Sports injuries - Shoulder
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam preparation for A2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
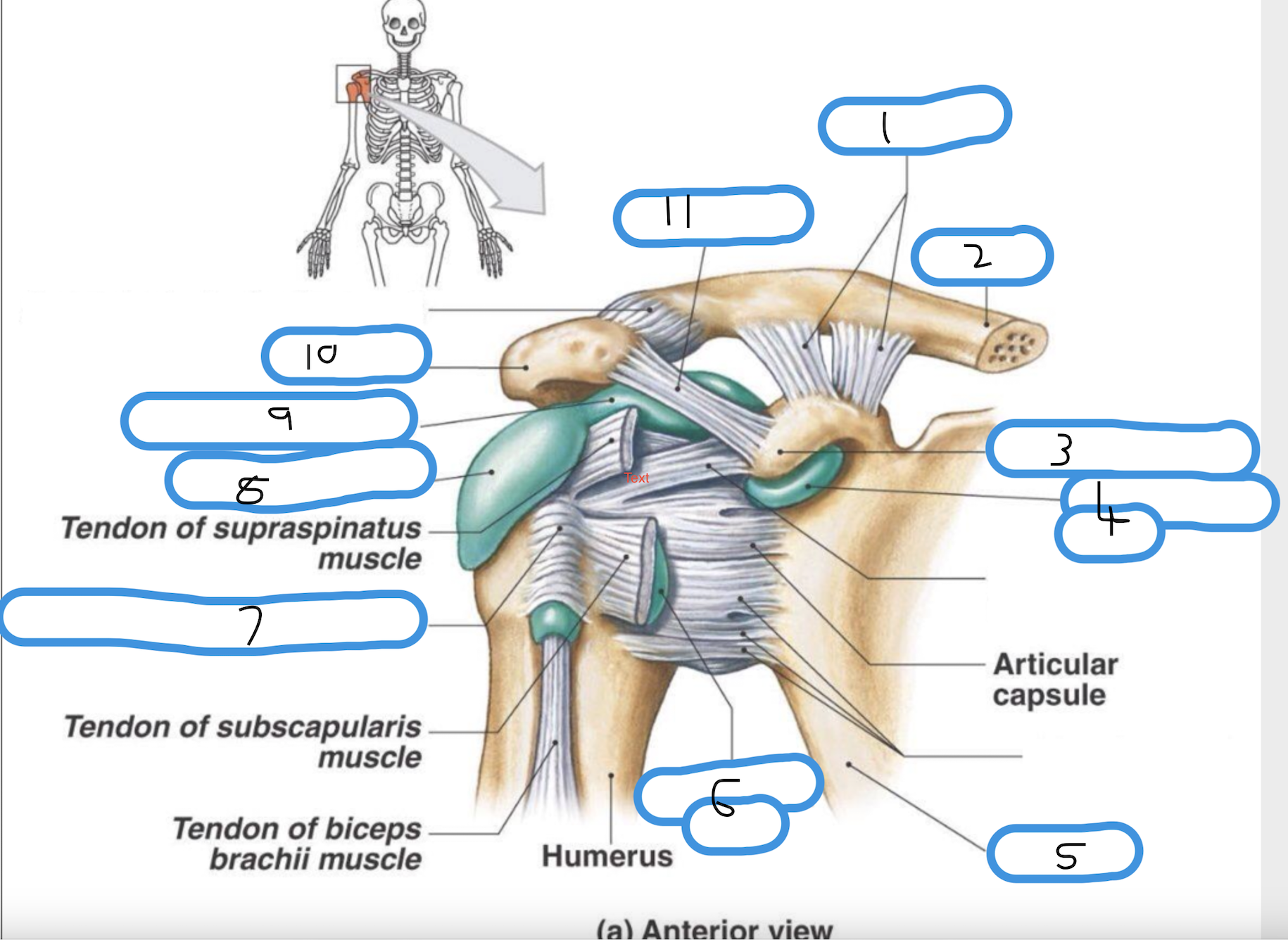
Label diagram from 1-12
coracoclavicular ligament (trapezoid and conoid)
clavicle
coracoid process
sub coracoid bursa
scapula
subscapular bursa
transverse humeral ligament
sub deltoid bursa
sub acromial bursa
acromian process
coracoacromial ligament
deltoid ligament (superior, middle, inferior)
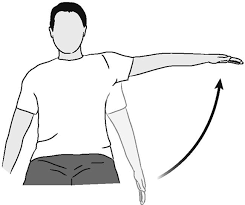
muscles involved in shoulder abduction
deltoid middle
supraspinatus
biceps brachii (long head)
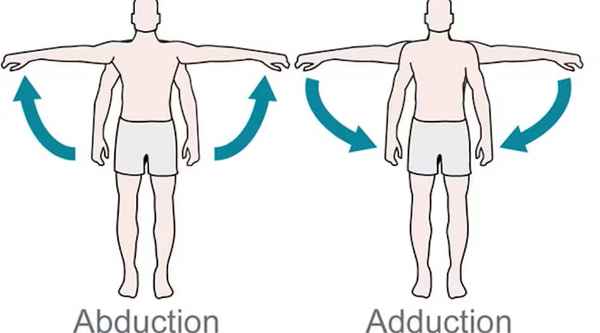
muscles involved in shoulder adduction
pectoralis major (sternal)
teres major
latissimus dorsi
coracobrachialis
triceps brachii (long head)
biceps brachii (Short head)
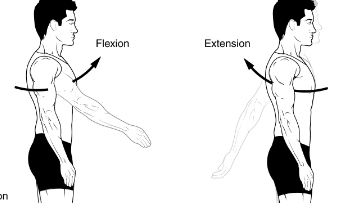
muscles involved in shoulder flexion
deltoid anterior
pectoralis major (clavicular)
coracobrachialis
biceps brachii (short head)
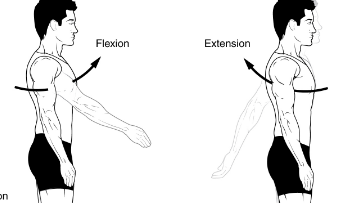
muscles involved in shoulder extension
deltoid posterior
pectoralis major (sternal)
teres major
latissimus dorsi
triceps brachii (long head)
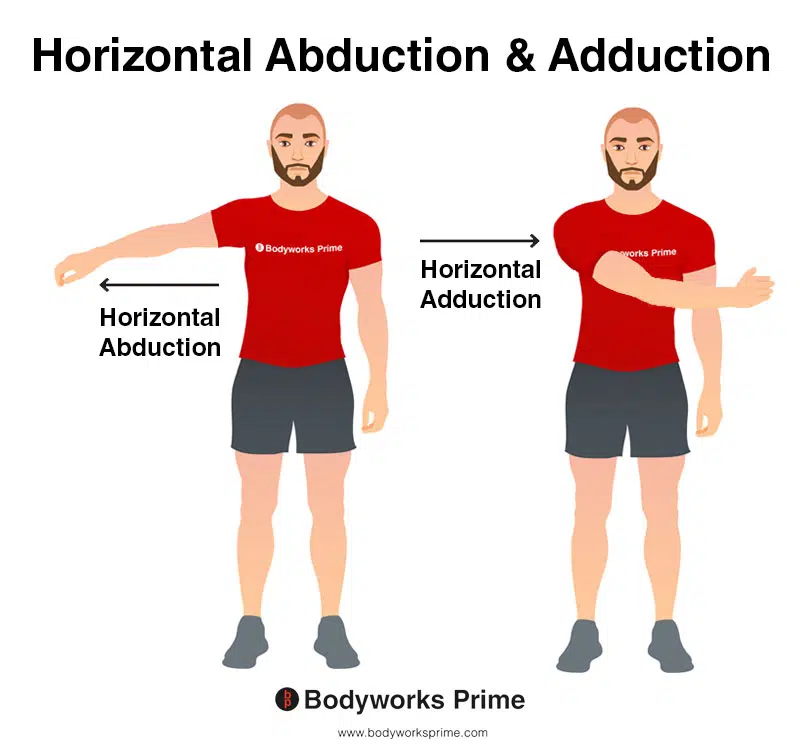
muscles involved in shoulder horizontal abduction
deltoid posterior and middle
latissimus dorsi
teres minor
infraspinatus
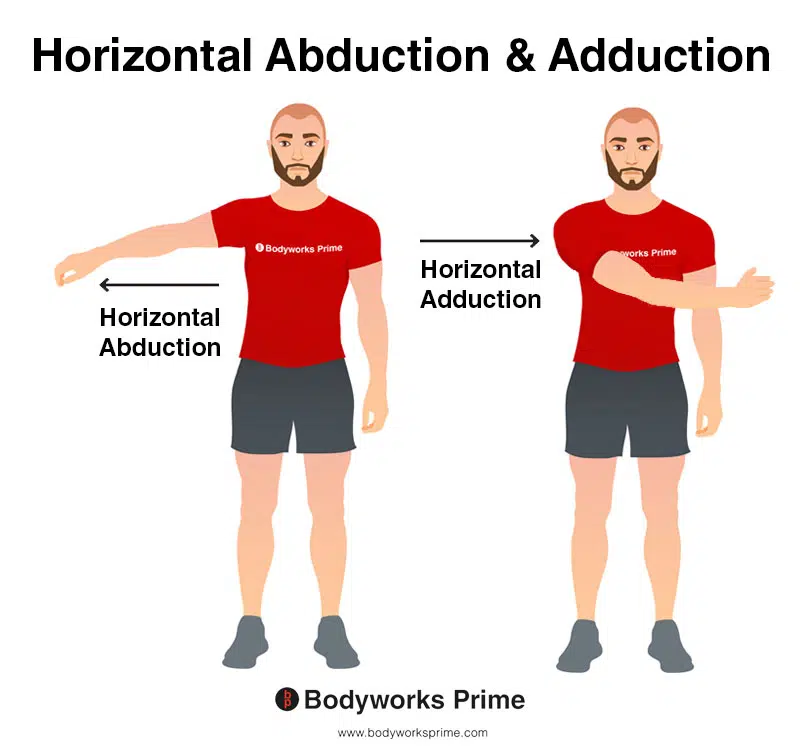
muscles involved in shoulder horizontal adduction
deltoid anterior
pectoralis (sternal and clavicular)
coracobrachialis
biceps brachii (short head)
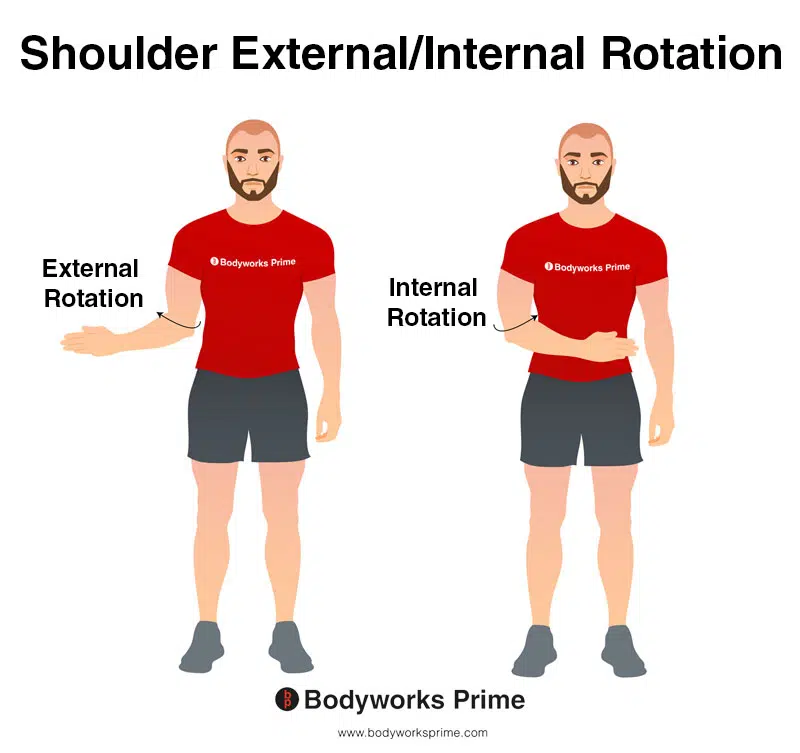
muscles involved in shoulder external rotation
deltoid posterior
infraspinatus
teres minor
supraspinatus
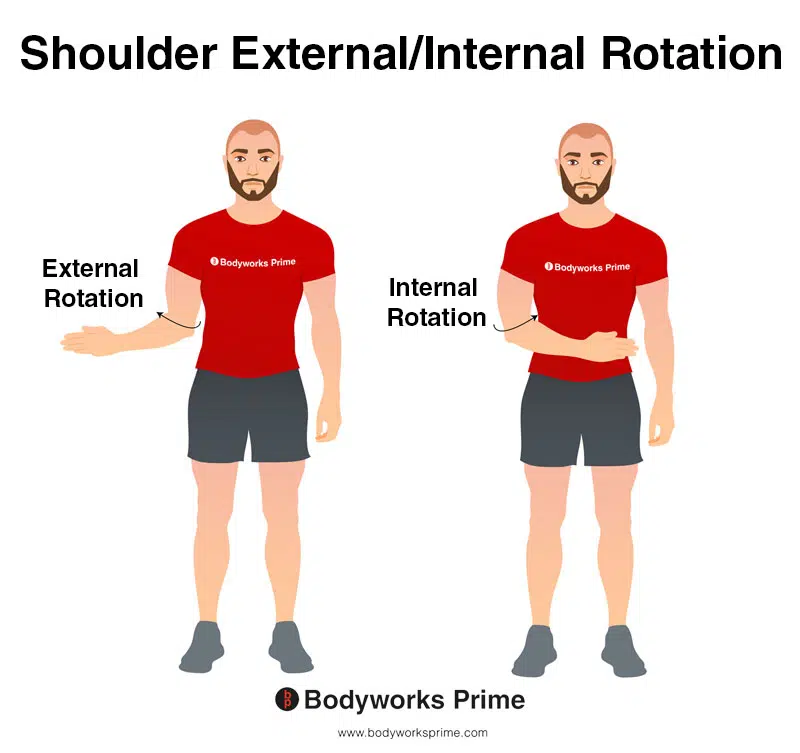
muscles involved in internal rotation
deltoid anterior
pectoralis major (sternal and clavicular )
teres major
latissimus dorsi
subscapularis
biceps brachii (short head)
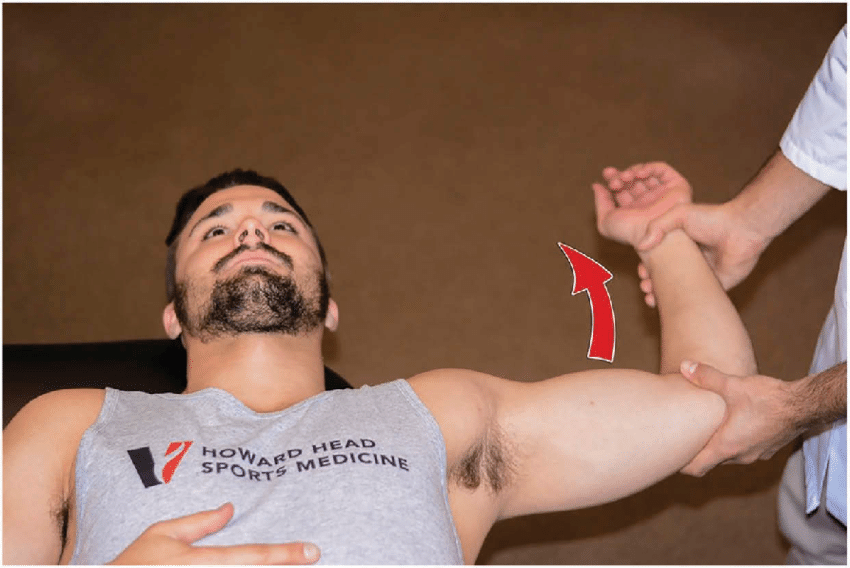
Apprehension test (purpose, how and positive sign)
purpose - anterior humeral instability
how - arm abducted at 90 degrees and slowly externally rotated
positive sign - apprehension/ facial grimace before full ROM
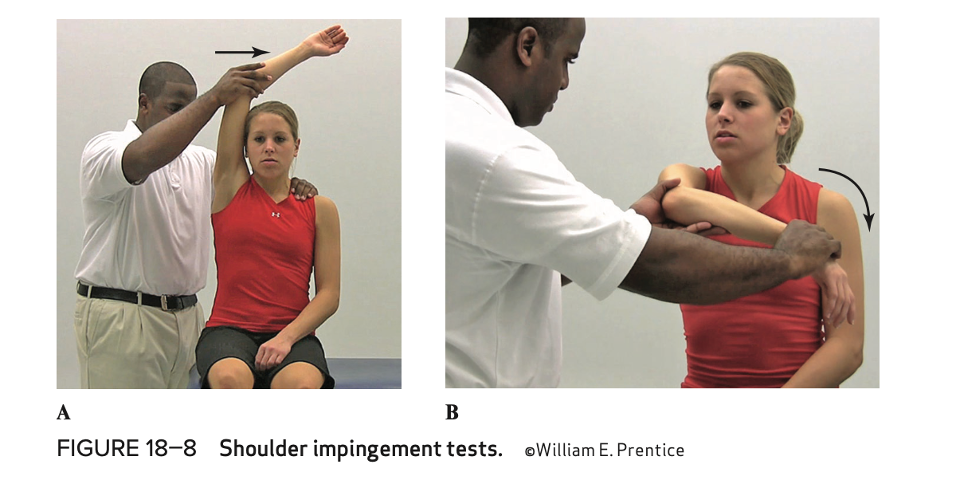
Shoulder impingement test (purpose, how, positive sign )
purpose - impingement of soft tissues
how - horizontal adduction and forced internal rotation, forced flexion and adduction overhead
positive sign - pain/facial grimace on movement
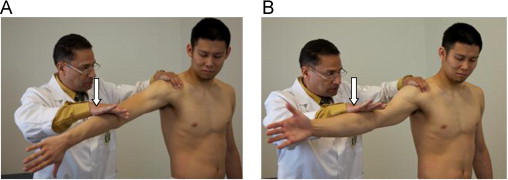
Supraspinatus weakness test - empty can/ full can (purpose, how, positive sign)
purpose - injury / weakness to supraspinatus
how- arm at 90 degrees forward flexion, thumbs up, downward pressure is applied
positive sign - pain/ weakness/ strength difference between arms
Sternoclavicular instability test (purpose, how, positive sign)
purpose - instability/ sprain of SC joint
how - apply pressure to proximal clavicle in anterior, superior and inferior directions
positive sign - pain/ excessive movement
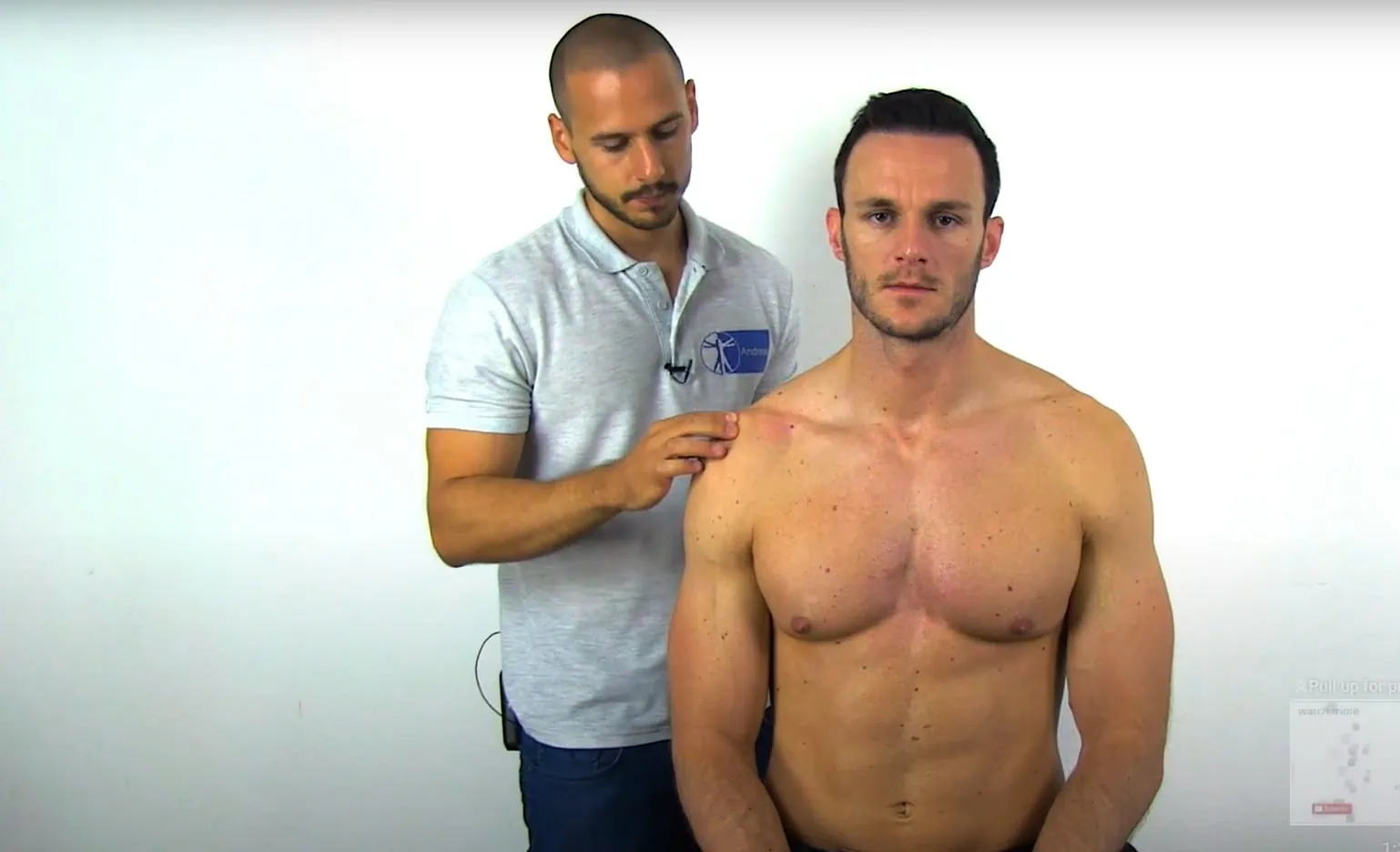

Acromioclavicular instability test (purpose, how, positive sign)
purpose - instability/ sprain to AC joint
how - palpate for misalignment of acromion and distal clavicle, apply pressure to distal clavicle in all 4 directions
positive sign - pain/ excessive movement
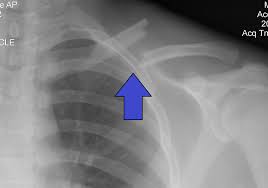
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptomsand management
Clavicle fracture
moi = fall on outstretched arm/ tip of shoulder, direct blow (MTB, cycling - most common)
signs and symptoms = pain, redness and swelling, supports arm on injured side, lower and deformed clavicle
management = immobilisation in sling (6 weeks), clavicle strap, physio, rehab and strengthening
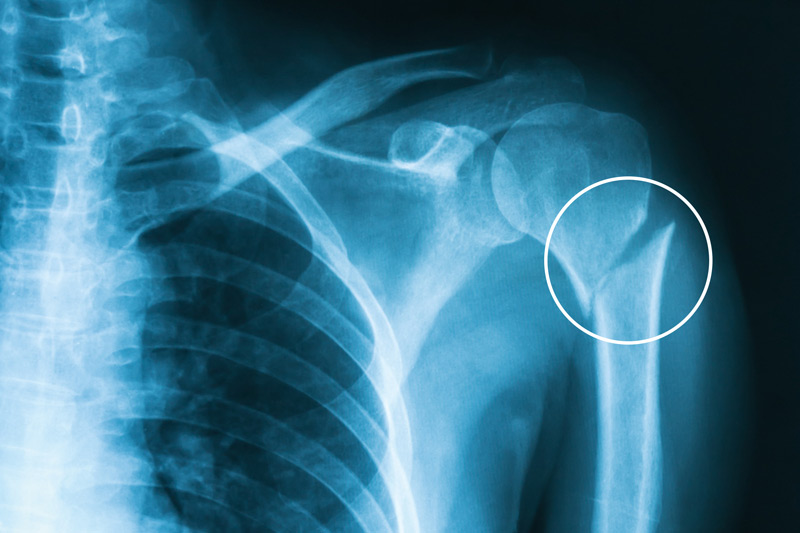
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptomsand management
humerus fracture
moi - fall on outstrectched arm / direct blow (often with disclocation)
signs and symptoms - pain , redness and discolouration, sweling, tenderness, inability to move arm
management - splint and sling, pain relief, refer to medical professional
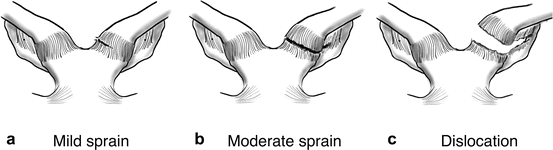
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptomsand management
sternoclavicular joint sprain
moi - indirect/ direct impact
signs and symptoms: grade 1 - mild pain, point tenderness, no instability, grade 2 - moderate pain, swelling, point tenderness, joint sublaxation, inability to abduct/adduct through full rom , visable deformity, grade 3 - severe pain, swelling, complete disclocation , rupture of sternoclavicular ligament. posterio-retro sternal disclocation - medical emergecy (trachea and blood vessels
management - POLICE, immbolizatation in sling for 6 weeks
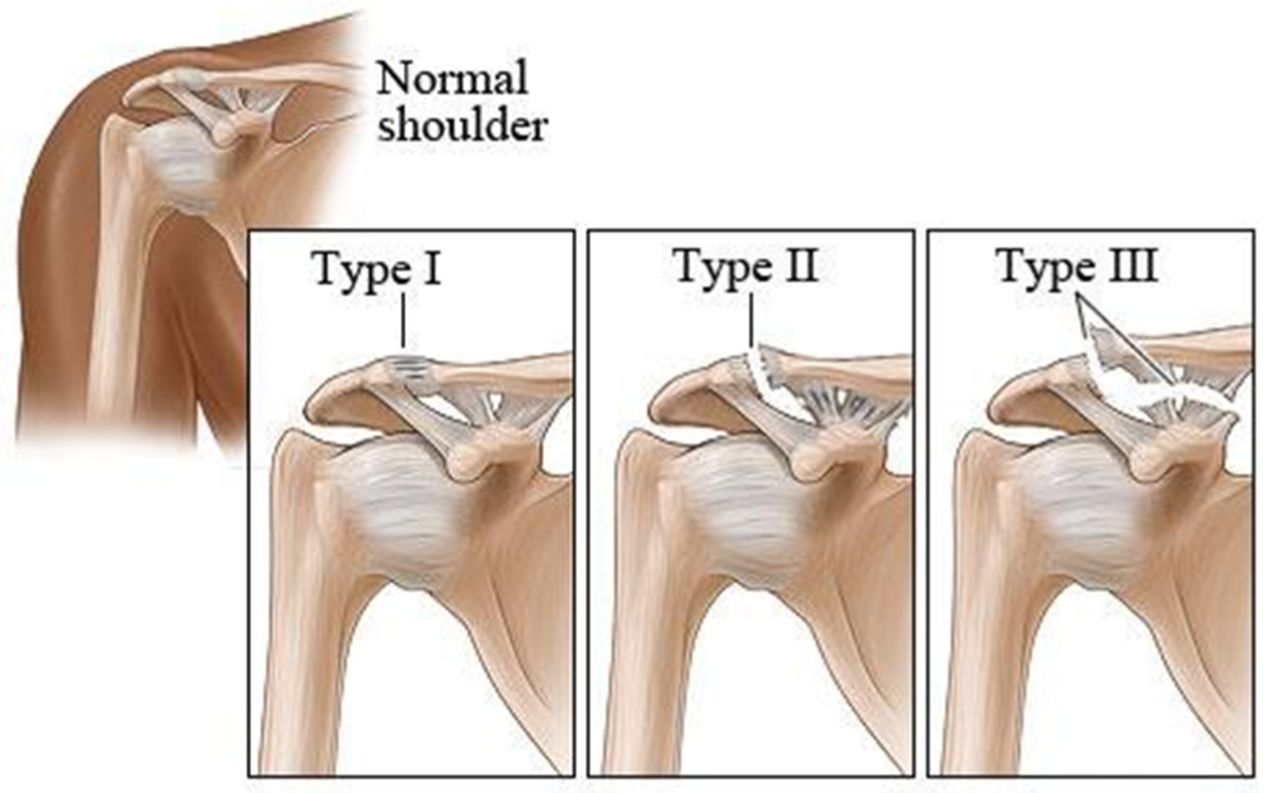
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptomsand management
acromioclavicular joint sprain
moi - fall on outstreched arm/ tip of shoulder
signs and symptoms - grade 1 - mild pain, point tenderness, no visable deformity, mild stretching on coracoclavicular and aromioclavicular ligaments, grade 2 - moderat pain, pint tenderness, swelling, rupture of acromioclavicular ligament, unable to abduct/adduct shoulder through full rom , grade. 3- severe pain, point tenderness, rupture of acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligamanets, complete disclocation managament - POLICE, immobilisation in sling for 6 weeks, mobilization, flexibility and strengthening
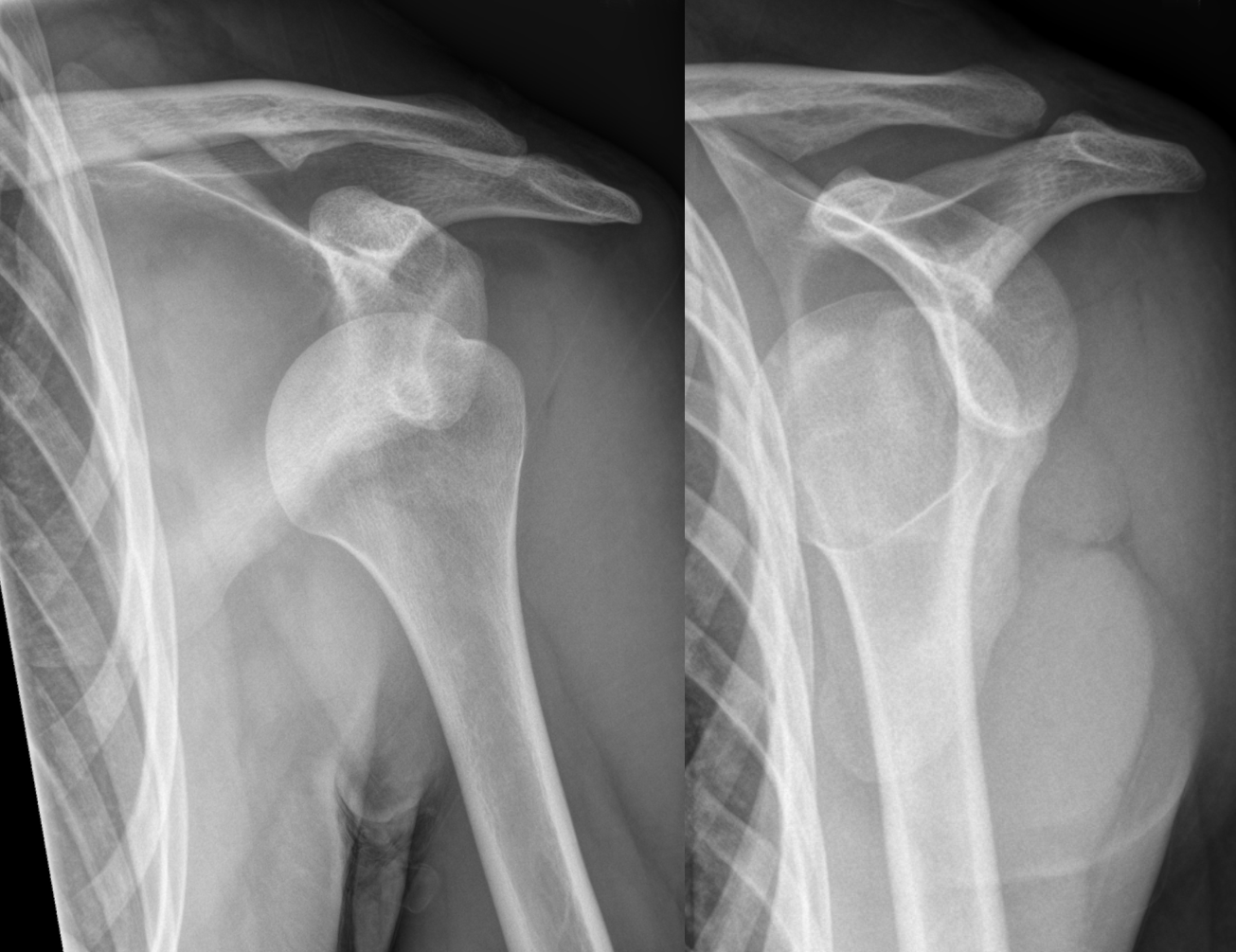
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptomsand management
glenohumeral disclocation
moi - anterior = abduction , external rotation and extension, inferior, posterior = abduction, internal rotation
signs and symptoms = flattened deltoid contour, inability to move arm, moderate - severe pain, nerve involvement - numbness/ tingling
management - do not relocate - damage to nerve and blood vessels, immobilise with sling, police, refer to medical professional to relocate, use protective gear /braces , restore ROM, stregthen, prevent reoccurence
what is primary shoulder impingement ?
structural narrowing of the subacromial space, leading to mechanical compression of the rotator cuff tendons/ bursa
factors contributing to intrinsic primary impingement
supraspinatus tendinosis (tendon degeneration)
hypo vascularity(reduced blood supply)
collagen fiber disorganisation (tendons weaken and loose elasticity as you age)
chronic microtrauma (from repetive movements)
calcific tendinopathy (calcium deposits from within the tendon)
extrinsic impingement syndrome
hooked acromion (type iii)
ac joint osteophytes (bone spurs)
thickened coracoacromial ligament
what is secondary impingement ?
functional instability of the GH joint, due to poor neuromuscular control/ instability, leading to mechanical compression of the rotator cuff tendon, subacromial bursa and long head of biceps tendon.
what are factors contributing to secondary impingement
GH joint instability = humeral head migrates superiorly due to labral injuries, capsular laxity and repetitive overhead movements, compression the subacromial structures
scapular dyskinesis = abnormal motion , position and stability of scapular, which leads to poor acromion positioning, reducing subacromial space
muscle imbalances/weakness = weakness of rotator cuff = less humeral head control. weakness of scapula stabilzes = functional narrowing of subacromial space during motion
symptoms of shoulder impingement
diffuse pain around acromion (overhead movements )
tightness in inferior and posterior joint capsule
pain within 70-120 degrees abduction
external rotators is weaker than internal rotators
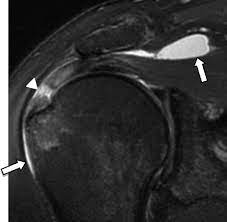
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptoms and management
subacromial bursitis
moi - direct impact, fall on tip of shoulder, result of shoulder impingement
signs and symptoms = pain with motion (abduction, adduction , internal rotation, flexion. tenderness on palpation
management = POLICE, pain relief, restore full ROM.
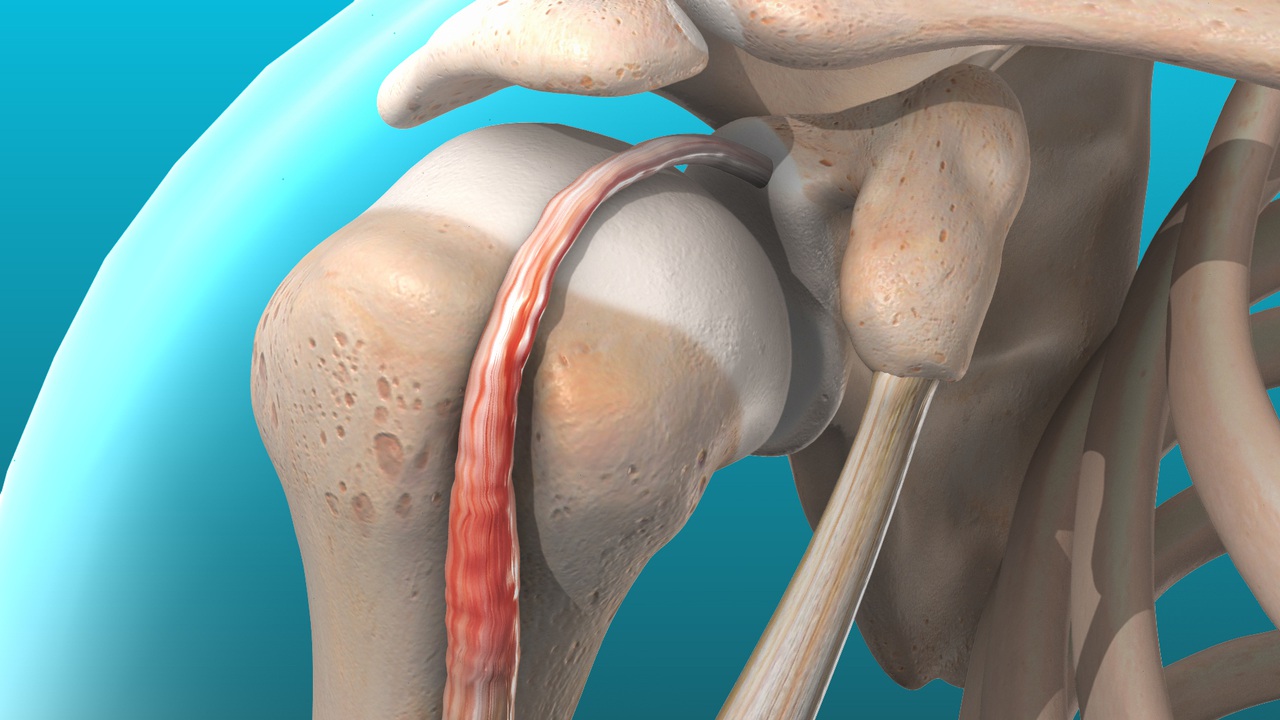
Diagnose this injury. Provide Moi, signs and symptoms and management
Biceps tenosynovitis
moi = repeated stretching of biceps in highly ballistic activities = leads to inflammation of tendon and synovial sheath, weak rotator cuff muscles
signs and symptoms = tenderness in upper anterior arm, swelling and increased warmth, crepitus, pain in dynamic overhead movements
management = POLICE, pain relief, rehab