Biology Test Review
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Characteristics of life
Composed of Cells – Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems
Adapt and Respond to Stimuli
Use Energy
Reproduce
Grow
Principles of Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells
The cell is the simplest unit that can carry out all life processes
All cells come from pre-existing cells
Living things depend upon the total activity of all their cells
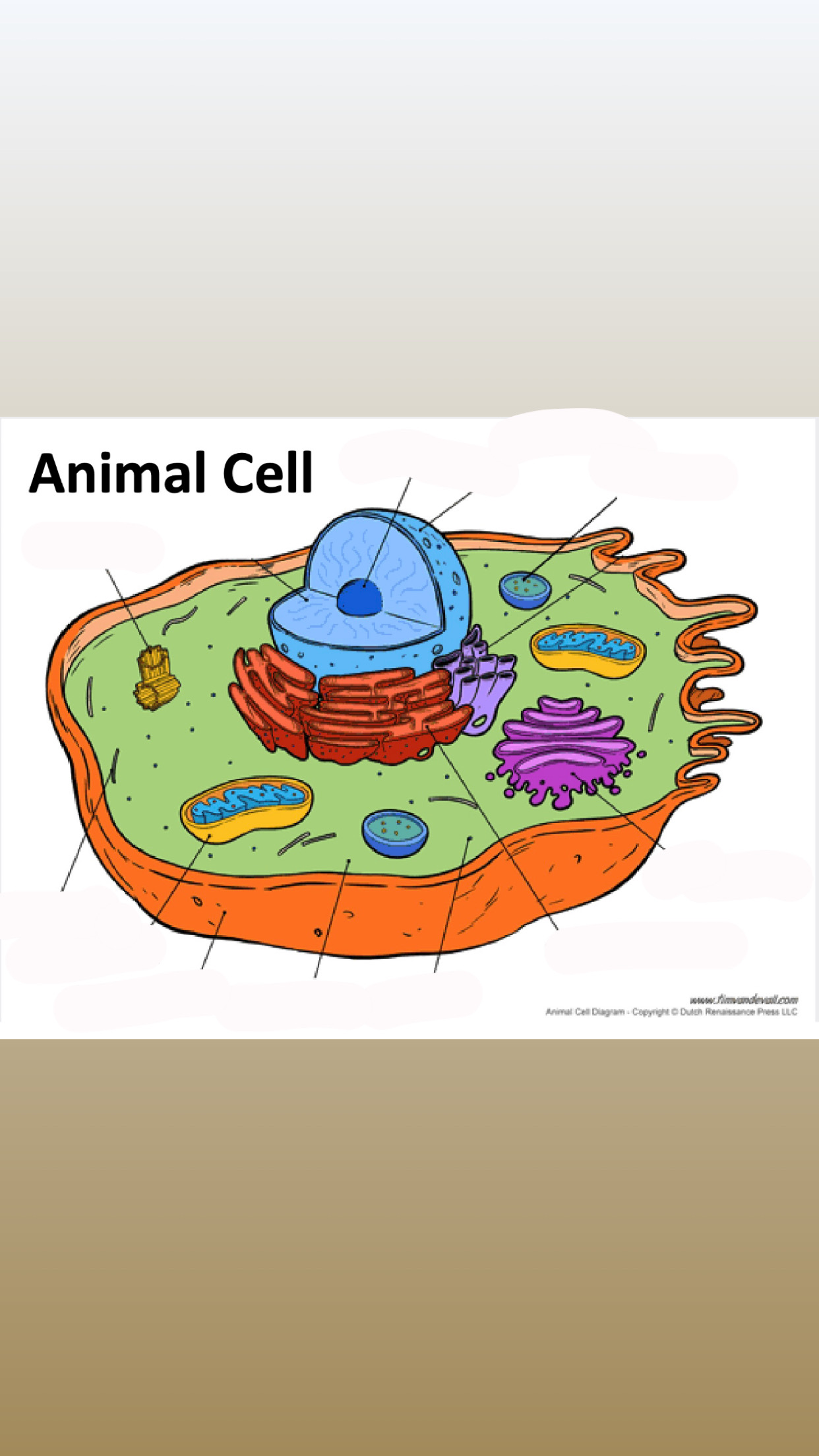
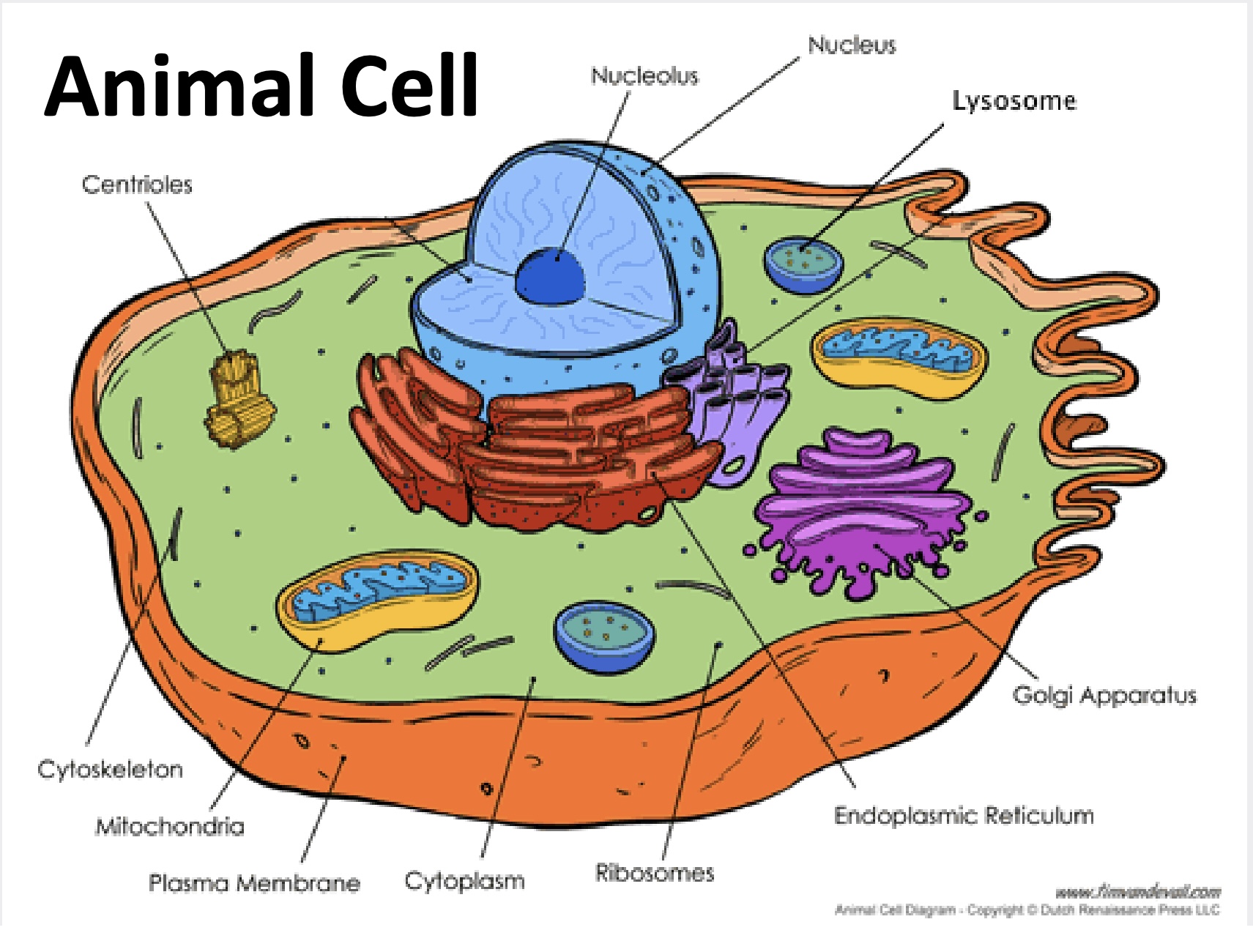
Plant vs Animal Cells
Plant Cells
Have a cell wall
Have chloroplasts and chlorophyll
One large central vacuole
Store energy as starch or oils
Animal Cells
Small vacuoles
Store energy as glycogen or fats
Have centrioles
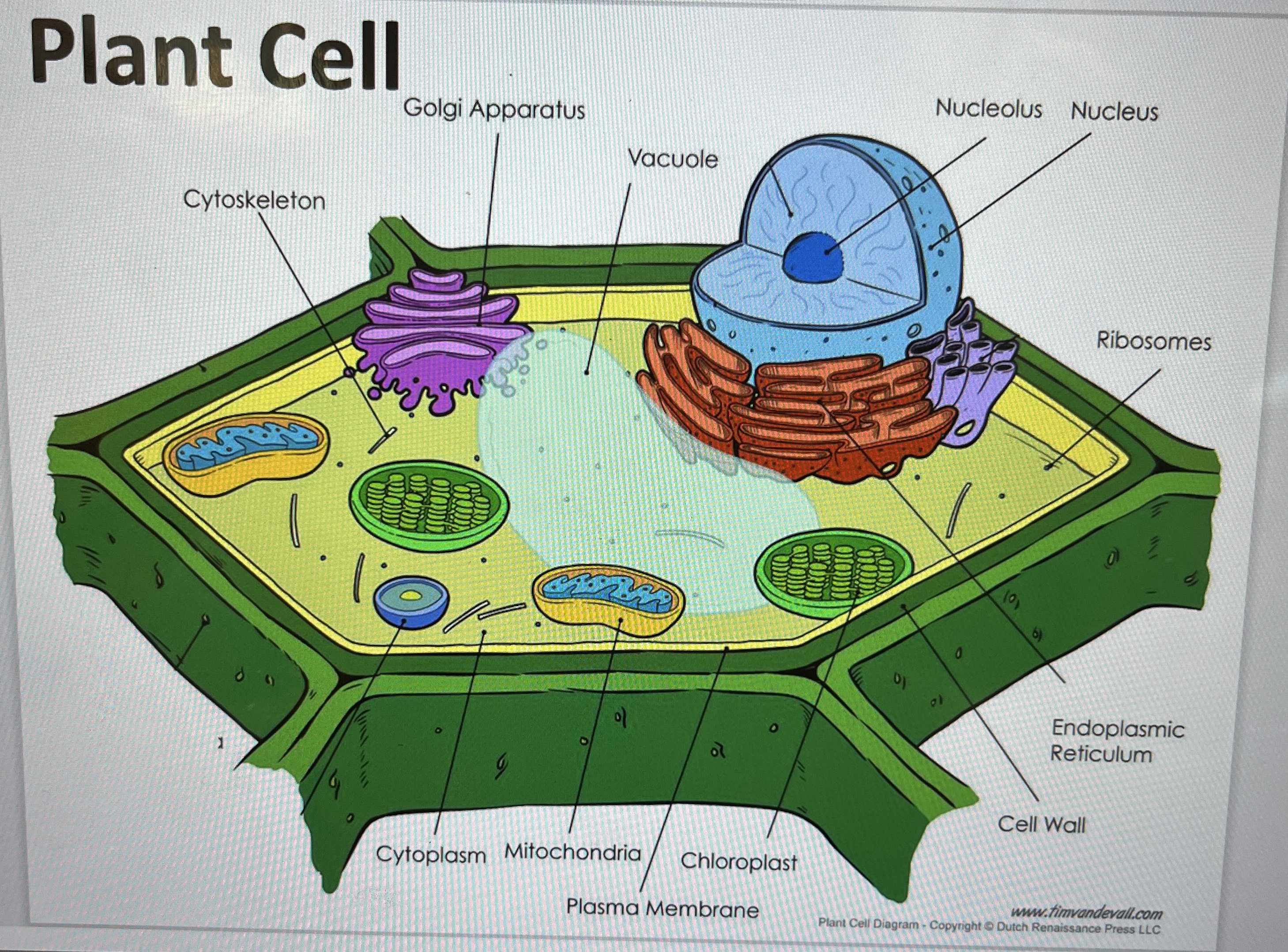
Cell Membrane (Plant & Animal)
Protective barrier, controls entry/exit
Made of lipid bilayer, allows diffusion
Cytoplasm (Plant & Animal)
Jelly-like, suspends organelles
Contains nutrients, allows material movement
Nucleus (Plant & Animal)
Control center: growth, activities, reproduction
Surrounded by nuclear envelope with pores
Contains DNA and nucleolus
DNA forms: Chromatin (uncoiled), Chromosomes (condensed for division)
Vacuole (Plant & Animal)
Stores water, nutrients, waste
Plant: one large central vacuole (firmness)
Animal: small vacuoles
Vesicles (Plant & Animal)
Small sacs for transport and storage
Mitochondria (Plant & Animal)
“Powerhouse” of cell
Converts sugar → energy for cell
Lysosomes (Animal Only)
Digestive enzymes: break down waste, bacteria, old organelles
Ribosomes (Plant & Animal)
Protein synthesis
Found in cytoplasm or on rough ER
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER: ribosomes, makes & transports proteins
Smooth ER: no ribosomes, produces fats/oils
Golgi Apparatus (Plant & Animal)
Modifies, sorts, packages proteins for cell or export
Cytoskeleton (Plant & Animal)
Protein filaments for shape & organelle movement
Plant-Only Parts
Cell Wall: rigid, supports/protects
Chloroplasts: chlorophyll, photosynthesis (CO₂ + H₂O → sugar + O₂)
Animal-Only Parts
Cilia & Flagella: movement (cilia: short/numerous, flagella: long/few)
Centrioles: microtubules, critical for cell division
Magnification
Formula:
Total Magnification = Ocular Lens × Objective Lens
Ocular lens = 10×
Low: 4× → 40×
Medium: 10× → 100×
High: 40× → 400×
Eyepiece (Ocular Lens):
Lens you look through; 10× magnification
Objective Lenses:
Main magnifying lenses (4× low, 10× medium, 40× high)
Revolving Nosepiece:
Holds objectives; rotates to change magnification
Stage:
Flat platform that holds the slide
Stage Clips:
Secure the slide on the stage
Diaphragm:
Controls how much light passes through the specimen
Condenser Lens:
Focuses light onto the specimen
Lamp / Light Source:
Provides light
Coarse Adjustment Knob:
Large focus movements (LOW power only)
Fine Adjustment Knob:
Small, precise focus (medium & high power)
Arm:
Supports upper parts; used to carry microscope
Base:
Bottom support; keeps microscope stable
Tube:
Keeps eyepiece and objectives at correct distance
What is the Cell Cycle?
The cell cycle is the series of stages a cell goes through to grow, copy its DNA, and divide into two new cells.
Why Do Cells Divide?
Growth – more cells make tissues and organisms bigger
Healing & Repair – replace damaged or dead cells (cuts, bruises)
Reproduction – create new cells
Main Parts of the Cell Cycle
There are 4 main sections. Most of the time is spent in interphase.
1⃣ G1 Phase (Growth Phase)
Cell grows
Performs normal functions
Makes proteins and organelles
~50% of the cycle
2⃣ S Phase (DNA Replication)
DNA is copied
Each chromosome is duplicated
~33% of the cycle
3⃣ G2 Phase (Second Growth Phase)
Cell grows more
Prepares for division
Checks DNA for errors
~12% of the cycle
➡ Interphase = G1 + S + G2
4⃣ M Phase (Cell Division)
Includes mitosis and cytokinesis
DNA and organelles are divided evenly
Produces 2 identical daughter cells
~5% of the cycle
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Happens when a cell is damaged or no longer needed
Prevents damaged cells from becoming harmful (ex: cancer)
DNA Terminology
Chromatin
Uncondensed / uncoiled DNA
Thread-like appearance
Found when the cell is not dividing (interphase)
Chromosome
Condensed / tightly coiled DNA
Visible during cell division
Often appears X-shaped
Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome
Sister Chromatids
Two identical chromatids
Joined together at a centromere
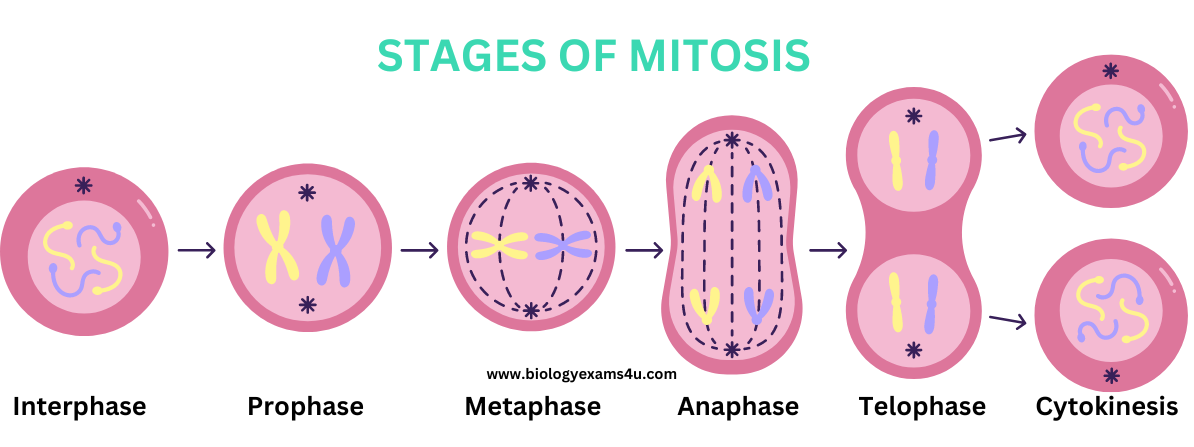
Stages of Mitosis
(Remember: I Party Mainly At The Club)
1⃣ Prophase (Condensation)
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
Nuclear membrane dissolves so chromatids can separate
Centrioles migrate to poles
Spindle fibers form and attach to centromeres
Sometimes divided into early and late prophase
2⃣ Metaphase (Line Up)
Chromosomes line up at the equatorial plate (middle of cell)
Sister chromatids face opposite directions
Centrioles reach poles
Spindle fibers ensure proper alignment
3⃣ Anaphase (Separation)
Sister chromatids separate at centromere → now called single-stranded chromosomes
Pulled to opposite poles by spindle fibers
4⃣ Telophase (Daughter Cell Formation)
New nuclei form around separated chromosomes
Spindle fibers disappear
Cytokinesis occurs:
Animal cells: cell pinches in half
Plant cells: new cell wall
Result: 2 identical daughter cells
Cells return to G1 phase of interphase
Why is Mitosis Needed?
To produce 2 identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.
Ensures each new cell has a complete copy of DNA and enough organelles to function.
Needed for:
Growth – making more cells for tissues and organisms
Healing & Repair – replacing damaged or dead cells
Reproduction – creating new cells
1. What is Cancer?
Group of diseases where cells grow and divide out of control.
Occurs when DNA controlling the cell cycle is mutated.
At least one checkpoint fails, so cells don’t stop dividing.
Causes of Cancer
Mutations in DNA controlling cell division
Carcinogens: tobacco, UV & X-ray radiation, some viruses (HPV)
Hereditary factors: increase risk but not guarantee
Random mutations
3. Tumours
Mass of abnormal cells that don’t perform normal functions.
Types:
Benign: harmless, don’t spread, can crowd nearby cells.
Malignant: cancerous, invade tissues, can metastasize (spread to other parts).
6. Treatments of Cancer
Surgery
Removes cancer tissue physically
Pros: may remove entire tumour
Cons: may not work if spread, near vital organs
Radiation Therapy
Focused radiation damages DNA of cancer cells
Pros: effective at stopping division
Cons: can harm healthy cells, side effects, possible secondary cancer
Chemotherapy
Drugs stop division or kill cancer cells
Pros: works if cancer has spread
Cons: toxic to healthy cells (hair loss, nausea, fatigue)
Newer Treatments:
Personalized Medicine: genetic info used to target treatment
Biophotonics: uses light to detect & treat cancer precisely
Oncolytic Virotherapy: viruses designed to attack cancer cells
Cytosponge: capsule collects esophagus cells for early detection
What are Stem Cells?
Undifferentiated cells (no specific job yet)
Rare and valuable for growth and repair
Purpose of Stem Cells
Replace or regenerate damaged tissues
Grow new cells for organs and body parts
Used in medicine for: cancer, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, strokes, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis
3. Where Stem Cells Are Found
Umbilical cord blood – safe, after birth, discarded cord
Adult tissues – bone marrow, liver, fat; limited differentiation
Embryos – harvested around day 5 after conception; can become any cell type
Plant stem cells: called meristematic cells, found in roots and shoots, continuously make new cells
Importance of Stem Cells
Basis for cellular differentiation → specialized cells like muscle, nerve, blood, bone, skin
Critical for regeneration (e.g., liver, skin, fingertip in humans)
Potential for organ regeneration could change healthcare, economy, and politics
Stem Cells in Plants
Called meristematic cells
Found in roots and shoots
Continuously produce new cells for growth and repair
Stem Cell Controversy
Early stem cell research used embryonic stem cells, often taken from unused embryos from IVF treatments
Ethical concerns arose because obtaining these cells destroys the embryo
In 2006, scientists developed induced pluripotent stem cells where adult cells are reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells, reducing ethical concerns
Levels of Organization of an Organism
Cell – Basic unit of life; carries out all life processes
Tissue – Group of similar cells working together for a specific function
Organ – Structure made of different tissues working together to perform a job
Organ System – Group of organs working together to carry out a major function
Organism – Entire living thing; all organ systems working together
4 Types of Animal Tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Function: Covers body surfaces, lines organs & cavities, protects, absorbs, and secretes
Characteristics: Cells tightly packed, forms continuous sheets, has a free surface
Connective Tissue
Function: Supports, protects, binds other tissues, stores fat, transports substances (blood)
Characteristics: Few cells, lots of extracellular matrix (fibers & fluid)
Muscle Tissue
Function: Produces movement of body or internal organs
Characteristics: Long cells (fibers), can contract, types: skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Nervous Tissue
Function: Transmits electrical signals, coordinates body functions, responds to stimuli
Characteristics: Made of neurons (nerve cells) + supporting cells (glial cells)
Integumentary System
(Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands)
Protects body
Regulates temperature
Prevents water loss
Sensory reception
Digestive System
(Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas)
Breaks down food
Eliminates waste
Liver produces bile; pancreas produces enzymes and insulin
Small intestine absorbs nutrients
Circulatory / Cardiovascular System
(Heart, blood vessels, blood)
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones
Removes wastes
Regulates body temperature
Heart pumps blood; arteries carry oxygenated blood; veins carry deoxygenated blood
Respiratory System
(Nose, trachea, lungs, diaphragm)
Gas exchange (O₂ in, CO₂ out)
Maintains blood pH
Lungs contain alveoli; diaphragm helps breathing
Muscular System
(Skeletal muscles, tendons)
Movement, posture, heat production
Works with skeletal system; skeletal muscles contract to move body parts
Skeletal System
(Bones, cartilage, ligaments, joints) – Supports & protects organs, produces blood cells, stores minerals, allows movement
Excretory / Urinary System
(Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra) – Removes wastes, regulates water & salt balance
Nervous System
(Brain, spinal cord, nerves) – Controls body functions, responds to stimuli, coordinates other systems
Endocrine System
(Glands: thyroid, adrenal, pituitary, pancreas) – Produces hormones regulating growth, metabolism, reproduction, homeostasis
Reproductive System
(Ovaries, testes, uterus, penis, vagina) – Produces gametes, supports offspring development
Immune / Lymphatic System
Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, lymph vessels) – Protects from infection, transports lymph, removes toxins/pathogens
key differences between the organ systems of a human, frog and earthworm.
Humans
Most complex organ systems
Circulatory: 4-chambered heart
Respiratory: lungs only
Digestive: stomach, liver, pancreas
Excretory: kidneys filter blood
Frogs
Similar systems to humans but simpler
Circulatory: 3-chambered heart
Respiratory: lungs and skin
Digestive: shorter digestive tract
Excretory: waste exits via cloaca
Earthworms
Simplest organ systems
Circulatory: closed system with aortic arches
Respiratory: diffusion through skin
Digestive: long, segmented tube
Excretory: nephridia in each segment for waste removal
Homeostasis:
The process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment (temperature, water balance, pH, etc.) despite changes outside the body.
Interdependence of organ systems:
Organ systems rely on each other to function properly; one system failing can affect others.
Importance of homeostasis:
Keeps cells and tissues working efficiently
Prevents illness or death
Allows the organism to survive in changing environments
Examples of interdependence:
Respiratory & Circulatory: The lungs bring in oxygen, which the blood carries to all cells; the circulatory system also carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs for removal.
Digestive & Circulatory: The digestive system breaks down food into nutrients, which the circulatory system delivers to cells for energy and growth.
X-Ray
How it works: High-energy radiation passes through body; absorbed by dense materials like bones.
Medical info: Shows broken bones, lung/heart problems, detects some cancers.
Pros/Cons: Quick, painless, non-invasive / Radiation can harm DNA.
Fluoroscopy
How it works: Continuous X-ray beam; contrast dye may be used.
Medical info: Real-time organ movement; blood vessels (angiograms).
Pros/Cons: See organs in motion / Radiation exposure; dye can cause reactions.
Ultrasound
How it works: Sound waves reflect off organs → images on screen.
Medical info: Fetus development, soft tissues, heart, guiding biopsies.
Pros/Cons: Safe, no radiation, real-time / Cannot see through bone or gas
CT Scan
How it works: Multiple X-rays from different angles → computer creates 3D image.
Medical info: Bones, soft tissues, blood vessels; detects bleeding, cancer, injuries.
Pros/Cons: Quick, detailed / Radiation exposure.
MRI
How it works: Magnets + radio waves interact with hydrogen atoms → detailed images.
Medical info: Brain, heart, liver, soft tissue, inside bones; detects cancer & diseases.
Pros/Cons: Very detailed, no radiation / Expensive, can feel confined.
Nuclear Medicine
How it works: Radioisotopes absorbed by tissues → camera detects radiation → image.
Medical info: Organ function, cancer detection, blood circulation.
Pros/Cons: Functional info, can treat some cancers / Radiation exposure.
PET Scan
How it works: Radioisotopes emit positrons; often combined with CT for detailed view.
Medical info: Detects cancer, heart disease, brain disorders.
Pros/Cons: Shows function and structure / Expensive, radiation exposure.
Immunization
Definition: Process of making a person immune to a disease.
Purpose: Helps prevent infection and spread of diseases in the community
Vaccine
Definition: Substance that stimulates the immune system to produce immunity.
Types:
Live attenuated: Weakened germ
Inactivated: Killed germ
Subunit: Part of the germ
Toxoid: Immunity to a toxin produced by the germ
Why yearly vaccines?
Some diseases (like influenza) mutate each year.
Immunity can wane over time, so yearly shots keep protection up to date.
Examples of Routine Vaccines in Ontario:
MMR (measles, mumps, rubella), HPV, polio, tetanus, whooping cough, meningitis
Public Health Units
Protect community health and prevent disease spread.
Roles: Vaccinations, health education, screening programs, outbreak control.
Health Education & Screening
Examples: HIV awareness, nutrition programs, mammograms, Pap tests, colorectal screening.
Benefits: Early detection, disease prevention, better health outcomes.
Pandemic Response Example (COVID-19)
Measures: Borders closed, business closures, PPE, testing, social distancing, hand washing.
Purpose: Slow disease spread, prevent healthcare overload, reduce deaths.
Other Public Health Tips
Healthy diet, exercise, avoid smoking, UV protection, vaccines, participate in screening programs.