PPN 301 - CLASS 4(5) LABOUR AND DELIVERY
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is the process of labour
labour is the process of moving the fetus, placenta and membranes out of the uterus and through the birth canal
usually begins between the 37th and 42 week of gestation
changes occur in the woman’s reproductive system in days and weeks before labour begins
BEFORE LABOUR BEGINS - prep phase
increase Braxton hicks contraction
cervical ripening (softens)
oestrogen, relaxin, and prostaglandins break down in cervical connective tissue
increase in the excitability of the uterine musculature
Mechanical stretching of the uterus also helps to increase contractility
increase oxytocin receptors and levels of oxytocin (ferguson reflex)
uterus becomes more sensitive and is ready to contract
Onset and signs preceding labour
These are signs before true labour that are getting the body ready for labour - baby moving towards the pelvis, small blood vessels break, and bloody discharge occurs
lightening or dropping
increase vaginal discharge; bloody show
backache
stronger braxton hicks contractions
weight loss of 0.5-1.5 kg (before labour starts)
surge of energy (also called nesting)
flulike symptoms
increased vaginal discharge; bloody show
cervical ripening
possible rupture of membrane
True labour
TRUE LABOUR
CONTRACTIONS
increase in intensity
increase in duration
discomfort begins in back, radiates around abdomen
become progressively closer together (ask time contractions)
do not dissapear with walkin
CERVICAL
begins to efface and dilate
SHOW
may or not be present
FALSE LABOUR
CONTRACTIONS
do not increase in intensity
do not increase in duration
discomfort usually in abdomen(alone)
do not become progressively closer
may disappear with walking
CERVIX
no cervical change
SHOW
not present
WHAT ARE THE 5 P’S OF LABOUR
labour is a combination of all of these factors
powers (contractions)
strength and pushing
passageway
birth canal
passenger (fetus and placenta)
position of mother
baby and alignment
psychological response
mothers emotional state
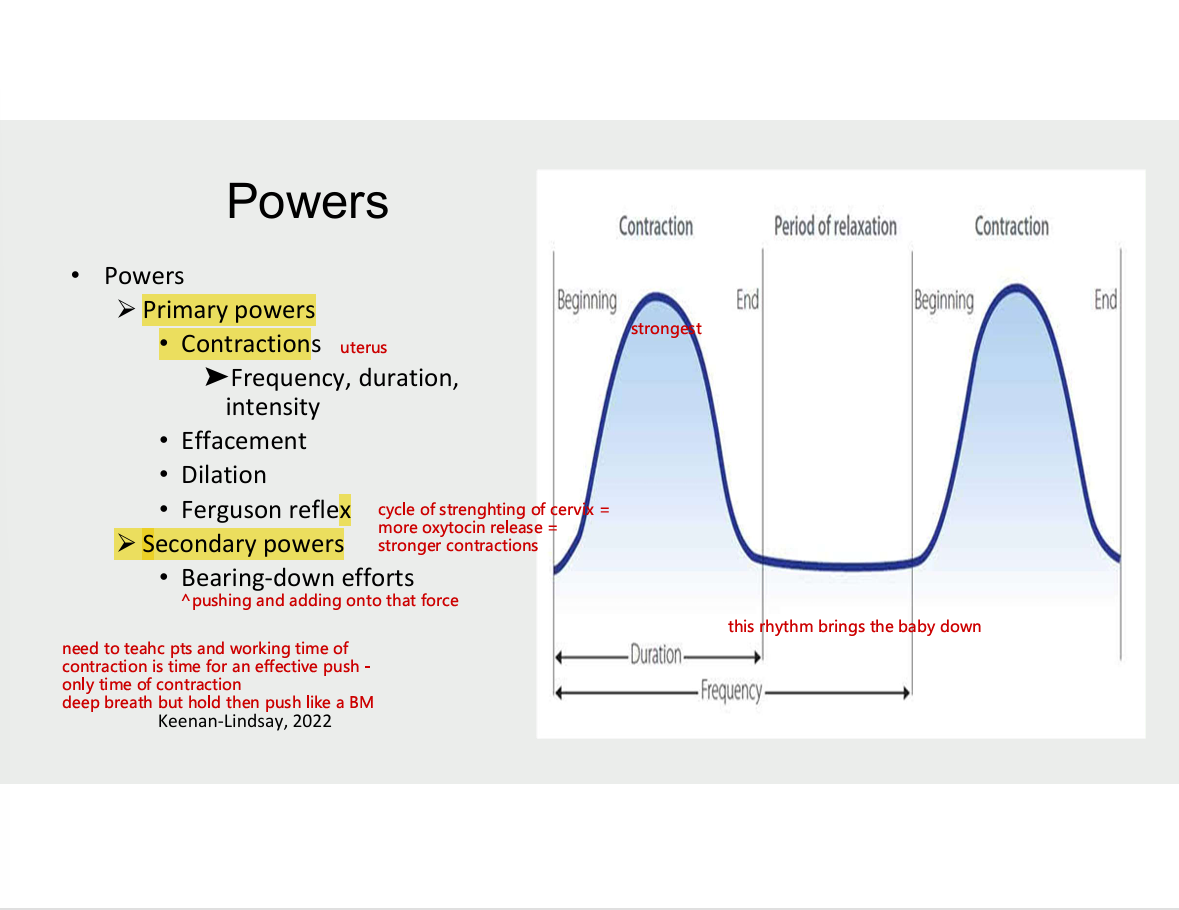
5 P’S OF LABOUR - Powers
primary powers
contractions
frequency, duration, intensity
effacement
dilation
ferguson reflex
secondary powers
bearing-down efforts (pushing and adding onto that force)
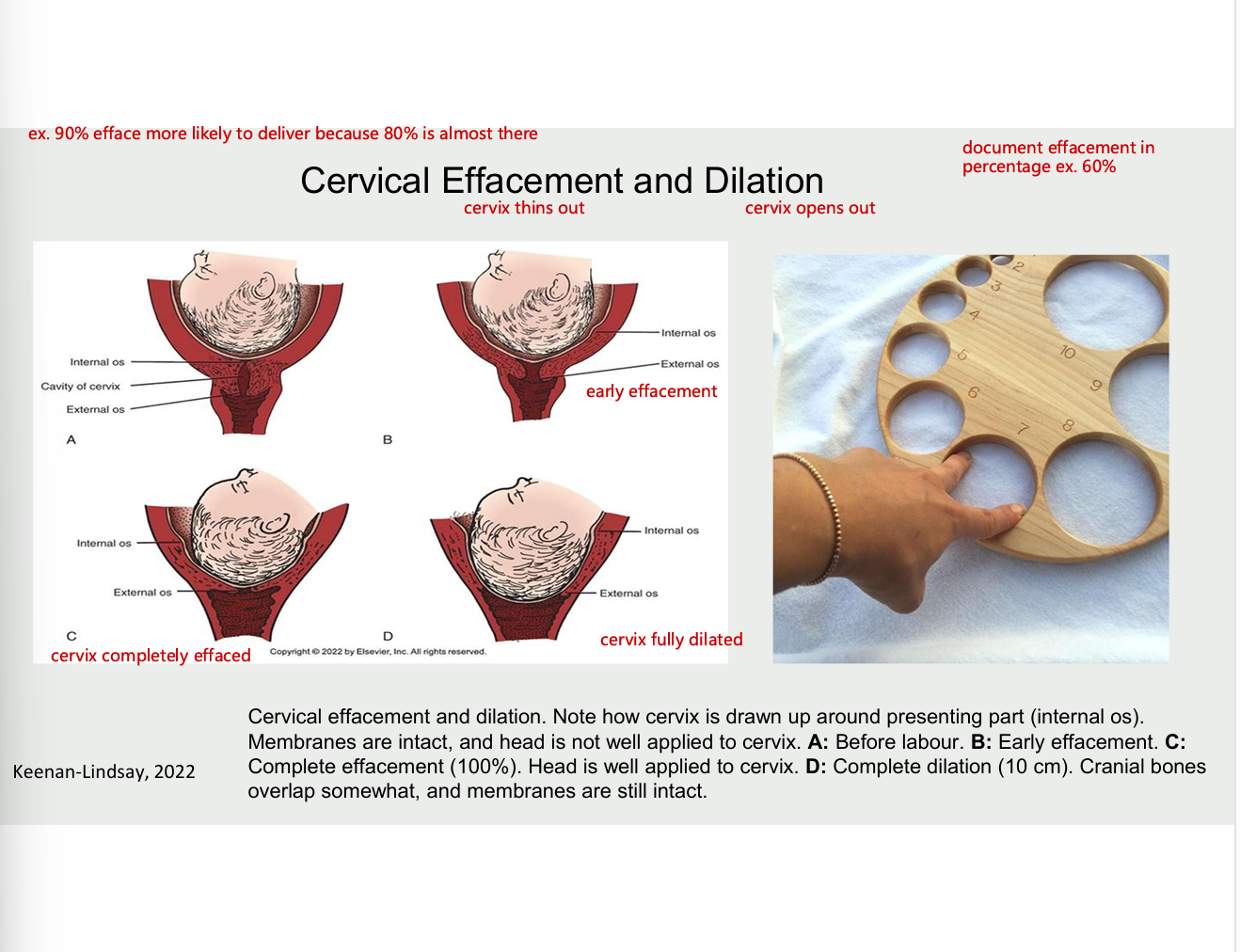
cervical effacement (cervix thins out) and dilation (cervix opens out)
diagram
5 P’S OF LABOUR - passenger (baby and placenta)
fetal presentation
cephalic/vertex - head as presenting part (head down feet up) - common and favourable position
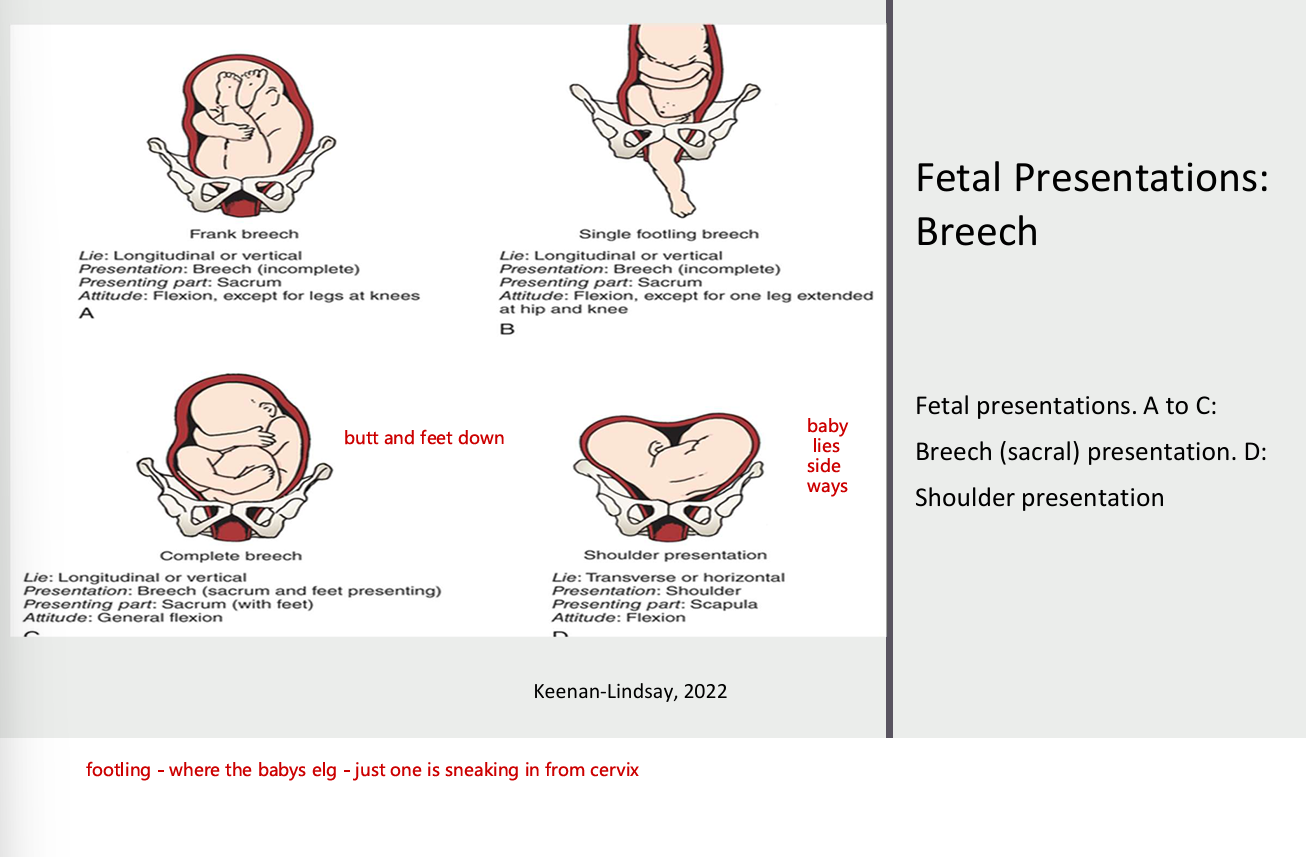
breech - buttox as presenting part (butt down)
shoulder/transverse - shoulder as presenting part (or shoulder in the way)
size of fetal head
fetal lie - baby aligned with mothers spine - look at vertebrae for the mom - longitudinal align vertically transverse - across, slanted - oblique
fetal attitude - how baby holds self - ideally chin tucked in
fetal position
station - how far baby’s head has descended into pelvis
engagement
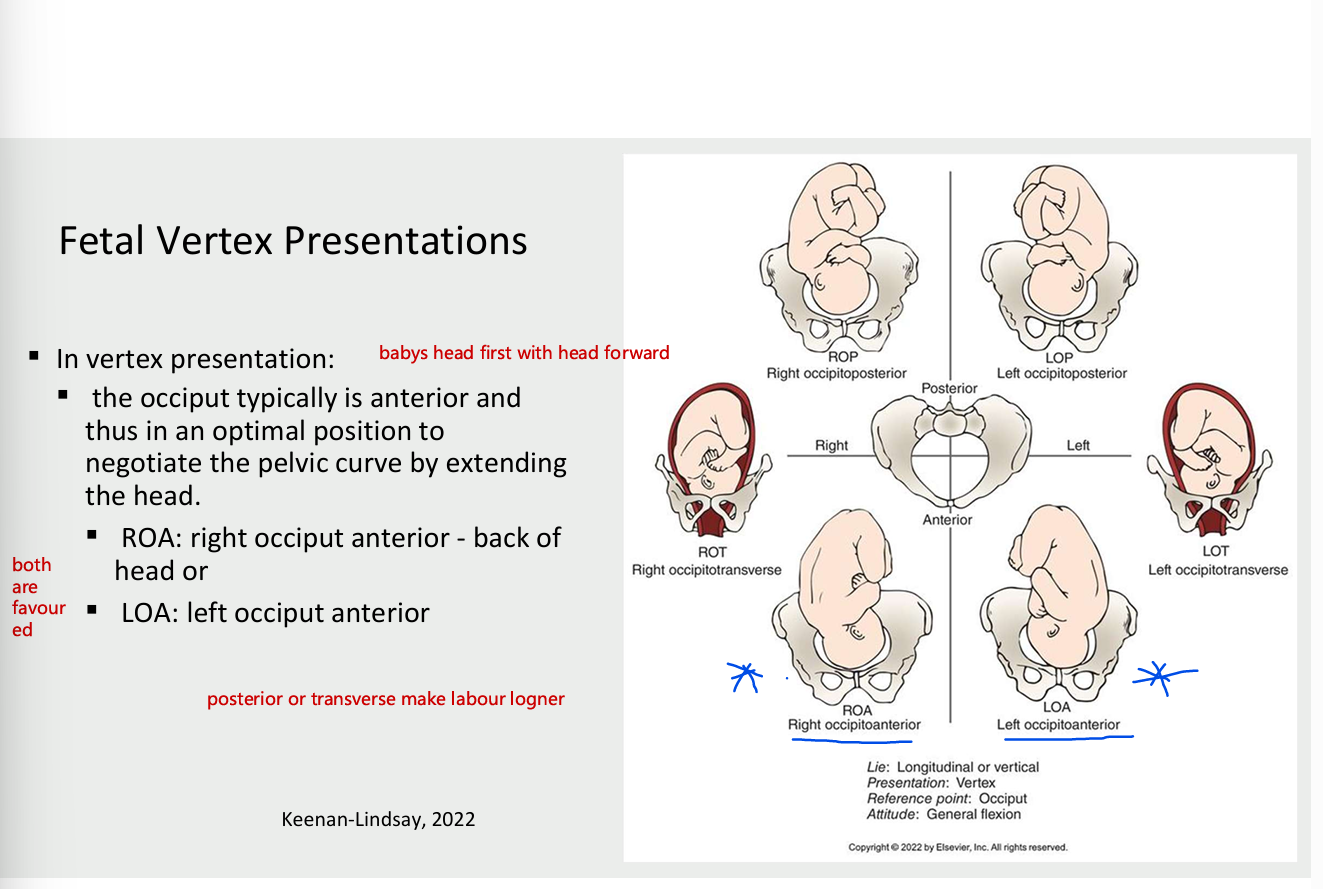
fetal vertex presentation
vertex presentation
occiput typically is anterior and thus is the optimal position to negotiate the pelvic cure by extending the head
ROA- right occiput anterior - back of the head
LOA - left occiput anterior
fetal presentations: Breech
fetal presentations, A to C
breech (sacral) presentation. D: shoulder presentation
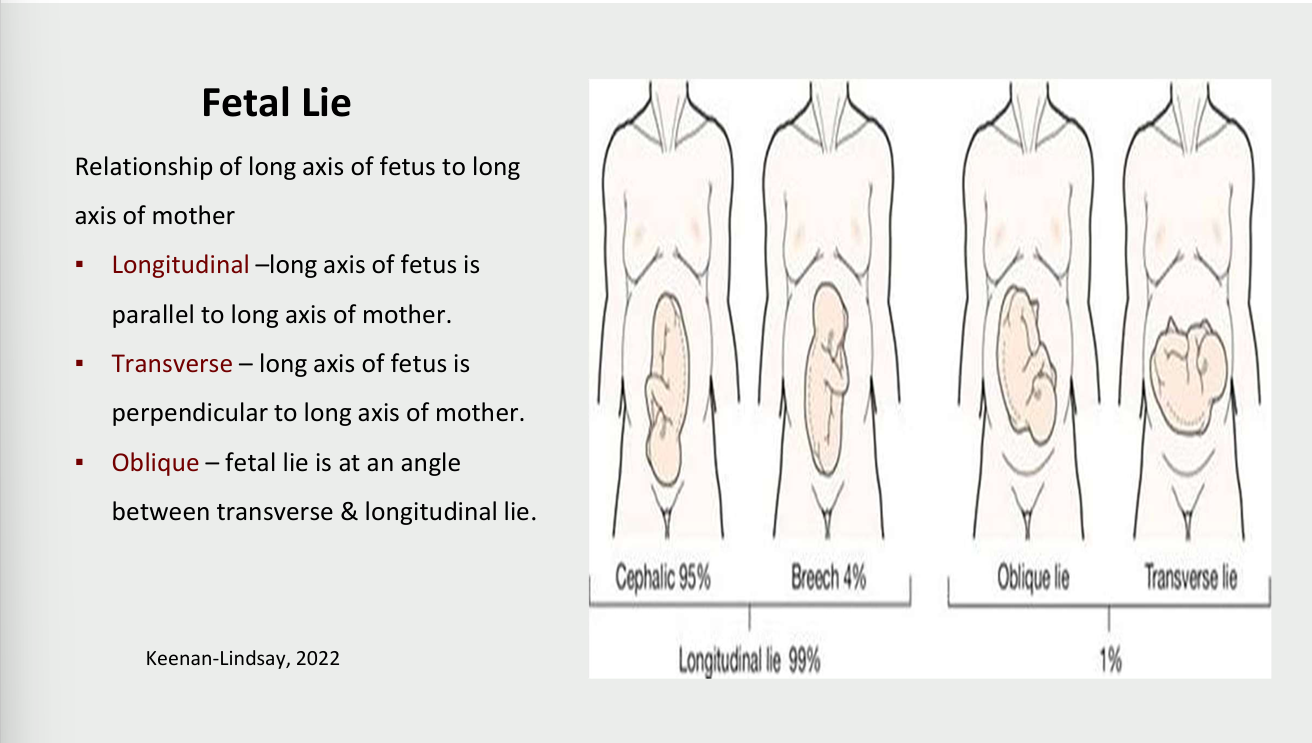
Fetal lie
relationship of long axis of fetus to long axis of mother
longitudinal - long axis of fetus is parallel to long axis of mother
transverse - long axis of fetus is perpendicular to long axis of mother
oblique - fetal lie is at an angle between transverse and longitudinal lie
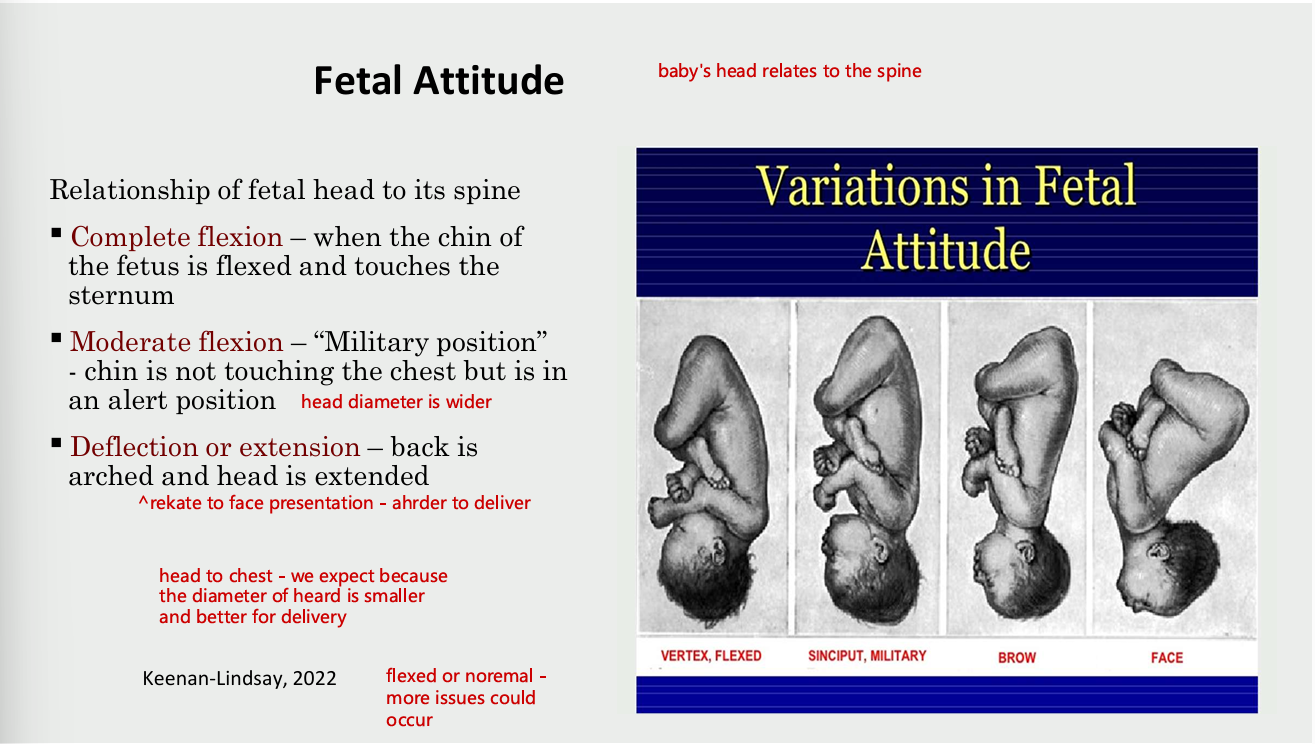
Fetal attitude (baby’s head in relation to spine)
relation of fetal head to its spine
complete flexion
when the chin of the fetus is flexed and touches the sternum
moderate flexion
military position - chin is not touching the chest but is in an alert position (head diameter is wider)
deflection or extension
back is arched and head is extended (relate to face presentation - harder to delivery
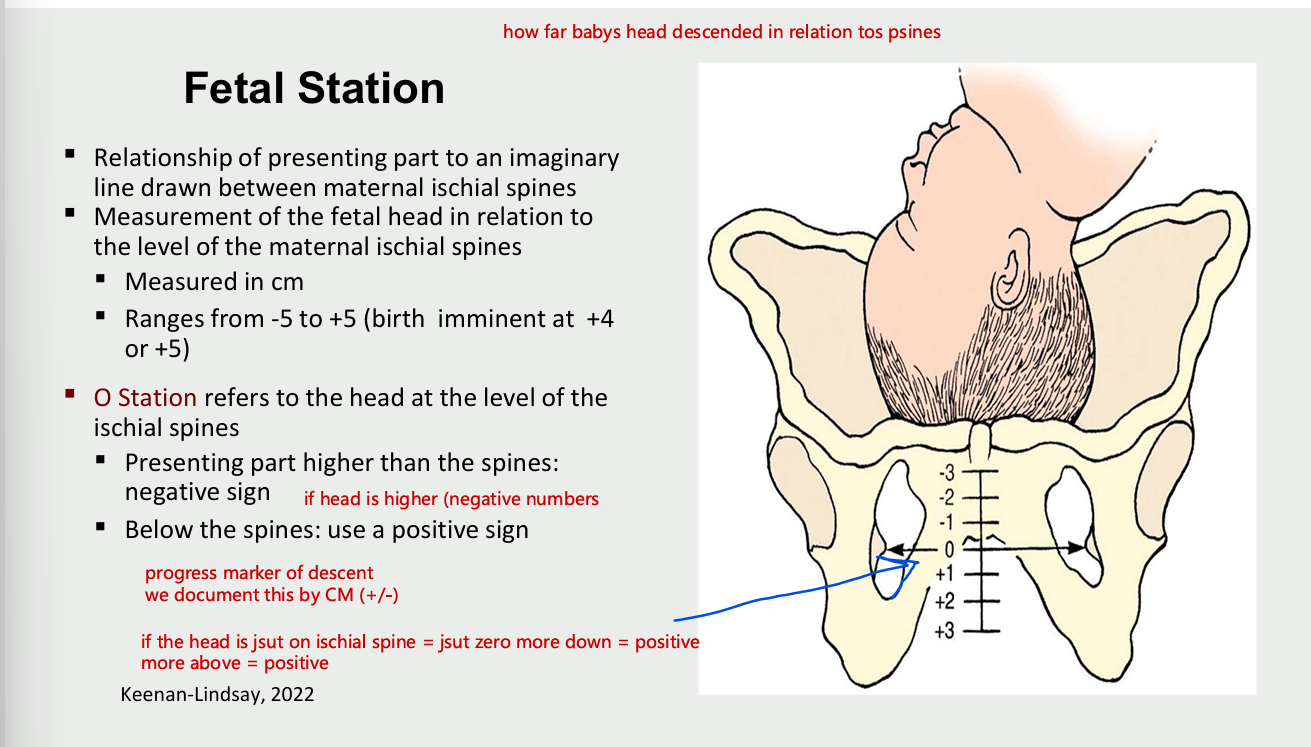
fetal station
relationship of presenting part ot an imaginary line drawn between maternal ischial spines
measurement of fetal head in relation to level of maternal ischial spines
measure in cm
ranges form -5 to +5 (birth imminent at +4 or+5)
O station refers to the head at the level of the ischial spines
presenting part higher than the spines: negative sign (if head is higher negatives
below the spines - positive sign
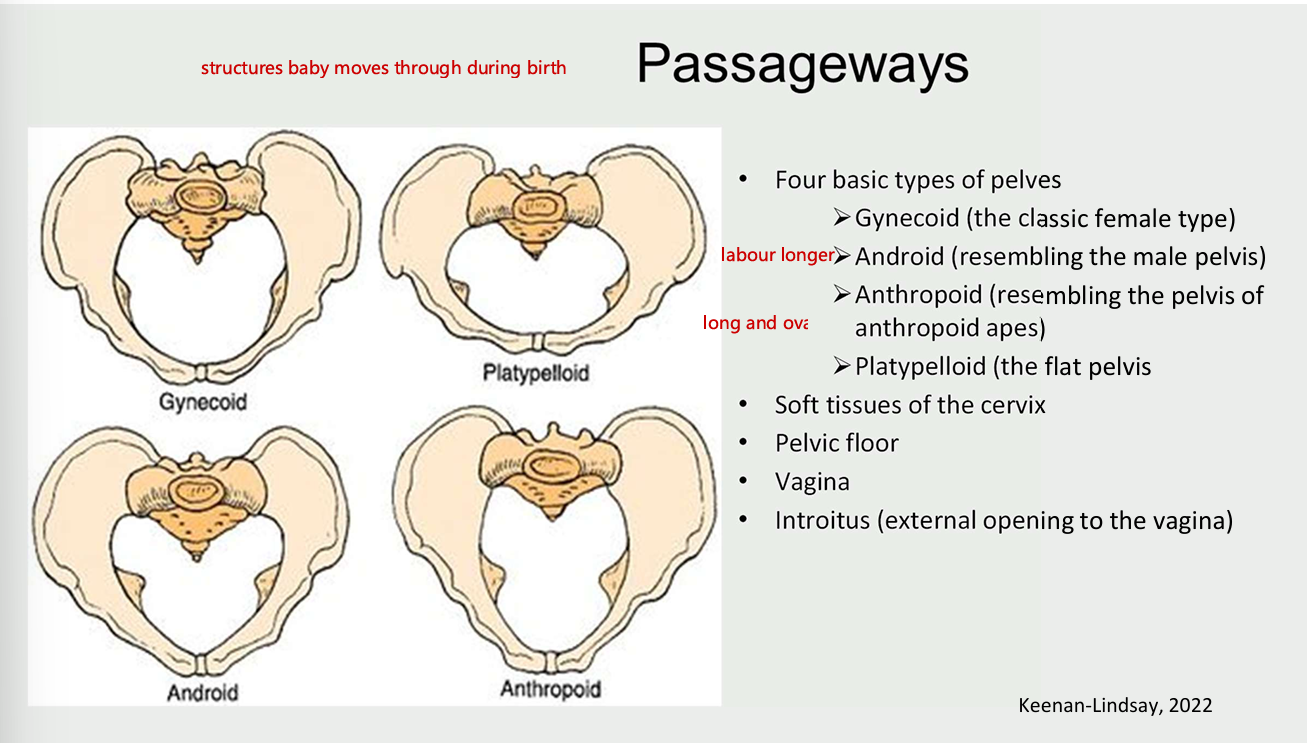
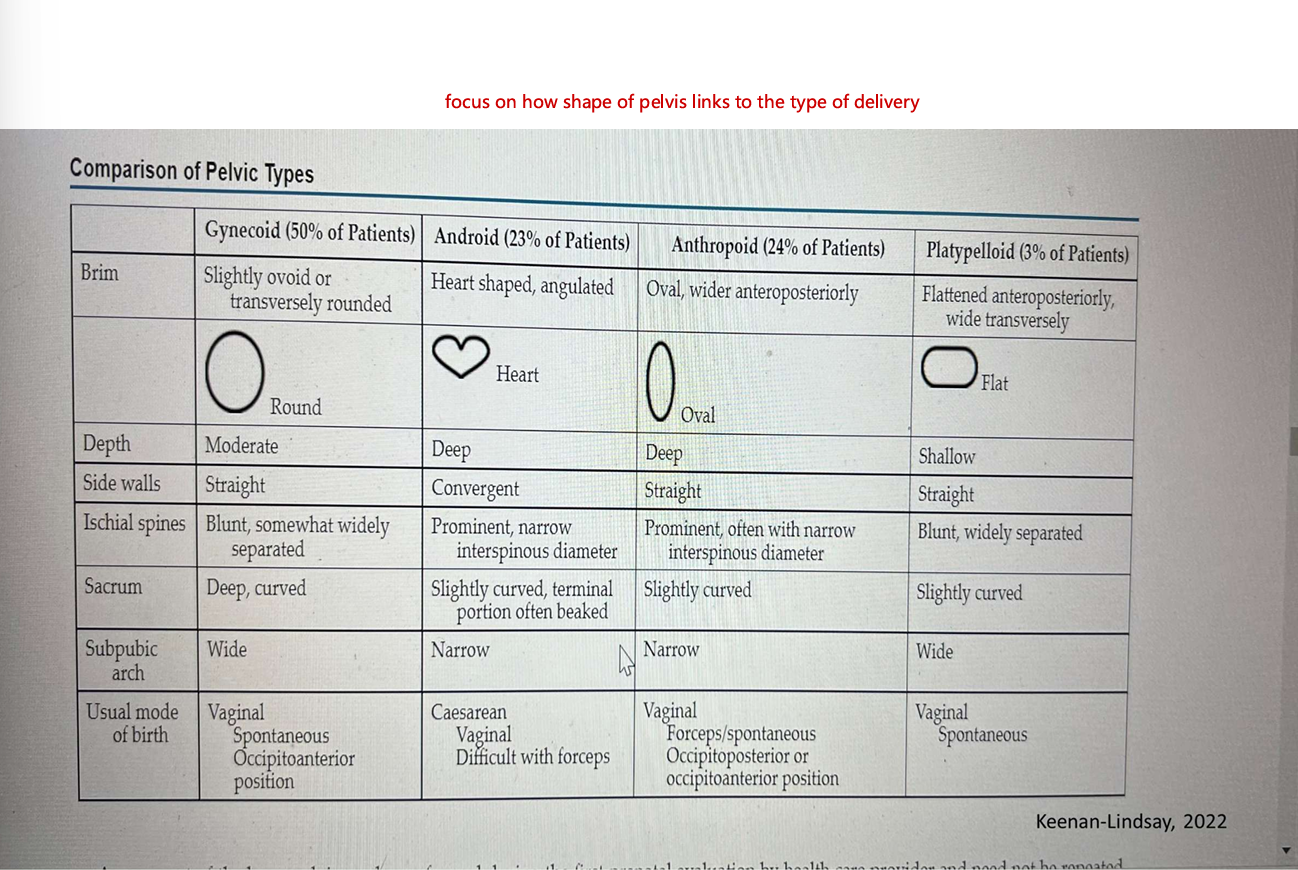
5 P’S OF LABOUR - passageways (structures the babay moves through during birth
4 basic types of pelves
gynecoid (classic female type)
android (resembling the male pelvis)
anthropoids (resembling the pelvis of anthropod apes)
platypelloid (the flat pelvis)
soft tissue of the cervix
pelvic floor
vagina
introitus (external opening to the vagina)
comparison of pelvic types and shapes
5 P’S OF LABOUR - position
position of a labour woman
position affects a woman’s anatomical and physiological adaptations to labour
frequent changes in position
relieve fatigue
increase comfort
improve circulation
labouring woman should be encouraged to find most comfortable position
gravity promotes descent of the fetus
5 P’S OF LABOUR - psychological response
patient extremely anxious (emotional stress)
emotional factors related to the patient
amount of sedation required for the patient
stages and process of labour
first stage
onset of contractions to full dilation of the cervix
latent phase
active phase
second stage
full dilation of cervix to birth
pushing
third stage
birth of the fetus until delivery of the placenta
fourth stage
2 hours post delivery of the placenta
stages and process of labour - latent and active phase
latent phase
onset of regular contraction, progress in effacement of the cervix and little increas ein descent
up to 3-4 cm of dilation (depending on whether nullipara or multiparous)
active phase
rapid dilation of the cervix and increased rate of descent of the presenting part
4-10 cm of dilation (baby descends more rapidly)
Nursing care during the first stage of labour
assessment
determination of true or prelabour
psychosocial factors
history of sexual abuse
stress in labour
caring for trans and gender nonconforming persons
cultural factors
physical examination
general systems assessment
vital signs
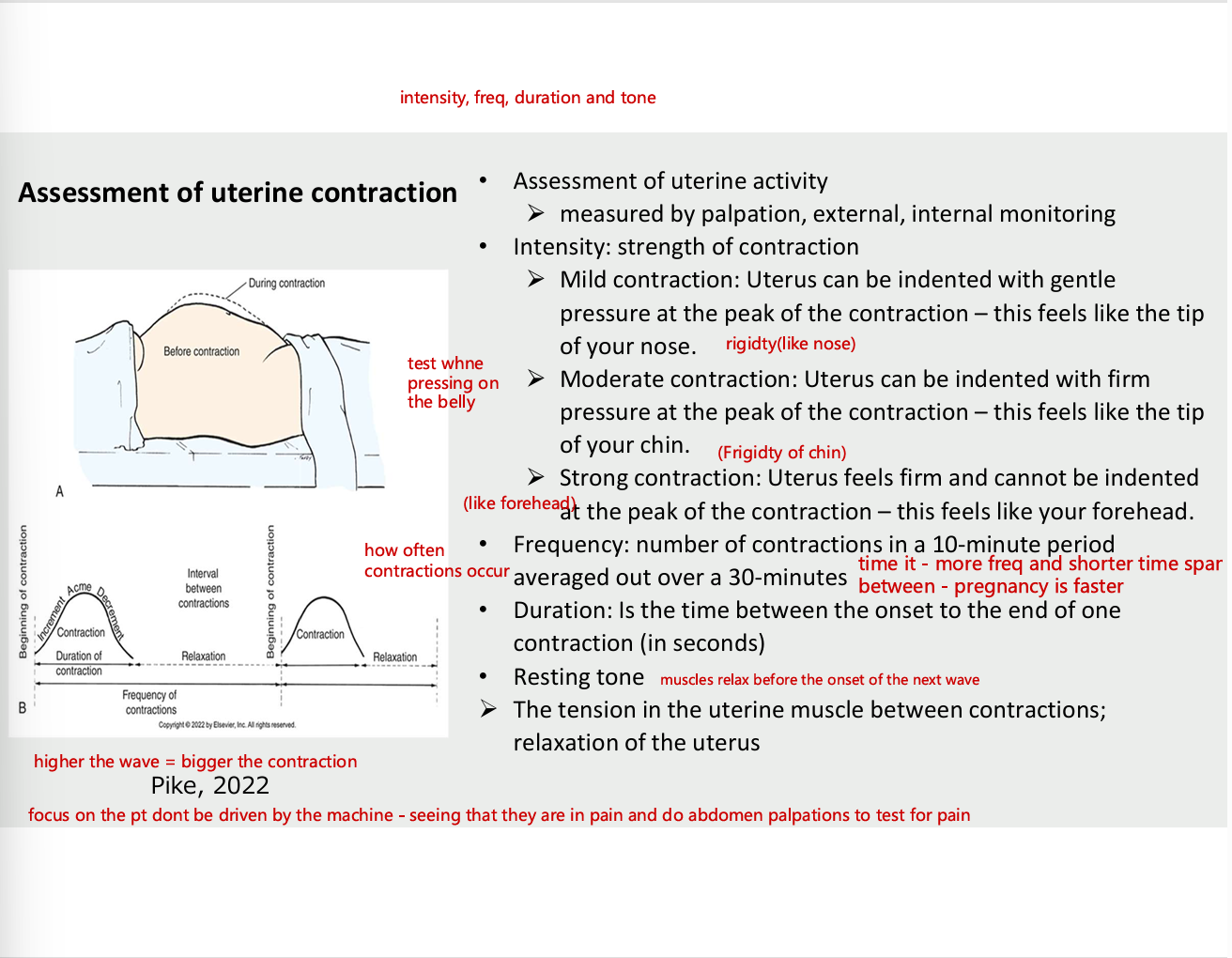
Assessment of uterine contraction
assessment of uterine activity
measured by palpation, external , internal monitoring
Intensity- strength of contraction
mild contraction - uterus can be indented with gentle pressure at the peak of the contraction - this feels like the tip of your nose (rigid)
moderate contraction - uterus can be indented with firm pressure at the peak of the contraction - this feels like the tip of chin
strong contraction - uterus feels firm and cannot be indented at the peak of the contraction - feels like forehead
frequency
number of contractions in 10 min period averaged out over 30 min (more fre and shorter span between)
duration
is the time between the onset to the end of one contraction (in seconds)
resting tone (muscles relax before onset of the next wave
the tension in the uterine muscles between contractions; relaxation of the uterus
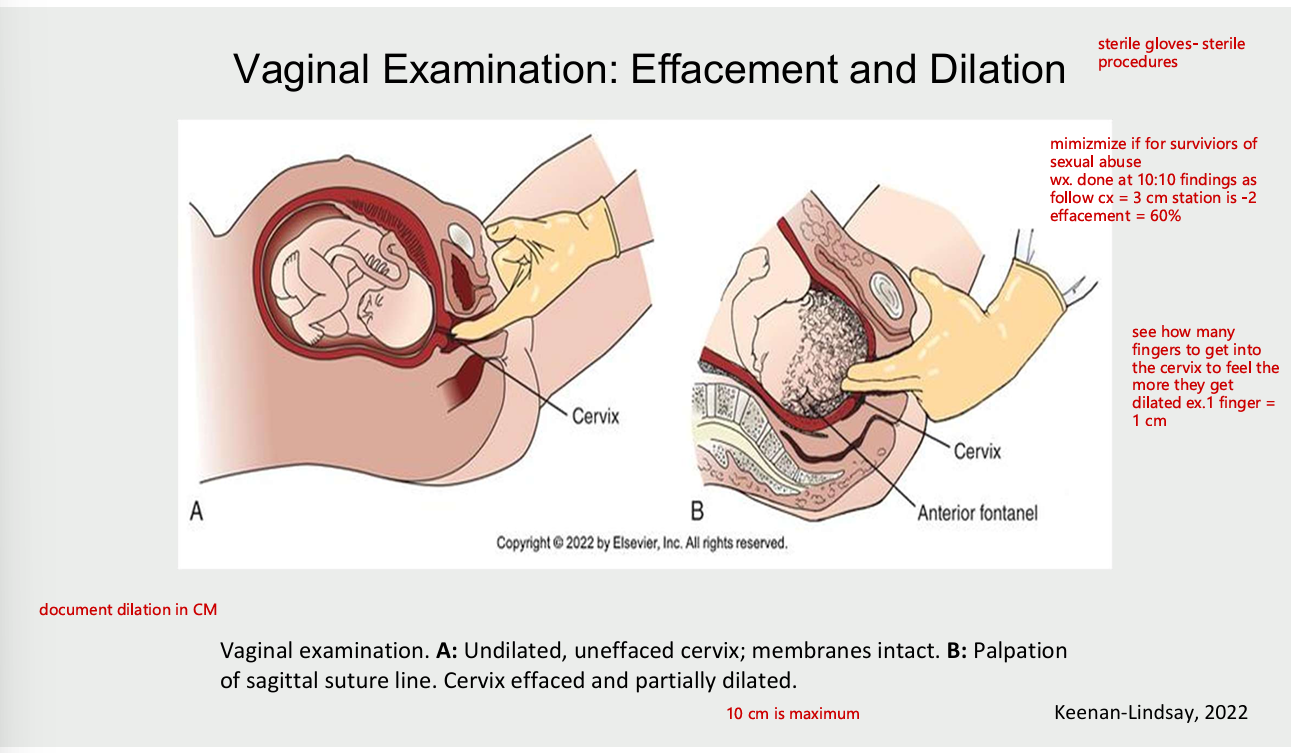
vaginal examination: effacement and dilation
physical nursing care
provides encouragement, feedback for relaxation, companionship
helps to cope with contractions
provides distractions
encourages use of focusing techniques
helps to concentrate on breathing techniques if required
uses comfort measures
assists patients into comfortable position
informs patient of progress; explains procedures and routines
gives praise
offers fluids, ice chips as ordered
support patient who has nausea and vomiting ; give oral care as needed
reassure regarding signs of end of first stage
panting respirations
if patient begins to push prematurely
giving praise ex. you’re doing great
positions for labour and birth
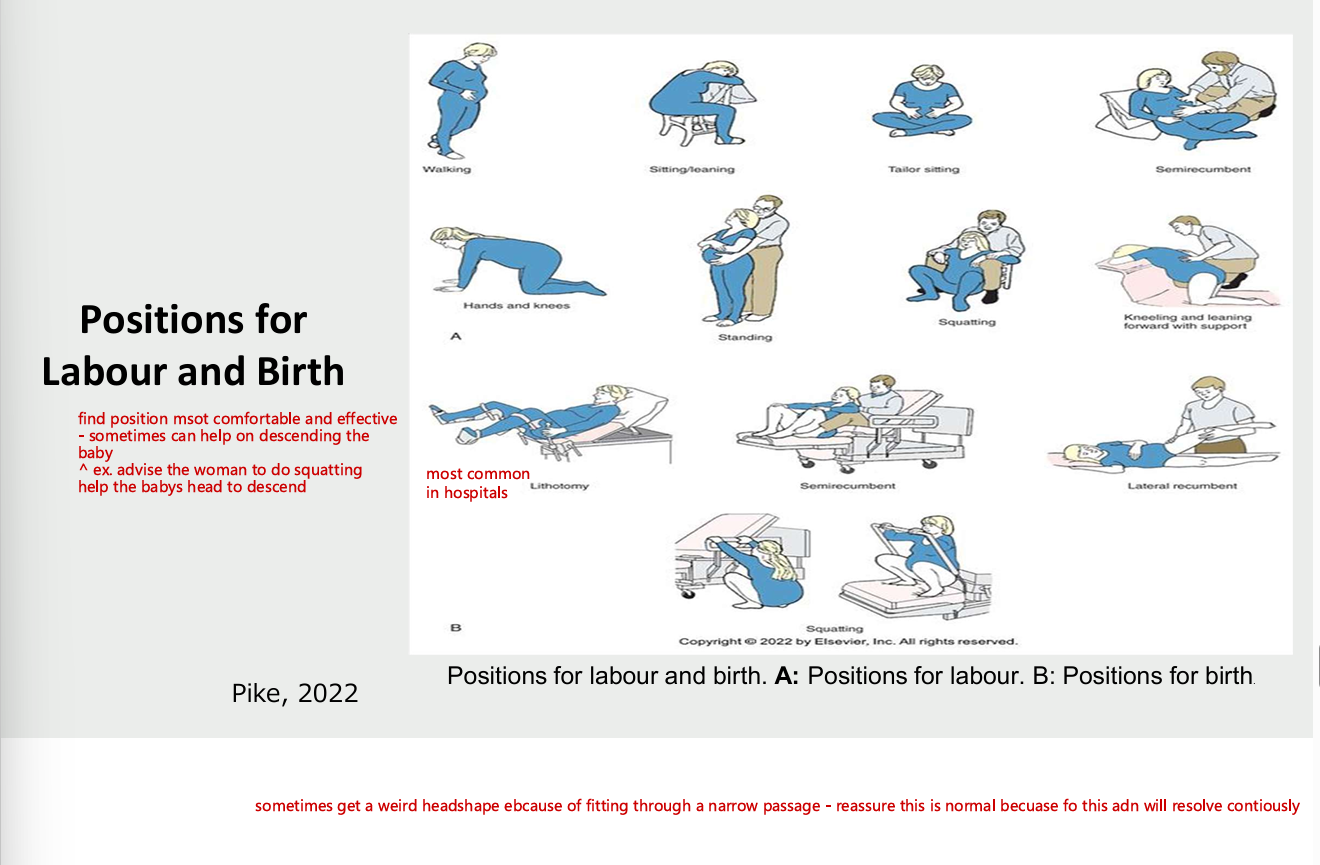
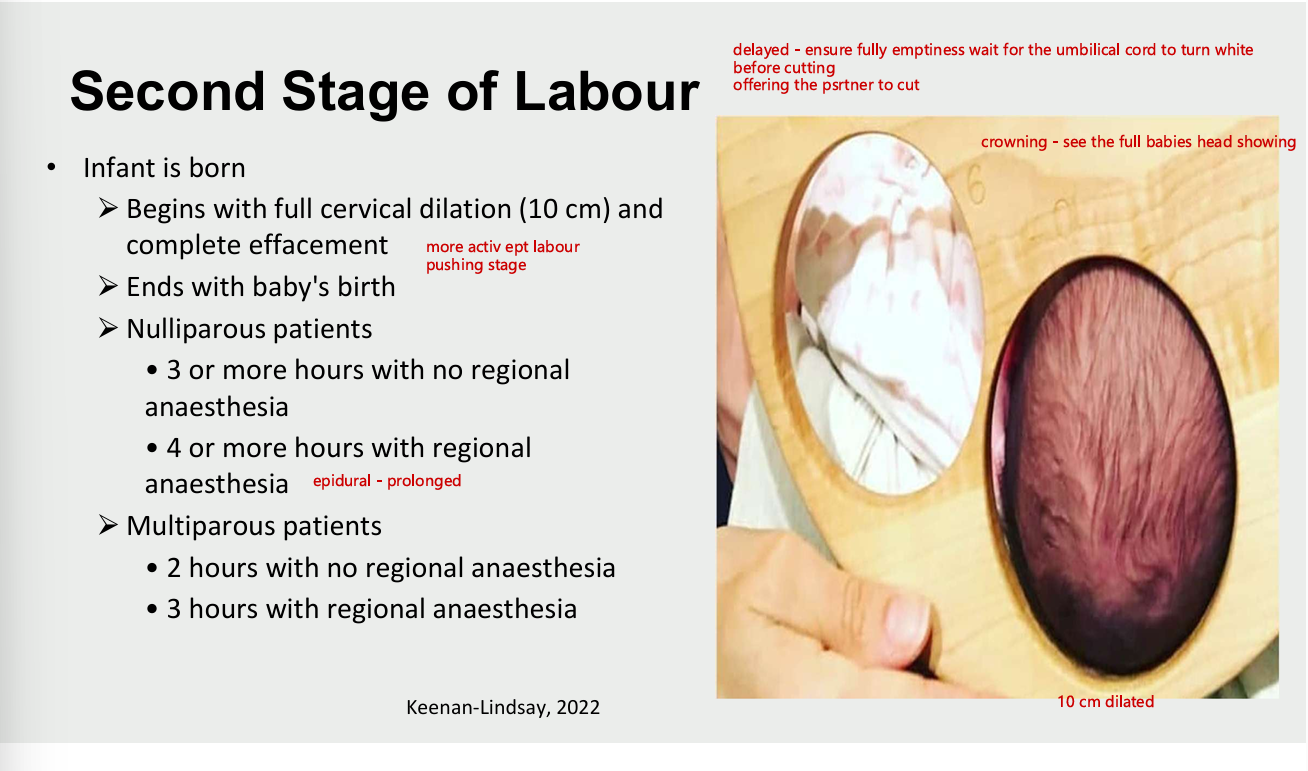
second stage of labour
infant is born
vegins with full cervical dilation (10cm) and complete effacement
ends with baby birth
nulliparous patients
3 or more hrs with no regional anaesthesia
4+ hrs with regional anaesthesia
multiparous woman
2 hrs with no regional anaesthesia
3 hrs with regional anaesthesia
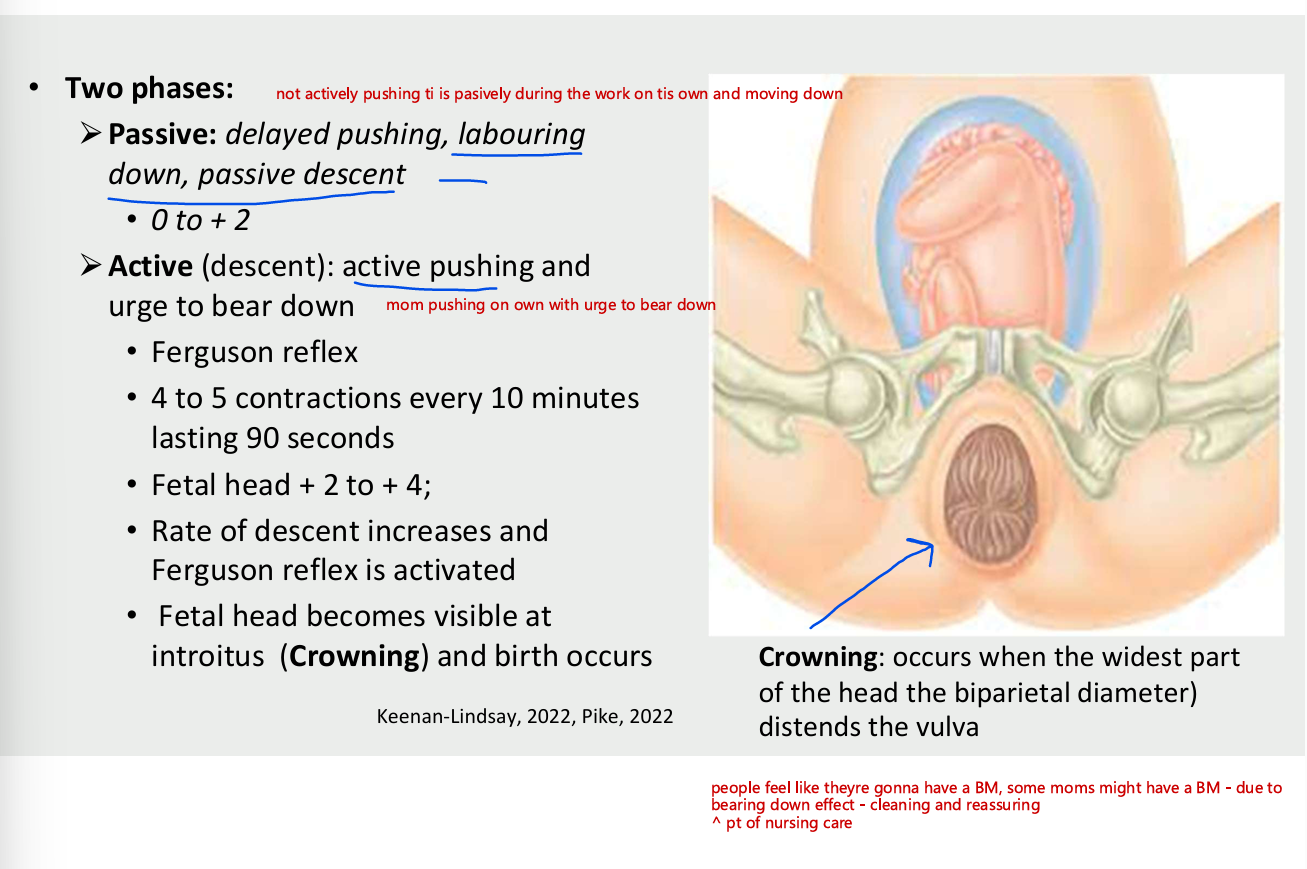
second stage of labour = two phases
passive
delyayed pushing, labouring down, pasive descent
0 to +2
active (descent) - active pushing and urge to bear down
ferguson reflex
4-5 contractions every 10 mins lasting 90 seconds
rate of descent increases adn ferguson reflex is activated
fetal head becomes visible at introitus(crowning) and birth occurs
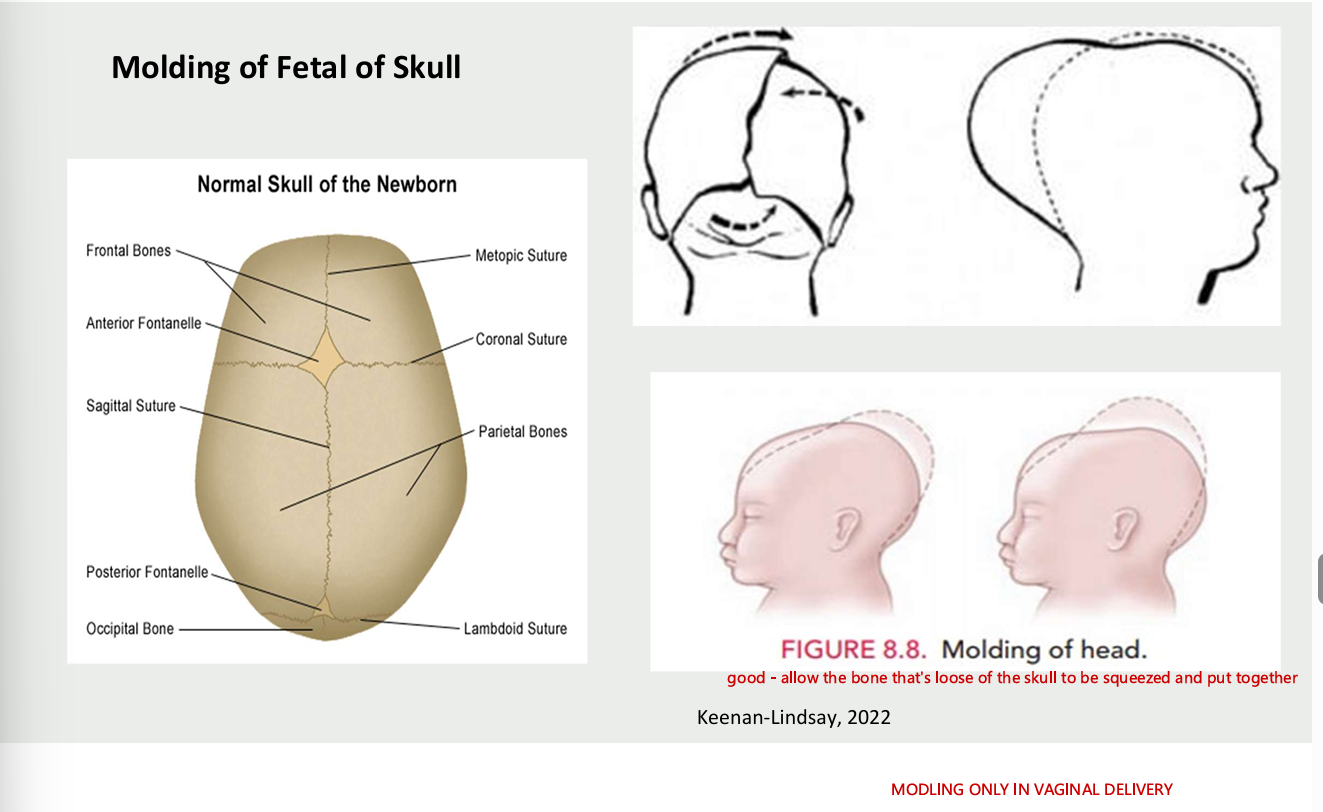
molding of fetal skull
only in vaginal delivery
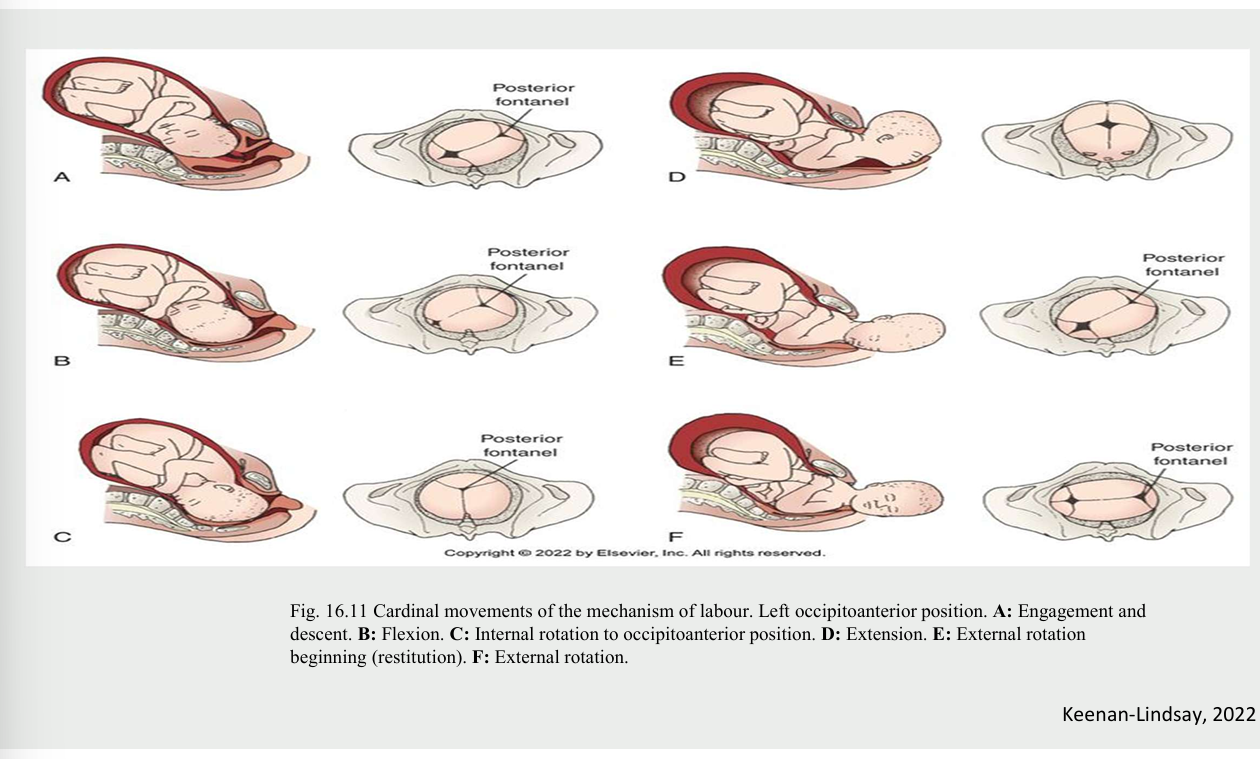
cardinal movements of the mechanisms of labour (happens in certain order
engagement - head into pelvic inlet
descent - fetal head is forced downwards on to the cervic
flexion - fetus flexes the ehad so that the vertex is leading (chin to chest)
internal rotation - of fetal head (usually to OA)
extension - delivery of head - occiput face then chin
restitution and external rotation - realigns head wtih back and shouldersS

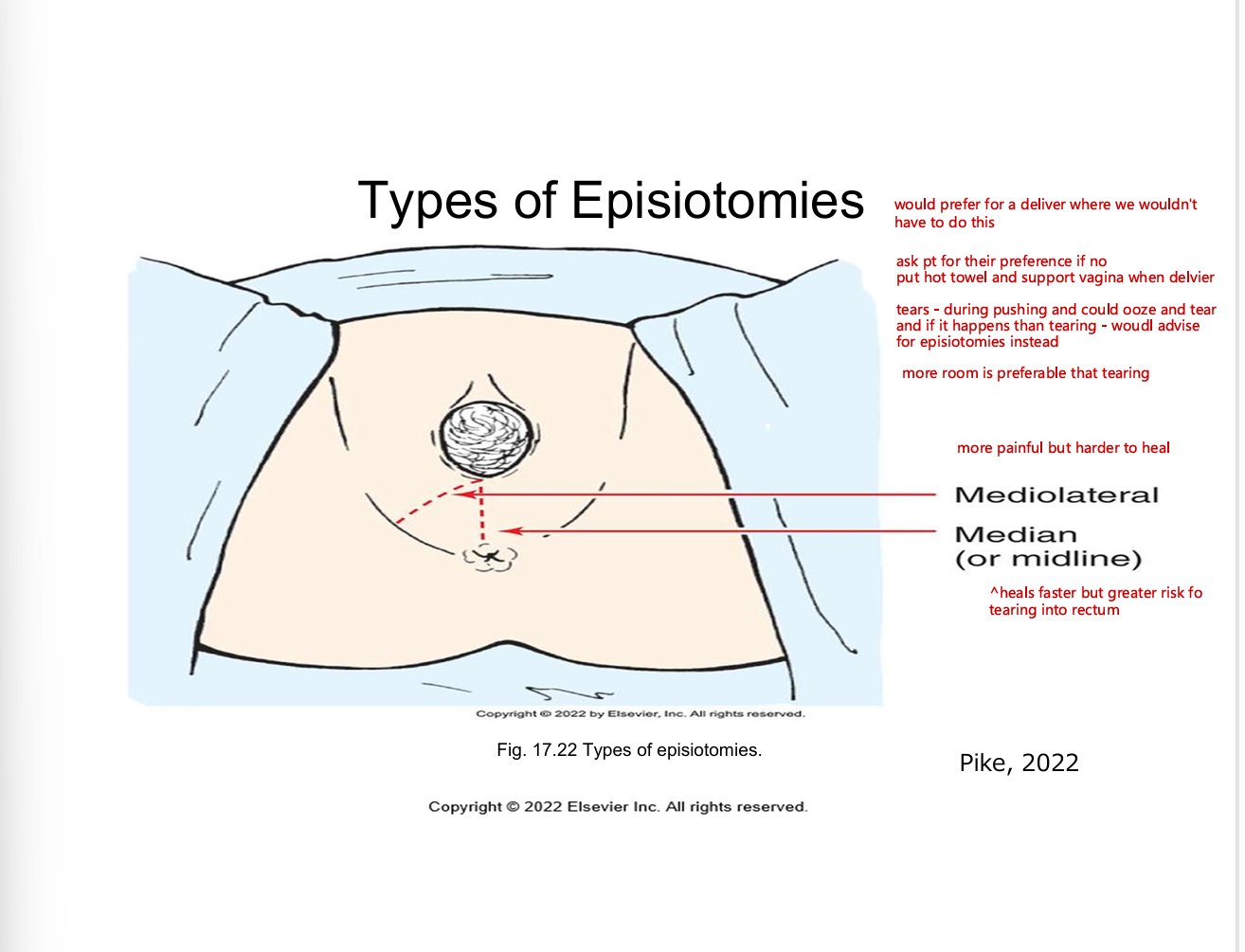
types of episiotomies
nursing during the second stage of labour
passive
help patient to rest in a position of comfort - encourage relaxation to conserve energy
promotes progress of fetal descent and onset of urge to bear down by encouraging position changes, pelvic rock , ambulation, and showering
active pushing (descent) phase
help patient to change position adn encourage spontaneous bearing down efforts
help patient to relax and conserve neergy between contractions
provide comfort and pain relief measures as needed
provide comfort and pain relief as needed
cleanse perinium proptly if fecal material is expelled
coach pt to pant during contractions and to gently push between contractions when head is emerging
provide emotional support , encouragement, positive reinforcements
keep patient informed regarding process
offer mirror to watch birth or encourage patient to feel top of fetal head as they are pushing
assessment and care of newborn
care focused on assessing and stablizing the newborn
agar score
immediate skin to skin recommended for healthy term newborn after vaginal or c section
positively affect parent-infant bonding
breast feeding duration
cardiorespiratory duration
cardiorespiratory stability
body temperature
delayed cord clamping recommended until 1-3 mins after birth or until after the cord stops pulsating
improves both the short and long term hematological status of the newborn
physiological transfer of the blood to new born
palcental transfusion of up to 30% of the total fetal placental blood volume
stem cells, rbc, whole blood
ask if aprtner would like to cute the cord is so instruct to cut it 2.5 cm above the clamp
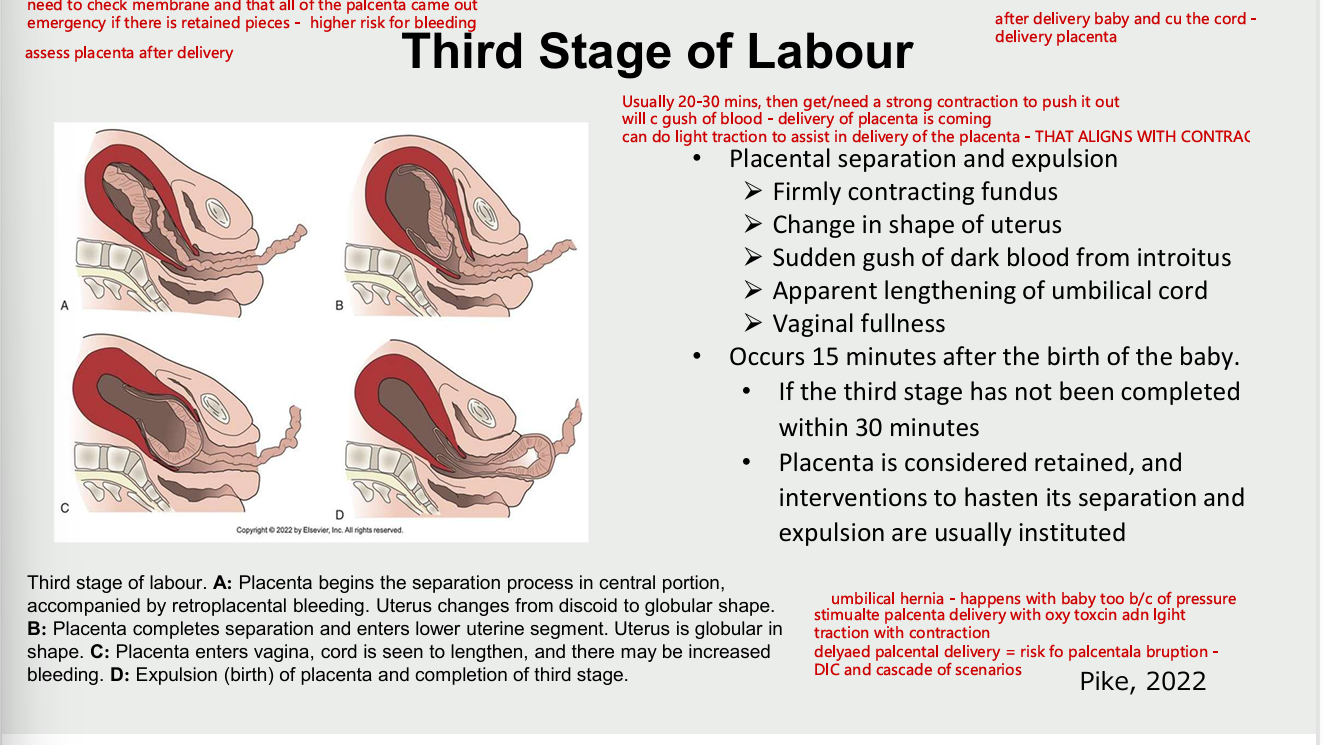
third stage of labour
placental separation and explusion
firmly contracting fundus
change in shape of uterus
sudden gush of dark blood form introitus
apparent lengthening of umbilical cord
vaginal fullness
occurs 15 mins after birth of baby
if third stage is not completed within 30 mins of
placenta considered retained and interventions to ahsten its separation and explusion are initiated
third stage of labour - passive and active management
passive management (expectant)
invovles patiently watching for signs that the placenta has separated from the uterine wall spontaneously and monitoring for spontaneous expulsion
no oxytocic (uteronic) medications are given
Separation and expulsion is facilitated by gravity or nipple stimulation promotes the release of endogenous oxytocin
active management
administration of an oxytocic medication after the birth of the anterior shoulder of the fetus
recommend active management of the third stage of labour
decreases the rate of postpartum hemorrhage cause by uterine atony
gentle and control cord traction following uterine contraction and seperation of the placenta
examination of placenta
ensure that no portion remains in the uterine cavity (ex. no fragments of the placenta or membranes are retained
contains about 15-20 lobes
vessels (2 arteries and 1 vein)
membranes should be complete with no holes
fourth stage of labour
begins with the expulsion of the palcenta and lasts until the patient is stable within the first 2 hrs
crucial time for the patient and newborn to acquaint with each other and family memebers
nursing care include assessment - vital signs, uterus , bladder, bleeding, perineum
vital signs
first hour every 15 mins
if all parameters are stabalized within the normal range repeat once every second hour

uterine assessment AFTER BIRTH - FUNDUS
firm with uterus located midline
fundus not firm = massage it gently to contract
place hands appropriately massage gently only until firm
observe perineum for amount and size of expelled clots
expel clots while keeping hands placed over the uterus
with the upper hands, firmly apply pressure downward toward the vagina
observe perineum for amounts and size of expelled clots
accompanied by discomfort advise pt to take deep breaths throughout
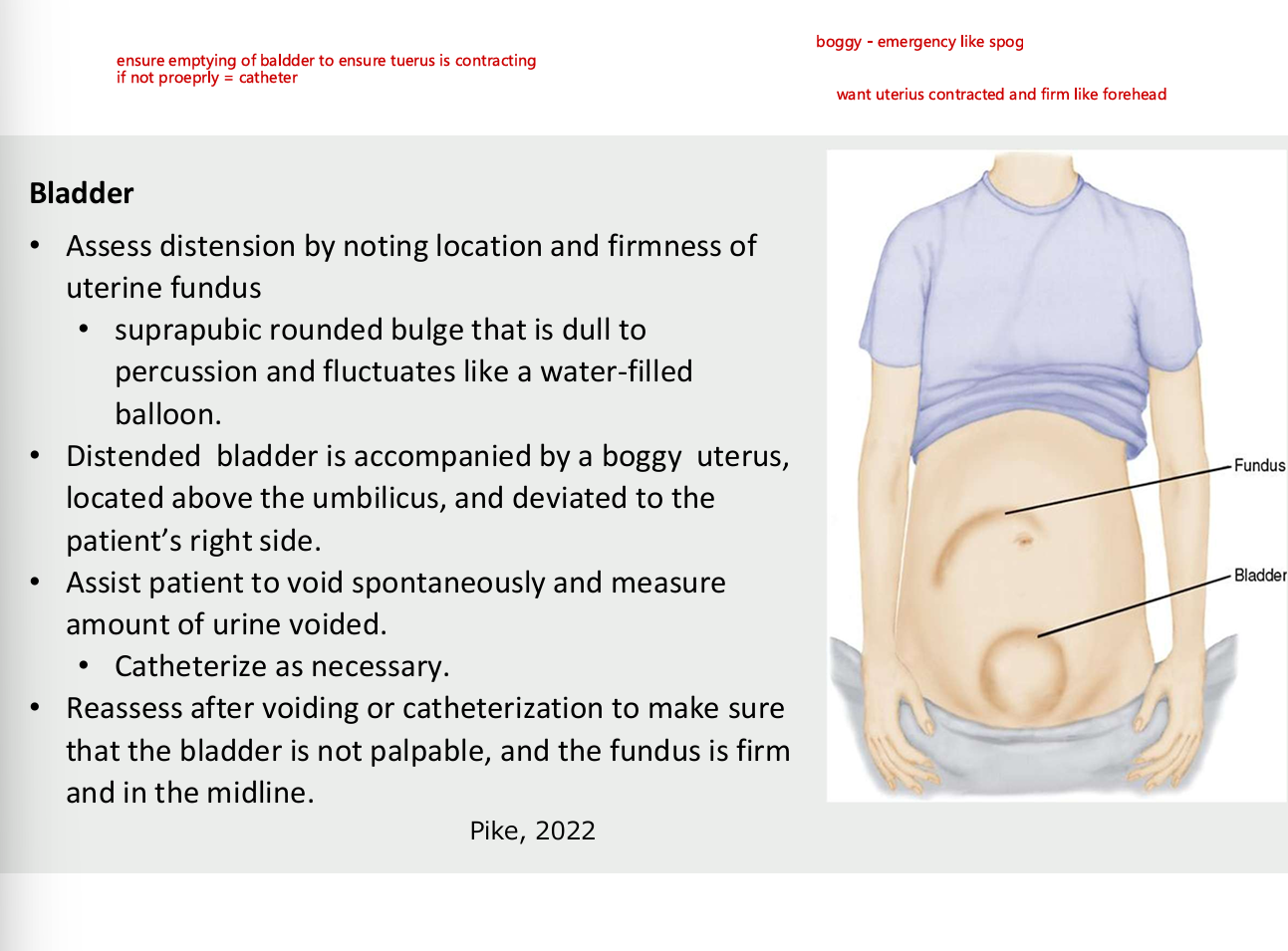
bladder - after birth
assess distension by noting location and firmness of uterine fundus
suprapubic rounded bulge that is dull to percussion and fluctuates like water filled balloon
distended bladder is accompanied by a boggy uterus, located above the umbilicus and deviated to the patient right side
assist patient to avoid spontaneously and measure urine voided - catheter as necessary
reassess after voiding or catherization to make sure that the bladder is not palpable and the fundus is firm in the midline
managing pain during labour and birth
visceral pain - distension of the lower uterine segment, stretching of cervical tissues as it effaces and dilates, pressuer and traction on adjacet structures (ex. fallopian tubes, ovaries, ligaments) and nerves, and uterine ischemia. located over lwoer portion of abdomen
referred pain - originates in uterus, radiates to abdominal wall, lumbosacral area of the back, iliac creasts, gluteal area, down thighs
somatic pain - intense , shapr, burning and well localized
second stage of labour pain
distension of and traction on peritoneum and uterocervical supports during contractions
pressure against the bladder and rectum
stretching and distension of perineal tissues and the pelvic floor to allow passage of the fetus
laceration of soft (ex. cervix)
responses to pain
perception of pain
pain threshold is remarkably similar in all persons, regardless of gender, social, ethnic or culturla differences
pain tolerance
expression of pain
increasing anxiety, writhing, crying, groaning, gesturing (hand clenching, wriging), excessive muscular excitability
factors influencing pain resp
physiological factors
culture
anxiety and fear
previous expereince
gat control theory of pain
supportive
environment
child birth preparation methods
expereince of trauma
non pharmacological pain management
comfort measures
relaxation
imagery and visualization
music
touch and massage
breathing techniques
effleurage and counter pressure (long stroking mvoements) and counter pressure
hydrotherapy - water birth
laughing has (nitric oxide)
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
acupressure and acupuncture
application of heat and cold
hypnosis
biofeedback
aromatherapy
intradermal sterile water block
maternal position and movement
pharmacologicla management
first stage
systemic analgesia
opioid agonist analgesics
opioid agonist-antagonist analgesics
Opioids decrease the heart rate, RR, BP of labouring pt which affects fetal oxygenation
monitoring vital signs, FHR pattern before and after administration of opioids critical
epidural (block) analgesia
combined spinal- epidural (CSE) analgesia
nitrous oxide (laughing gas)
pudendal block
potential side effects spinal and epidural anaesthesia
hypotension
20%drop from preblock baseline level ro less than 100 mmhg systolic
fetal bradycardia
absent or minimal fetal HR variability
imparied placental perfusion
infeffective breathing pattern may occur during
interventions
turn pt to lateral position or palce pillow wedge under one hip to displace uterus off the ascending vena cava and descending aorta.
Maintain intravenous (IV) infusion at rate specified or increase administration to provide fluid bolus per hospital protocol.
Administer oxygen by nonrebreather face mask at 8 to 10 L/min if signs of hypoxia or hypovolemia in labouring patient.
Elevate labouring patient’s legs.
Notify the primary health care provider and anaesthesiologist.
Administer IV vasopressor (e.g., ephedrine 5 to 10 mg or phenylephrine 50 to 100 mcg) as per primary health care provider’s order if previous measures are ineffective.
Remain with the patient; continue to monitor maternal blood pressure and FHR every 5 minutes until conditio
Local anaesthetic toxicity
Lightheadedness
Dizziness
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Metallic taste
Numbness of the tongue and mouth
Bizarre behaviour
Slurred speech
Convulsions Loss of consciousness
High or total spinal anaesthesia
Fever Urinary retention Pruritus (itching)
Limited movement
Longer second-stage labour
Increased use of oxytocin
Increased likelihood of forceps- or vacuum-assisted birth
Postdural puncture headache