Unit 2- Movement & Support; Skeletal System Vocab
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
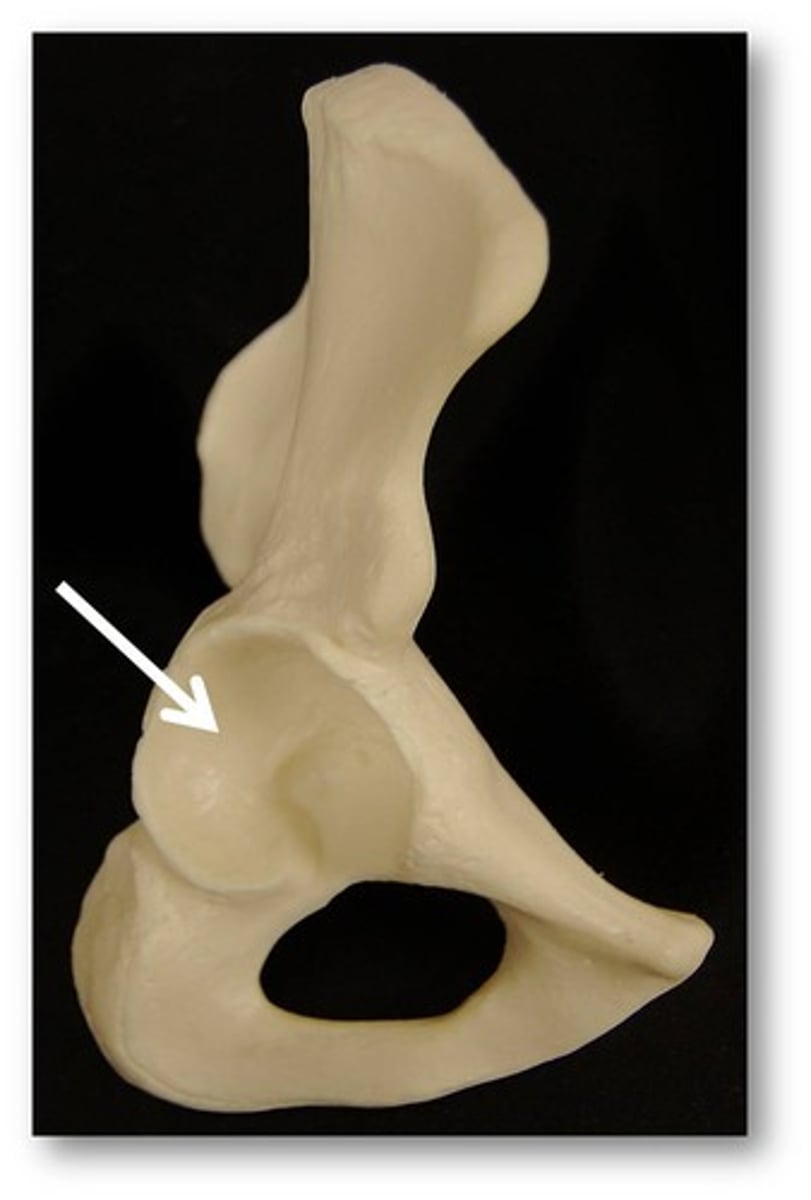
Acetabulum
Socket of hipbone, where the femur head fits.
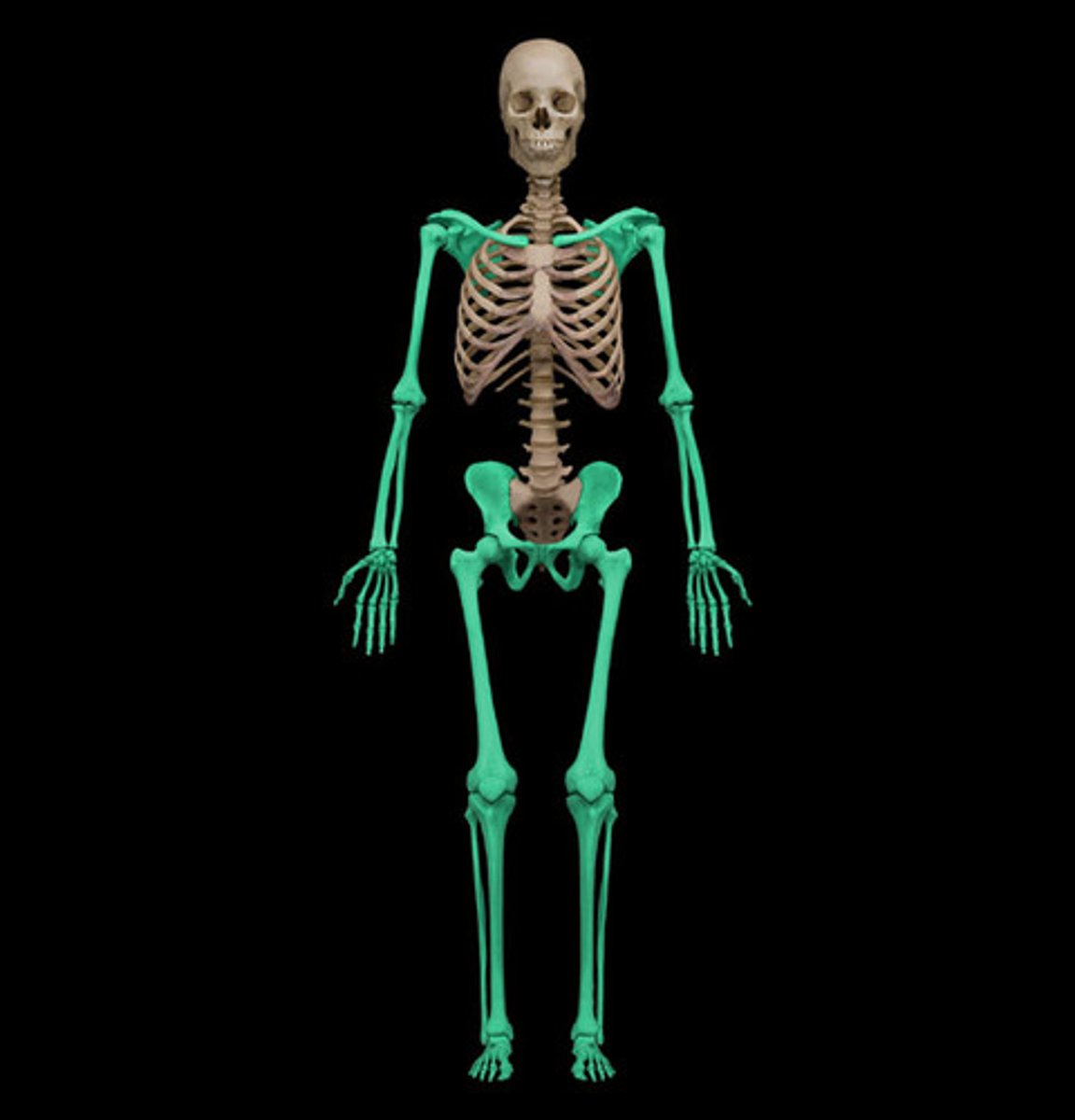
Appendicular skeleton
Bones and limbs.
Articulur cartilage
Connective tissue that covers ends and joints, creating low-friction movement.
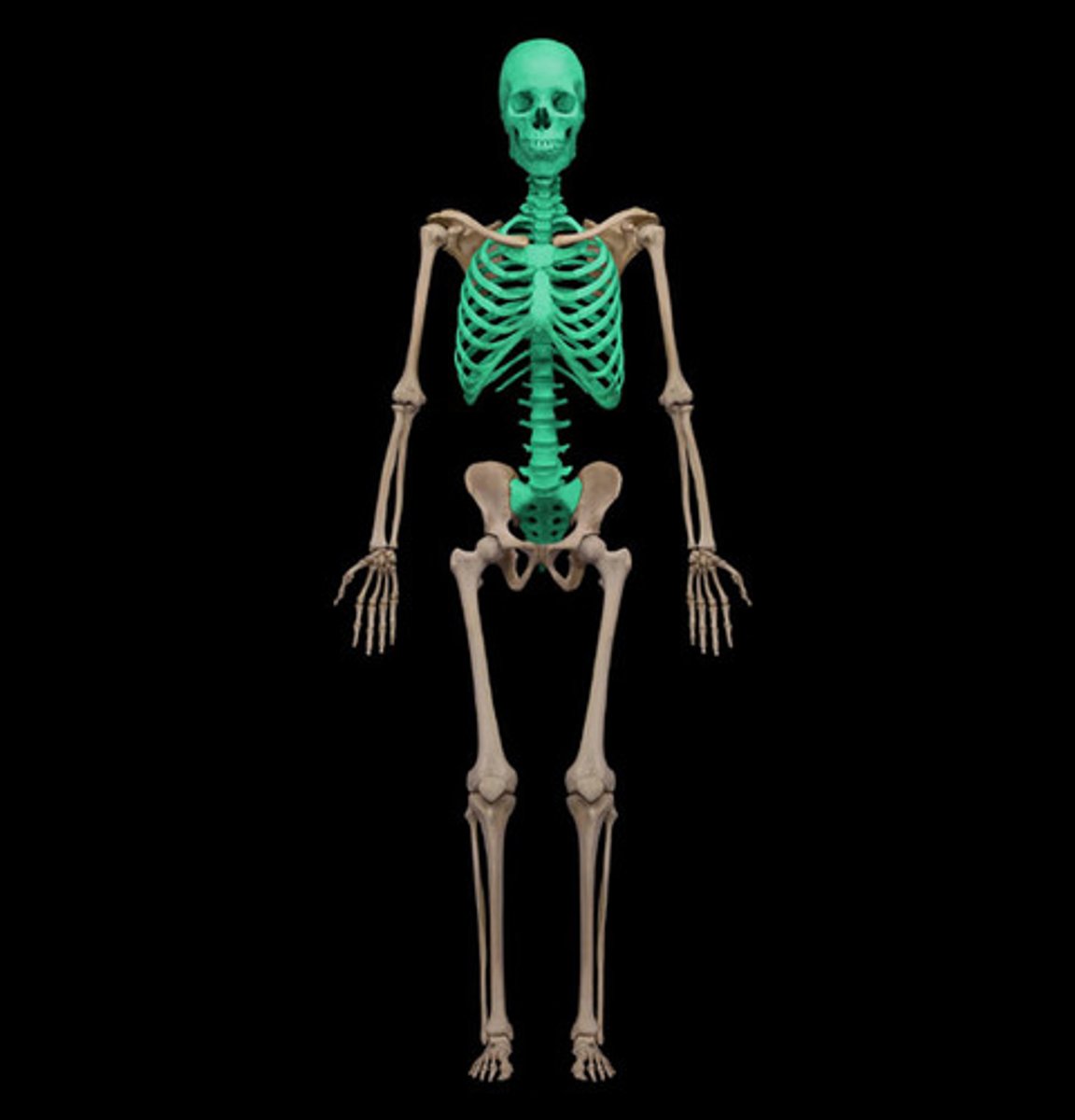
Axial Skeleton
Body's central axis.
Bursa
Fluid-filled sac that cushions joints.
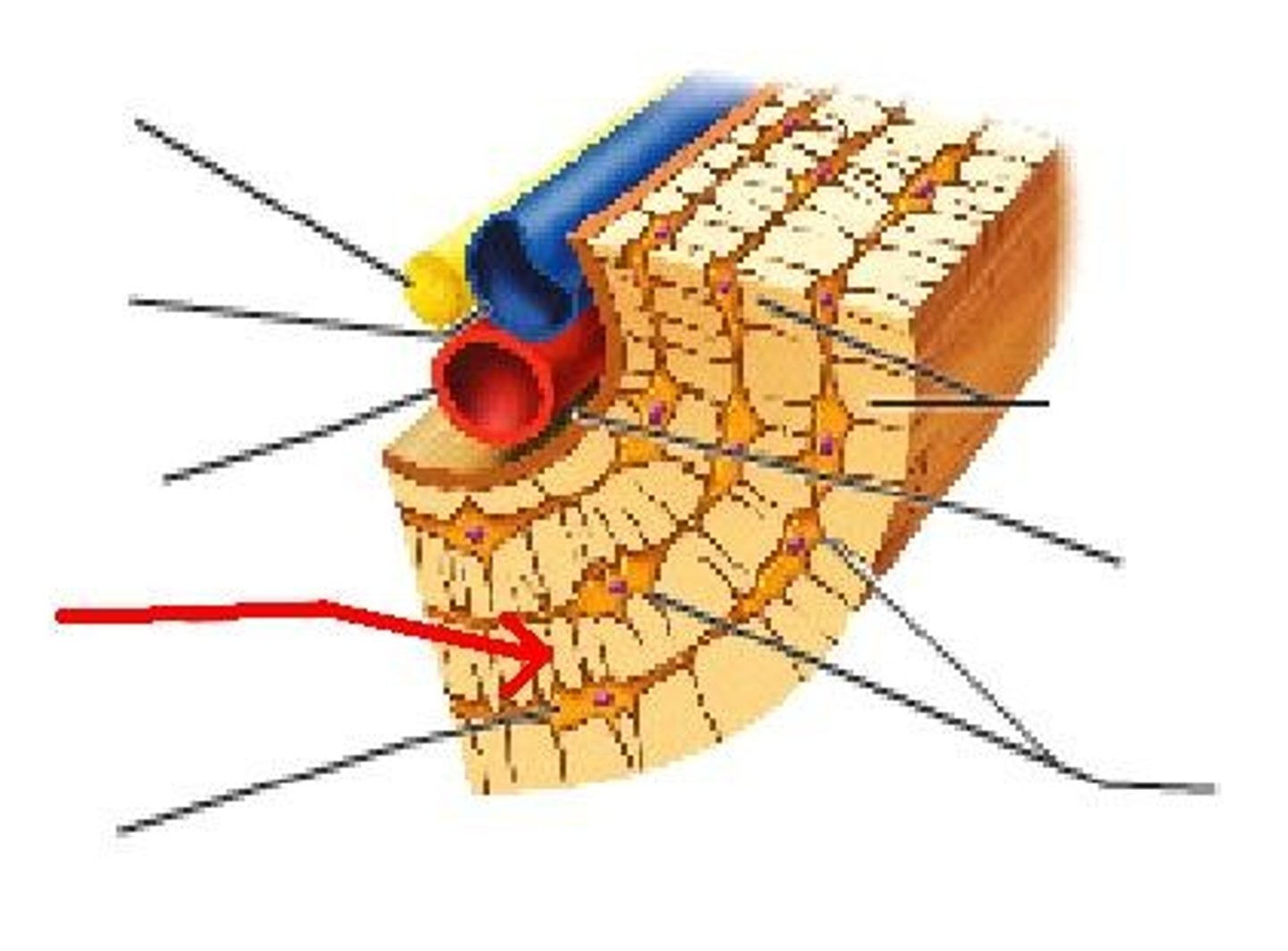
Canaliculi
Small channel or duct.
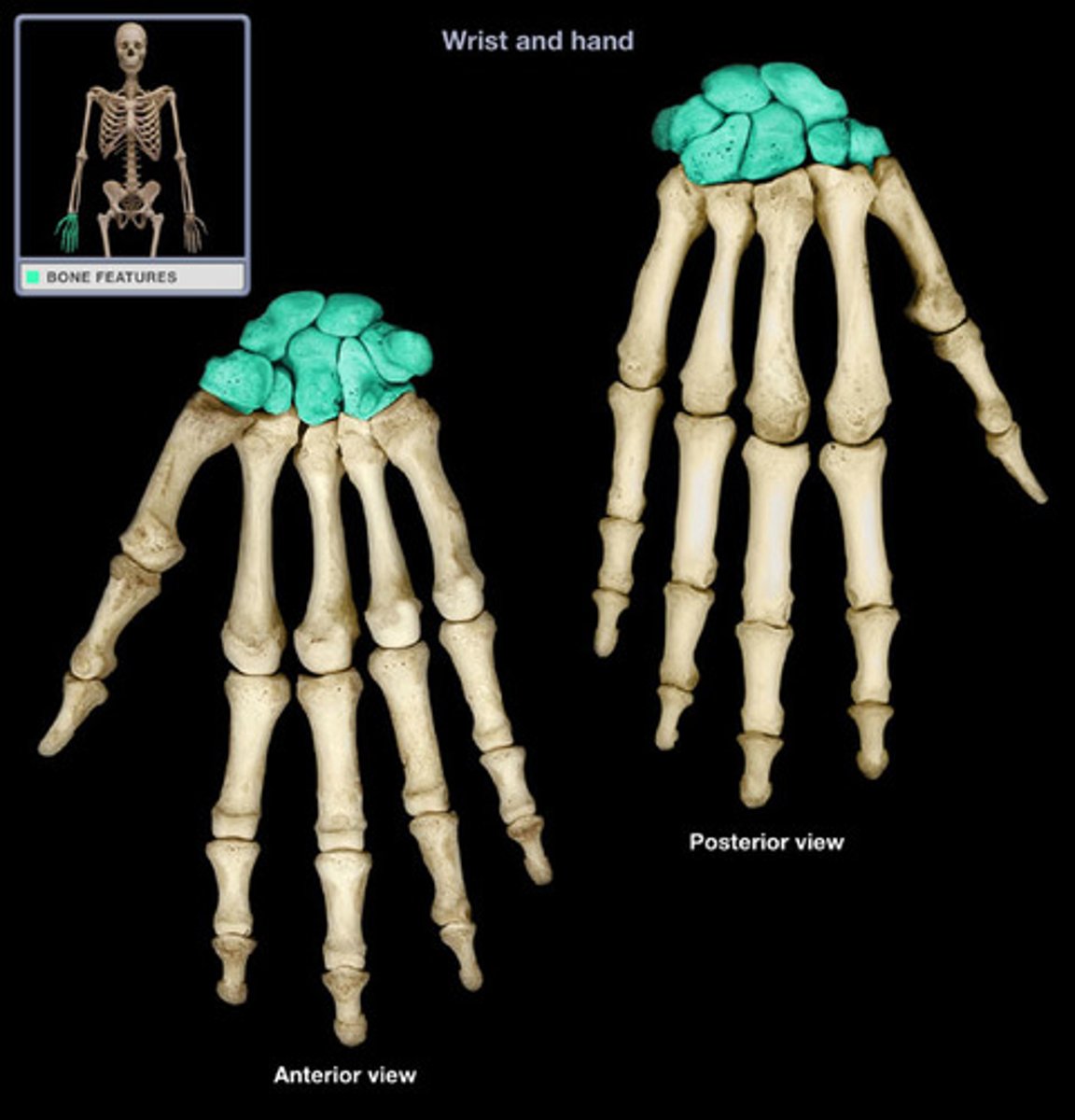
Carpals
Wrists.
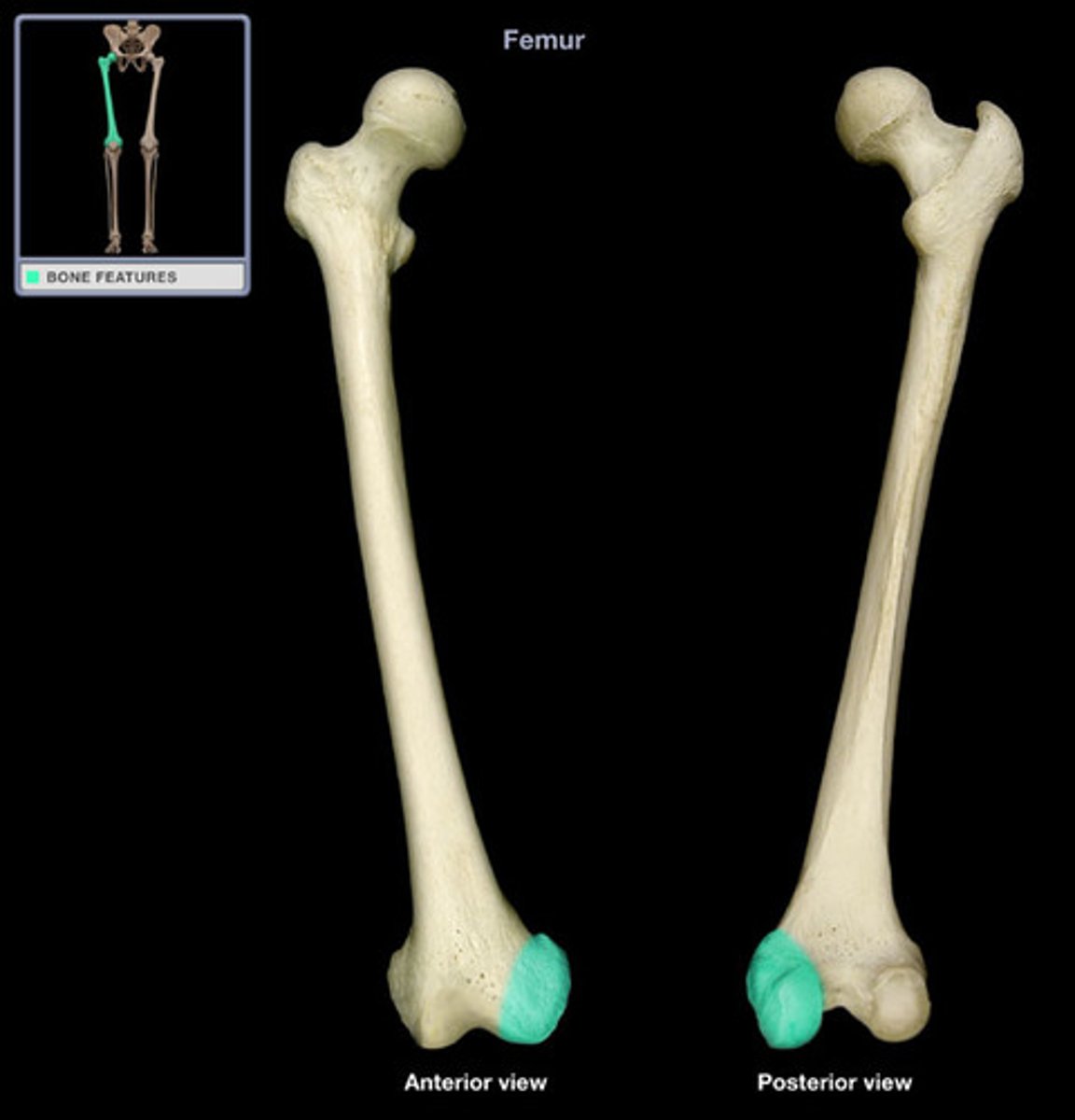
Condyle
A rounded protuberance at the end of some bones, forming an articulation with another bone.
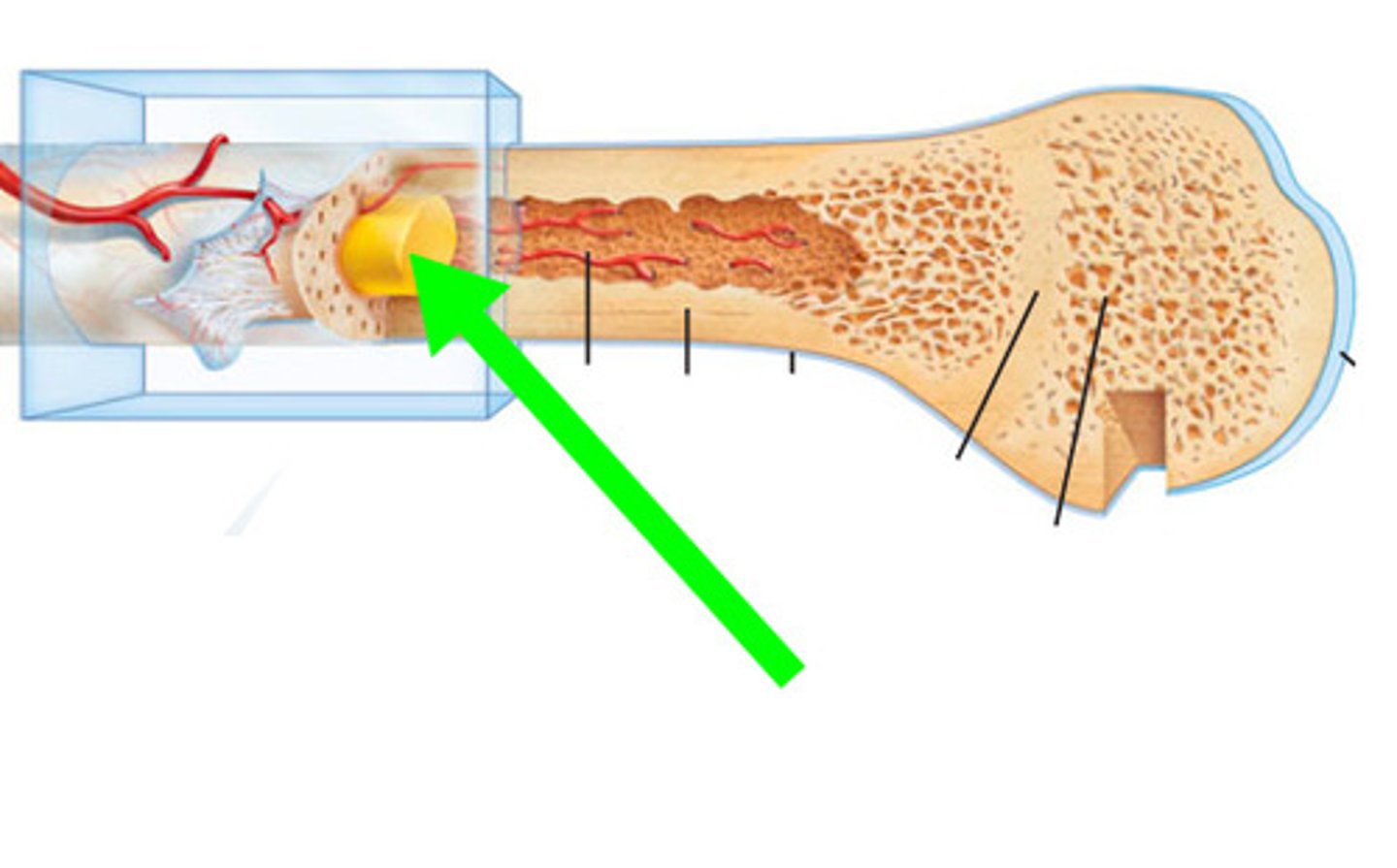
Diaphysis
The shaft or central part of a long bone.
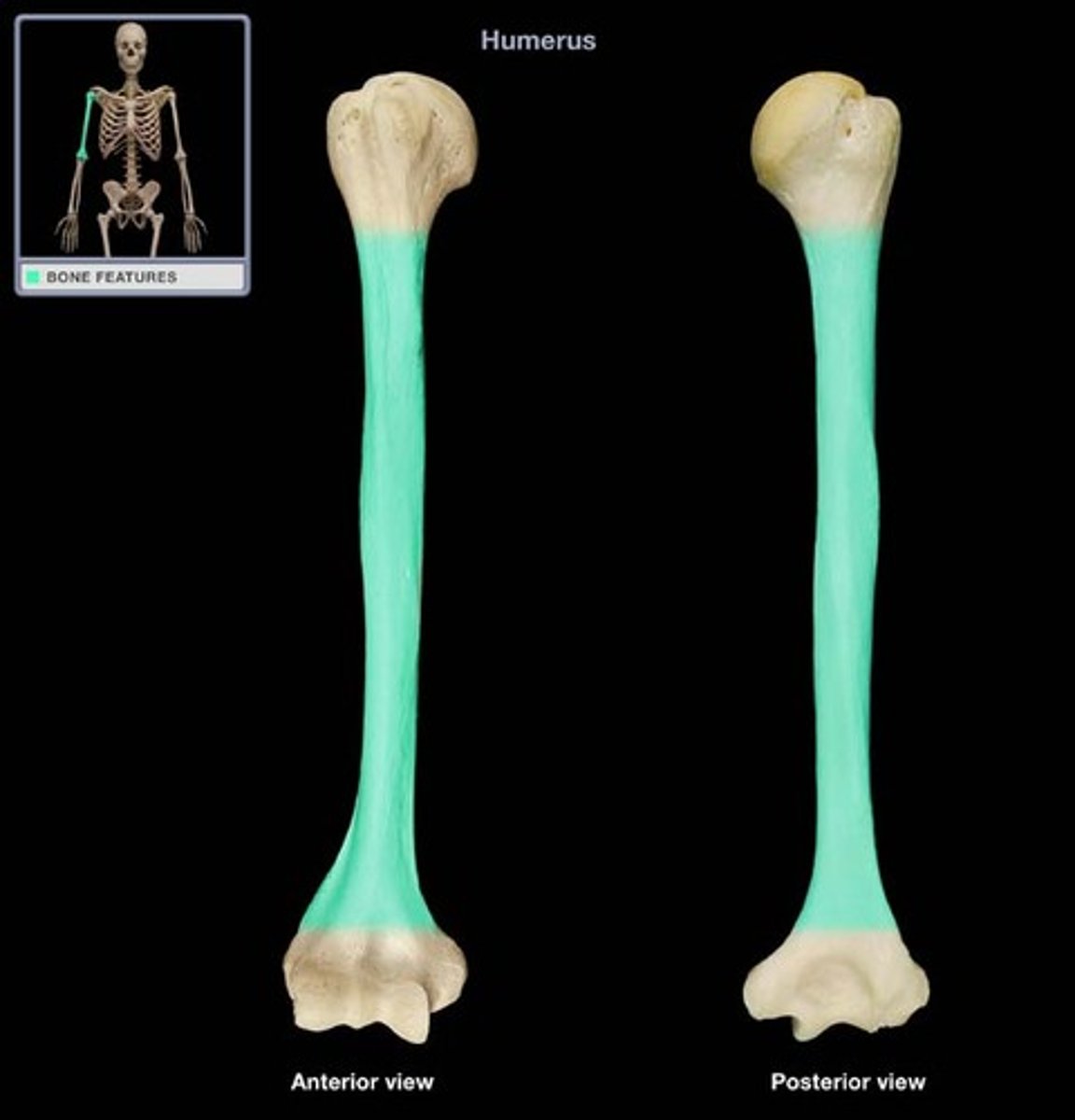
Endochondral bones
Bones that develop from a model of hyaline cartilage, which is then gradually replaced by bone tissue through a process called endochondral ossification
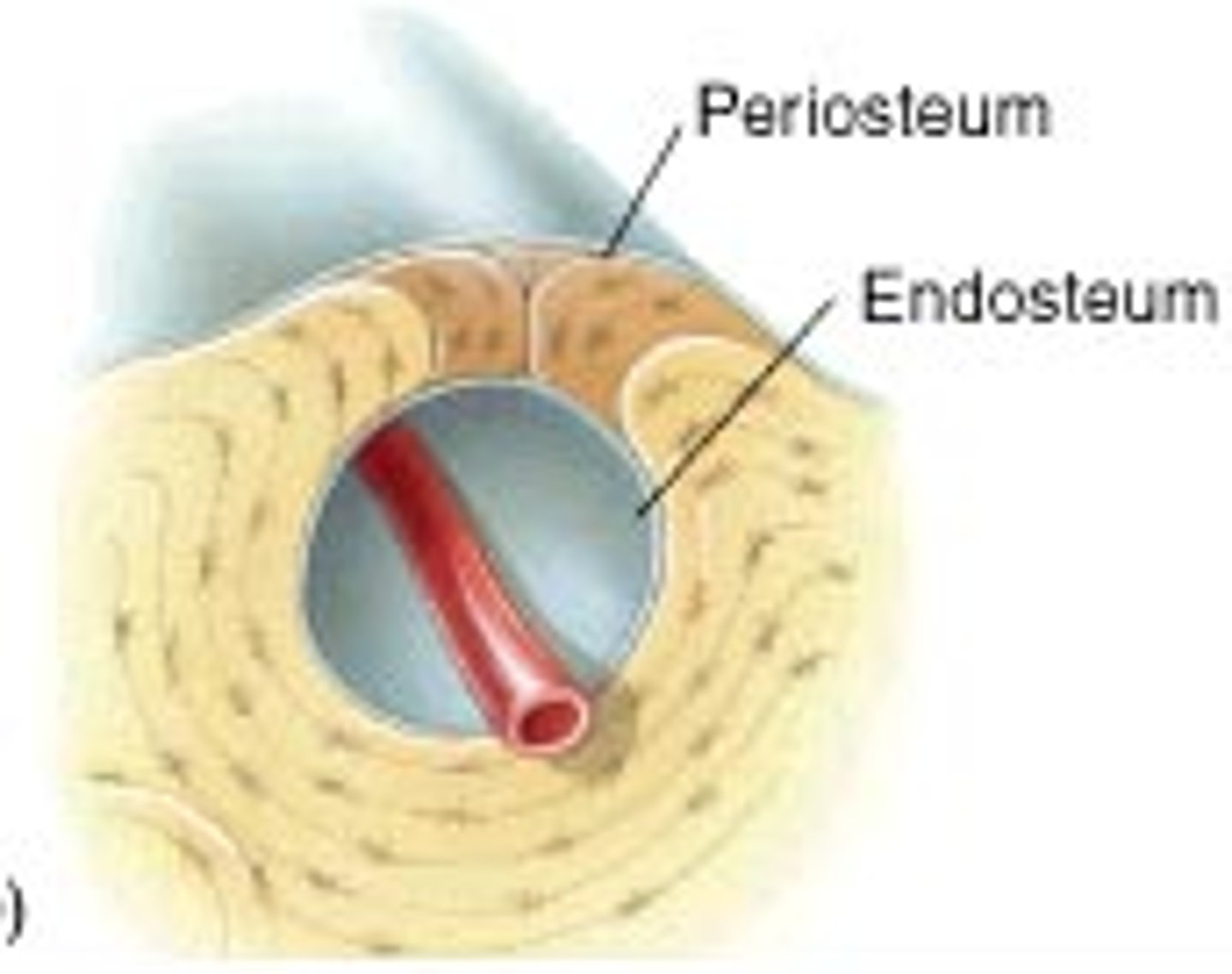
Endosteum
A delicate, vascular membrane lining the inner surfaces of bones, including the medullary cavity and the surfaces of trabeculae in spongy bone.
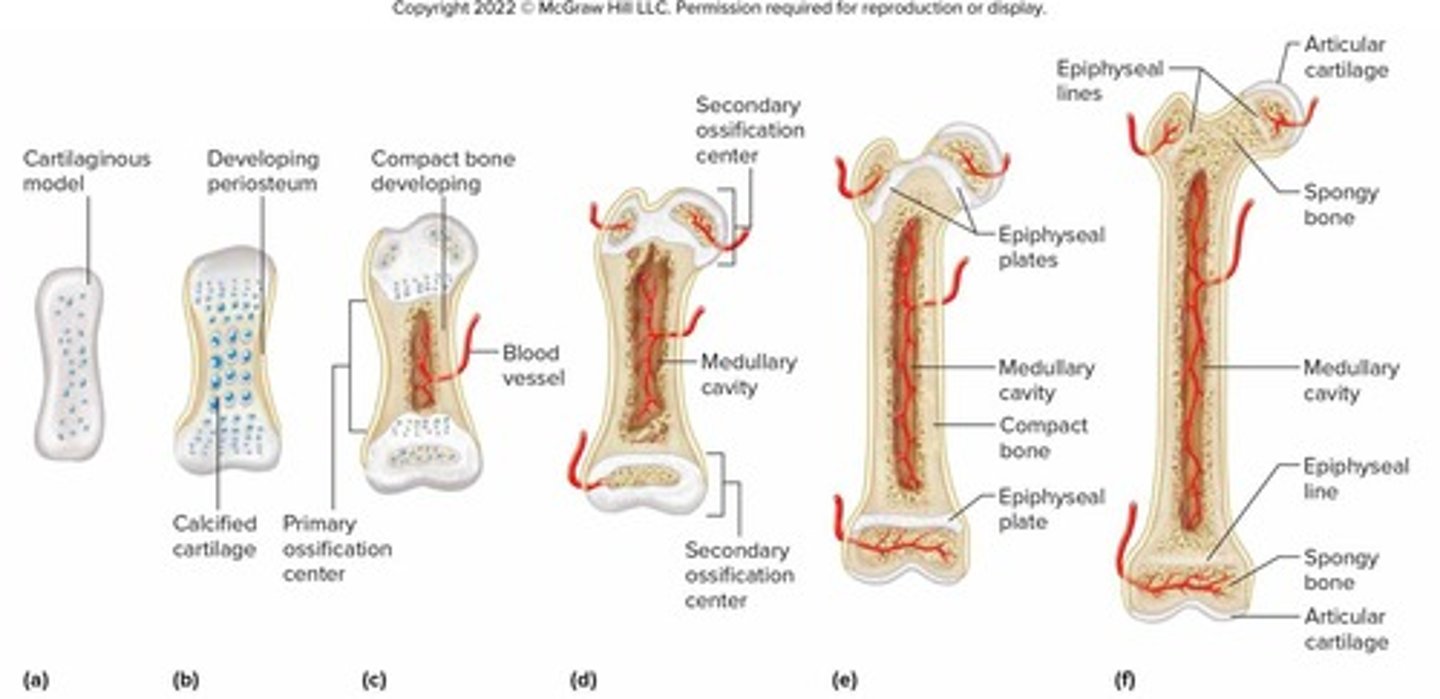
Epiphyseal plate
A layer of hyaline cartilage located in the long bones of children and adolescents where longitudinal growth occurs.
Epiphysis
The end part of a long bone, initially growing separately from the shaft.
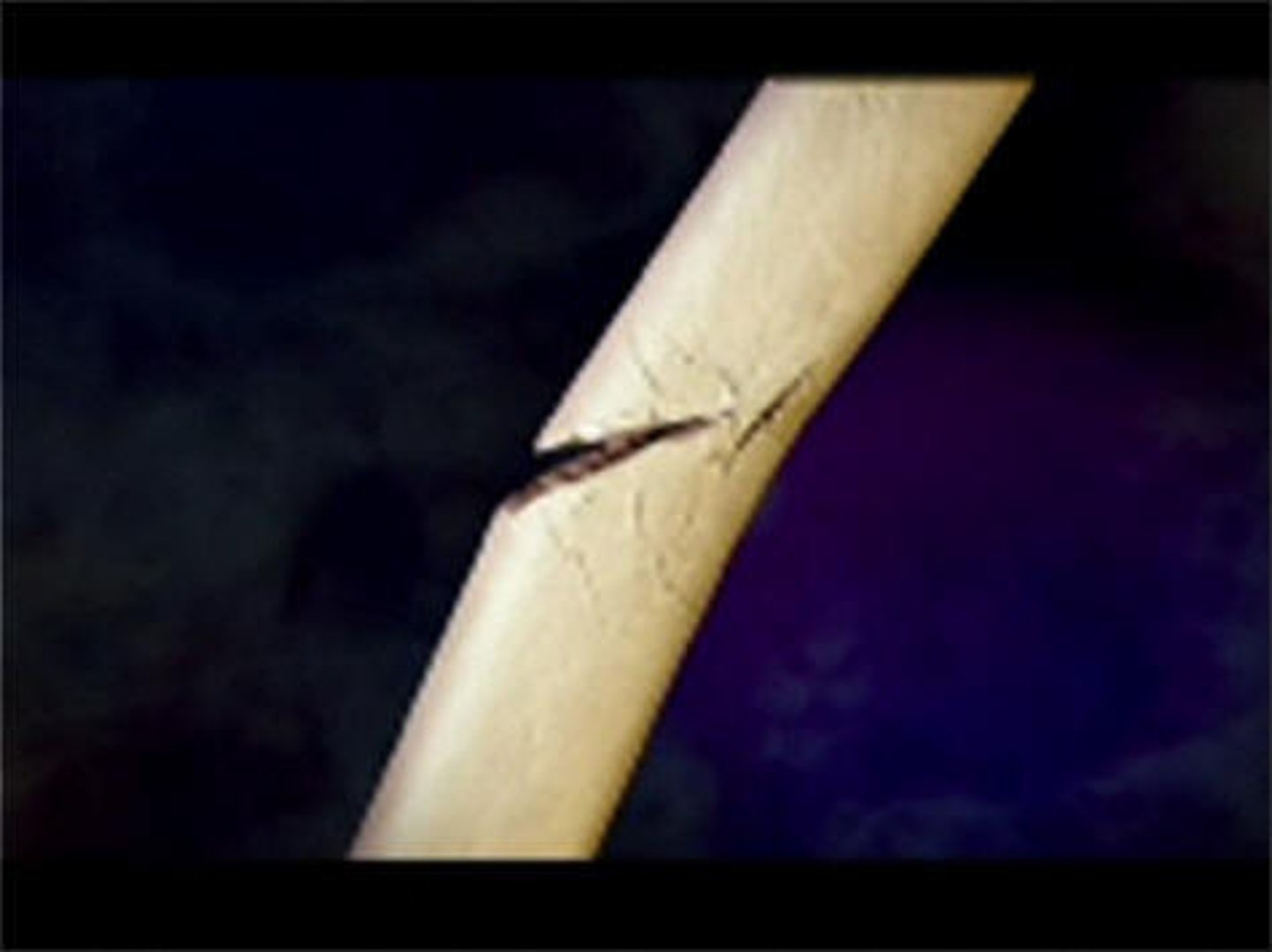
Fracture
A broken or cracked bone.

Glenoid cavity
A shallow depression on a bone into which another bone fits to form a joint, especially that on the scapula into which the head of the humerus fits.
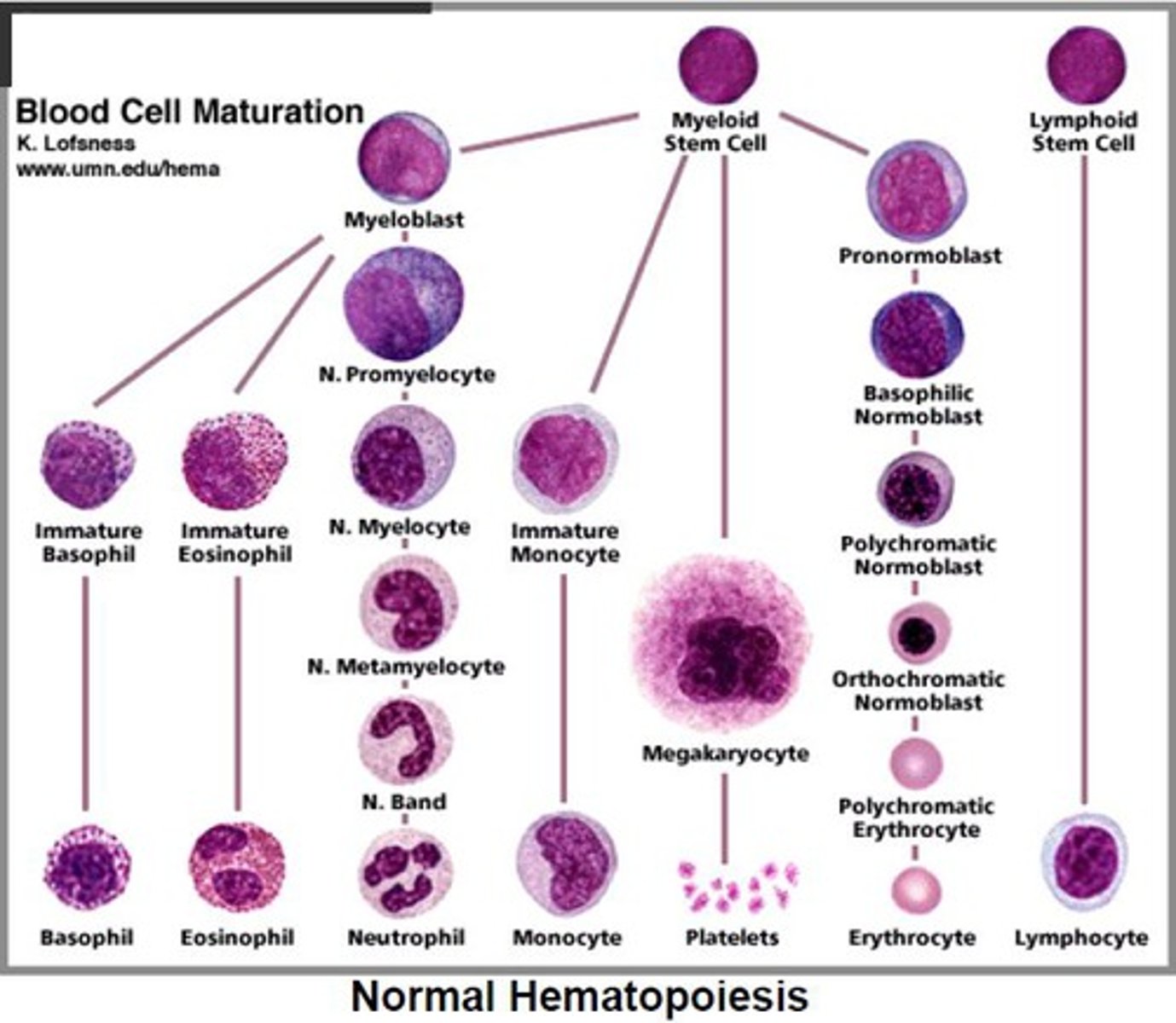
Hematopoiesis
The formation of blood cellular components.
Intervertebral disc
Fibrocartilaginous structures that cushion and connect the vertebrae in the spinal column.
Intramembranous bone
A process of bone formation that occurs directly within a membrane of connective tissue, without the involvement of cartilage as an intermediate.
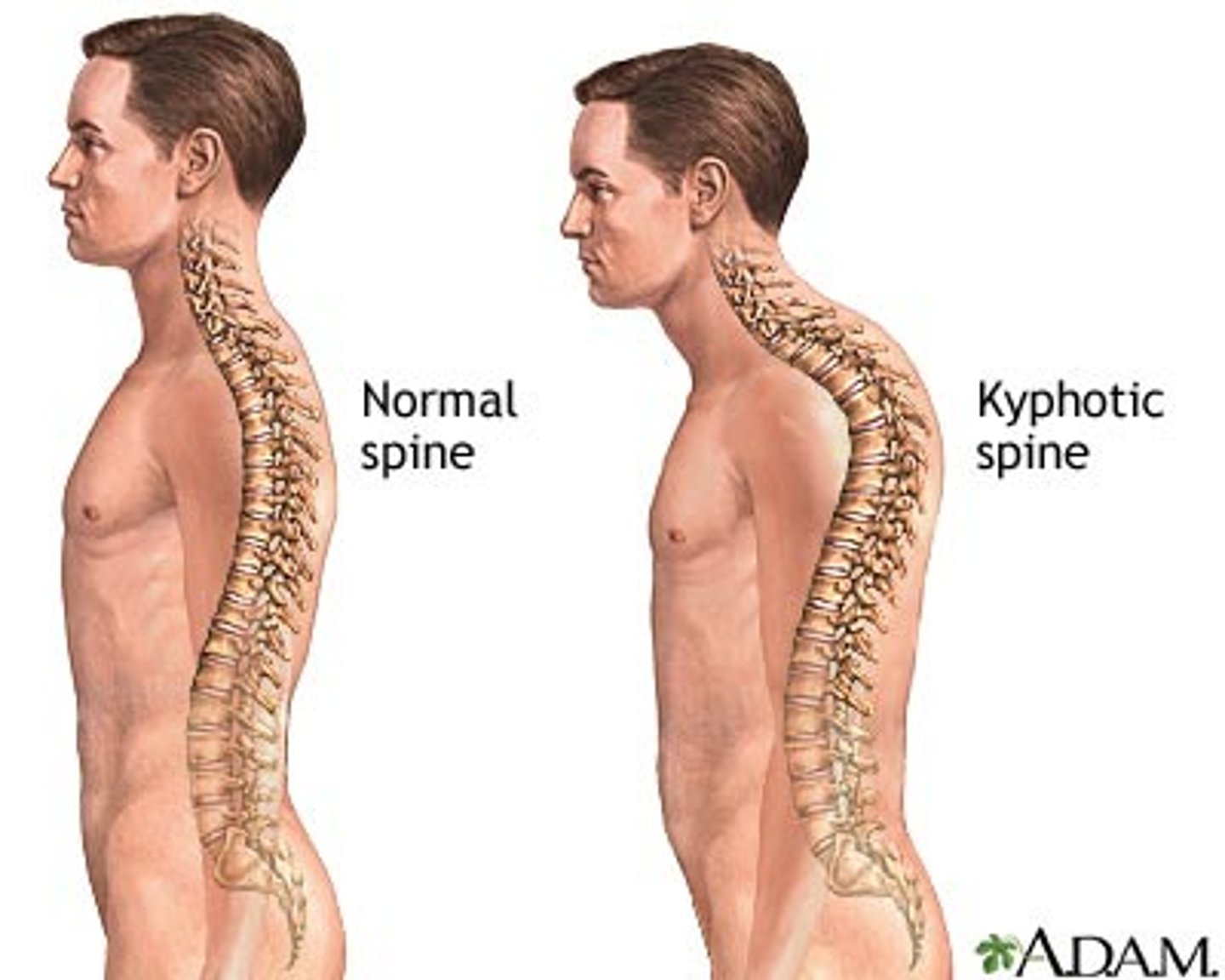
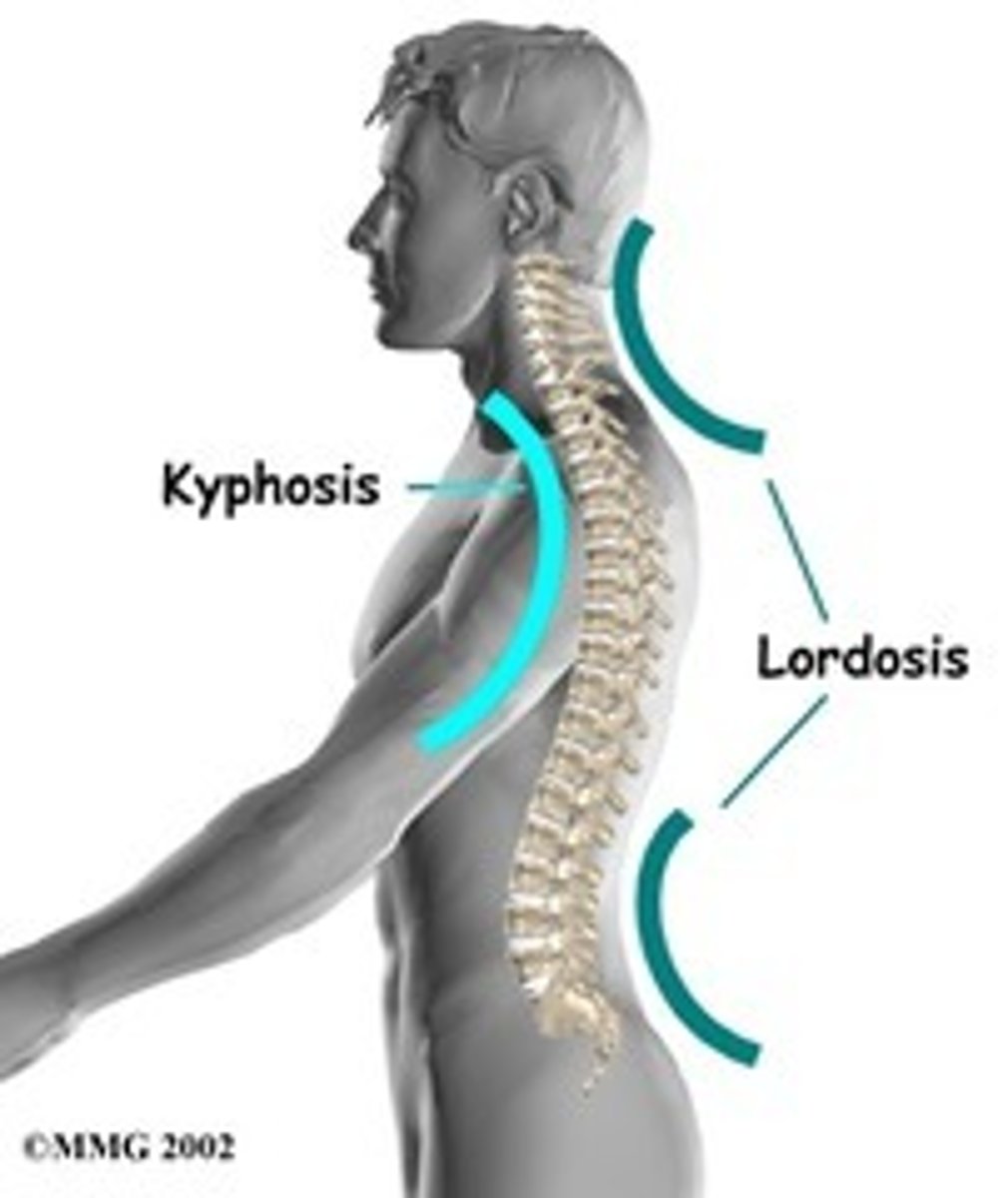
Kyphosis
Excessive forward curve of spine.
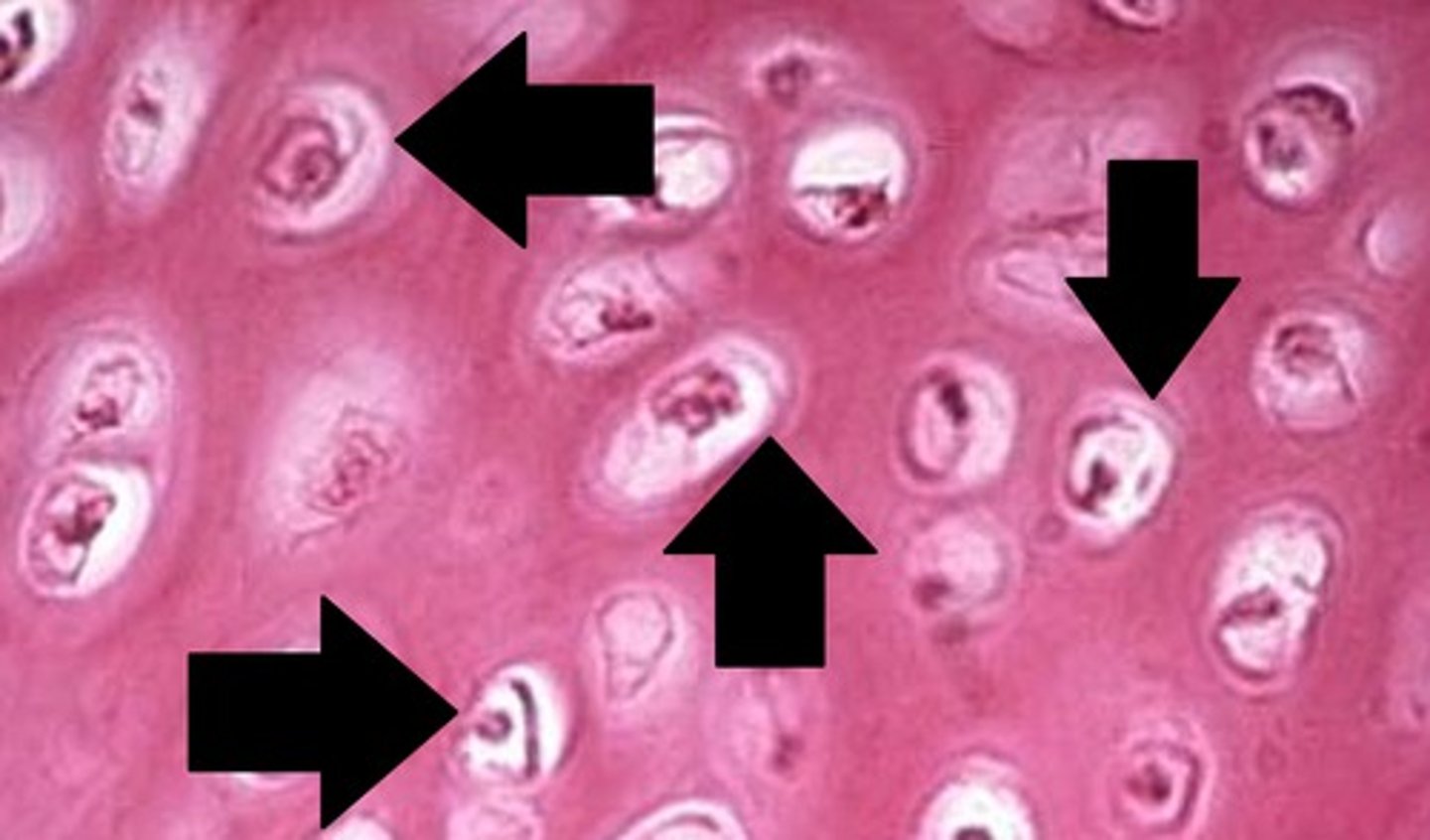
Lacunae
An unfilled space or interval; a gap.
Lamella
A thin, plate-like layer of tissue found in various biological structures.
Lordosis
Excessive inward curve of spine.
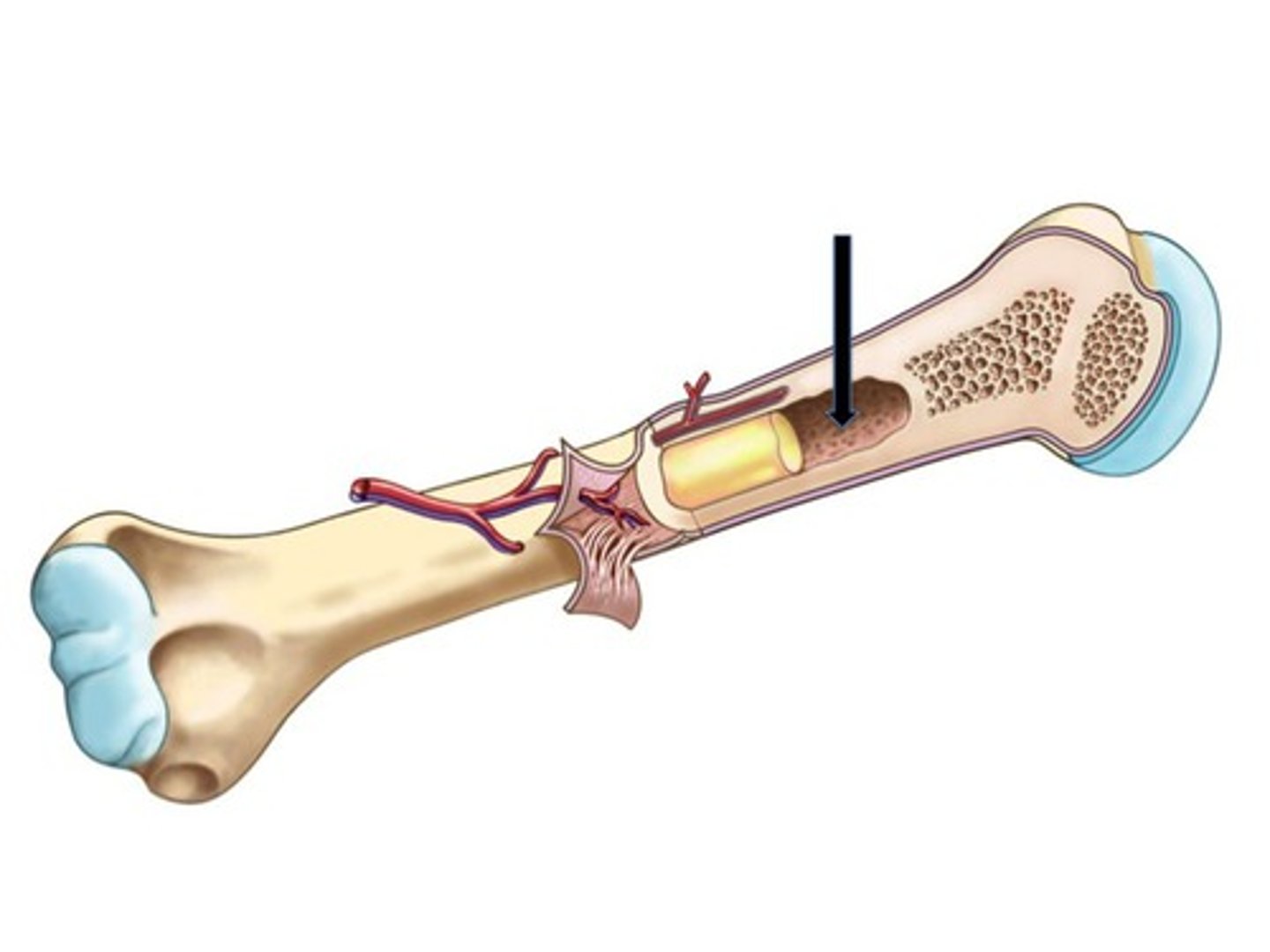
Medullary cavity
The hollow space in the shaft of long bones that contains bone marrow.
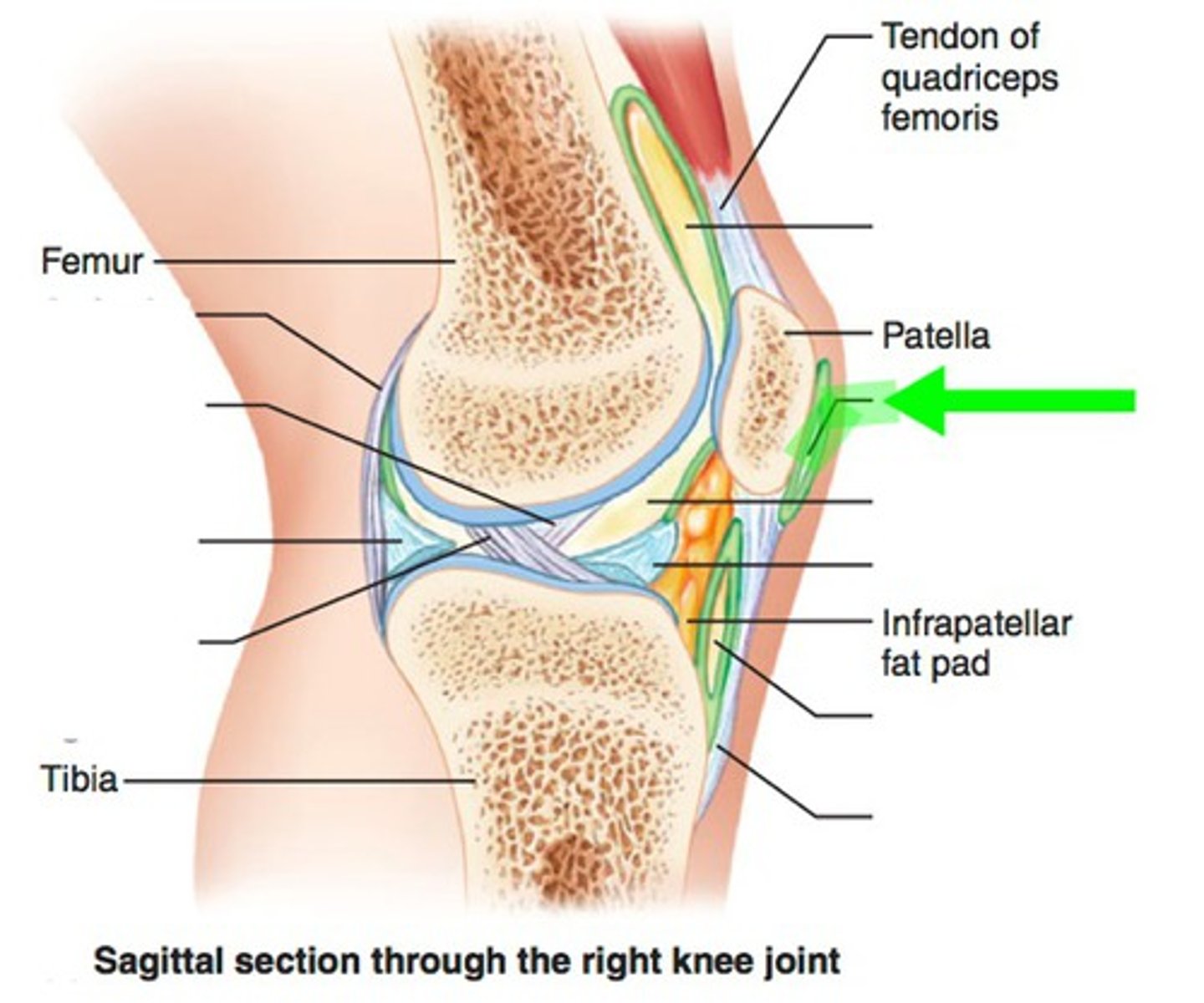
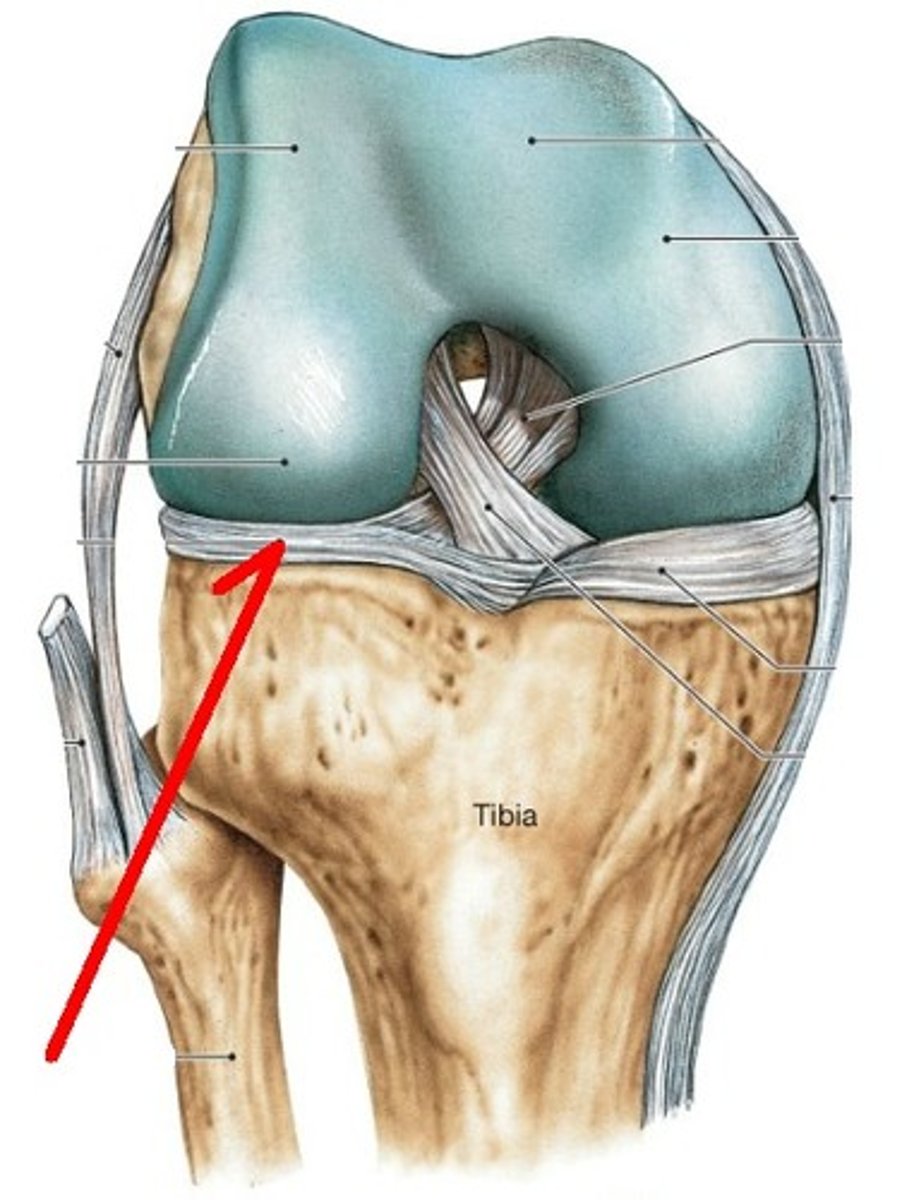
Meniscus
A crescent-shaped piece of cartilage that cushions the knee joint
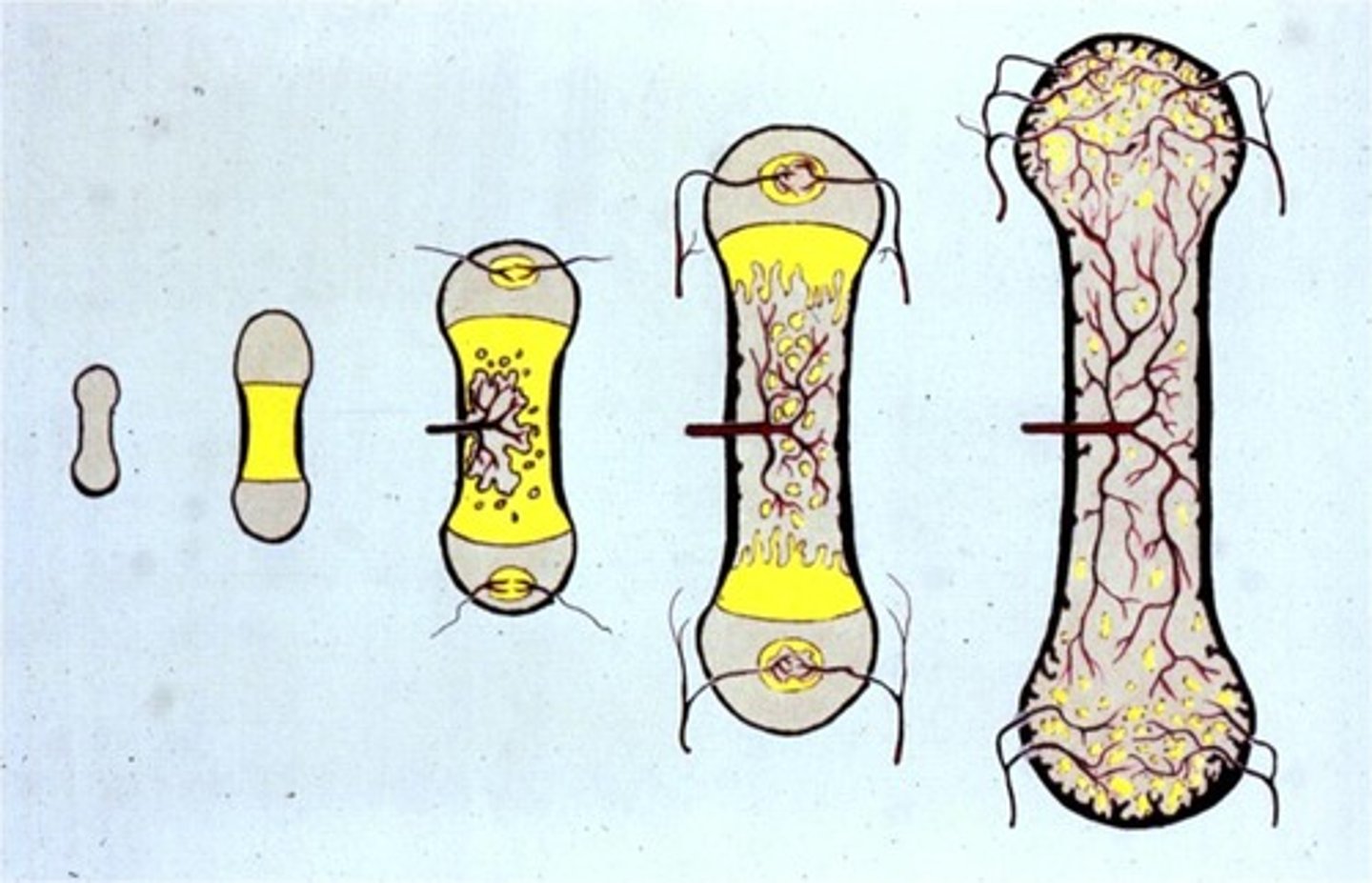
Ossification
Process of bone formation.
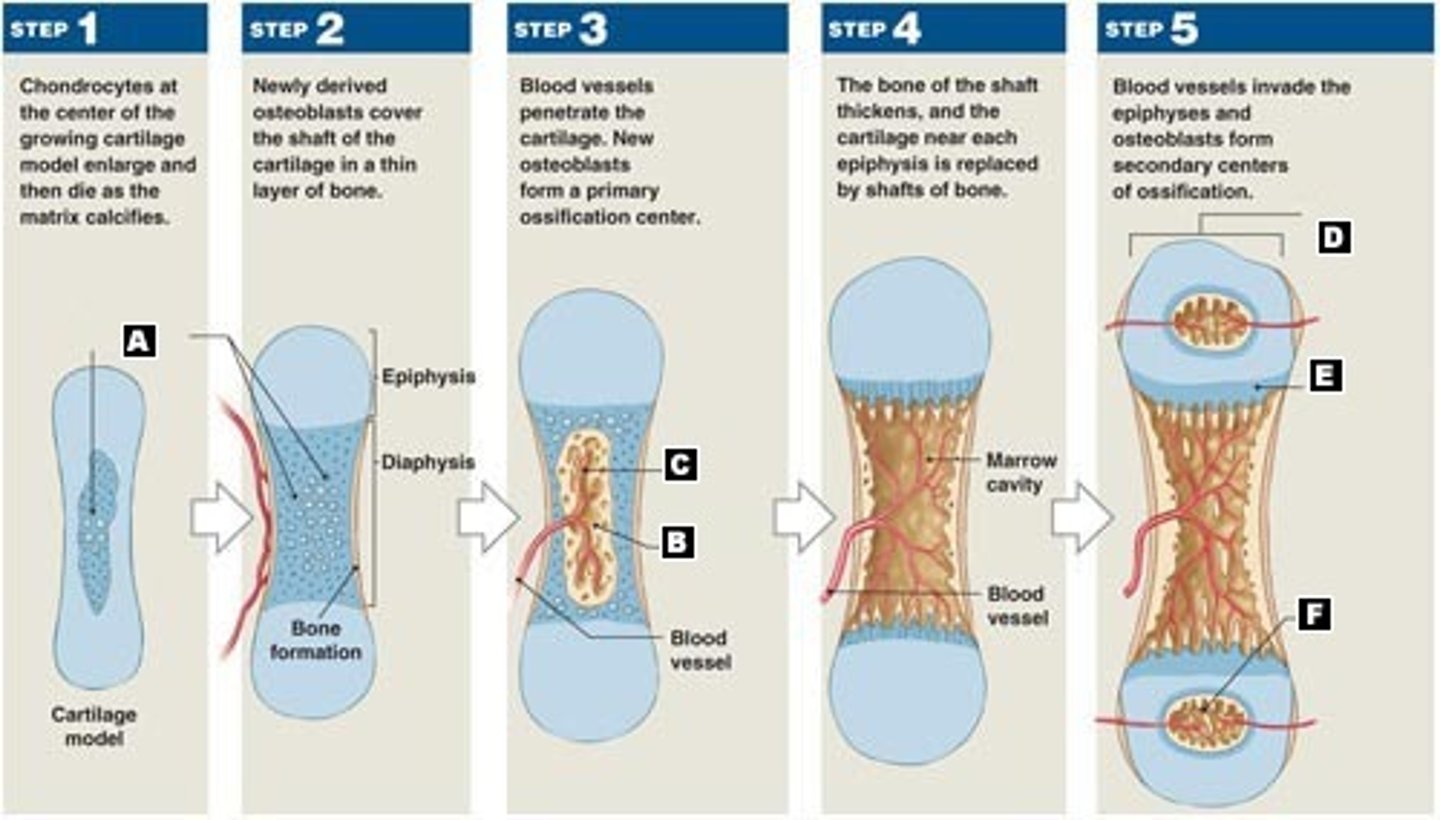
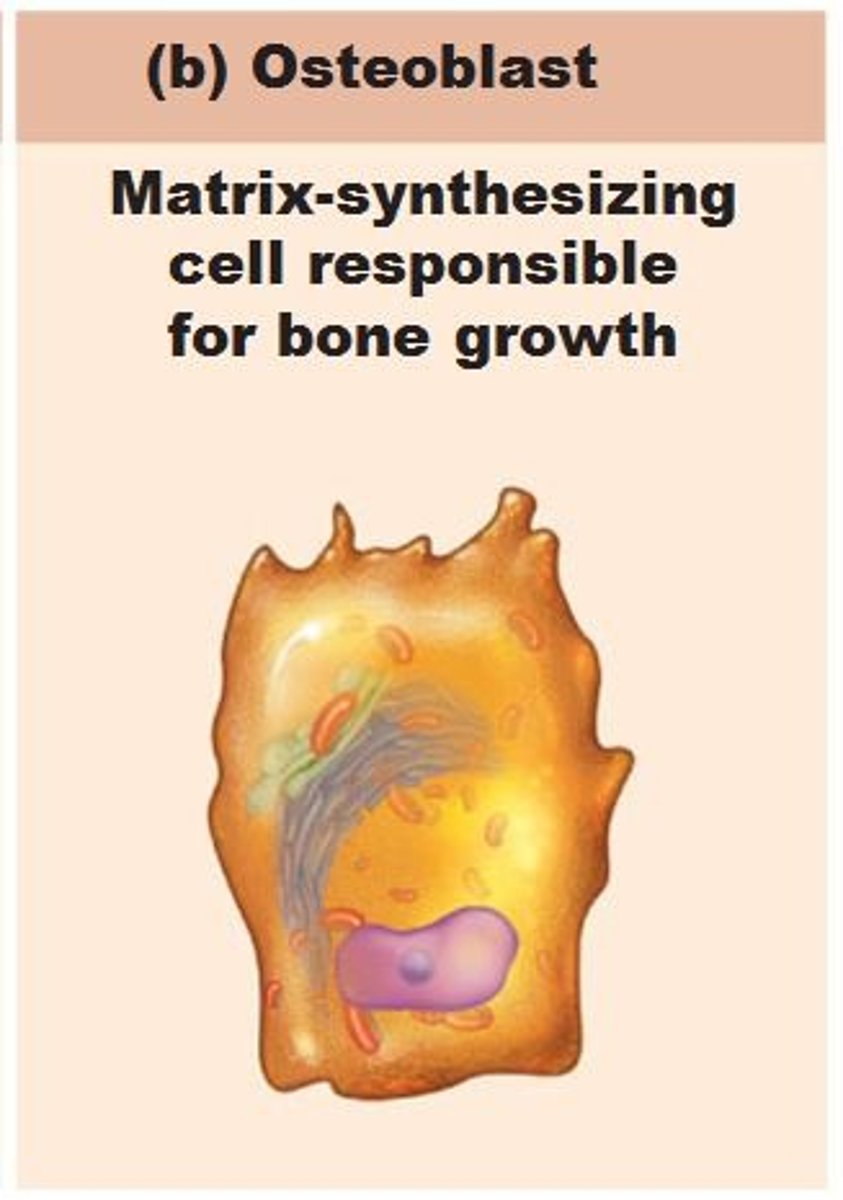
Osteoblast
Specialized cells responsible for building and maintaining bone tissue.
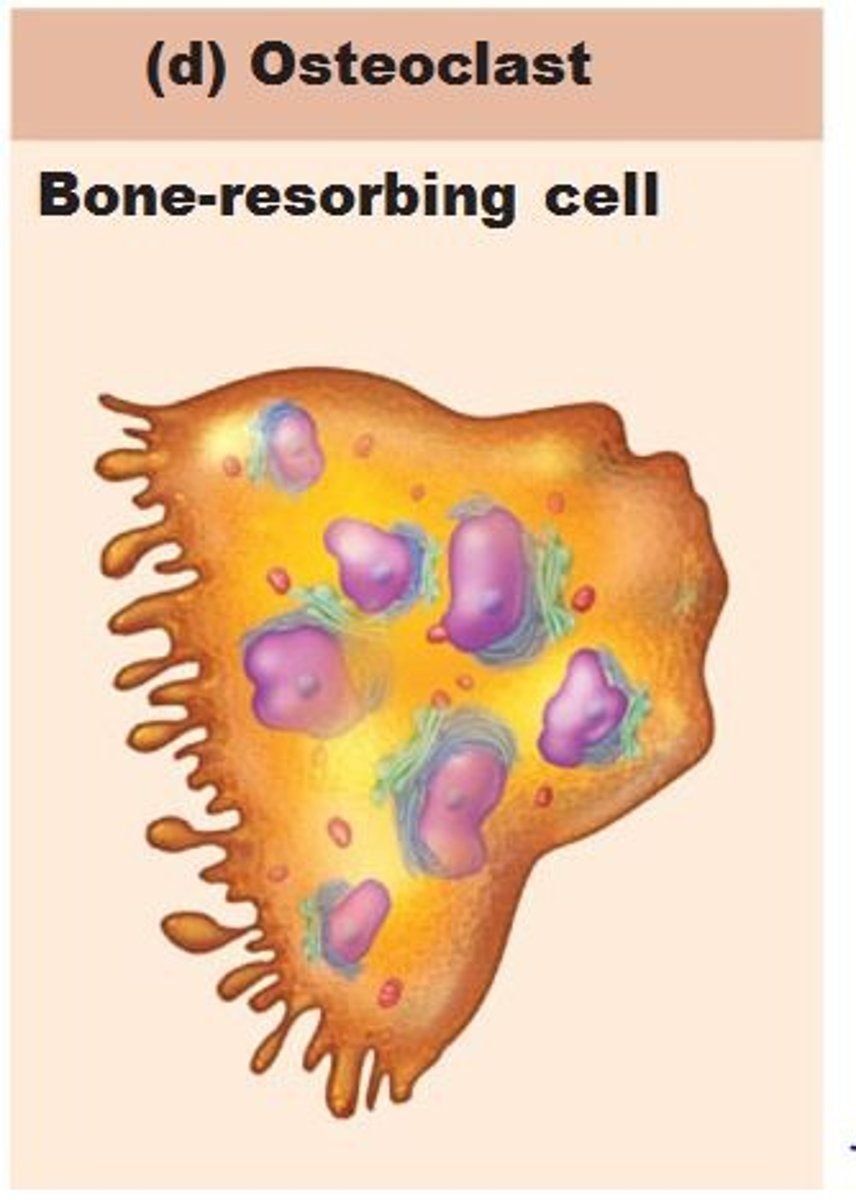
Osteoclast
A large, multinucleated cell in the body's bone tissue responsible for bone resorption, or the breakdown of old or damaged bone
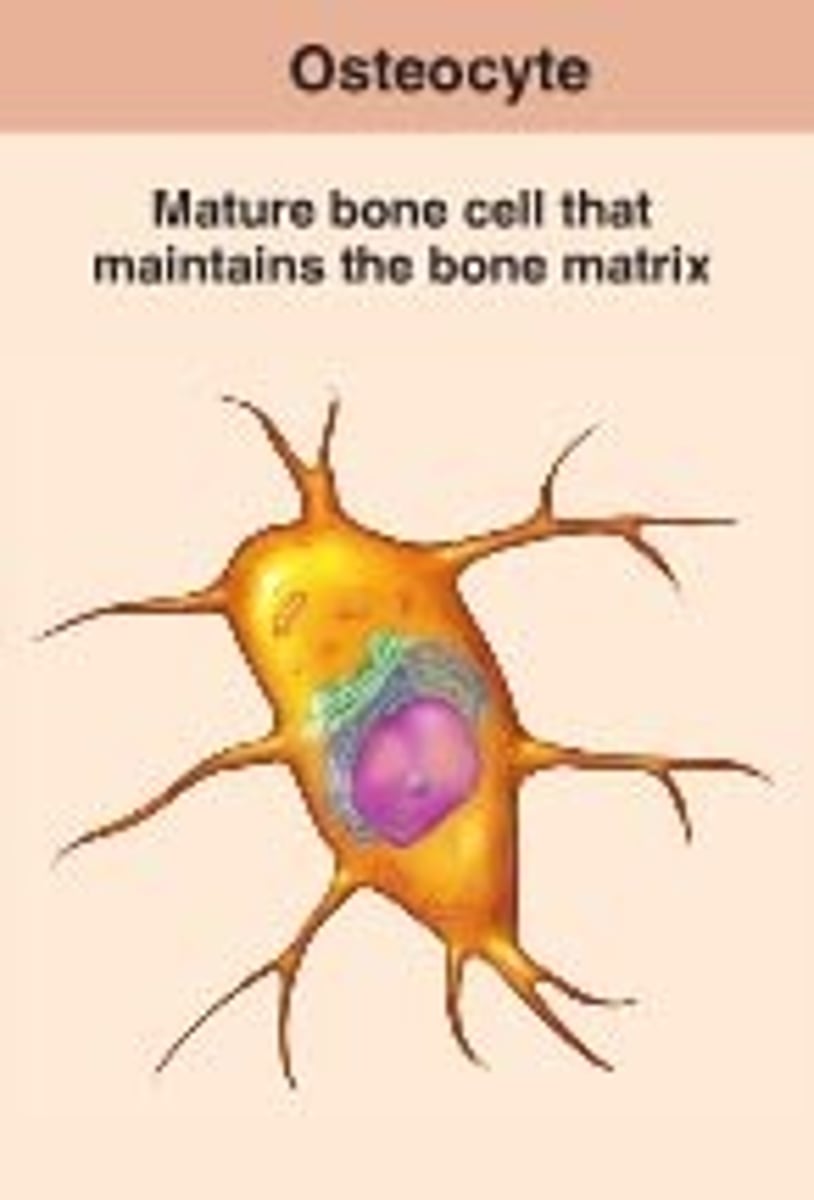
Osteocyte
One of the 4 types of bone cells. AKA, a bone cell.
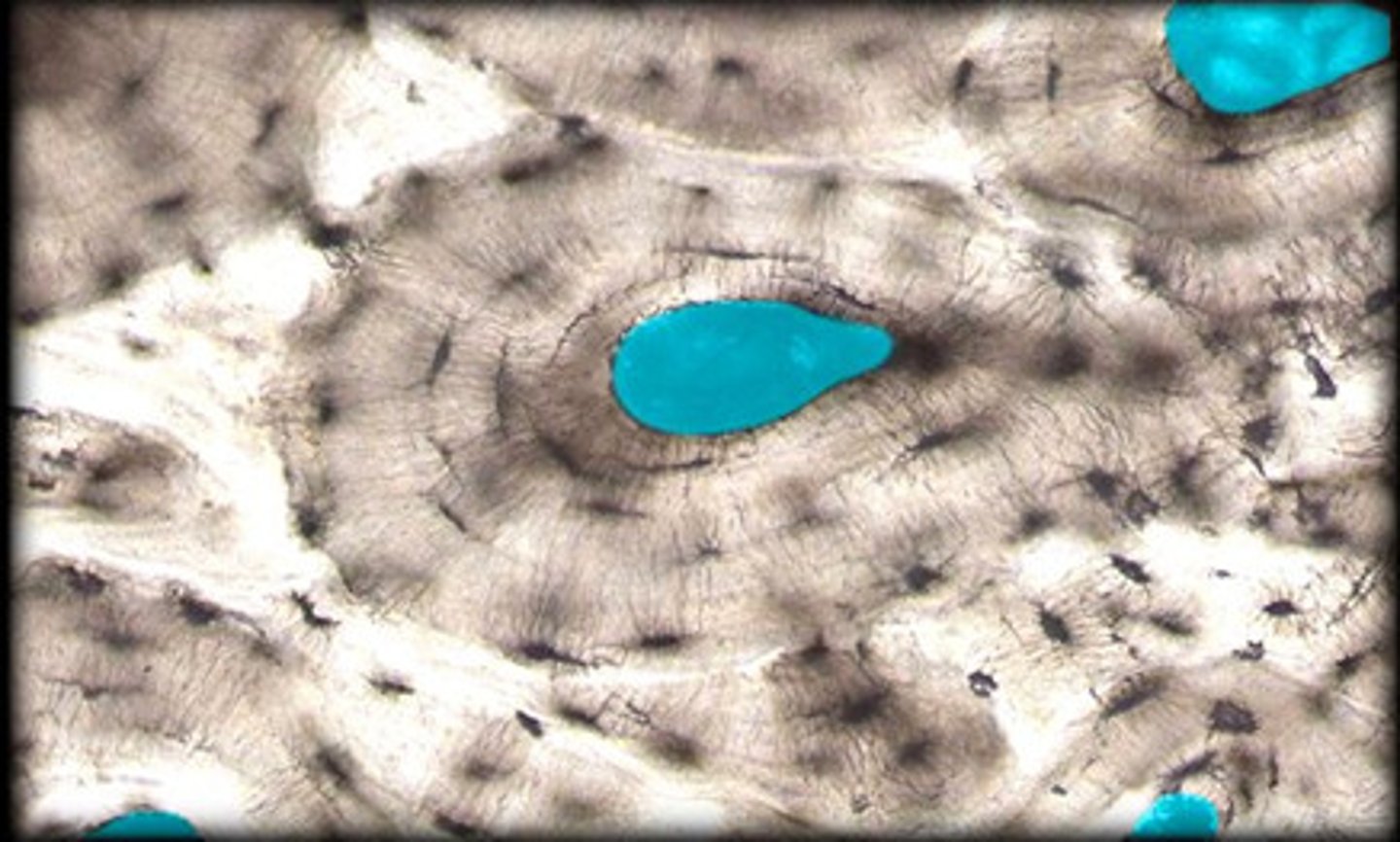
Osteon
The fundamental structural and functional unit of compact bone, consisting of concentric rings of bone tissue called lamellae surrounding a central Haversian canal.
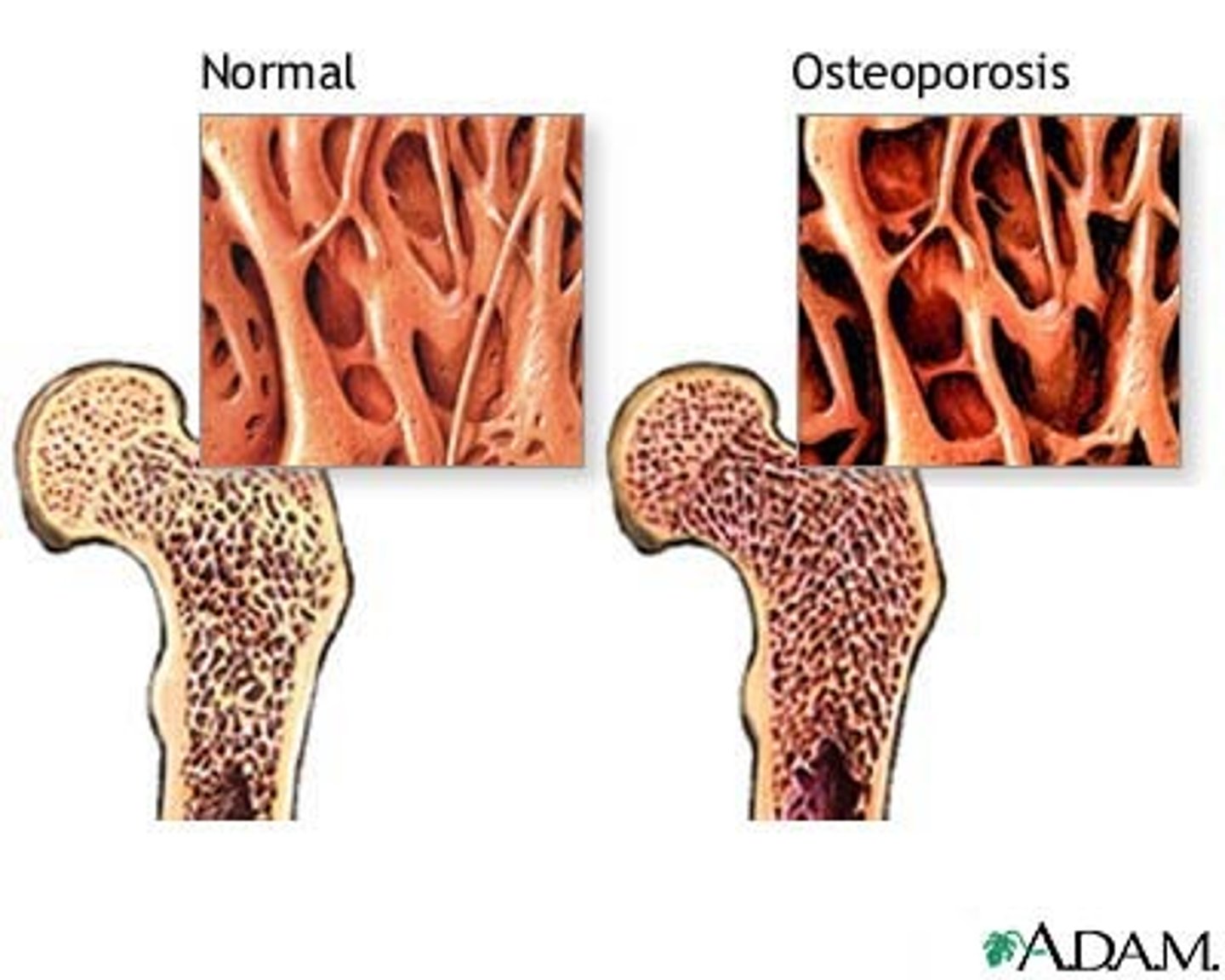
Osteoporosis
Silent disease where the mass of the bone decreases.
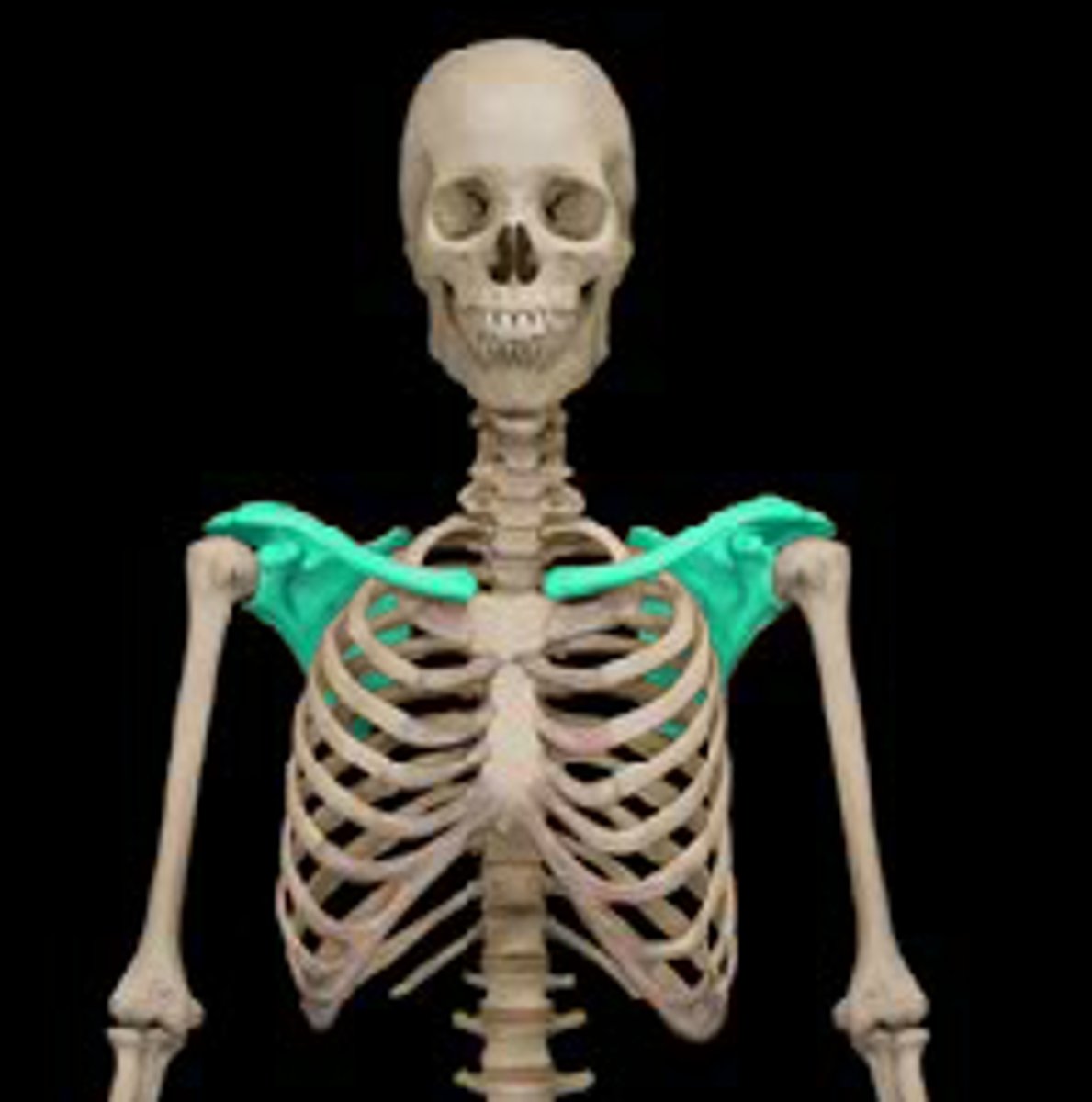
Pectoral girdle
The bony structures that connect the upper limbs to the axial skeleton (skull, spine, and rib cage).
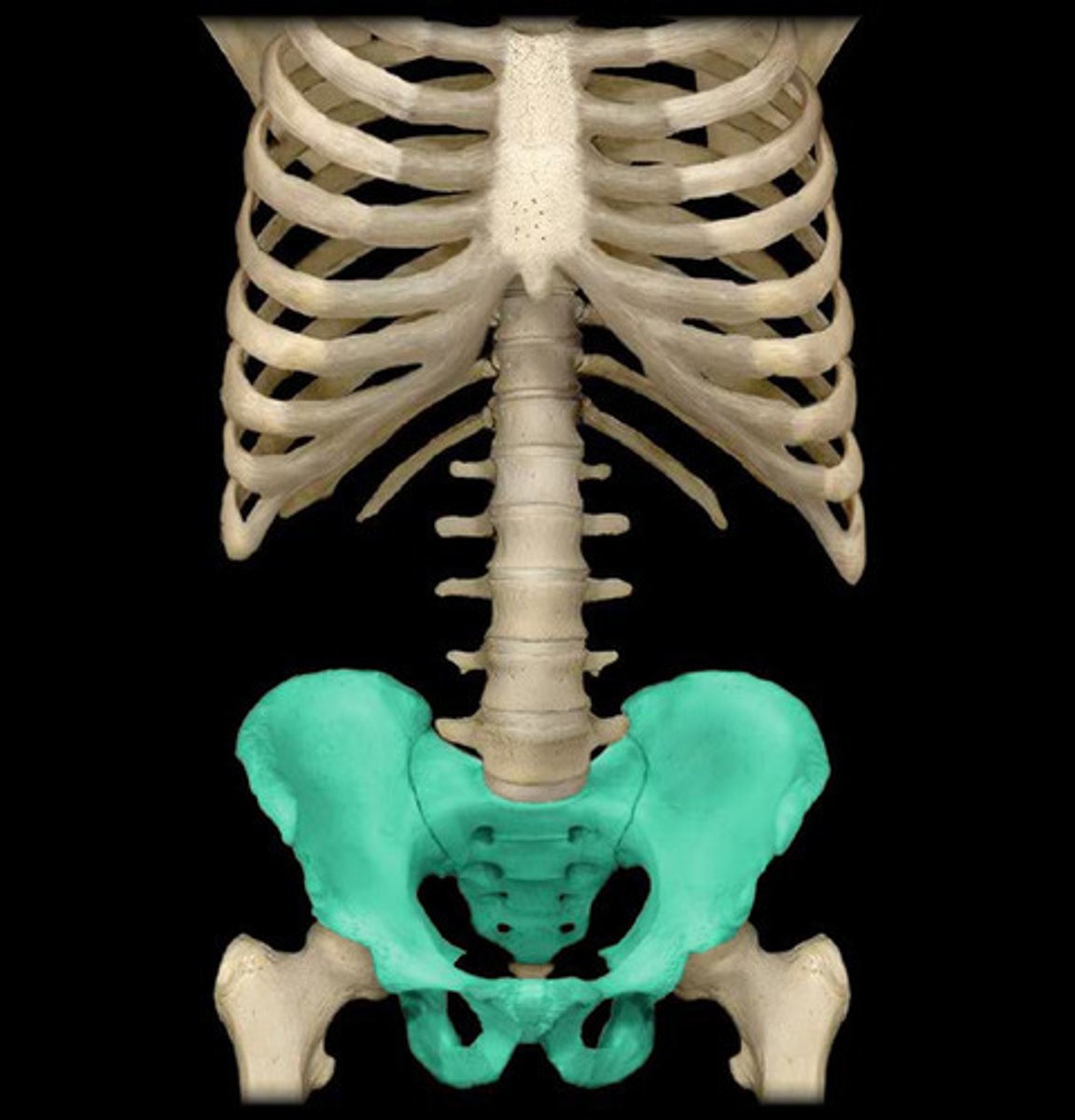
Pelvic girdle
A ring-shaped structure that connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton (spine).
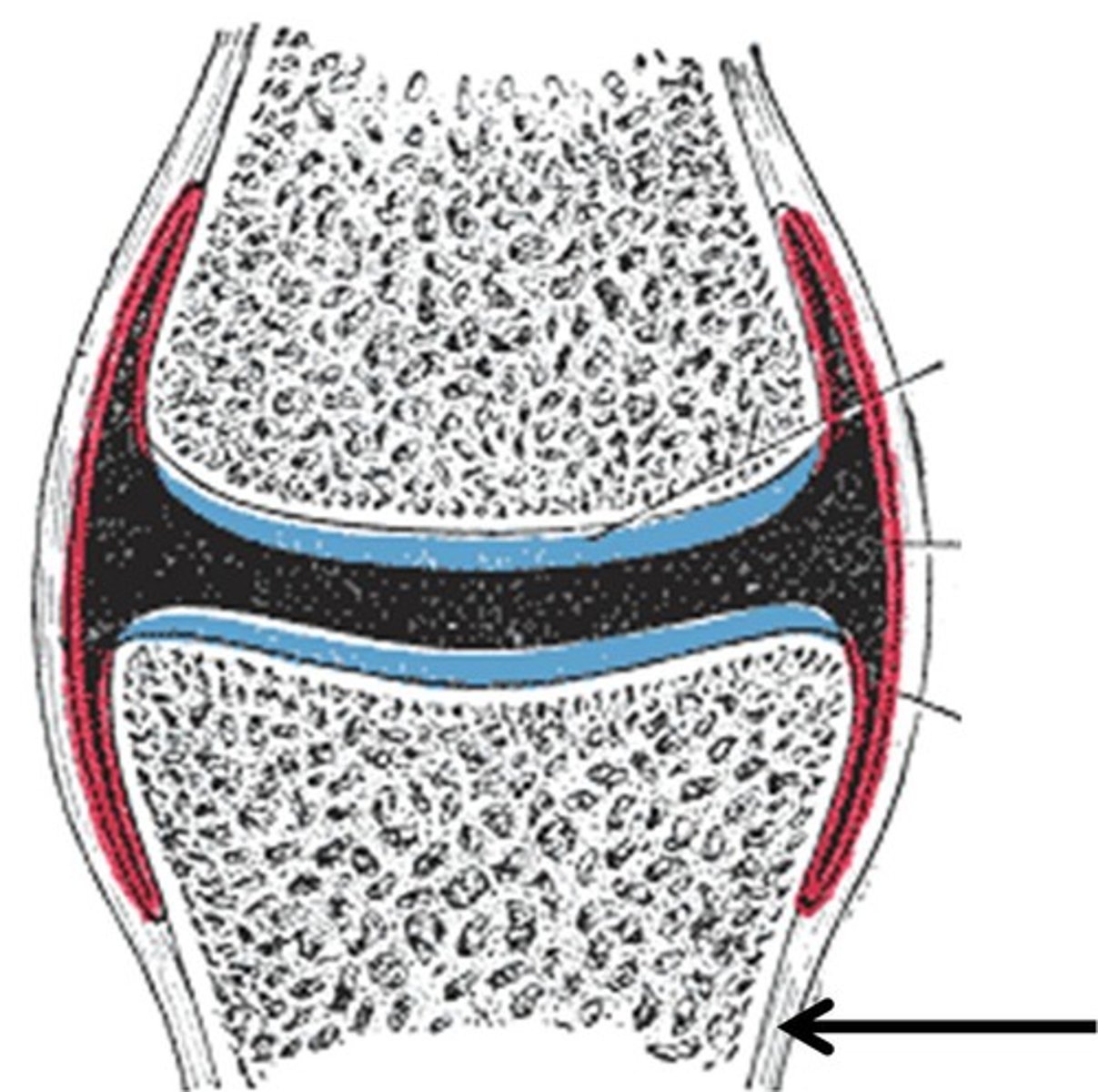
Periosteum
A dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones except at the surfaces of the joints.
Red marrow
The spongy tissue in bones responsible for producing all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, through hematopoietic stem cells.
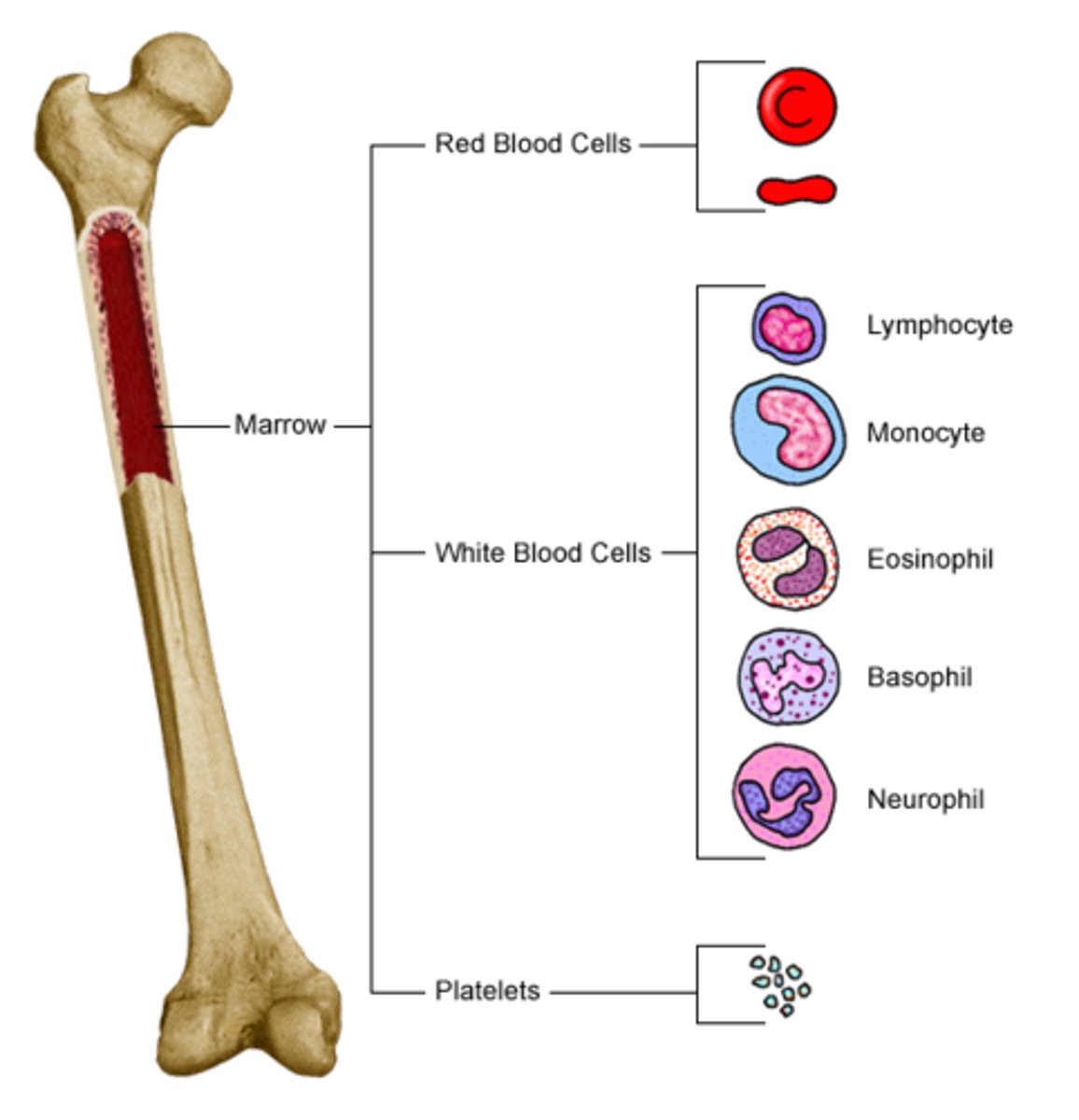
Trabeculae
The thin columns and plates of bone that create a spongy structure in a cancellous bone
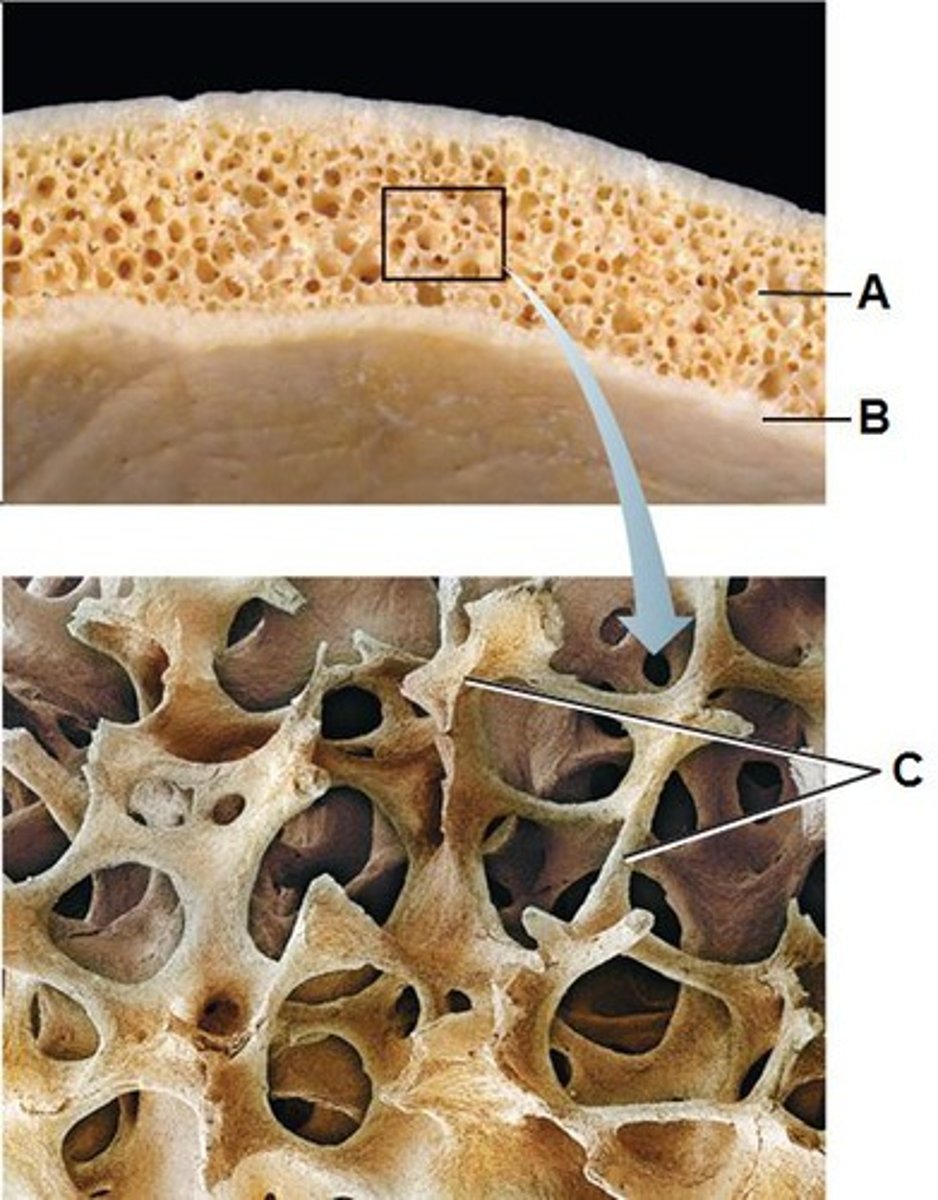
Yellow marrow
Found in the large, central cavities of mature bones and is composed mostly of fat cells, which give it its yellow color and serve as an energy reserve.