Chemistry Regents Review
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Daltons Theory
Hard Sphere and Smallest Indivisible Particles
JJ Thompson Theory
Used a cathode ray tube to discover the electron
Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment
An atom is made up of Mostly empty space
The nucleus is small, dense, and positively charged
Wave mechanical model (electron cloud theory)
An atom is located within an orbital with in the Electron cloud
Proton
1 atomic mass unit
+1 Charge in the nucleus
Atomic Number
Atomic number
The periodic table is organized through atomic number
Neutron
1 amu or u, 0 charge, located inside nucleus
Atomic mass - atomic number= neutron
Electron-
0 amu or u or 1/1836 of the mass of a proton, -1 charge, located outside nucleus
Atomic Number/ Nuclear charge-
number of protons in the nucleus, found on the periodic table
Ex:
Atomic Mass/Mass#/Nucleons-
mass of an elements naturally occurring isotopes. protons + neutrons make up an elements mass.
Isotope-
is an element that contains the same atomic # different atomic mass, different # of neutrons.

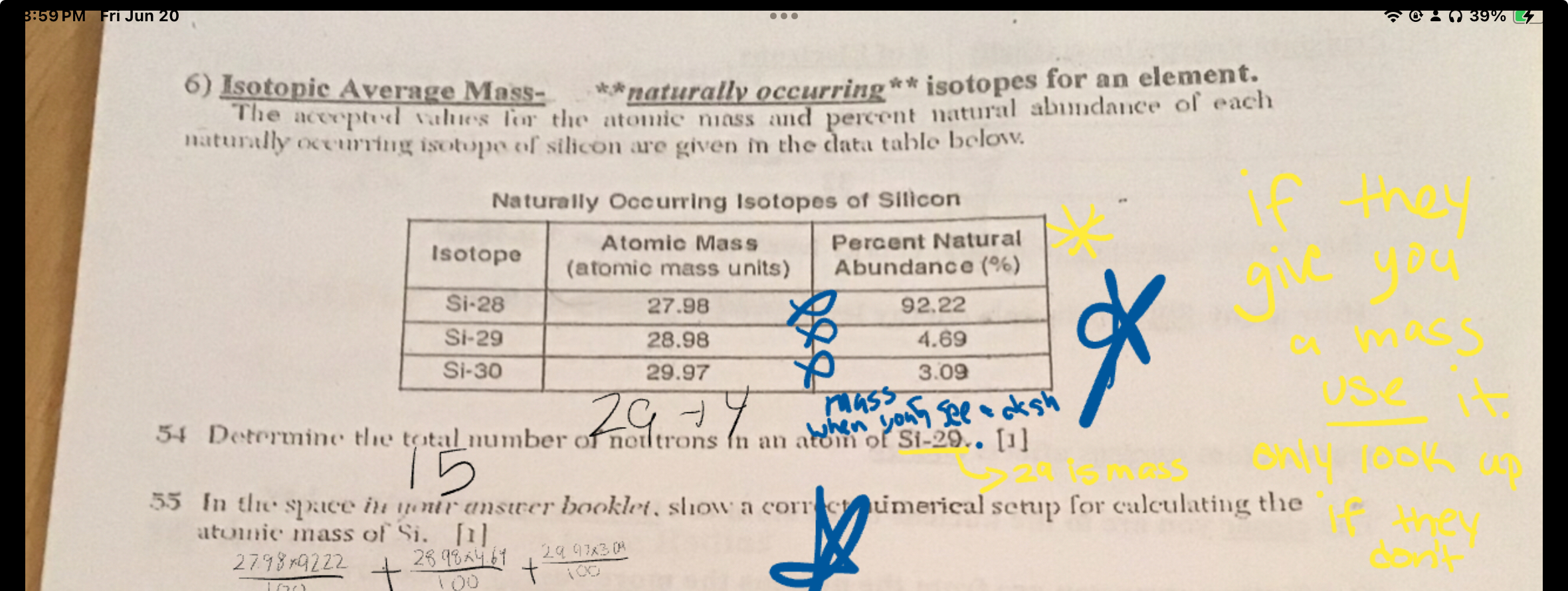
Isotopic Average Mass-
The acceptod values for the atomic mass and percent natural abundance of each naturally occurring isotope of silicon are given in the data table below.
Ground state clectron configuration-
When an electron is at the lowest energy level, Electron figuration is found on the periodic table
Excited state electron configuration
When an electron absorbs energy and jumps up to a higher energy level

Bright light spectrum
When an Electron and side state(emits) Energy and falls back to the ground state in the form of light

Principal energy level (shell)
Fr: 2-8-18-32-18-8-1
You can use FR to compare how many occupied principal levels there are and how many filled principal levels there are
Distance from nucleus, affects energy
The closer you are to the nucleus of an atom, the less energy and electron has
The further way you are from the nucleus, the more energy and electron has
think of rubber band
Valence electrons
Outermost electrons within the electron configuration
Ex: Se=2-8-18-6

All Atoms
All atoms are electrically neutral
Equal protons and equal electrons
ZERO Charge
Ions
(+) or (-) charged particles
(+) charge = lose electrons
(-) charge = gain electrons
Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius
Radius- measures half the diameter of the atom

Periodic trend
The periodic table is arranged according to atomic number, not atomic mass
The number of protons tells you the atomic number of an element element
Period (Principal energy Level, Shells)
Horizontal rose, moving from left to right across the periodic table
Groups
Vertical columns, 18 in total, elements in groups have similar characteristics because they have the same number of valence electrons
Group 1 (alkali) Metals
1 word for group 1
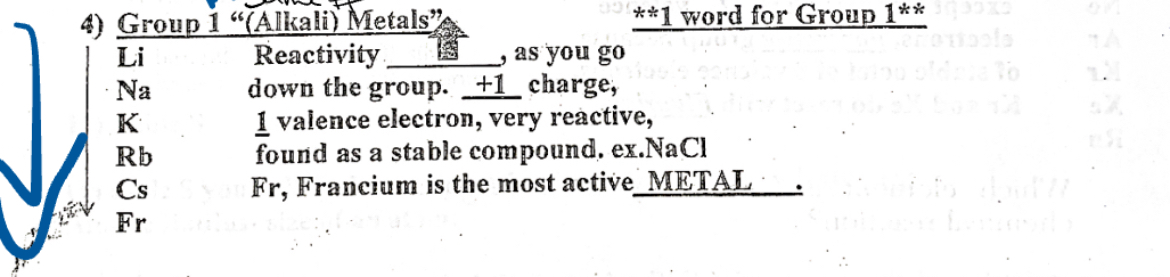
Group 2 (Alkaline earth) metal
Two words for group 2
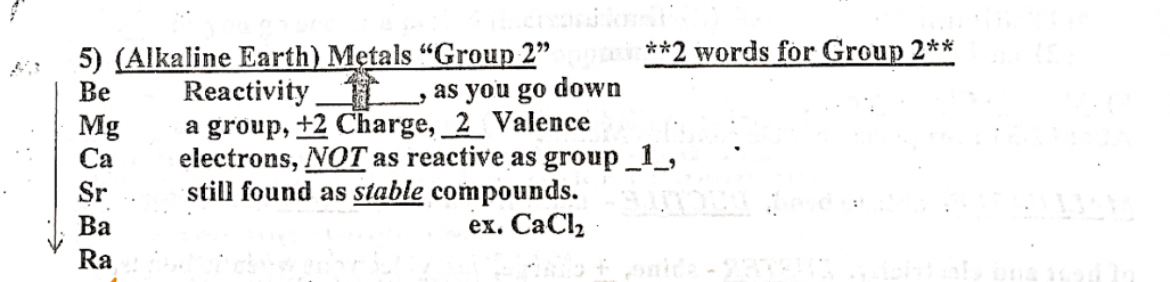
Transition metals (Group 3-12)

Halogens
Diatomic elements:elements that naturally exist as molecules composed of two atoms of the same element bonded together

Group 16 (Noble Gases)
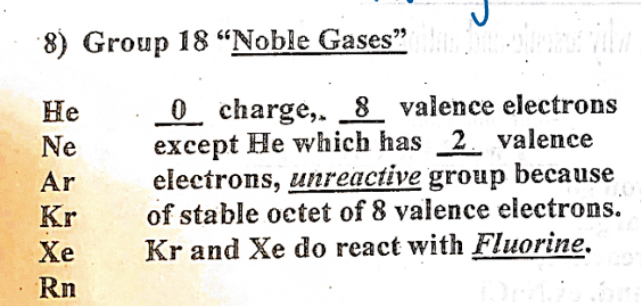
Metallic Character
Malleable to bend
Make make two wire
Good conductor of heat and electricity
Luster-shine
Loses electron when it bonds
HMP,LE,LI
Characteristics of nonmetals
Dull, poor conductors of heat and electricity
brittle in the solid state ex: glass
negative charge gained electron
all three phases of matter are LMP, HI, HE
Ionization energy
Amount of energy needed to remove an electron
Group 18 elements have the highest ionization energy because they already have a filled electron shell, and Noble gases, don’t want to lose their valences electron
Electronegativity
Attraction for electrons
Chlorine is the most electronegative
Group 18 elements have no electronegativity number because they are noble gases
Group 1 elements have the low electronegativity value because they have one valence electron
Ex: FR=0.2 weakest F=4.0 strongest
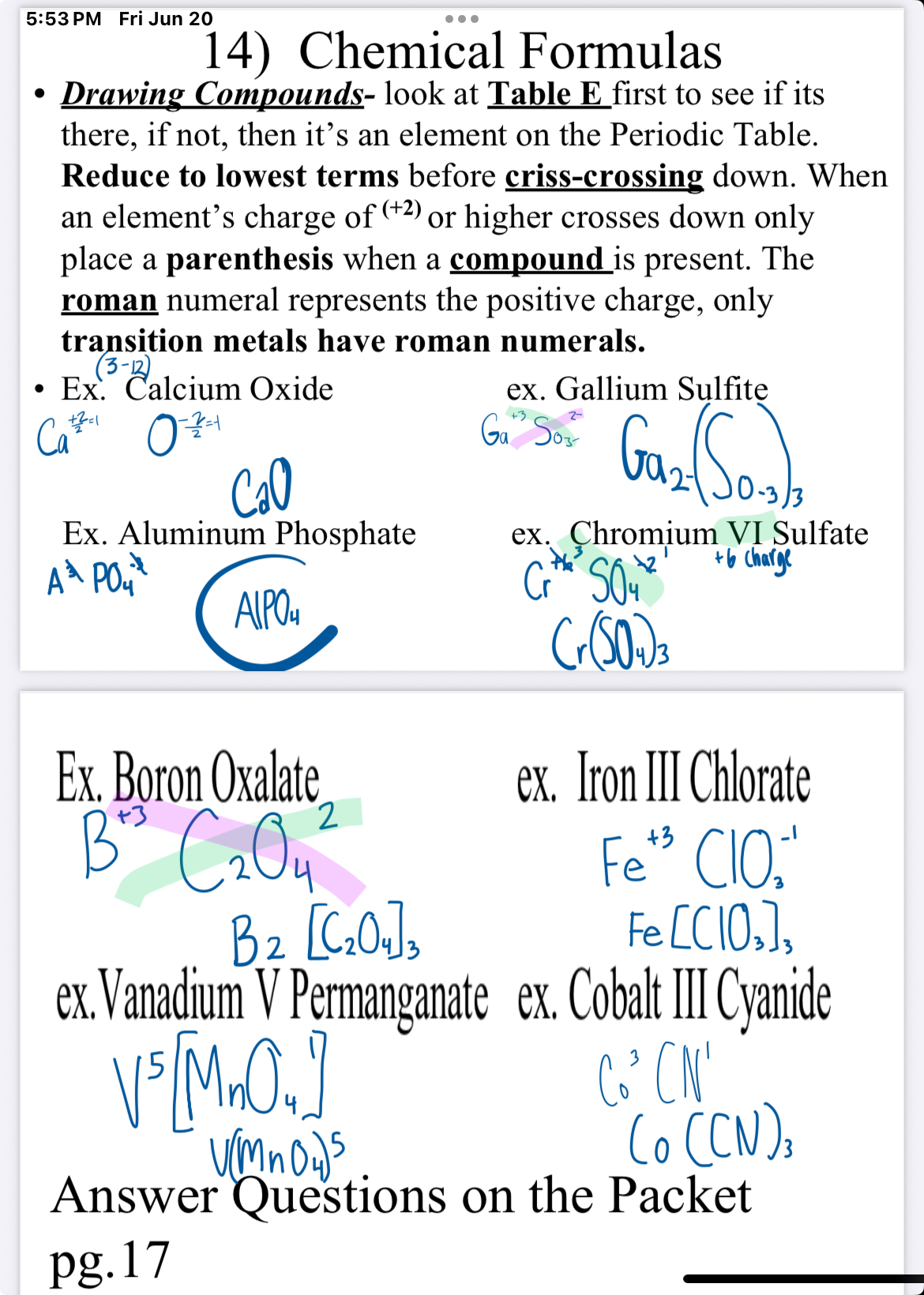
Drawing compounds
Drawing compound look at table E First to see if it’s there, if not, then it’s an element on the periodic table. Reduce the lowest terms before crisis crossing down. When an element crosses down only place a parentheses when a compound is present. The Roman numeral represents the positive charge, Only transition metals have Roman numerals
Naming compound
When naming compounds be aware that transition metals produce Roman numerals if a substance is not on table E then it ends ide.
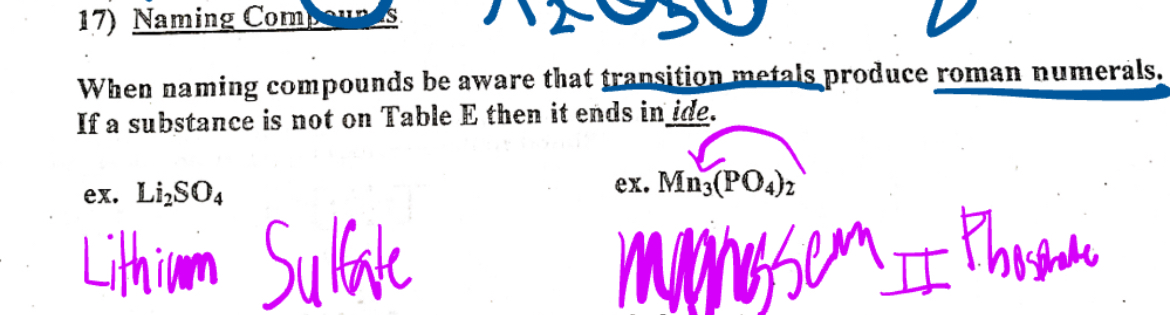
Determining which group an element belongs
By looking at the number of atoms an element has, we can determine both the charge and the group number by reversing the number of atoms up Left side elements has a positive charge and right side elements have a negative
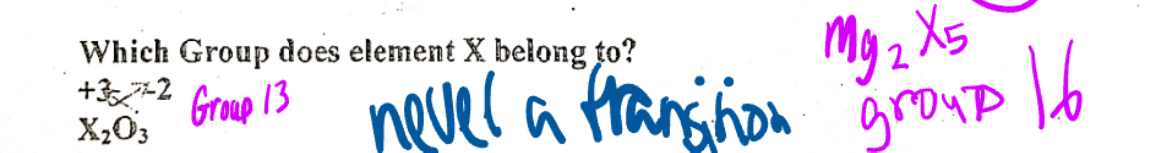
BARF
broken/Absorbed
Release/Form

Ionic bonds
Bond between a metal and a nonmetal to form a stable octet of electrons
Transfer of electrons to form ionic bonds
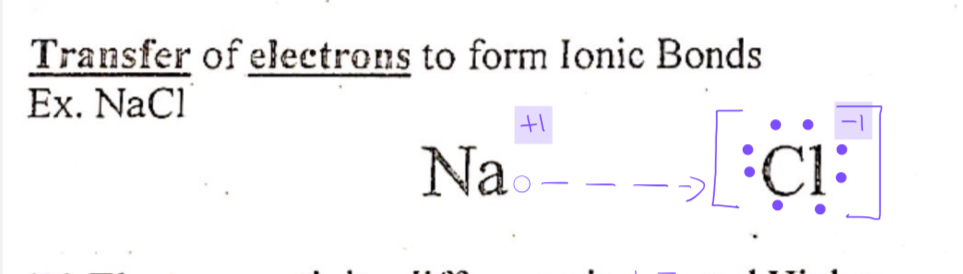
Polar
1.7⬆ Ionic
1.6-1 polar
0 nonpolar
characteristics of ionic solids(Salt)
Hard
High melting point
Crystalline structure
Poor conductor of as solid, good conductor as a liquid or aqueous because a free moving ions
Covalent bonds
Sharing of electrons between nonmetals to form a stable octet of valence electrons
Nonpolar covalent bond
Equal sharing of electrons between two of the same(Diatomic) Nonmetals
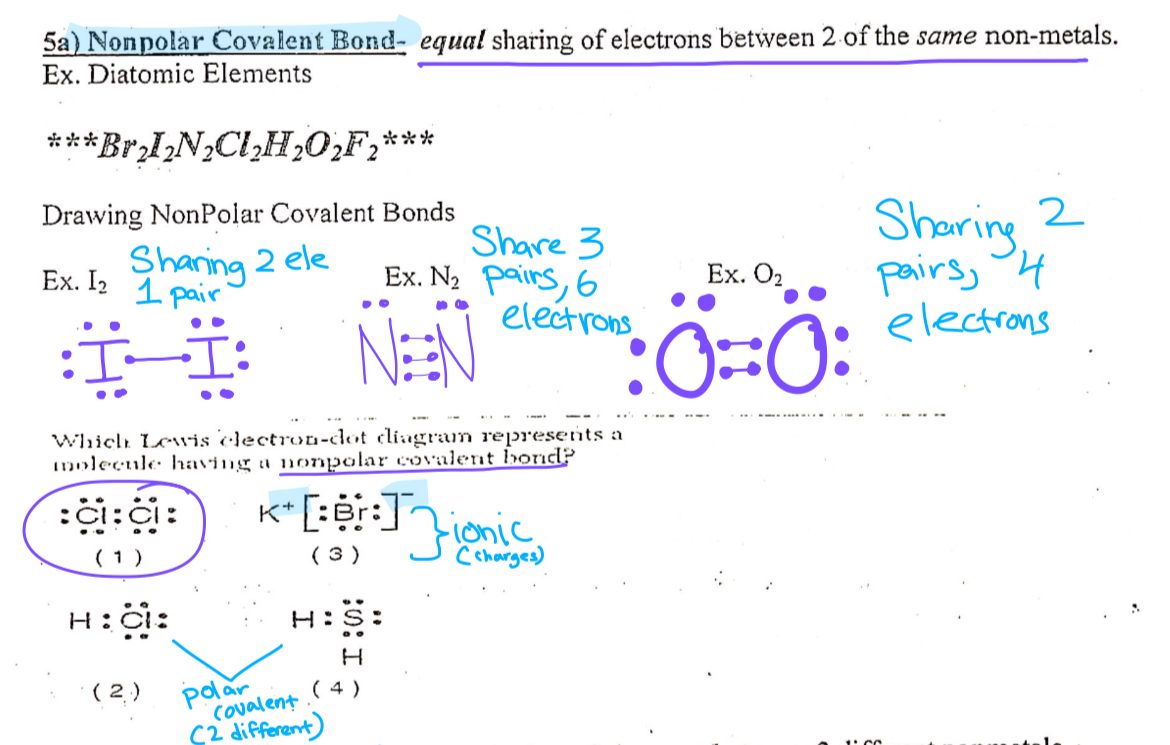
Polar covalent bond
Unequal sharing of electrons between two Different nonmetals
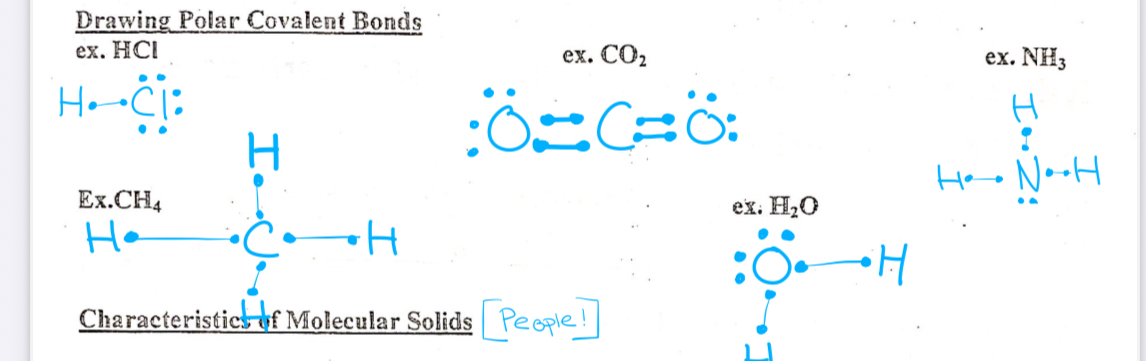
Characteristics of molecule solids(People)
Soft
Low melting point
Poor conductor of electric electricity
Both ionic and covalent bonds
Compounds that both contain ionic and covalent bonds must fit a criteria with at least three or more elements
Is usually combined with a table E element
Ex: NaCIO3 = Na, CI, O
Metallic bonds
A metal by itself represents a metallic bond, Positive ions immerse in a sea of mobile electrons
Hydrogen bonding
When hydrogen bonds with fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen (FON)
These compounds have unusually high melting points and high boiling points
Van Der Waals Force of Attraction (London Dispersion Forces)
Attraction increases as distance decreases, and mass increases
intermolecular forces
The attractive forces between molecules. Higher the melting point or boiling point the stronger, the intermolecular forces of attraction, the lower and weaker the intermolecular forces of attraction.
my answer is either strong or weak.(high melting/boiling point equals strong=low melting/boiling points equals weak’
SLG

molecule ion attraction
Ionic compounds (salt) Bonds with a water molecule
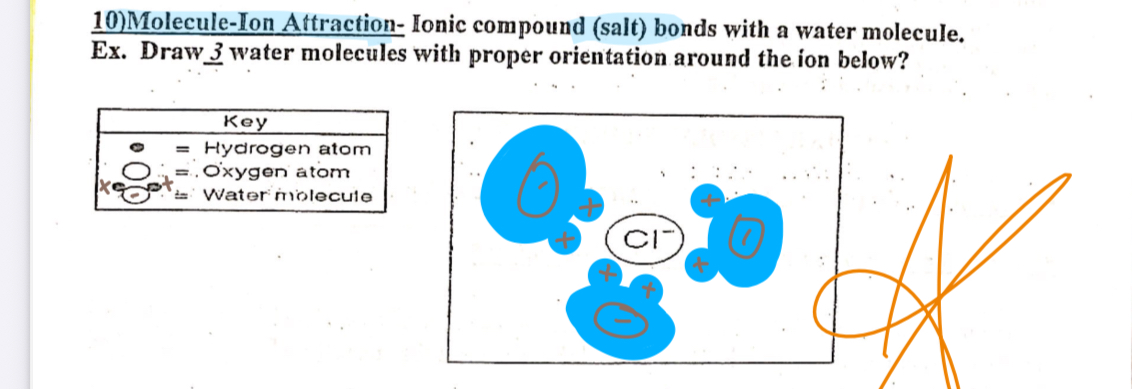
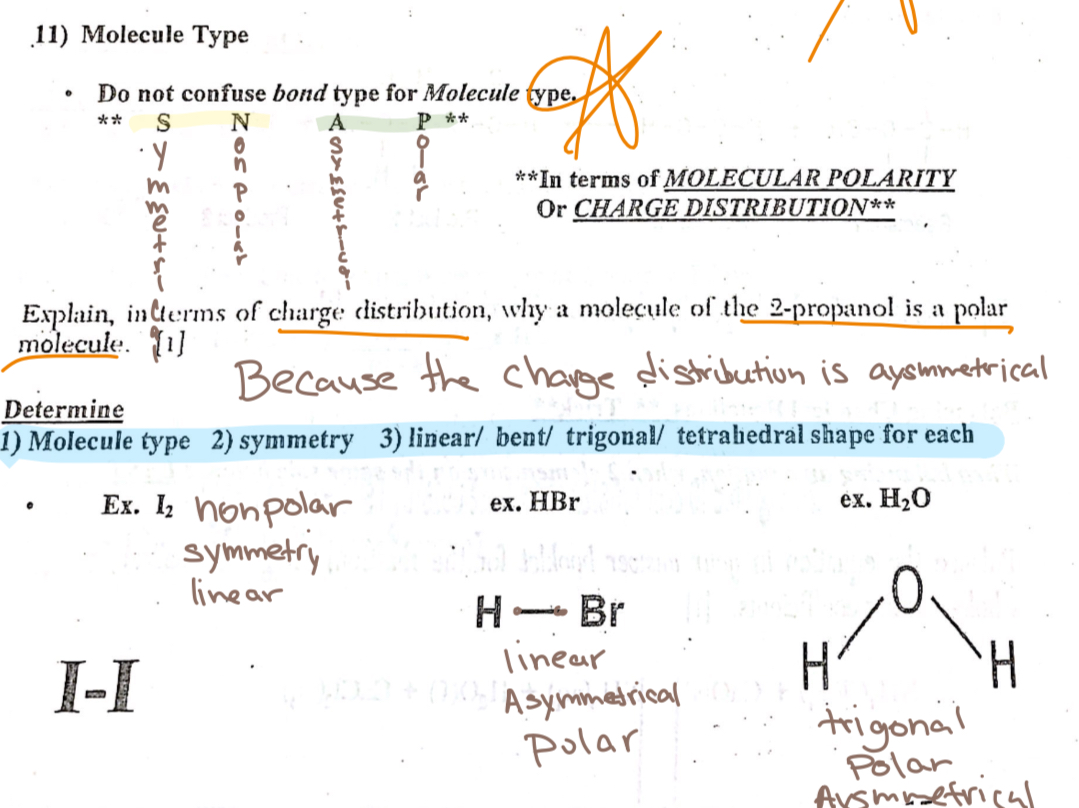
Molecule Types
Symmetrical/Nonpolar
Asymmetrical/polar
Balancing equations
When two elements are on the same side balance last
Get the items to equal up
Formula (Molecular Mass)
Finding the mass of each element and multiplying them by the number of atoms that determine the gram formula mass
% Composition
Mass of part/mass of whole x 10
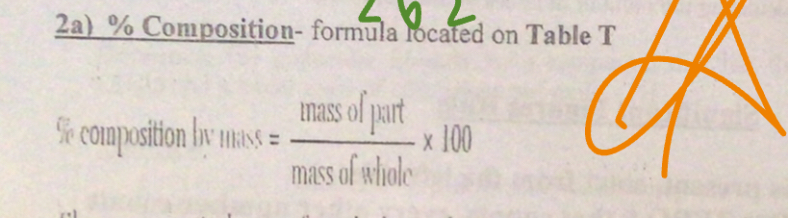
Percent composition of hydrate
Hydrate-A salt that contains a loosely bonded water molecule, Think of CuSo4 o 5H2O (Blue salt)
Big # - Small #/Big # x 100
Anhydrous-when water evaporates leaving just salt

Mole Conversions
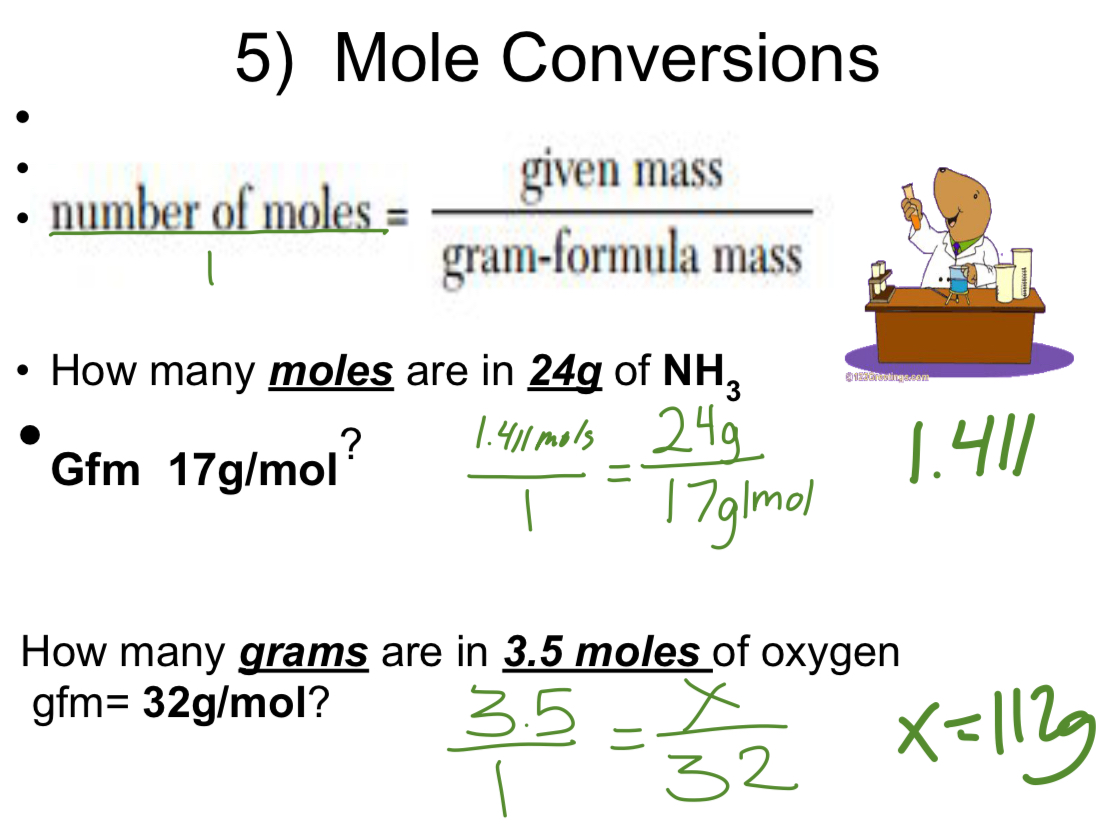
Significant Figures
When a decimal point is present start from the left side
Once you find the first 90 number that counts, every other number counts
When a decimal point is not present start from the right side once you find the first non-zero number that counts, every other number counts
Empirical formula
Compound which has been reduced to the lowest term
Ex: So3,CH4, H2O
Single and double replacement reaction
Single replacement-When an element and a compound are on each side of the arrow
Double replacement reaction-2 compounds exchange ions with each other, two compounds are in each side
Percent error
Measured value= Experimental value

Molecular formula
Find the imperial formula mass
Mole formula on table T
Multiply imperial formula by answer to step two

Law of conservation of mass
Mass of reactants must be equal to mass of products

Four Chemical Reactions
Synthesis Two or more substances combined to form a compound
Decomposition when a compound breaks into elements or substances
Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve
**Solution is made up of two parts**
Solute:substance being dissolved ex:NaCI
Solvent: Substance that Is doing the dissolving ex: Water
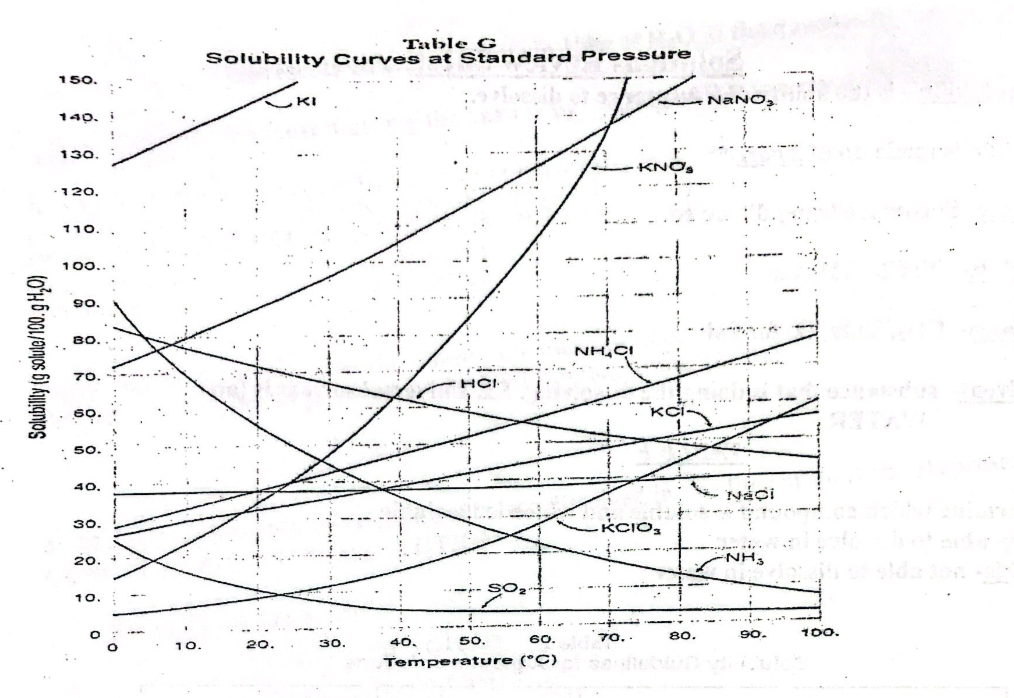
Table G
Supersaturated: Above the line
Saturated: on the line
Under saturated: under the line
most soluble is the highest curve for that temperature and lowest solubility is the lowest curve for that temperature**
Molarity
The number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 L of solution represents concentration of a solution

Parts per million(ppm)
Commonly used as a measure of small levels of pollutants An air, water, body fluids

Electrolytes
Substances which are soluble and can break up into ions which conduct electricity(ABS-ACID BASE SALTS)
Acid-HCL(AQ) BASE-NaOH(AQ) SALTS-NaCL(AQ)
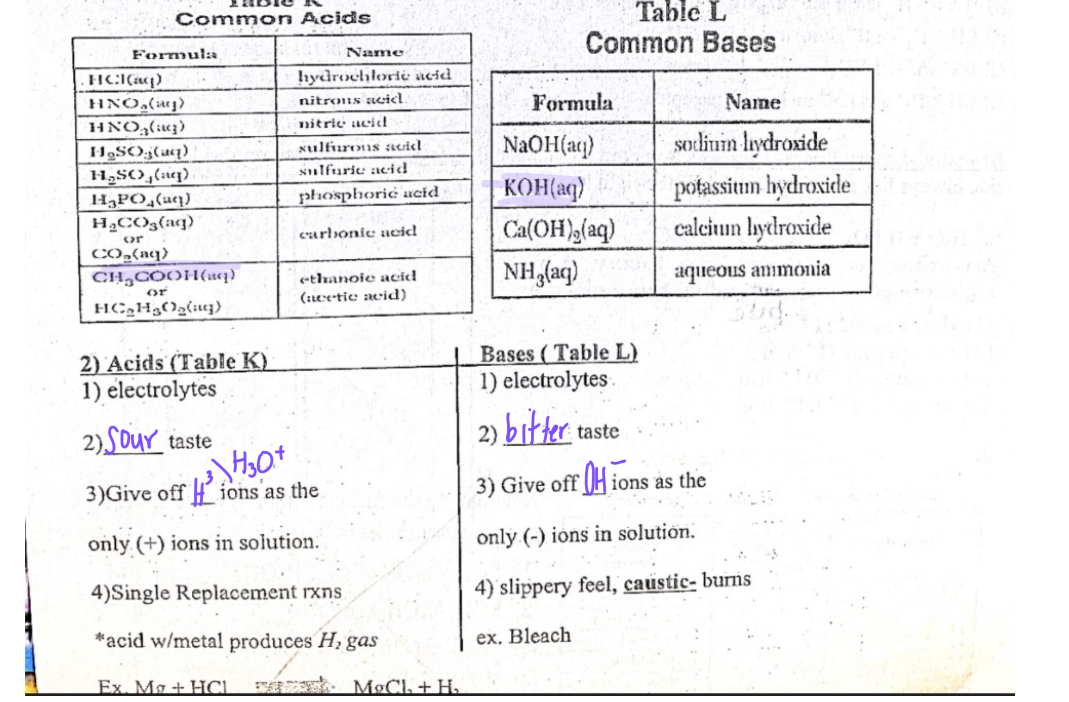
Nonelectrolyte
Substances which are highly soluble, Poor conductor of electricity, Does not break into ions
Alcohol-CH3OH SUGAR-C6H12O6
Salt/Anti Freeze
When added to H2O freezing point decreases and boiling point increases
Table H:Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure is amount of pressure needed to have a substance boil or turned into vapor/gas. Direct relationship between VP and temp
Propanol boils at the lowest temperature and has the weakest intermolecular forces Ethanoic acid boils at the highest temperature having the strongest intermolecular force of attraction
Kinetic theory of gases
a real gas behaves most like an ideal gas under high temperature and low pressure ex: flat soda

Different molecular structure different Priorities
Substances with the same element like 02 and 03 are both carbon and have different molecular structures in different properties
3 Heat Formulas
Q=m x c x T
Q=Heat M=Mass C=Specific heat value T=Temp change
Q=m x Hf
Q=Heat(kj) m=mass(g) Hf**Heat of Fusion
Q=m x Hv
Q=Heat(kj) m=mass(g) Hv**Heat of Vaporization
Physical vs Chemical Change
Physical change is the same thing on both sides and chemical is new or different form.
Heat
Heat travels from high temperature to low temperature
Mixtures😣
Homogeneous Mixture uniform, same, even distribution of particles throughout
Ex. Anything with (aq) is the answer, KC(aq)
Heterogeneous Mixtures- particles are distributed unevenly throughout.
Ex. Soil, or Salad dressing
Separation of mixtures:A) filtering (insoluble solid) ex. Sand from water. B) boiling or evaporation or distillation, (soluble solid)
ex. such as Salt water, or 2 different liquids) ex. Water and Alcohol
Matter and Energy
Substances- are composed of elements and compounds.
Substances- are composed of elements and compounds.
Compounds- 2 or more different elements, CHEMICALLY combined, CAN be decomposed, FIXED ratio of elements.
Mixtures- 2 or more elements are PHYSICALLY combined, VARIED ratio of elements, can be physically separated.
Combined Gas Law
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
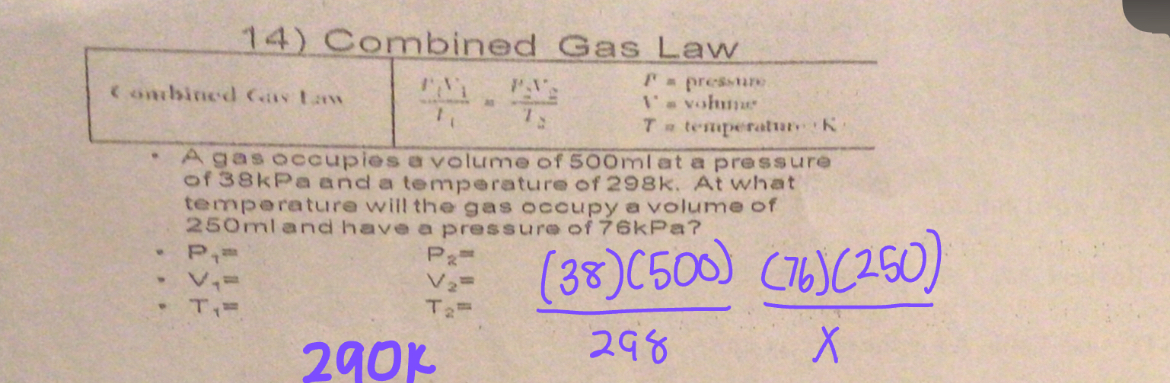
Boyles Law
the relationship between pressure and volume (inverse)
The word constant means to cross out,
In Boyles Law, Temperature is constant.
STP- use Table A for the correct units.
Ex. If 80ml of a gas is compressed from 60kpa to 30 kpa at constant temperature, what is the new volume?
Charles Law
the relationship between temperature and volume. ** Temp has to be in
KELVIN™* YOU must convert CELSIUS into KELVIN by using TEMP FORMULA
the word constant means to cross-out.
Charles Law pressure is constant. V1/T1 = V2/T2
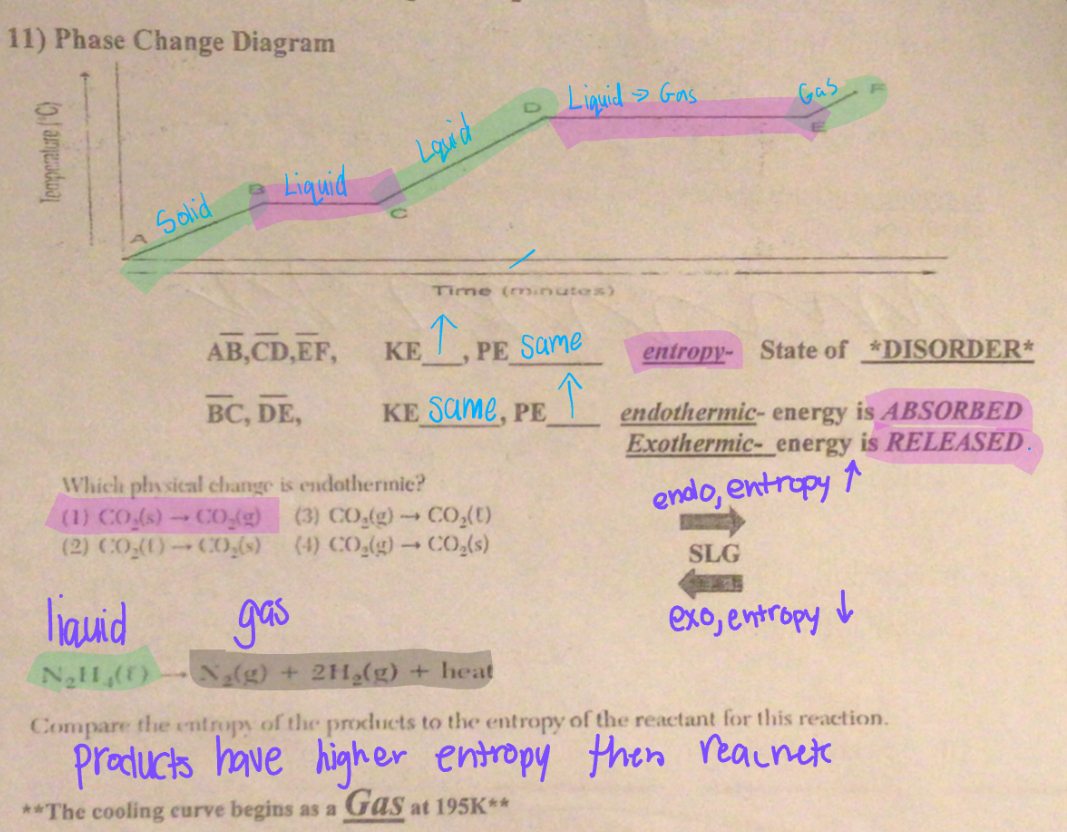
Phase Change Diagram
EQUAL VOLUME= EQUAL # OF MOLECULES
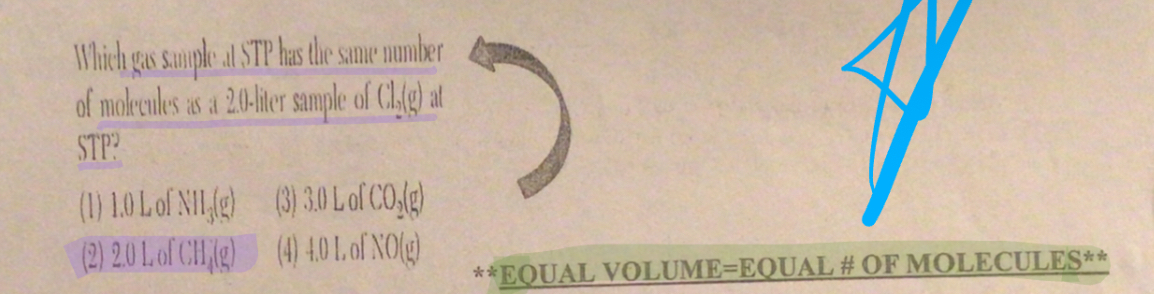
Arrhenius Acid
Gives off H+ or H2O+ hydronium ions in solution
Arrhenius Base
Gives off OH (Hydroxide ions) In solution, metal with an OH ion
Ex: NAOH, Ca OH2
Bronsted-Lowry Acids
Donate H+(Proton) To a base, has one more H+ Ion. An acid on the left-hand side always has a conjugate base on the right hand side

Bronsted-Lowry Bases
Except a proton from an acid, one less H+ ION. A BASE ON THE LEFT HAND SIDE ALWAYS HAS A conjugate ACID ON THE RIGHT HAND SIDE.

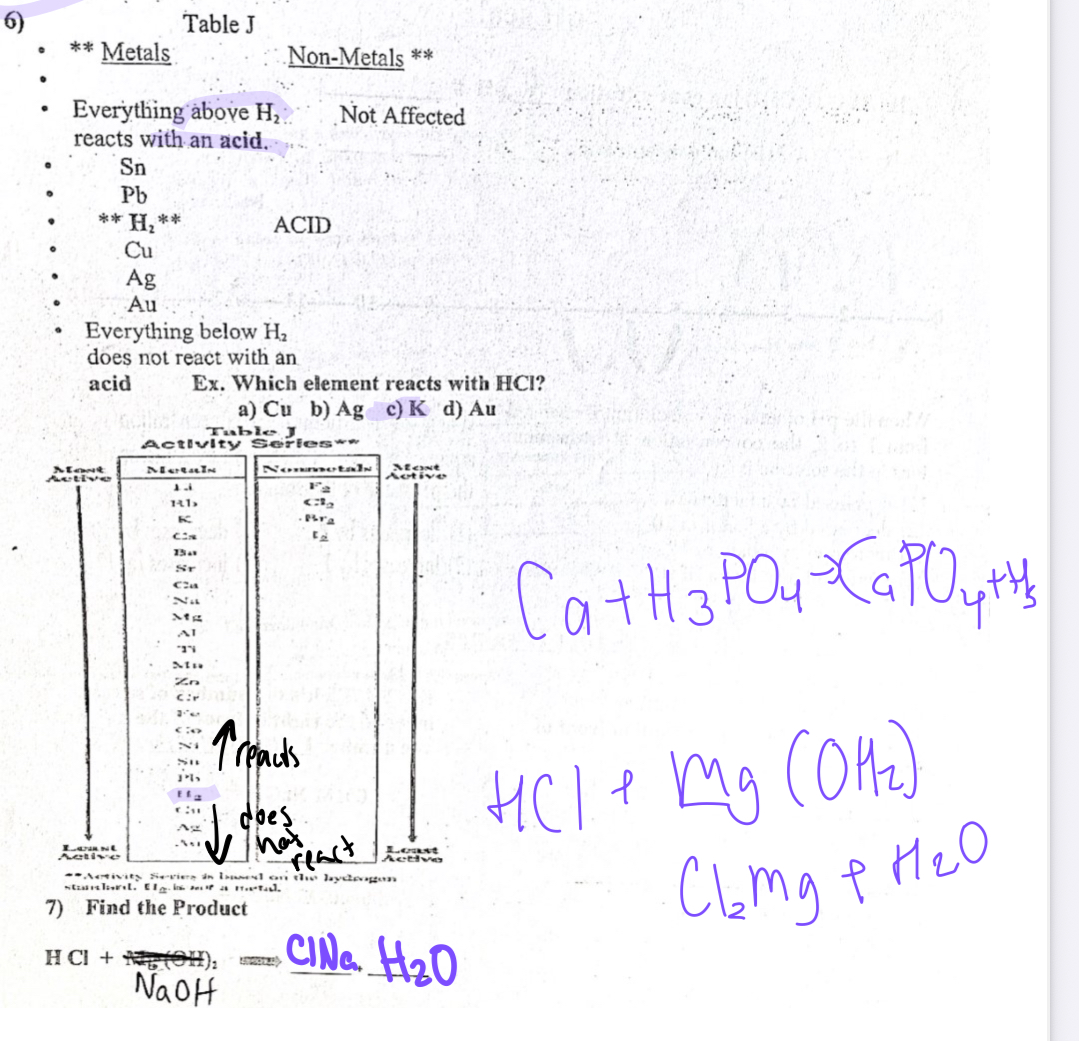
Table J
Everything above, H2 reacts with an acid
Everything below H2 does not react with an acid
Kinetics and Equillibrium
Potential Energy- stored energy
Kinetic energy- energy in motion
Activatation energy- energy need to start a reaction
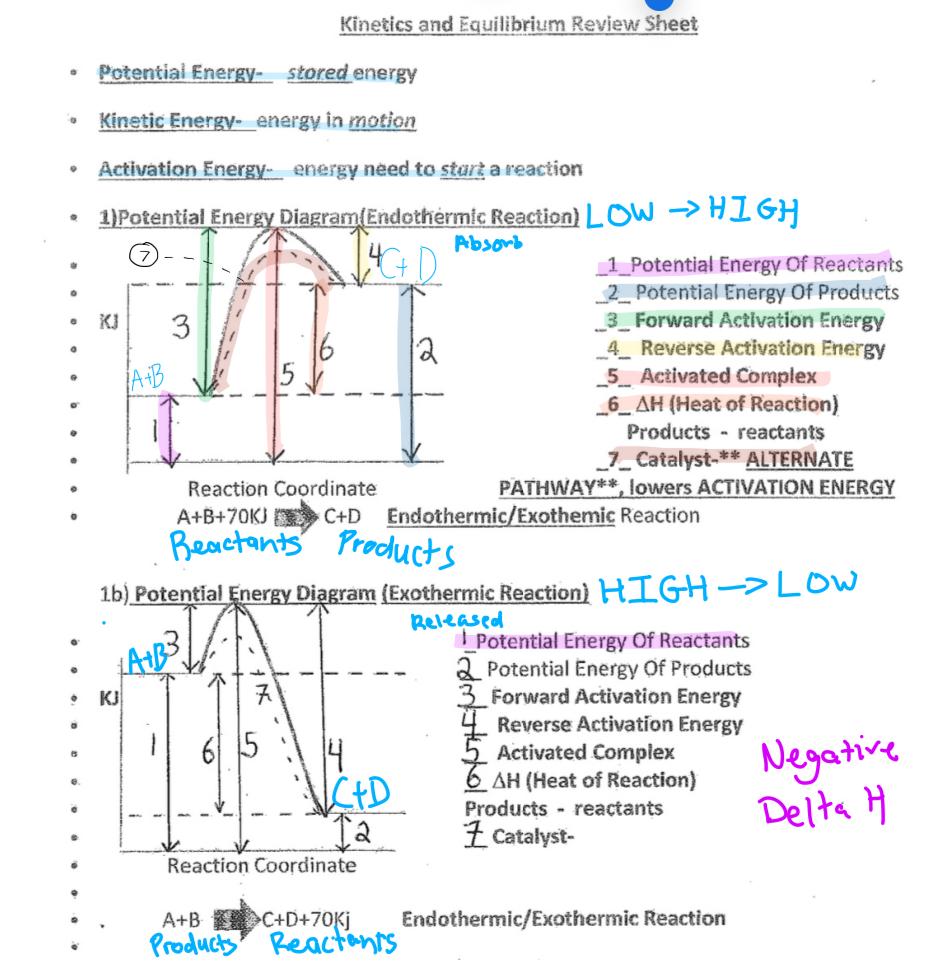
Factor affecting reaction rates
If you increase the temperature, The number of effective collisions increase thus reaction rate increases.
If you increase the CONCENTRATION, # of effective collisions increases , thus reaction rate increase
By increasing the SURFACE AREA, # of effective collisions increase, reaction rate increase the number of reaction sites increases the number of total collisions.
By adding a CATALYST, the reaction rate increases because the reaction speeds up by lowering the ACtavation energy without getting used up and providing an alternate pathway for the reaction.
Equilibrium
When the forward and reverse reaction of a chemical reaction precedes that equal or same rates
Phase equilibrium
When the rate of the Ford reaction equals rate of reverse reaction
Solution equilibrium
Rates of dissolved equal rates of unsolved(Saturated solution)
Chemical equilibrium
When concentrations of the products and reactants remain constant.
Rates are equal concentrations are constant
Temperature
Decrease your stay increase shift away

Pressure
Pressure only affects gases
As the pressure increases, you shift towards the side with less moles

Concentration
As the concentration increase, Shift away from the side where it increase, The side, The concentration always increases.
Concentration increases away(CIA)
Systems of nature
Low energy and high entropy/disorder
Ph Sacle
If a concentration increases by a factor of 10, it decreases by 1, and if a concentration decreases by 10 increases by one