Radiolucent Lesions Part 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is the acronym for multilocular RL jaw lesions?
MACHO
M: Odontogenic myxoma
A: Ameloblastoma
C: Central Giant cell granuloma
H: (Hemangioma) venous malformation
O: Odontogenic keratocyst, ossifying fibroma
What is odontogenic myxoma?
Uncommon benign mesenchymal tumor usually found in the posterior mandible premolar + molar areas; rarely found in ramus and condyle
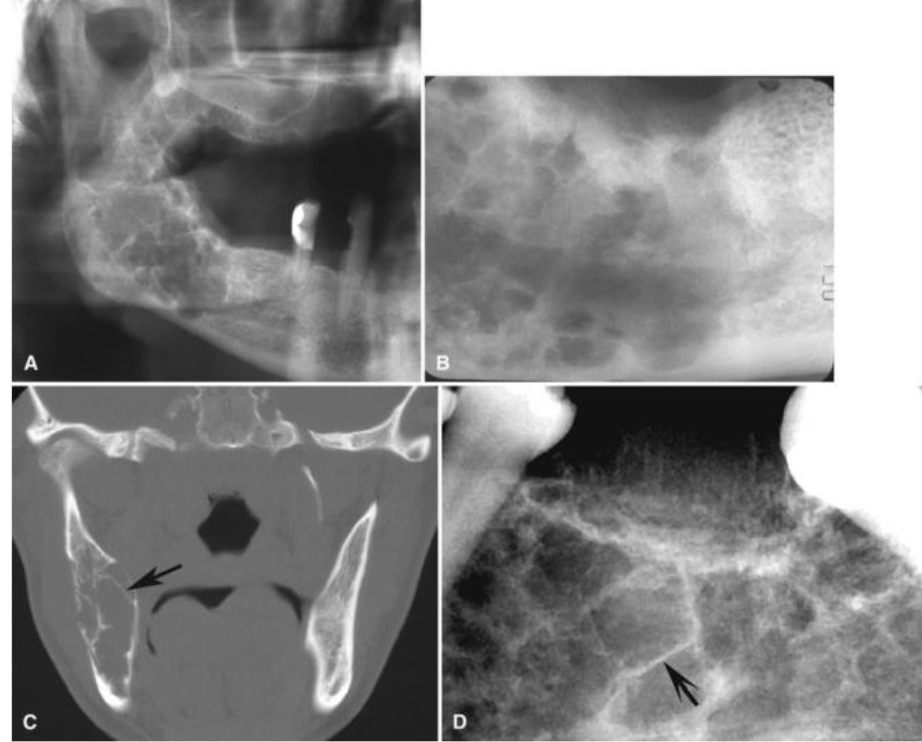
What would you see radiographically in odontogenic myxoma?
Characteristic septa which may be straight and thin (tennis-racket-like pattern) or curved and coarse
What are some imaging features of odontogenic myxoma?
Not encapsulated, tend to infiltrate the surrounding cancellous bone —> high recurrence
Where would you find odontogenic myxoma?
3:1 mandible, molar/premolar areas, rarely in ramus, condyle and zygomatic process
What are the edge borders of odontogenic myxoma?
Can be ill-defined (instinct borders) especially in maxilla OR can be well-defined and corticated
What is the shape of odontogenic myxoma?
Multilocular
What is the internal structure of odontogenic myxoma?
Radiolucent with septa, most are curved but characterically straight, thin septa (tennis racquet)
What are some other structures that odontogenic myxoma can affect?
Displaces and can loosen teeth; rarely resorbs
When large can cause considerable expansion
What number of lesions in odontogenic myxoma?
It is solitary
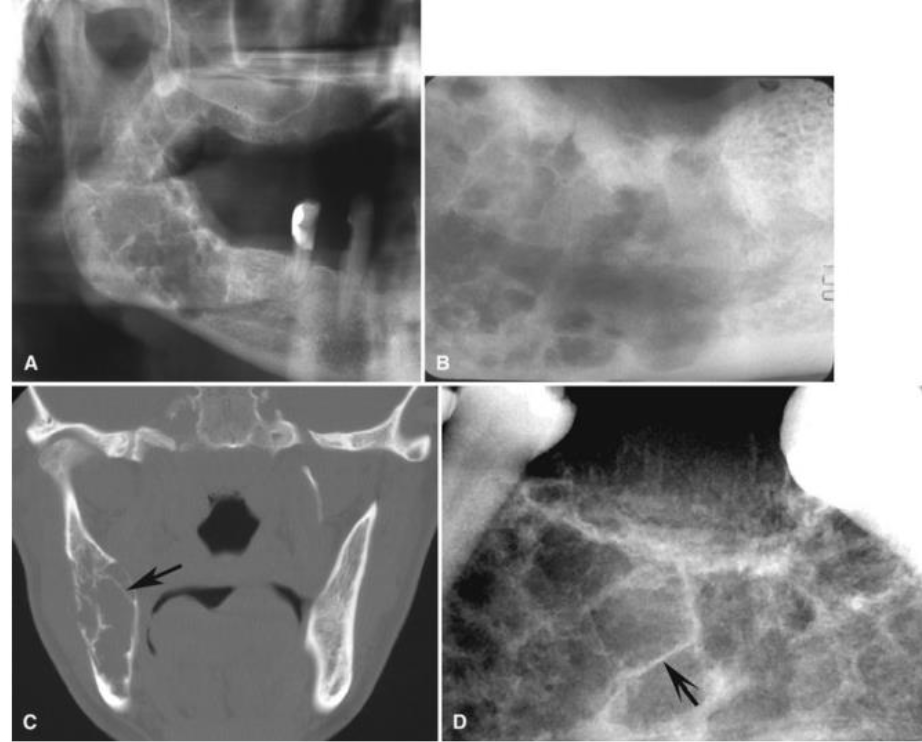
How would you describe odontogenic myxoma radiographically?
“Honeycomb” appearance
Less well-defined in maxilla
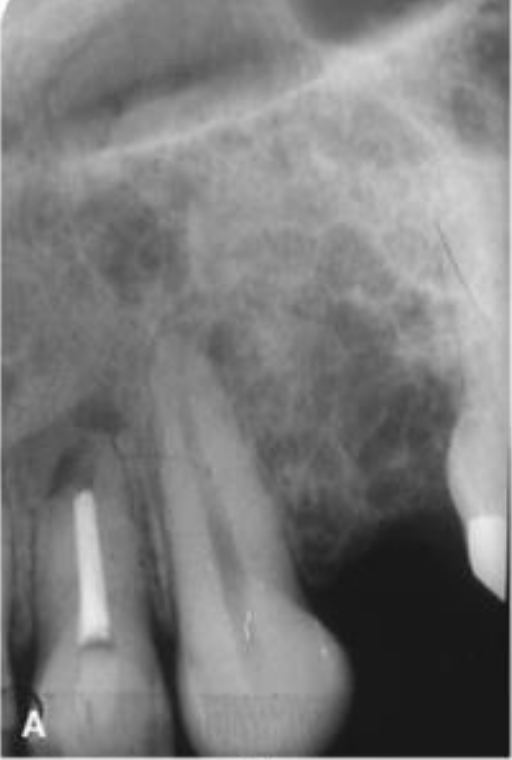
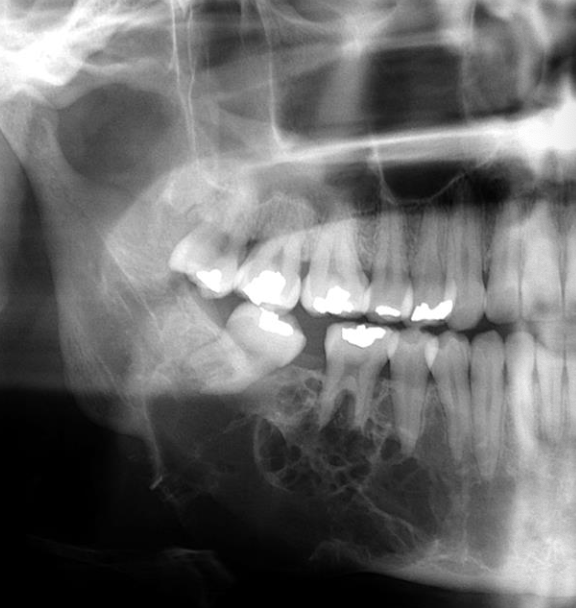
What is this
Odontogenic myxoma —> tooth displacement is relatively common, but root resorption is less frequently seen
Sharp straight septum
Odontogenic Myxoma
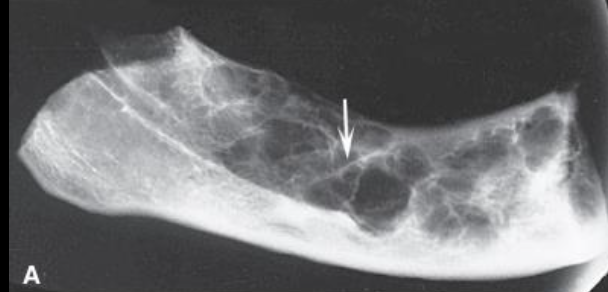
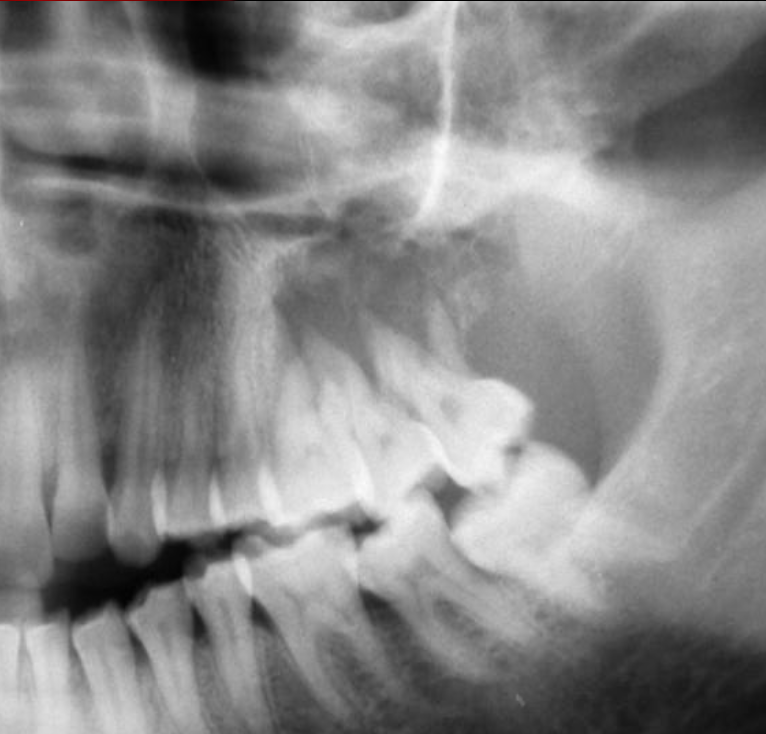
Axial CT image with some straight septa
Odontogenic Myxoma
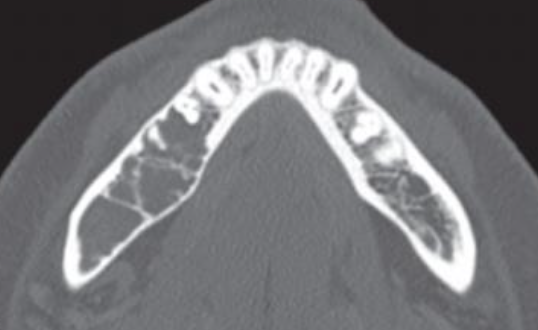
What are the subtypes of ameloblastoma?
Central/solid/conventional
Unicystic
Peripheral (soft tissue)
Desmoplastic
Malignant (spreads)
What is the location of ameloblastoma?
Posterior mandible (molar, ramus) (80%)- maxilla 3rd molar
Maxillary tend to be more aggressive (extend into sinus/nasal fossa)
Often associated with impacted tooth
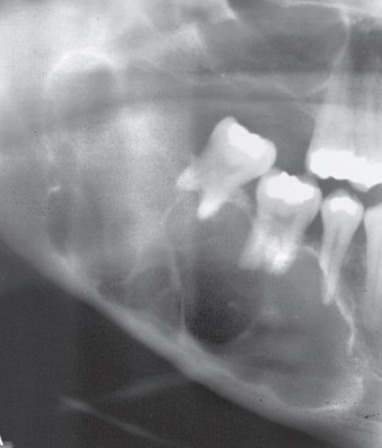
What are the edge borders of ameloblastoma?
Well-defined, corticated borders
Maxilla can be more ill-defined
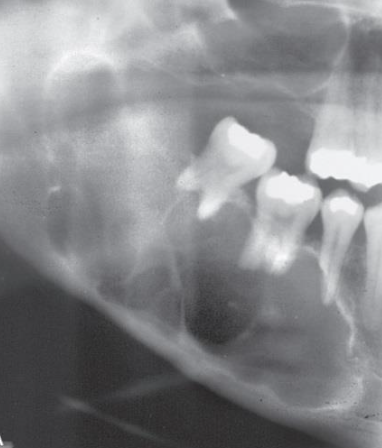
What is the shape of ameloblastoma?
Multilocular, “soap-bubble” “honeycomb” —> irregular or scalloped shape
Can have unilocular appearance
>2cm at discovery
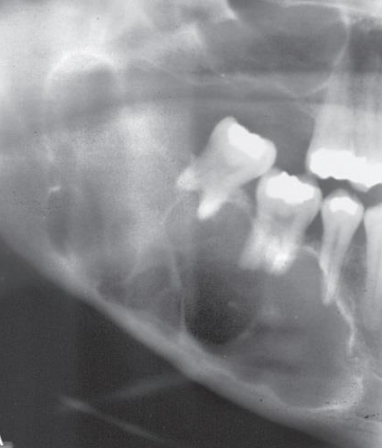
What is the internal structure of ameloblastoma?
Radiolucent with thick curved septa
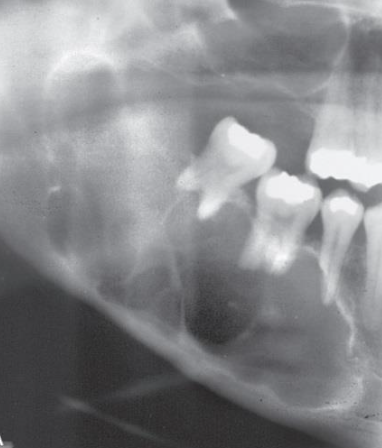
What impact does ameloblastoma have on other surrounding structures?
Expansion! Tooth displacement and resorption common, may thin and perforate borders (aggressive)
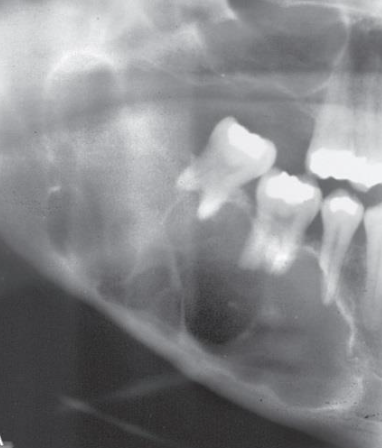
What is the “number” in ameloblastoma?
Solitary, recurrence is common
Diagnostic imaging of ameloblastoma
“honeycomb” or “soap-bubble”
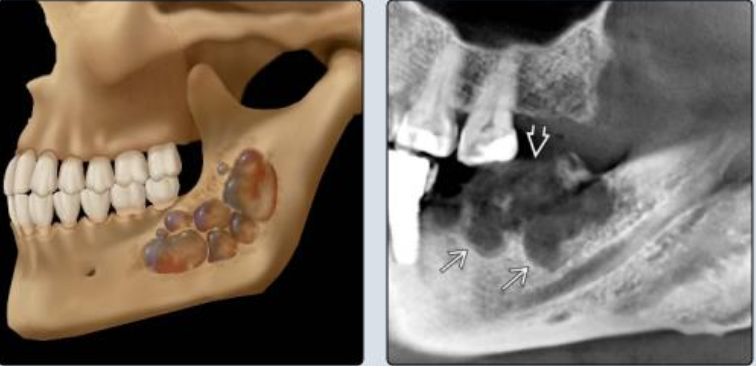
Multilocular ameloblastoma
Large multilocular lesion in the mandible. Note the coarse, curved septa
Small loculations more common in the anterior mandible (black arrows) and the larger loculations in the posterior mandible white arrows).
Note expansion and perforation of borders
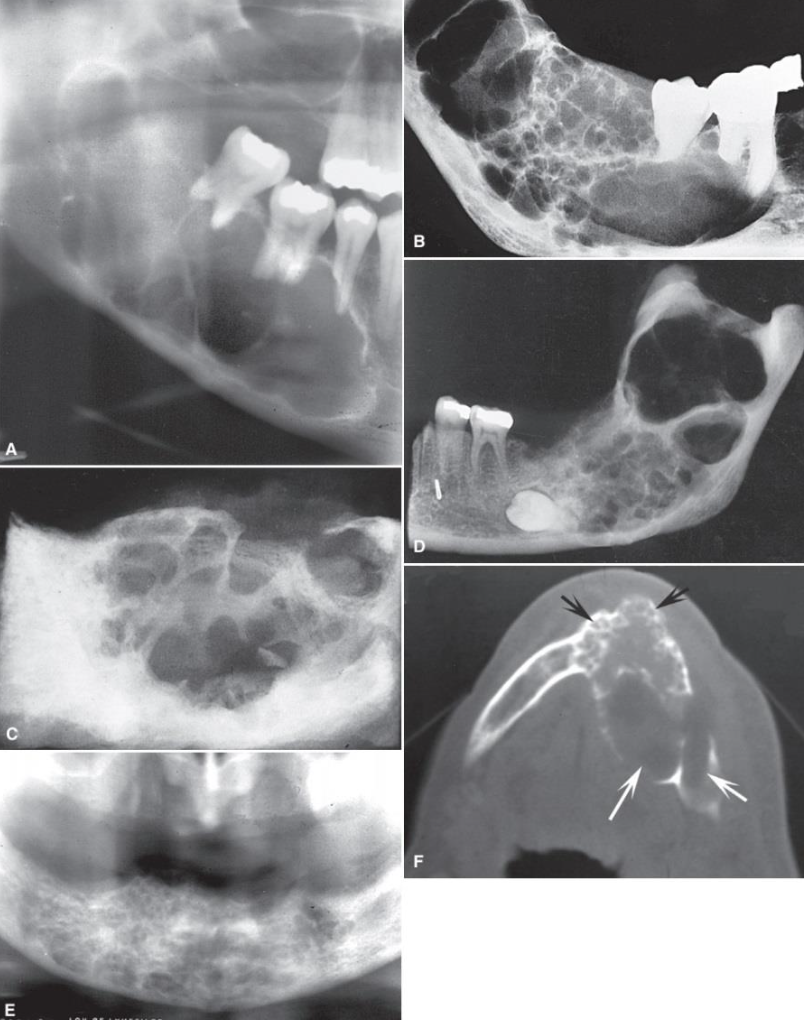
Ameloblastoma
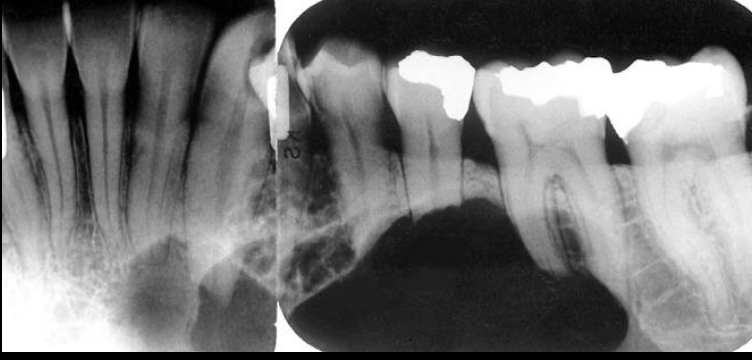
Root resorption of the premolars and canine adjacent to a radiolucent ameloblastoma in the left mandible
Ameloblastoma
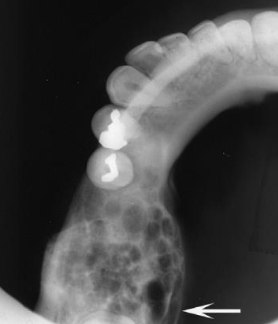
Occlusal film demonstrating expansion of the lingual cortex with maintenance of a thin outer shell of bone (arrow).
Ameloblastoma
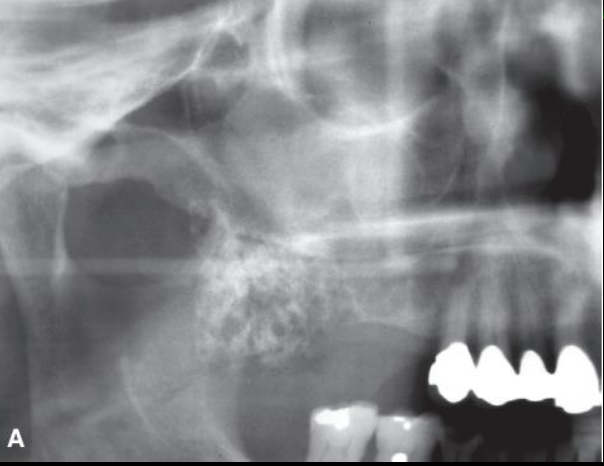
Multilocular appearance in tuberosity region. it is impossible to determine the extent of the lsion with the panoramic film
Ameloblastoma
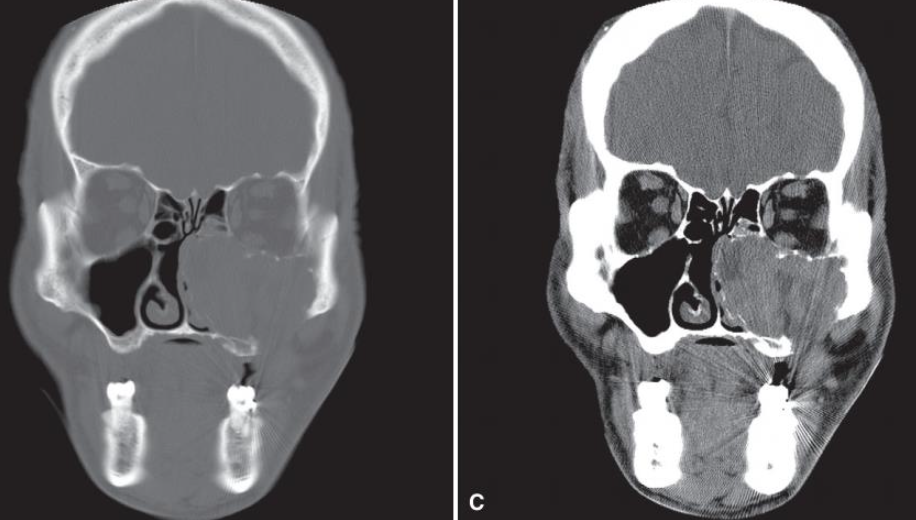
The aggressive nature of the tumor as it has grown into the sinus and nasal fossa and perforated the lateral cortical plate of the maxilla
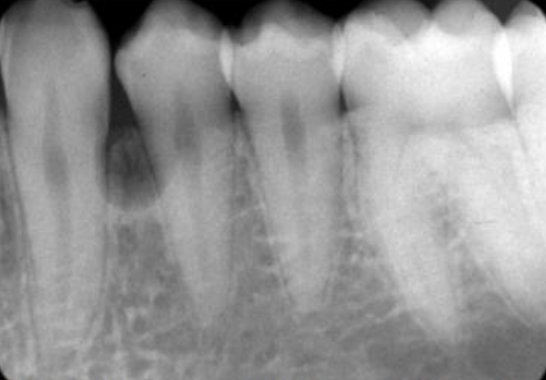
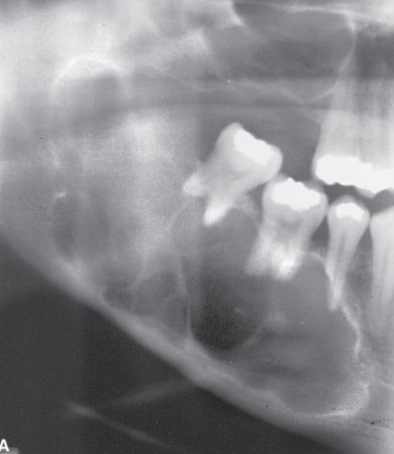
What is this?
A small unilocular ameloblastoma developing near the crest of the alvegolar process of the mandible
What are some characteristic features of unicystic ameloblastoma
Seen in younger patients
More likely unilocular and pericoronal
More favorable clinical behavior and response to treatment
May recur after a long delay
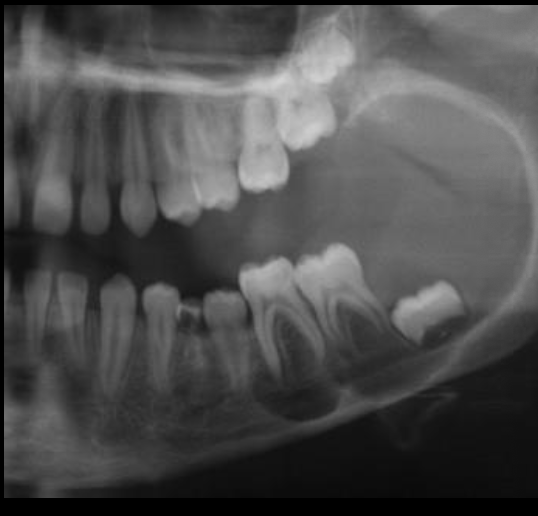
What is this?
Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
What is Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
Benign idiopathic or reactive lesion* formed following hemorrhage into bone with incomplete healing
Which populations would you see Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Adolescents and young adults;
> 60% of cases occur in those younger than 20 yrs.
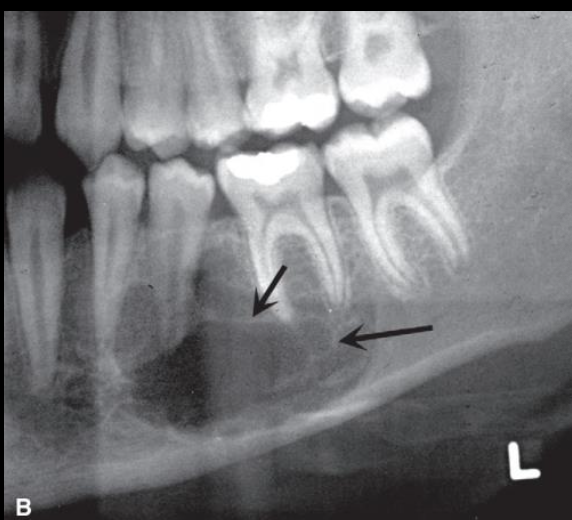
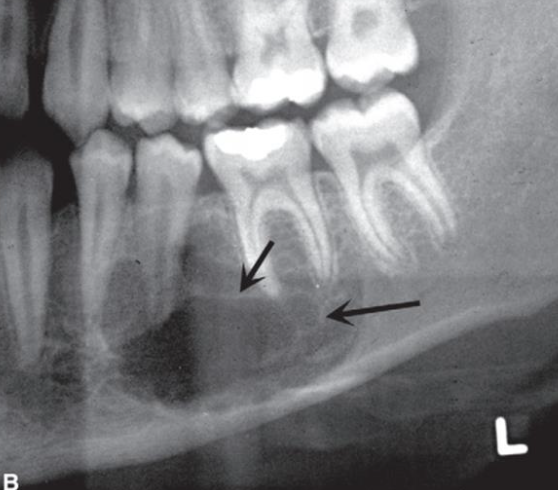
How would you describe Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Radiolucent to granular with wispy septa
Displace and resorb teeth
Expansile
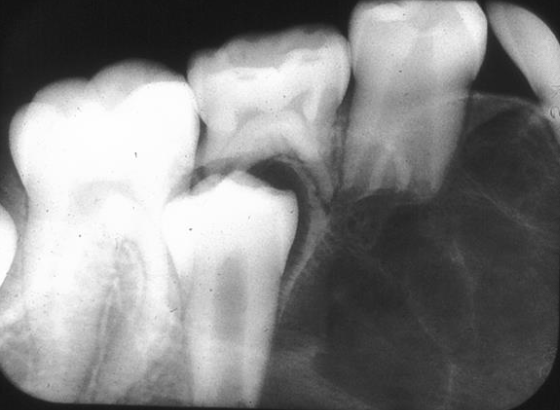
Where would you find Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Mandible > Maxilla
Anterior to first molar
Often crosses midline
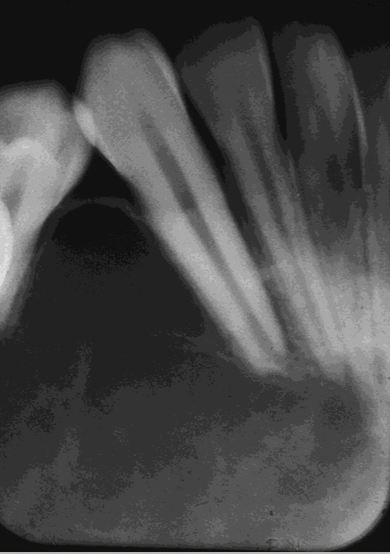
What are the edge borders of Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Well-defined, slight to no cortication
What is the shape of Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Undulating, expanded margins
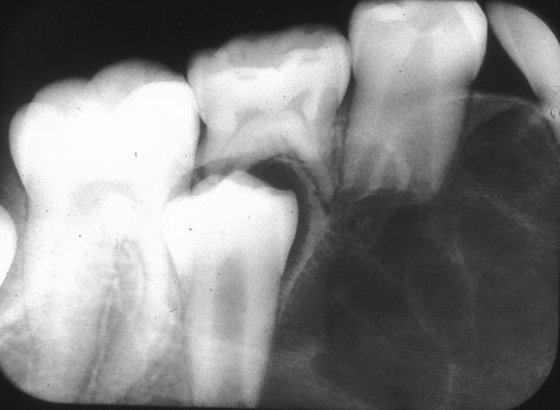
What internal structures do you see in Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Radiolucent to granular
Wispy septa
Septa may be at 90degrees to cortex
What effect does Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG) have on other structures?
Tooth displacement and root resorption is common, and it is expansible
What is the “number” in Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)?
Solitary, high recurrence rate
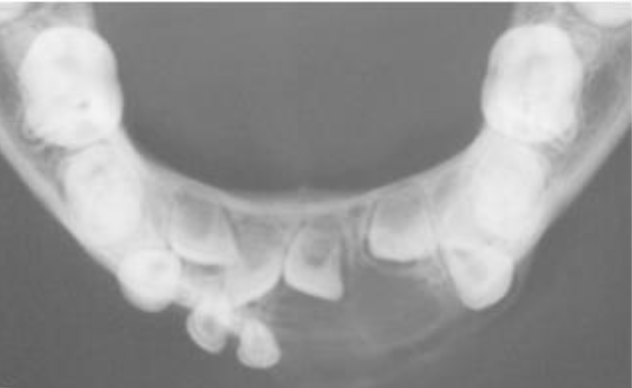
Occlusal radiograph
Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
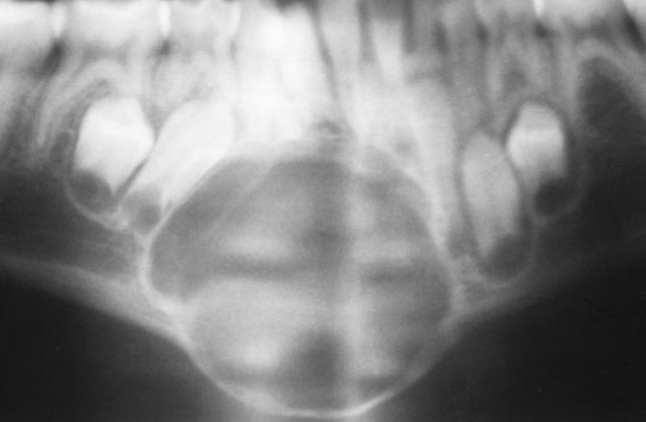
Usually expansible
Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
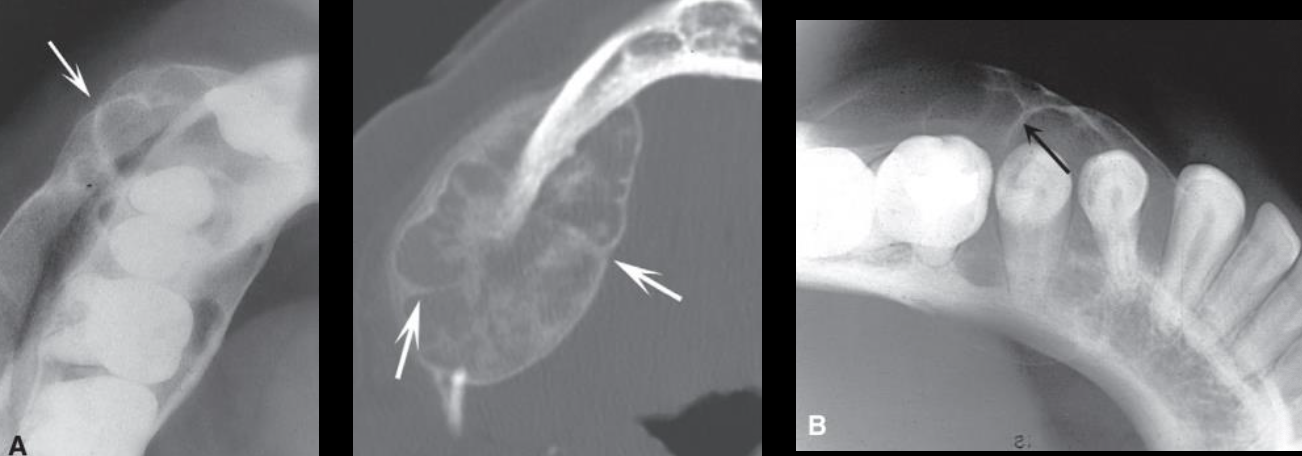
Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
Characteristic expansion: uneven, indented in areas of septation, septation at right angles to cortices, cortices can appear granular
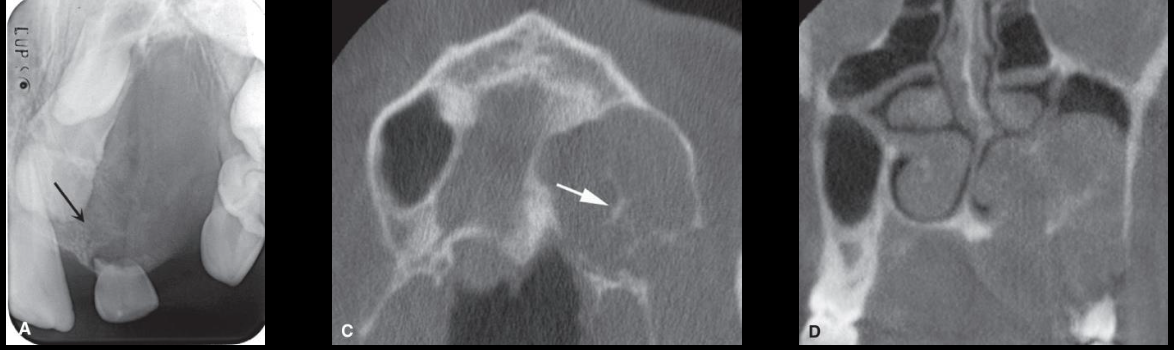
Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CGCG)
Poorly calcified “wispy septa",” granular especially seen in anterior maxilla
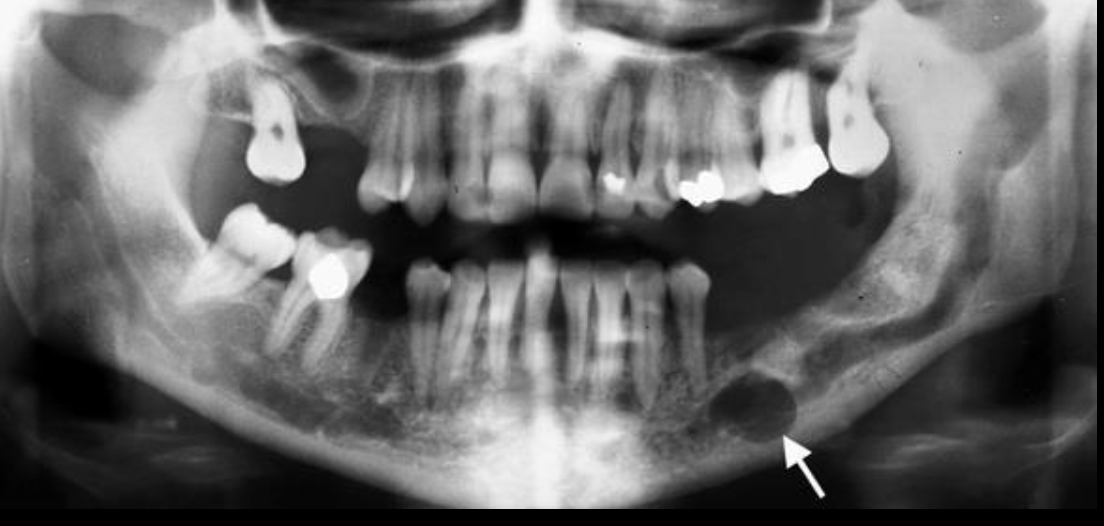
Vascular malformation inside of IAC