Biochemistry II Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 4: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Pro)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Lesson 4: Fatty Acid Oxidation
Lesson 4: Fatty Acid Oxidation
Triacylglyceride molecules can be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol can be broken down for use as energy via ______________ and fatty acid chains can be broken down for use as energy via ______________.
(A) glycolysis, beta-oxidation
(B) beta-oxidation, glycolysis
(C) pentose phosphate pathway, glycogenolysis
(D) glycogenolysis, pentose phosphate pathway
(A) glycolysis, beta-oxidation
Triacylglyceride molecules can be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol can be broken down for use as energy via glycolysis and fatty acid chains can be broken down for use as energy via beta-oxidation.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
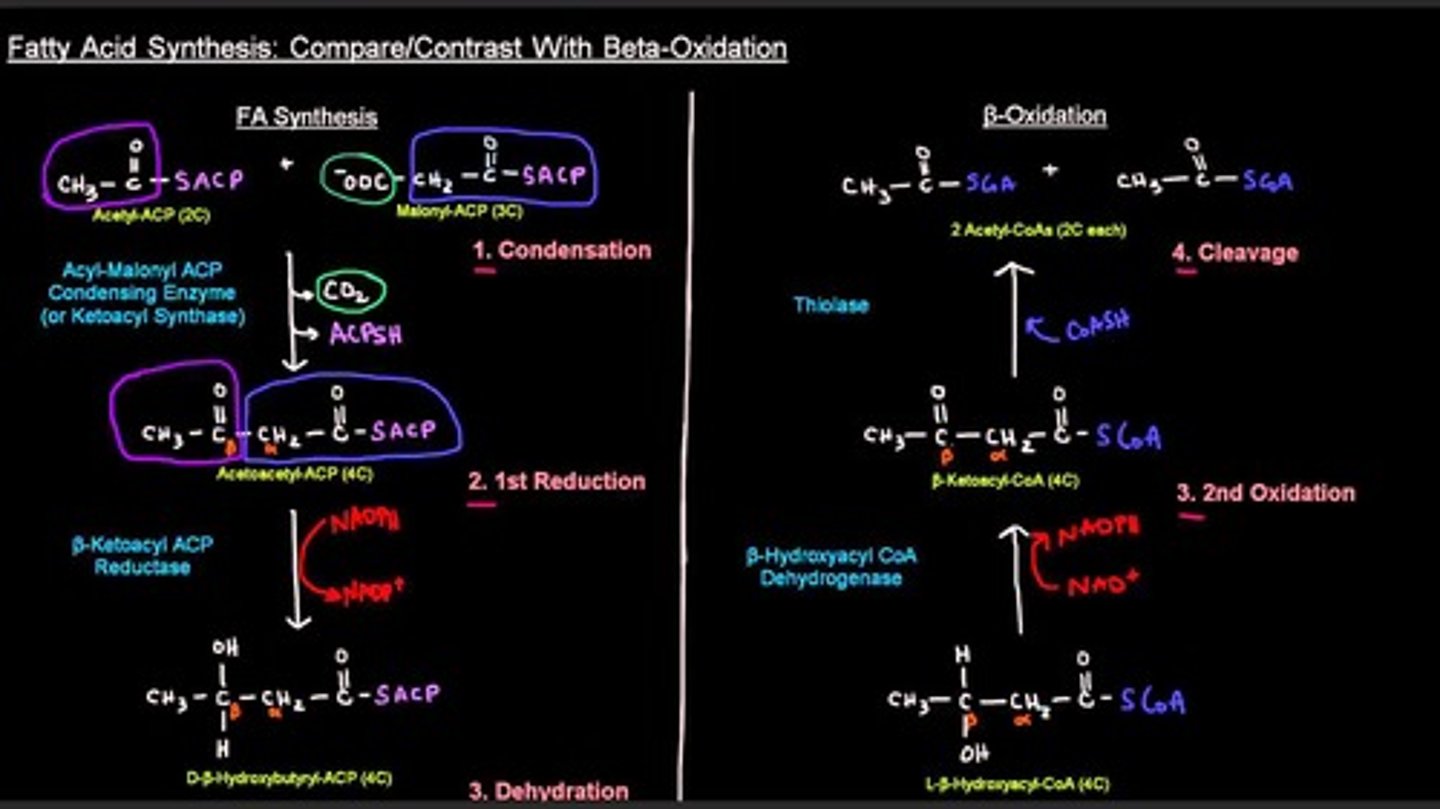
Compare beta-oxidation and fatty acid synthesis?
They are almost the same exact pathway except that they are going in opposite directions. The goal of beta-oxidation is to break fatty acids down into two-carbon acetyl-CoA molecules while the goal of fatty acid synthesis is to combine acetyl-CoA molecules together in the formation of a long-chain fatty acid.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
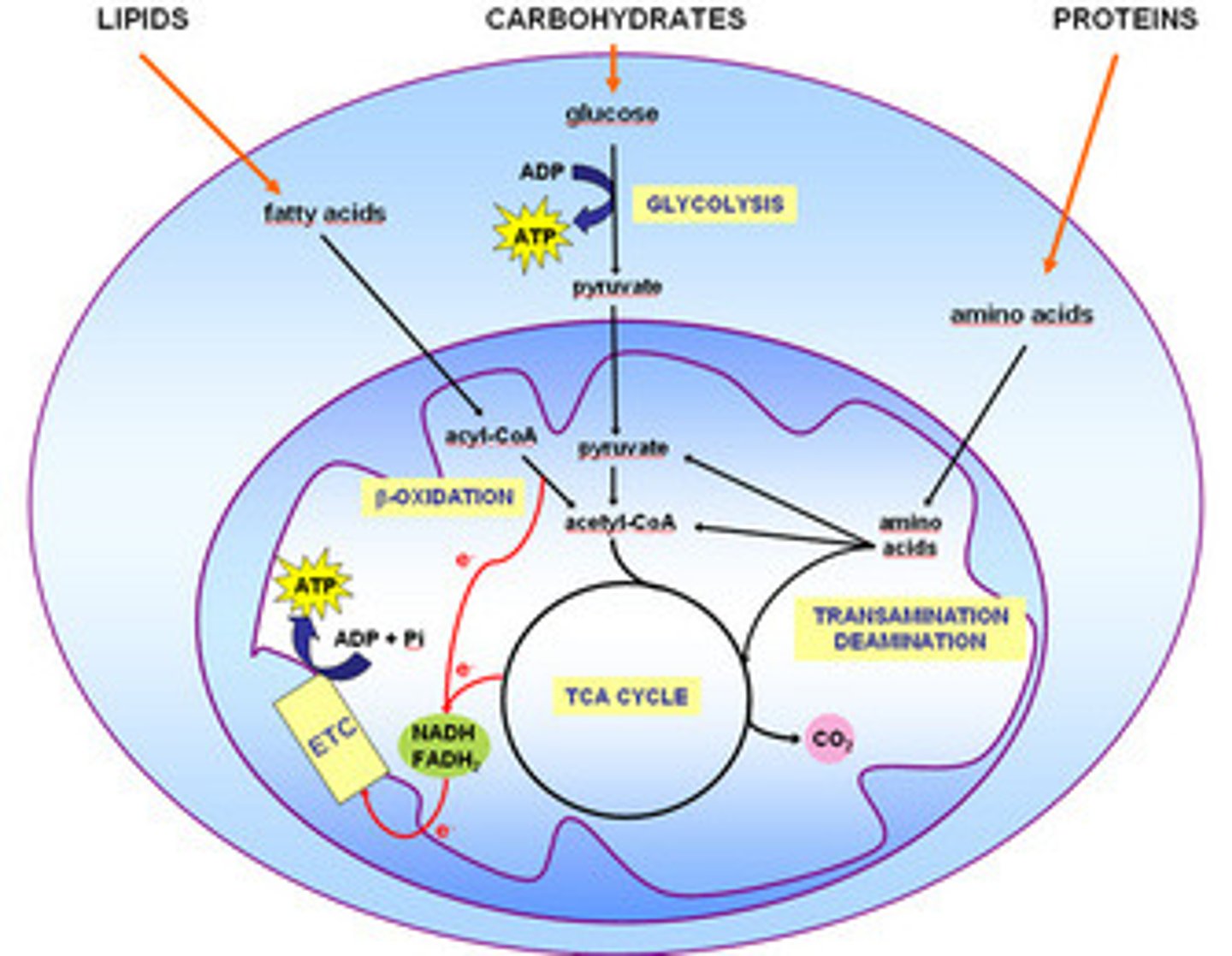
Let's Review -- Where does each of the following metabolic pathways take place in the cell?
(1) Glycolysis
(2) Gluconeogenesis
(3) The Linking Step
(4) The Kreb's Cycle
(5) The Electron Transport Chain
(6) Fatty Acid Synthesis
(7) Beta-oxidation
(1) Glycolysis - Cytoplasm
(2) Gluconeogenesis - Liver
(3) The Linking Step - Mitochondrial Matrix
(4) The Kreb's Cycle - Mitochondrial Matrix
(5) The Electron Transport Chain - Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
(6) Fatty Acid Synthesis - Cytoplasm
(7) Beta-oxidation - Mitochondrial Matrix
CRB Which of the following is NOT a type of fatty acid oxidation that occurs in cells?
(A) Alpha-oxidation of branched chain fatty acids
(B) Peroxisomal Beta-oxidation
(C) Peroxisomal Omega-Oxidation
(D) Endoplasmic Reticulum Omega-Oxidation
(C) Peroxisomal Omega-Oxidation
CRB Match each of the following conditions to the length of the fatty acid.
I. 2-12 Carbons
II. 14-20 Carbons
III. >20 Carbons
(A) Must be oxidized elsewhere.
(B) Can freely diffuse into the mitochondria
(C) Must use a Carnitine Shuttle to enter Mitochondria.
I. 2-12 Carbons - (B) Can freely diffuse into the mitochondria
II. 14-20 Carbons - (C) Must use a Carnitine Shuttle to enter Mitochondria.
III. >20 Carbons - (A) Must be oxidized elsewhere.
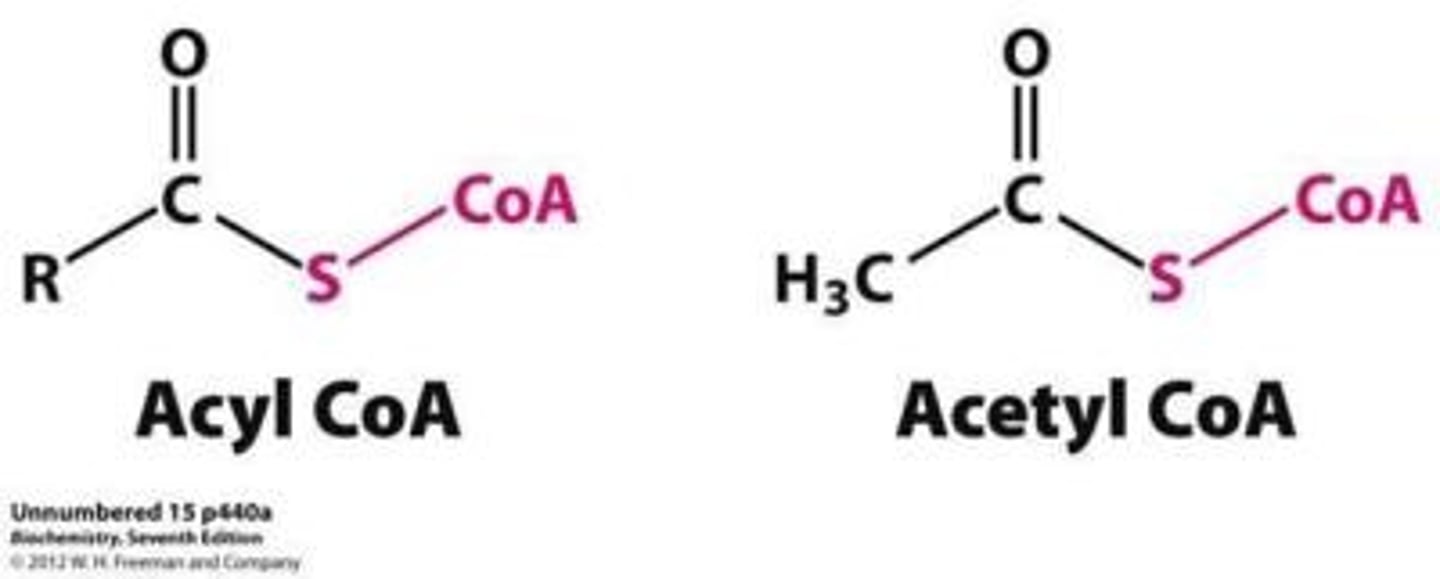
Compare the structure of acyl-CoA versus acetyl-CoA.
Acyl-CoA is a fatty acid with a CoA instead of an OH group.
Acetyl-CoA is an acetyl group with a CoA attached.
The breakdown of fatty acids consists of three main steps. Put them in order from first to last:
I. Oxidation
II. Transportation
III. Activation
(A) II > III > I
(B) III > II > I
(C) I > II > III
(D) I > III > II
(B) III > II > I
The breakdown of fatty acids consists of the following steps in order:
III. Activation
II. Transportation
I. Oxidation
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
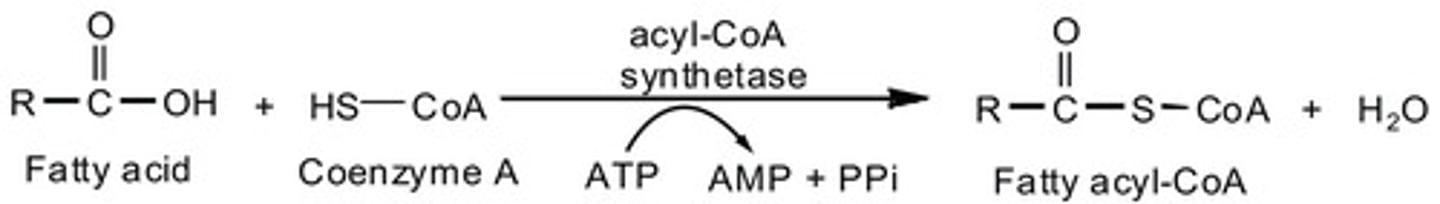
Draw out the pathway of the first step involved in the breakdown of fatty acids: activation. Include all enzymes, substrates, and energy substrates.
It is absolutely necessary to be able to do this for the MCAT. And because it is so challenging to memorize all of this point blank, we've created our Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course: https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
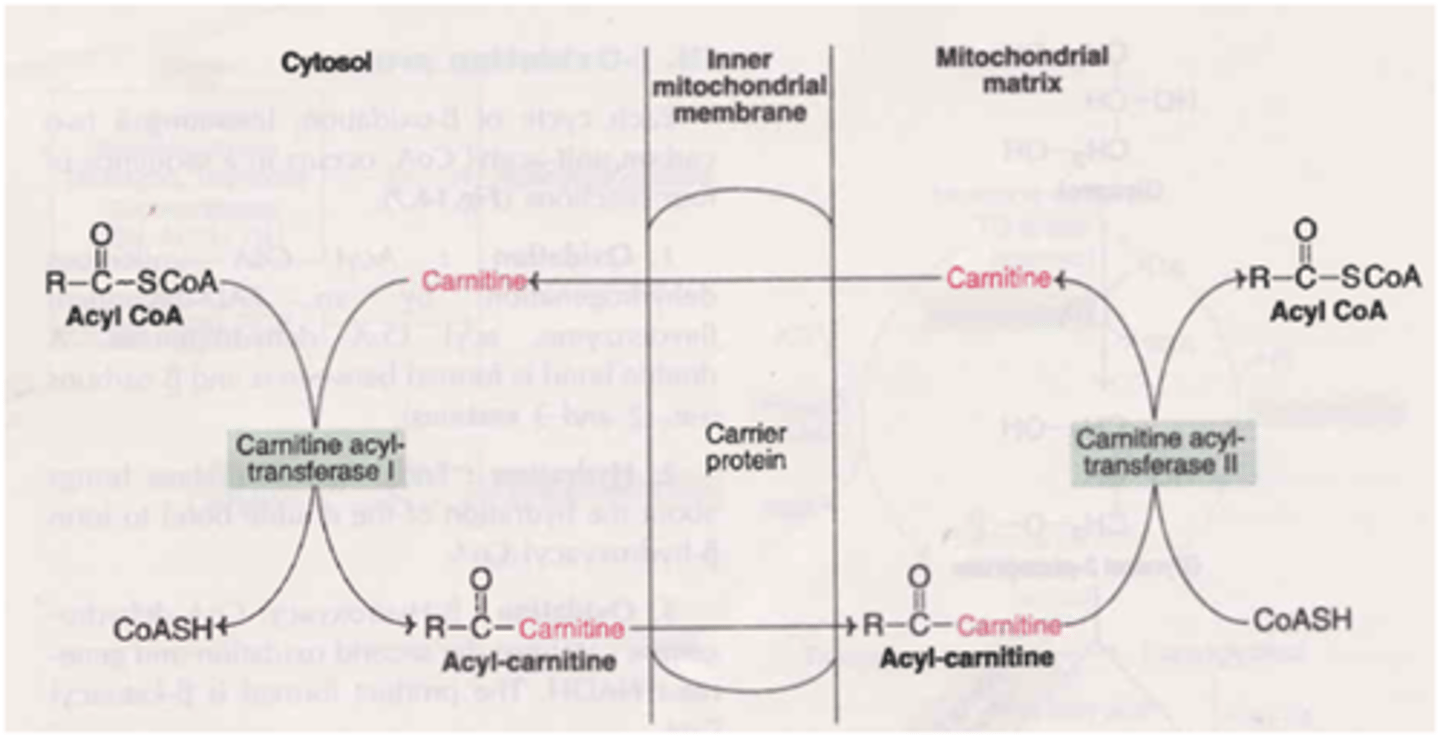
Draw out the pathway of the second step involved in the breakdown of fatty acids: transportation. Include all enzymes, substrates, and energy substrates.
It is absolutely necessary to be able to do this for the MCAT. And because it is so challenging to memorize all of this point blank, we've created our Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course: https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
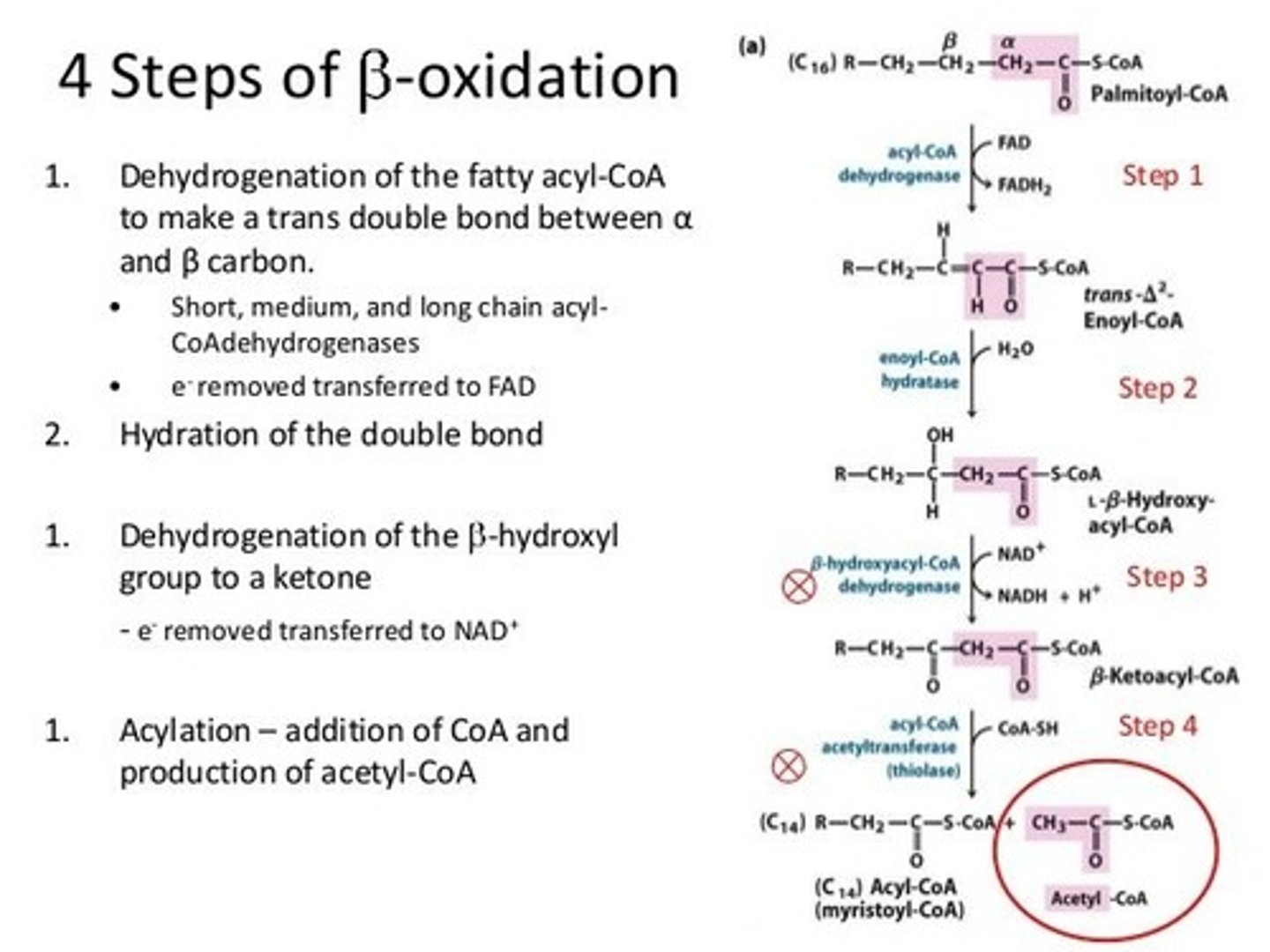
Draw out the pathway of the third step involved in the breakdown of fatty acids: beta-oxidation. Include all enzymes, substrates, and energy substrates.
It is absolutely necessary to be able to do this for the MCAT. And because it is so challenging to memorize all of this point blank, we've created our Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course: https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
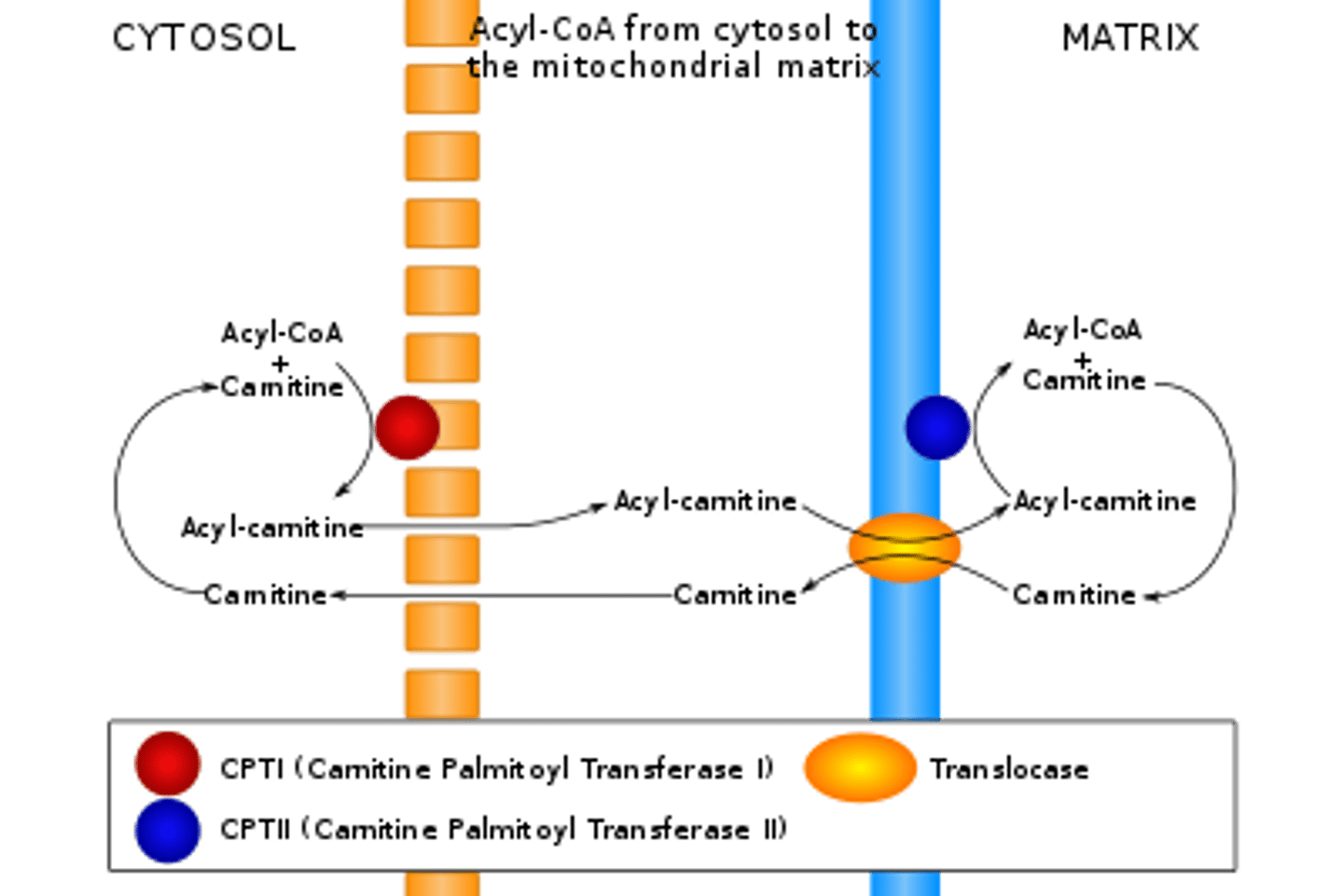
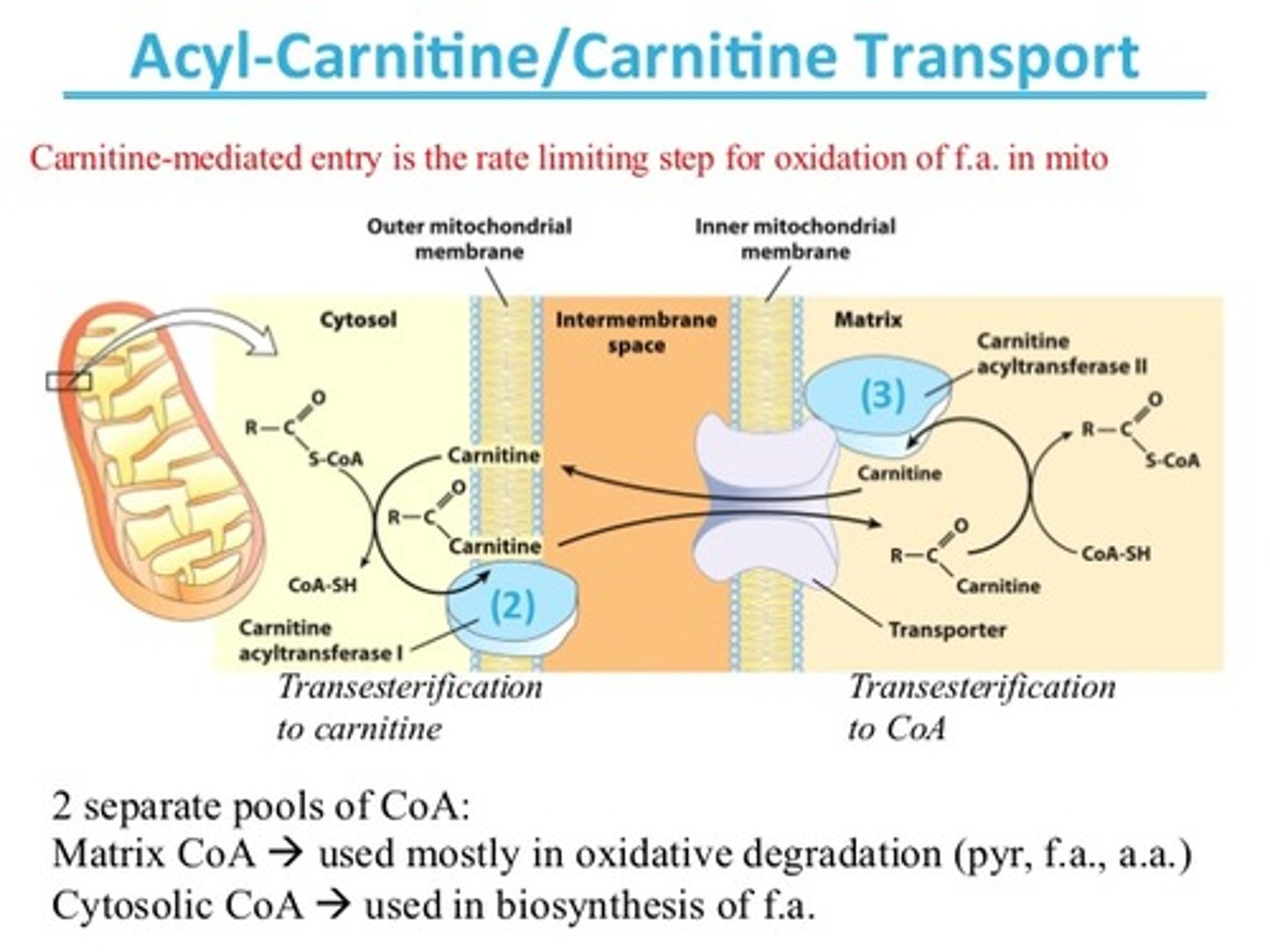
What allows acyl carnitine to traverse the outer mitochondrial membrane? The inner mitochondrial membrane?
Acyl carnitine is simply able to diffuse across the outer mitochondrial membrane due to its high permeability.
The inner mitochondrial membrane, on the other hand, is very impermeable; thus, acyl carnitine needs to be transported across with the help of acyl carnitine translocase.
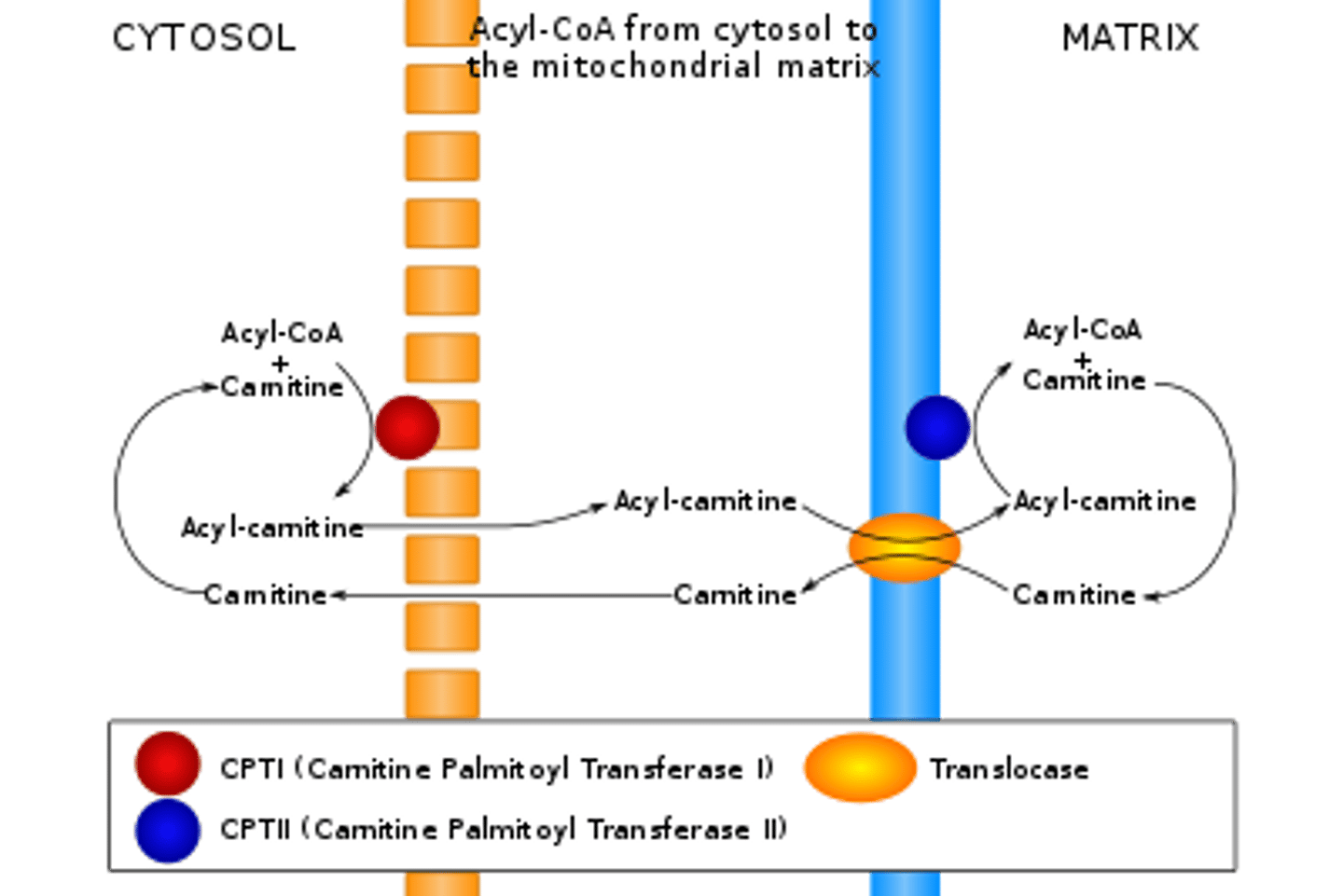
Why doesn't carnitine build up inside the mitochondrial matrix?
Acyl carnitine translocase acts as an antiport. As it transports an acyl carnitine into the matrix, it also transports a carnitine out of the matrix, back to the intermembrane space.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
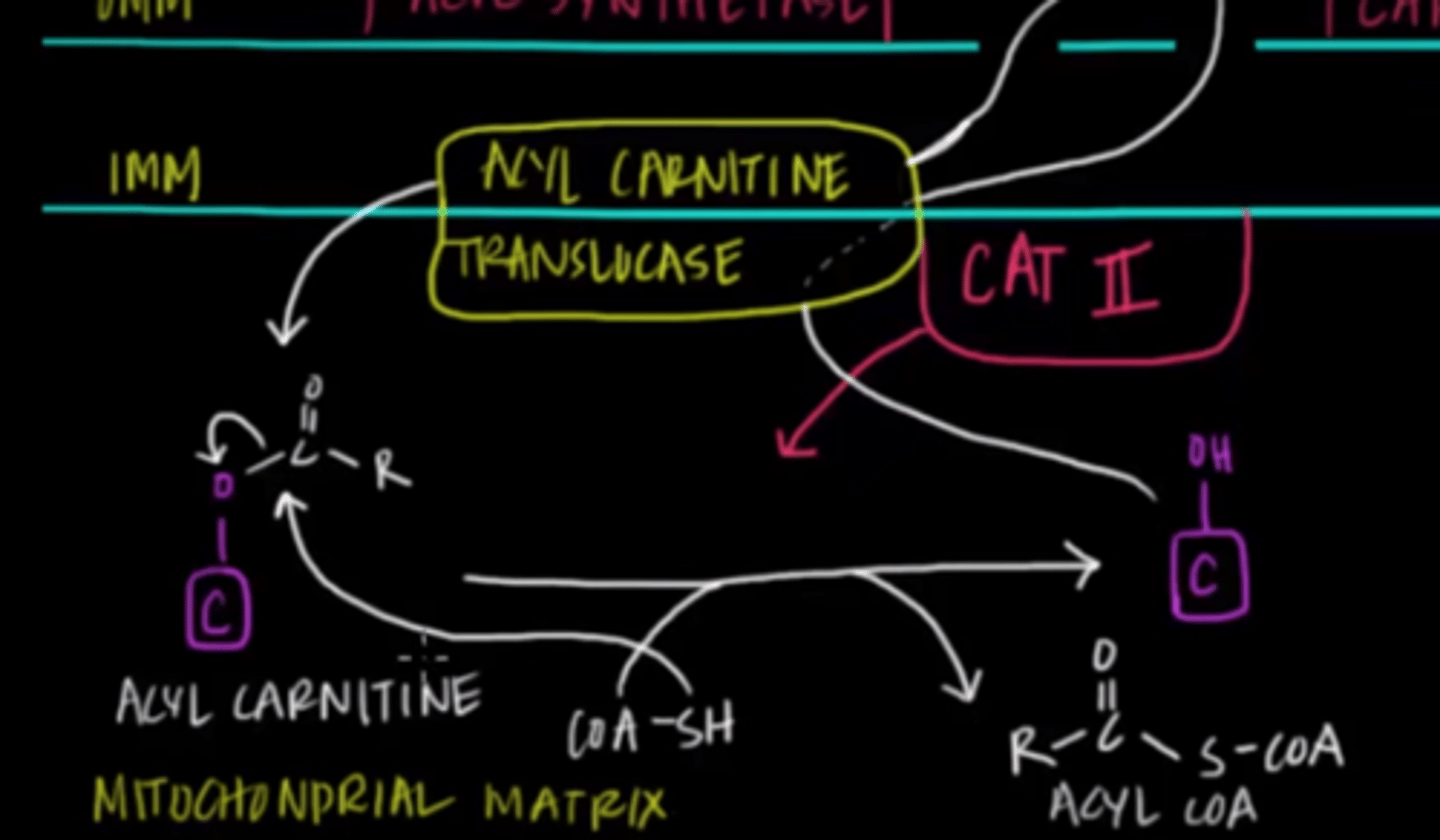
A 20-carbon fatty acid is broken down via beta-oxidation into 10 acetyl-CoA molecules. ___ FADH2 will be produced and ___ NADH will be produced.
(A) 10, 10
(B) 10, 20
(C) 9, 9
(D) 9, 18
(C) 9, 9
A 20-carbon fatty acid is broken down via beta-oxidation into 10 acetyl-CoA molecules. 9 FADH2 will be produced and 9 NADH will be produced.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? NADH and FADH2 produced from the breakdown of fatty acids must be shuttled before they can be used in the Electron Transport Chain.
False. Because Beta-Oxidation mainly occurs in the mitochondria, the NADH and FADH2 can easily be used by the Electron Transport Chain without relying on shuttles.
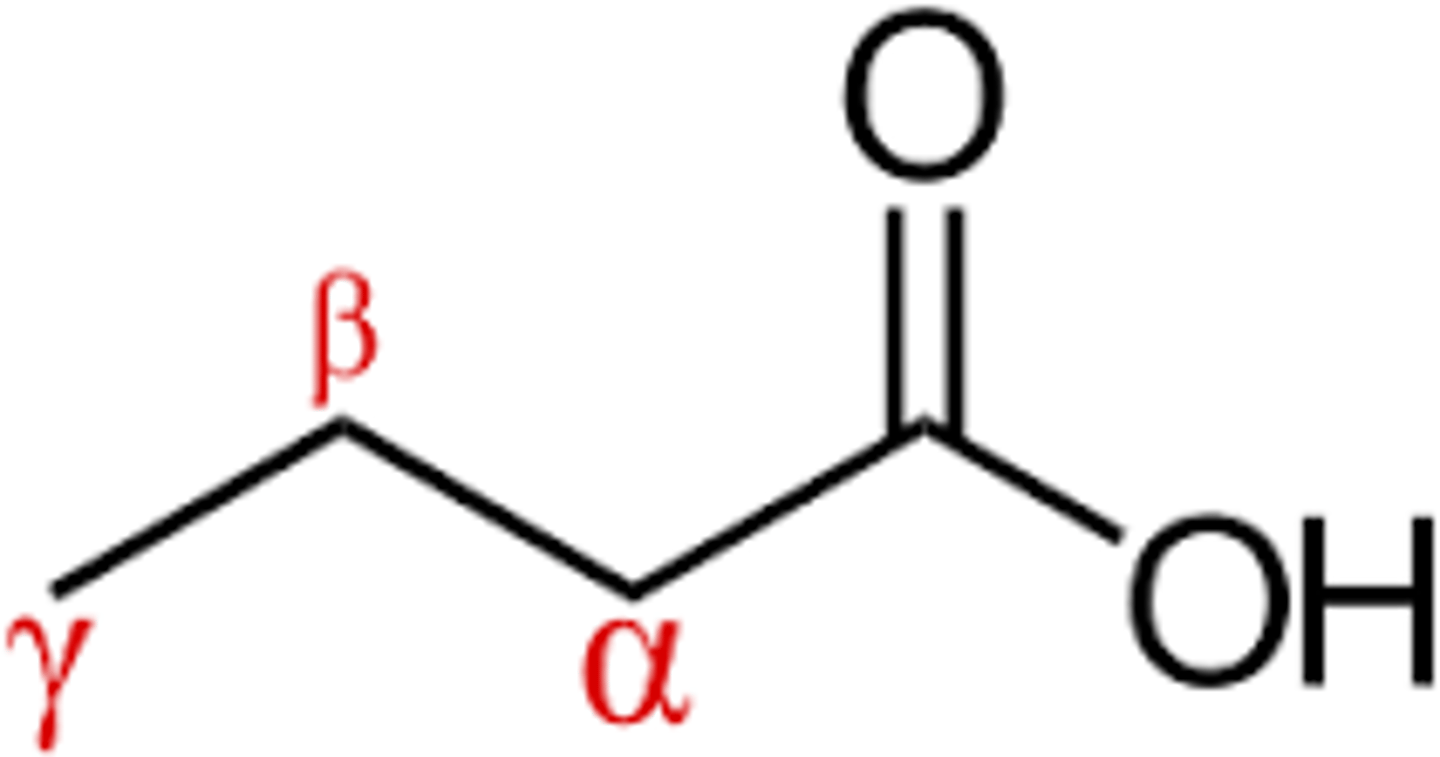
Why is fatty acid oxidation called "beta-oxidation"?
Beta-oxidation refers to the fact that it is the β-carbon that is being oxidized during this process.
Which enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step of beta-oxidation?
(A) Acyl Synthetase
(B) Carnitine Acyl Transferase I
(C) Acyl Carnitine Translocase
(D) Carnitine Acyl Transferase II
(B) Carnitine Acyl Transferase I
Carnitine acyl transferase I is the enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step of beta-oxidation.
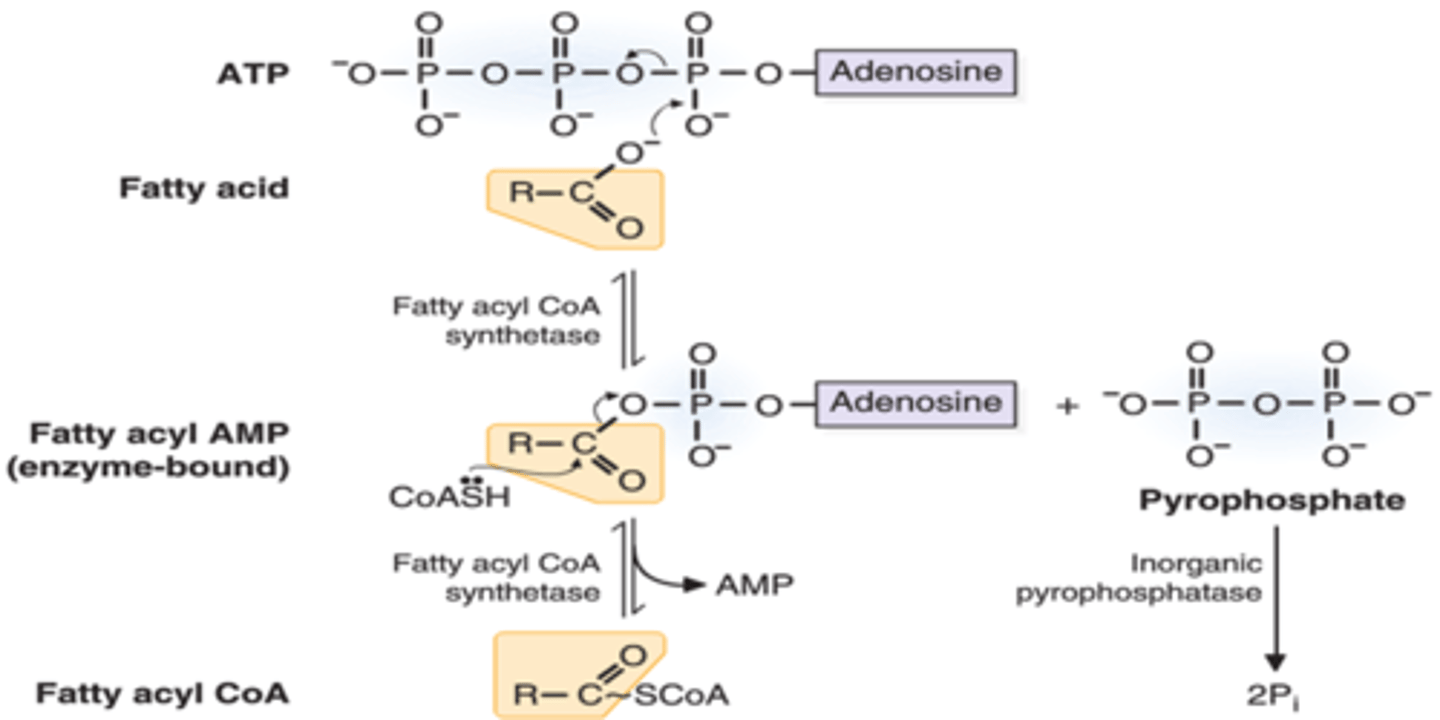
CRB True or false? Fatty-Acyl-CoA Synthetase needs to attach a CoA group to the fatty acid before the rate-limiting step.
True. Fatty-Acyl-CoA Synthetase needs to attach a CoA group to the fatty acid before the rate-limiting step.
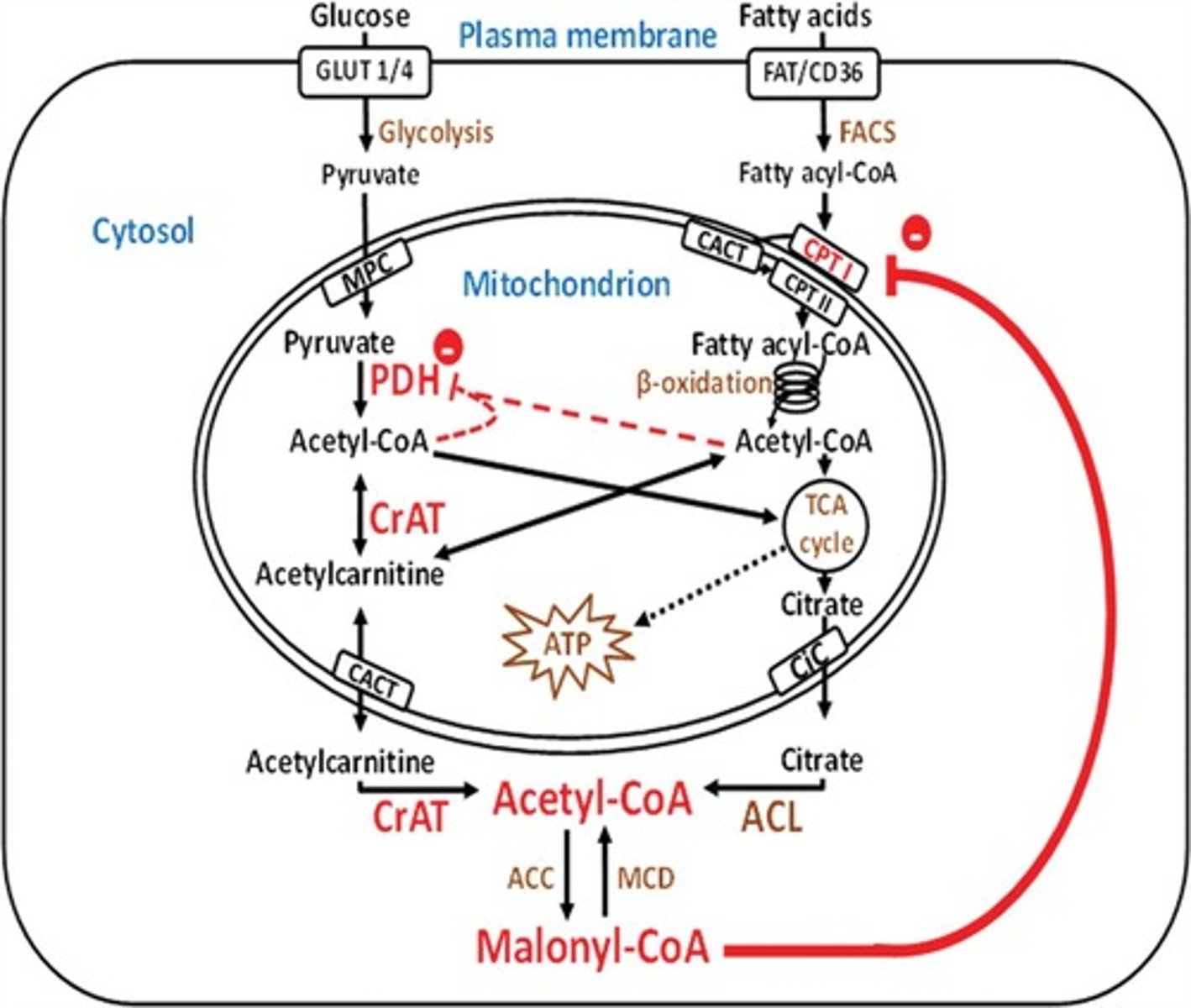
Does malonyl-CoA activate or inhibit Carnitine acyl transferase I? Why does this make sense?
Malonyl-CoA inhibits Carnitine acyl transferase I. This makes sense because malonyl-CoA is the starting substrate for fatty acid synthesis; thus, high levels of malonyl-CoA indicate that fatty acid synthesis is active. If we are building up fatty acids, we don't want to be breaking them down at the same time.
Glucocorticoids activate gluconeogenesis, resulting in the conversion of amino acids into glucose. Why might having an excess amount of glucocorticoids result in weakness and fatigue?
Amino acids come from the proteins that make up muscles. Gluconeogenesis for an extended period of time will result in the breakdown and weakening of muscles.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
Typically, the brain is reliant on glucose as its primary energy source. During times of starvation, however, the brain switches to a reliance on:
(A) fatty acids
(B) amino acids
(C) glycogen
(D) ketones
(D) ketones
Typically, the brain is reliant on glucose as its primary energy source. During times of starvation, however, the brain switches to a reliance on ketones. Fatty acids are unable to cross the blood-brain barrier and we don't want to use too many amino acids.
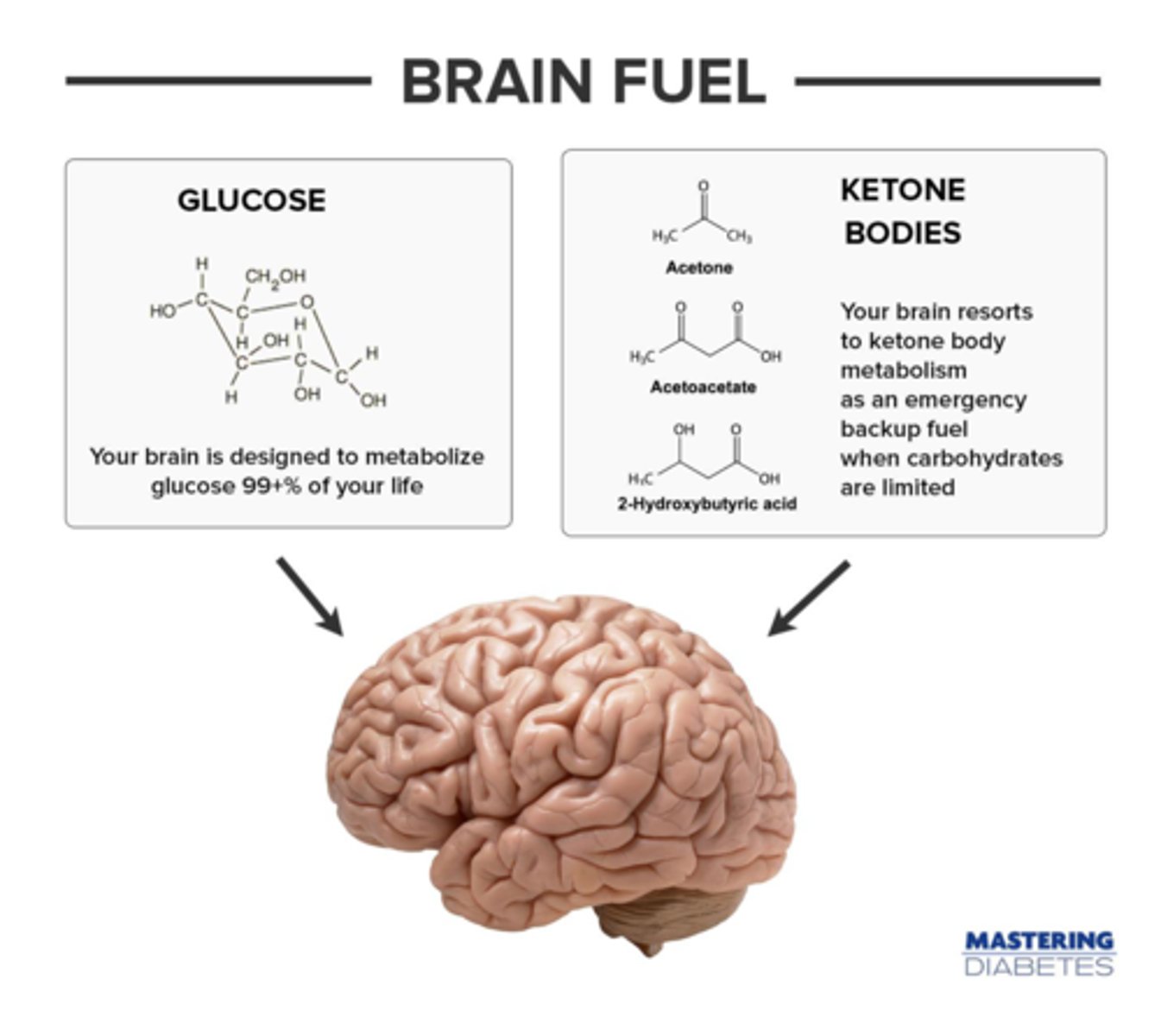
True or False? When fasting, fatty oxidation is upregulated due to an increase in glucagon and a decrease in insulin. After several days, however, as levels of acetyl-CoA rise, beta-oxidation is inhibited.
False. Beta-oxidation is not downregulated due to the presence of acetyl-CoA. This allows fatty acid levels to continue rising.
The excess acetyl-CoA molecules in the fasting state are used to produce:
(A) fatty acids
(B) amino acids
(C) glycogen
(D) ketones
(D) ketones
The excess acetyl-CoA molecules in the fasting state are used to produce ketones.
In the fed state, these excess acetyl-CoA can be used to create fatty acid stores.
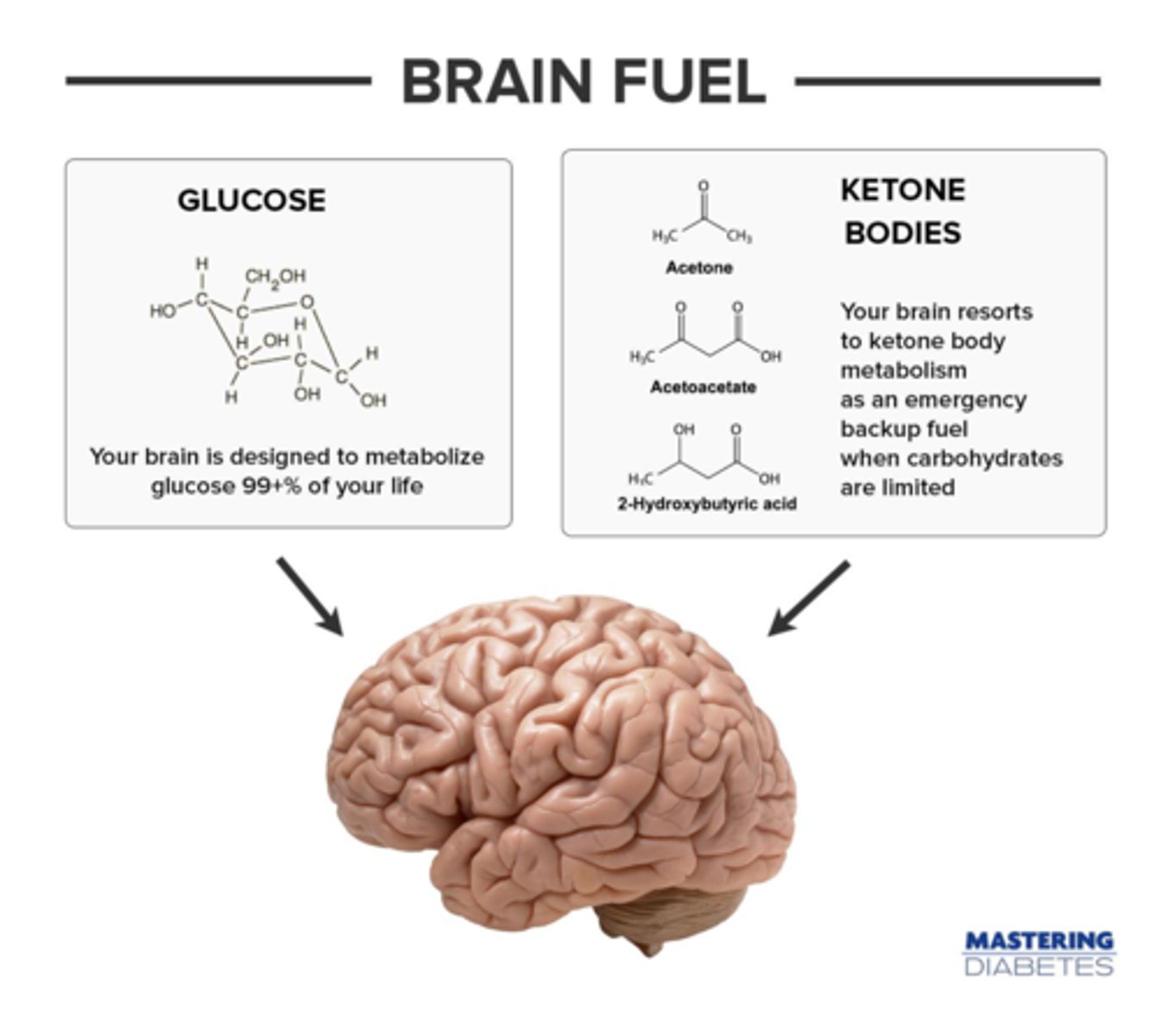
CRB Which of the following ketones are most commonly used as energy sources in various tissues?
I. Acetoacetate
II. 3-Hydroxyacetone
III. 3-Hydroxybutyrate
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) I and III only
Acetoacetate and 3-Hydroxybutyrate are the most common ketones used for energy by various tissues.
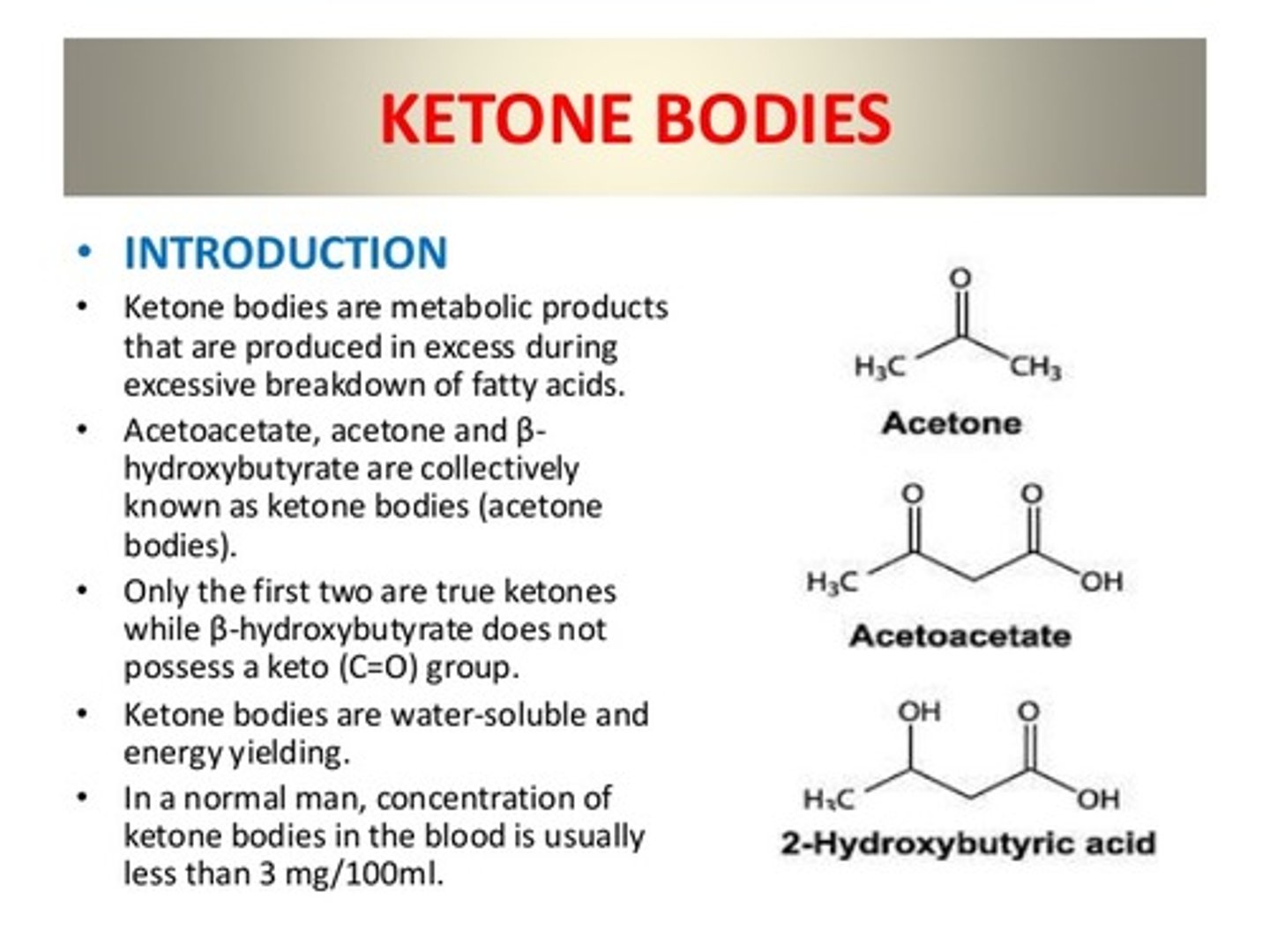
True or False? Ketogenesis primarily occurs in the kidney.
False. Ketogenesis primarily occurs in the LIVER.
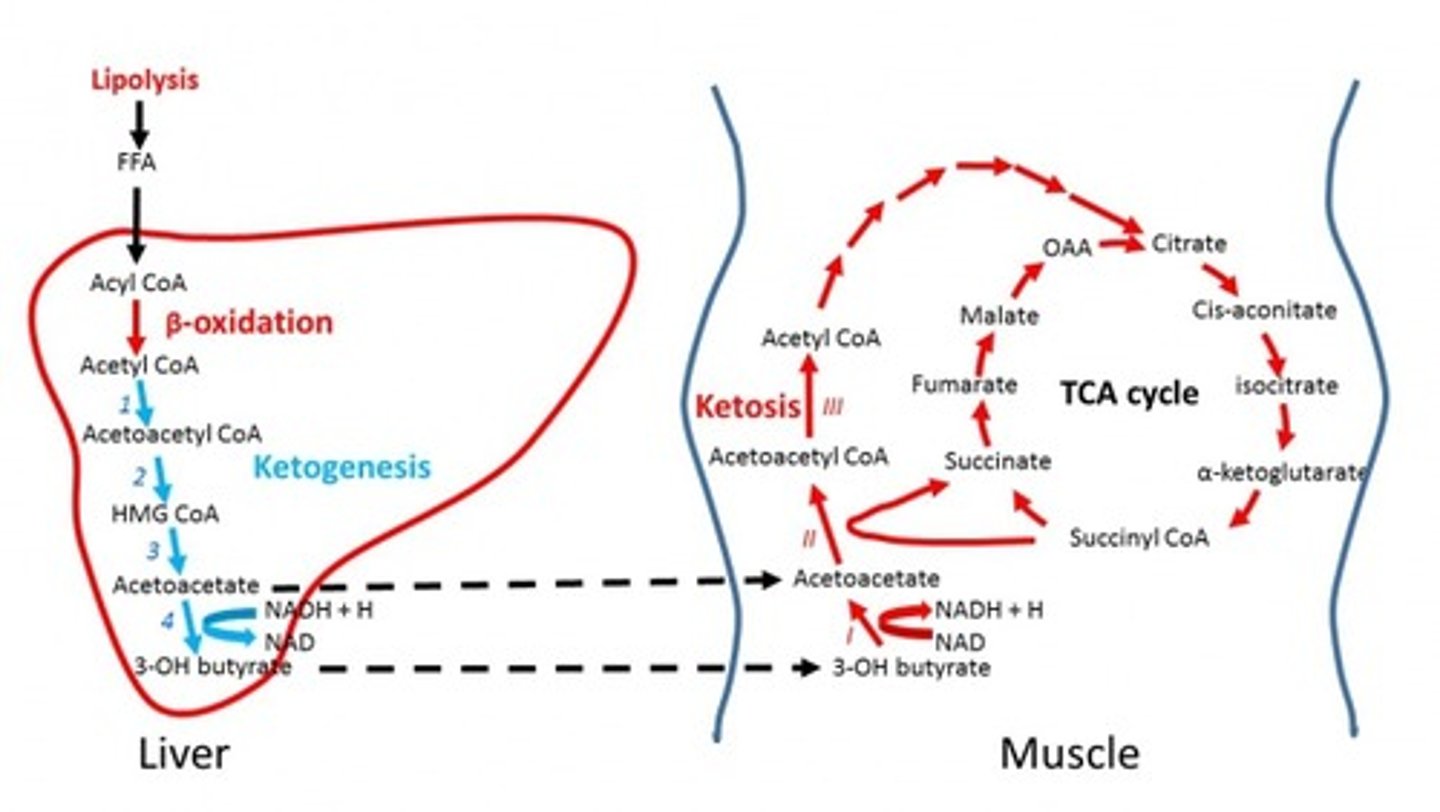
Ketogenesis is a mechanism used by our bodies to prevent the wasting away of our muscles. In what way does ketogenesis prevent the breakdown of muscle?
Ketogenesis provides an alternative energy source during periods of starvation. This means that the body will not need as much glucose; thus, gluconeogenesis will slow down.
Compare essential versus non-essential amino acids.
Essential amino acids are amino acids that our body cannot synthesize; thus, we need to get these from our diet.
Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by our bodies.
Amino acids can be used to make which of the following?
I. Protein
II. Glucose
III. Fatty Acids
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Amino acids can be used to make protein, glucose, or fatty acids.
Struggling to memorize the metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and beta-oxidation)? Learn them like the back of your hand using Andrew's Metabolic Pathways Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-metabolic-pathways-mastery-course/
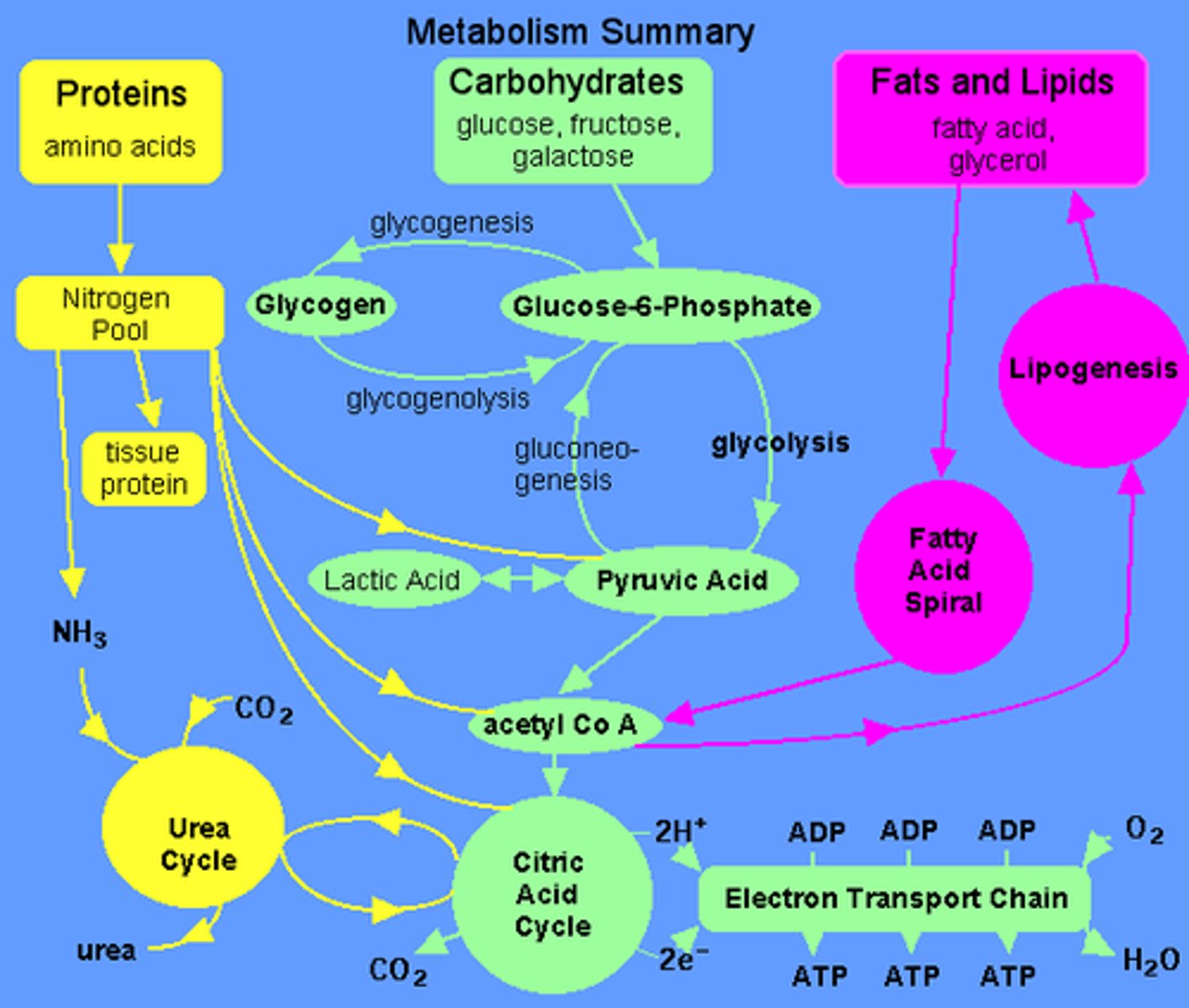
Compare glycogenic versus ketogenic amino acids.
Glycogenic amino acids feed into gluconeogenesis.
Ketogenic amino acids feed into ketogenesis/fatty acid synthesis.
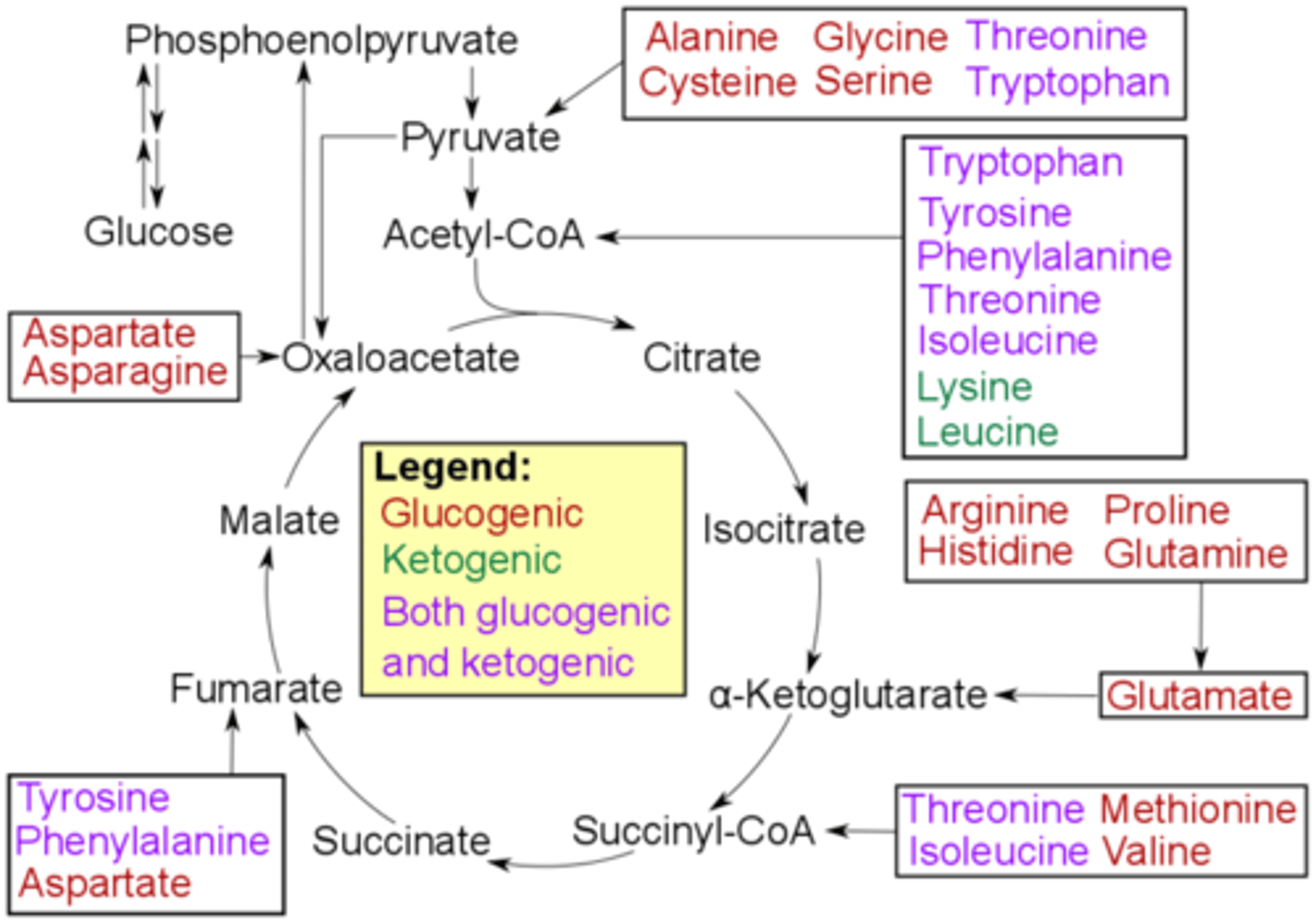
Which two amino acids are strictly ketogenic?
(A) Proline and Phenylalanine
(B) Glutamate and Glycine
(C) Lysine and Leucine
(D) Arginine and Aspartate
(C) Lysine and Leucine
Lysine and leucine are the only two amino acids that are strictly ketogenic.
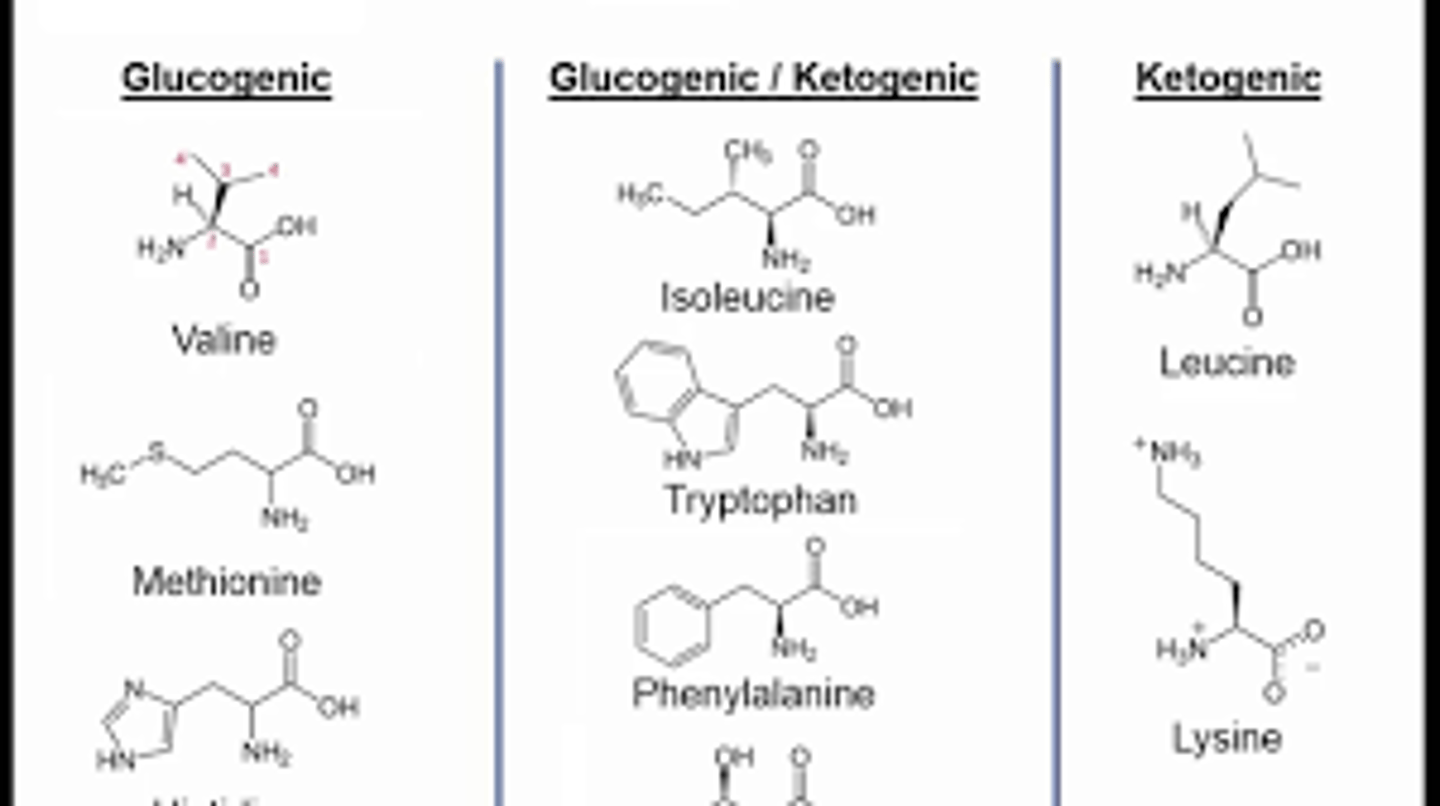
In the fasted state, amino acids are sent to the ___________ where they are converted into glucose via gluconeogenesis.
(A) Spleen
(B) Liver
(C) Pancreas
(D) Kidney
(B) Liver
In the fasted state, amino acids are sent to the liver where they are converted into glucose via gluconeogenesis.
True or False? Amino acids are unique in that they contain an amino group, which is useful in the synthesis of ketones.
False. Amino acids are unique in that they contain an amino group, which cannot be used for energy. It is a waste product that is toxic to our bodies at high levels; thus, it needs to be excreted.
Describe the pathway by which the amino group of an amino acid travels from a skeletal muscle cell to the bladder.
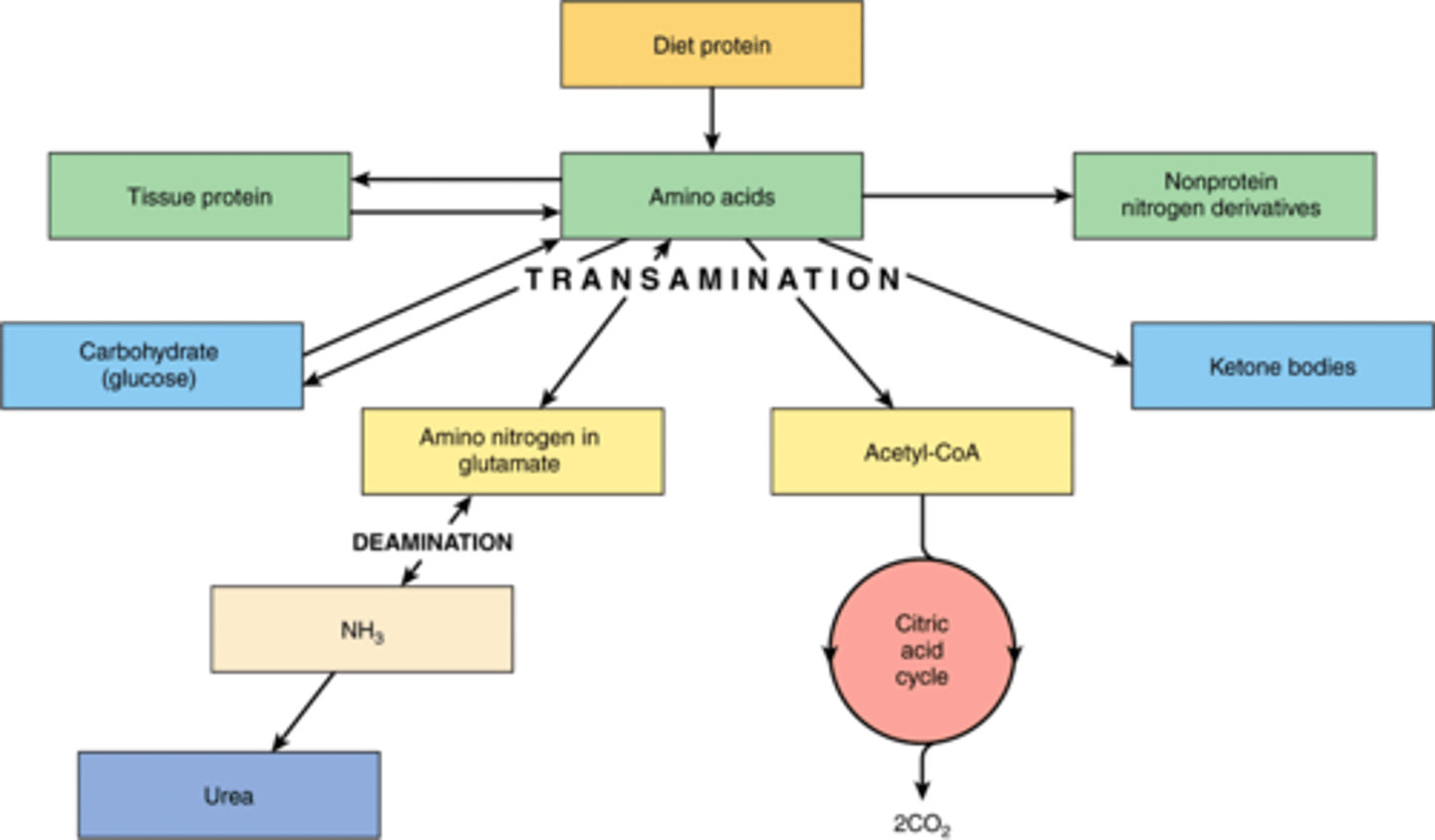
The amino group is transferred to alpha-ketoglutarate, converting it into glutamate. This reaction is catalyzed by a transaminase, which converts the amino acid into an alpha-ketoacid that can be used for energy. the glutamate carries the amino group to the liver where it is converted into urea via the urea cycle. From there, the urea travels to the kidney, where it is filtered into the bladder for excretion.
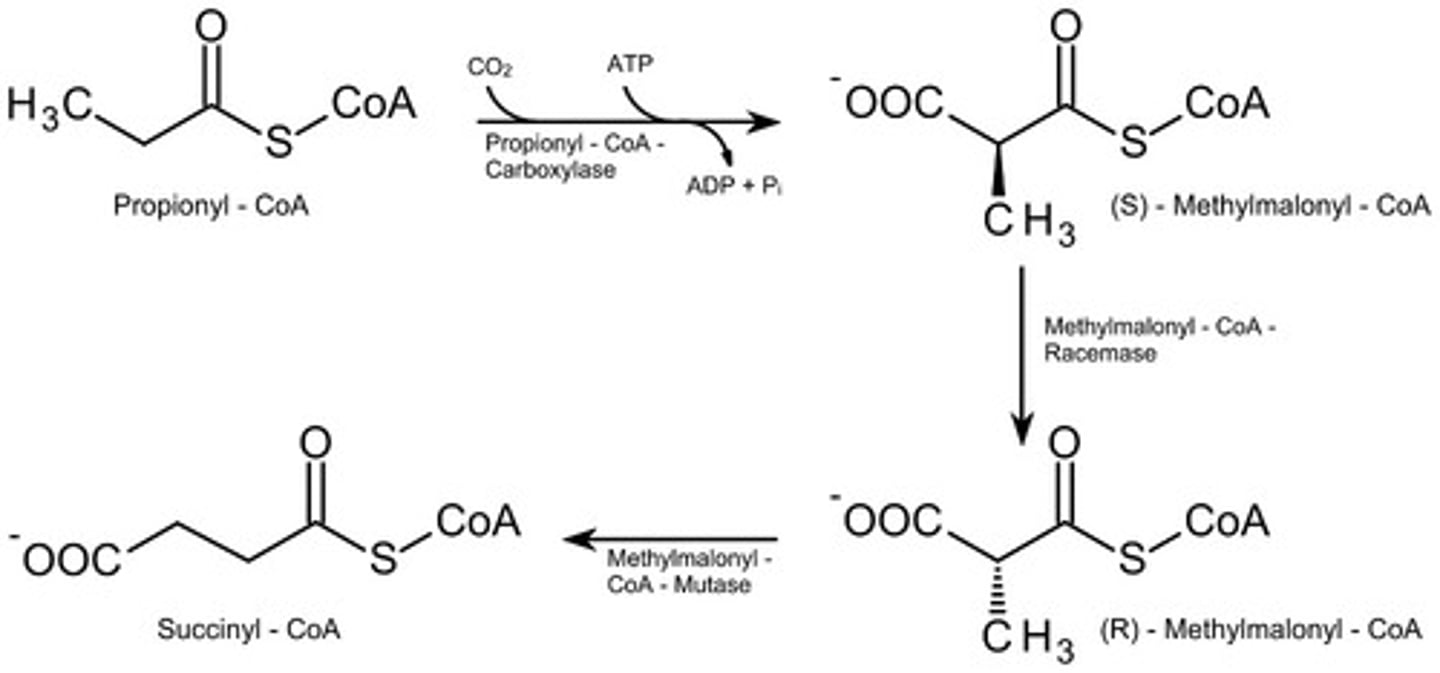
CRB Fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons must also be Oxidized for energy. Which of the following statements about this oxidation are true?
I. In the first cycle, instead of an Acetyl CoA being formed, a Propionyl-CoA will be formed.
II. Propionyl-CoA can be converted into Succinyl-CoA using vitamins B7 and B12.
III. Succinyl-CoA can be converted to Malate and enter Gluconeogenesis.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Below are true statements about the oxidation of odd-number of carbon Fatty acids:
I. In the final cycle, instead of 2 Acetyl CoA being formed, 1 Acetyl CoA and 1 Propionyl-CoA (3C) will be formed.
II. Propionyl-CoA can be converted into Succinyl-CoA using vitamins B7 and B12.
III. Succinyl-CoA can be converted to Malate and enter Gluconeogenesis.
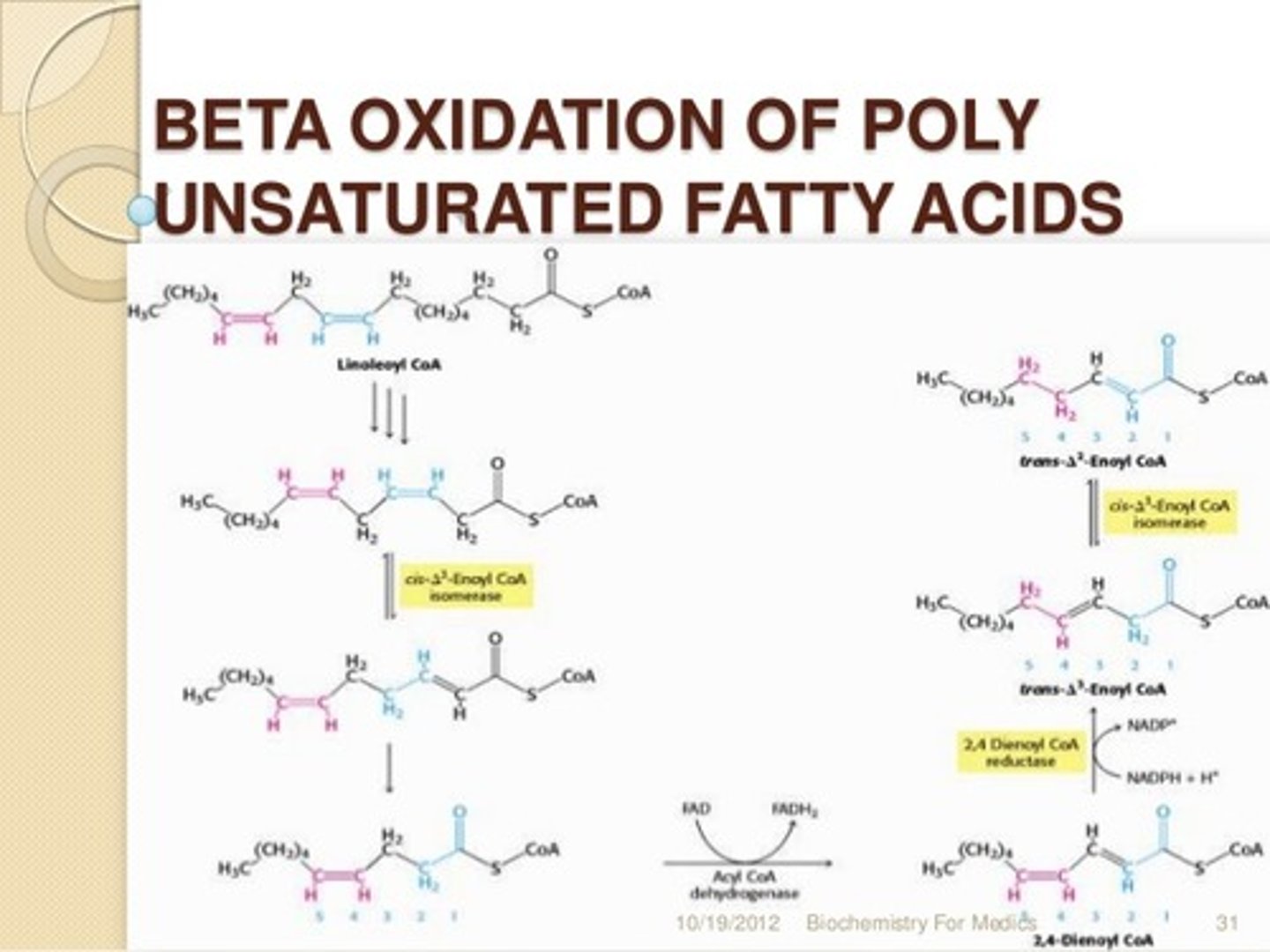
CRB True or false? Isomerases and Reductases are both needed for monounsaturated fatty acids to undergo Beta-Oxidation.
False. Isomerases are needed for monounsaturated fatty acids to undergo Beta-Oxidation. Reductase enzymes are not needed unless the fatty acid is Polyunsaturated.