Biology HL - B4.1 - adaptations to the environment
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
habitat
place where a community, species, population or organism can survive and reproduce
adaptations of maram grass
high resistance
fine, narrow leaves resisting strong winds and sandblasting
thick outer layer of waxy cuticle resists water loss
rolled leaves reduce SA for evaporation, conserving water
hairs inn the inner leaf epidermis reduce evaporation and air flow over the stomata to tolerate dessication
sunken stomata and rolled leaves decrease the humidity gradient and reduce water loss
extensive root systel allows for coping with moving sand and low nitrate in top soil
maram grass in embryo dunes
few odd plants
maram grass primary dune
larger tufts
little water
more biomatter
maram grass in mature dunes
less; more competition
range of tolerance and zones of stress
zones of stress; end of zone of tolerance
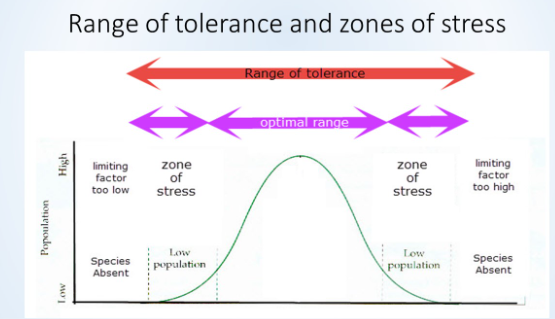
range of tolerance
range of environmental conditions in which a species can survive
limiting factors
a factor that can restrict the growth, distribution or abundance of a species
mangroves ideal conditions
brackish water: not salty nor fresh
constant flooding
little light
mangroves/ Rhizophora apiculata adaptation
stilt roots; gives structural integrity
halophyte; can survive in salty water
specialised roots; pneumatocytes; they respire even in waterlogged soil
seeds start to germinate while still attached to parent plant
what are coral reefs
slow growing plants which live in symbiosis with algae
produce a calcified skeleton out of their polyps
coral reef conditions
warm water (23-28)
sunlight for zooxanthellae
salt water; won’t growth at mouth of rivers
clear water; so no farming/freshwater treatment. no sediment
moderate wave action; not too strong
need inundation
alkaline water
types of adaptation
genetic changes/ natural selection
behavioral changes and physiological responses
factors ( in general ) which affect marine ecosystems
temperature
water depth
salinity
Biome definition
large community of fauna and flora in a large geographical location with distinct biotic and abiotic factors and adaptations for them
main predictive factors of what biome one will be
temperature
rainfall
why do members in the same biome share features
convergent evolution;
they all adapt to the same environment and are therefore bound to have similar adaptations
characteristics of tropical rainforests
high precipitation ( 1500-2000mm )
high temperatures
low sunlight
low seasonal variation
characteristics of grasslands
low to moderate temperature ( 10-25 C° )
low to moderate precipitation (250-1000m)
high light intensity
high seasonal variation
characteristics of taiga biome
low temperatures ( -20 - 10 C° )
moderate rainfall
high seasonal variability
temperate biome
moderate temp ( 20C°)
moderate to high rainfall ( 500-1500mm )
moderate light intensity
moderate seasonal variation
tundra biome
low temperatures ( -30 - 10 )
low rainfall
moderate to high light intensity
high seasonal variability
desert biome
high temperature
low precipitation
high light intensity
low seasonal variation
plant adapted to desert
ocotillo
deep root system which allows access to water deeper down, and extensive shallow root system to absorb as much water as possible during rainfall
chlorophill containing bark allows it to perform photosynthesis
no leaves as water would be lost by evapotranspiration
thorny stems expand to store water during rainfall and deter herbivores
small leaves sprout after rainfall to perform photosynthesis
bright red flowers to attract pollinators
animal adapted to desert
gila monster
fat storage in tail
bumpy scales on skin allows to retain moisture
slow metabolic rate allows to go long time without water
venomous saliva; for predators and prey
plant adapted for rainforest
giant water lilly
giant waxy leaves with 3M of diamater; wax is hydrophobic, allows to float
large flower with strong fragrance attracts pollinators
root system which allows to anchor to soil of lake and absorb nutrients
animals adapted for rainforest
orchid mantis
female looks like orchid, which attracts pollinators
example of mimicry
male is small and plain, allowing it to camouflage in the trees
chemoautotrophs
oxidation of non-organic molecules, in unhospital conditions, eg sewers, geothermal vents