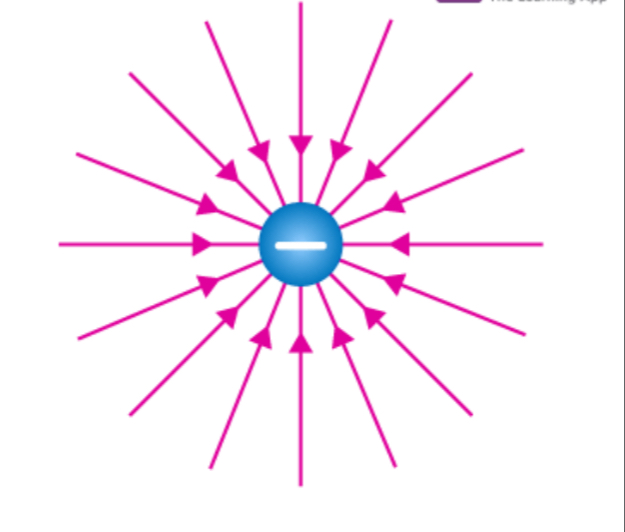
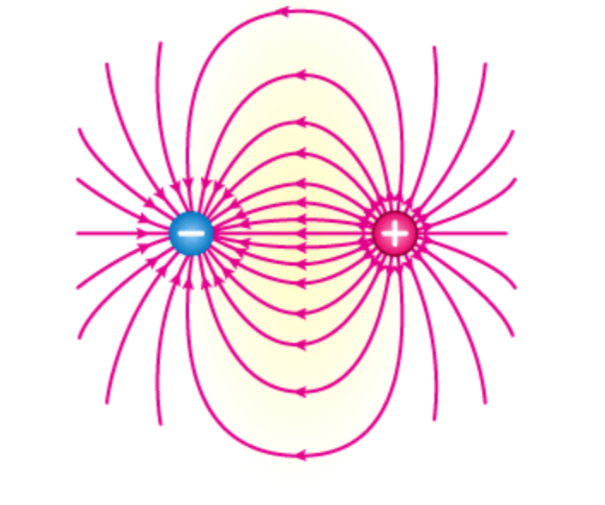
Electric Dipole
Electric field lines go from positive charge to negative charge to show attraction, Two particles that generate their own electric field, we can add fields together to create a total electric field.
* Principle known as superposition
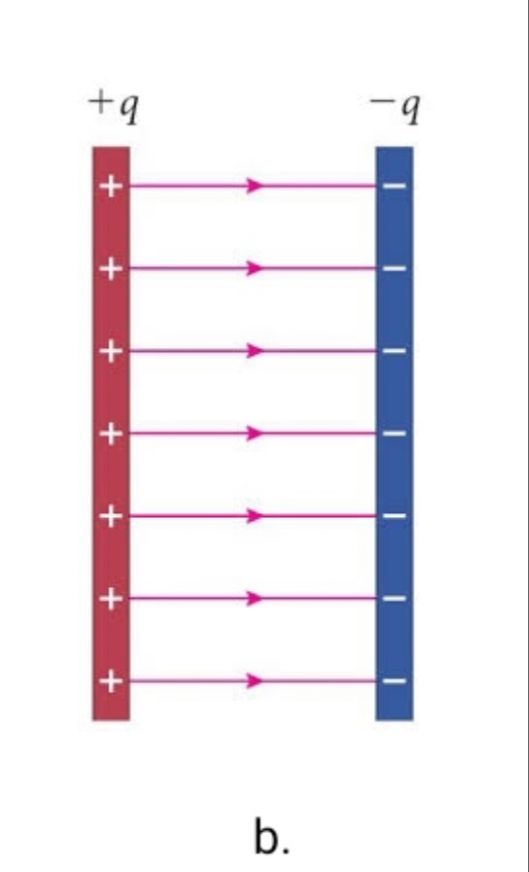
Four important properties of electric field lines
1) The field lines must be tangent to the direction of the field line at any point
2) the greater the line density the greater than magnitude of the field
3) lines ALWAYS START FROM POSITIVELY CHARGED OBJECTS AND END ON NEGATIVELY CHARGED OHJECTS
4) Lines never cross
Equilibrium
When electric charges are at equilibrium a = 0 m/s², Fnet = 0 N, E / Electric field = 0 N/C
Since electric field represents electric forces acting on nearby charges when there is no force there is no electric fields.
Waves transfer
energy from one place to another
* ** WAVES DONT TRANSFER MATTER
Fundamental Forces
Strongest: Strong nuclear force → Binds protons & neutrons to create nucleus
2nd strongest: Electromagnetic force → Affects charged particles
2nd weakest: Weak nuclear force → Radioactive decay & converts neutrons → protons
Weakest force: Gravitational force → Attracts objects with mass
If a waves undergoes refraction, diffraction, or reflection
Wavelength always stays the same