DFDDS EXAM II PPT7 - SUSPENSIONS
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Which of the following ROA typically does NOT involve application of pharmaceutical suspensions
A) topical
B) intramuscular
C) intravenous
D) rectal
C) intravenous
Which of the following is NOT cake desired feature of pharmaceutical suspensions
A) settle slowly and redisperses quickly
B) cakes quickly
C) uniformity
D) sufficient physical and chemical stability
B) cakes quickly
Is flocculation desirable in preparation of suspensions? (Yes or No?)
yes
why: ideals property = *settles slowly, disperses
settle quickly, but they settle in a compact state (very loose settling) when shaken, it's resuspensed quickly which is favorable for being able to shake a drug and pour it into a bottle for a patient
flocculation allows you to avoid compact caking of the drug
flocculated means: the drug particles do ___ touch each other but they travel as one _____
this causes lots of gaps in between, meaning it will _____ completely settle (loose compaction)
not ; unit ; not
which of the following accurately characterizes colloidal dispersions?
a) particles diffuse very rapidly
b) particles diffuse very slowly
c) particles invisible in electron microscope
d) particles visible in ordinary microscope
e) particle size range in 0.5 - 10μm
b) particles diffuse very slowly
smaller particle size = faster diffusion
what type of flow is shown on the graph below?
a) Newtonian flow
b) non-Newtonian flow
c) non-Newtonian pseudoplastic flow
d) non-Newtonian dilatant flow
c) non-Newtonian pseudoplastic flow
what is the viscosity in part B vs in part A of the graph
in part B, viscosity in LOWER
why: as you apply force, the rate of flow increases (bc viscosity is less)
higher the slope = lower the viscosity
lower the slop = higher the viscosity
glycerin acts as a ______ _______ to help the insoluble antacid powder particles before they are dispersed in the liquid vehicle and to ensure the powder is evenly distributed with minimal clumping
wetting agent
correctly identify the mechanism by which polymers act as a flocculating agent
a) by reducing the electrical barrier between particles
b) by adsorption on the particle surface
c) by forming a protective layer around the particles
d) by increasing the electric barrier between the particles
b) by adsorption on the particle surface
______ are soluble, clear, and transparent liquids
______ are insoluble, cloudy/opaque, and heterogeneous mixtures with particles that will settle out over time if left undisturbed
solutions ; suspensions
liquid dispersions are heterogeneous systems—systems containing __________ matters or globules distributed throughout a medium
particulate
dispersions contain two phases:
∙ the ________ phase (internal phase): usually the suspended particles (a solid phase in a liquid vehicle)
∙ the ________ phase (dispersing phase/dispersion medium): usually the suspension liquid (a liquid phase in a another liquid)
dispersed ; continuous
____ _______ can be referred to as the dispersed phase, internal phase, or discontinuous phase.... just know they all mean the same thing
drug particles
______ is known as the aqueous phase, dispersing phase, dispersion medium, continuous phase, external phase, and the suspended phase ... just know they all mean the same thing
water
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
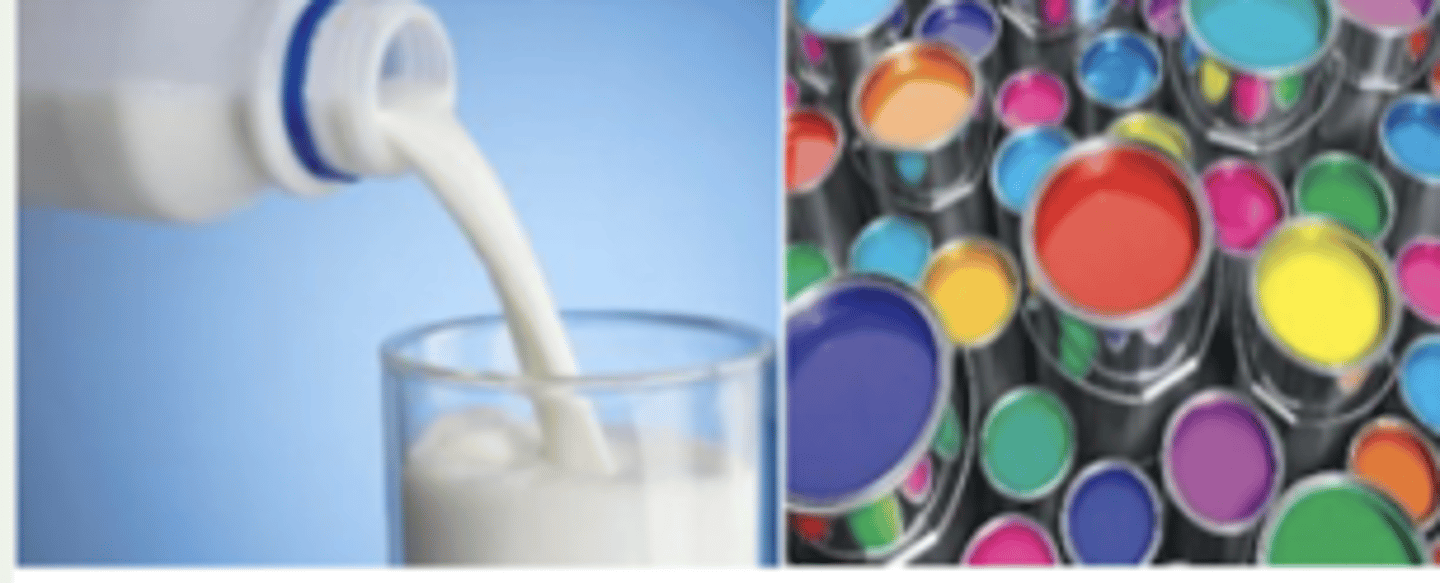
examples include: milk, fog, paint, colloidal polymer dispersions and other milky/non-transparent liquids
colloidal dispersion

match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particle size = < 1 nm
molecular dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
examples include: magmas, gels, and other jelly-like substances
fine dispersion

match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particles are invisible under an ordinary microscope but can be seen under an electron microscope and diffuse very slowly
colloidal dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
examples include: blood, suspensions, and emulsions
coarse dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particle size = 0.5 - 10 μm
fine dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
examples include: glucose solution and saline since both dissolve in water
molecular dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particle size = 10 - 50μm
coarse dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particles are visible under a microscope but do NOT diffuse
fine dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particles are invisible under an electron microscope and undergo rapid diffusion
molecular dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particle size = 1 - 500 nm
colloidal dispersion
match the term: molecular dispersion, colloidal dispersion, fine dispersion, coarse dispersion
particles are larger and visible under microscope, but do NOT diffuse
coarse dispersion
suspensions: a dispersion of finely divided solid materials suspended in a liquid medium in which the drug has ________ solubility in water
suspensions are made by reducing the drug particle size and dispersing the particles in water so it can become a liquid dosage form that is easier to ______
minimum ; swallow

____ suspensions have 2.5-10% (w/v) of solids (ex: antacids, antibiotics)
____ suspensions are used for radiologicals and for treating intestinal disorders
oral ; rectal
_________-used suspensions have 20% (w/v) of solids (ex: calamine lotion)
________ suspensions are used for delivery of drugs to the eye (ex: anti-inflammatory drugs, Nevanac)
________ are formulated as suspensions where solid particles are dispersed in a volatile propellant (ex: intranasal & pulmonary delivery of drugs to the lungs via inhalation, like albuterol)
externally ; topical ; aerosols
________ suspensions are generally used for intra-muscular injections and have 0.5 - 30% (w/v) solids (ex: antibiotics, steroids)
these types of suspensions are ______ to intramuscular (IM) injections, and are based on PARTICLE SIZE LIMITS
parenteral ; limited
suspensions are a good dosage form for _______ drugs and have reasonably smaller _______ than solutions (bc the goal is not to dissolve the med)
insoluble ; volume
suspensions have greater stability against chemical degradation (ex:_______ and ______) compared to aqueous solutions bc solid particles in a liquid limit the amount of drug in the dissolved state which is where most chemical rxns occur
hydrolysis ; oxidation
suspensions are better at _______ disagreeable tastes of drugs than solutions and are easier to ______ compared to solid dosage forms
suspensions are a good _______ dosage form for water insoluble drugs
masking ; swallow ; topical
for a sustained effect, suspensions can be used for ______ _______, where the drug dissolves slowly, leading to slower absorption and release over a long time
depot therapy
depot therapy def: a formulation of a drug designed to release slowly into the body over an extended period of time
(T or F?) parenteral suspensions can be administered intravenously (IV) and intramuscularly (IM), depending on the medication and its drug particle size
false
why: only parenteral suspensions can be administered INTRAMUSCULARLY
a disadvantage of suspensions is that the drug is not water soluble, so it's unable to dissolve in the oral cavity (in _____), which is why flavoring ISN'T required
however in some circumstances where the drug is extremely bitter and minimally water soluble, flavoring may be added to enhance patient _______
saliva ; compliance
suspensions have difficulty maintaining ______ and accuracy of doses due to the ________ of powders in the liquid medium
uniformity ; settling
suspensions can undergo ________ which can result in the compaction of particles that form a ____ which is hard to redisperse and affects the dosage of the drug when administered
sedimentation ; cake
name the three KEY DISADVANTAGES of suspensions:
(hint: DSC)
∙ inadequate dispersion
∙ settling of dispersed particles
∙ _______ of drug particles in the sediment (that resist re-dispersion)
suspensions should settle ______ but re-disperse quickly upon only mild shaking and should avoid forming a hard ____
suspensions must remain sufficiently _____ for at least the period between shaking the container and removing the required doses (why you have to shake the bottle after adding half the amount of water when reconning, before you add the other half of water)
slowly ; cake ; uniform
an ideal suspension would have sufficient physical, chemical, and _______ stability, along with a pleasant _____
microbiologic ; taste
suspensions should be easy to ____, easy to ______ on skin, or easy to ____
trying to push particles through a syringe needle can create lots of ____ ______, potentially hurting the patient or causing the needle to ____ ____ and wasting some of the drug
pour ; spread ; flow
back pressure ; burst open
in a flocculated suspension, particles settle _______ in a short period of time
the settled particles are described as having a large ______ of sedimentation
quickly ; height
in flocculated suspensions: once the height of the sediment settles "enough", it will remain the ____
same
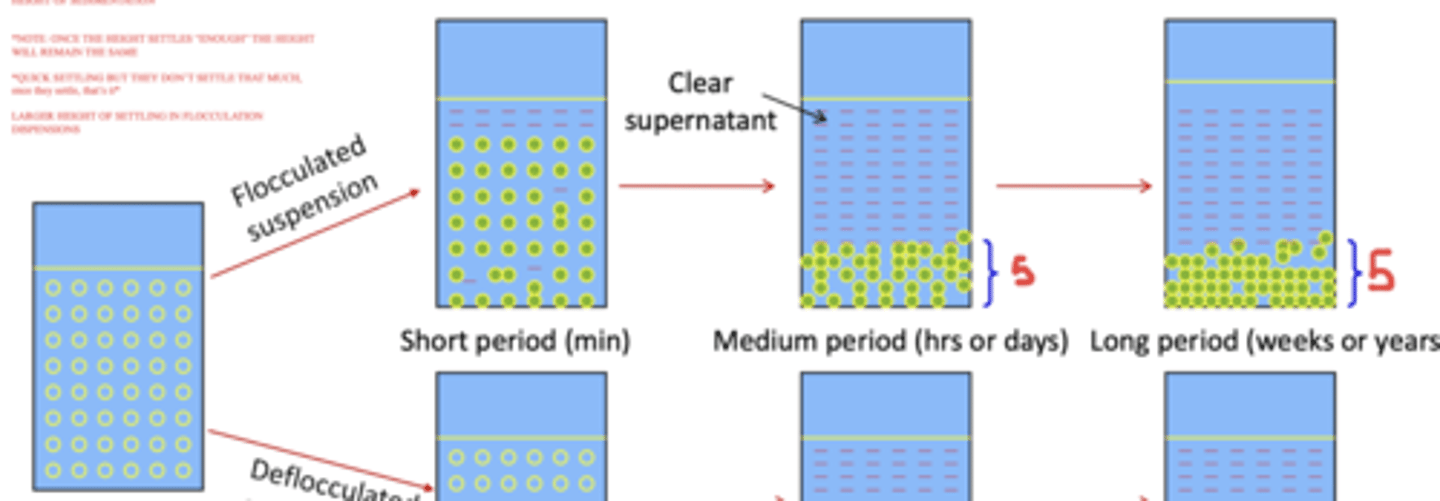
(T or F?) in a deflocculated suspension, particles settle rapidly and form a cake within a short period of time
false
in a deflocculated suspension, particles ____ initially settle, however over a period of hours/days the particles will have settled at the bottom of the bottle
after weeks/years, the particles in a deflocculated suspension settle even more, resulting in a very _____ height of sedimentation
don't ; small
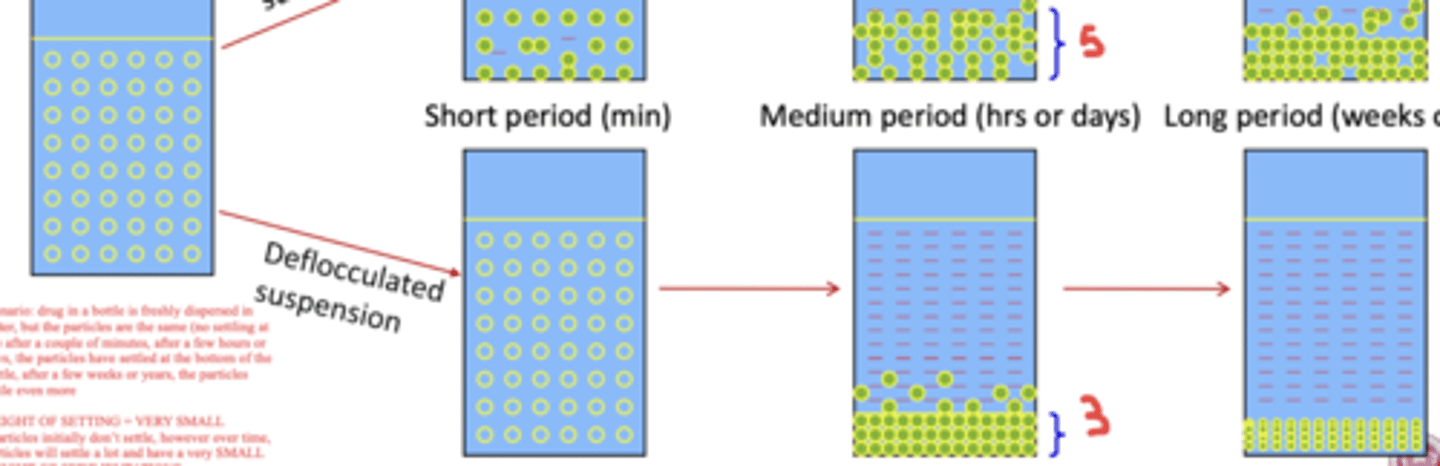
________ suspensions are more favorable than ________ suspensions
flocculated ; deflocculated
flocculated suspensions are characterized by particles that are in the form of _____ or aggregated which are _____ bonded to one another, leading to rapid sedimentation
because the aggregates are easily re-suspendable, they resist complete ______ and are less prone to _______
flocks ; weakly
settling ; compaction
deflocculated suspensions have particles in a individual/separate state that settle slowly into a _____-______ arrangement
this type of arrangement can lead to the formation of a hard _____ which is difficult to ______
closely-packed
cake ; redisperse
slow sedimentation and a slower rate of dispersion describes a ________ suspension
quick sedimentation and quick rate of dispersion describes a ________ suspension
deflocculated ; flocculated
________ (η) is the ratio of force applied (shearing stress, _) to the rate of flow (rate of shear, _) of a liquid
*write the letter that represents*
simple def: a property of a liquid that describes its resistance to flow
viscosity ; F ; G
the rate of viscosity and force/flow rate equation describes the force applied to the rate at which the liquid flow
ex: in order to get a liquid with high viscosity (honey) to flow at the same rate as a liquid with lower viscosity (water), you need to apply more force
write the equation:
η = F/G
F = the shearing stress
G = rate of shear
the η = F/G equation identifies that G (rate of shear) is _________ proportional to viscosity
inversely
since G (rate of shear) is inversely proportional to η (viscosity),
a HIGH rate of flow indicates a liquid with ____ viscosity
a LOW rate of flow indicates a liquid with ____ viscosity
low ; high
*think: the thicker the liquid is, the harder/slower it is to flow*
if you were to solve for G (rate of shear) of a liquid, what would be the equation?
G = (1/η) F
the equation shows that G (rate of shear) is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to F (shearing stress) and is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to η (viscosity) of a liquid
if (1/η) is the slope:
a HIGH slope means the liquid flows very easily (high G, rate of shear) and indicates a _____ viscosity (η)
a LOW slope means the liquid flows with greater resistance (low G, rate of shear) and indicates a _____ viscosity (η)
low ; high
(T or F?) viscosity influences the physical stability of suspensions
true
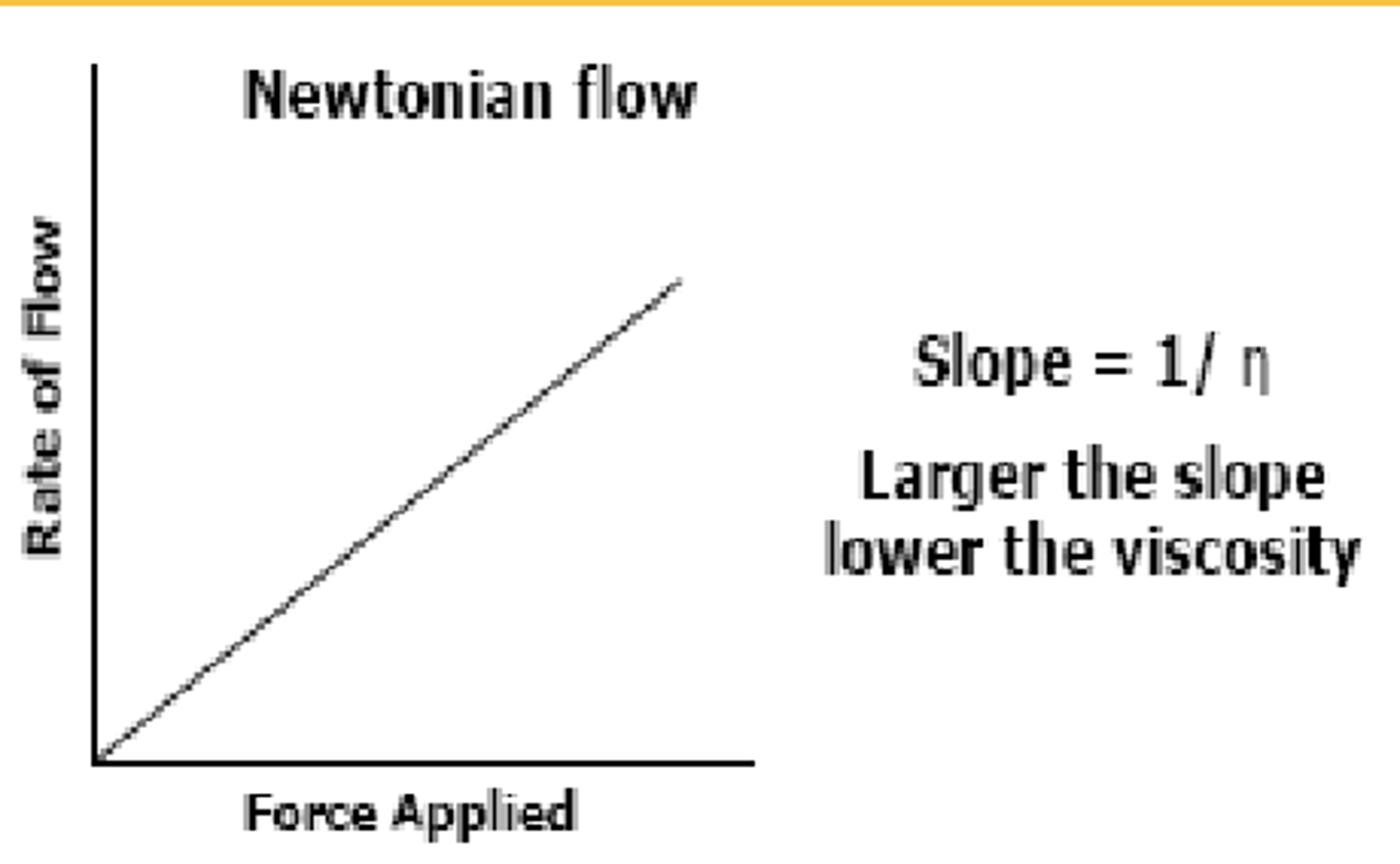
_________ Flow is a simple/direct relationship
the liquid starts flowing the moment force is applied (even if it's extremely small), and as you increase the force, the flow rate increases proportionally
this indicates that the viscosity of the fluid is ______ and does not change with the force applied (ex = water)
a larger slope (curve) on the graph indicated (lower or higher?) viscosity
Newtonian ; constant ; lower
in ___-________ __________ Flow, flow will not occur until a certain ________ force is applied
the minimum force required to initiate flow is called the "______ value"
Non-Newtonian Plastic
minimum
yield value
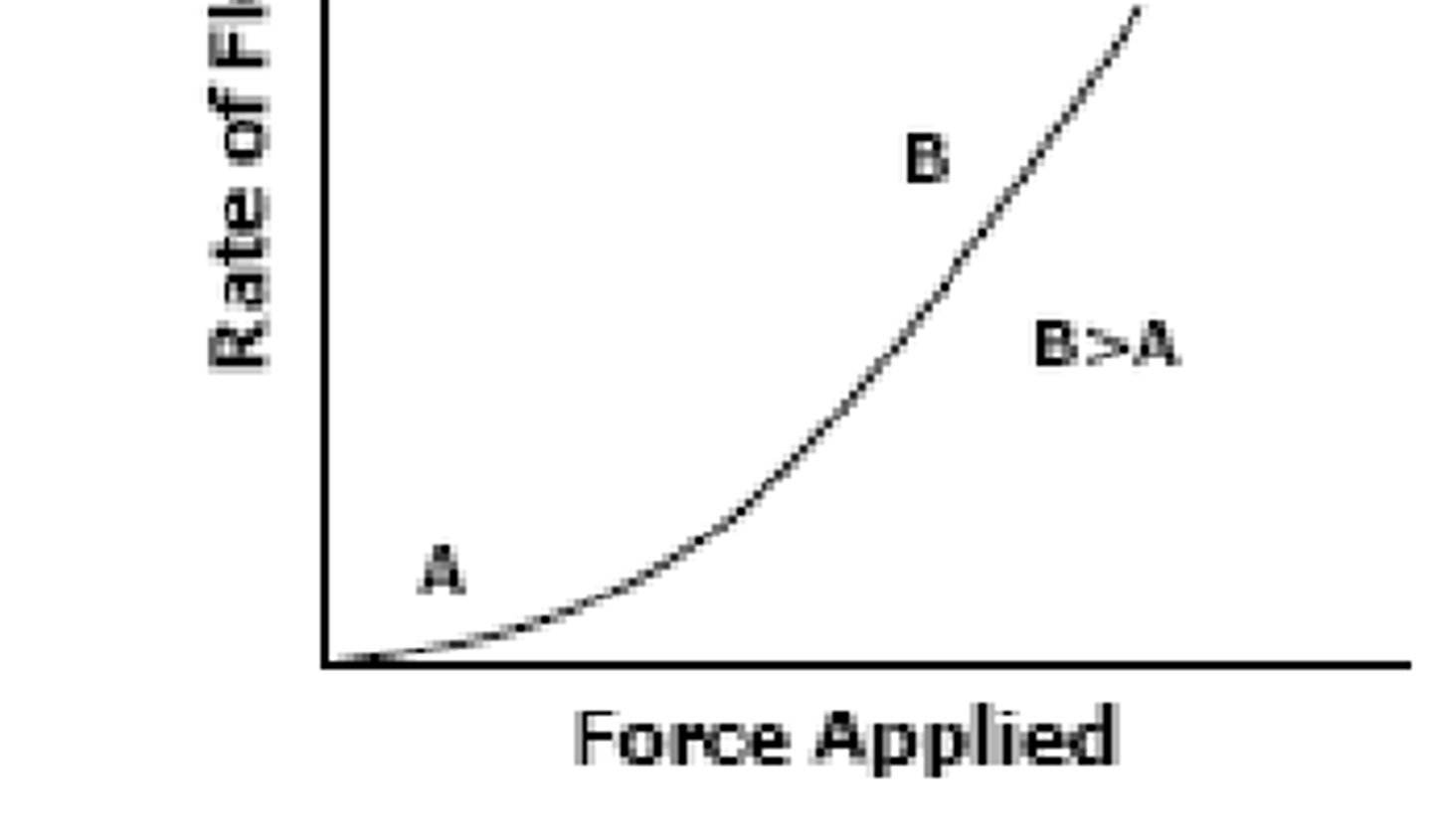
in Non-Newtonian Plastic Flow (B>A):
when the minimum force required to initiate flow is _______, flow will begin (initially: small slope, higher viscosity, represented by A)
as more force is applied, the flow rate will ______ and the slope of the graph becomes ________ (indicates that as the viscosity decreases, liquid will flow more easily, represented by B)
exceeded ; increase ; larger
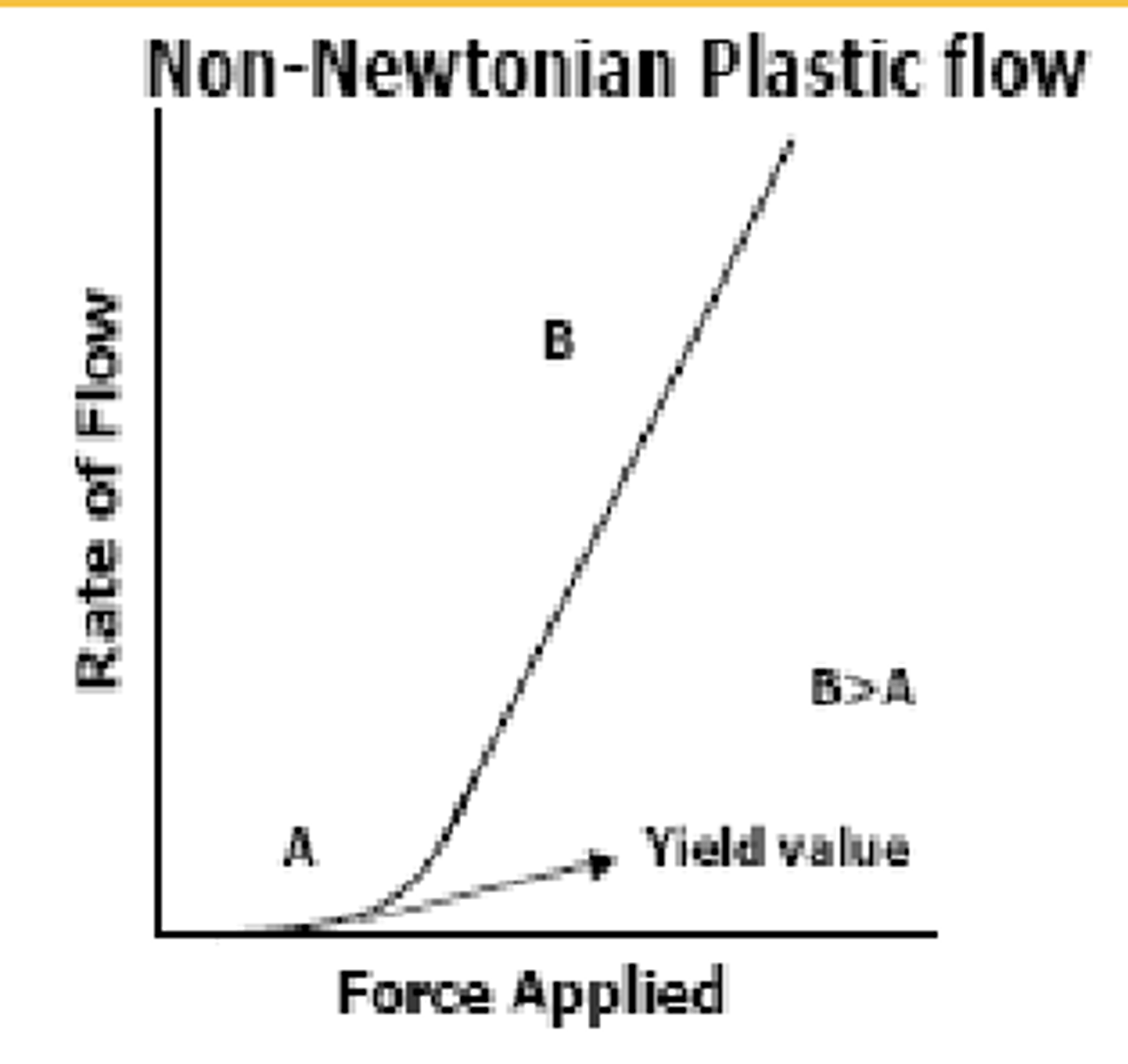
an example of Non-Newtonian Plastic Flow are ________ since they won't come out of the tube/container when you tip it upside down, but will easily spread on skin when minimum force is applied
once the force is removed, it will remain on the skin
ointments
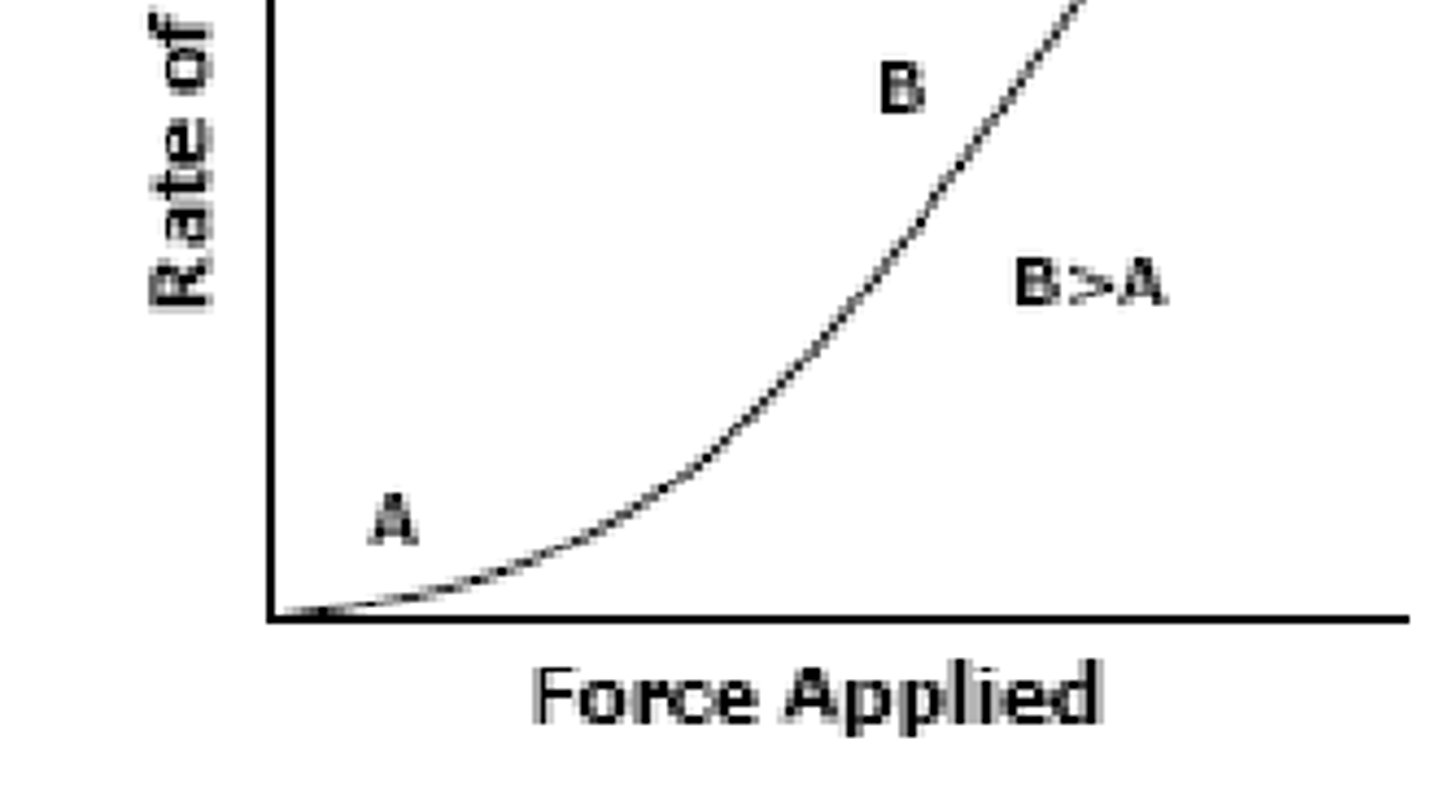
___-_________ ____________ Flow is characterized by liquid that starts flowing immediately when a force is applied (no minimum force requirement), and decreases in viscosity as you increase the force (flows more easily) (B>A)
ex: creams & (flocculated or deflocculated?) suspensions
Non-Newtonian Pseudoplastic ; flocculated
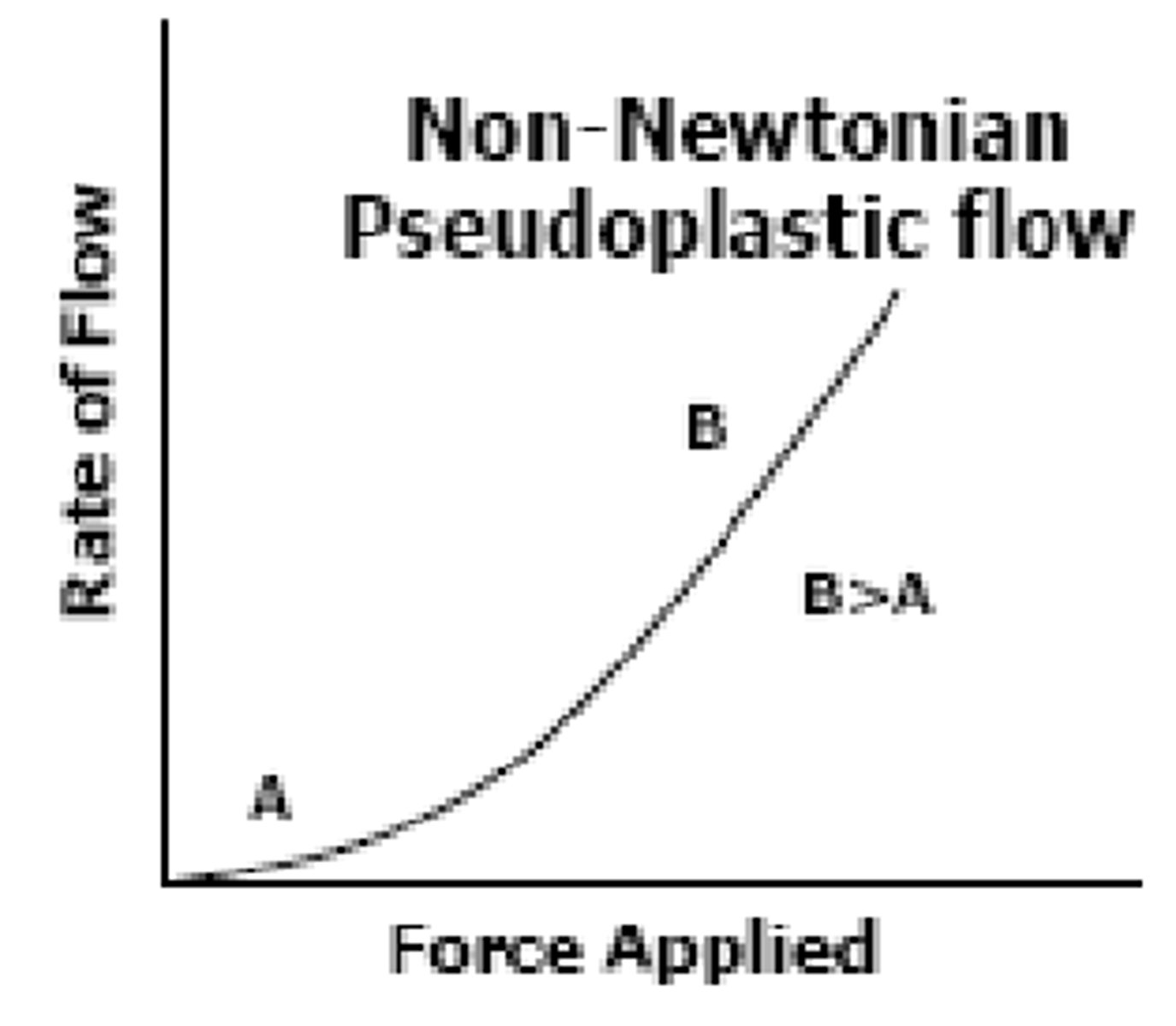
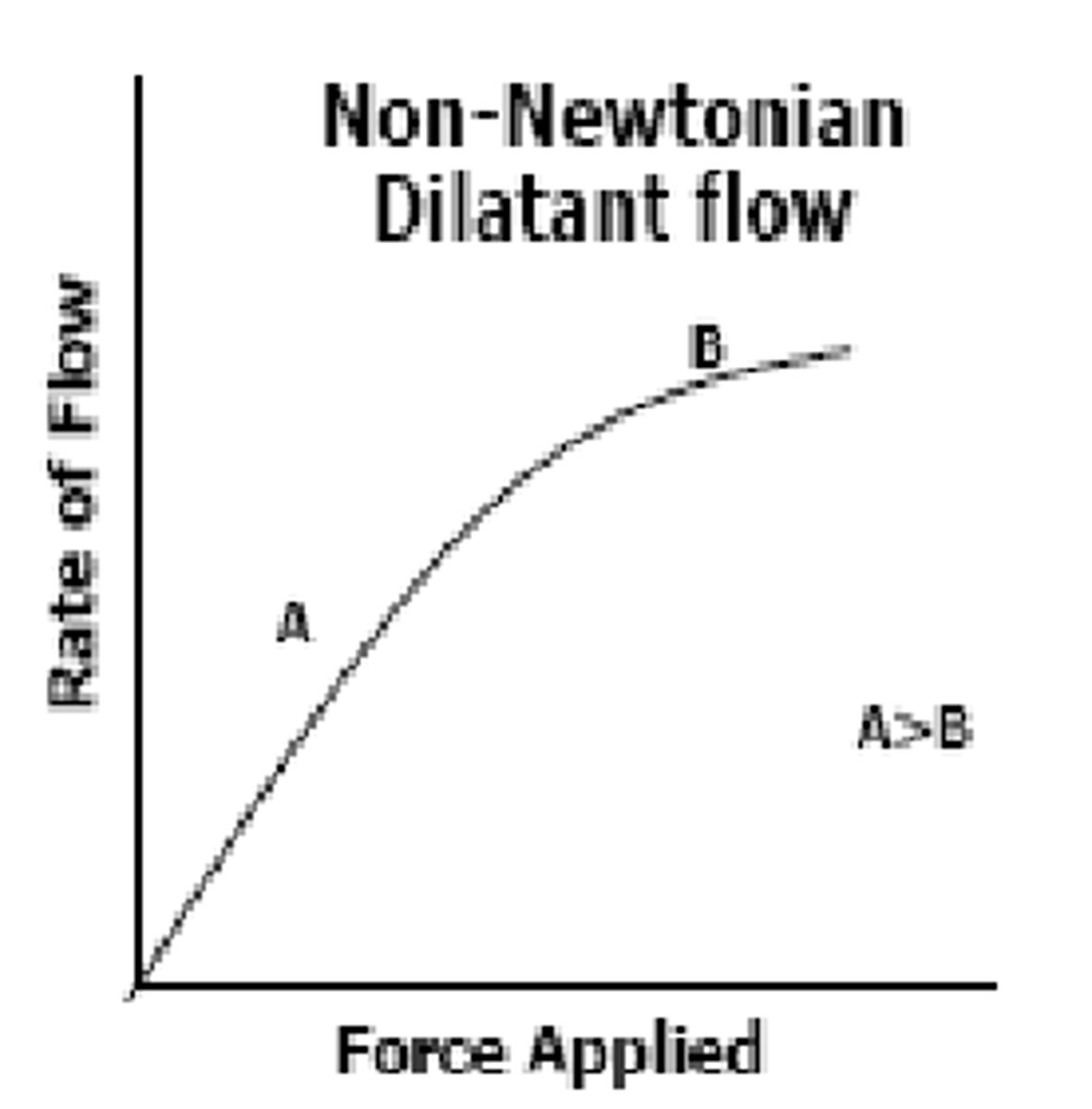
___-_________ _________ Flow is characterized by liquid that initially flows well with small force, but as you increase the force, viscosity increases (liquid becomes thicker) and is more resistant to flow (A>B)
because of this, you can't ______ these liquids too much or they will resist flow (ex: deflocculated suspensions)
Non-Newtonian Dilatant ; shake
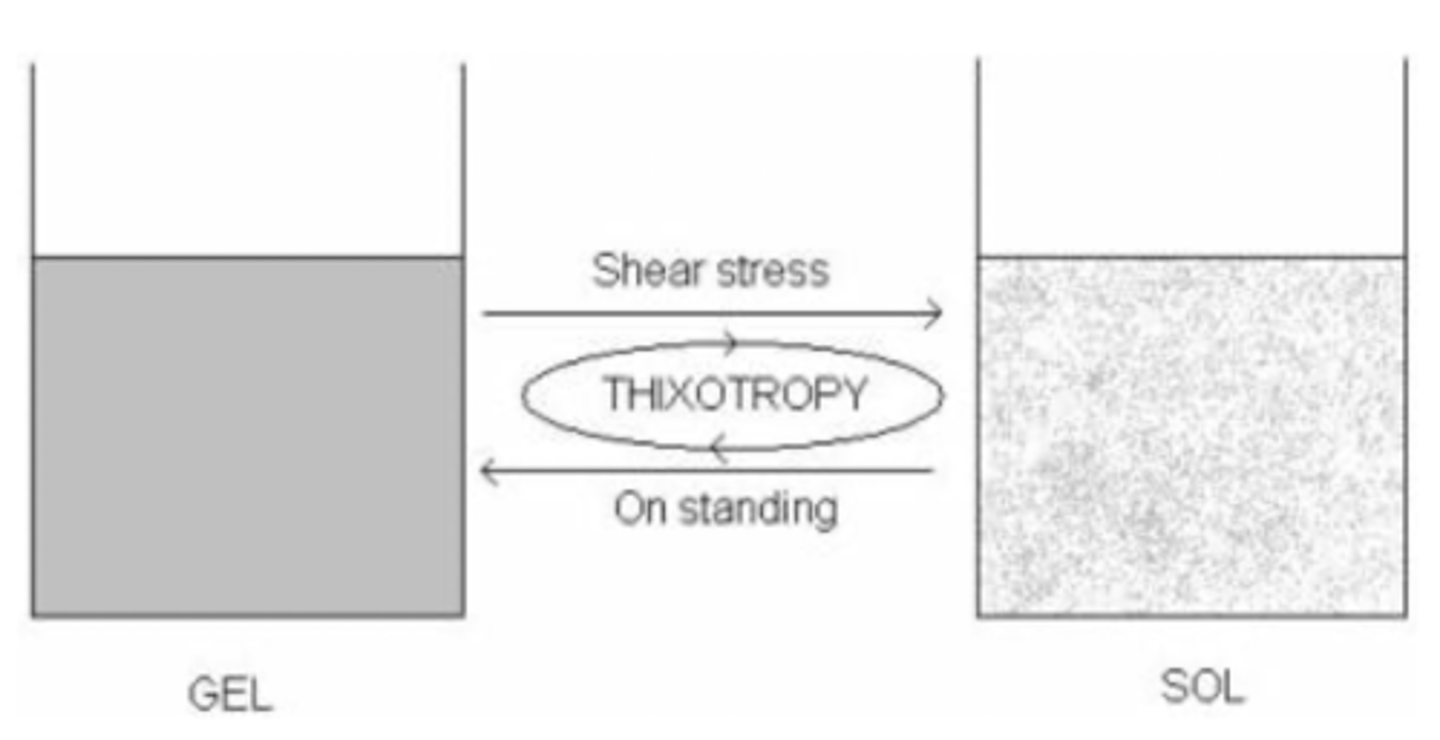
________ is a desirable property in suspensions and is characterized by a substance that starts off as a ___ but turns into a ______ when force is applied
when the force is removed, it will convert back to its ______ state and the process will repeat whenever force is applied
thixotropy ; gel ; solution
original
when no force is applied, a thixotropic substance is a _______ and has NO FLOW
when a force is applied, a thixotropic substance becomes a ______ and STARTS FLOWING
ex: ketchup will not flow until you apply force by shaking it
gel ; liquid
thixotropy is a desirable property in suspensions bc it helps keep the particles ______ ________, ensuring that a uniform dose of medicine is delivered every time it's used
when shaking turns a gel into a liquid solution, the particles will be uniformly dispersed and will get trapped if the liquid reverts back to gel
evenly distributed
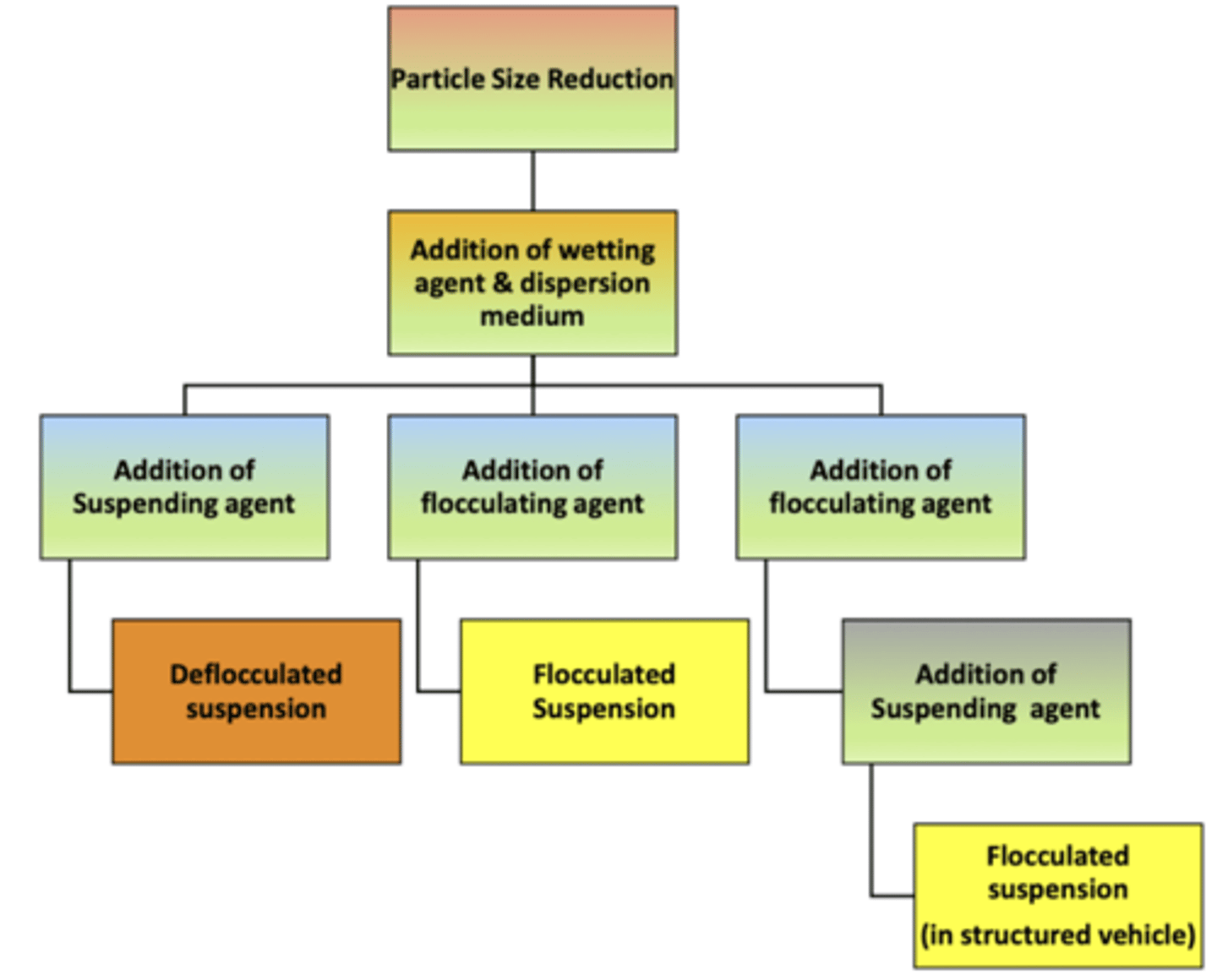
name the 3 methods of suspension preparation: (hint: DCF)
∙ __________ suspension: using a suspending agent to prepare this type of suspension
∙ __________ flocculation: using flocculating agents
∙ __________ suspension: occurs in a structured vehicle
deflocculated ; controlled ; flocculated
when making a stable suspension, the two initial steps (for all 3 methods of preparation) are:
1) _______ _____ reduction: using a mortal + pestle to grind solid particles will help them stay mixed in a liquid longer
2) adding a _______ ______: since solid particles often don’t mix well with water, a substance is added to help the particles get wet and disperse evenly in the liquid
particle size ; wetting agent
when preparing a (controlled) flocculated suspension:
a __________ ______ will be added to the mixture to help the particles loosely stick together to aid in the formation of flocks which settle quickly but are easy to re-disperse when shaken
flocculating agent
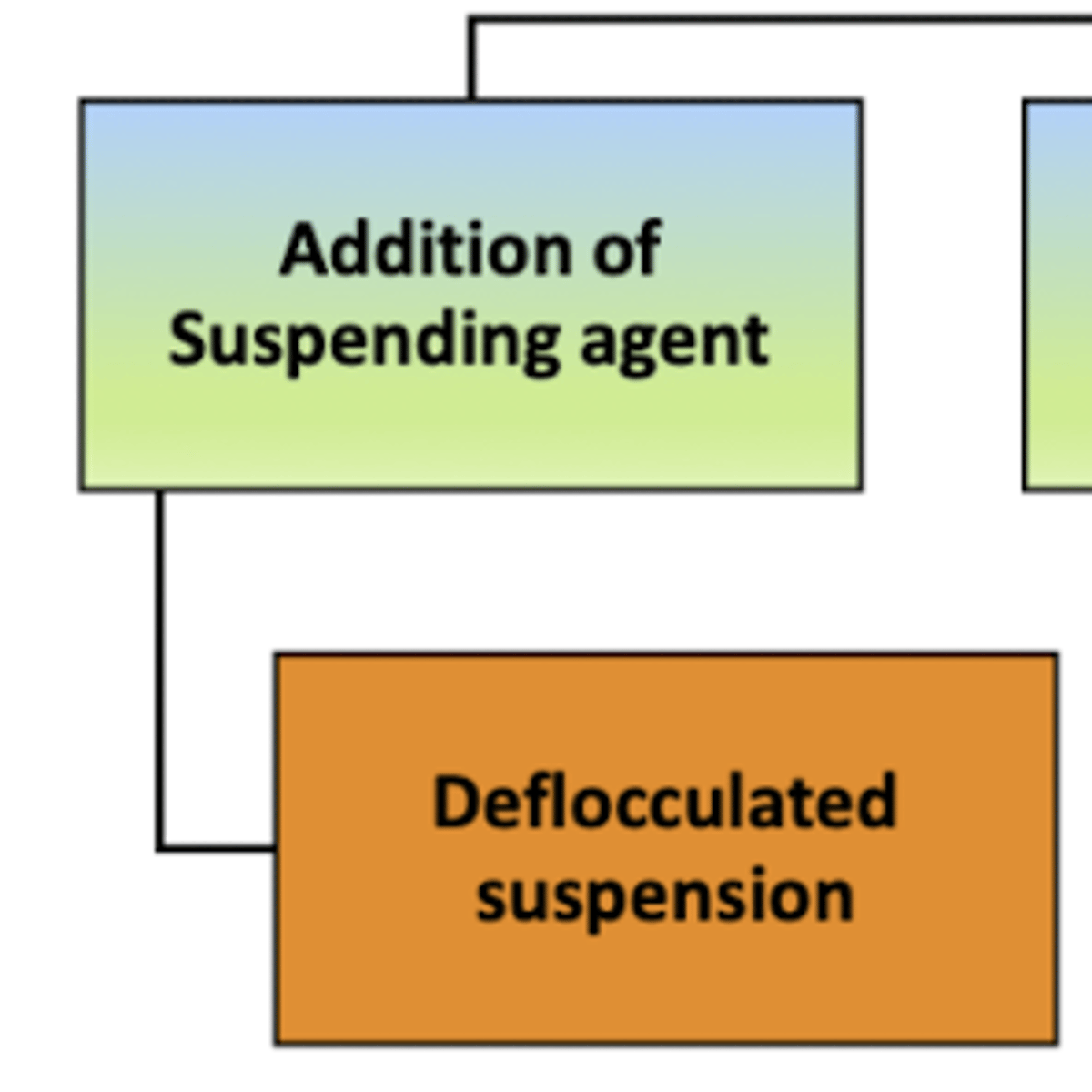
when preparing a deflocculated suspension:
a __________ ______ will be added to the mixture to help each individual particle stay separate and suspended in the liquid for a long time
suspending agent
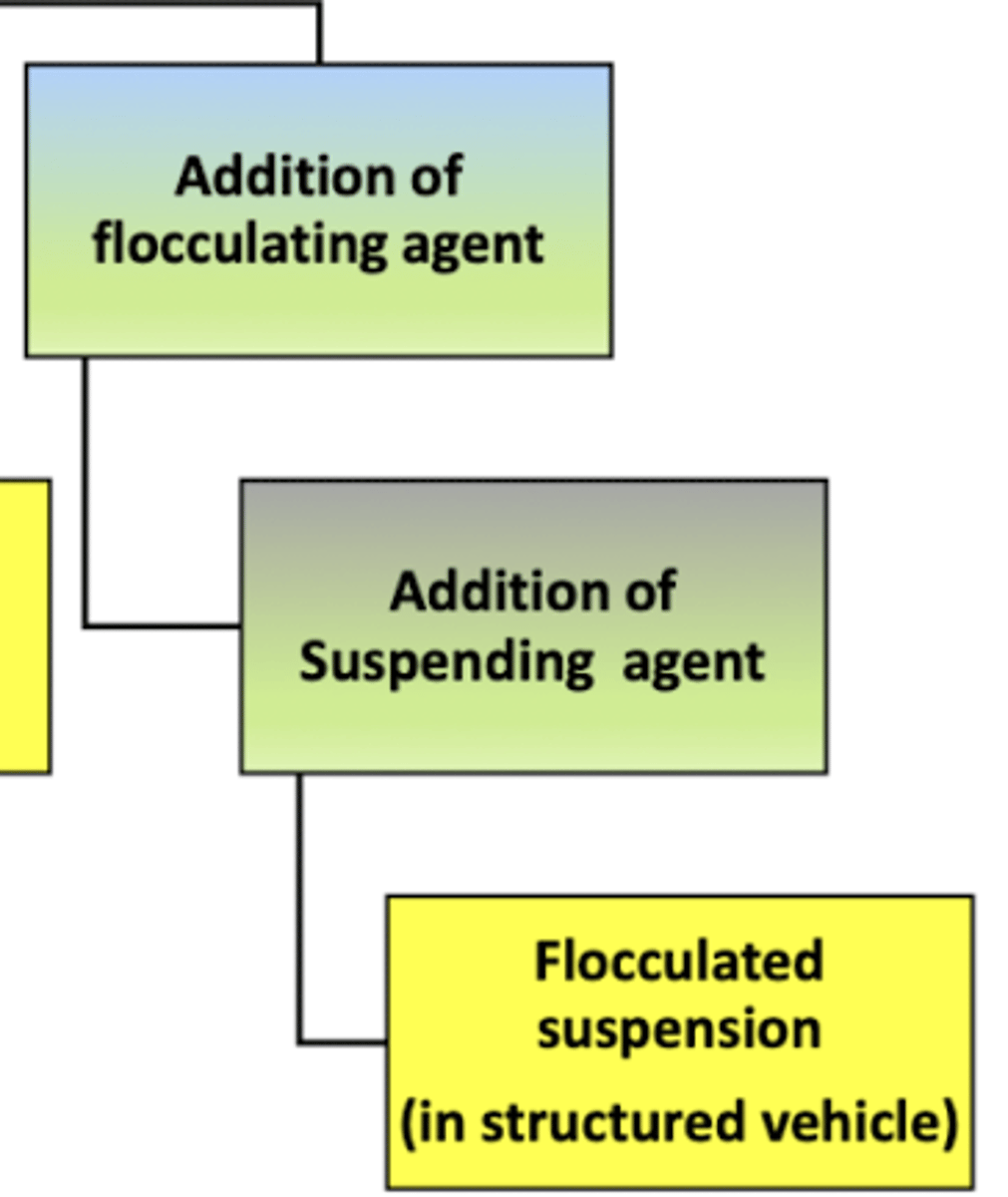
when preparing a flocculated suspension in a structured vehicle:
a __________ ______ and a __________ ______ will be added to the mixture to help increase the liquid's viscosity (thicker) and allow the particles to form flocks
the flocks will help slow down the settling of particles and the more viscous liquid will add thickness/structure to the mixture
suspending agent ; flocculating agent
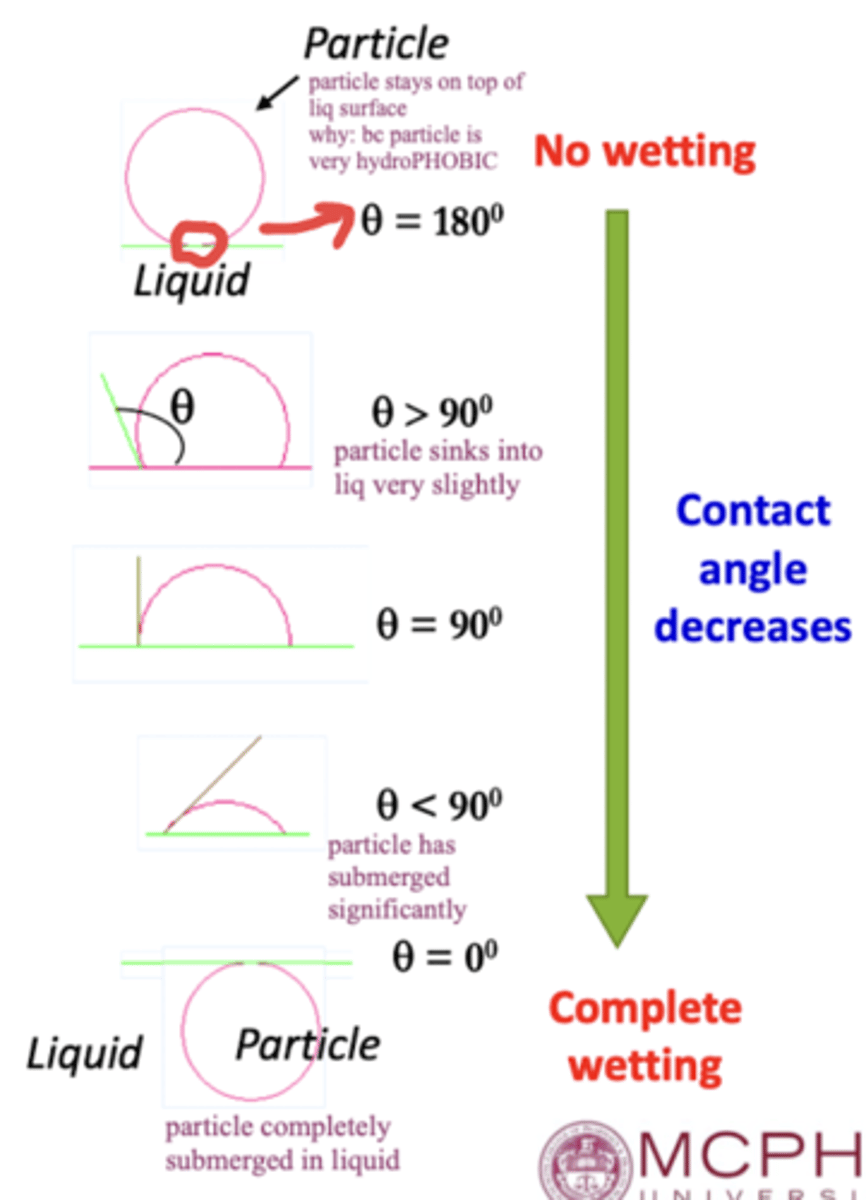
the ______ ____ (𝜃) is the key measurement in the concept of wetting, and is the angle between a liquid and the surface over which it spreads
it ranges from ___ to ___ degrees
contact angle ; 0 ; 180
a LOW contact angle (< 90°) indicates ____ wetting
a HIGH contact angle (> 90°) indicates ____ wetting
high ; low
wetting is most important for the ______ dispersion during the preparation of an insoluble powder in a vehicle
**wetting particles allow the particles to flow nicely**
initial
common wetting agents include: _______, _______, or ________
all three of these wetting agents act as a bridge between the ________ particles and the liquid, lowering the contact angle and allowing the liquid to spread over the particles to help them disperse evenly
alcohol ; glycerin ; surfactants
hydrophobic
a contact angle of 0° represents ______ wetting (particle is completely submerged in liquid)
a contact angle of 180° represents ______ wetting (particle stays on top of the liquid surface bc it's hydrophobic)
complete ; no
(T or F?) wetting agents function to increase the contact angle, and thereby prevent liquid from spreading over the surface of a particle
false
why: wetting agents act as a BRIDGE between the particle and the liquid to bring both phases together and DECREASE the contact angle
suspending agents function to ______ the rate of sedimentation and enhance the _______ of the suspension
the concentration of suspending agents is usually 0.5 - 5% w/v
reduce ; appearance
the best suspending agents for uniform dispersion of particles have two special properties (hint: think of the graphs):
___-________ _________ Flow: get thinner with force (shaking), then get thicker when force is removed ultimately preventing settling
_________: gel at rest, liquid when shaken, repetitive conversion
Non-Newtonian Pseudoplastic Flow ; thixotropy
common types of suspending agents:
∙ ________ hydrophilic polymers
∙ ________ hydrophilic polymers
∙ inorganic _____
natural ; synthetic ; clays
bentonite and veegum are examples of (what type of suspending agent?) and are often used to prepare milk of magnesia or aluminum hydroxide type suspensions
inorganic clays
tragacanth, xanthum gum, and acacia are all examples of (what type of suspending agent?) and may have microbial contamination
natural hydrophilic suspending polymers
methyl celluose and carboxy methyl cellulose are examples of (what type of suspending agent?) and have controlled purity (maybe microbial contamination)
synthetic hydrophilic polymers
controlled flocculation prevents the formation of a compact _______ (cake) that is difficult to redisperse
it works by adding _______ agents to the mixture to reduce (not remove) and control particle surface _____ to an optimum level
sediment ; flocculating
name 3 common flocculating agents that are used depending on the physicochemical properties of the suspension:
electrolytes, surfactants, polymers
if all the particles in a suspension have positive charges, they will _____ each other
flocculation works to _____ this by bringing the charges closer together by reducing (not removing) the charges on the particle surface so they can get close to each other, but will not touch
repel ; prevent
many drug particles in liquid have the same electrical charge which causes them to naturally _____ each other
electrolytes are _____ compounds (like salts) that act by REDUCING the electrical barrier between the particles so they can come closer together and ideally form a flock
repel ; ionic
the effectiveness of an electrolyte depends on 3 things:
∙ the ______ charge of the drug particles (since different particles have varying charges (ex: +1 or -4,) so you need to choose either a strong or weak electrolyte to reduce the electrical barrier)
∙ the ______ of the electrolyte ("how strong its charge is")
∙ electrolyte _______ (may be dilute, it depends on the charge of the particle)
surface ; valency ; concentration
example of valency of electrolyte:
Ca2+ is a _______ electrolyte and therefor has _______ reducing capacity
strong ; strong
*Ca2+ would be a good choice if you want a significant reduction of a surface charge on a particle (ex: -2 or -4)*
polymers are high molecular ______ compounds that are particularly useful for drugs that do not carry a charge
weight
polymers work as flocculating agents by absorbing/attaching to the surface of particles and then forming _____ with other particles using the parts of the polymer chain that ______ outwards to form flocks
bridges ; projects
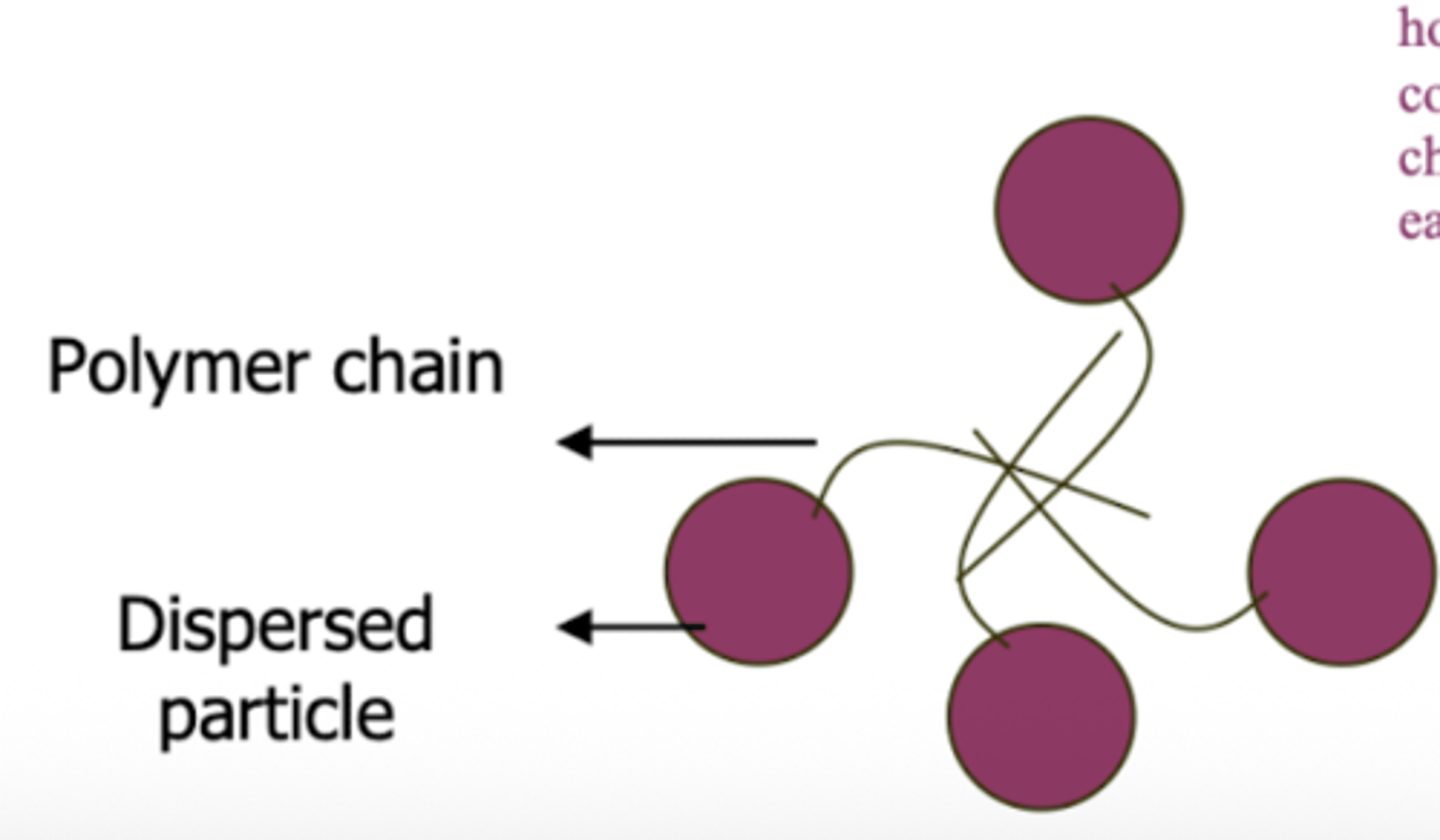
polymers can ____ the charge of a particle if the particle is charged
mask
xanthum gum and polyacrylamide are examples of _______ (flocculating agents)
polymers
sodium phosphate and postassium chloride are examples of _______ (flocculating agents)
electrolytes
docusate sodium is an example of an ______ ________ (flocculating agent)
tweens or spans are examples of ______ ________ (flocculating agents)
ionic surfactant ; non-ionic surfactant
example scenario: a drug disposed in water has no charges and requires a flocculating agent
which type of flocculating agent would you use and why?
polymer
why: if there's no charge, you don’t need to use an electrolyte or surfactant
*polymers are the best choice bc they absorb onto the particle surface and the other free end of the chain reacts with other particles to allow flocculation to occur*
surfactants are both ____ and ______ molecules that can be used to make particles clump together (flocculate) in a liquid to create a stable suspension
name the two types of surfactants:
______ surfactants & ___-_____ surfactants
polar ; nonpolar
ionic ; non-ionic
ionic surfactants act as flocculating agents by _______ the charges on the particle surface
non-ionic surfactants act as flocculating agents by forming a _________ _____ around the particles
reducing ; protective layer
(T or F?) ionic surfactants reduce charges on a particle's surface by getting in between the charged particles and neutralizing them so they can get close enough to each other to form a flock
true
non-ionic surfactants do NOT have a _____ but instead have long nonpolar _____ that can wrap around multiple particles at once to form a protective layer or bridge, allowing flocculation to occur
charge ; chains