Low Back Pain and Cervical Spine
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
5 Vertebral segments, 5 lumbar nerve root, spinal cord terminates between T12 and L2
Anatomy of the lumbar zone of the spine
cartilaginous joints (slightly moveable separated by fibrocartilaginous disc)
Vertebral bodies of the spine are considered
cushion, shock absorption,
What is the purpose of the nucleus pulposus (center of the disc)?
muscular strain, ligamentous sprain, facet joint injury, fracture
Localized pain (usually midline or off midline) is typically indicative of
spinal cord/nerve root compression (get a description of the distribution)
Radiating pain is usually a concern for
acute
Which onset is associated with one specific mechanism of injury/event
Chronic
Which onset is related to overuse injury (accumulative microtrauma), degenerative, and/or postural abnormalities
Pain from inflammation (strain, sprain, contusion)
This type of pain persist despite changes in spine position
Pain from mechanical nature (nerve root compression)
This type of pain varies depending upon spine positioning and can be relieved or exacerbated
Curvature (normal/absent/exaggerated lordosis, scoliosis), position of shoulder and pelvis should be level, soft tissue symmetry, skin markings (hairy patch, cafe au lait spots, birth marks)
Spinal inspection should look at
Spinous processes (step-offs (spondylolisthesis), absence (spina bifida)), pelvic iliac crest at L4/L5. sacroiliac joints, greater trochanters, paraspinal muscles, sciatic area
Spinal palpation should look at
L2, 3
Spinal level of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
L2, 3, 4
Spinal level of the femoral nerve
L4, 5, S1, 2, 3
Spinal level of the sciatic nerve
Iliopsoas (raise against resistance), Quadriceps (extend/flex knee against resistance - femoral nerve), Hip adductor group (adduct leg against resistance - obturator nerve)
Muscle testing of L1, 2, 3
Anterior thigh between inguinal ligament and knee joint
Area for sensation testing of L1, 2, 3
tibialis anterior (deep peroneal, tibial nerve), resistance against dorsiflexion and inversion
Muscular exam for L4
Patellar reflex
L4 reflex
sensation of medial side of lower leg
L4 Dermatome
Extensor hallucis longus (deep peroneal nerve) → extension of the big toe
Muscular exam for L5
Sensation of the dorsum of the foot
L5 Dermatome
Peroneus longus and brevis (superficial peroneal nerve - plantar flexion and eversion), gastrocneius-Soleus complex (tibial nerve - plantar flexion)
Muscular exam for S1
Achilles reflex
S1 reflex
Sensation of lateral malleolus and lateral/plantar surface of the foot
S1 dermatome
Principal nerve supply for bladder and bowel function
Neurological exam for S3, S4
Around the anus (S2 (outer), S3 (middle), S4/5 (inner))
Dermatome for S3, S4
Superficial anal reflex (external sphincter contracts in response to touch)
Reflex for S3, S4
upper motor neuron lesion
A positive babinski (great toe extends while others fan out) means what
presence of CNS disease
A positive Clonus (on releasing the foot, it beats over 5 times before resting) means what
Hamstring tightness (posterior thigh pain), Sciatic pain (extends all the way down - lower leg and dorsiflex)
Pain on a straight leg raise test (lift leg with knee in extension while supine) means what
heavy lifting (me), poor conditioning (also me), obesity, weak abdominal core
Risk factors for Low Back Pain
Increases with Age (35-55 y/o), often resolves in 4-6 weeks (few become chronic), very common reason for office visits
Epidemiology Stats for Low Back Pain

Midline vs. off midline, radiation, associated bladder or bowel dysfunctions
When working up low back pain what do we absolutely HAVE to find out in the hx?
musculoligamentous injury, disc herniation, vertebral fractures, discitis (RARE)
With midline back pain think
Sacroiliitis, trochanteric bursitis, hip arthritis
With off midline back pain think
Hx of cancer (spine is a common site for metastasis), unexplained weight loss, pain lasting more than 1 month or refractory, pain at night or increased by rest, hx of IV drug use, active or recent infection elsewhere (common site of osteomyelitis), immunosuppression
Red flags for Low back pain

lumbar sprain/strain, age related intervertebral disc or facet disease (arthritis), herniated disc, spondylolisthesis
Types of Mechanical lower back pain
NSAIDs, rest, PT, PO corticosteroids, IM steroid injection
45 y/o male presents to the clinic for low back pain that started after helping his friend move. He states that he was lifting and twisting to hand boxes over. Pain radiates into the buttocks and the back is stiff (decreased ROM due to pain). He also reports muscle spasms that worsen with activity. On physical you notice paraspinal muscle tenderness and loss of lumbar lordosis. What is your treatment plan since it’s giving mechanical and acute?
Lumbar 2 view (AP, lateral), flexion/extension views (assess stability or functional fusion)
What is the 1st line imaging for lower back pain (cheap, useful in trauma but not for neural structures)?
MRI (good for specifics)
If we’re thinking a nerve pathology associated back pain or there is a concern for infection/mass what we are ordering?
poor posture, muscular weakness/imbalance
An increased lordotic curve of the cervical spine is indicative of
indicative of muscular spasm/guarding, nerve root impingement
A decreased lordotic curve of the cervical spine is indicative of
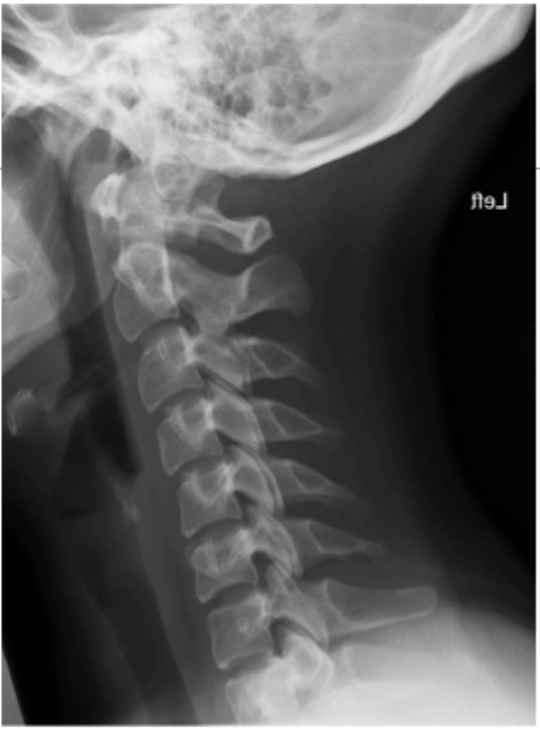
Head posture, bilateral comparable muscle mass, tone and contour of upper extremities
Inspection of the cervical spine looks for
C7 should be most prominent, tenderness of spinous process could be a result of whiplash, SCM, lymph node chain, carotid pulse, thyroid gland, parotid gland, trapezius muscle, greater occipital nerve
Palpation of the cervical spine looks for
unstable spine (trauma)
When are we NOT doing a ROM on the cervical spine?
above, below
Cervical nerves 1-7 exit _______ the cervical vertebrae while 8th exits ______ C7
Musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar
5 nerves of the brachial plexus
Deltoid (axillary - abduction), Bicep (Musculocutaneous - flexion)
Muscular testing of C5
sensory testing of the lateral arm (axillary) - on top of the bicep
C5 dermatome
bicep reflex
C5 reflex
Wrist extension (radial nerve - ERCB, ECRL, ECU), Bicep (musculocutaneous - flexion)
Muscular testing of C6
Sensory testing of the lateral forearm, thumb, and index fingers (musculocutaneous) - Wreck ‘em
C6 dermatome
brachioradialis reflex
C6 reflex
Triceps (radial - extension of the arm), Wrist flexion (FCR, FCU - median, ulnar), finger extension (EDC, EDI, EDM - radial)
Muscular testing of C7
sensory testing of the middle finger 🖕
Dermatome for C7
triceps reflex
C7 reflex
Finger flexors (FDS, FDP - median, ulnar), interossei (median, ulnar - finger abduction)
Muscular testing of C8
sensory of ring and little finger, medial forearm
C8 Dermatome
mechanical neck pain
Pain along the paraspinal muscles and ligaments with associated spasms, stiffness, and tightness of upper back and shoulders - usually lasts up to 6 weeks
poor posture, stress, poor sleep, poor head position when being alive
Possible causes of mechanical neck pain
Sudden hyperextension-hyperflexion (MVA, contact sports, blow to the head)
MOI for cervical sprain/strain (AKA whiplash)

C-collar immediately (until we r/o severe injury), X-rays AP/lateral, CT if really concerned for fracture
45 y/o female presents to the ER after being rear-ending on 410. She reports neck pain and stiffness as well as dizziness. What is your gameplan rn?
NSAIDs, Muscle relaxants (maybe), PT
45 y/o female presents to the ER after being rear-ending on 410. She reports neck pain and stiffness as well as dizziness. Imaging is negative, so we’re thinking it’s just whiplash. What is your treatment plan
spinal cord compression, spinal cord shock, neurogenic shock
Common cervical trauma injuries due to cervical fracture or dislocation
herniated disc, hemorrhage, contusion
Common cervical trauma injuries due to cervical nerve root injury
ABCs (avoid head-tilt chin lift), apply C-collar if complaining of neck pain, evaluate GCS, complete neuro, rectal exam, X-rays (lateral is standard for trauma), CT or MRI (for any neuro deficit)
Eval for cervical trauma
Sober and coherent patient
C-spine can only be cleared on a
Xray ( 🏆 may show spondylosis), MRI (cervical nerve compression), EMG/NCV (tests nerve root function) → refer to specialist
55 y/o male presents to the clinic for sharp, burning neck pain that radiates down both arms. ROM of the neck is decreased due to pain. On physical exam you note decreased muscle strength and sensation along the C7 and 8 dermatomes. What imaging you want?
compression of Cervical spinal nerve from arthritis or herniated disc
Causes of cervical radiculopathy (root commpression)
Distraction test (symptoms are relieved by passive traction force), Cervical compression (axial traction increases symptoms), Spurling’s (positive in symptoms intensify when head is rotated with axial downward pressure)
Special tests for for cervical neck radiculopathy
cervical CORD compression
Cervical myelopathy is from
Large disc herniation (or anything that compress the spinal cord)
45 y/o female presents to the ED for neck pain. She notes that her arms and legs “feel tingly” and bladder/bowel dysfunction. On physical exam you note an unsteady gait, balance issues, reflexes are 4+ bilaterally. Flexion of the neck worsens her symptoms. What is typically the cause of this presentation?
Hoffman’s (Index and thumb flex when the middle finger’s nail is flicked), Wrist clonus
Pathological reflexes of the Cervical spine → GET AN MRI
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Compression of the subclavian artery and/or brachial plexus between the clavicle and 1st rib OR tightened anterior and middle scalene muscles - presentation includes complex neuro and vascular symptoms
typically affect the radial side of the forearm and hand, muscle fatigue, ischemic pain, discoloration, paresthesia
Vascular Symptoms of Thoracic outlet syndrome
Weakness, numbness, muscle wasting, paresthesias
Neurogenic Symptoms of Thoracic outlet syndrome
Palpate the radial pulse with the patient’s head turned toward that same side, abduct and externally rotate the arm and have the patient take a deep breath (positive if diminished but compare to the other side)
Describe Adson’s test for Thoracic outlet syndrome
EMG/NCV, CT angio, MRI, arteriography → call neuro and vascular (diagnosis of exclusion)
Workup for Thoracic outlet syndrome
PT (scapular and shoulder muscular stabilization exercises, posture, ergonomics educations), weight loss, NSAIDs, Surgery for refractory symptoms
Management for thoracic outlet syndrome
Torticollis (wry neck)
Painfully twisted and tilted neck can be congenital or acquired (resolves in several days or a couple of weeks)
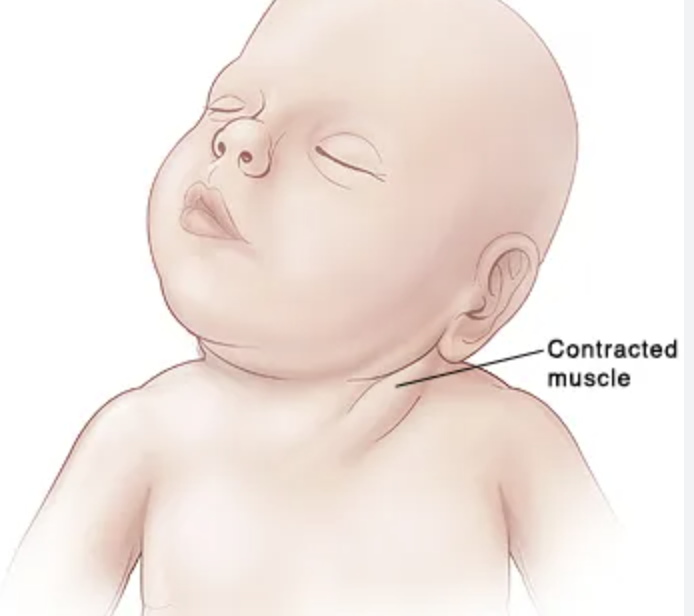
While in the womb, baby’s neck is in the wrong position, injury to head or neck that causes swelling, cervical dystonia
Causes of Torticollis
Often self-limiting, PT, stretching exercises/massage, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, Botox for chronic spasms
Treatment for Torticollis