Health Records and Professional Ethics in Radiology
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
Health Information Management
All health care providers are required to maintain all patient care information that applies to an individual patient.
Health Records
Concentrate, within a single record, all patient care information that applies to an individual patient.
Health Information Department Functions
Support the current and continuing care of patients, maintenance of health information, and support the institution's administrative processes.
Patient Billing and Accounting Processes
Records maintained by the health information department for patient billing and accounting processes.
Reimbursement Formulas
Many reimbursement formulas are contingent upon medical records and their accuracy.
Performance Improvement Programs
Maintain records for utilization management, risk management, and quality management or performance improvement programs.
Patient Privacy and Security
Ensure patient privacy and security issues.
Legal Compliance
Ensure compliance with legal requirements.
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act 1996, a federal law that required the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information.
HIPAA Privacy Rule
Addresses the use and disclosure of individuals' health information by entities subject to the Privacy Rule.
Protected Health Information
Health information that is protected under the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Individuals' Rights
Individuals have rights to understand and control how their health information is used.
Major Goal of the Privacy Rule
To ensure that individuals' health information is properly protected while allowing the flow of health information needed to provide and promote high quality health care.
Balance of Privacy and Information Flow
The Privacy Rule strikes a balance that permits important uses of information while protecting the privacy of people who seek care.
Continuity of Care
Health records promote effective communication and ensure continuity of care.
Service-oriented Health Information Department
The Health Information department is service-oriented.
Documentation Errors
Discuss the procedure for correcting or amending documentation errors in a patient health record.
Coding in Radiologic Procedures
Identify coding as it relates to radiologic procedures and the reimbursement impact for health care facilities.
Confidential vs Non-Confidential Information
Differentiate between confidential and non-confidential information.
Health Services Research
Support health services research as part of health information management.
APC
Ambulatory Patient Classification
CPT
Current Procedural Terminology

ICD-10-CM
International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition, Clinical Modification
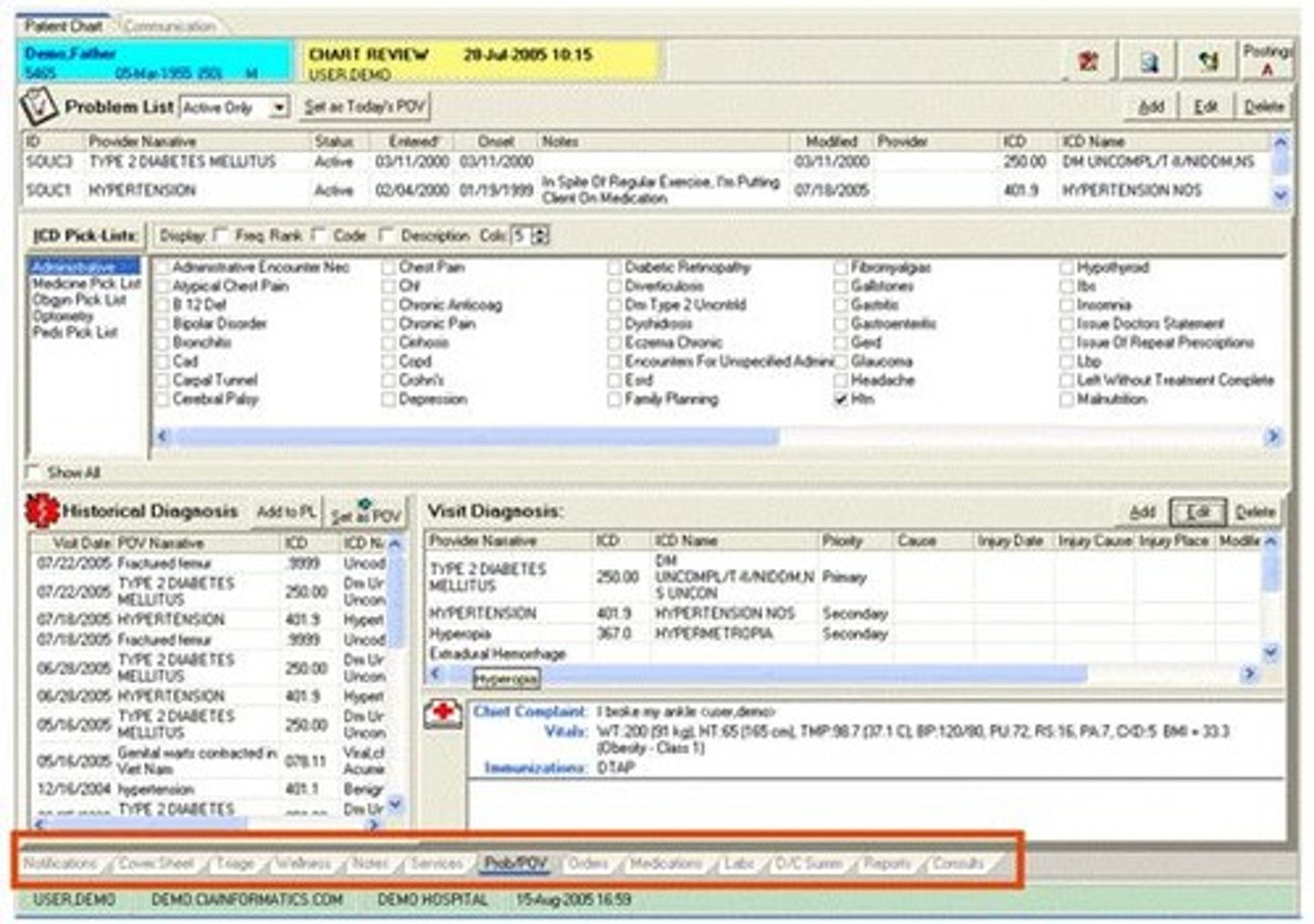
DRG
Diagnosis-Related Group
TJC
The Joint Commission
HFAP
Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program
PPS
Prospective Payment System
CPT-4
listing of medical terms and codes for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures used for coding for physician reimbursement (used for both inpatient and outpatient)
ICD-10-CM
classification system that is used for diagnosis coding in all health care settings in the United States
DRG
categorizes into payment groups patients who are medically related with respect to diagnosis and treatment and statistically similar with regard to length of stay
TJC
organization that accredits hospitals and other health care institutions in the United States
HFAP
performs functions similar to TJC
PPS
system for Medicare patients whereby payment groups are established in advance; hospitals get paid up front
EMR/EHR
electronic health record system generally considered as the portal through which clinicians access a patient's health record, order treatments or therapy, and document care delivered to patients; allows providers to gather multiple types of data about a patient
PA chest (single view)
71010
MR cervical spine/contrast
72142
Health Records Coding
Converts diagnoses and procedures into a numerical system
Accurate coding
greatly impacts reimbursements from Medicare and third-party payers.
Health Record Content
All departments that take part in the care of a patient must document that care in the health record.
Charting
Documenting in the patient's record, or charting, should be done by radiologists and radiographers when a patient receives either diagnostic or therapeutic radiologic services.
Medical necessity
a diagnosis or sign or symptom for which the test is being performed must accompany each request for all procedures ordered.
Patient ID and demographics
Information identifying the patient and their demographic details.
Medical history
A record of the patient's past health issues and treatments.
Conclusion and impression on admission
The assessment made by the healthcare provider upon the patient's admission.
Diagnostic and therapeutic orders
Instructions for tests and treatments to be performed.
Clinical observations
Notes made by healthcare providers regarding the patient's condition.
Report of relevant physical examination
Documentation of the findings from the physical examination of the patient.
Consultation reports
Reports from specialists who have evaluated the patient.
Diagnostic and therapeutic reports
Documents detailing the results of diagnostic tests and therapeutic interventions.
Final diagnosis and prognosis
The conclusive diagnosis made and the expected outcome for the patient.
Discharge summary
A summary of the patient's hospital stay and instructions for follow-up care.
Postmortem results
Findings from examinations conducted after a patient's death.
Psychologic needs summary
An overview of the psychological support required by the patient.
Physical examination report
A detailed account of the physical examination findings.
Treatment plan
A documented strategy for managing the patient's condition.
Evidence of informed consents
Documentation showing that the patient has agreed to treatment after being informed of the risks.
Progress notes
Ongoing documentation of the patient's condition and treatment progress.
Reports of surgical and invasive procedures
Documentation of surgeries and other invasive treatments performed on the patient.
Records of donations and implants
Documentation of any organ donations or implants related to the patient.
Conclusions at termination of stay
Final assessments made at the end of the patient's hospital stay.
Discharge info given to patient and family
Information provided to the patient and their family upon discharge.
Follow-up care instructions
Guidelines provided for the patient's care after discharge.
Patient demographic information
Details about the patient's identity and background.
Specific procedure requested
The particular medical procedure that has been ordered.
Ordering physician
The doctor who has requested a specific procedure or treatment.
Documentation of medical necessity
Records that justify the need for a specific medical service or procedure.
Requires a diagnosis or symptoms
Indicates that a medical procedure must be supported by a diagnosis or presenting symptoms.
Procedure results
Outcomes or findings from a medical procedure performed.
Dosage required for therapeutic and radionuclide procedures
The specific amount of medication or radioactive material needed for treatment.
Special reports documenting evaluation or treatment of a patient
Detailed reports that provide insights into the patient's evaluation or treatment.
Provided by radiologist
Indicates that the report or findings were generated by a radiologist.
Patient images kept in department PACS system
Medical images of the patient stored in the Picture Archiving and Communication System.
Report also maintained in radiology EHR
The report is also stored in the electronic health record of the radiology department.
Reports must be signed by interpreting radiologist. Electronic signature
All reports need to be signed by the radiologist who interpreted them, using an electronic signature.
Reports are transcribed. Voice-activated transcription
Reports are converted into written form using voice-activated transcription technology.
Do's
Guidelines for proper documentation practices in medical records.
Don'ts
Prohibited actions when recording information in medical records.
Patient identification data
Information used to identify the patient within the medical records.
Medical history of the patient
A comprehensive record of the patient's past medical conditions and treatments.
Clinical observations, including results of therapy
Notes on the patient's clinical status and the outcomes of any therapies administered.
Informed Consent
A process ensuring the patient is aware of and agrees to the treatment or procedure.
Incident Report
A document detailing incidents or occurrences that deviate from standard patient care.
Quality assurance
A process that monitors and evaluates the quality of the care and services provided to patients within a health care facility.
CQI measures
Continuous Quality Improvement measures used to enhance the quality of services.
Radiology order
A request for service that must accompany a diagnosis or sign or symptom for which the test is being performed.
EMR
Electronic Medical Record, where results of the procedure should be documented as soon as possible after completion.
Health Insurance Companies
Entities that require medical records to support the diagnosis for reimbursement under the diagnosis-related group (DRG) and the prospective payment system (PPS).
DRG
Diagnosis-Related Group, a system implemented by the government in 1983 for reimbursement purposes.
PPS
Prospective Payment System, a method for reimbursing healthcare providers.
Failure to Record Data
The requirement that records must be in ink or verifiable if using an Electronic Health Record system.
Performance Improvement
A process that includes monitoring and evaluating the quality of care and services provided to patients.
Utilization
The measurement of how services are used within a healthcare facility.
Risk management
The identification and mitigation of risks within a healthcare setting.
Infection control
Measures taken to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare facilities.
Surgical case review
An evaluation of surgical cases to ensure quality and safety.
Medication usage
The assessment of how medications are prescribed and administered.
Health record review
The process of evaluating patient records for accuracy and completeness.
Blood usage review
An analysis of how blood products are utilized in patient care.
Pharmacy and therapeutic review
An evaluation of pharmacy practices and therapeutic outcomes.
Case management
The coordination of patient care to ensure effective treatment.