Ch 4. Integumentary System Vocabulary Flashcards
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards provide definitions for key terms related to the integumentary system, aiding in understanding and retention of vocabulary essential for the subject.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Integumentary System
The system comprising the skin and its associated glands, hair, and nails.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of the skin, consisting of four to five layers of epithelial cells.
Dermis
The layer of skin beneath the epidermis, containing connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels.
Subcutaneous Tissue
The layer beneath the dermis, consisting mostly of fat and connective tissue.
Keratin
A protein that thickens and toughens the skin and is a major component of hair and nails.
Melanin
A dark pigment responsible for giving color to the skin, hair, and eyes, providing protection against UV radiation.
Sebaceous Glands
Glands in the skin that secrete sebum to lubricate hair and skin.
Sudoriferous Glands
Sweat glands that help regulate body temperature through perspiration.
Onychomycosis
A fungal infection of the nail.
Melanoma
A type of skin cancer that originates from melanocytes and has a high potential for metastasis.
Psoriasis
A chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells forming scales and red patches.
Dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin, often resulting in redness and itching; includes forms like atopic and contact dermatitis.
Pressure Ulcer
A sore from prolonged pressure on the skin, commonly occurring over bony areas.
Rule of Nines
A method to estimate the total body surface area affected by burns utilizing percentages.
Vacuum-Assisted Closure
A wound treatment method that uses negative pressure to promote healing.
Debridement
The process of removing dead or damaged tissue to enhance healing.
Dermatology
The branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of skin disorders.
Exudate
Fluid emitted from a wound or tissue, which may contain blood, pus, or other substances.
Scleroderma
A chronic autoimmune disease causing thickening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues.
Kaposi Sarcoma
A type of cancer that often appears as red or purple lesions on the skin, associated with immunosuppression.
What are the five layers of the skin?
The five layers of the skin are the stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale.
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer of the epidermis, consisting of dead, flattened skin cells that provide a protective barrier. Gives color so skin/protects against sunlight.
Stratum lucidum
A thin, translucent layer of the skin found only in thick skin areas like palms and soles, providing additional protection.
Stratum granulosum
A layer of the epidermis where keratinocytes begin to undergo apoptosis, accumulating keratohyalin and creating a waterproof barrier.
Stratum spinosum
The layer of the epidermis between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale, characterized by spiny projections and the presence of desmosomes, providing strength and flexibility to the skin.
Stratum basale
The deepest layer of the epidermis where keratinocytes are generated, contributing to skin regeneration and containing melanocytes, which produce melanin.
Sudoriferous glands (sweat glands)
Exocrine glands in the skin that produce sweat, helping to regulate body temperature and maintain homeostasis.
Sebaceous glands
Exocrine glands in the skin that secrete sebum (oily fluid), which lubricates and waterproofs the skin and hair.
roots pertaining to skin
derm/o, dermat/o
skin
kerat/o
keratin, horny layer of the skin
melan/o
dark, black, melanin
hidr/o
sweat, perspiration
seb/o
sebum, sebaceous gland
trich/o
hair
onych/o
nail
Burn categorization
refers to the classification of burns based on the severity of tissue damage, such as first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree burns.
first degree burn (superficial)
a mild burn that affects only the outer layer of skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain.
second degree burn (superficial partial thickness)
a burn that affects both the outer layer and underlying layer of skin, resulting in blisters, swelling, and severe pain.
third degree (deep partial thickness)
burn that extends through all layers of skin (epidermis and dermis), causing white or charred skin, numbness, and potential damage to underlying tissues.
fourth (full thickness)
degree burn that affects all layers of the skin and may also damage muscles, bones, and tendons, resulting in a leathery appearance and painless sensation due to nerve damage.
Lund and Browder method
a clinical tool used to assess the percentage of body surface area burned in patients, factoring in the patient's age and growth stage.
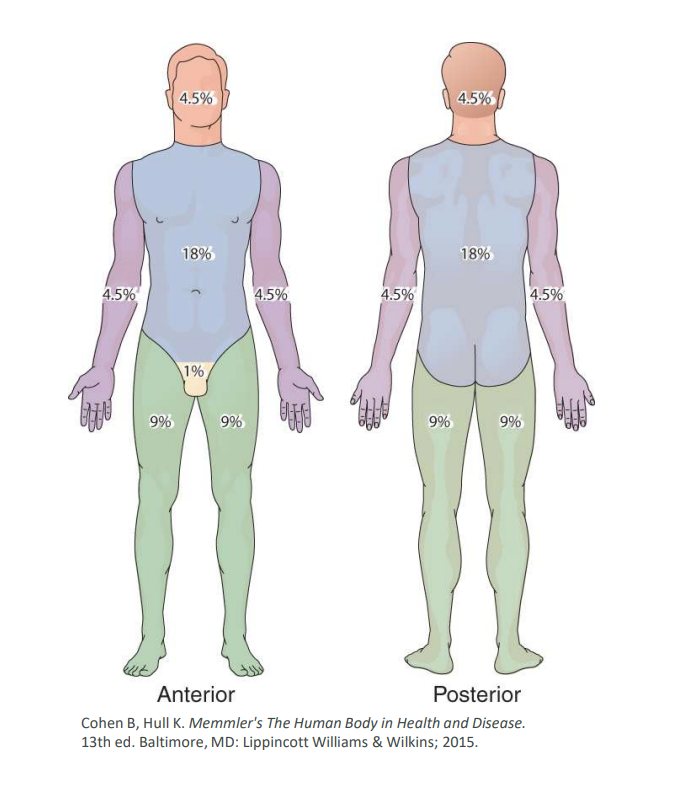
rule of nines
a method for estimating the total body surface area burned, dividing the body into sections, each accounting for approximately nine percent.
Dermatitis
inflammation of the skin that results in redness, swelling, and often itching. It can be caused by various factors, including allergies, irritants, and genetic predisposition.
Ex. Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
other forms: contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and statis dermatitis
psoriasis
chronic growth of epidermis/ a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell proliferation, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the skin.
treatments:
topical agents (corticosteroids, vitamins A and D, etc)
exposure to UV light
systemic suppression of immune system
autoimmune disorders: pemphigus
a group of rare autoimmune diseases that cause blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, resulting from the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues.
lupus erythematosus
a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and damage to various body tissues, including the skin, joints, and internal organs.
scleroderma
a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the hardening and tightening of skin and connective tissues, affecting internal organs and blood vessels.
skin cancer
a group of diseases involving the uncontrolled growth of skin cells, often triggered by excessive sun exposure or genetic factors.
common types:
squamous cell carcinoma
basal cell carcinoma
melanoma
kaposi sarcoma
squamous cell carcinoma
a type of skin cancer arising from squamous epithelial cells, often appearing as a firm red nodule, a scaly patch, or a sore that heals poorly.
basal cell carcinoma
a type of skin cancer originating from basal cells in the epidermis, characterized by pearly or waxy bumps and often found on sun-exposed areas of the skin.
melanoma
the most serious type of skin cancer, developing from melanocytes, characterized by dark growths or moles that may change in color, size, or shape.
kaposi sarcoma
a type of cancer that causes lesions on the skin, commonly associated with immunocompromised states, particularly HIV/AIDS.
key terms disorders:
aropic dermatitis
Hereditary, allergic, chronic inflammation of the skin with pruritus (itching); eczema
cicatrization
The process of scar formation; a scar is a cicatrix
debridement
Removal of dead or damaged tissue, as from a wound
dehiscence
Splitting or bursting, as when the layers of a wound separate Inflammation of the skin, often associated with redness and itching; may be caused by allergy, irritants (contact dermatitis), or a variety of diseases
dermatology
Study of the skin and diseases of the skin
dermatome
Instrument for cutting thin sections of skin for skin grafting
eczema
A general term for an inflammation of the skin with redness, lesions, and itching; atopic dermatitis
erythema
Diffuse redness of the skin
escharotomy
Removal of scab tissue (eschar) resulting from burns or other skin injuries
evisceration
Protrusion of internal organs (viscera) through an opening, as through a wound
exudate
Protrusion of internal organs (viscera) through an opening, as through a wound
keloid
A raised, thickened scar caused by tissue overgrowth during scar formation
pressure ulcer
An ulcer caused by pressure to an area of the body, as from a bed or chair; decubitus ulcer, bedsore, pressure sore
pruritus
Severe itching
acne
An inflammatory disease of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles usually associated with excess secretion of sebum; acne vulgaris
actinic
Pertaining to the effects of radiant energy, such as sunlight, ultraviolet light, and xrays
albinism
A hereditary lack of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes
alopecia
Absence or loss of hair; baldness
Baeu lines
White lines across the fingernails; usually a sign of systemic disease or injury
bromohidrosis
Sweat that has a foul odor because of bacterial decomposition; also called bromidrosis bromhidrosis
carbuncle
A localized infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, usually caused by staphylococcus, and associated with pain and discharge of pus
comedo
A plug of sebum, often containing bacteria, in a hair follicle; a blackhead (plural: comedones)
dermatophytosis
Fungal infection of the skin, especially between the toes; athlete's foot (root: phyt/o means “plant”)
diaphoresis
profuse sweating
dykeratosis
Any abnormality in keratin formation in epithelial cells
ecchymosis
A collection of blood under the skin caused by leakage from small vessels
erysipelas
An acute infectious disease of the skin with localized redness and swelling and systemic symptoms
erythema nodosum
Inflammation of subcutaneous tissues resulting in tender, erythematous nodules; may be an abnormal immune response to a systemic disease, an infection, or a drug
ichthyosis
A dry, scaly condition of the skin (from the root ichthy/o, meaning “fish”)
impetigo
A bacterial skin infection with pustules that rupture and form crusts; most commonly seen in children, usually on the face
keratosis
Any skin condition marked by thickened or horny growth. Seborrheic keratosis is a benign tumor, yellow or light brown in color, that appears in the elderly. Actinic keratosis is caused by exposure to sunlight and may lead to squamous cell carcinoma
lichenification
Thickened marks caused by chronic rubbing, as seen in atopic dermatitis (a lichen is a flat, branching type of plant that grows on rocks and bark)
mycosis fungoides
A rare malignant disease that originates in the skin and involves the internal organs and lymph nodes. There are large, painful, ulcerating tumors
nevus
A defined discoloration of the skin; a congenital vascular tumor of the skin; a mole, birthmark
paronychia
Infection around a nail. Caused by bacteria or fungi, and may affect multiple nails
pediculosis
infestation with lice
petechiae
Flat, pinpoint, purplish red spots caused by bleeding within the skin or mucous membrane (singular, petechia)
photosensitization
Sensitization of the skin to light, usually from the action of drugs, plant products, or other substances
purpura
A condition characterized by hemorrhages into the skin and other tissues that appear as purple discolorations.
rosacea
A condition of unknown cause involving redness of the skin, pustules, and overactivity of sebaceous glands, mainly on the face
scabies
A highly contagious skin disease caused by a mite
senile lentigines
Brown macules that appear on sun-exposed skin in adults; liver spots
shingles
An acute eruption of vesicles along the path of a nerve; herpes zoster (HER-peze ZOS-ter); caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox
tinea
A fungal infection of the skin; ringworm
tinea verscolor
Superficial chronic fungal infection that causes varied pigmentation of the skin
urticaria
A skin reaction marked by temporary, smooth, raised areas (wheals) associated with itching; hives