Sociology Pt 2
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
What is Culture?
shared symbols and their meaning
encourages us to interpret the meaning of the structure
ex. middle finger is one or “fuck u”
encourages us to interpret the meaning of the structure
ex. middle finger is one or “fuck u”
2
New cards
How do we observe culture?
obvious when the assigned meaning is contrasted
why we can see something we disagree with as ideology
if common sense, human nature or self-evident then its probs culture
why we can see something we disagree with as ideology
if common sense, human nature or self-evident then its probs culture
3
New cards
What is dominant culture?
the overarching system of meaning that authorizes and justifies the existing structure (including existing social inequalities)
4
New cards
What is subordinate culture?
System of meaning that contests the dominant cultured
5
New cards
What are the dominant and subordinate cultures of pre-modernity?
Dominant: divine right of kings
Subordinate: human beings are fundamentally equal in God’s eyes
Subordinate: human beings are fundamentally equal in God’s eyes
6
New cards
What are the dominant and subordinate cultures of modernity in the West?
Dominant: the grind
Subordinate: anti the grind
Subordinate: anti the grind
7
New cards
What are the dominant and subordinate cultures of Modernity in the USSR?
dominant: capitalist economies are detrimental to human flourishing
subordinate: challenges the political legitimacy of the communist regimes
subordinate: challenges the political legitimacy of the communist regimes
8
New cards
What are the dominant and subordinate cultures of postmodernity?
considerable cultural fragmentation, no societal-level agreement on meaning of experiences and events
9
New cards
what is cultural fragmentation?
the meanings associated with objects are eroded
10
New cards
What is cultural consensus?
assignment of the same meanings to the same objects
11
New cards
Pre-modernity vs modernity vs post modernity?
Pre-modernity: same sermon form same pastor
Modernity: three tv stations
Post modernity: individual instagram feeds from everyone
Modernity: three tv stations
Post modernity: individual instagram feeds from everyone
12
New cards
What is settled culture?
structure and culture are mutually reinforcing
culture takes form of traditions and common sense
culture has a weak direct effect on individual behaviour and is in the background
allow for easy social reproduction
Swindler’s theory
culture takes form of traditions and common sense
culture has a weak direct effect on individual behaviour and is in the background
allow for easy social reproduction
Swindler’s theory
13
New cards
What is unsettled culture?
structure is out-of-sync with existing traditions
culture takes the form of novel ideology
culture propels people to act in ways against their habits and traditions
culture takes the form of novel ideology
culture propels people to act in ways against their habits and traditions
14
New cards
What does Swindler apply the theory of settled/ unsettled times to?
revolutionary historic change
Decision to divorce or stay married
Decision to divorce or stay married
15
New cards
What were the settled times of pre-revolutionary medieval Europe?
strict boundaries between royalty vs. common people
Culture: divine right of kings supported by religious doctrine
Culture: divine right of kings supported by religious doctrine
16
New cards
What were the unsettled times of the french revolution?
existing structure no longer supports social reproduction for the common people
indebted monarchy raise taxes and common people struggle
indebted monarchy raise taxes and common people struggle
17
New cards
What are the settled and unsettled times of marriage?
settled: daily routines, no thought on the meaning of the marriage'
unsettled: routine doesnt help relationship and leads to unhappiness. unhappiness leads to contemplation
unsettled: routine doesnt help relationship and leads to unhappiness. unhappiness leads to contemplation
18
New cards
What is the culture that merits divorce and saving the marriage?
divorce: “i deserve to be happy” “we don’t love each other anymore”
save it: “marriage is hard work” “everyone has rough patches”
save it: “marriage is hard work” “everyone has rough patches”
19
New cards
What do settled and unsettled times determine?
the intensity of peoples engagement with culture
Cultures impact on behaviour and social reproduction/change
\*people can hold beliefs without acting on them\*
Cultures impact on behaviour and social reproduction/change
\*people can hold beliefs without acting on them\*
20
New cards
Unsettled times vs. unsettled lives
times: existing relationship between structure and culture no longer function, people no longer rely on tradition and routine, engagement with new ideas lead to social change
lives: habits and routines no longer function, engagement with different cultural narratives leads to different decision, change in ones life
lives: habits and routines no longer function, engagement with different cultural narratives leads to different decision, change in ones life
21
New cards
How are culture and agency connected?
constricts things we think of as possible behaviours
ex. showing up to class naked is not seen as an option when getting dressed
Whether or not you attach yourself to one meaning or another that affects what you’ll see as possible options
ex. showing up to class naked is not seen as an option when getting dressed
Whether or not you attach yourself to one meaning or another that affects what you’ll see as possible options
22
New cards
What is socialization?
the process through which culture is internalized
transfer of socially meaningful knowledge from one group that already has those values to another
transfer of socially meaningful knowledge from one group that already has those values to another
23
New cards
Socialization of chimpanzee?
tried to socialize baby chimpanzee into family, raised with human son, instead son was socialized as a chimpanzee
24
New cards
Nature vs. nurture
think of as continuum
nature is biological determinism
nurture is empiricism
nature is biological determinism
nurture is empiricism
25
New cards
What is biological determinism?
genetics and the biological systems
they produce imbued individuals with particular qualities: temperament, intelligence, behaviour, etc
they produce imbued individuals with particular qualities: temperament, intelligence, behaviour, etc
26
New cards
What is empiricism?
people experience’s account for the way they develop
27
New cards
Why can’t we test nature vs. nurture empiracally?
ethical reasons
the difference is confounded in the wild
genetics and socializations are also confounded experiences
the difference is confounded in the wild
genetics and socializations are also confounded experiences
28
New cards
Confounded meaning?
both are involved and you can not disentangle the effect of one from the other
29
New cards
Why is the difference between nature vs nurture difficult?
the same trait may be understood differently depending on the social context (ex. bar fight vs football)
all traits require some level of nurture
human beings are radically open to nurture
even behaviours seen as human require socialization (walking on two legs, speaking languages)
all traits require some level of nurture
human beings are radically open to nurture
even behaviours seen as human require socialization (walking on two legs, speaking languages)
30
New cards
Explicit socialization vs implicit socialization?
explicit: purposeful, declarative instruction of knowledge
Implicit: automatic, unconscious transmission of social knowledge
Implicit: automatic, unconscious transmission of social knowledge
31
New cards
What is primary socialization?
process of acquiring the basic skills needed to function in society during childhood
consists of:
* languages
* rules of social interaction
* sense of self
consists of:
* languages
* rules of social interaction
* sense of self
32
New cards
How does media socialize people (what do animals do all day ex)?
animal species and job are related variables
information about species leads to categories of employment
teaches that when lower class people get higher skilled or higher authority jobs they fail
information about species leads to categories of employment
teaches that when lower class people get higher skilled or higher authority jobs they fail
33
New cards
What is gender socialization?
the process of learning and internalizing gender differentiation
ex. talk more to female babies, rougher with male babies, colours of toys
ex. talk more to female babies, rougher with male babies, colours of toys
34
New cards
What is gender essentialism?
the idea that differences between men and women are biologically based
this is confounded by gender socialization
this is confounded by gender socialization
35
New cards
What is secondary socialization?
explicit and implicit socialization that occurs outside the context of the childs primary socialization environment
two sources of social knowledge: authority figures, peer groups
two sources of social knowledge: authority figures, peer groups
36
New cards
What is peer group socialization?
peers engage with social knowledge received from primary socialization, here they can challenge and reject it, can result in deviant behaviour
37
New cards
how is socialization and culture linked?
socialization is the process by which culture is concretized at the level of in the individual
38
New cards
what is social interaction?
the micro-level encounters between individuals
responsible for early socialization
always involved in socialization
the smallest unit in sociology
responsible for early socialization
always involved in socialization
the smallest unit in sociology
39
New cards
how is social interaction linked to other aspects of society
socialization is a mechanism that explains agency
culture gets internalized
culture gets internalized
40
New cards
What does G.H Mead say about the development of the self?
“The Self, as that which can be an object to itself, it is essentially a social structure, and it arises in social experience”
4 stages of social development
4 stages of social development
41
New cards
What is the first stage of social development?
imitation (infancy and toddlerhood)
ex. parent sticks out their tongue → baby sticks out their tongue
don’t need to understand language for this
ex. parent sticks out their tongue → baby sticks out their tongue
don’t need to understand language for this
42
New cards
What is the second stage of social development?
role-playing (pre-school)
child takes on the role of the other during play
“playing doctor,” “playing house”
children role play what they witness
this play is essential for the development of socially mature adults
child takes on the role of the other during play
“playing doctor,” “playing house”
children role play what they witness
this play is essential for the development of socially mature adults
43
New cards
What is third stage of social development?
simultaneous appreciation of multiple roles (school age)
team sports, board games
kids develop the ability to predict others experiences
team sports, board games
kids develop the ability to predict others experiences
44
New cards
What is fourth stage of social development?
internalization of the generalized other (maturity)
become socially mature
no need to think consciously about what their behaviour looks like to others
become socially mature
no need to think consciously about what their behaviour looks like to others
45
New cards
What is the generalized other?
The organized community or social group which gives to the individual his unit of self.
Attitudes of the generalized other are the attitudes of the whole community
(attitudes depend on the society they’re embedded in)
Attitudes of the generalized other are the attitudes of the whole community
(attitudes depend on the society they’re embedded in)
46
New cards
How do Games and play affect the development of self (Mead)?
provide a space for kids to practice taking the position of the other
position-taking is explicit so it’s not incorporating the other into one’s own personality
position-taking is explicit so it’s not incorporating the other into one’s own personality
47
New cards
What is social interaction and the “self”?
social interaction → development within one’s self of an implicit appreciation of the orientation of society towards one’s self
doesn’t mean someone will always coform but if they don’t conform they are aware of it
the generalized other
doesn’t mean someone will always coform but if they don’t conform they are aware of it
the generalized other
48
New cards
What does Erving Goffman say?
social interaction amounts to a relationship between individuals who take on roles in particular settings
ex. doctor-patient
ex. doctor-patient
49
New cards
What is a role?
prescribed ways of interacting that are conditioned by a particularly social time and space
ex. teacher, student, etc
social interaction occurs as much between people and roles
existence of roles becomes clear when they do not fit into the role
must have defined front and back stages
ex. teacher, student, etc
social interaction occurs as much between people and roles
existence of roles becomes clear when they do not fit into the role
must have defined front and back stages
50
New cards
What is the sick role?
role people adopt when ill, nonparticipant in public life, withdraw from responsibility while still seen as worthy of resources
51
New cards
What are the two components of a role?
1. appearance (uniform)
2. manner (how they carry themselves)
52
New cards
What is setting?
human interaction is conditioned by the character of the space in which it takes place
53
New cards
What is frontstage?
activities involve the coordination of roles to present a certain kind of interactive experience to the audience
ex. front of restaurant
must be defined for roles
ex. front of restaurant
must be defined for roles
54
New cards
What is backstage?
also a setting with roles, actors coordinate to produce the situation of the front stage
ex. back of the restaurant
must be defined for roles
ex. back of the restaurant
must be defined for roles
55
New cards
What is social structure?
relatively stable patterns of social relations/interactions
influences behaviour by making it easy to fit and difficult to deviate from the structure (bypasses subjectivity)
why people conform to things they don’t agree with in postmodern society
influences behaviour by making it easy to fit and difficult to deviate from the structure (bypasses subjectivity)
why people conform to things they don’t agree with in postmodern society
56
New cards
social structure vs individual choice
structure has a larger impact on our life outcomes than our individual choices
ex. when dating its now easier to use an app even if u don’t want to
ex. when dating its now easier to use an app even if u don’t want to
57
New cards
What are the three levels of social structure?
microstructure, macrostructure, global structure
58
New cards
What is microstructure?
patterns of relatively intimate social relations formed during face-to-face interactions
ex. friends, family
ex. friends, family
59
New cards
What is macrostructure?
overarching patterns of social relations that lie outside and above a person’s circle of intimate acquaintances
ex. university of manitoba
ex. university of manitoba
60
New cards
What is global structure?
patterns of social relations that lie outside and above the national level
ex. global economy
ex. global economy
61
New cards
What are networks?
a set of social individuals that are linked by communication
describes social structure
ex. economic exchange, friendship
describes social structure
ex. economic exchange, friendship
62
New cards
What is a node?
an individual point of contact
ex. individuals, organizations, countries
mostly microstructures
ex. individuals, organizations, countries
mostly microstructures
63
New cards
What is a dyad?
a social relationship between two nodes
most basic unit of network structure
takes two to make but only one to die
ex. best friends
most basic unit of network structure
takes two to make but only one to die
ex. best friends
64
New cards
What is a triad?
a social relationship between three nodes
65
New cards
What do you need to know for network analysis?
1\. number of nodes
2\. number of connections
3\. centrality
* measure relative number of connections enjoyed by each node
4\. path distance
* number of connections to go through to get from one node to another
2\. number of connections
3\. centrality
* measure relative number of connections enjoyed by each node
4\. path distance
* number of connections to go through to get from one node to another
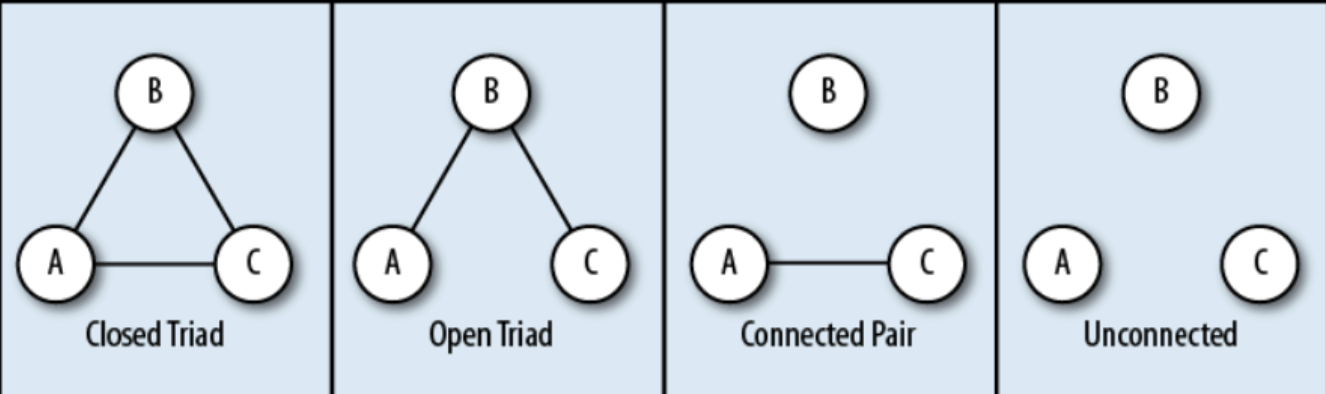
66
New cards
What is network analysis?
reveals the objective structure of a social group without necessitating any analysis of the content of interaction
67
New cards
how does the environment affect network composition?
objective organization of the built environment influences the structure of social networks
ex. cubicle vs open office
ex. cubicle vs open office
68
New cards
What is social capital?
networks or connections that people have that can be accessed or deployed for social gain
about the quality of connections
increased network centrality = increased social capital
about the quality of connections
increased network centrality = increased social capital
69
New cards
What is the strength of Weak ties?
study in connections and finding a job
DV: time to find a job
People with weak ties are more likely to be hired
DV: time to find a job
People with weak ties are more likely to be hired
70
New cards
What is the relationship between structural position and having good ideas?
1. managers constrained in a closed discussion network were less likely to have valuable ideas
2. no control variables are associated with the idea value when network density is considered
probability of a raise decreases with network constraint
71
New cards
What is a structural hole?
space between two networks that might connect
72
New cards
What is bridging connection?
connection that allows info to flow from one dense network to another dense network
73
New cards
What are spontaneous networks?
microstructures
ie. friends
ie. friends
74
New cards
What are organizations?
formal networks (allows them to develop into bureaucracies)
structure of the network is concrete such that the network structure is independent of the individual who occupy them
structure of the network is concrete such that the network structure is independent of the individual who occupy them
75
New cards
What is a bureaucracy?
a large impersonal organization comprising many clearly defined positions arranged in a hierarchy
have permanent salaried staff and written goals or rules
have permanent salaried staff and written goals or rules
76
New cards
What is the iron cage of bureaucracy?
Max Weber
as social structure becomes increasingly formalized, the possibility that an individual could act in a way that deviates from the expectations of the structure decreases
ex. lost luggage
particularly institutions
as social structure becomes increasingly formalized, the possibility that an individual could act in a way that deviates from the expectations of the structure decreases
ex. lost luggage
particularly institutions
77
New cards
What are institutions?
made up of multiple organizations that are formally networked
ex. the criminal justice system has police, prosecutors, courts, etc
ex. the criminal justice system has police, prosecutors, courts, etc
78
New cards
What is institutionalization?
the process by which informal networks become formally organized and formally recognized
is both structural and cultural
is both structural and cultural
79
New cards
How does culture affect institutionalization?
culture can influence the public opinion of an institution
80
New cards
How is institutionalization studied historically?
Particular character today can only be understood if we reference the history of how they occurred
the institution could be organized differently so to understand why it is not, must look at the historical network
the institution could be organized differently so to understand why it is not, must look at the historical network
81
New cards
Institutional change
unlike formal networks, institutions are resistant to change
Weber: “the iron cage of bureaucracy”
Weber: “the iron cage of bureaucracy”