igcse cie chemistry
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
solids
1. particles vibrate at a fixed position
2. little kinetic energy
3. strong forces between particles
liquids
1. particles are more spaced apart
2. intermediate forces between particles
3. higher vibration
4. do not have fixed positions
gases
1. particles are much further apart
2. large amounts of kinetic energy
3. not held in fixed positions
4. very weak forces between particles
melting
solid to liquid
boiling
liquid to gas
evapouration
surface liquid to gas

freezing
liquid to solid

condensation
gas to liquid

gas compression
the pressure within the container will increase
brownian motion
random particle movement in suspension
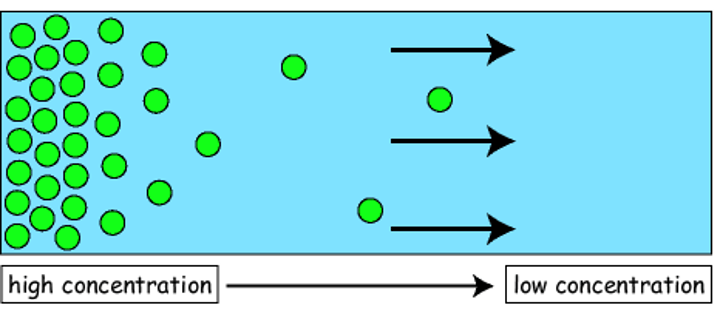
diffusion
the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration down a concentration gradient as a result of random movement
- no energy is required for this process
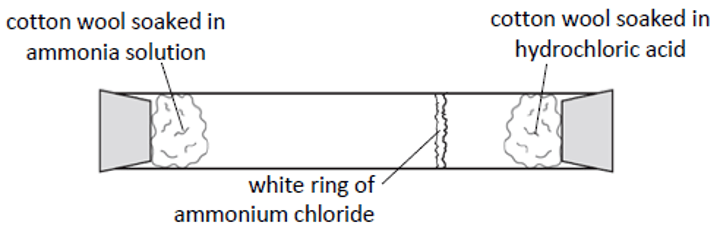
ammonia and hydrochloric acid diffusion
1. place substances in opposite ends of the glass tube
2. a white ring of ammonium chloride will form where the ammonia and hydrochloric acid meet
3. the location of the white ring determines the rate of diffusion; middle of the tube means the substances diffused equally
4. usually forms closer to the hydrochloric acid because ammonia has a smaller atomic mass and diffuses quicker
apparatus
gauze, evaporating basin, tripod, beaker, conical flask, filter funnel, filer paper, measuring cylinders, scales, thermometer, stopwatch, pipettes (titration), burette
solute
solid which dissolves in a solvent
solvent
liquid in which the solute dissolves
solution
mixture of solute and solvent
saturated solution
cannot dissolve any more solute into the solvent (at its maximum capacity
filtration
insoluble solute from a solvent (e.g. sand and water)
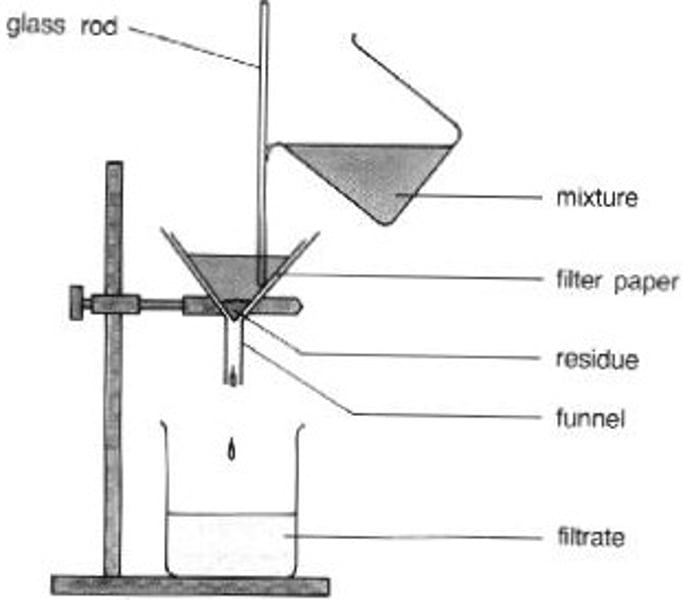
evaporation
soluble solvent from a solvent (e.g. salt water)
simple distilation
separate liquids at different boiling points
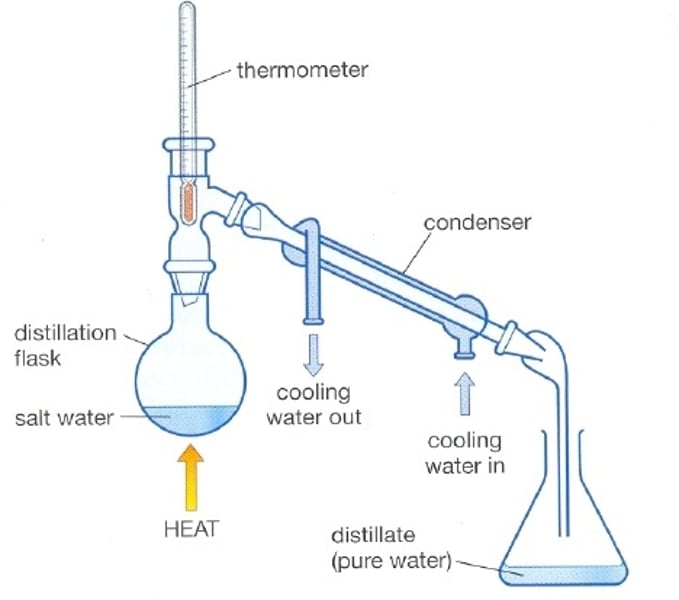
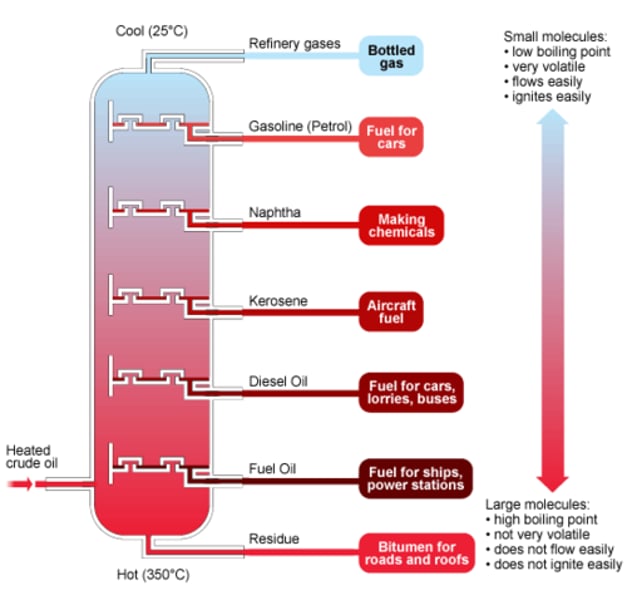
fractional disillation
separates many liquids at different boiling points
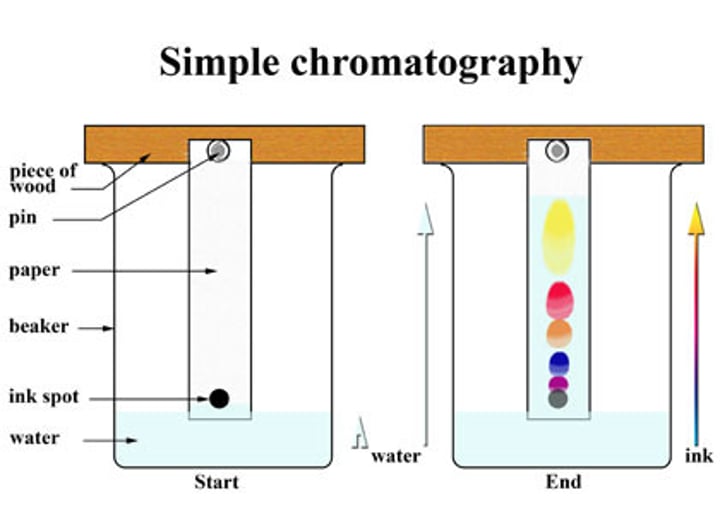
chromotography
separation of inks and dyes; ink that travels furthest is the most soluble
Rf formula
distance travelled by component / distance travelled by solvent
importance of purity
- drug safety
- prevention of contamination
- needed for food
What is the main ore of aluminium?
Bauxite
What are the steps involved in a blast furnace?
Burning of carbon (coke), reduction of carbon dioxide, reduction of iron(III) oxide, thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate, formation of slag
the blast furnace equations
1. C + O2 --> 2CO2
2. C + CO2 --> 2CO
3. 3CO + Fe2O3 --> 2Fe + 3CO2
4. CaCO3 --> CaO + CO2
5. CaO + SiO2 --> CaSiO3
What are the symbol equations for extracting iron from hematite?
(a) C + O2 → CO2, (b) C + CO2 → 2CO, (c) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2, (d) CaCO3 → CaO + CO2, (e) CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
electrolysis
decomposition of an ionic compound, when molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of an electric current
atoms
smallest particle of an element that can exist
element
substance made up of only one type of atom and cannot be separated by any chemical means
compounds
are substances made up of two or more different types of atom chemically joined together. These atoms cannot be separated by physical means.
mixture
two elements not chemically combined

pure substance
contains only one type of material; they have a fixed boiling point

molecule
two or more atoms bonded together
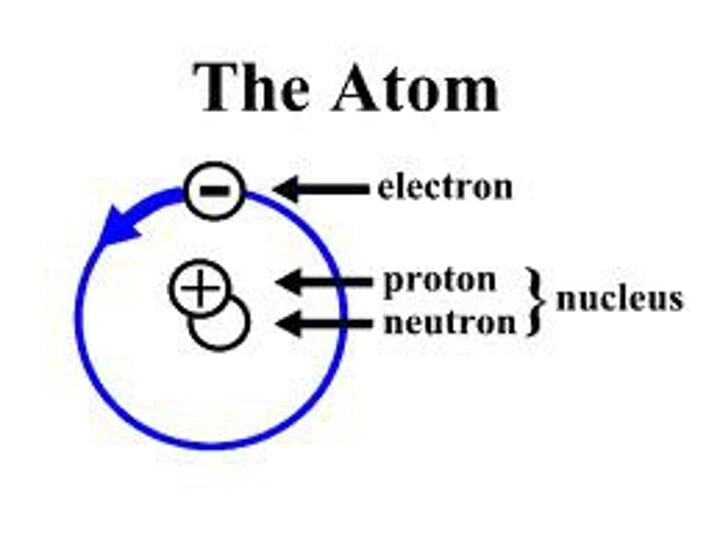
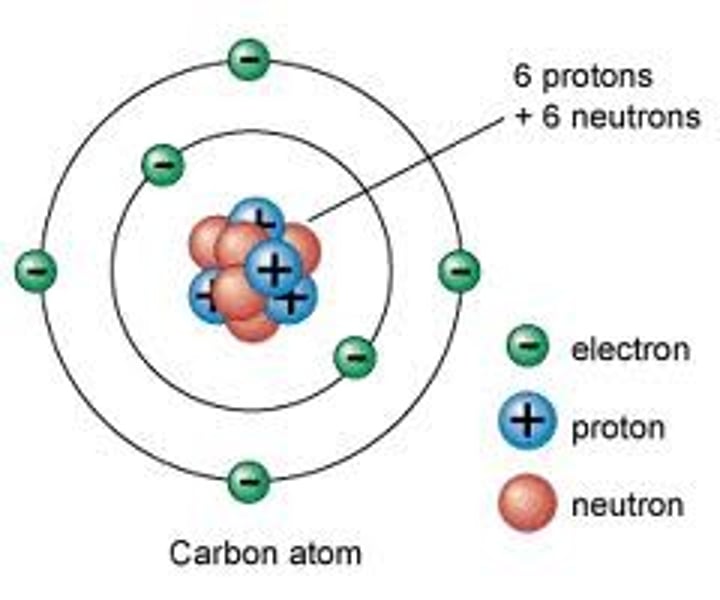
nucleus
contains protons and neutrons
mass of protons
1
mass of neutrons
1
mass of electrons
1/2000
relative charge of neutrons
0
relative charge of protons
+1
relative charge of electrons
-1
atomic number
number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom
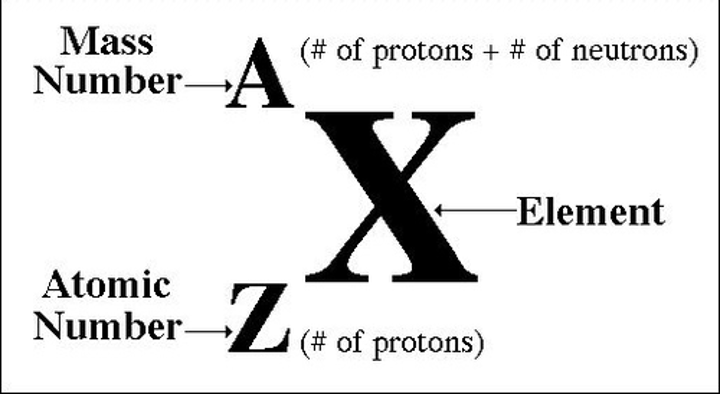
mass number
total number of protons and neutrons
nucleon number
total number of protons and neutrons (i.e. the mass number)
isotopes
atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons but the same number of protons
group numbers
corresponds to the number of electrons in outer shell
period number
corresponds to the number of shells
properties of the elements in the same group
they have the same properties due to the number of electrons in their outer shell
the noble gases
they are unreactive because they have a full number of electrons in their outer shells; will not bond
metals
1. high melting + boiling point
2. shiny and sonorous
3. good conductors of heat and electricity
4. malleable and ductile
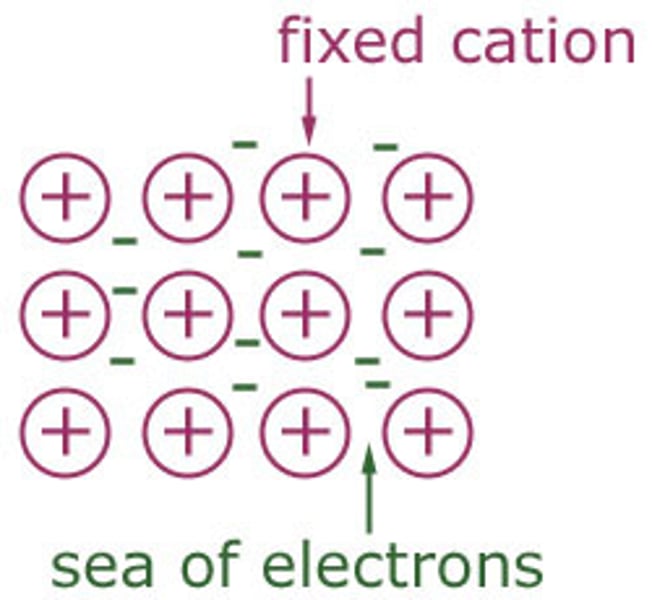
metal bonding
metals are made up of closely packed cations that are surrounded by a mobile sea of valence electrons
non-metals
1. low boiling + melting points
2. dull and brittle
3.poor electrical and thermal conductivity
non-metal bonding
the tend to gain electrons to become negative ions. forms acidic oxides and take part in covalent + ionic bonding
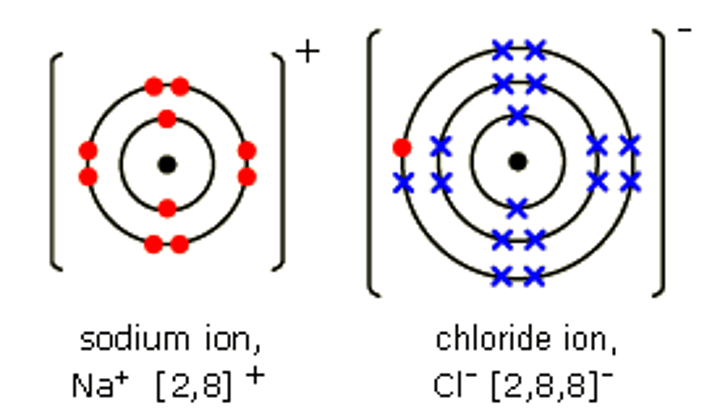
ion
charged particle formed from gaining or losing electron
ionic bonding
metal and non-metal elements bonding
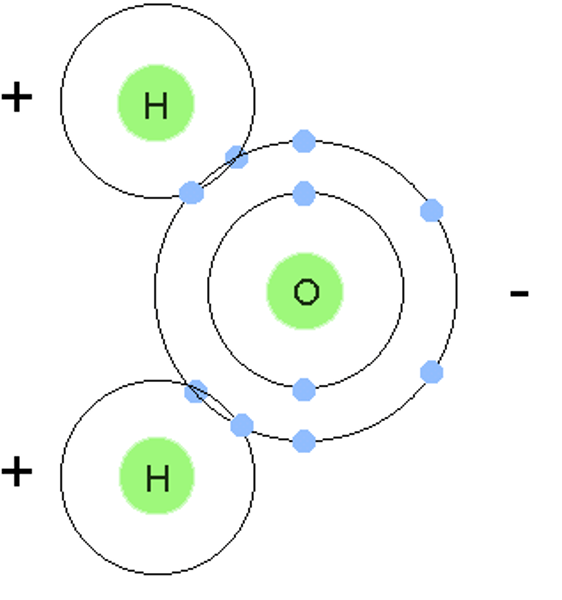
covalent bonding
non-metal and non-metal elements bonding
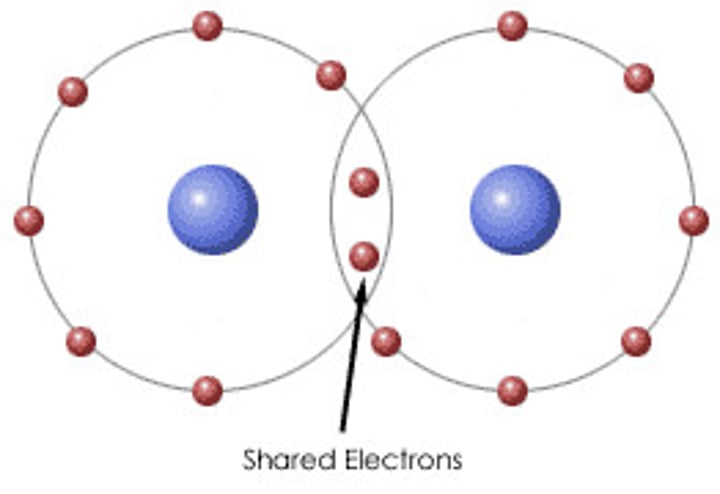
giant covalent structures
diamonds and graphite
allotrope
different forms of the same element
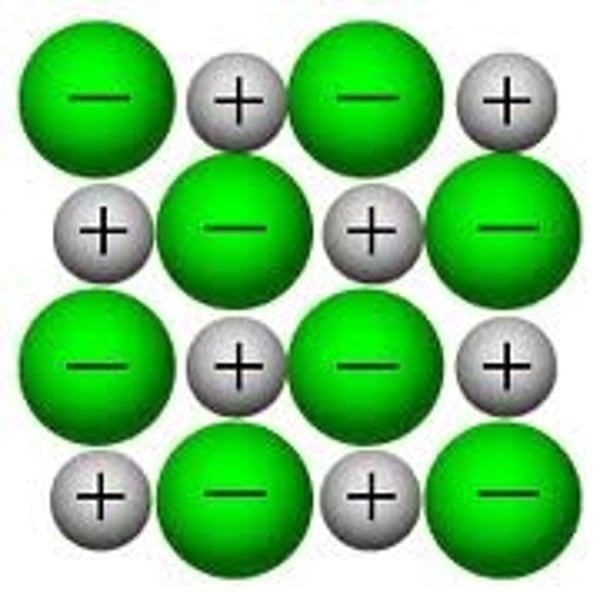
ionic bonds
the electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions (metals +ve and non-metals -ve)
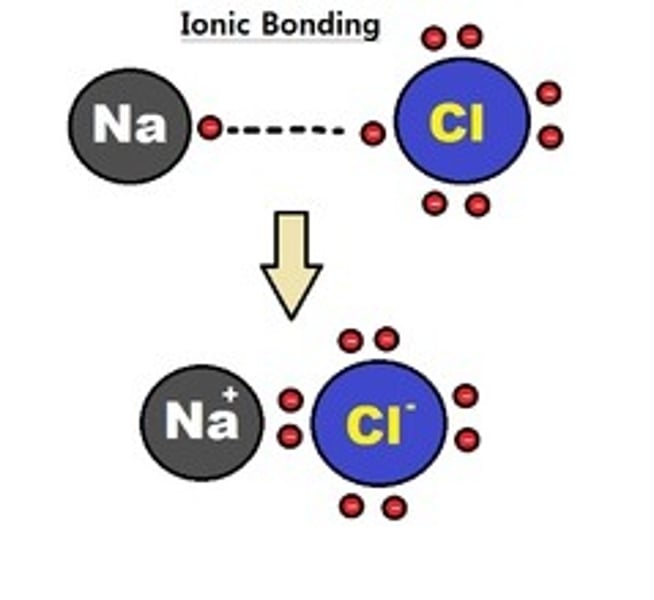
electricity and giant ionic structures
they do not conduct electrons when solid because ions are not free to move; however they do conduct electricity when molten or aqueous because ions are free to move
metallic bonding
electrostatic attraction between positive ions and the sea of delocalised electrons
how much (any) gas is occupied per 1 mol
24dm^3
diamond
1. high melting point
- tetrahedral structure
- C atom is bonded to 4 others
- many strong covalent bonds
- requires a lot of energy to break
2. does not conduct electricity because electrons are not free to move
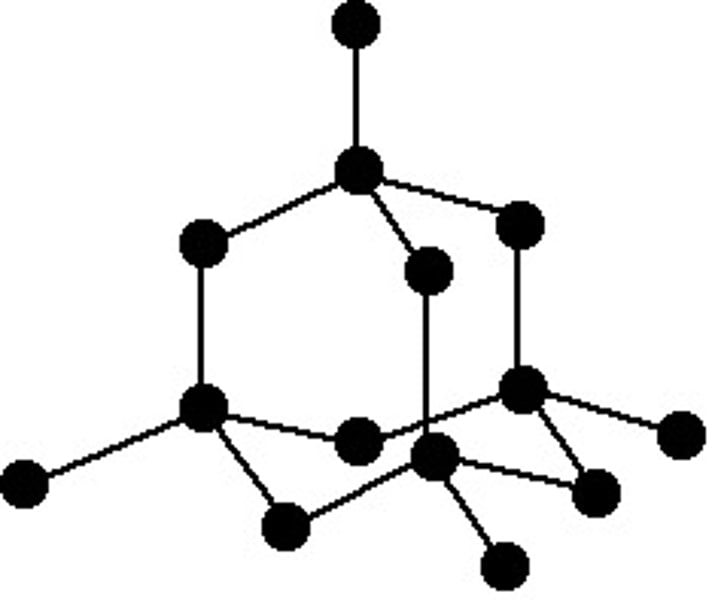
graphite
1. high melting point:
- C atom is bonded to 3 others; however this makes graphite's melting point slightly lower than diamonds
- many strong covalent bonds
- requires a lot of energy to break
2. conducts electricity because the charge is carried on the delocalised electron (C atom bonded to 3 others)
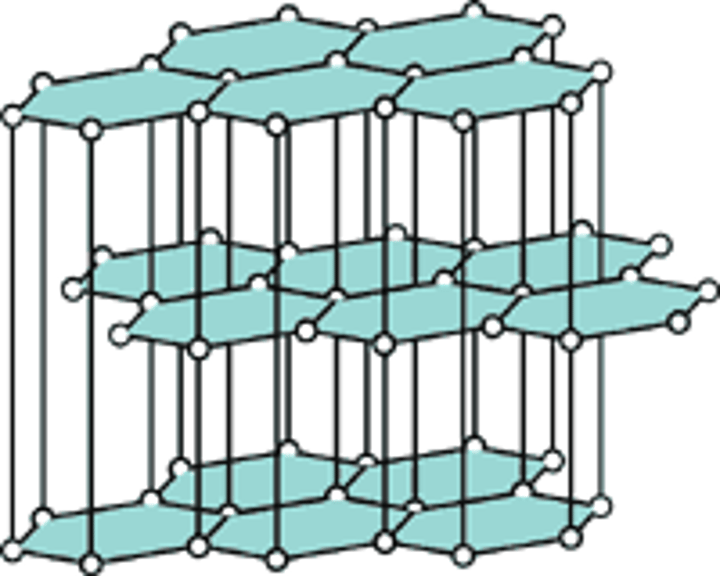
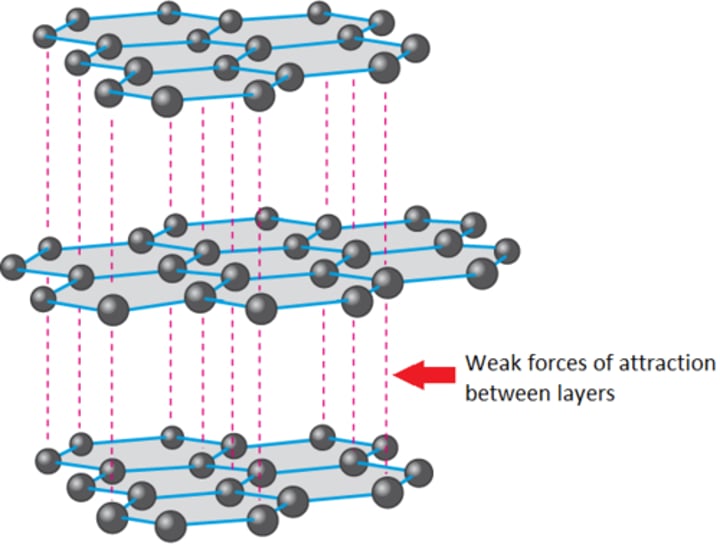
graphite as a lubricant
the structure of graphite has many layers of C atoms which breaks easily due to the weak intermolecular forces between them; the layers slide off each other when broken. this also requires little energy to break.
Ammonium
NH4+
Silver
Ag+
Copper
Cu2+
Lead
Pb2+
Zinc
Zn2+
anode in dilute aqueous solution
4OH- to 2O2 + 2H20 + 4e-
cathode
attracted to least reactive positive ion (e.g. H+)
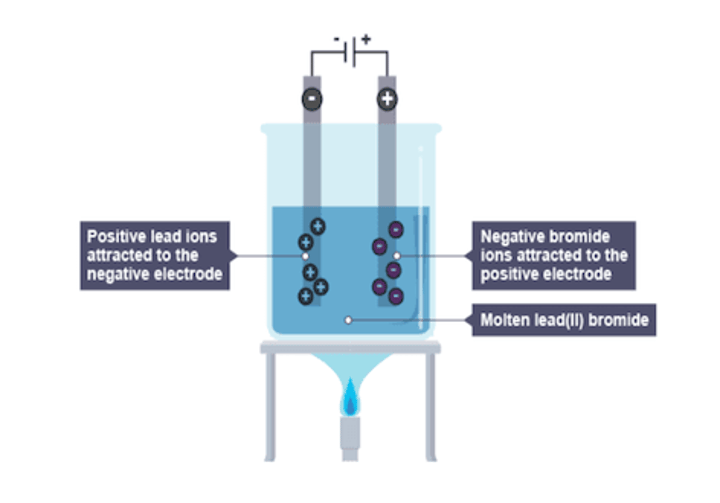
electrolysis in lead (II) bromide
compounds present: Pb2+, Br-
1. anode (+)
attracts: Br-
observations: lead drips in molten state
2. at the cathode (-)
attracts: Pb2+
observations: bromine gas is produced
electrolysis in concentrated aqueous sodium chloride
ions present: Na+, Cl-, H+. OH-
1. anode (+)
attracts: Cl- least reactive negative halogen ion
2. cathode (-)
attracts: H+ least reactive positive ion
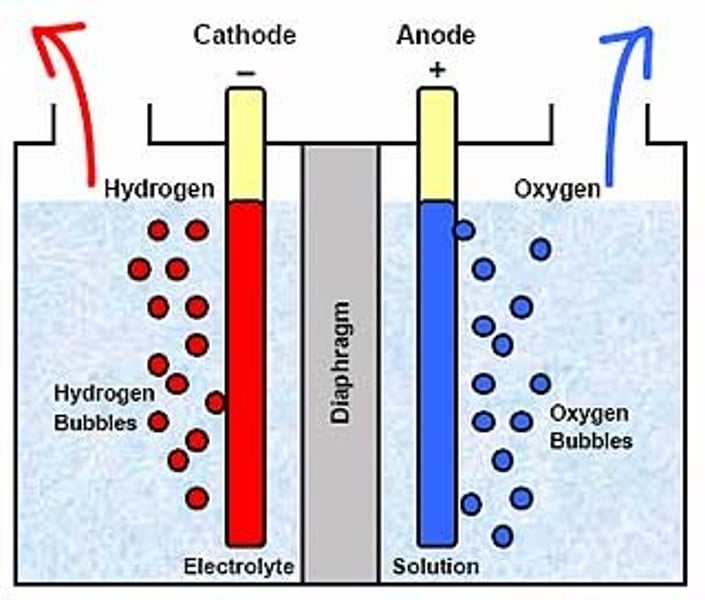
electrolysis in aqueous sulphuric acid
ions present: SO4^2-, OH-, H+
1. anode (+)
attracts: OH-
observations: colourless gas is given off; tested by relighting a glowing splint over oxygen
2. cathode (-)
attracts: H+ least reactive positive ion
observations: colourless gas is given off; tested by inserting lighted splint into test-tube containing hydrogen, a squeaky 'pop' sound is produced
conclusion for the electrolysis in aqueous sulphuric acid
anode: hydroxide ions move to the positive anode. every four hydroxide ions discharged produces an oxygen molecule
cathode: hydrogen ions move to the negative cathode and receive electrons to form hydrogen atoms. two hydrogen atoms combine to make a hydrogen molecule
electroplating
1. the metal coating of the object is the anode (+)
2. the object that is being coated is the cathode (-)
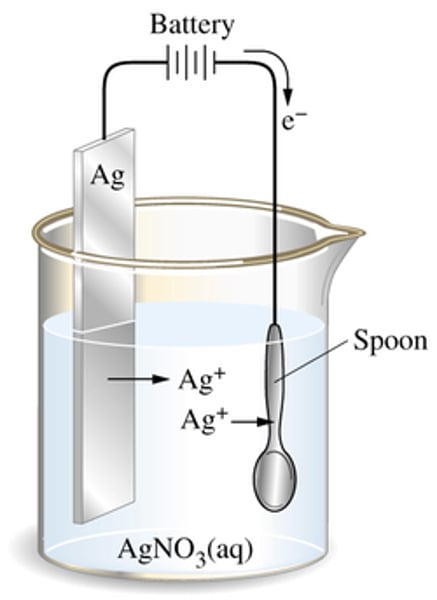
electrolyte
the solution of a soluble compound of the metal
uses of electroplating
- jewellery; usually copper coated with silver; silver is very expensive and rare
- steel bumpers on cars; chromium; very hard and shiny, however it's very expensive
- tin cans; steel coated with tin; tin is corrosive resistant
oxidation
the loss of electrons
reduction
the gain of electrons
redox
when the loss AND gain of electrons occur
reducing agent
causes other substances to be reduced however, reducing agents themselves are oxidised
oxidising agent
causes other substances to be oxidised however, oxidising agents themselves are reduced
rate of reaction: ^ in temp.
1. higher rate of reaction
2. increase in kinetic energy in particles
> leads to an increased frequency in particle collision
> this means an increase in successful particle collision
rate of reaction: ^conc.
1. more particles are present
2. more frequent particle collision
3. more successful particle collison
rate of reaction: ^s.a.
1. more area means more particles to collide
2. more successful particle collision
soluble
Sodium salts
Potassium salts
Ammonium (NH4+) salts
All nitrate salts
Most chlorides (not silver or lead)
Most sulphates (not barium, calcium or lead)
insoluble
Most carbonates (not Na+, K+ and NH4+)
Most hydroxides (not Na+, K+, NH4+, Ca2+(partially))
crystallisation
1. reacts (metal... and acid)
2. filter; gets rid of any undissolved solids
3. evap.; gets rid of excess water
4. cool; collect crystals formed
5. dry; leave crystals in warm place/on filter paper
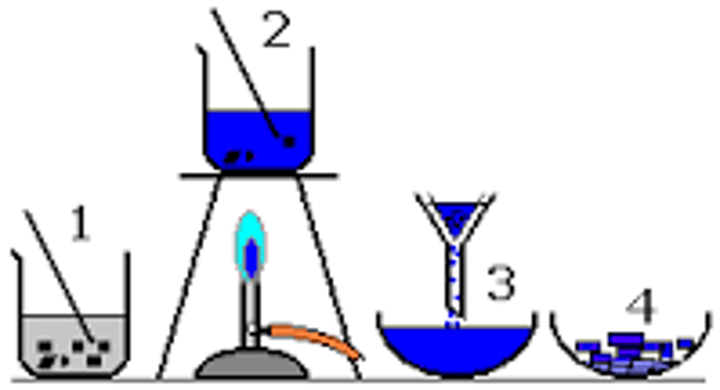
making insoluble salts
1. react (two soluble salts)
2. filter; gets rids of insoluble solids
3. wash; gets rids of insoluble solids
4. dry; leave ppt. in warm place/on filter paper
test for ammonium
sodium hydroxide:
- ammonia produced on warming
ammonia:
- none
test for copper
sodium hydroxide:
- blue ppt.
- insoluble in excess
ammonia
- blue ppt.
- soluble in excess: dark blue sol.
calcium
sodium hydroxide:
- white ppt.
- insoluble in excess
ammonia:
- no/very slight white ppt.
iron (ii)
sodium hydroxide:
- green ppt.
- insoluble in excess
ammonia:
- green ppt.
- insoluble in excess
iron (iii)
sodium hydroxide:
- red-brown ppt.
- insoluble in excess
ammonia:
- red-brown ppt.
- insoluble in excess
zinc
sodium hydroxide:
- white ppt.
- soluble in excess - colourless solution
ammonia:
- white ppt.
- soluble in excess - colourless solution
carbonate
1. dilute nitric acid
effervescence, co2 produced
chloride
1. dilute nitric acid
2. aqueous silver nitrate
white ppt.