Biology 30 UNIT 1 Nervous & Endocrine System
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
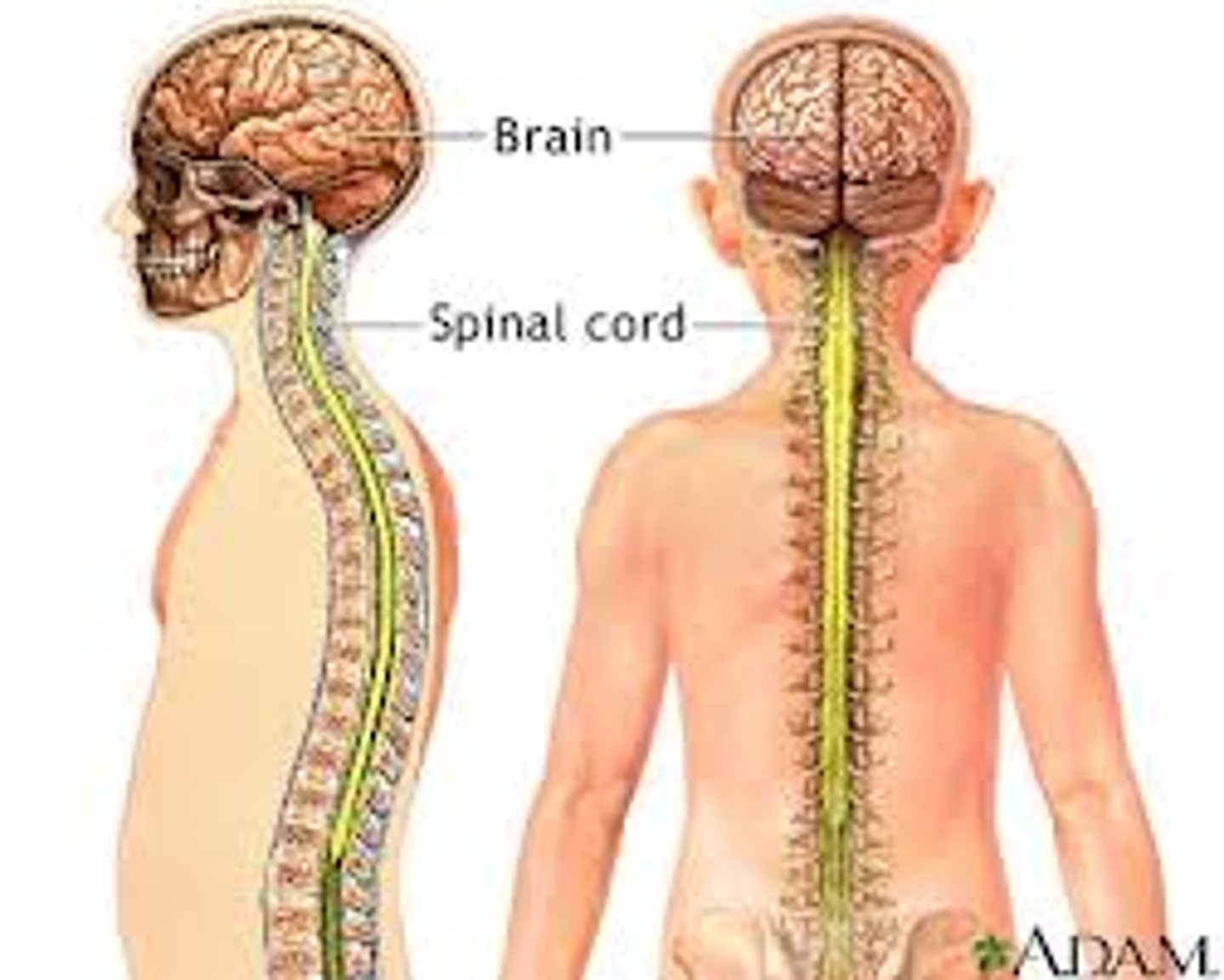
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Used for the body's mechanical and chemical actions.
- Made up of the brain and spinal cord
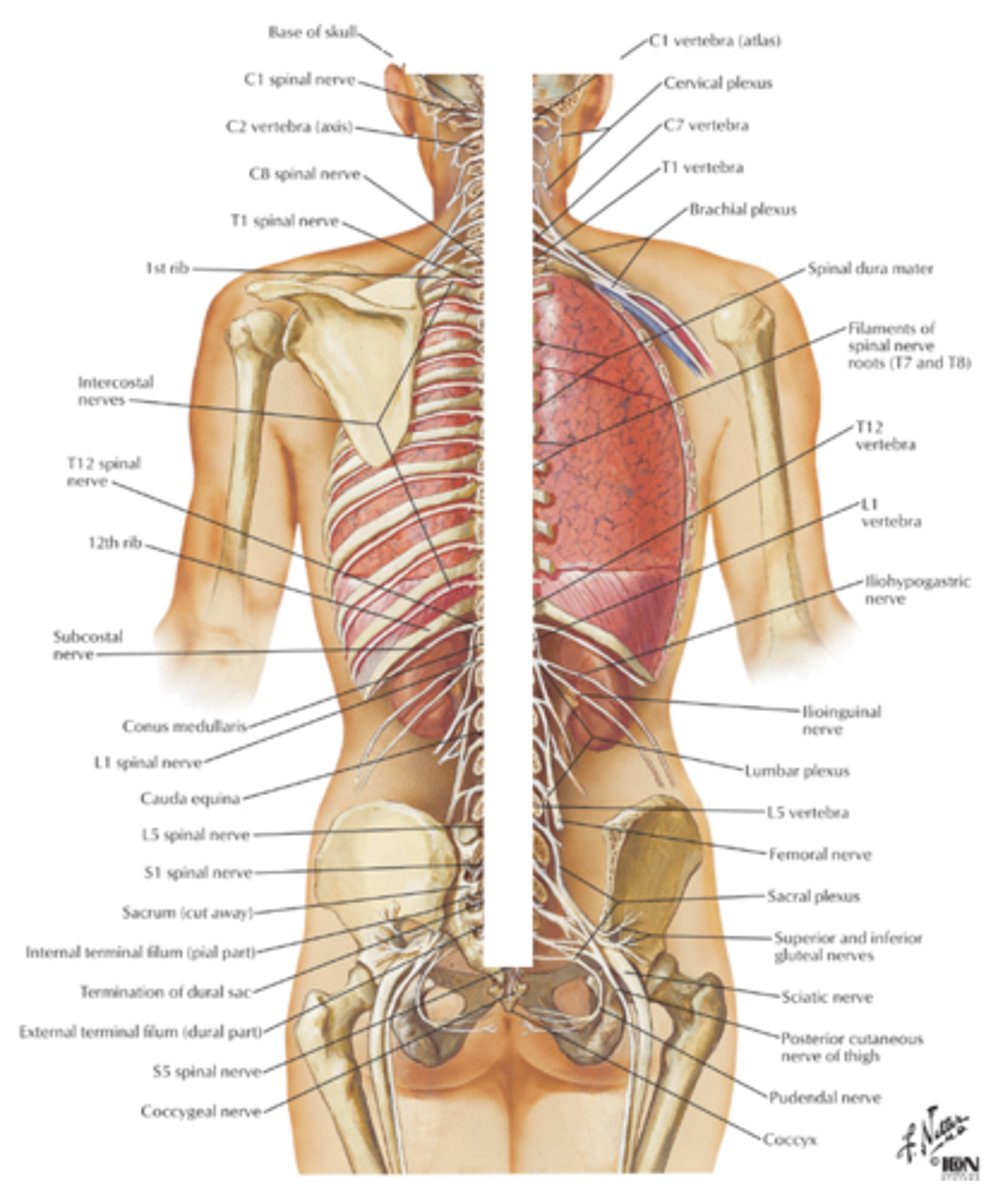
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Relay information between the Central Nervous System (CSN) and other parts of the body
- Excludes the brain and spinal cord
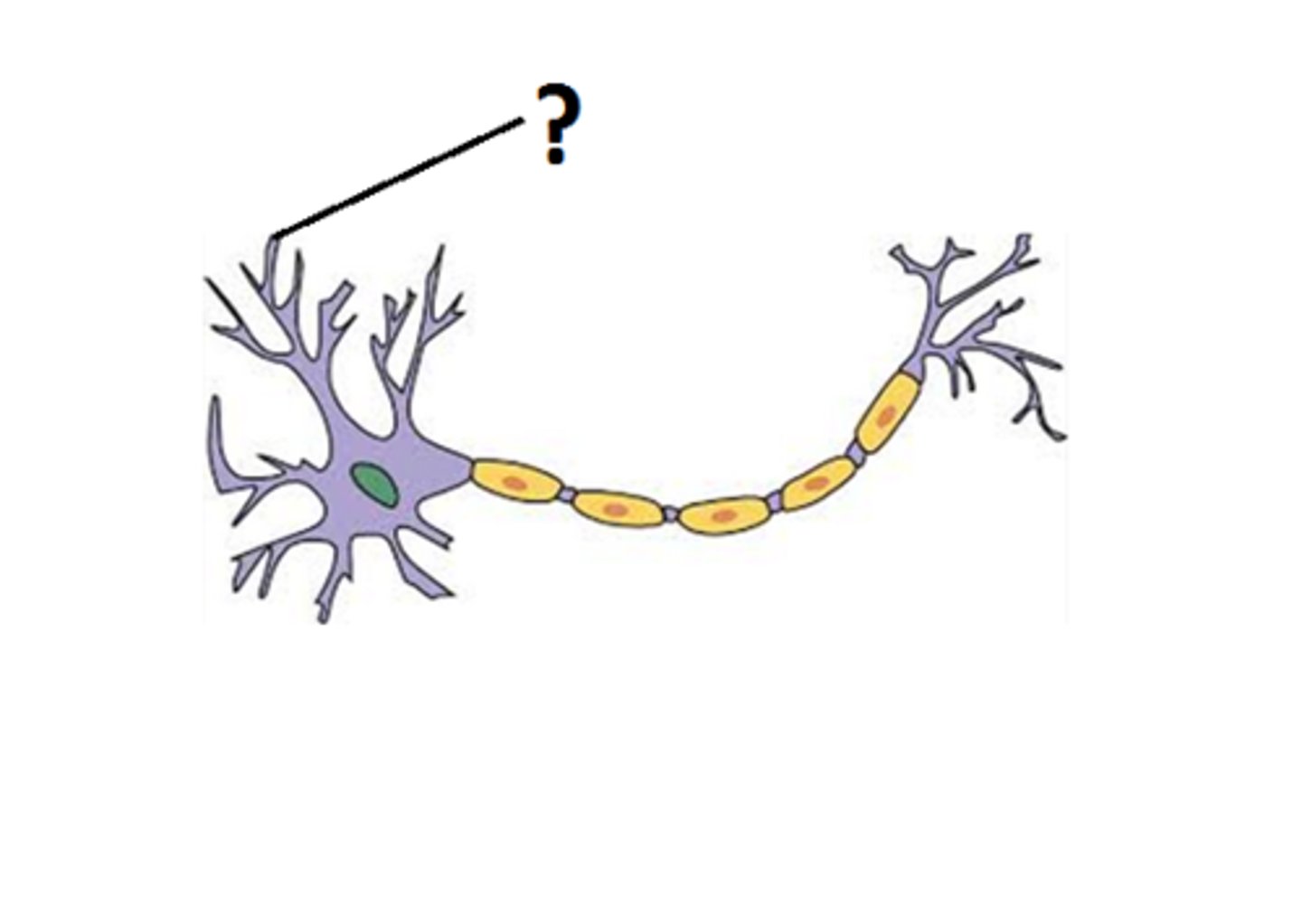
Dendrite
- Projection of cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body
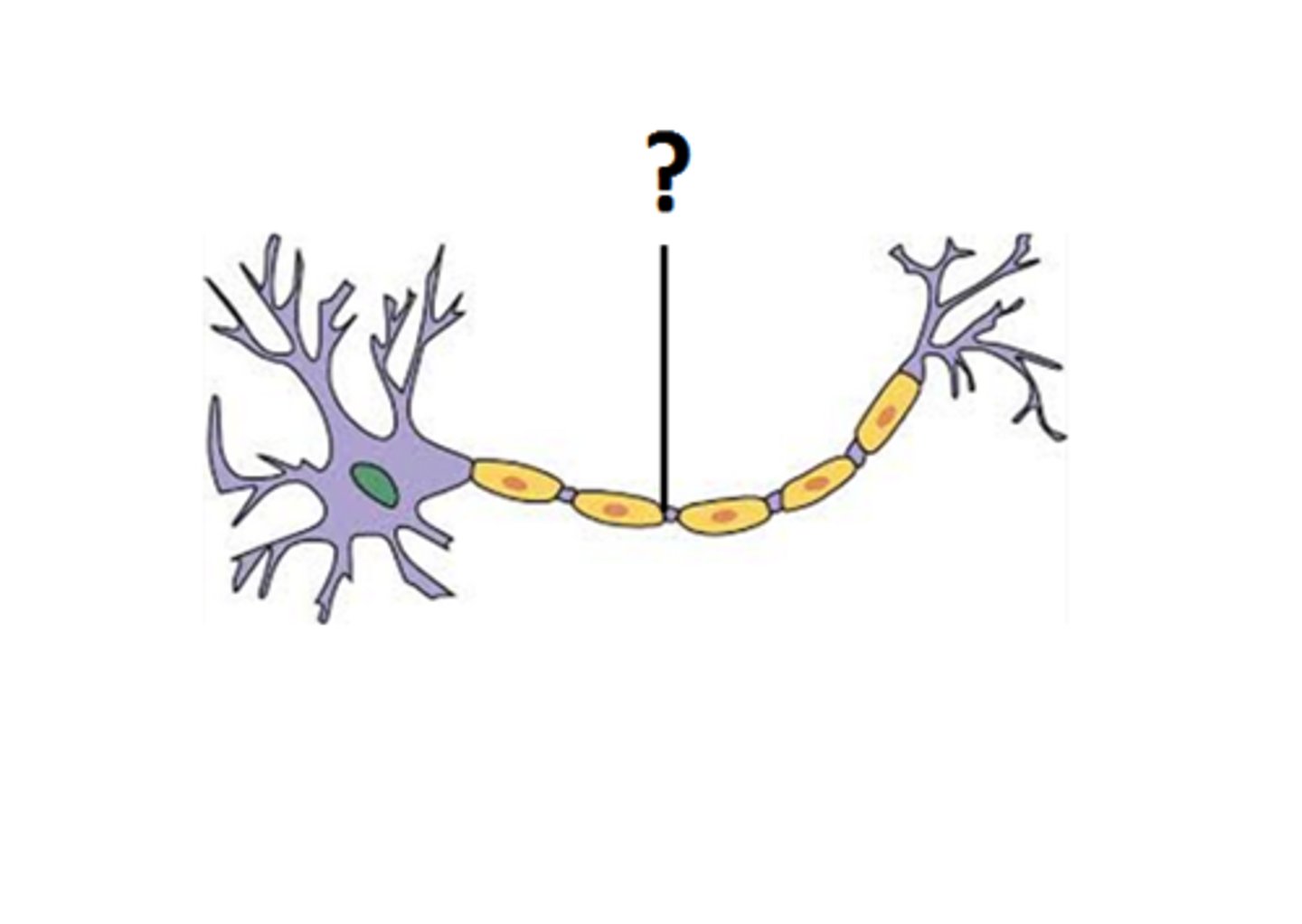
Axon
the extension of cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
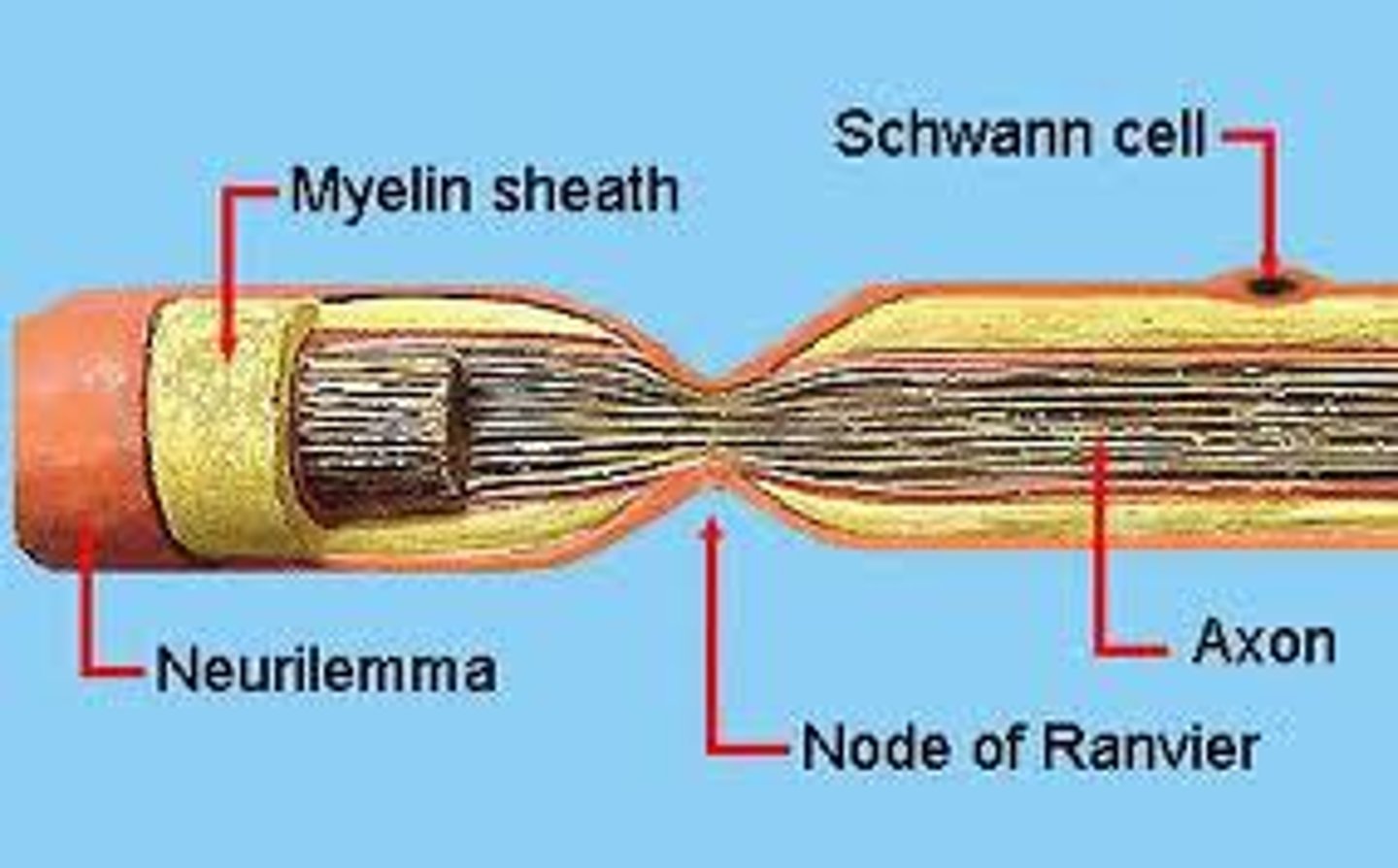
mylein sheath
- Layer of fatty tissue that covers many axons and helps speed neural impulses.
- Insulating covering
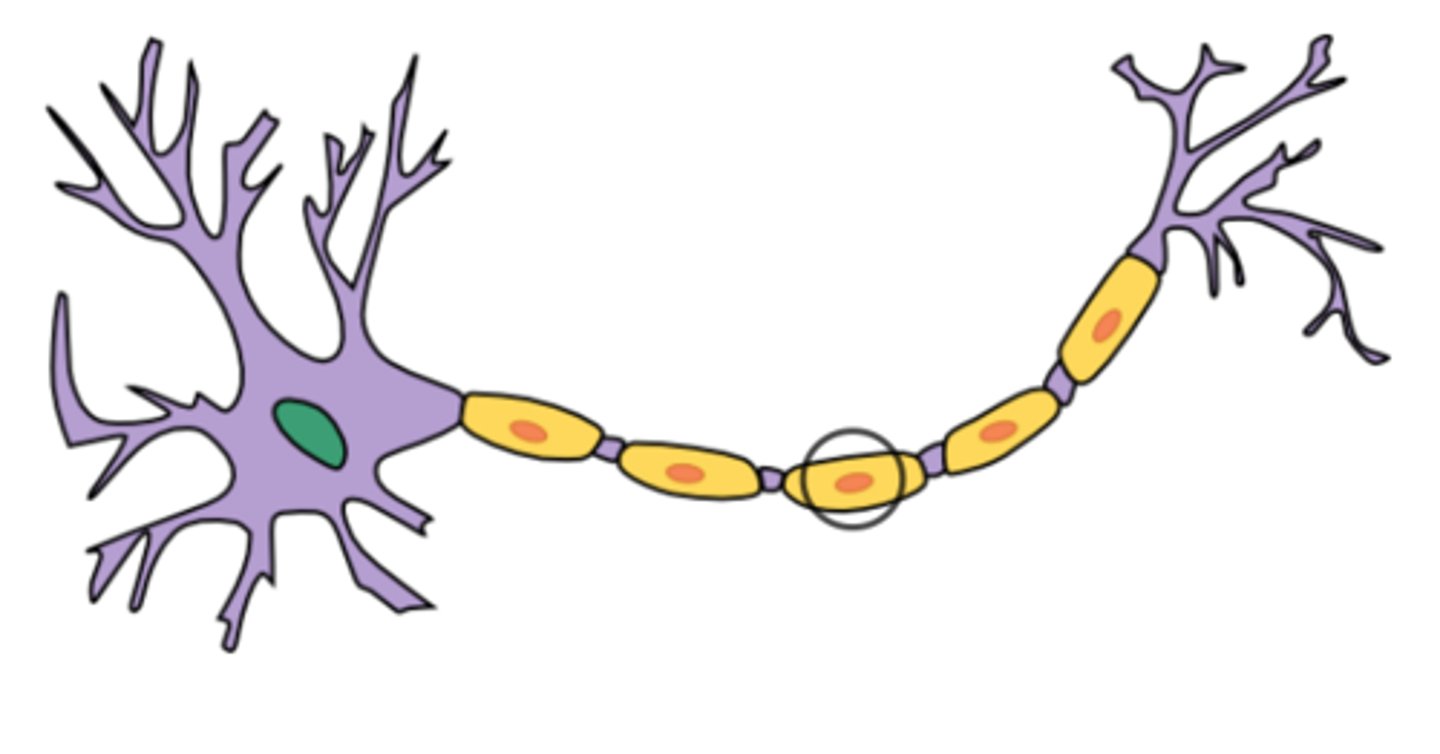
Schwann cells
- Responsible for the formation of myelin sheath.
Nodes of Ranvier
- Gaps along the myelin sheath
- Allows for the message to jump from nodes to node
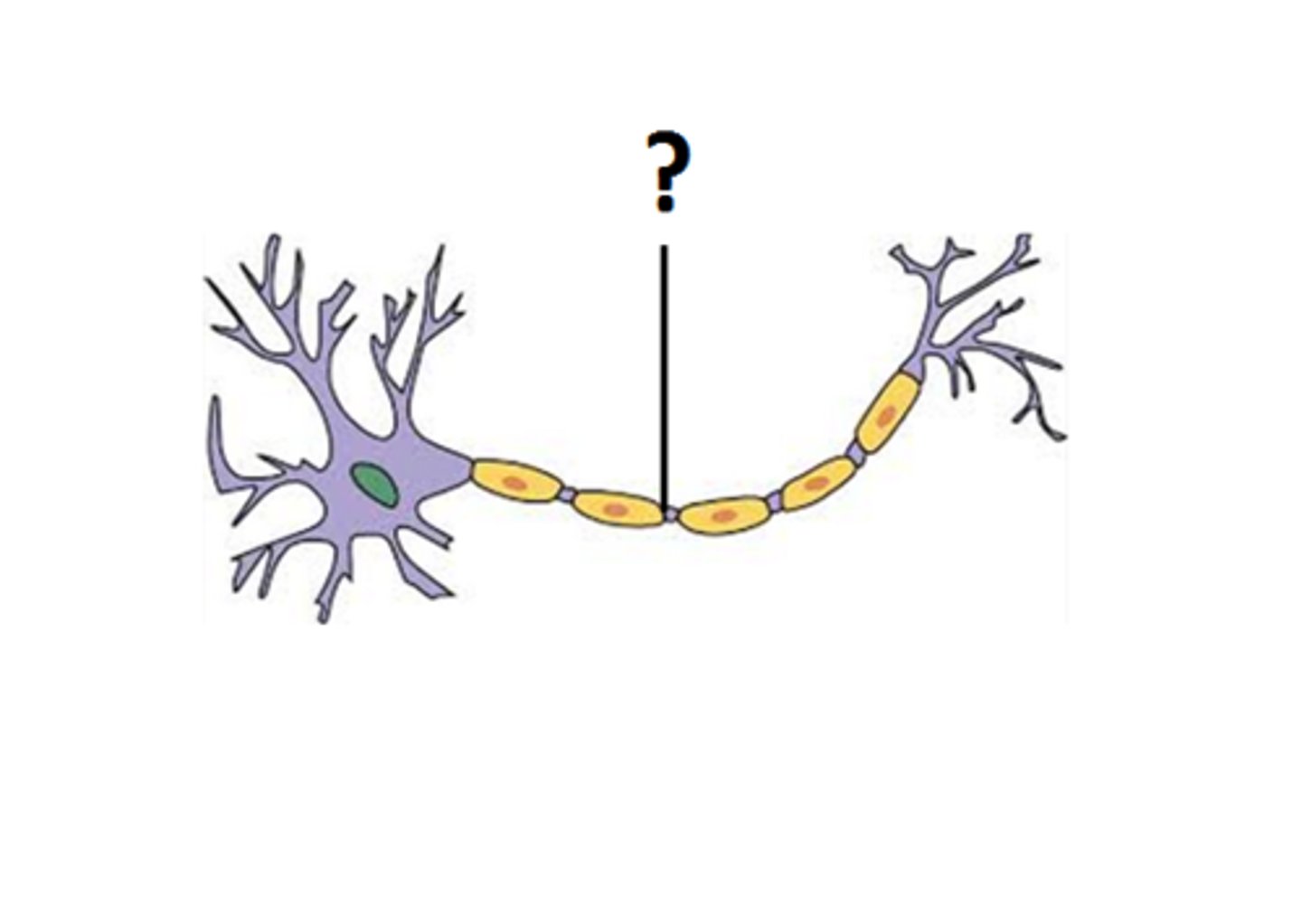
Neurilemma
A layer of cells that encases the axon.
types of neurons in the nervous system
sensory, interneurons, motor
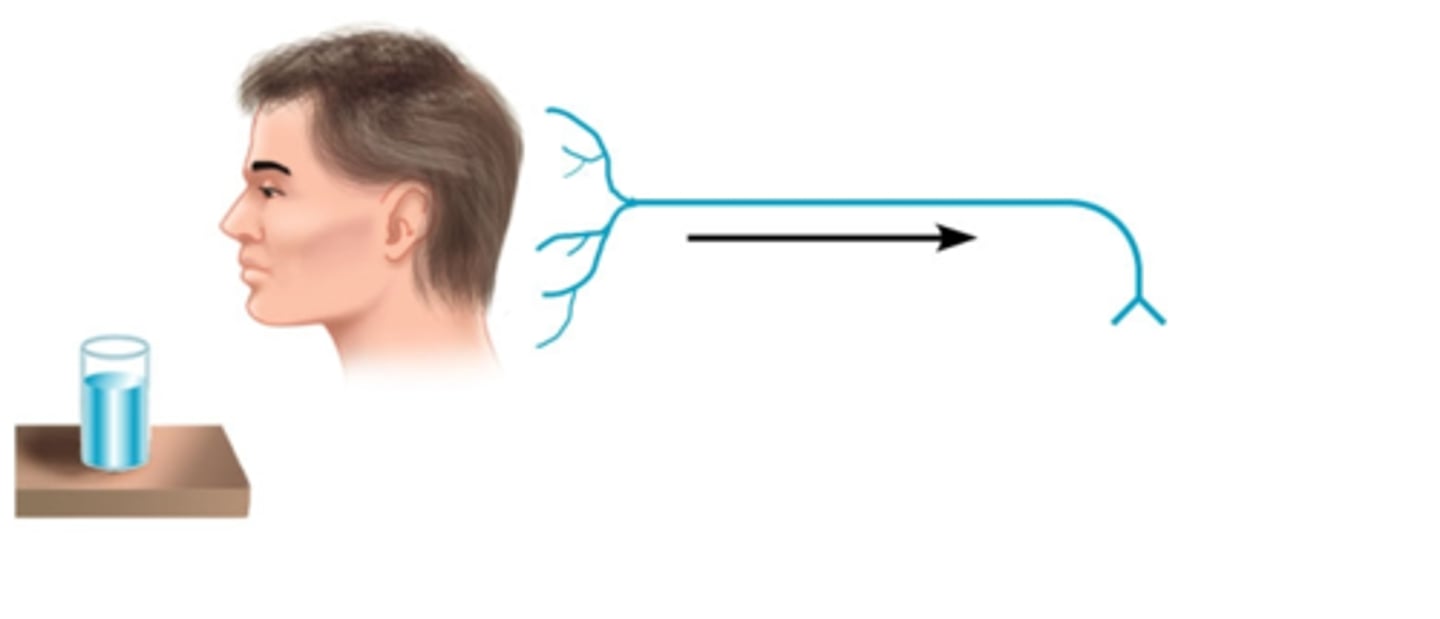
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord (CSN)
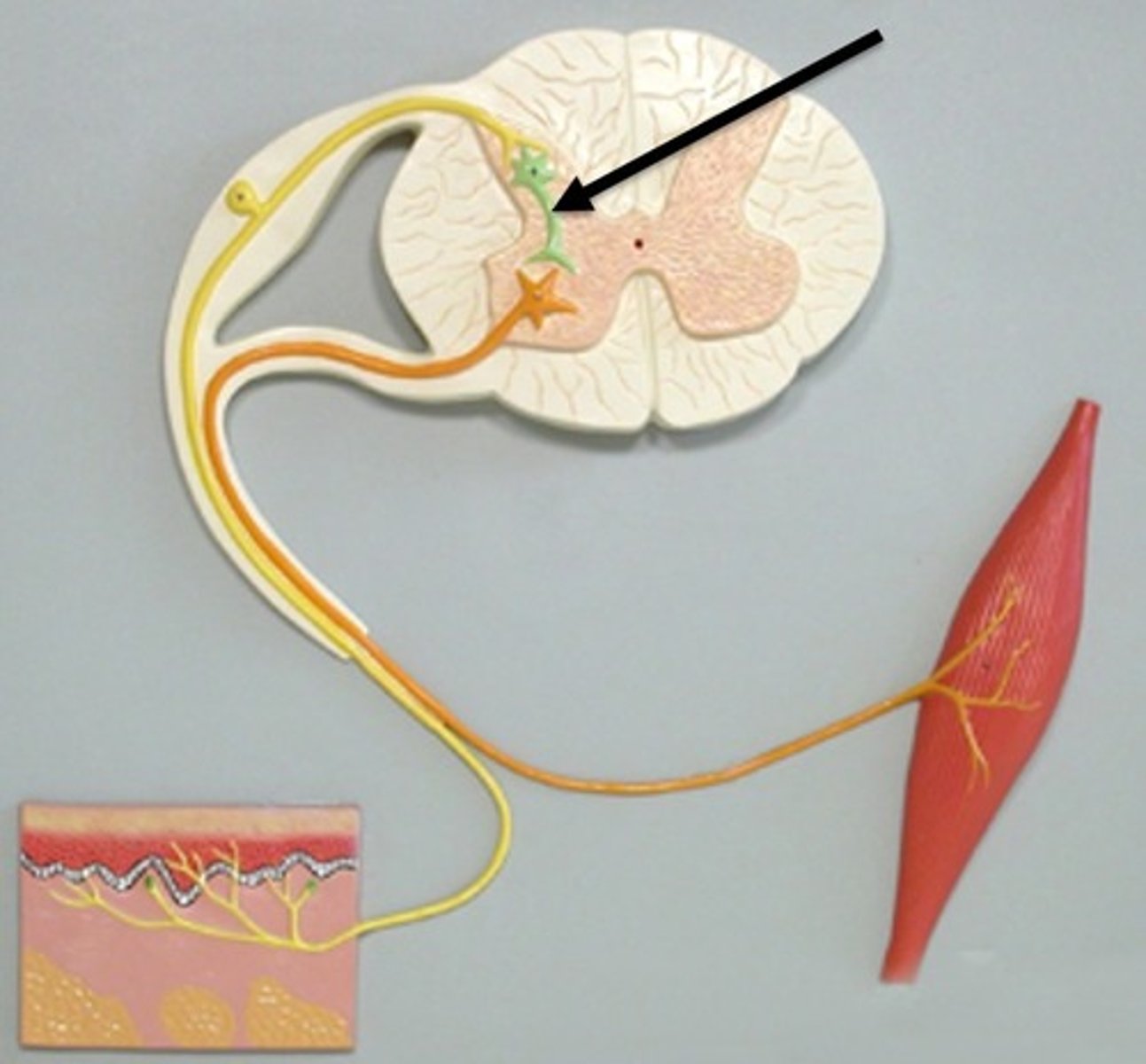
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
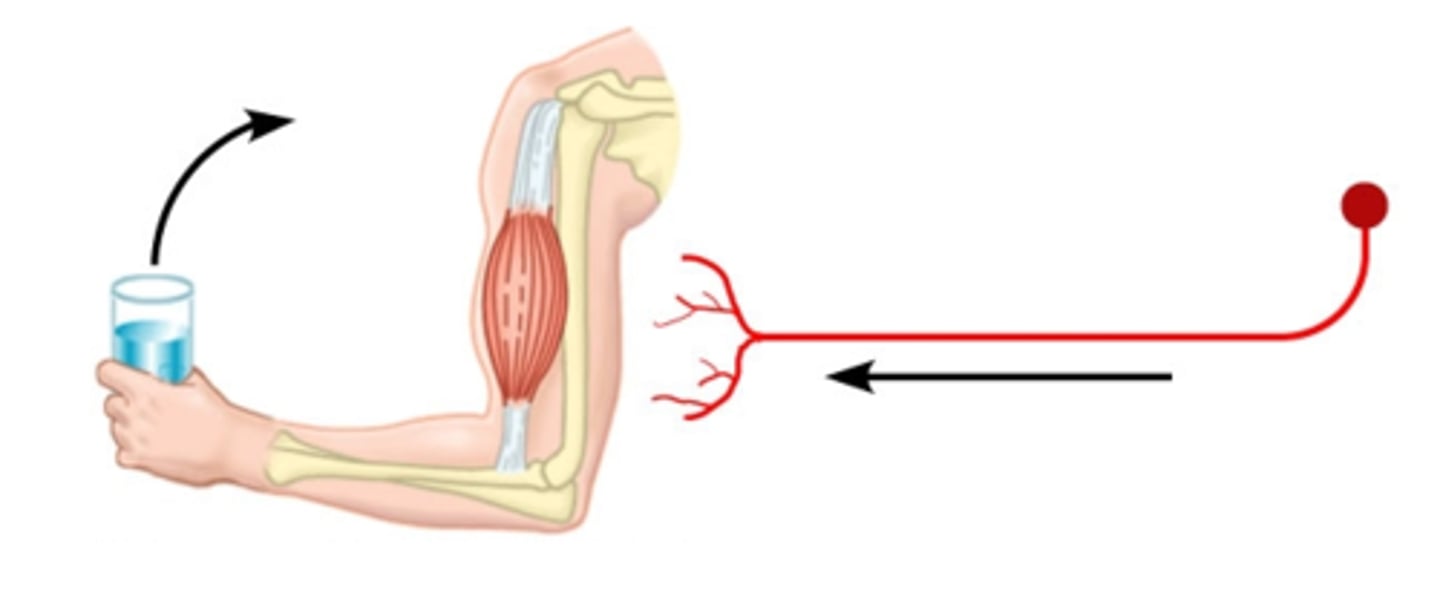
motor neurons
- Neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
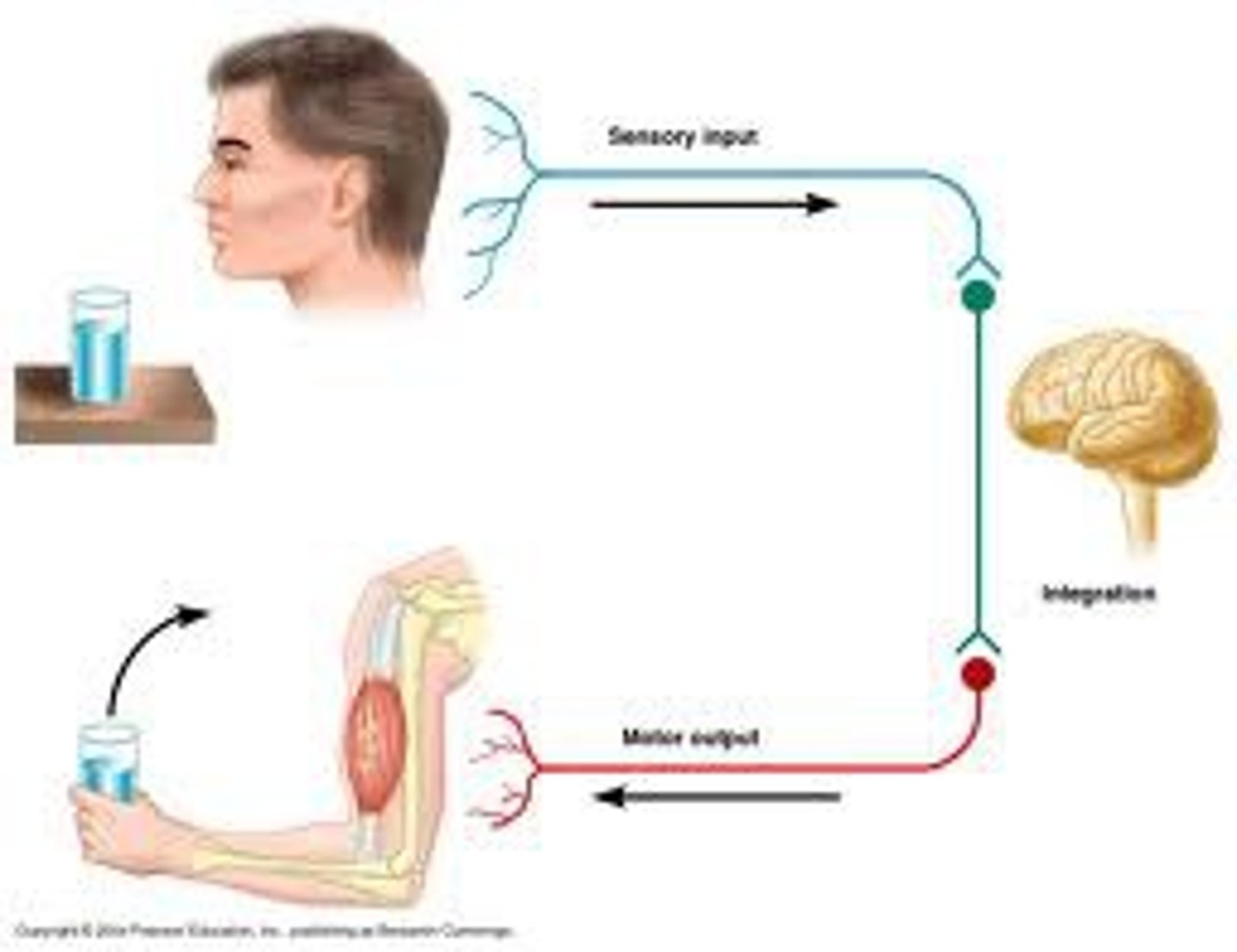
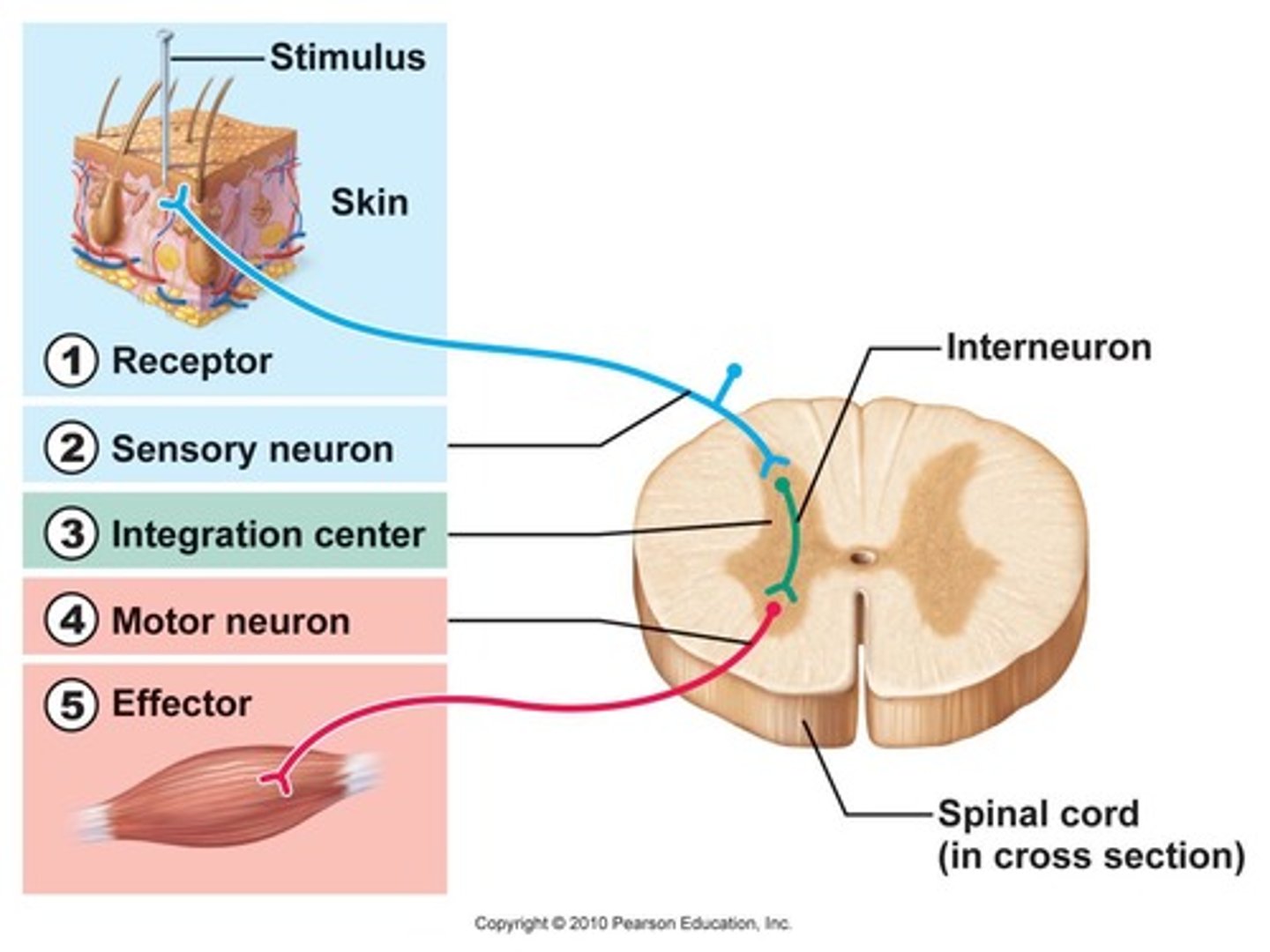
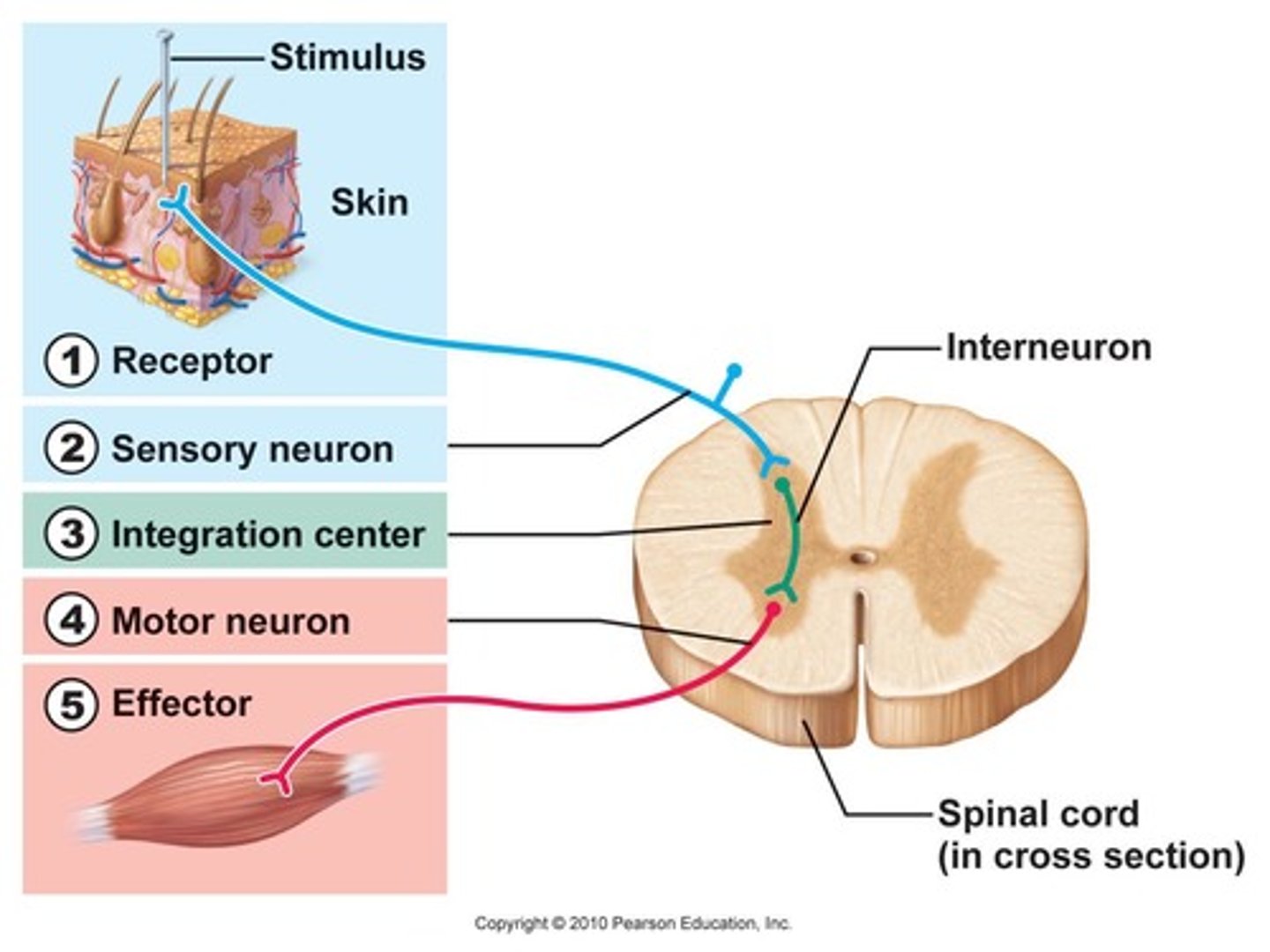
Reflex arc
sensory receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, and effector that are involved in a quick response to a stimulus
DOES NOT INVOLVE THE BRAIN
Why is the reflex arc so fast?
Because it involves very little synapses.
reflex arc components
1. sensory receptor
2. sensory neuron
3. interneuron
4. motor neuron
5. effector
action potential steps
(Rodger Didn't Really Have Raspberries)
1. Resting Potential
2. Depolarization to Threshold
3. Sodium-Channels activated and Rapid Depolarization
4. Inactivation of Sodium Channels and Activation of Potassium Channels
5. Repolarization
6. Hyperpolarization
7. Resting potential
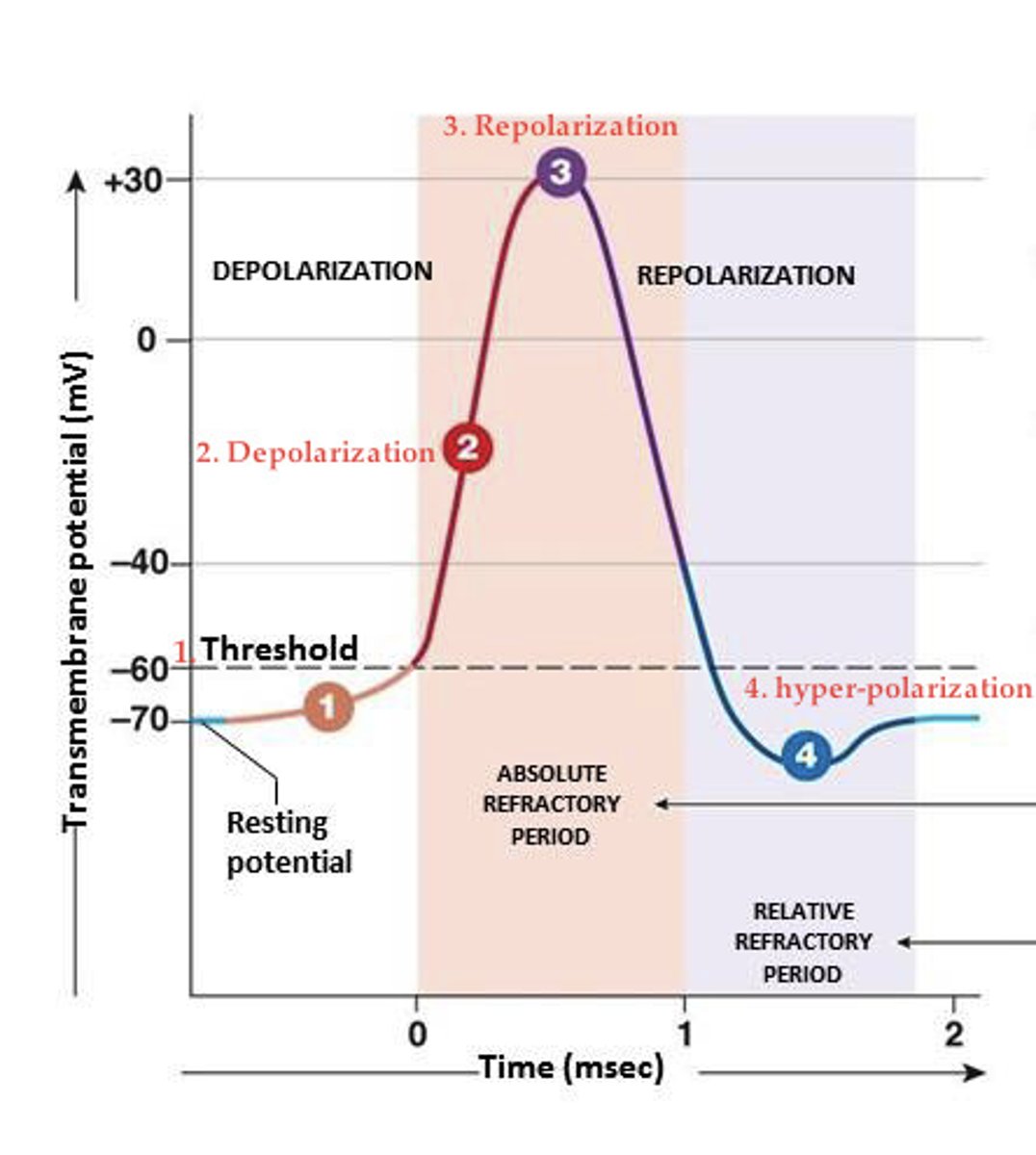
Resting potential
1. Sodium and potassium gated channels are closed
Depolarization
2. Stimulus initiates a graded potential large enough to pass the threshold and open voltage-gated sodium channels
3. Sodium-Channels activated and Rapid Depolarization: sodium rushes into the open channels causing rapid depolarization; inner membrane becomes more positive than negative
4. Inactivation of Sodium Channels and Activation of Potassium Channels: transmembrane potential reaches +30mV which closes the voltage-gated sodium channels and opens the voltage-gated potassium channels, moving them out and shifting the transmembrane potential back to resting levels.
Repolarization
5. The membrane continues to move toward resting levels; sodium channels stay closed, potassium channels stay open
Hyperpolarization
6. Potassium channels remain open and the inside of the cell becomes more negative than resting potential until the voltage reaches -90mV
Refractory period
7. Voltage-gated potassium channels close and transmembrane potential returns to normal due to the sodium-potassium exchange pump. Returns to homeostasis.
The time following an action potential during which a new action potential cannot be initiated
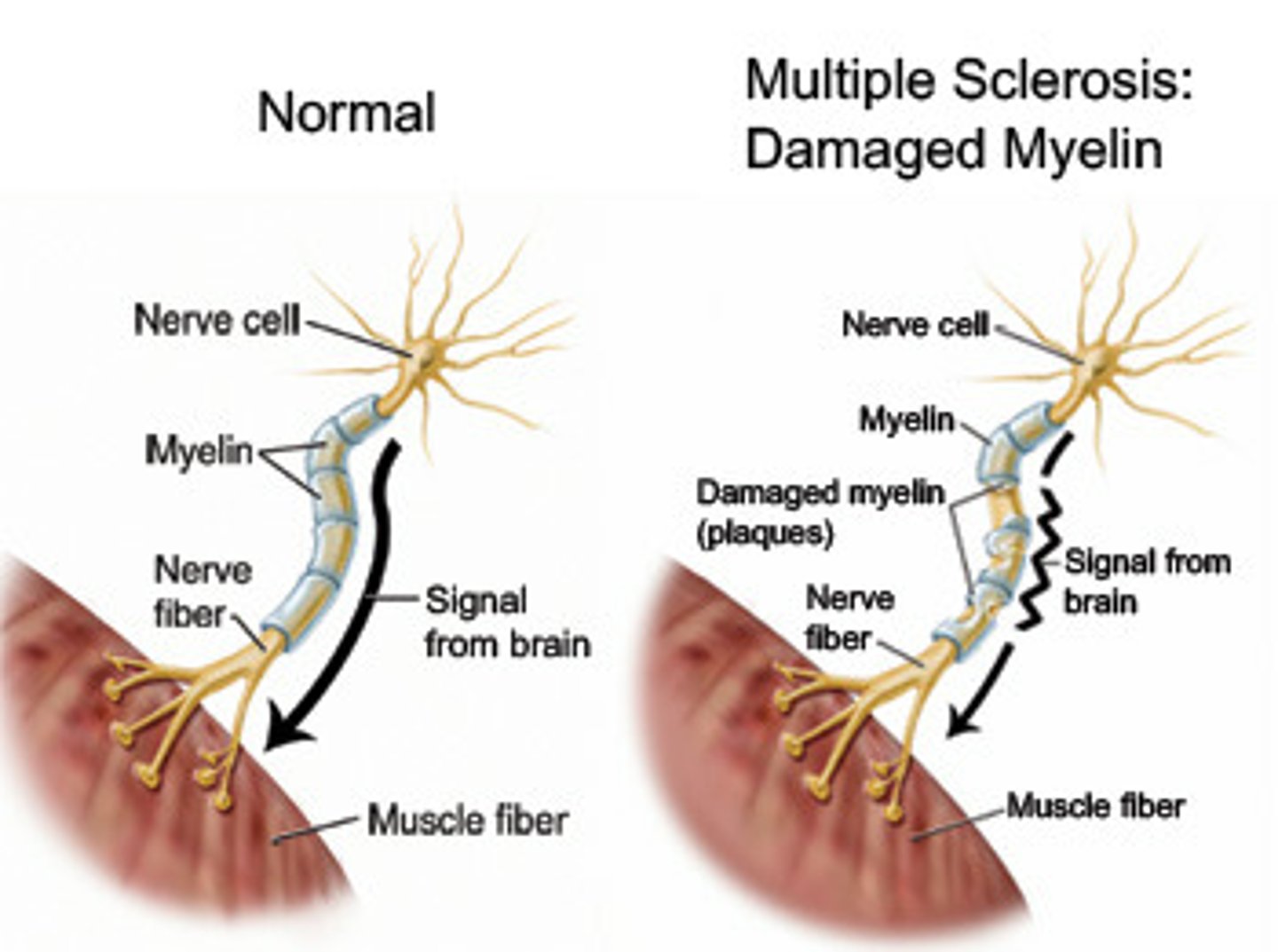
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
destruction of the myelin sheath on neurons in the CNS and its replacement by plaques of sclerotic (hard) tissue
all-or-none response
a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing.
Synaptic transmission process
1. Nerve stimulation depolarizes presynaptic terminals that in turn open neuronal (Ntype)
calcium channels
2. Calcium influx causes fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane;
neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis
3. Diffusion and reversible binding of transmitter with presynaptic (autoreceptors) and
postsynaptic receptors
4. Receptor response (ion channels open or G-proteins activate); generation of postsynaptic
potentials (EPSP/IPSP) or activation of signal transduction pathways
producing cellular or physiological responses
5. Degradation, diffusion and/or presynaptic re-uptake of the transmitter terminates its
action
6. Repolarization of postsynaptic membrane or breakdown of 2nd messengers terminates
the response
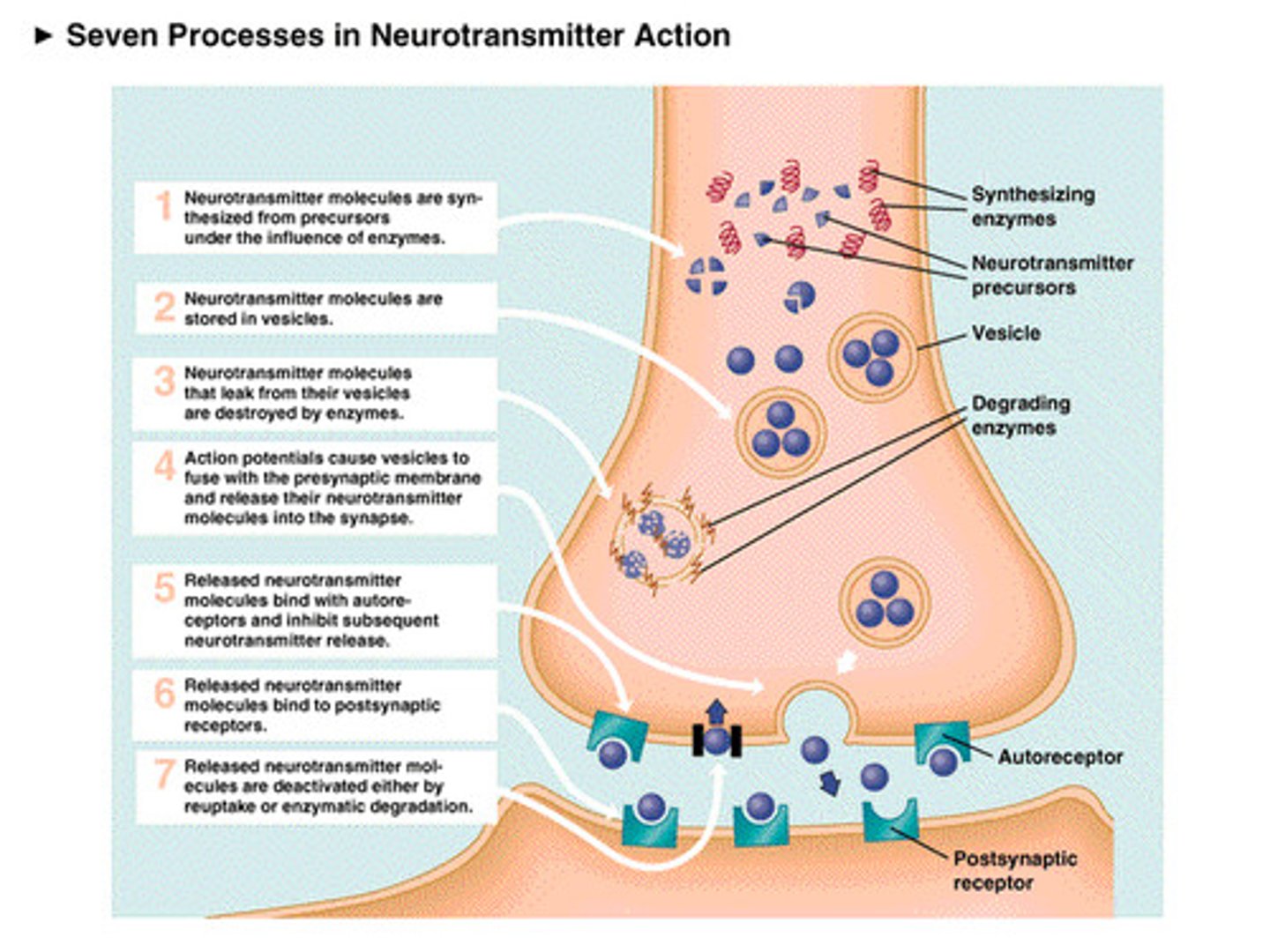
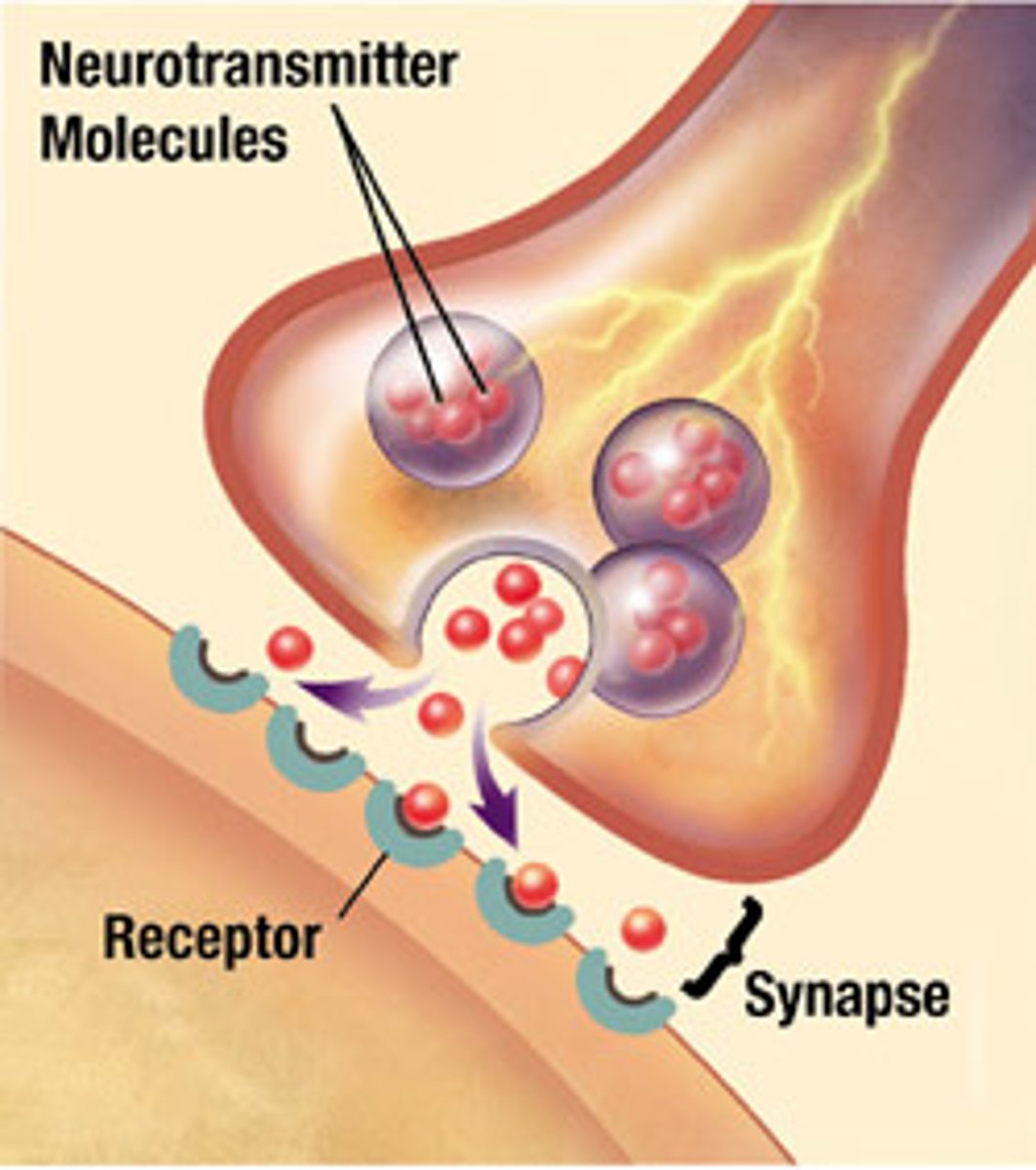
Synapse
Gap between neurons
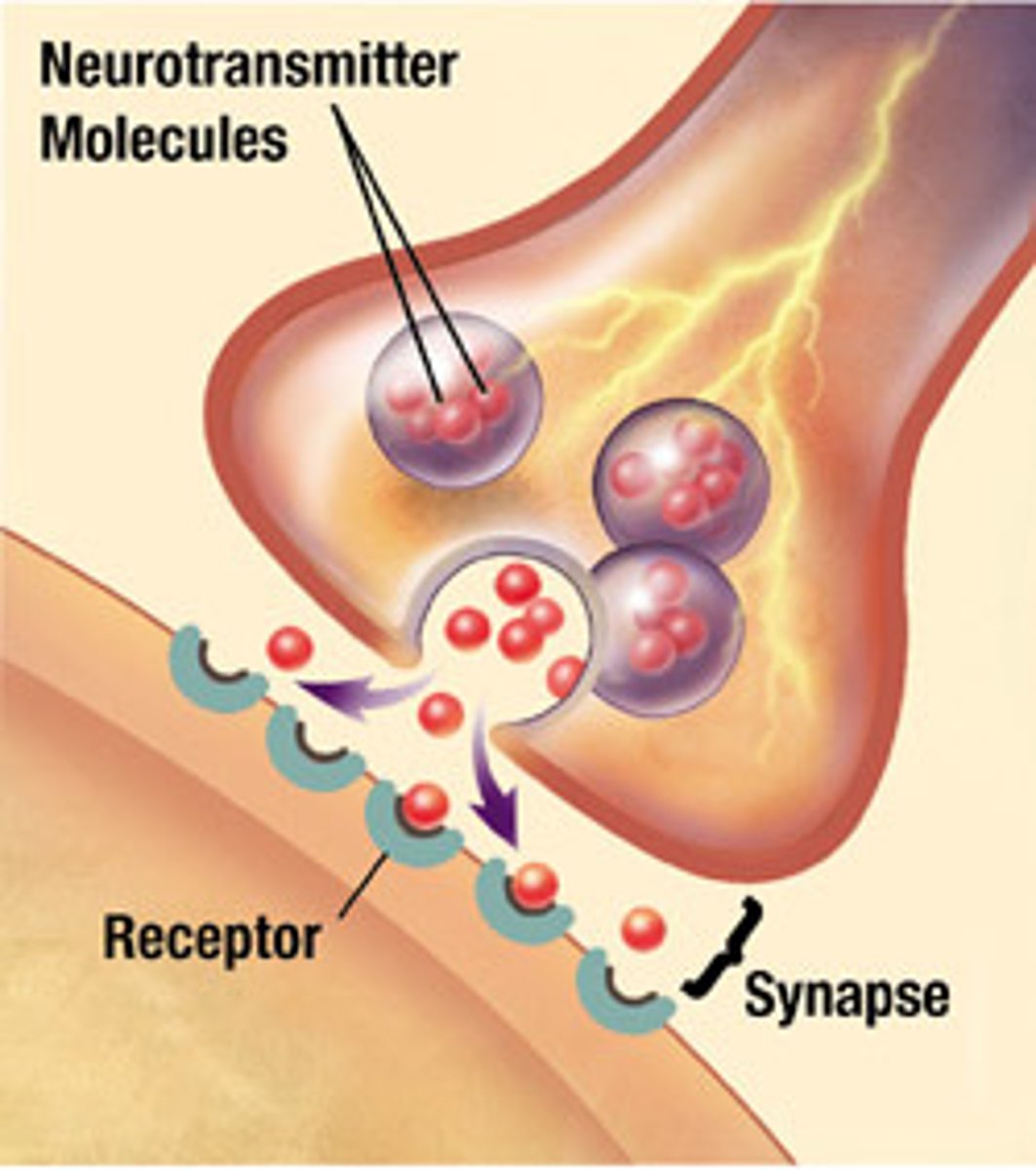
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
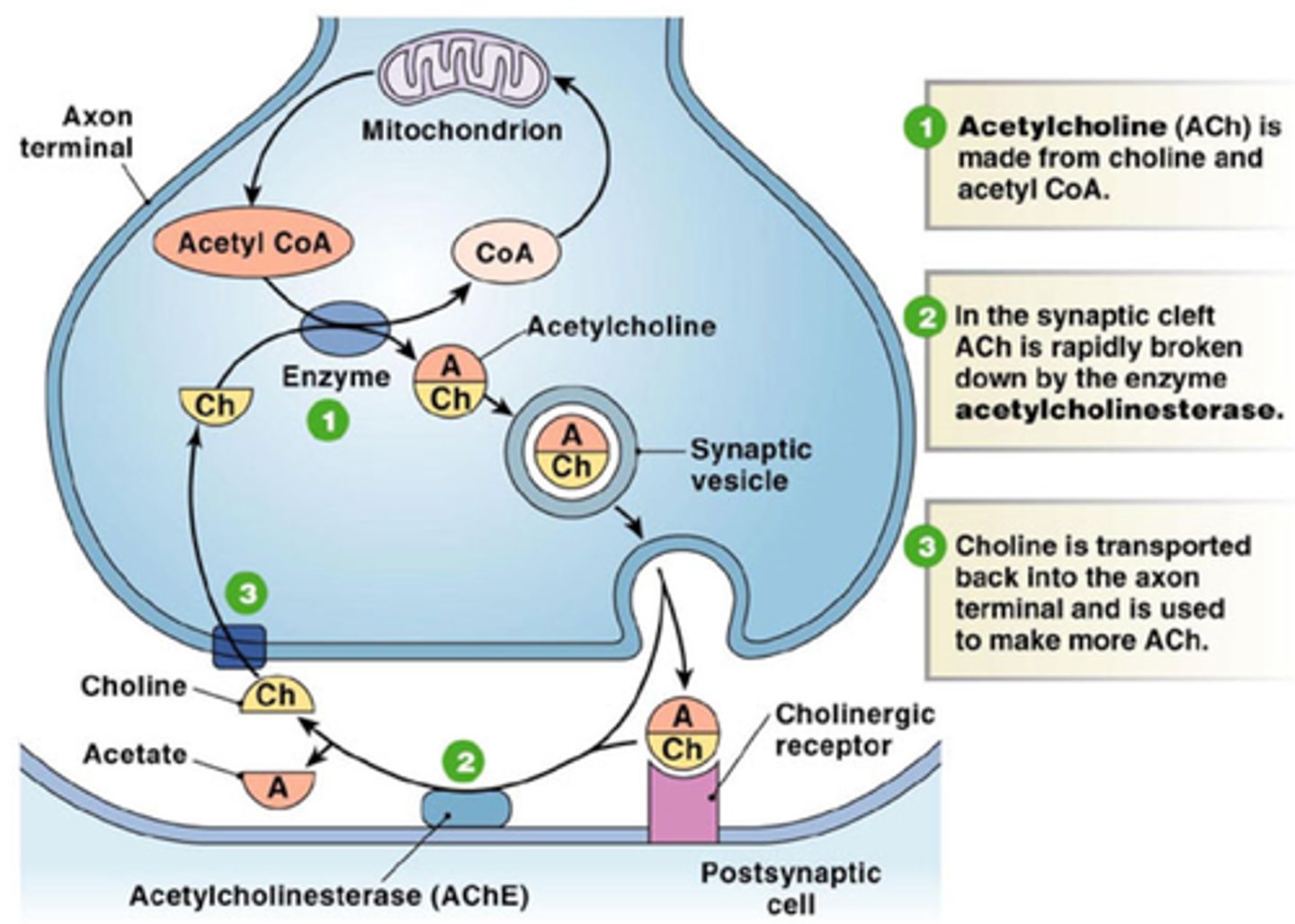
Acetylcholine (ACh)
most common neurotransmitter
Has an excitatory effect (opens Na+ channels to depolarize neuron and cause an action potential)
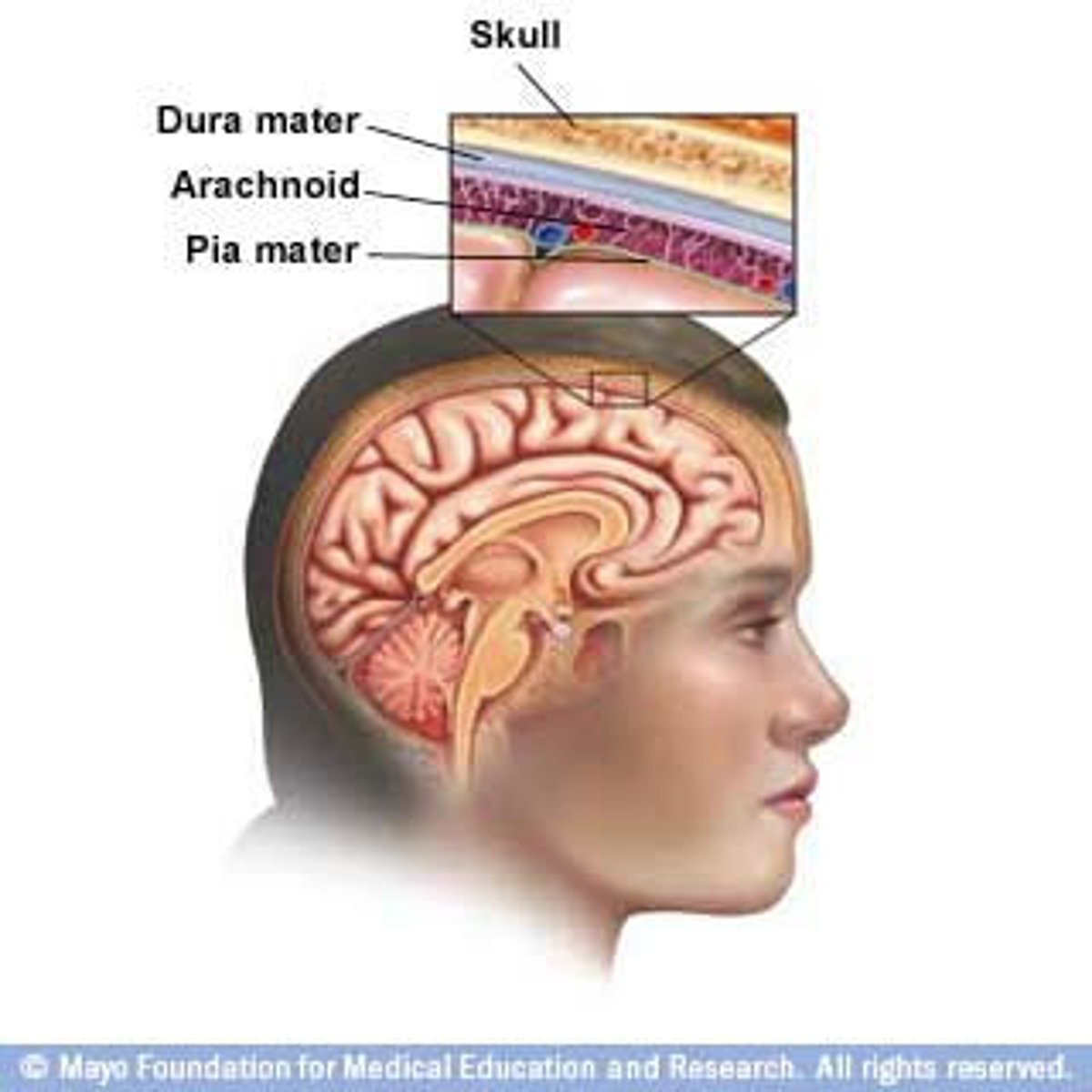
Protection for CNS
1. Skull and backbone
2. Meninges (3)
3. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
layers of meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
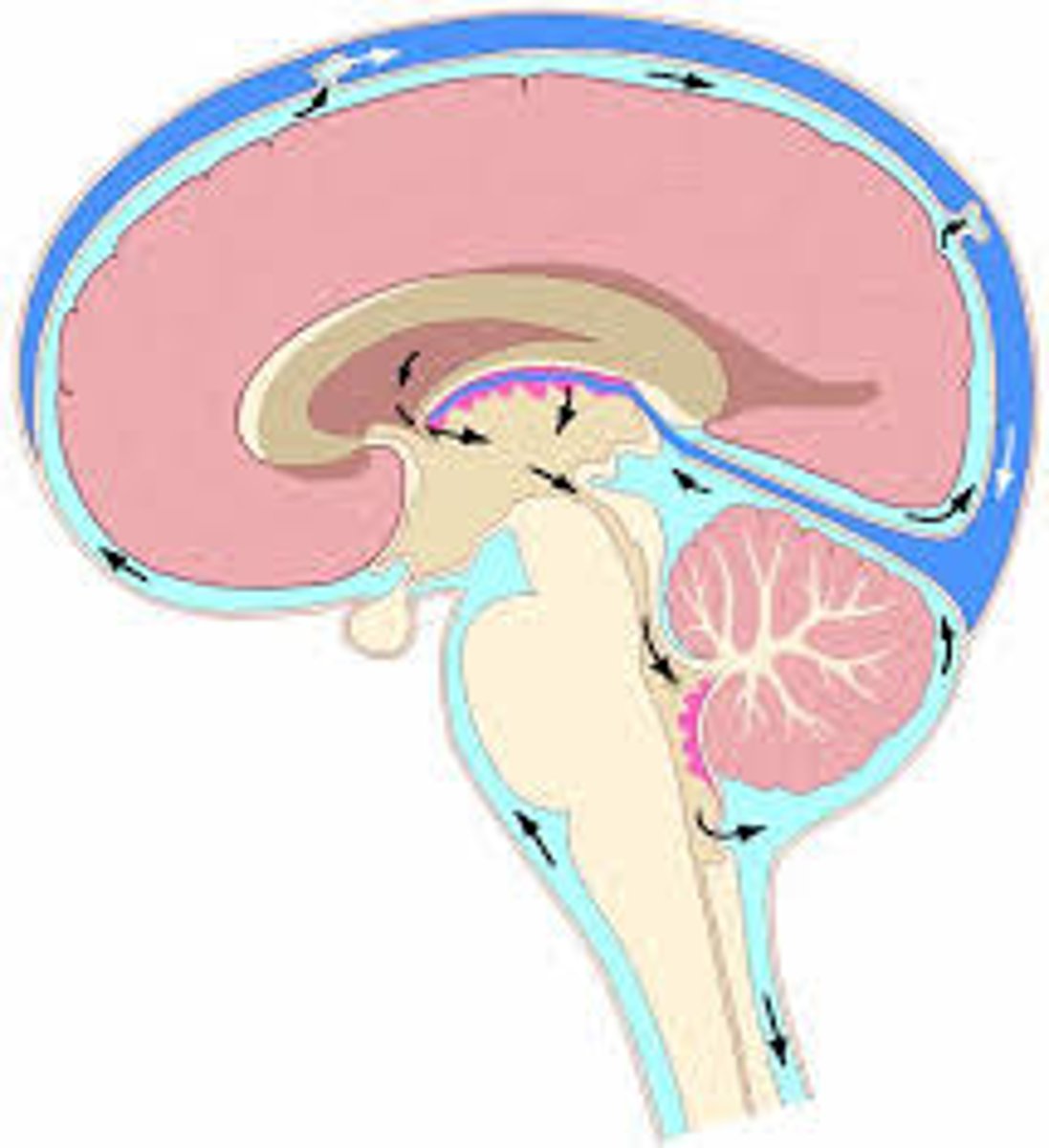
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- circulates throughout the brain and spinal cord
- Carries nutrients to brain and waste to the blood
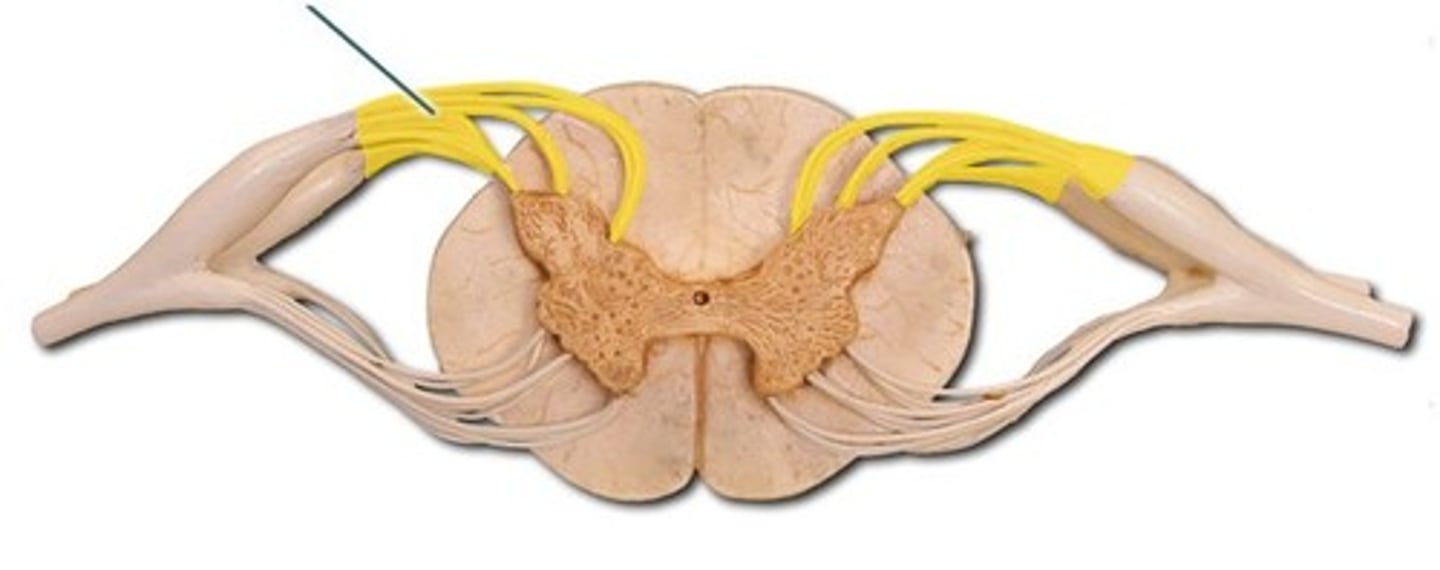
Spinal cord
- Carries sensory nerves from receptor to brain
- Carries nerve messages from brain to effector
dorsal spinal cord (dorsal root)
Brings information into spinal cord
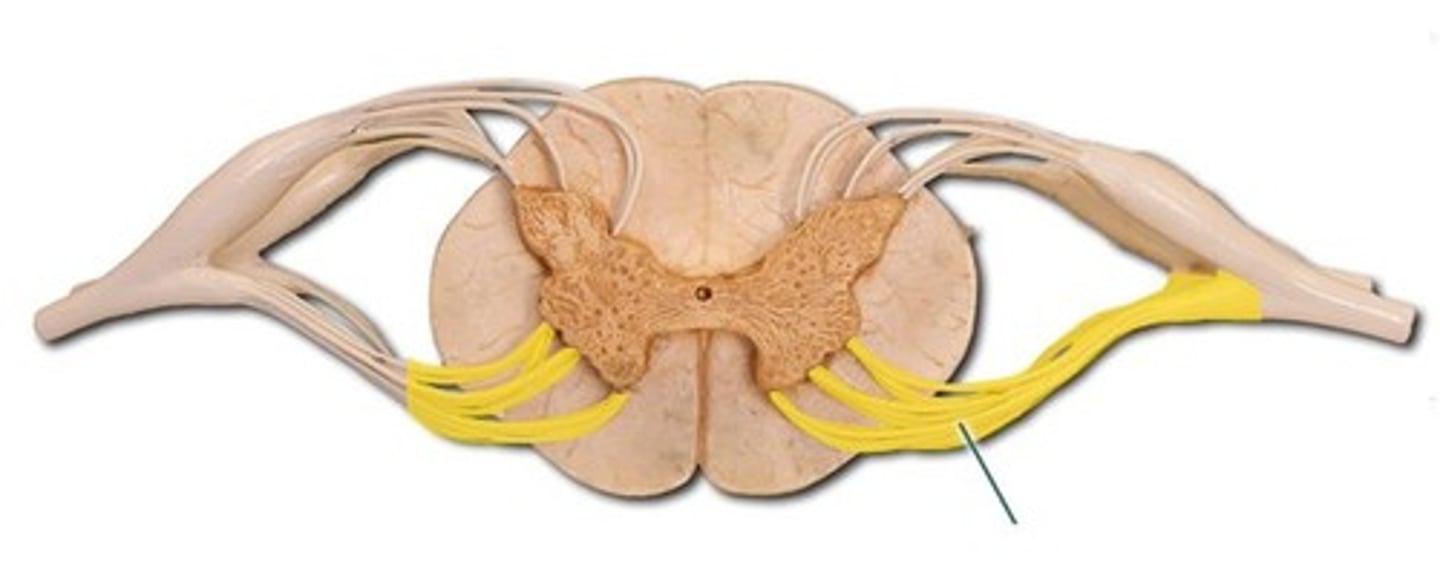
ventral spinal cord
Carries motor information from spinal cord to effectors
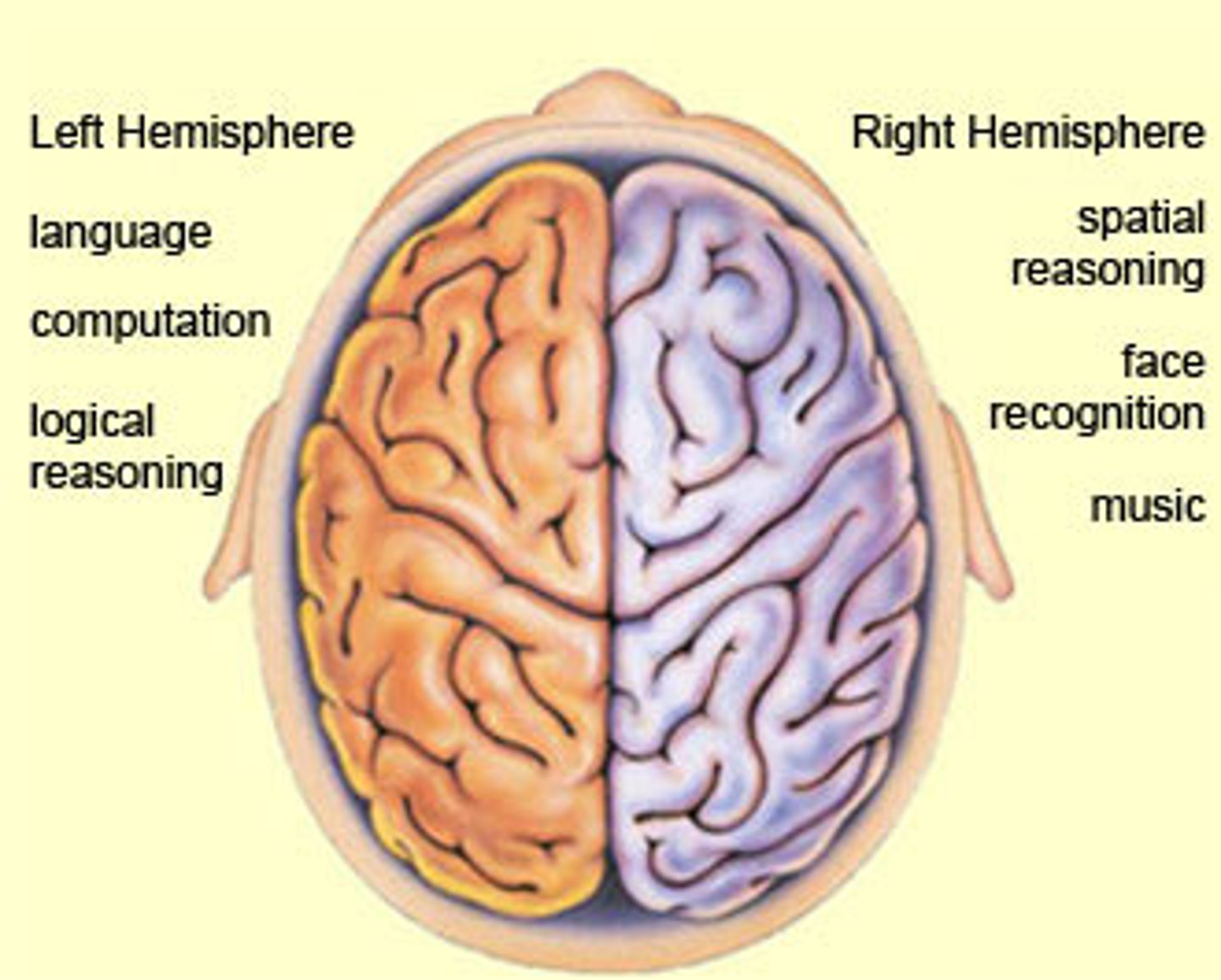
The brain hemispheres
left hemisphere specializes in math, logic, languages
right hemisphere specializes in music, visuals, facial recognition, spacial
Thalamus
Relay's incoming sensory information to cerebrum
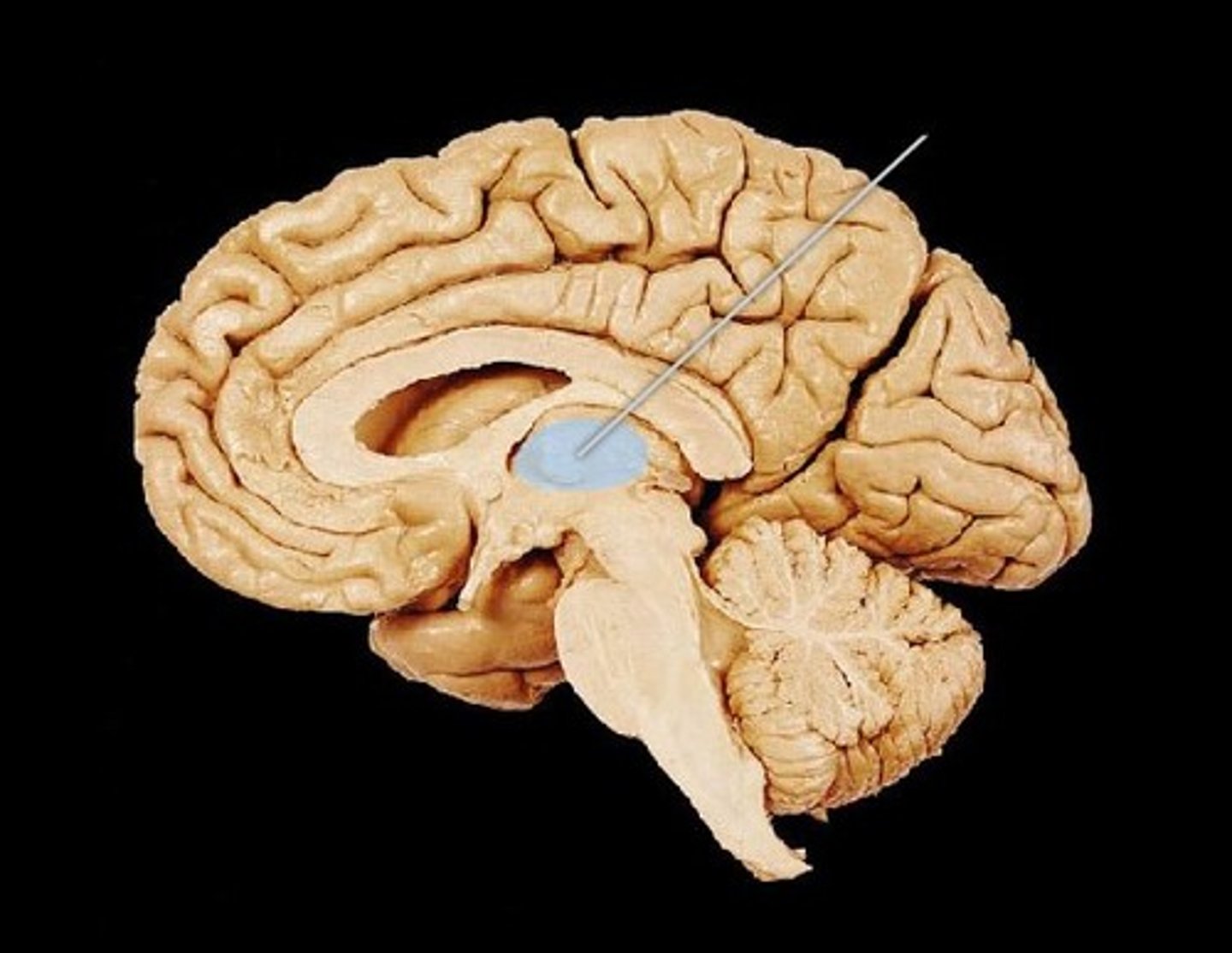
Hypothalamus
- Maintains homeostasis
- Connects the pituitary glands to the endocrine system
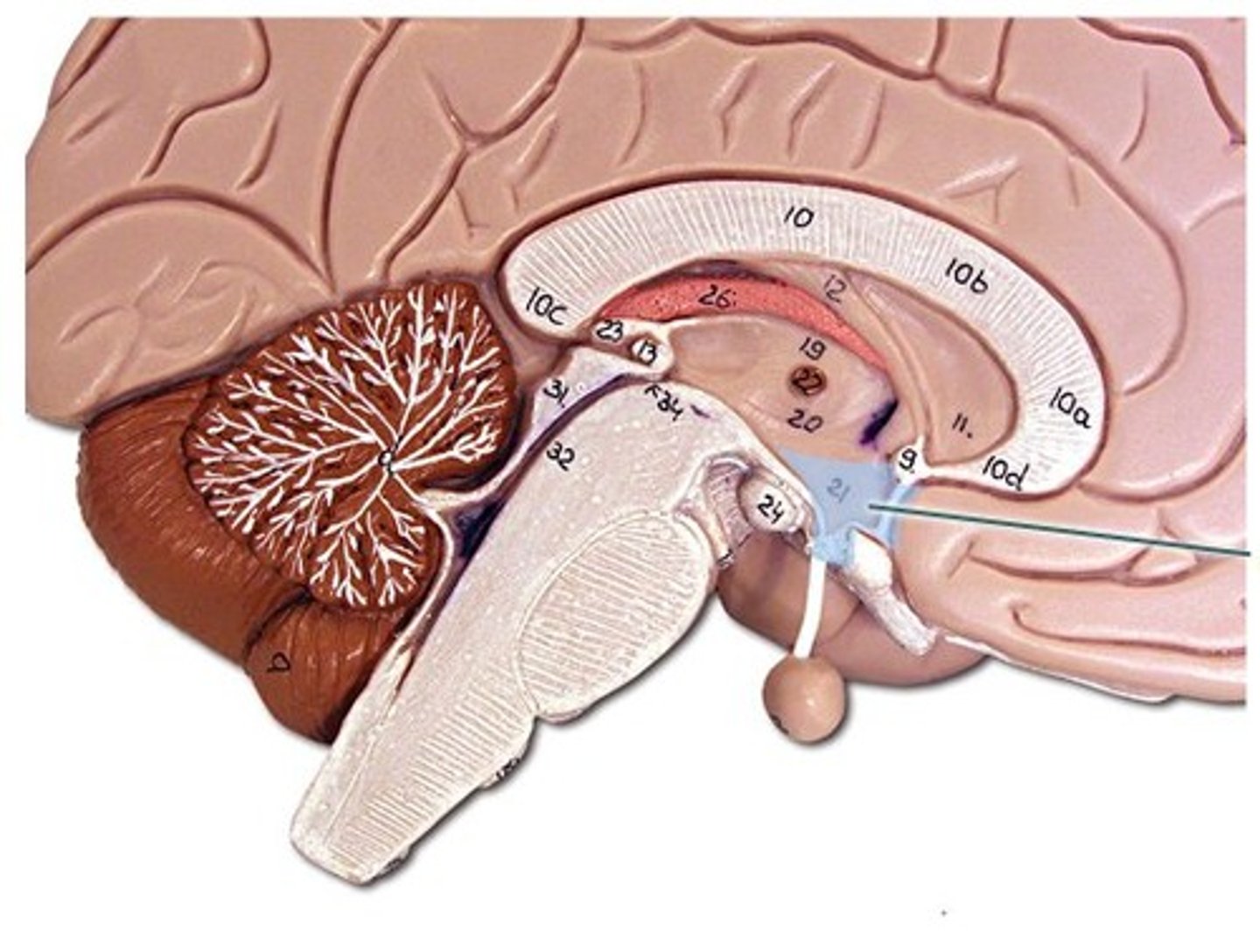
Cerebrum
- Largest part of the brain
- Outer layer of the cerebrum is called cerebral cortex and is made up of grey matter
myelinated nerve fibers
- White matter in PNS
- Protects the nerves from electric impulses
unmyelinated nerve fibers
- Grey matter
- The lack of myelinated sheath
- Therefore when it is damaged it will not repair itself
corpus callosum
Two hemispheres of the brain through a bundle of nerves.
Cerebrum lobes
frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital
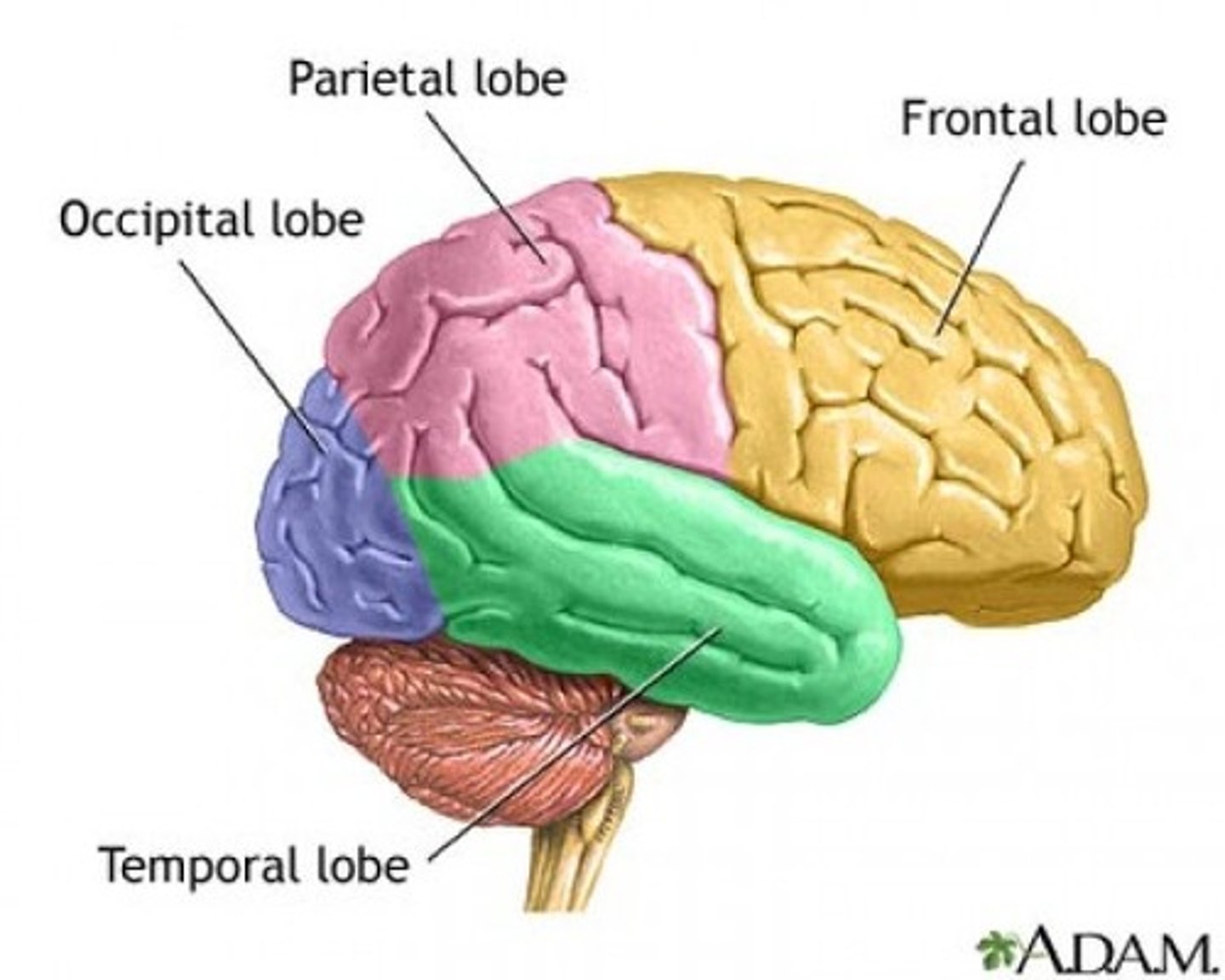
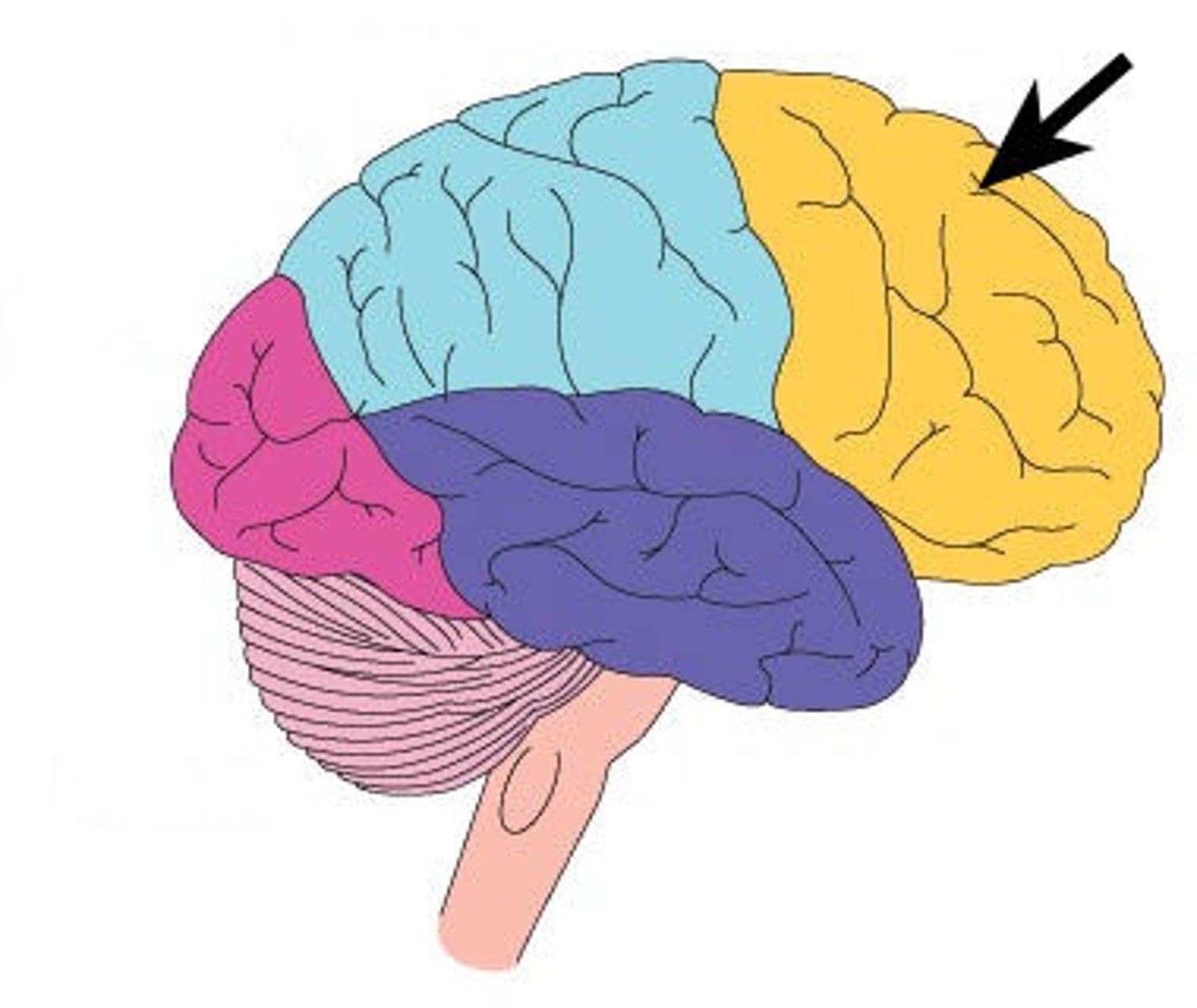
Frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for voluntary muscle movement, personality and intellectual activities
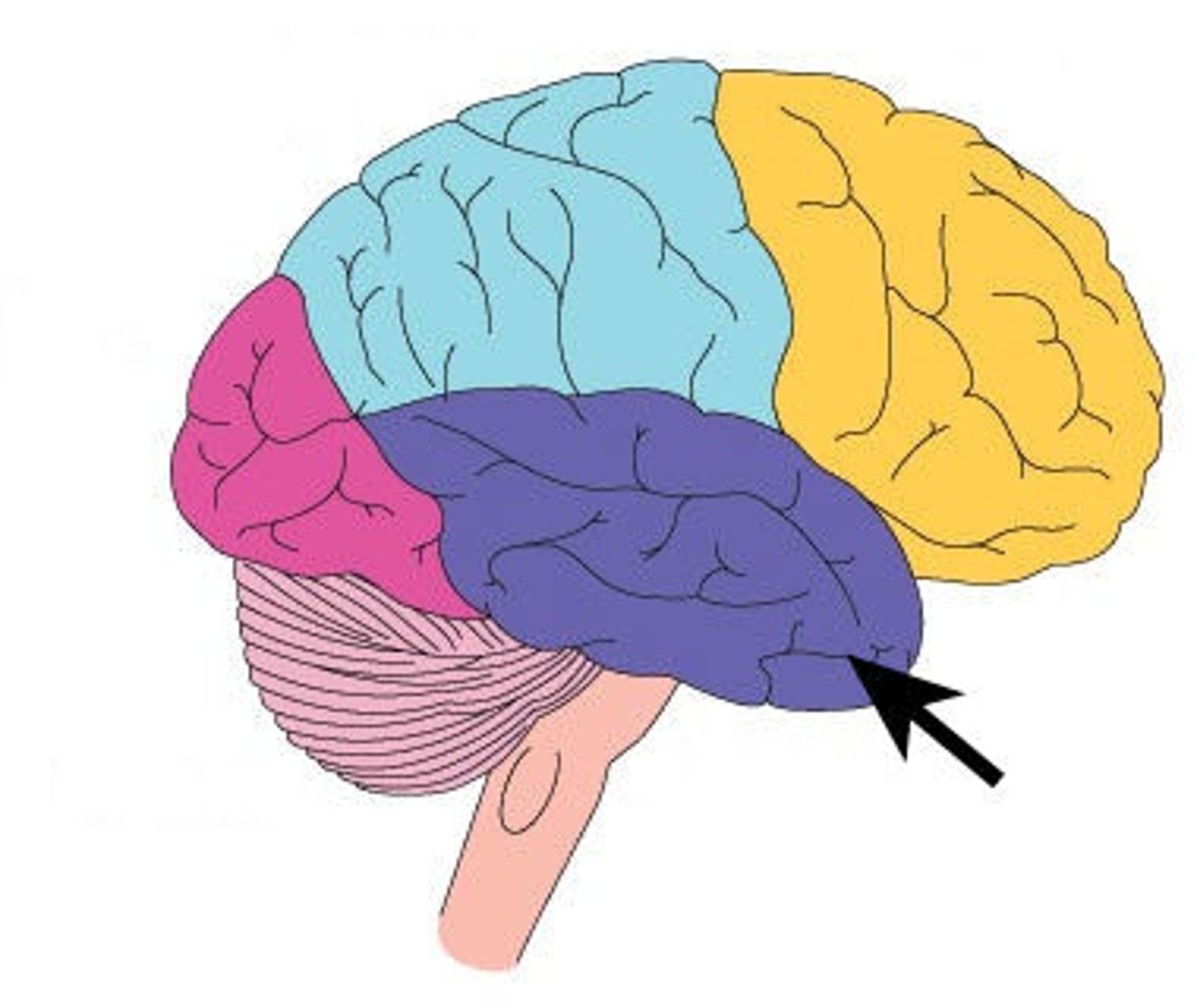
Temporal lobe
BY EARS
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for smell, sound, memory and language.
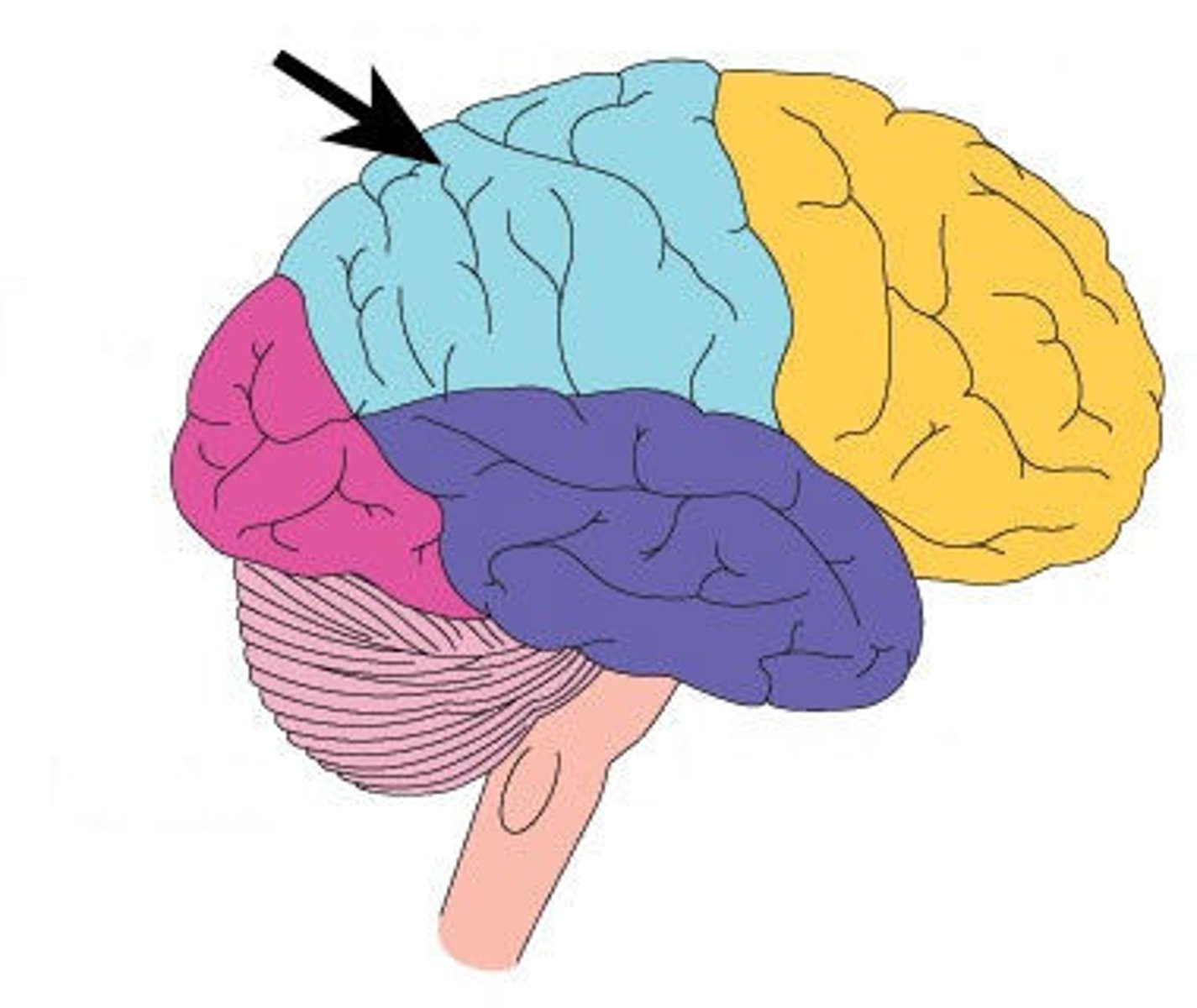
parietal lobe
TRIPLE T (Touch, Taste and Temperature)
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch, taste and temperature.
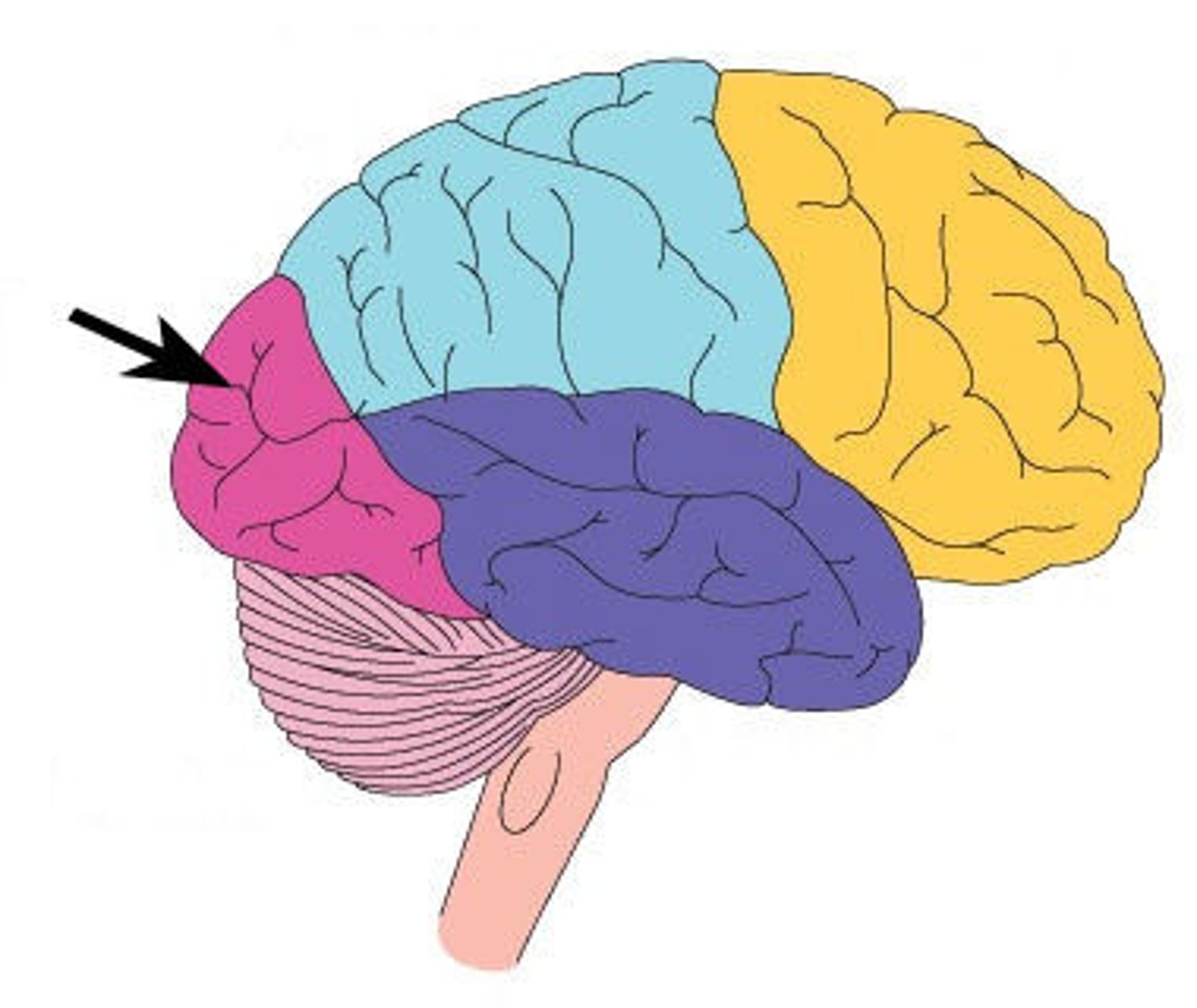
Occipital lobe
responsible for vision
Cerebellum
Largest section of the brain
controls limb movements, balance, and muscle tone
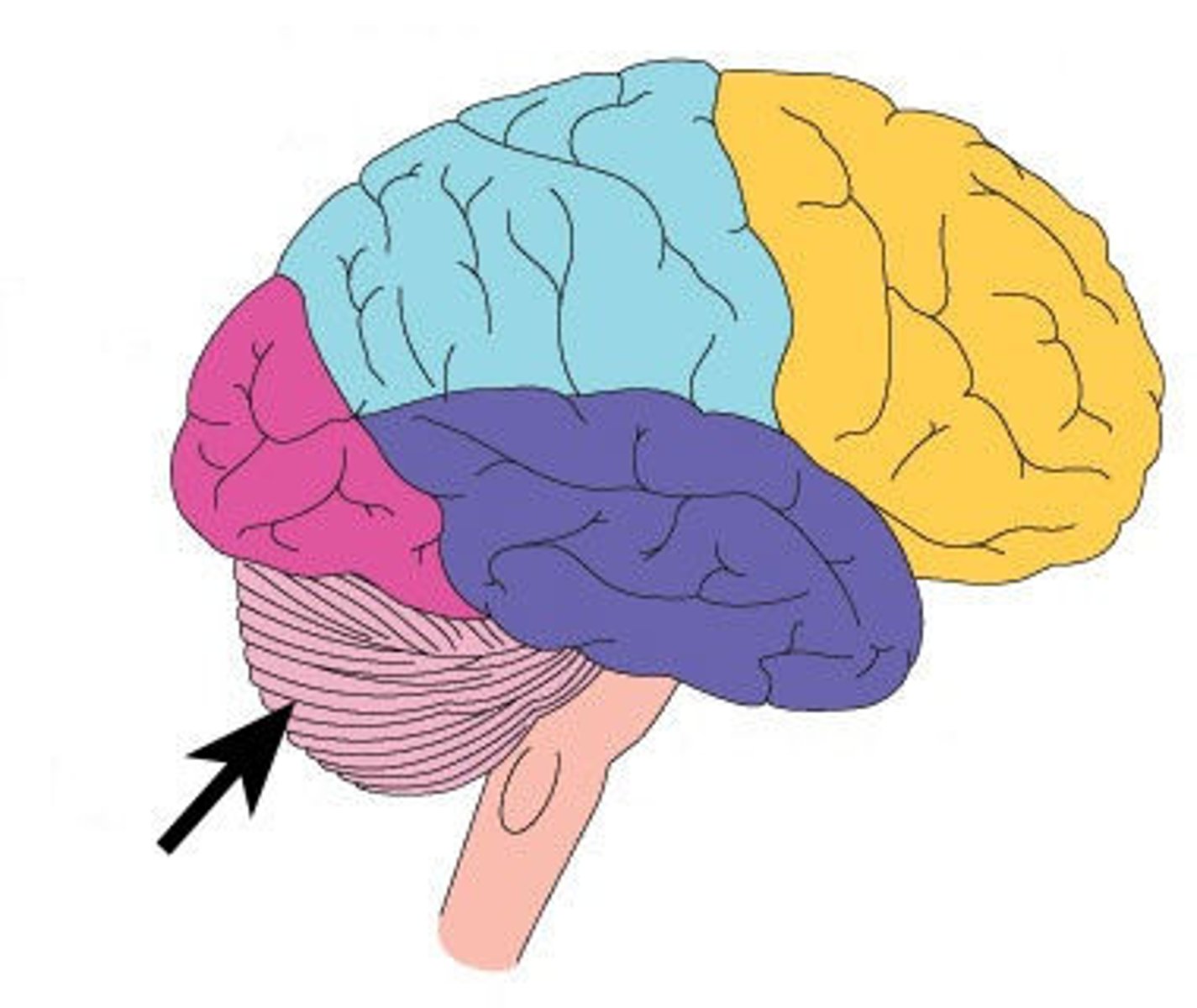
Pons
Means bridge
SECOND BIG BUMP
Passes information between cerebellum and the medulla
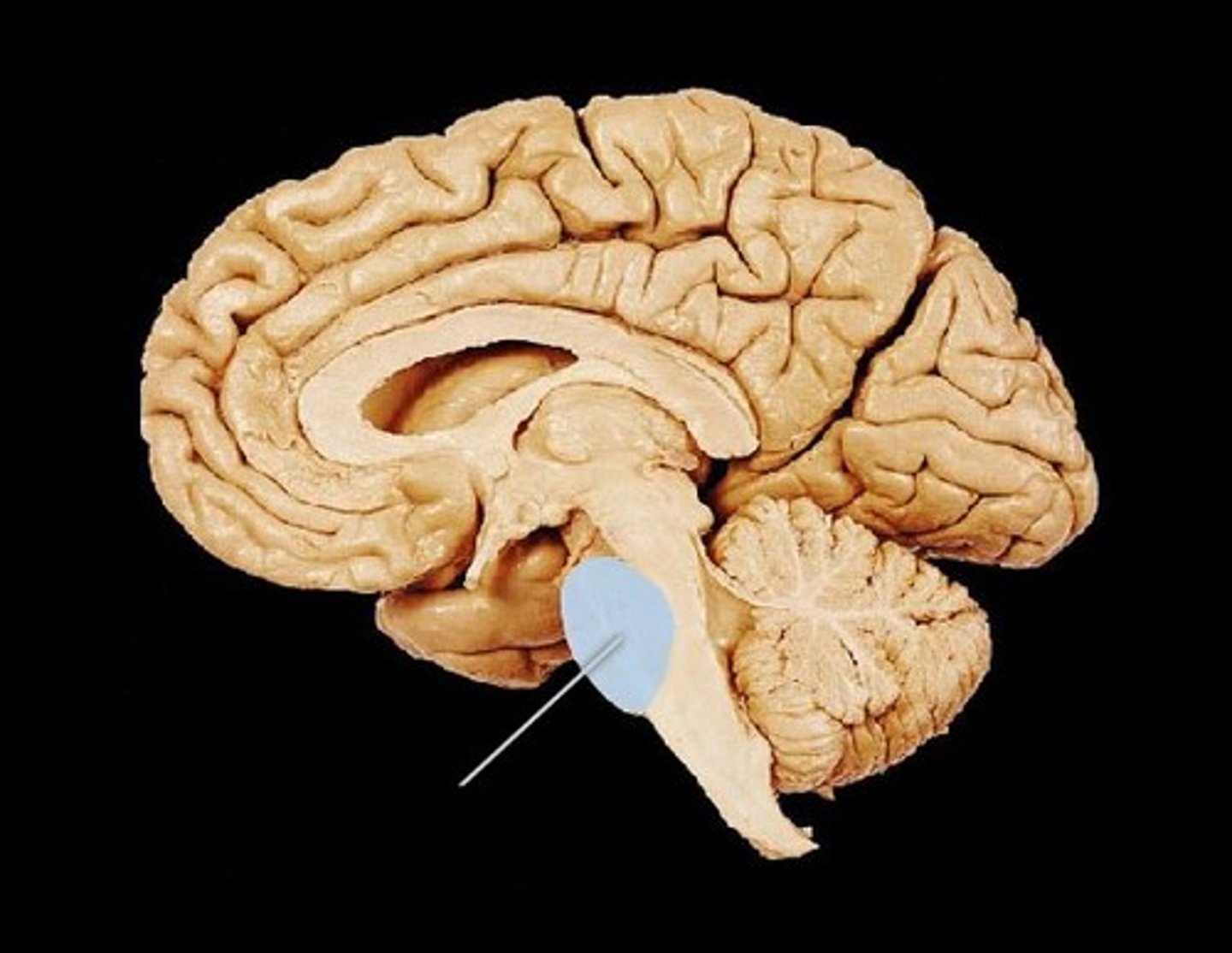
medulla oblongata
Connects the brain and spinal cord
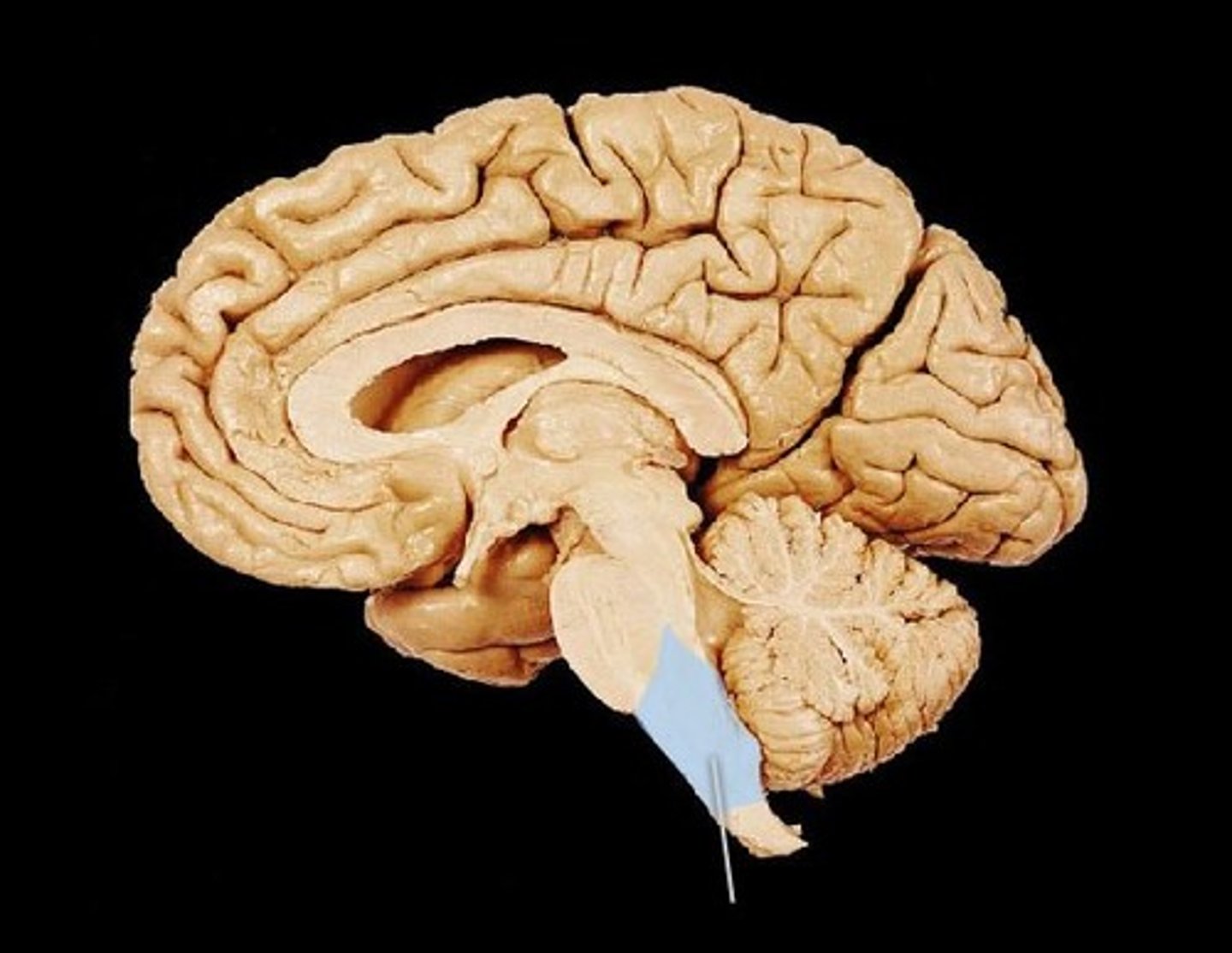
What does the medulla control?
- Breathing movements
- Diameter of blood vessels
- Heart rate
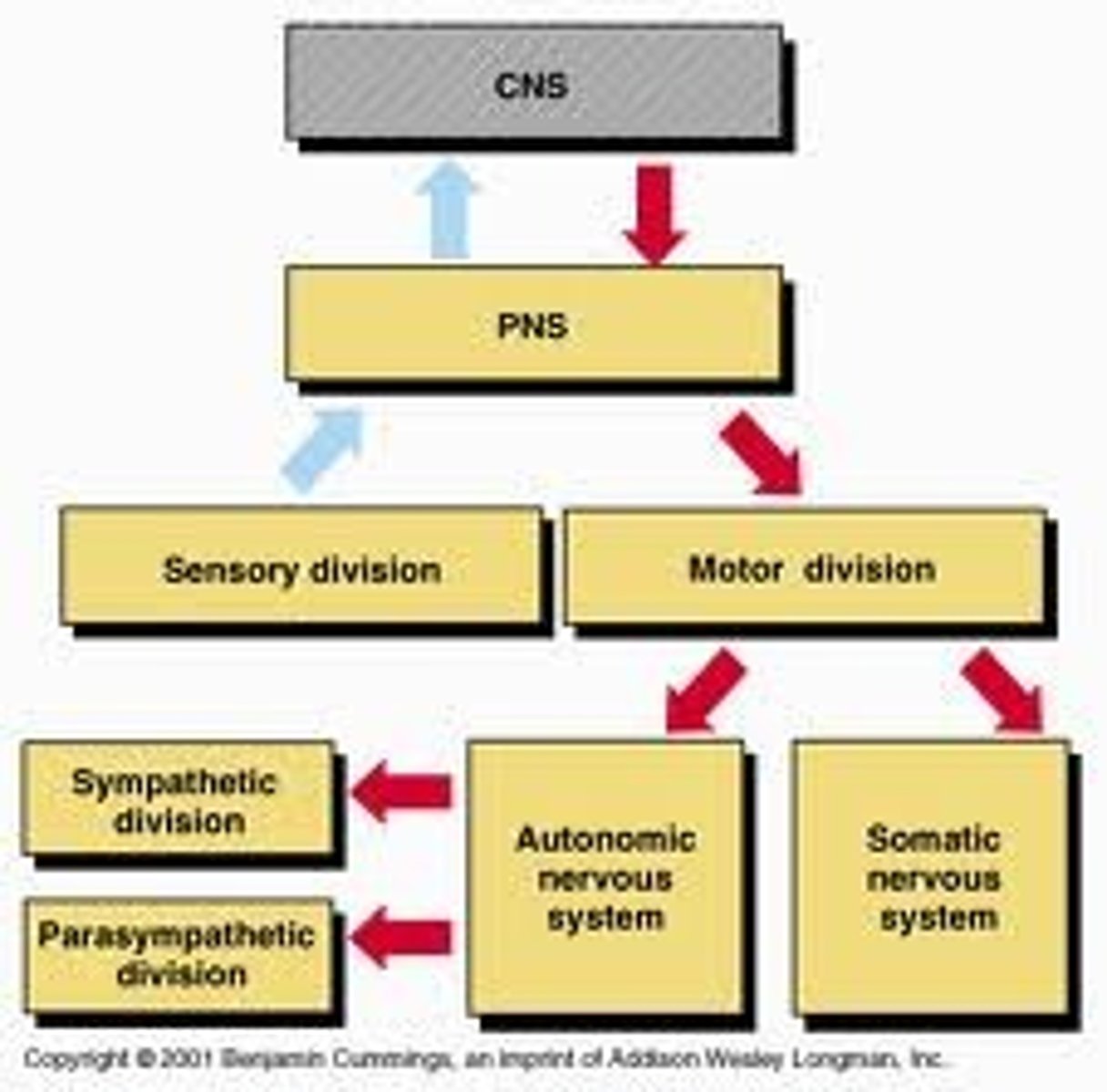
Two divisions of the peripheral nervous system
somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
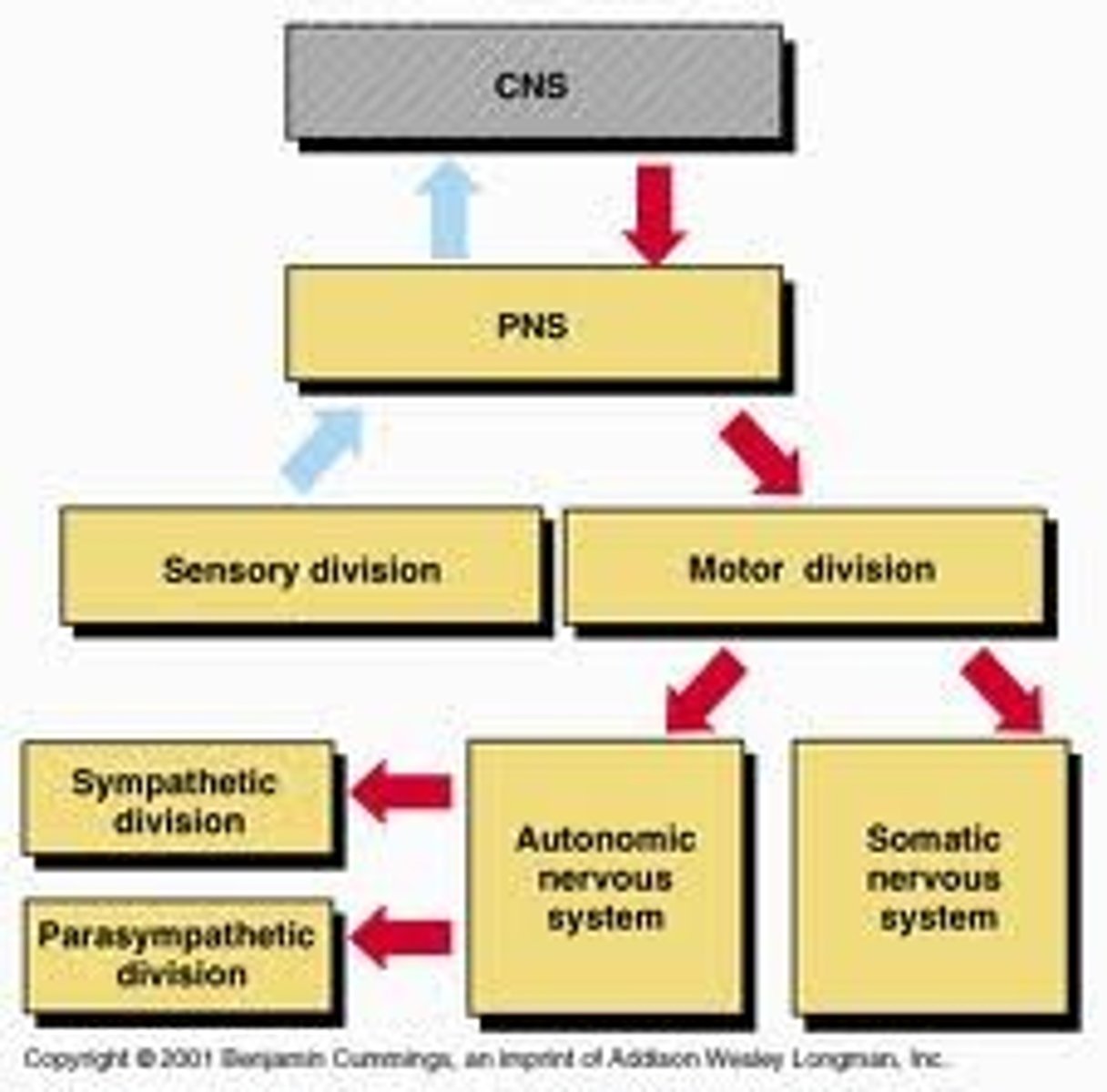
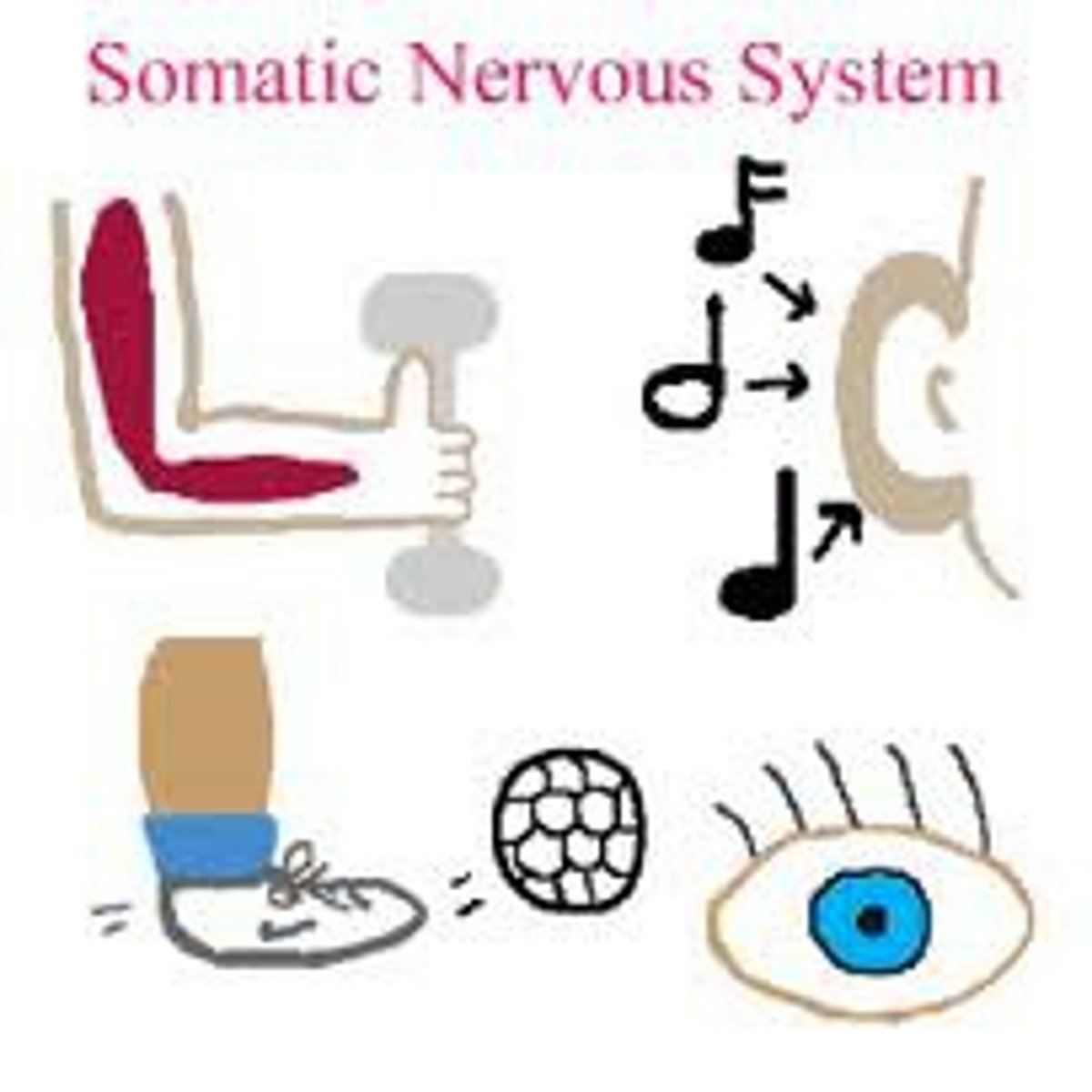
sensory-somatic nervous system
- Brings information from external environment to CNS and sends it back to skeletal muscles
- Voluntary (SOMATIC) control, except for reflex arc
- INCLUDES 12 CRANIAL NERVES AND 31 SPINAL NERVES
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
- Brings information about body's internal environment to CNS
- Regulates body by carrying signals to CNS to muscles and organs (Breathing, balances oxygen levels and blood pressure)
- COMPOSED OF TWO UNITS
1. Synaptic nervous system (fight or flight)
2. Parasympathetic nervous system (Rest and digest)
sensory information
- Sensory receptors convert one energy from (information) about the external environment into electro-chemical energy (nerve impulses) then relays it to the CNS
- Each individual receptor is capable of responding to only ONE kind of stimulus
sensory adaptation
- Occurs when you have adjusted to a change in the environment
- Threshold level has moved up
Three layers of the eye
1. Sclera
2. Choroid layer
3. Retina
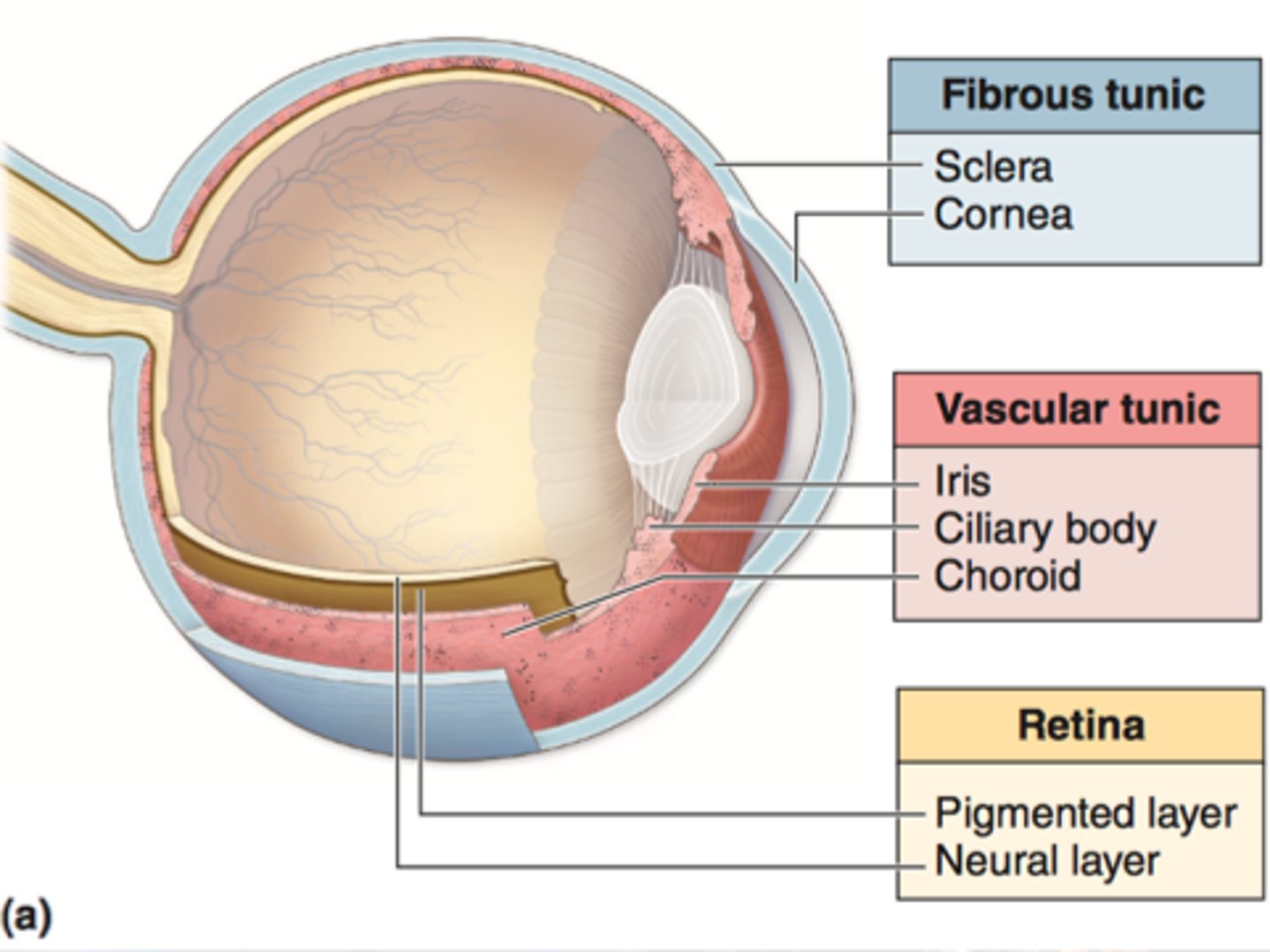
Sclera
- Outermost layer
- White part of the eye
- Maintains eye shape
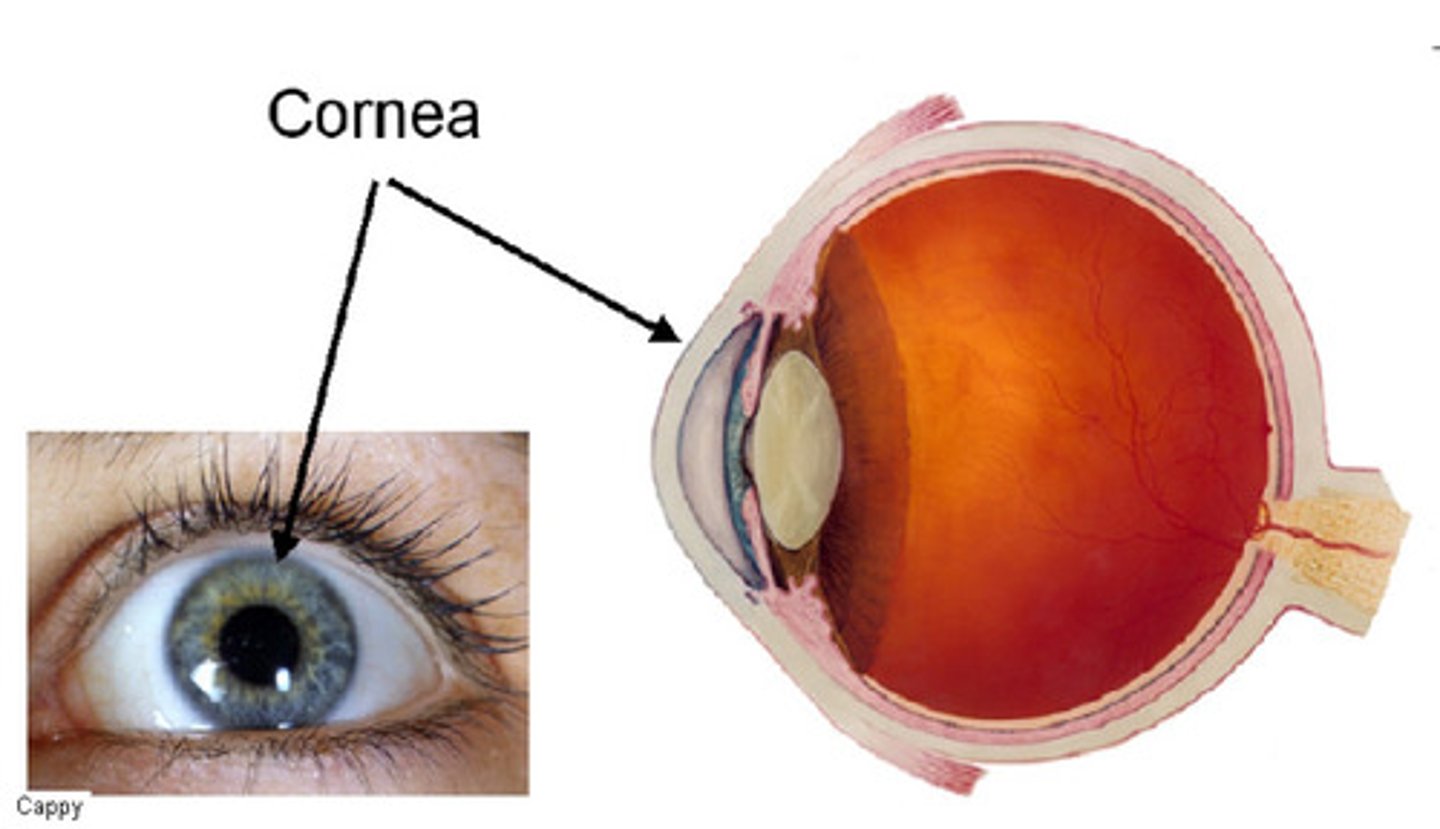
Cornea
- clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
- Acts as a window to bend light toward the pupil
- Requires oxygen from tears and nutrients from the aqueous humour
aqueous humor
- Transparent fluid behind cornea
- provides the eye with nutrients
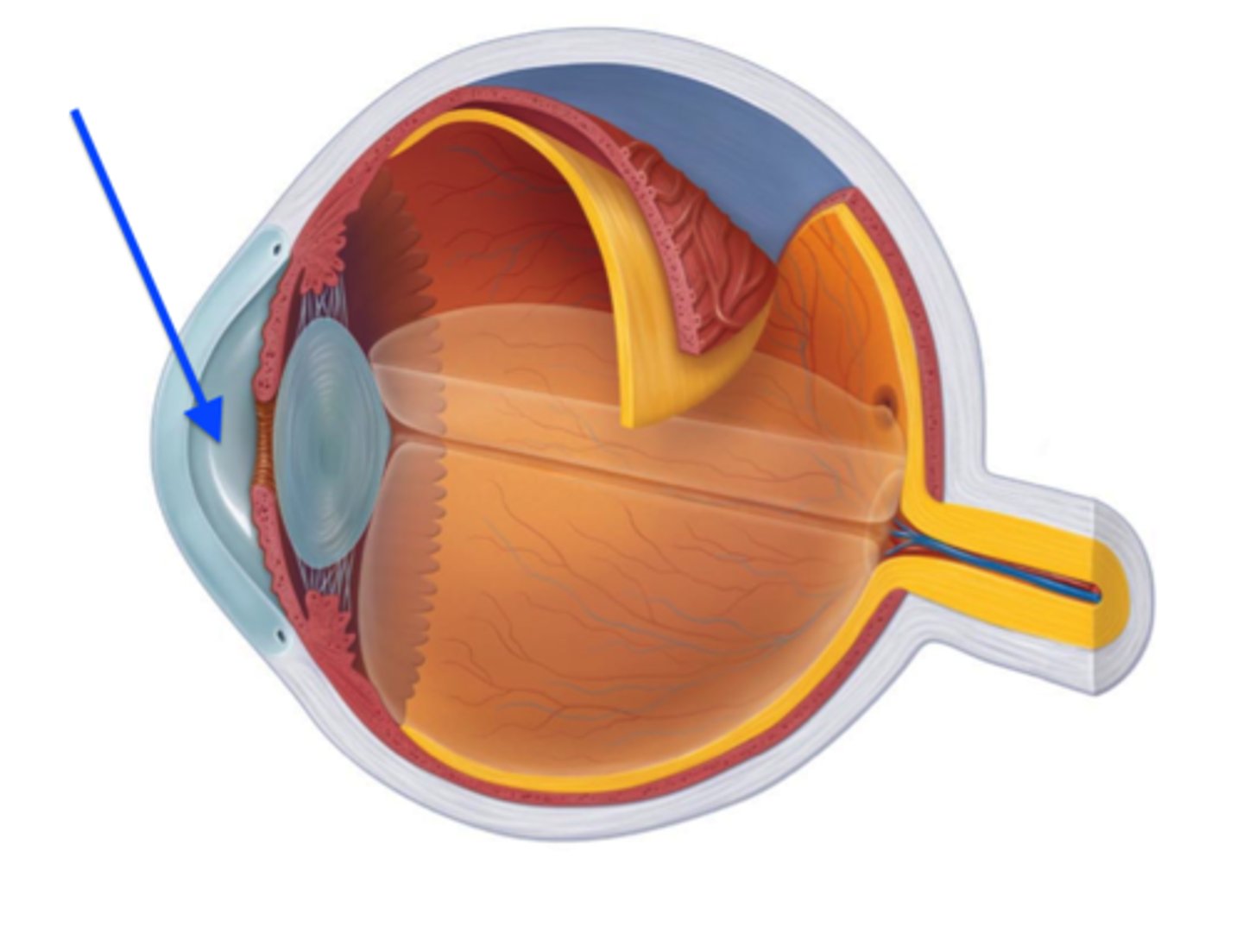
Choroid layer
- Pigmented to prevent light from shattering
- contains blood vessels
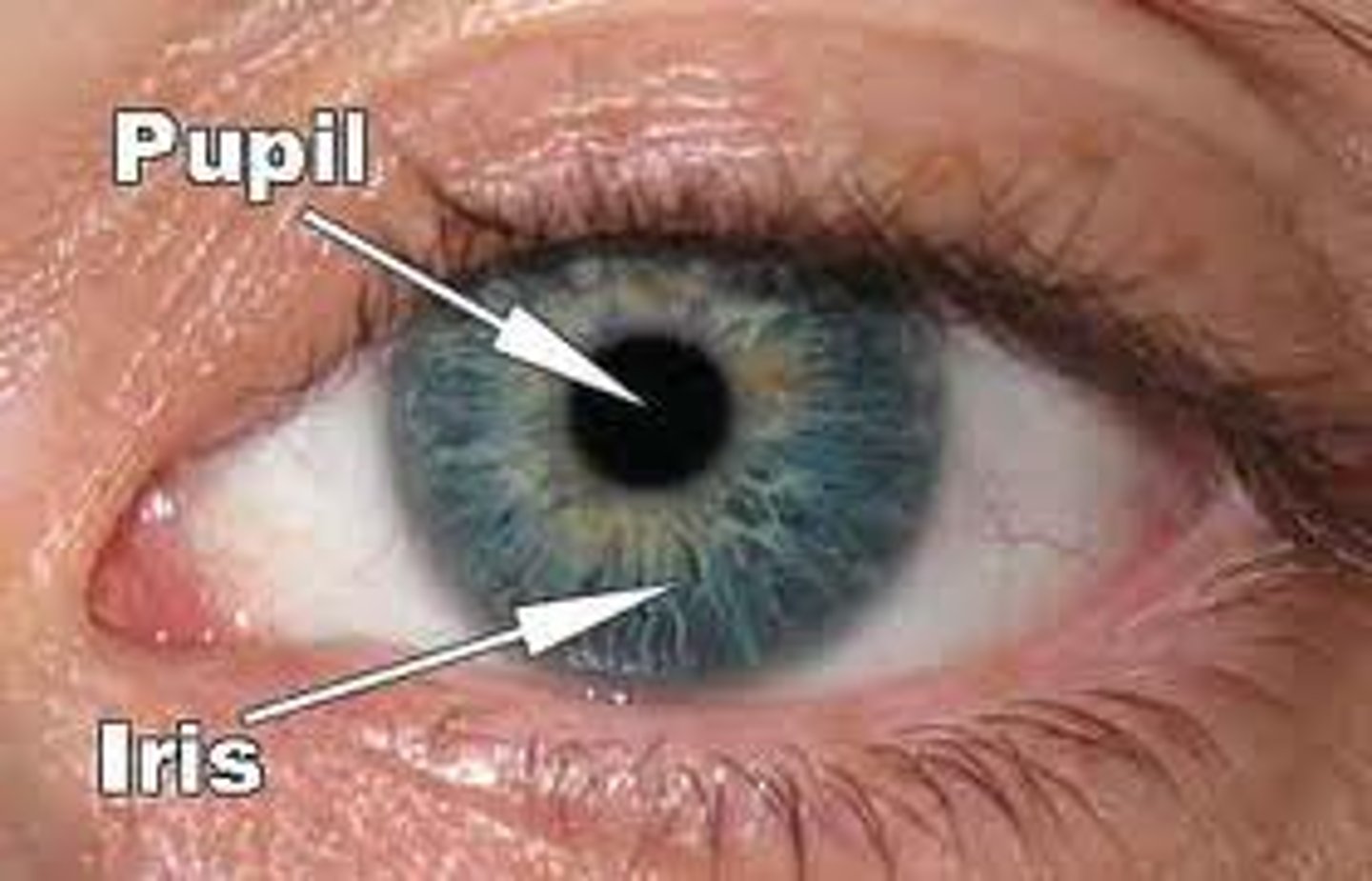
Iris
- Allows light into the eye
- Controls the size of the pupil
Lens
- Focuses light onto retina
vitreous humor
- Cloudy, jelly-like material
- Maintains shape of the eyeball
- Allows light to transmit to retina
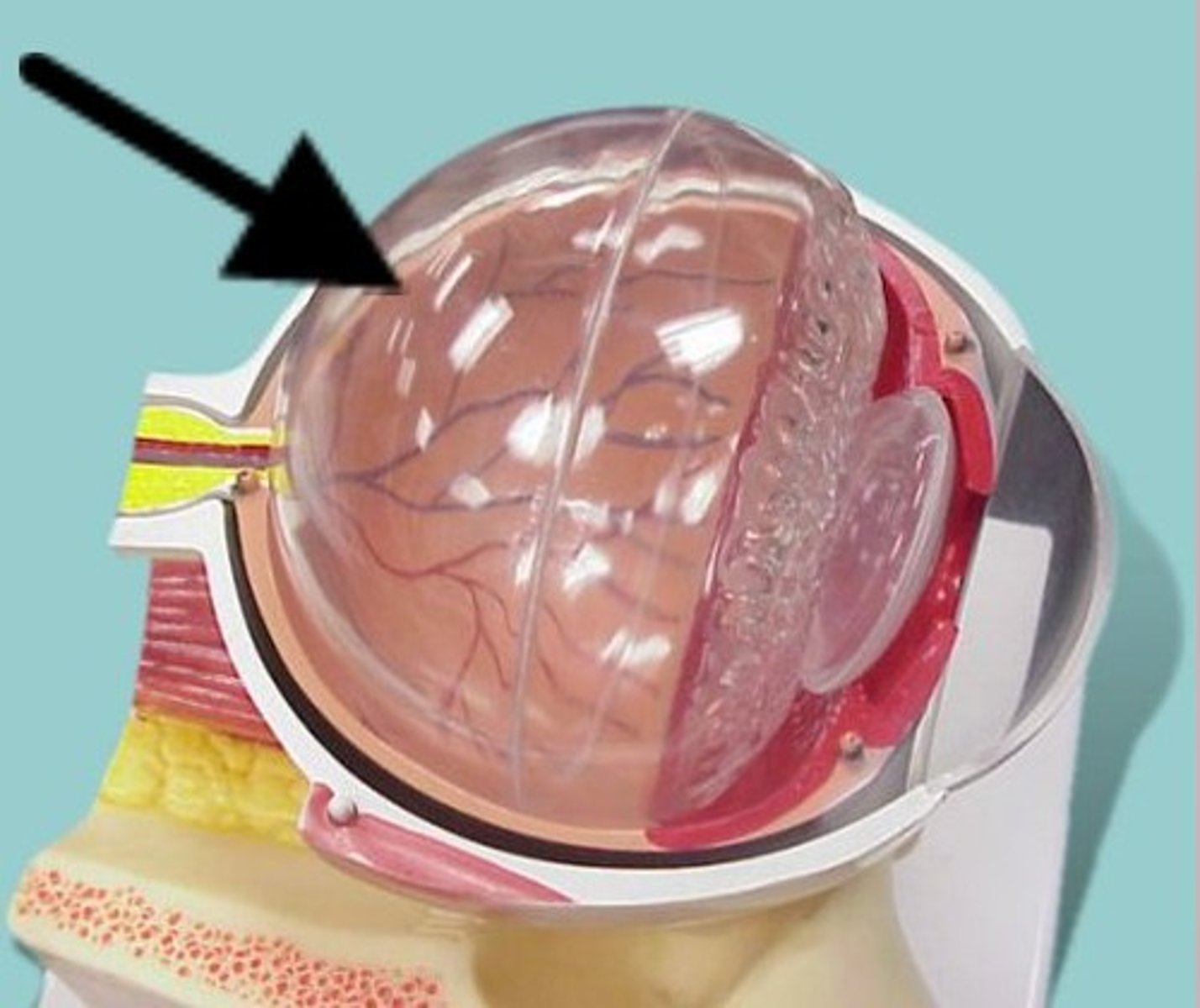
Retina
- Contains light-sensitive cells called rods and cones
Rods vs. cones
Rods = responds to low-intensity light (black and white)
Cones= responds to high-intensity light (colour)
fovea centralis
tiny pit or depression in the retina that is the region of clearest vision because it is packed with lots of rods and cones
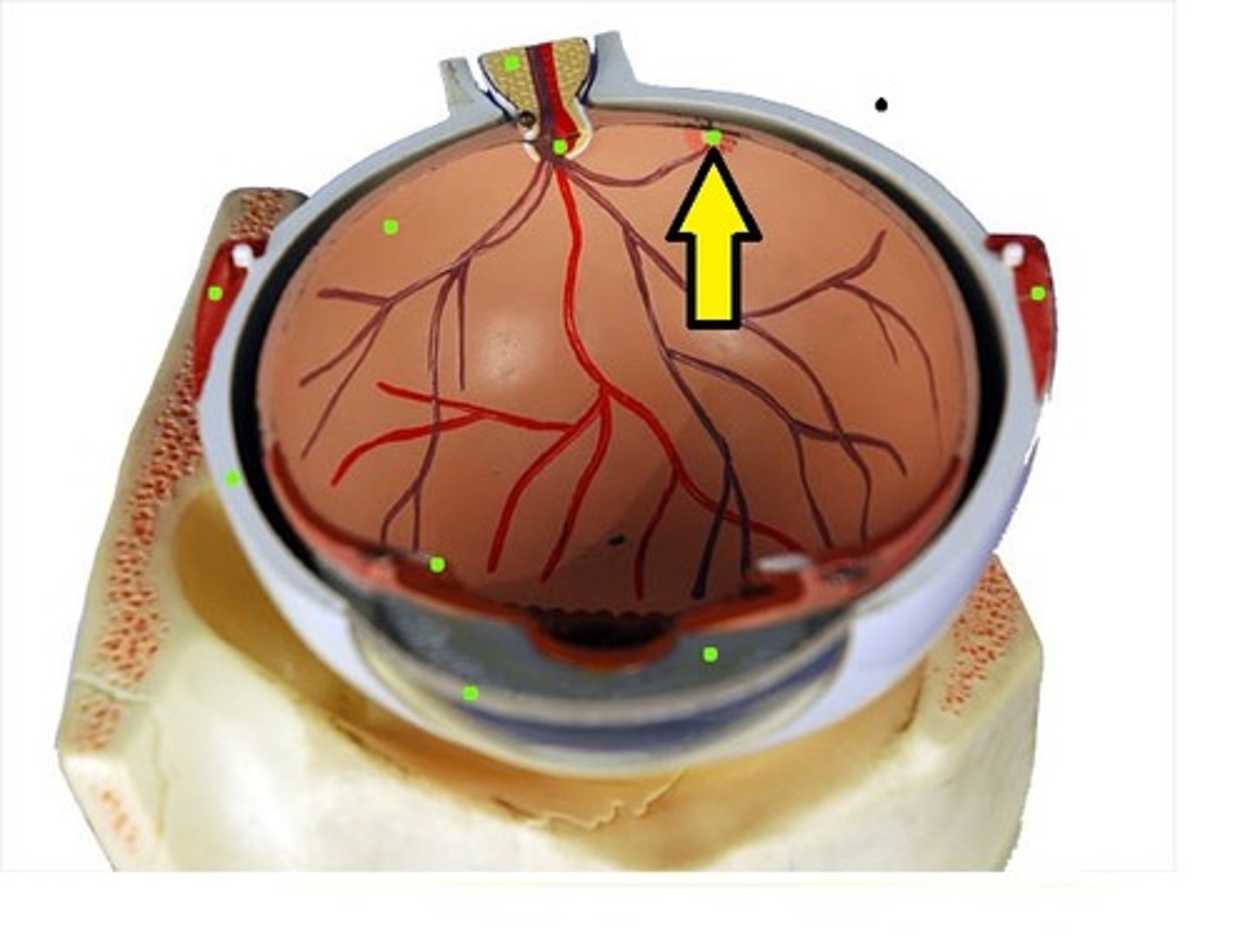
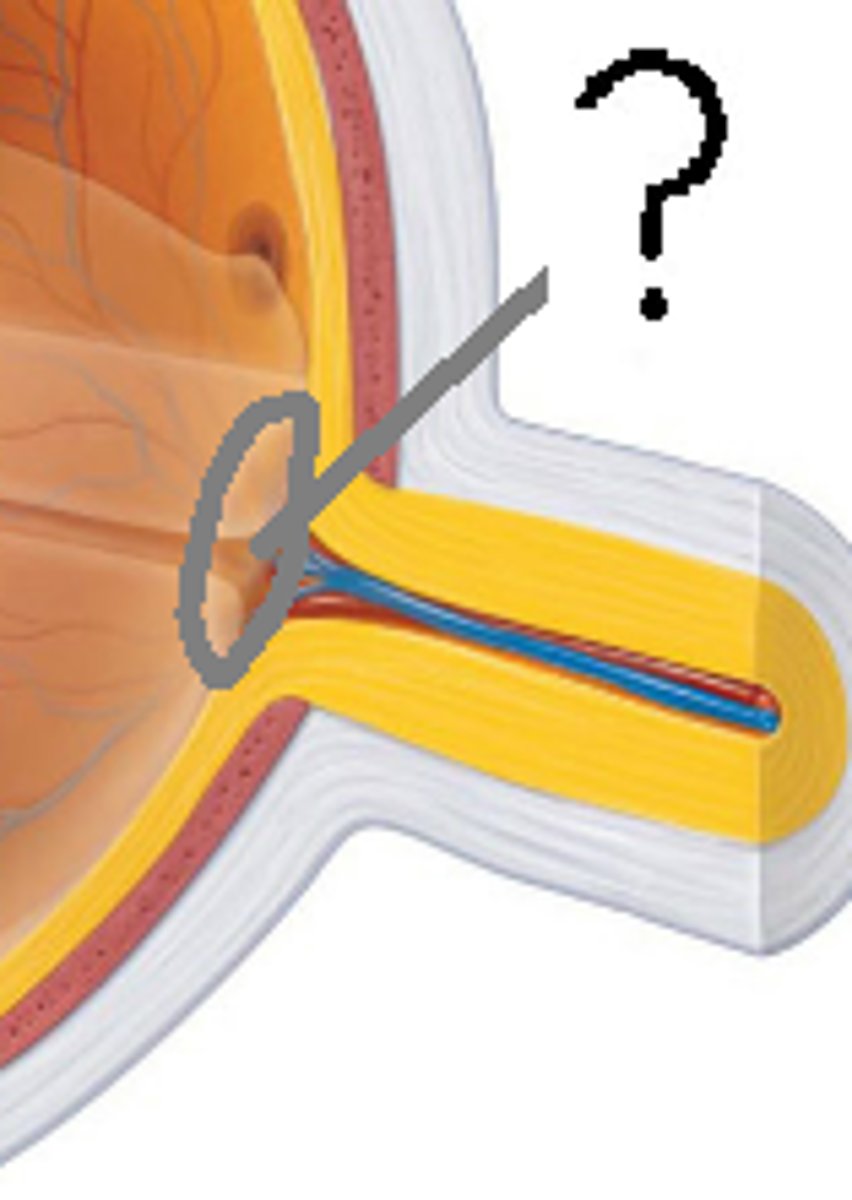
Blind spot
- No rods or cones where optic nerve comes in contact with the retina
colorblindism
- inherited condition
- where one lacks cones
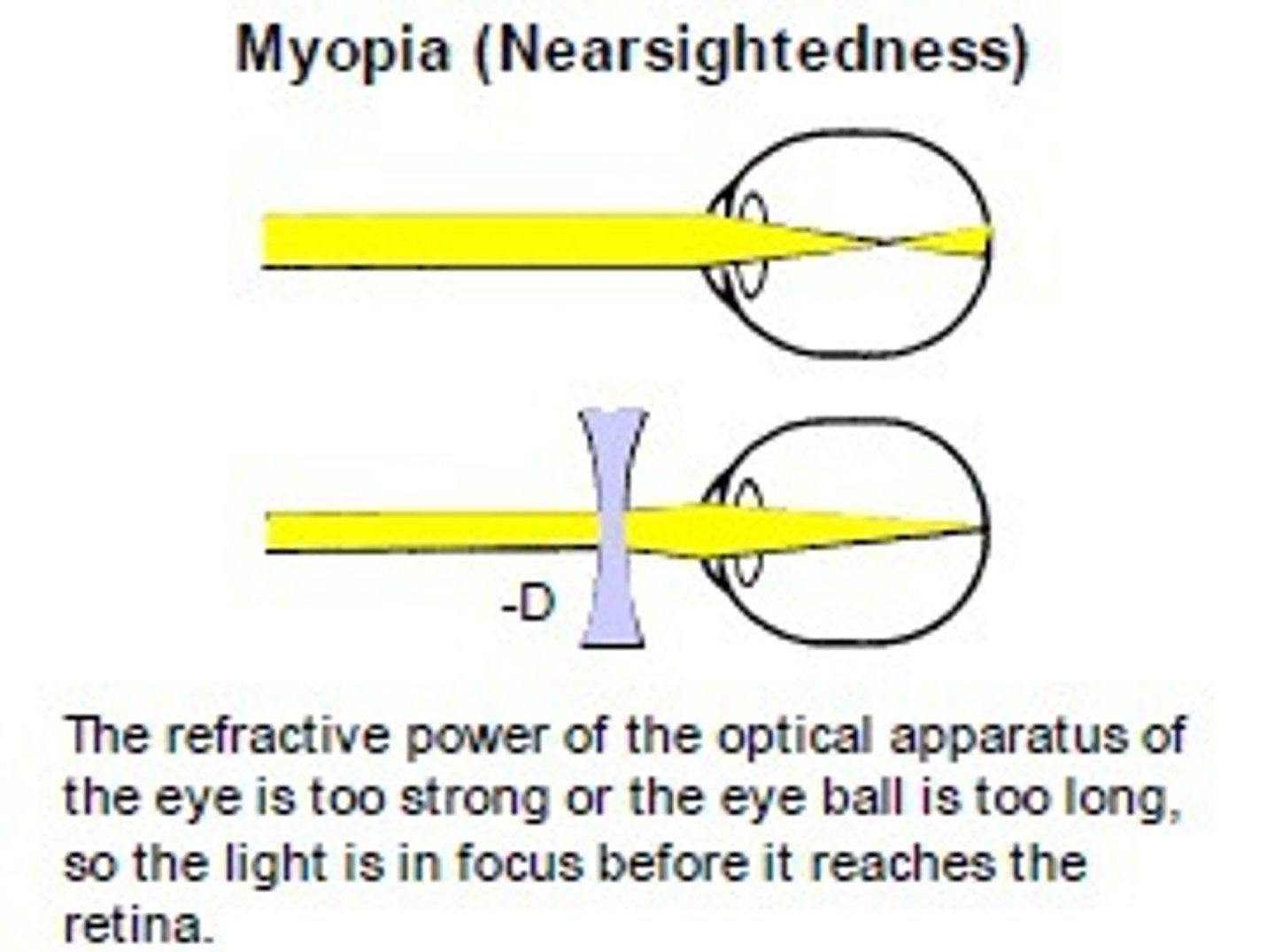
near-sightedness (myopia)
- Eye is too long
- Rays from distant object focuses in front of the retina
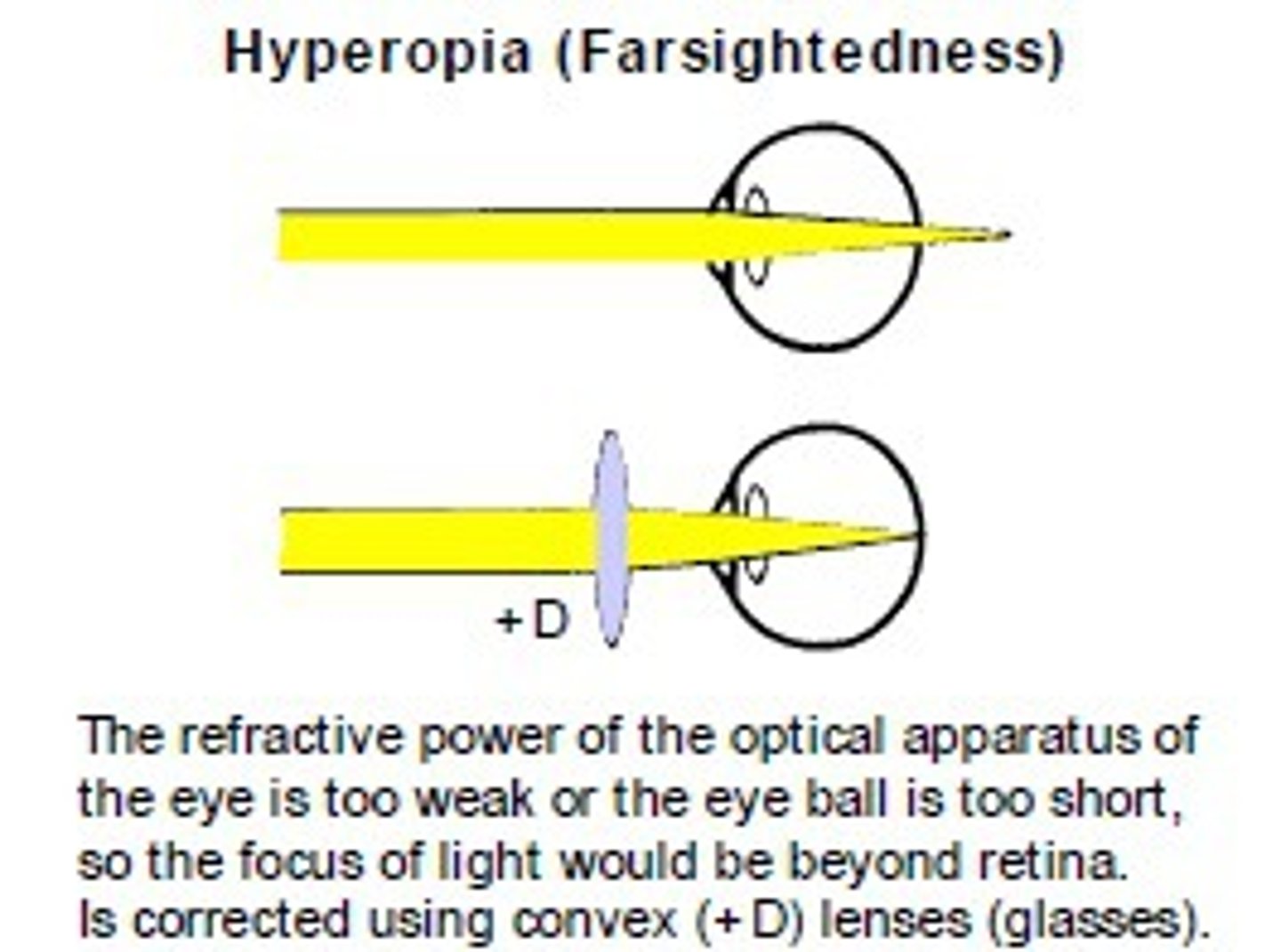
Far-sightedness (hyperopia)
- Eye is too short
- Rays from near object focuses behind the retina
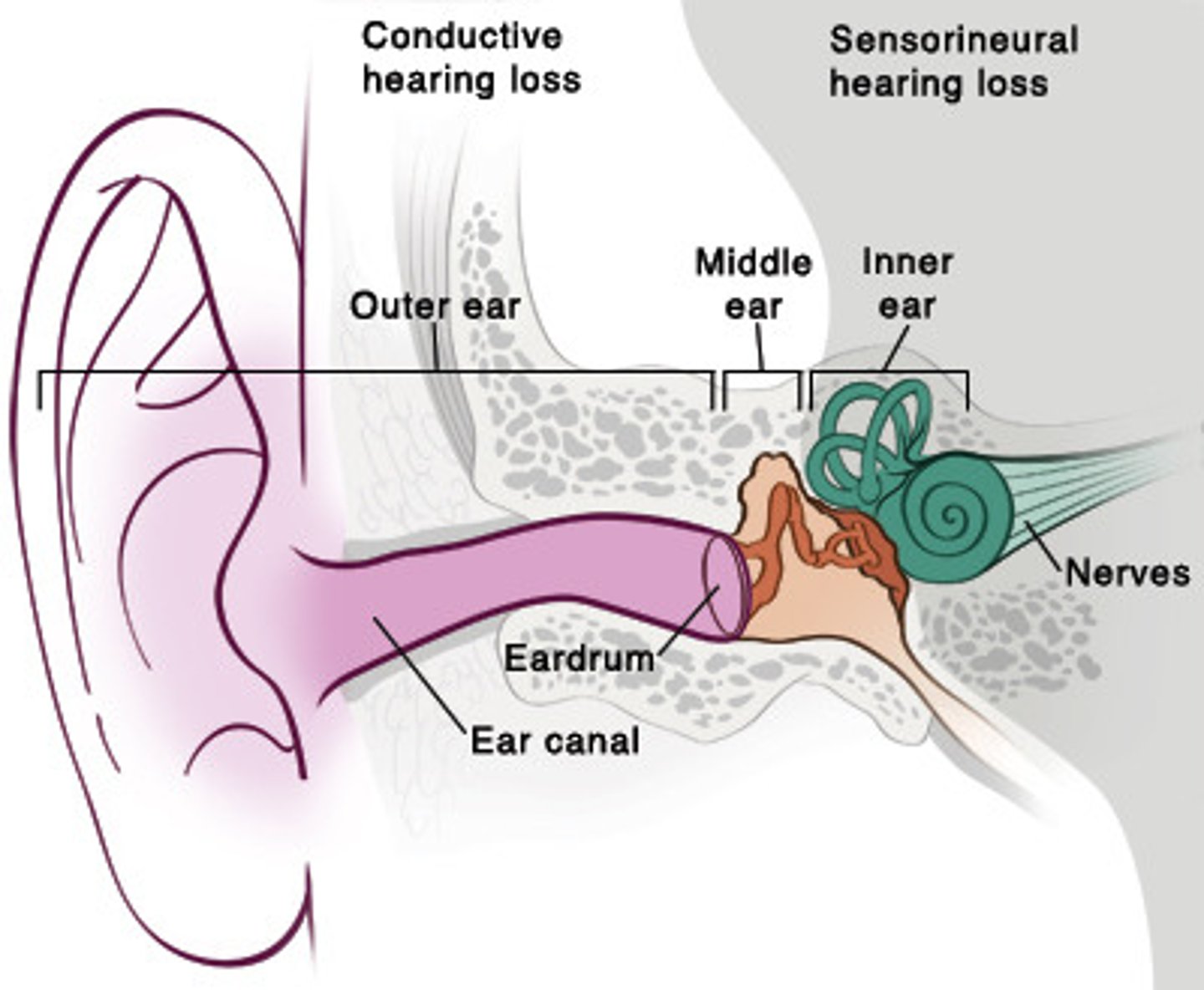
Structure of the ear
1. Outer
2. Middle
3. Inner
Outer ear
- FLUID FILLED
1. Pinna
2. Auditory Canal
Pinna
- Cartilage of the ear
- Funnels sound to auditory canal
Auditory canal
- Funnels sound to ear drum
- Contains specialized sweat glands produce ear wax to trap invading particles
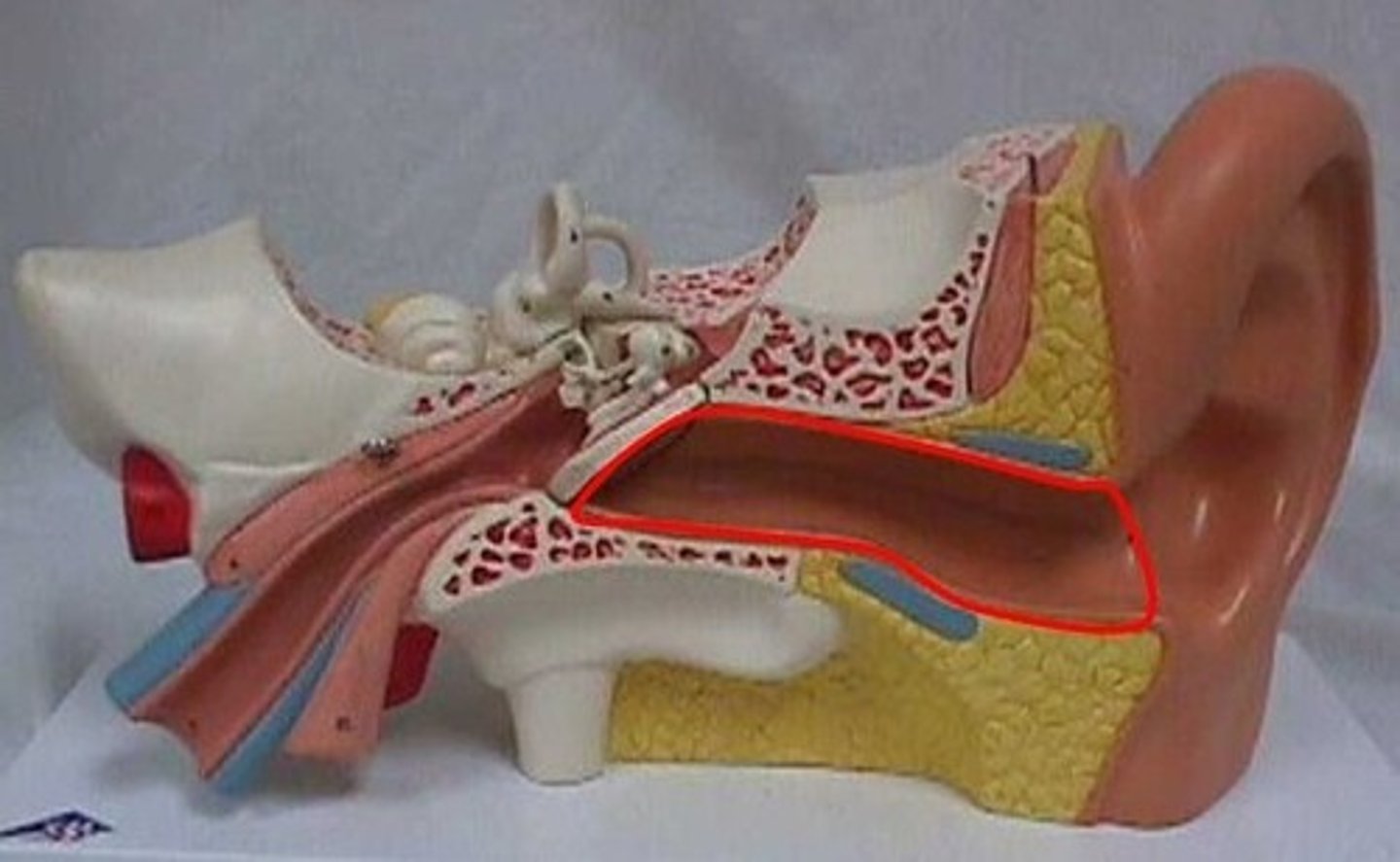
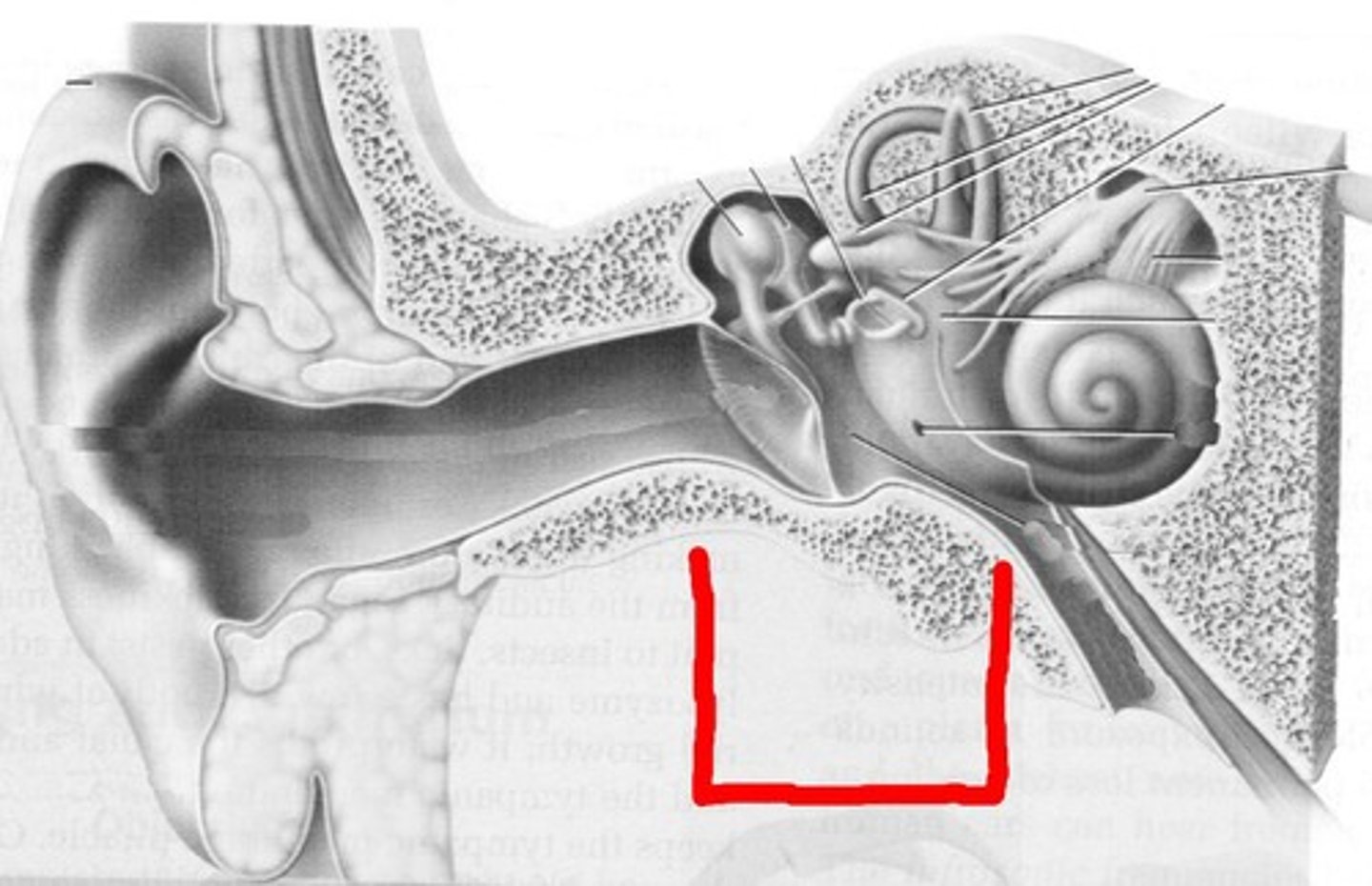
Middle ear
- AIR FILLED
1. Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
2. Ossicles
3. Eustachian tube
tympanic membrane
- AKA ear drum
- Separates the outer ear from the middle ear
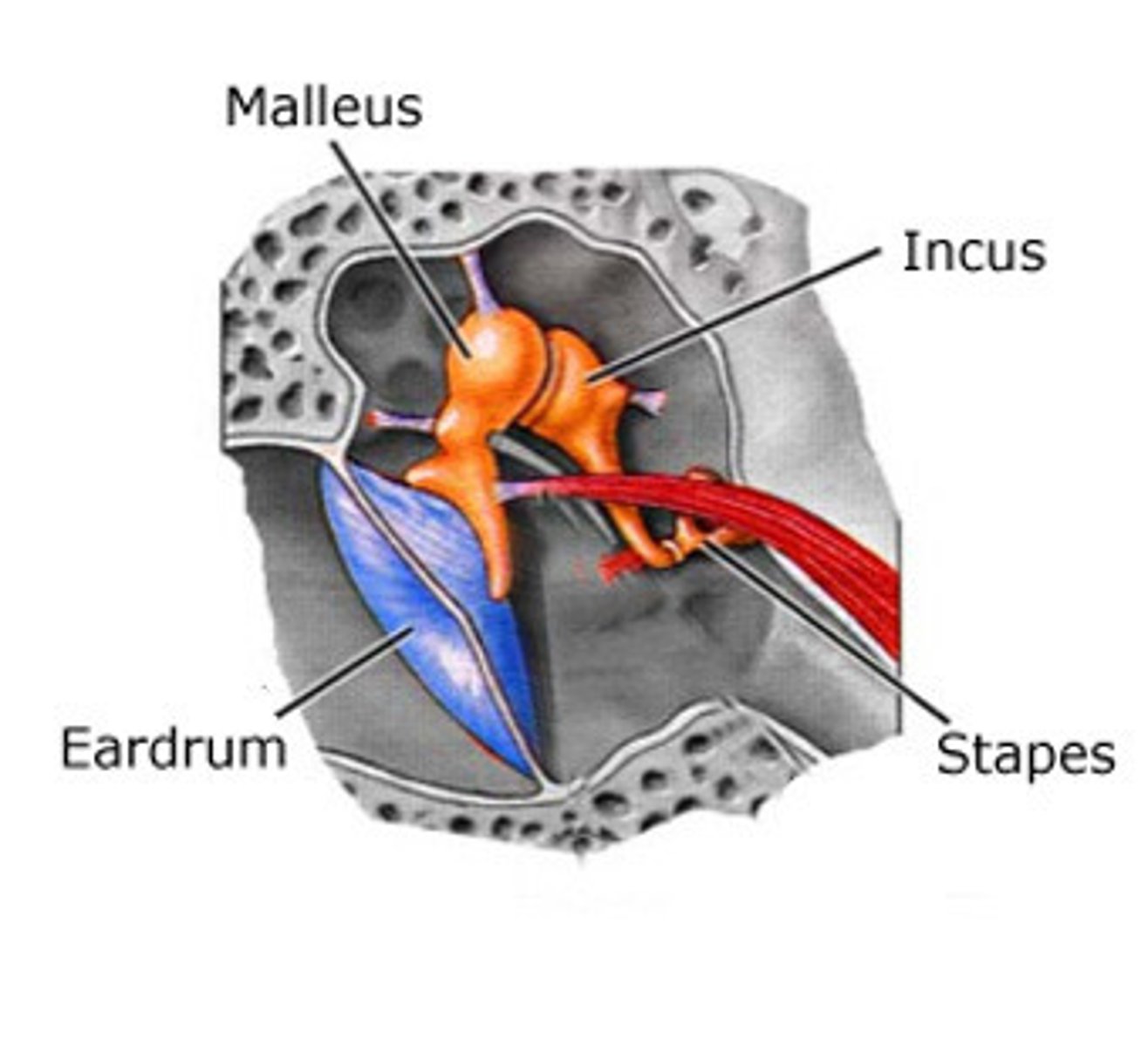
Ossicles
- Amplifies and passes sound from eardrum to oval window using three small bones
1. Malleus (The hammer)
2. Incus (The anvil)
3. Stapes (The stirrups)
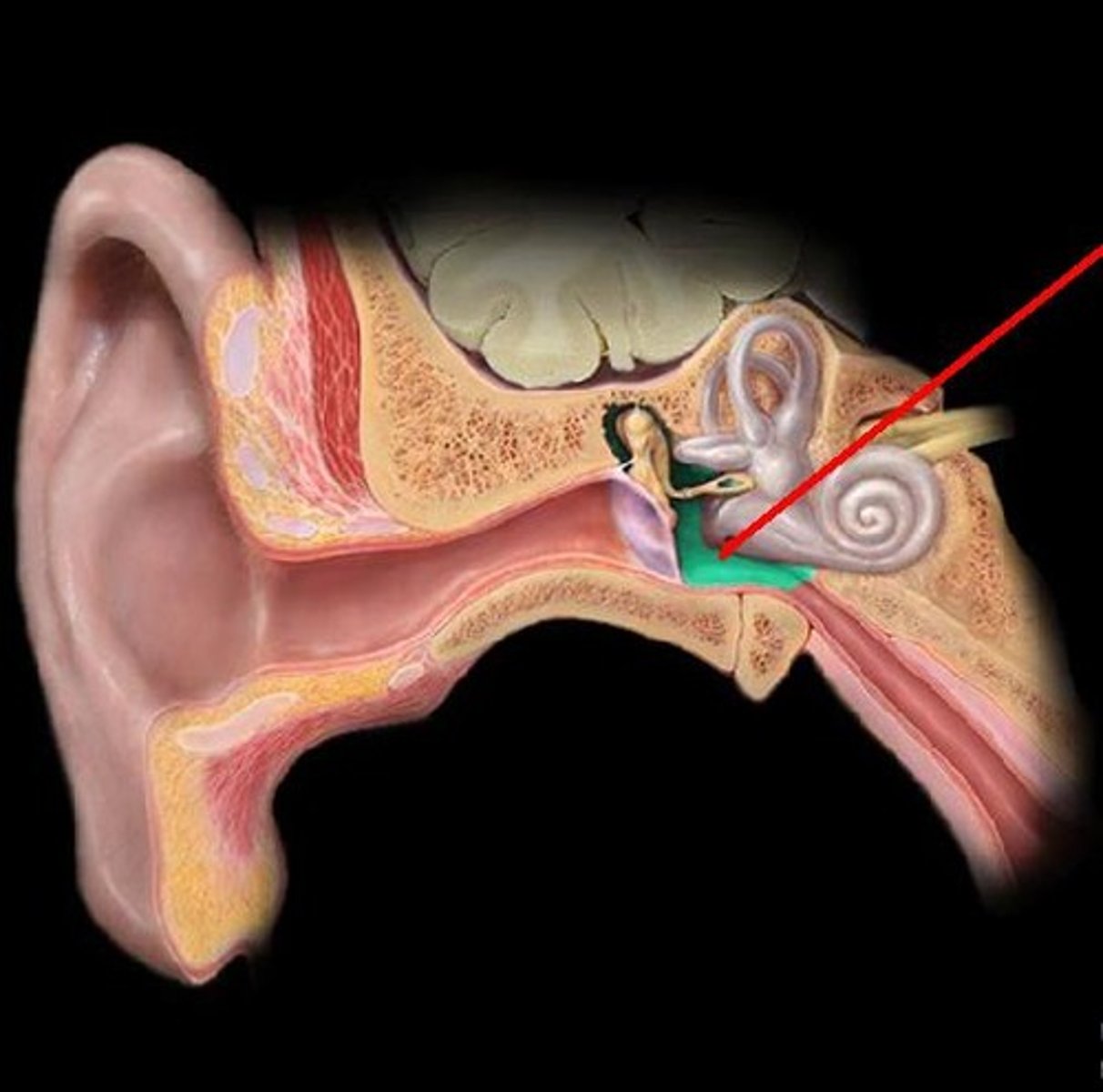
eustachian tube (auditory tube)
- Allows for air pressure equalization
- Connected to the throat
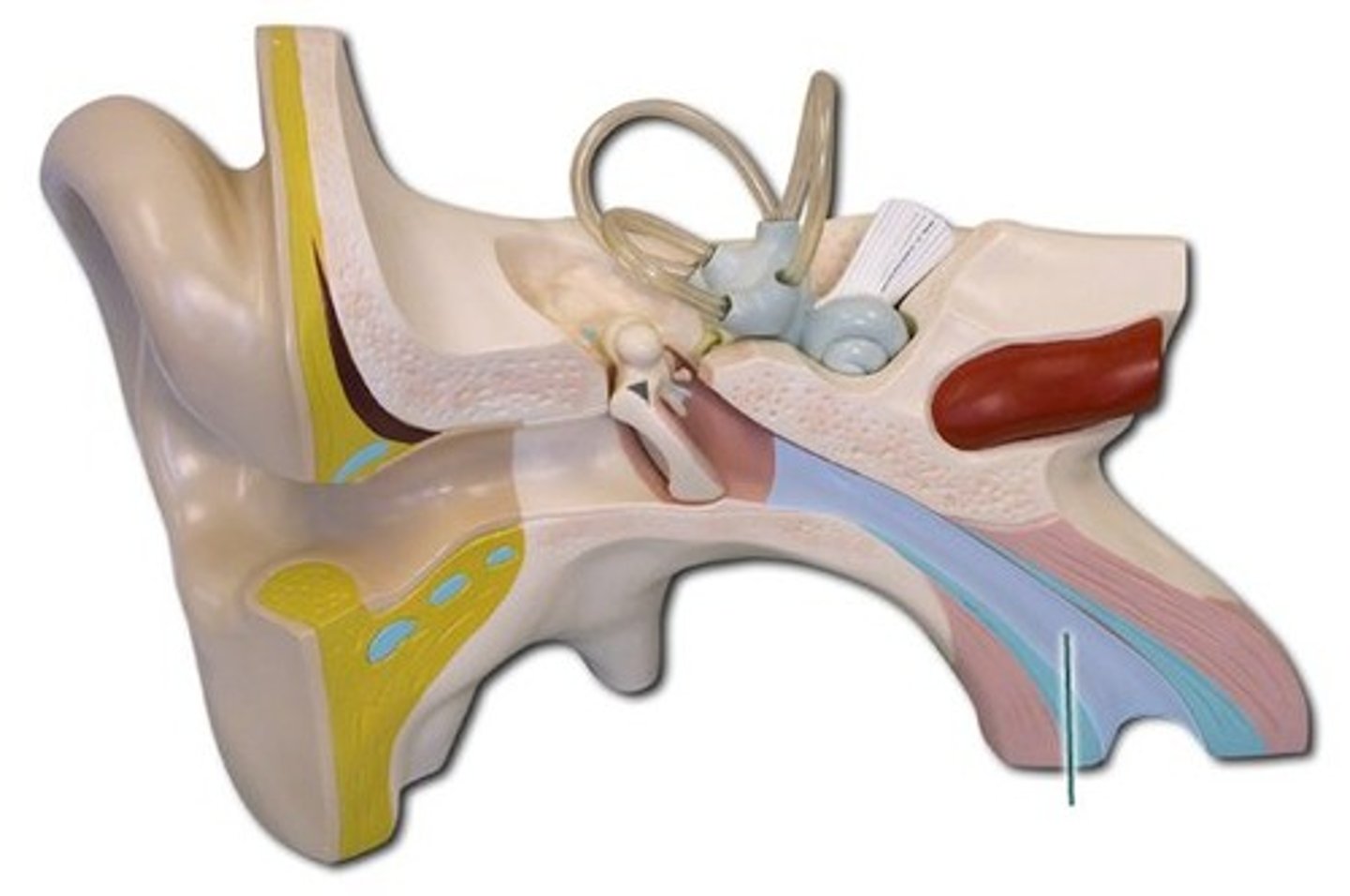
Inner ear
- Fluid filled
1. Semicircular canal
2. Vestibule
3. Cochlea
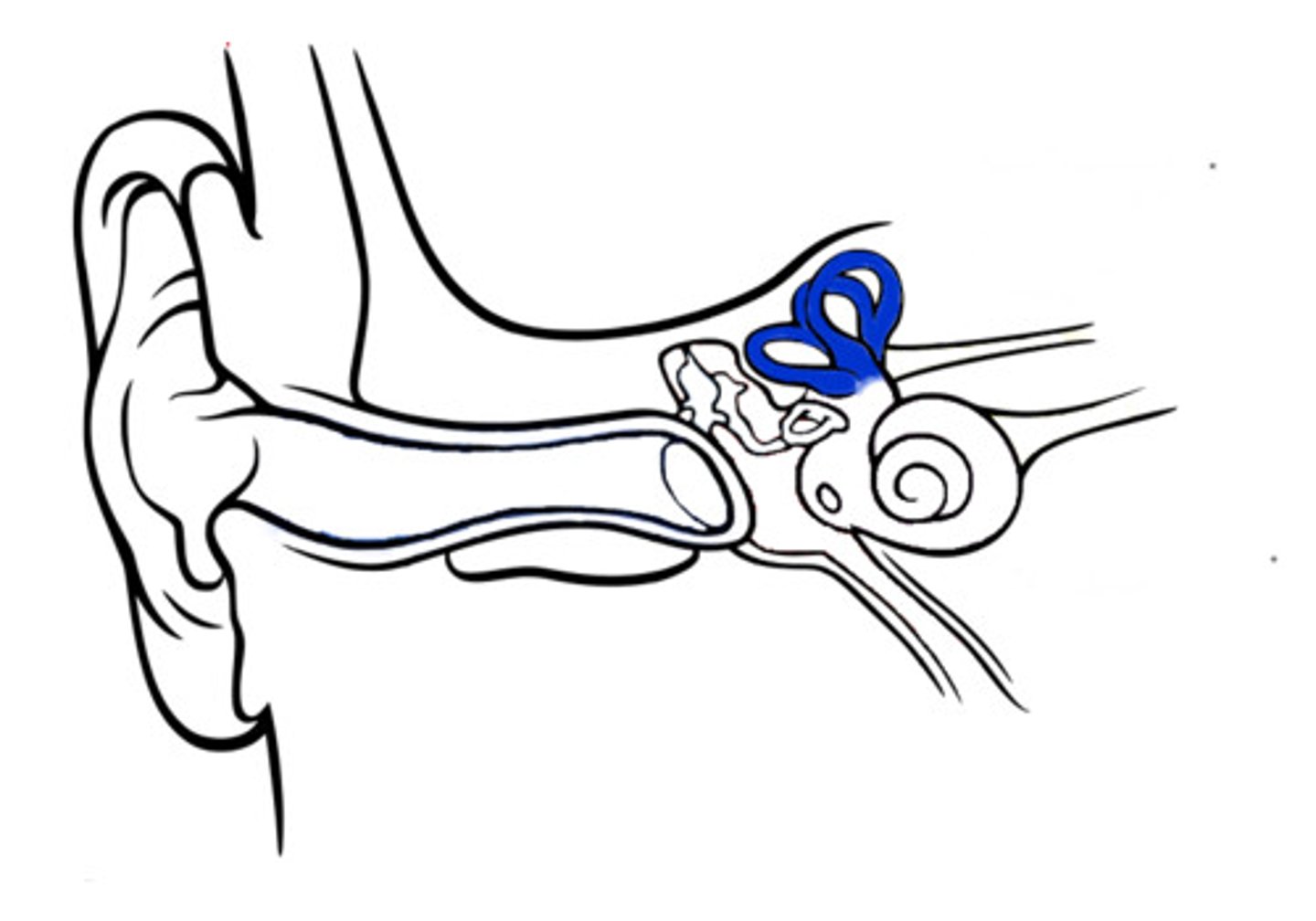
semicircular canal
- Helps with balance
- 3 fluid filled rings arranged in different angles
- Movement of fluid identifies body movement
vestibule
- Establishes head position
cochlea
- used for hearing
- shaped like a snail shell
- vibrations are converted into nerve impulses by the organ of corti
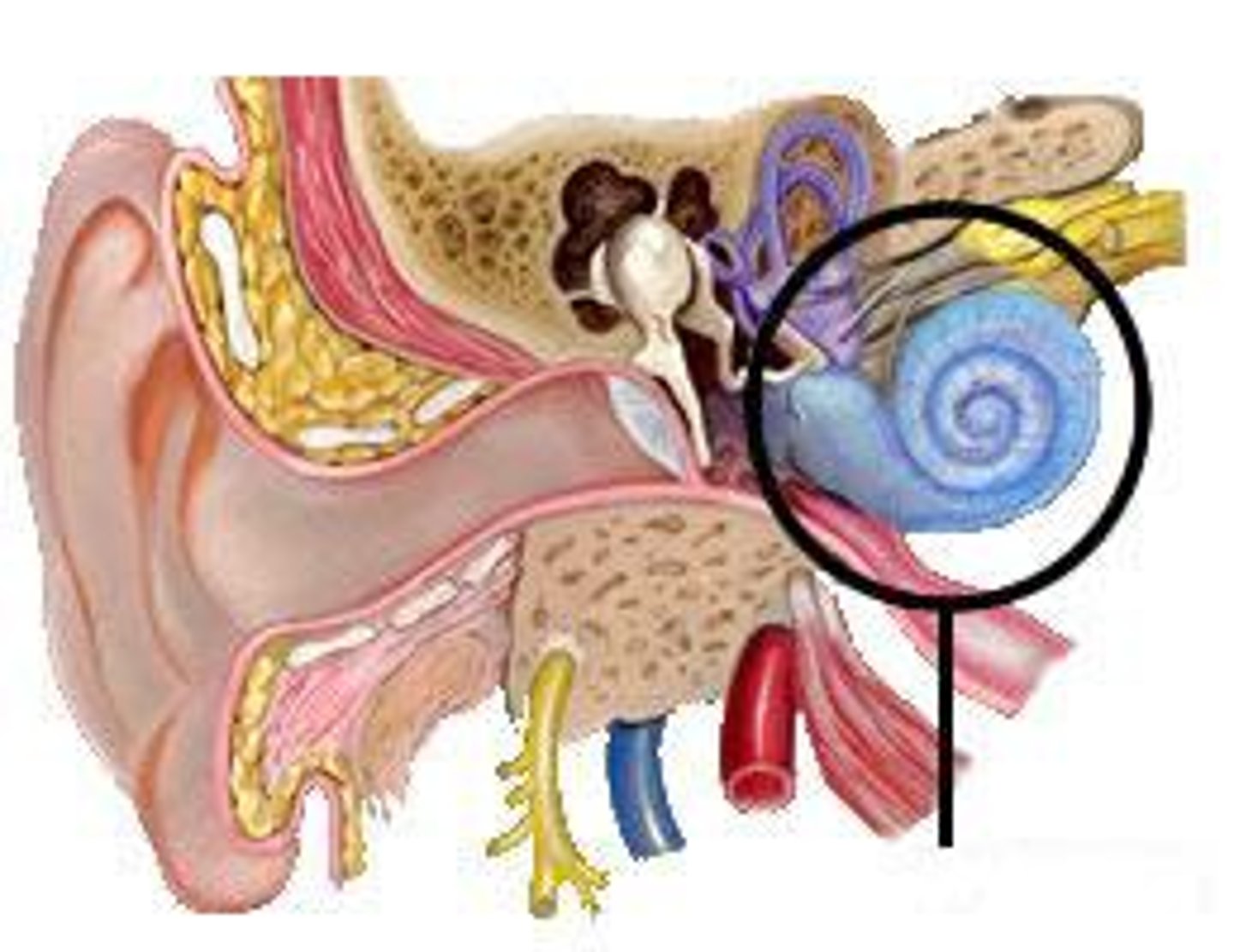
Organ of Corti (ear structure)
- In the middle of the cochlea
- Comprised of rows of hair cells
- Sound waves bends the hair cells which then enact an action potential to sensory neurons to CNS
3 functional components of homestasis
1. receptor
2. coordinating centre
3. effector
endocrine hormones
- produced by endocrine glands
- secreted into the blood
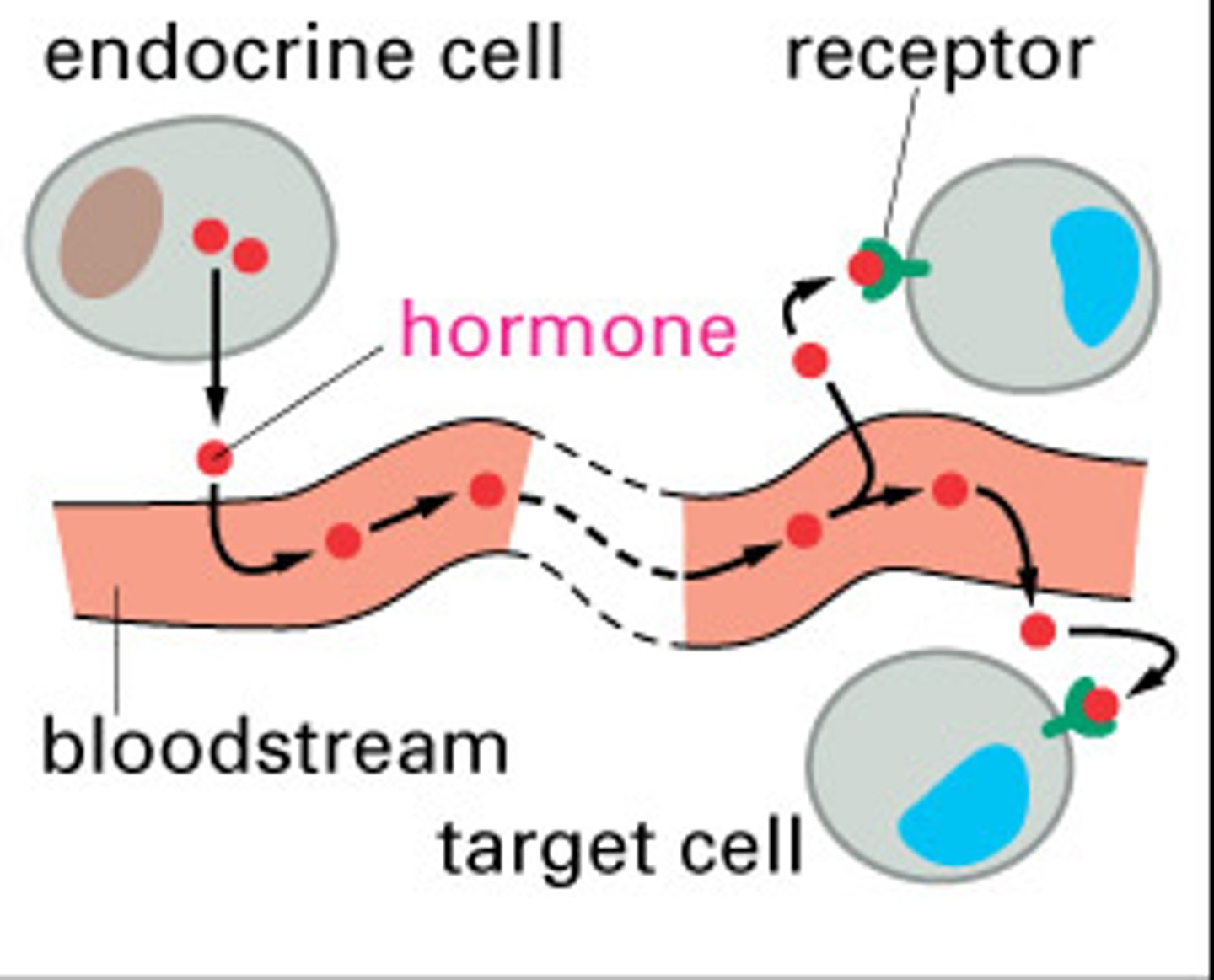
Nervous system vs endocrine system
anterior pituitary
- Makes (Synthesizes) hormones
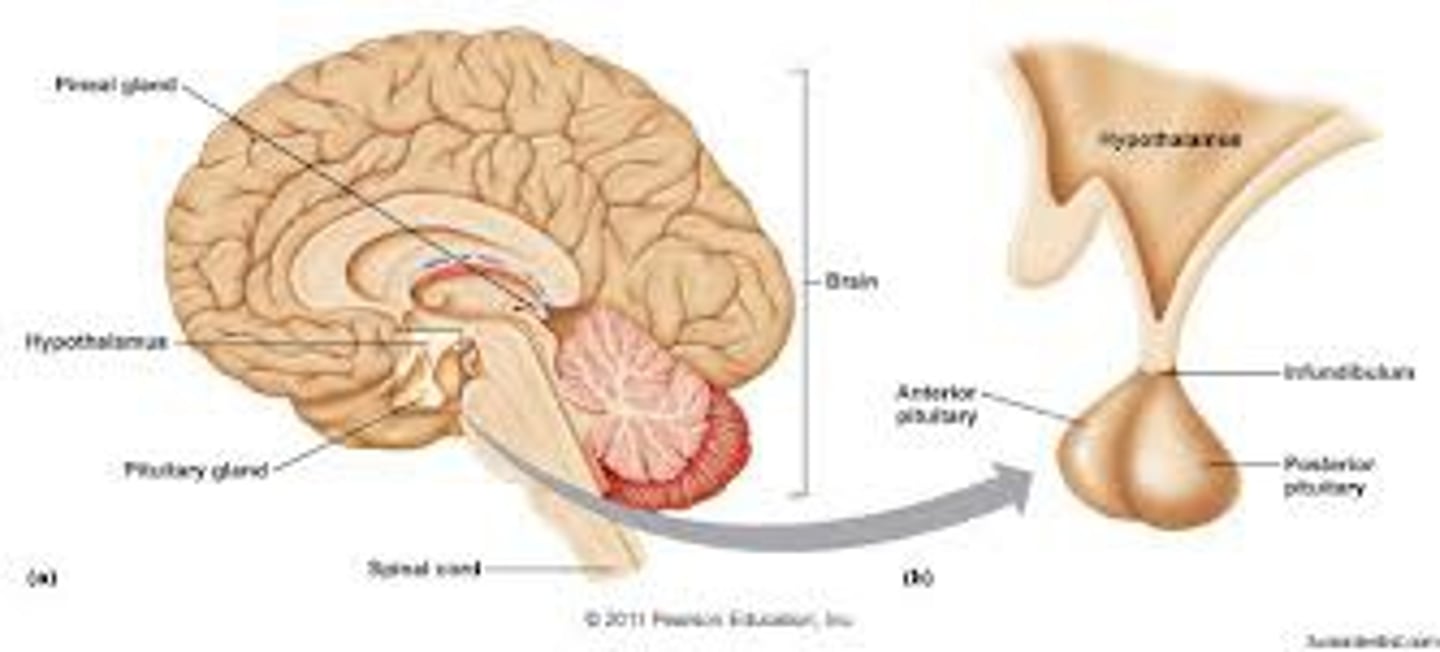
posterior pituitary
- stores hormones produced by the hypothalamus
- ONLY PRODUCED OXYTOCIN AND ADH
releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones
Releasing hormone = stimulates the pituitary to release a stored hormone
inhibiting hormone = stop the pituitary from releasing any hormone
Which two endocrine glands are in control of blood sugar?
1. Pancreas (Produces insulin and glucagon)
2. Adrenal glands (Produces epinephrine)
Homeostasis of blood glucose level
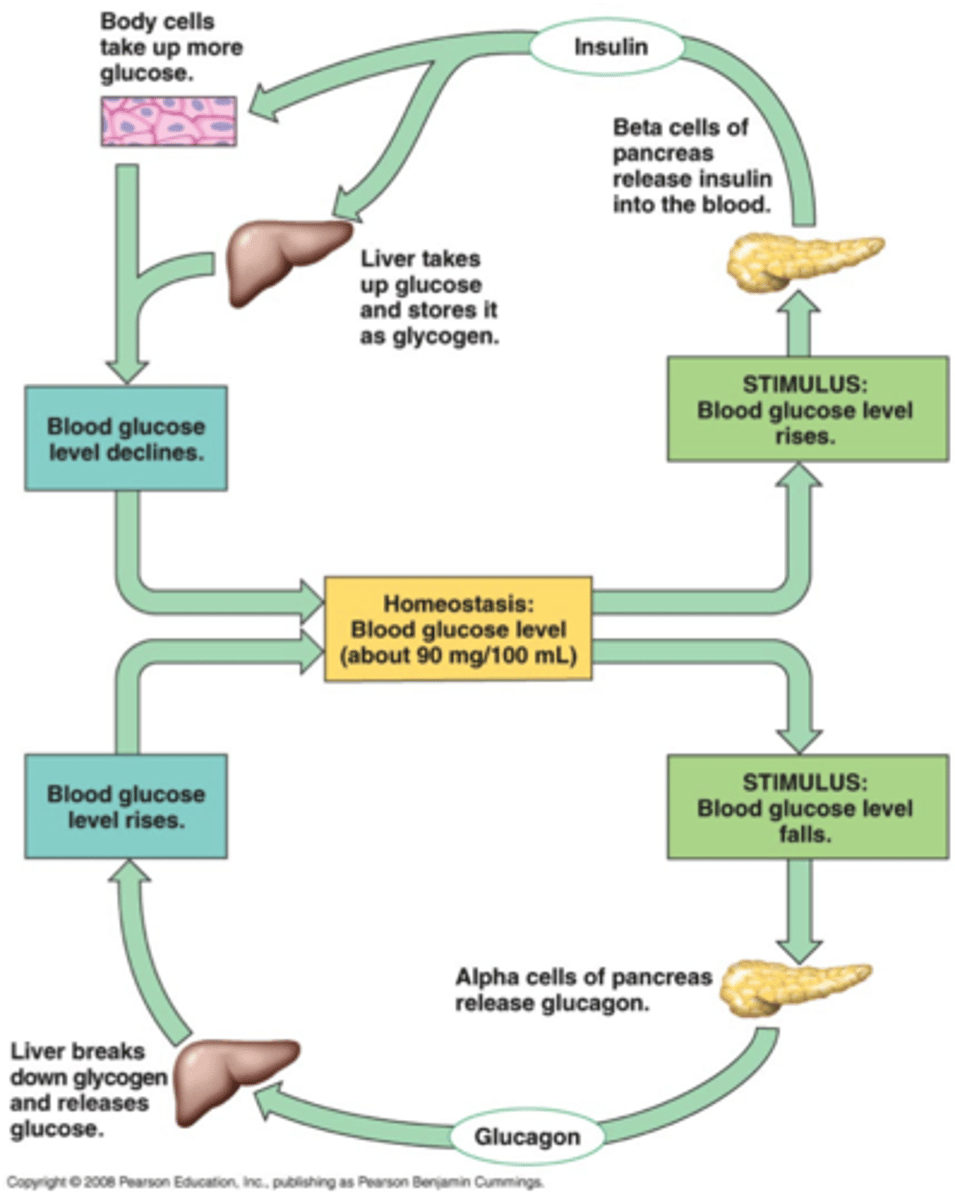
Effect of insulin
- Lowers blood glucose levels
- stimulates uptake of glucose into cells
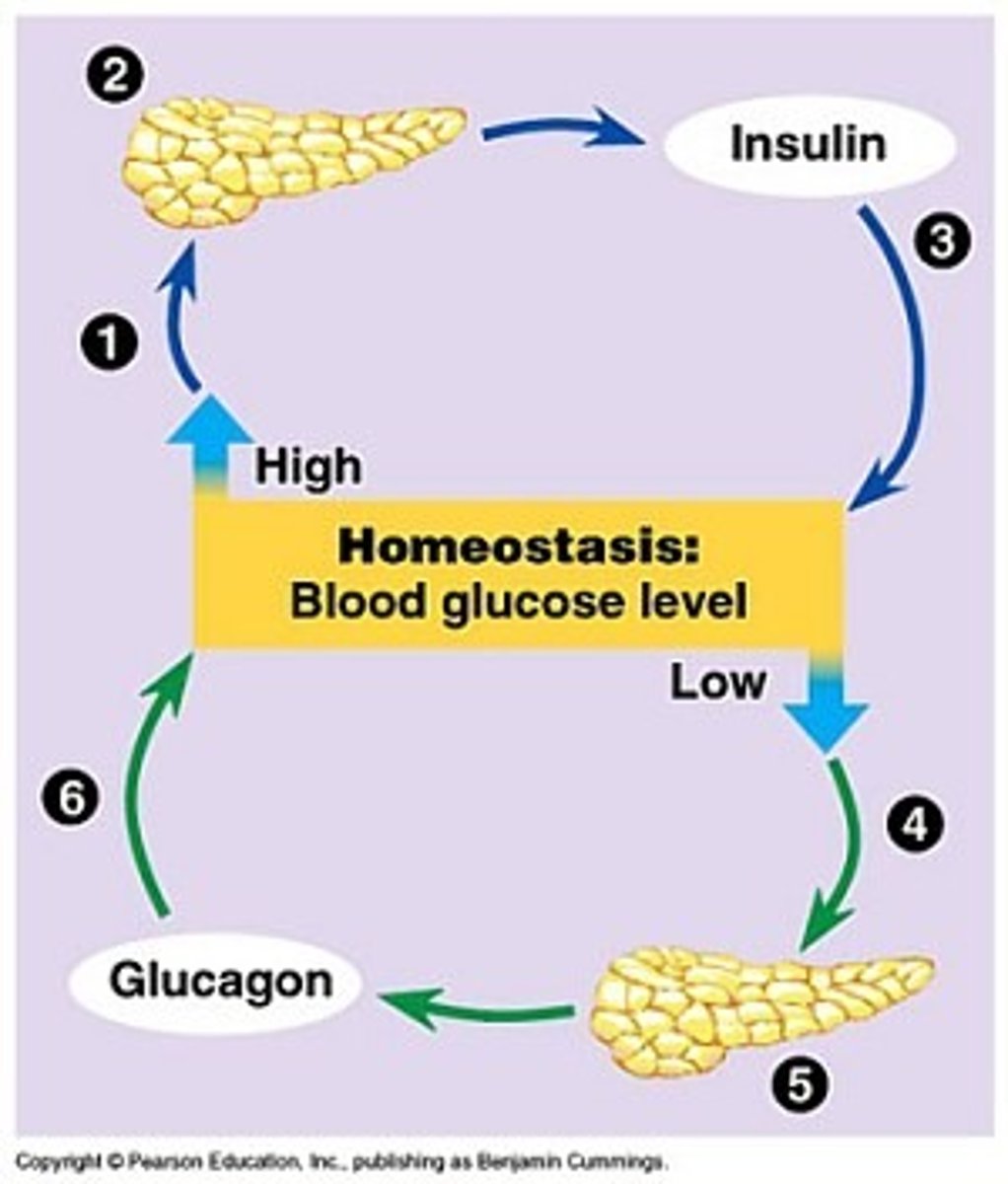
Effects of glaucagon
- Raises blood glucose levels by stimulating liver to convert glycagon to glucose
Diabetes Mellitus
- AKA sugar diabetes
- Body cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly
3 types of diabetes mellitus
1. Type 1 diabetes (unable to produce insulin)
2. Type 2 (not enough produced or not effective)
3. Gestational diabetes (PREGNANCY TEMPORARY)
3 types of treatments for diabetes mellitus
1. Pancreatic transplantation
2. Islet cell transplantation
3. Gene therapy
Pancreatic transplantation
- Replace the not working pancreas with a new one
islet cell transplantation
- Transplant working cells that produce insulin.
- Can keep original pancreas
Gene therapy
- Pancreas cells have a mutation that causes them not to produce insulin.
Adrenal cortex hormones
Produces Aldosterone and cortisol.
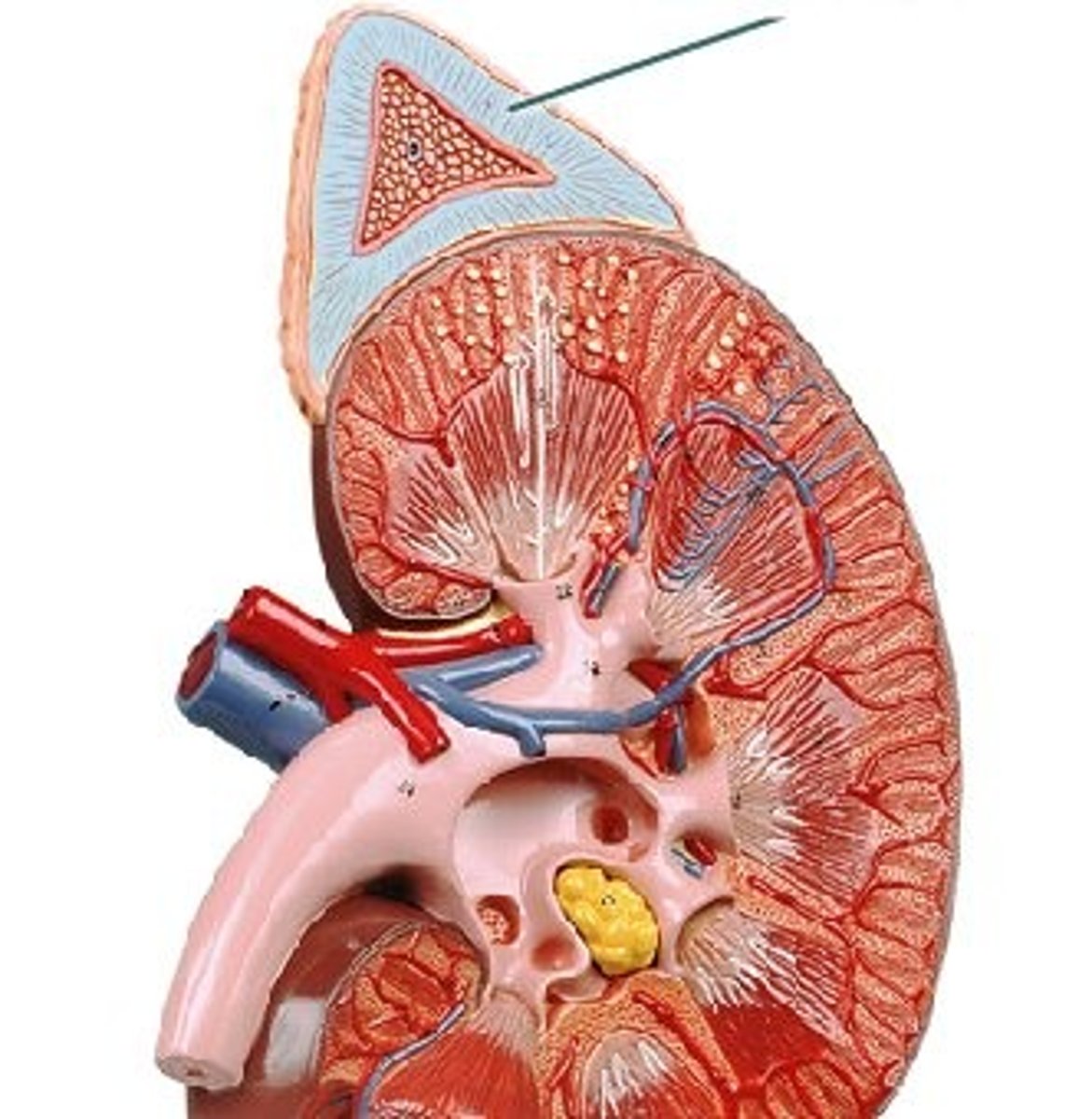
Aldosterone
ALDOSTERONE = reabsorbs sodium and water (targets the kidney)