H&I IV: Lifespan: Exam 2: Child abuse
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
4 main categories of child abuse
-physical abuse
-emotional abuse
-sexual abuse
-neglect
what is mandatory reporting
reasonable causes to suspect a child has been abused or neglected, we are required by law to report that suspicion
components of mandatory reporting
-Anyone can report but certain professionals are required by law to report concerns of abuse or neglect
-Reporters are protected from discharge for reporting child abuse.
-Reports must be made to law enforcement or either the child welfare agency or child protective services agency.
do children routinely make up false allegations of abuse
NO
what are sentinel injuries
potentially pre-cursors to further or worse abuse
what are the 6B's framework of sentinel injuries
Bruises
Breaks
Bonks
Burns
Bites
Baby blues
what is the most common abusive injury
bruise
abusive bruises characteristics
-in an unusual/protected area
-patterned bruises
-too many bruises
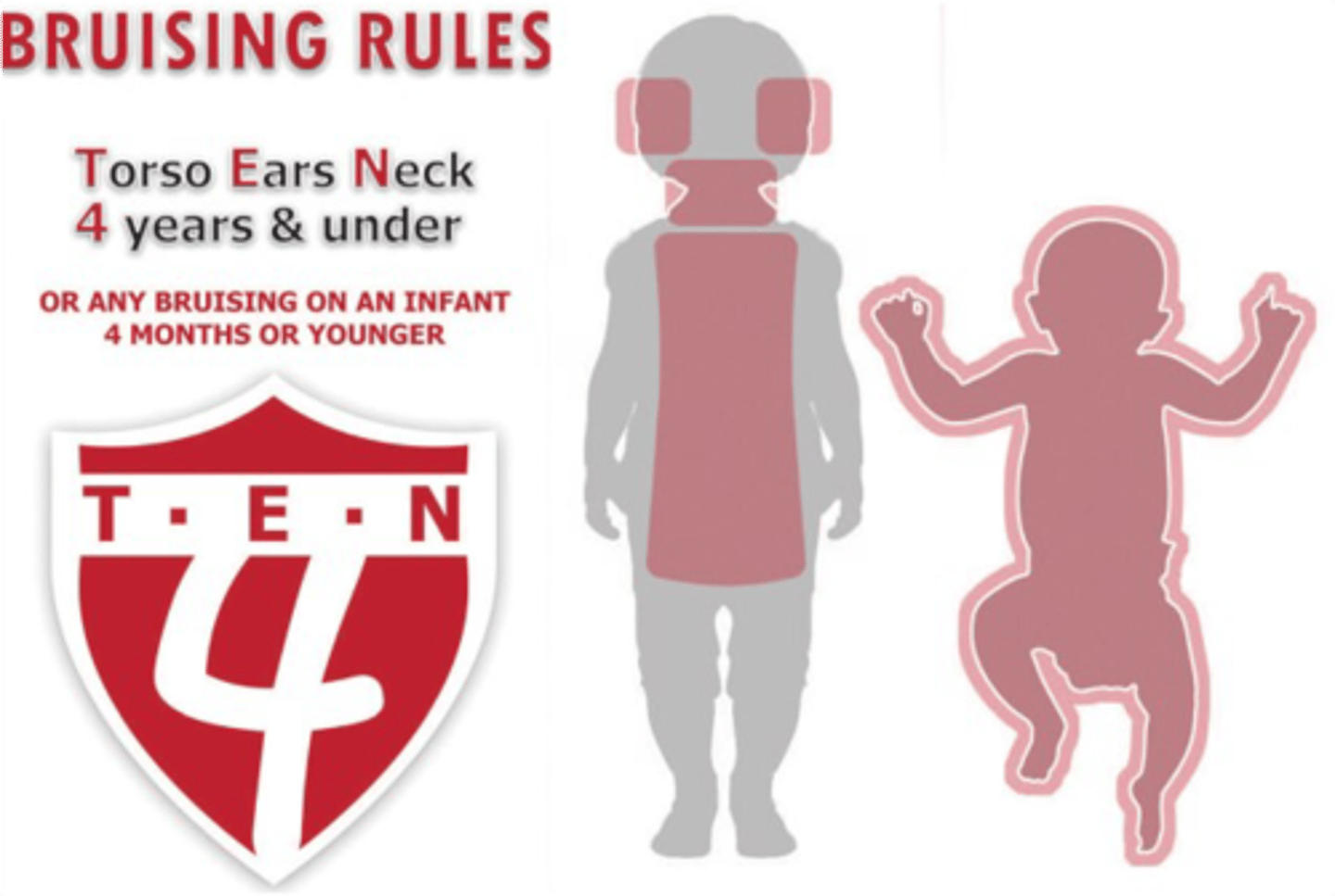
what is TEN-4 FACES bruising rule
Any bruise found in any of the following locations should trigger the possibility of pediatric physical abuse:
Torso
Ears
Neck
Any bruise in a child younger than 4 months old
-FACES
Frenulum
Angle of Jaw
Cheek
Eyelid
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
bruising rules diagram
breaks in abuse
1.Any fracture in a non-ambulatory infant or child
2.Femur fracture in an infant < 12-18 months of age
3.Humerus fractures in an infant < 18 months of age
4.Multiple fractures and/or an unexpected healing fracture
5.Skull fractures
6.Classic metaphyseal fractures (from being shaken violently back and forth)
1.Growing plates at each end of long bones)
7.Rib fractures (highest probability for abuse)
Bonks in child abuse
Subdural hematomas and retinal hemorrhages
-With or without additional injuries = Abusive Head Trauma (AHT)
what is AHT
constellation of brain injuries caused by the directed application of force to an infant or young child resulting in the physical injury to the head and/or its contents
-Signs of AHT can be subtle and non-specific.
-Skull fractures
-Additional injuries can include spinal, skin and skeletal injuries
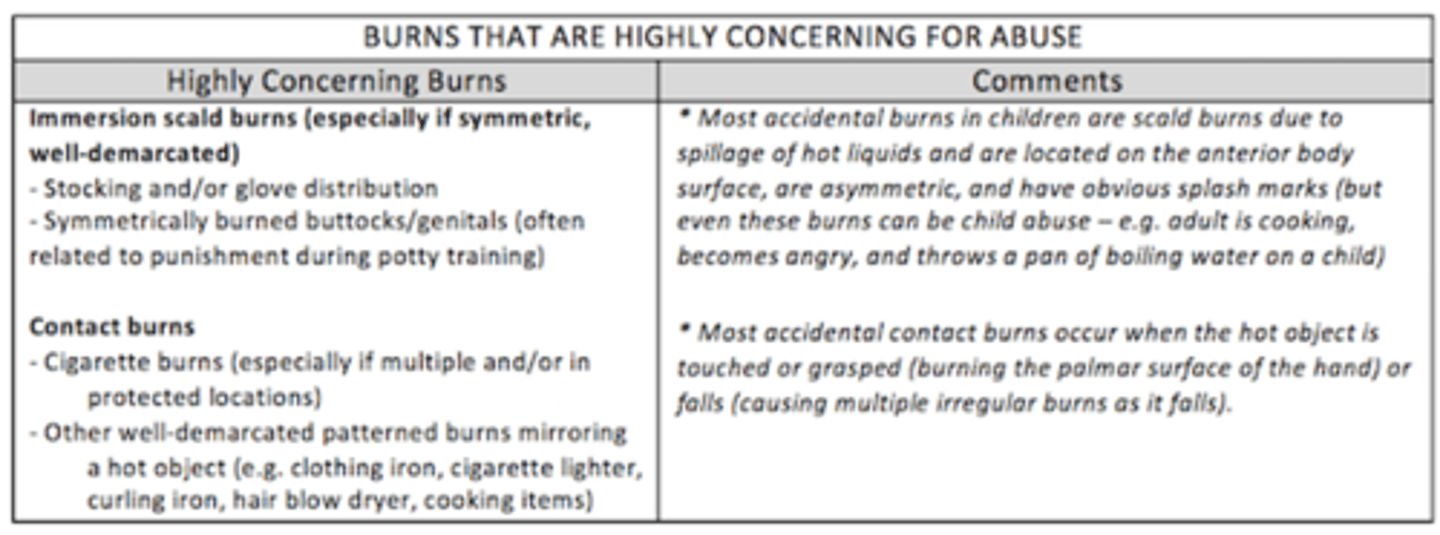
burns in abuse diagram
bites in abuse
human bites have typical, stereotyped pattern
baby blues (irritability) in abuse
Some severe injuries can present with very non-specific symptoms.
-Why it is so important to fully examine all concerning patients.
United nations human trafficking definition
“The recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring or receipt of persons, by means of the threat or use of force or other forms of coercion, of abduction, of fraud, of deception, of the abuse of power or of a position of vulnerability or of the giving or receiving of payments or benefits to achieve the consent of a person having control over another person, for the purpose of exploitation.”
LGBTQ considerations
Research shows that LGBTQQ people face barriers to seeking help that are unique to their sexual orientation and gender identity
barriers to LGBTQ seeking abuse help
-Legal definitions of domestic violence that exclude same-sex couples
-Dangers of "outing" oneself when seeking help and the risk of rejection and isolation from family, friends, and society
-The lack of, or survivors not knowing about, LGBT-specific or LGBT-friendly assistance resources
-Potential homophobia from staff of service providers
-Low levels of confidence in the sensitivity and effectiveness of law enforcement officials and courts for LGBT people
teen dating/intimate partner violence considerations
-The type of intimate partner violence that occurs between two young people who are, or who were once in, an intimate relationship.
-Can be any one or a combination, of the following:
Physical: pinching, hitting, shoving, or kicking.
Emotional: threatening a partner or harming his or her sense of self-worth.
name calling, controlling/jealous behaviors, consistent monitoring, shaming, bullying (online, texting, and in person), intentionally embarrassing him/her, keeping him/her away from friends and family.
Sexual: forcing a partner to engage in a sex act when he or she does not or cannot consent.
*** Important to screen during healthcare visits ***
national coalition against domestic violence statistics
-Nearly 21% of female high school students and 13% of male high school students report being physically or sexually abused by a dating partner
-Nearly 1.5 million high school students in the United States are physically abused by dating partners every year.
-Girls & young women aged 16 to 24 experience intimate partner violence at the highest rate of any age group, almost three times the national average.
munchausen by proxy syndrome (MBPS) considerations
-Illness that is fabricated or induced by another person
-Caretaker often with history of own abuse or neglectful childhood
-Caretaker often has healthcare background
-Characteristically, the caretaker thrives in the healthcare environment
10% are fatal
MBPS red flags
-Unexpected or prolonged recurrent or extreme rare illness
-Discrepancies between clinical findings and history
-Illness unresponsive to treatment
-Symptoms occurring only in the parent's presence
-Parent extremely knowledgeable about illness, procedures, and treatments
-Parent interested in interacting with the health team members
-Parent is overly attentive toward the child
-Family members with similar symptoms
MBPS nursing considerations
-Child's safety is the ultimate concern
-Coordinated evaluation by a collaborative team
-Maintain a trusting relationship with the parent or guardian
-Careful documentation
-Close monitoring
-If hospitalized - Covert video surveillance may be considered
documentation for child abuse
-remain objective
-use quotation marks to document using parent/childs words
safe haven law
Under Wisconsin law, a parent can leave their unharmed newborn child under 72 hours old with a:
-police officer
-911 emergency medical staff person
-hospital staff member
without fear of legal consequences
shaken baby syndrome (SBS) considerations
-Constellation of signs and symptoms resulting from violent shaking or shaking and impacting of the head of an infant or small child.
-The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) describes SBS as a subset of AHT with injuries having the potential to result in death or permanent neurologic disability.
-#1 trigger for SBS is frustration with a baby's crying (Think back to colic)
-SBS/AHT is the leading cause of physical abuse in the US
-Approximately 80% of SBS/AHT victims suffer life-long disabilities
-Approximately 25% of SBS/AHT victims die
why is SBS so dangerous
Violent shaking for just a few seconds has the potential to cause severe injuries. While shaking may cause injury to children of any age, children are most susceptible to being injured during their first year of life.
Factors that contribute to a baby's vulnerability include:
•Babies heads are heavy and large in proportion to their body size.
•Babies have weak neck muscles.
•Babies have fragile, undeveloped brains.
•There is a large size and strength difference between the victim and the perpetrator.
what is period of purple crying
-In 2006, Wisconsin passed legislation requiring hospitals, birthing centers, home visiting programs, child care providers, schools and all providers of prenatal, postpartum and young child care coordination services: to have educational materials about shaken baby syndrome/abusive head trauma available to parents.
-Starting in 2016, the Child Abuse and Neglect Prevention Board started a grant program to fund the implementation of Period of PURPLE Crying program in hospitals and birthing centers.