B1- cell level systems
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
what is the light microscope used for?
-viewing whole cells and large subcellular structures
explain process of using light microscope
specimen placed on glass slide, covered with a cover slip and placed on the stage, eye piece and objective lens magnify the object and lamp illuminates from underneath
what is the electron microscope used for?
viewing cells in detail, use a beam of electrons.
explain how you use an electron microscope
specimen is placed in a vacuum chamber/ electromagnets are used instead of lenses, picture is projected onto a TV screen
what is a stain?
can be used to colour cells to make them easier to see.
what is resolution?
ability to distinguish 2 or more objects
what is the equation for magnification?
magnification= size of image/ actual size
what are the subcellular structures found in animal cells?
nucleus, ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria
what are the subcellular structures found in plants?
nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, mitochondria, vacuole, chloroplasts
nucleus?
controls cell and contains genetic material in form of chromosomes
cytoplasm?
most chemical reactions take place
cell membrane?
barrier that controls passage of substances going in and out of cells, contains receptor molecules
mitochondria?
contains enzymes for respiration and is the site of respiration
ribosomes?
make proteins for cell using protein synthesis
cell wall?
made from cellulose and for structural support
vacuole?
contains cell sap, provides structure
chloroplasts?
contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis
what is a prokaryotic cell?
cell without a nucleus contains a loop of DNA instead (plasmid)
what other structures does a prokaryotic cell contain?
flagellum- for movement
ribosomes
cell membrane + wall (some)
cytoplasm
what is a eukaryotic cell?
contain a nucleus eg. animal and plant cells
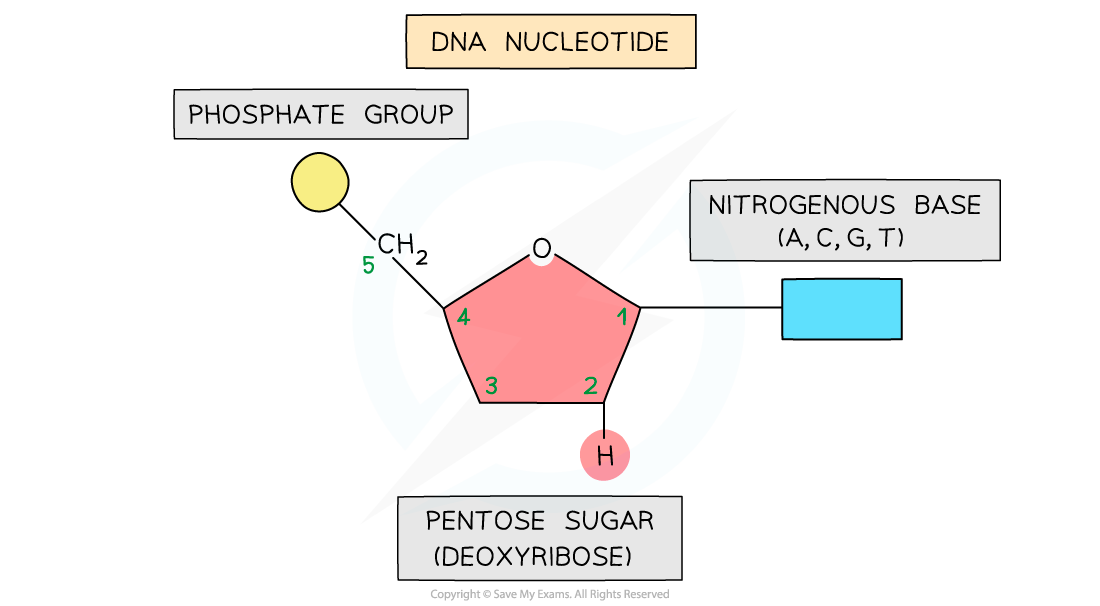
what is DNA?
DNA is a polymer made up of repeating units called nucleotides in two strands from nucleic acid that join up to form a double helix structure.
what is the structure of a nucleotide?
what is an enzyme?
it is a biological catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions
it’s made from proteins and amino acids which can be folded for the substrate to fit into
what is the active site?
part of enzyme where only a substrate with specific shape can fit into
what is the lock and key hypothesis?
substrate joins onto active site of enzyme
substrate fits into active site
substrate is broken down into products and enzyme can be reused
what do high temperatures cause?
increases activity of enzyme
it will work best once it reaches the optimum temp- usually at 37 degrees
if it gets any hotter, the active site will denature (change shape) and substrate can’t be catalysed
how does the pH affect enzymes?
if it changes away from the optimum, it will cause the enzyme to denature
what does amylase do?
breaks down starch into maltose
what does protease do?
breaks down proteins into amino acids
what does lipase do?
turns lipids (fats) into glycerol and fatty acids
what does carbohydrase do?
turn carbohydrates into glucose
what is aerobic respiration?
respiration containing oxygen
an exothermic reaction, happens in all plants and animals, mostly in mitochondria
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide +water
what is anaerobic respiration?
respiration without oxygen, only happens in emergencies
glucose = lactic acid
how does anaerobic respiration happen?
when your exercising and your body can’t supply enough oxygen to your muscles, so you start anaerobic respiration as there is an oxygen debt so it must be paid back to remove lactic acid in cells- causing heavy breathing
anaerobic respiration in plants
glucose = ethanol + carbon dioxide
happens in yeast cells called fermentation
eg. used for bread
what is photosynthesis?
coverts light energy into chemical energy and creates food for a plant
endothermic reaction
where does photosynthesis occur?
in chloroplasts in cells as it contains chlorophyll which attracts sunlight
equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water = oxygen + glucose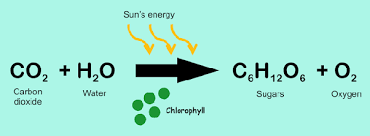
factors that affect photosynthesis?
temperature- higher temperature (30 degrees) speeds up photosynthesis, if it’s too high it can damage enzymes
light intensity- raised, increases photosynthesis
carbon dioxide- increased rate increases photosynthesis
experiment for photosynthesis
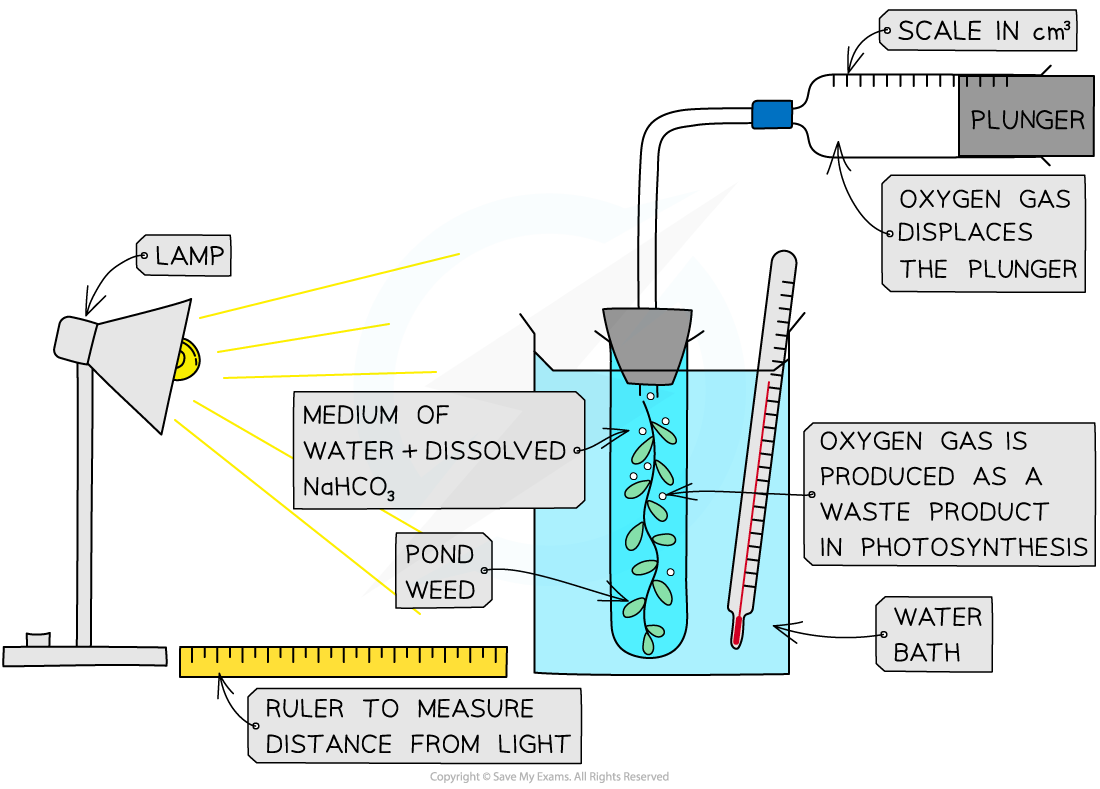
test for starch?
add iodine solution- brown colour to blue/black
test for carbs?
add Benedict’s solution, heat sample, will go from blue to orange/red
test for proteins?
add Biuret solution- light blue to pink/purple
test for lipids/fats?
add ethanol and water, shake sample, turns cloudy from clear solution