Lecture 14: Asymmetric Information 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is signalling?

How can sellers of high quality try to send a signal about the quality of their product?
By offering warranties
What is the problem with offering warranties?
Such signals will be useless if sellers of bad or low quality have the incentive to offer the same kind of warranties and mimic the sellers of good quality
What are the two types of workers?


b

1-b
How many goods are produced using what and by who?

What is the constant marginal production function for the good produced?

What assumption do we make about the labour market?
If each worker’s ability is observable, what is the wage rate for each worker? How do we denote it for each type of worker?
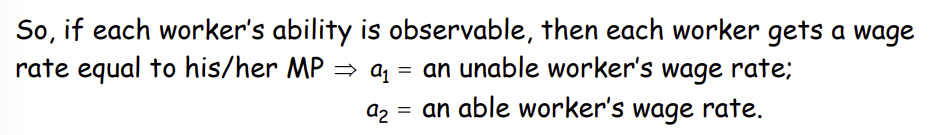
Therefore, will the equilibrium outcome be efficient?
Yes
Now, suppose each worker’s ability is unobservable but the fraction b is known to the firms. When a firm employs a worker, it expects him/her to be able/unable with a probability of what?
Able with a probability of b and unable with a probability of 1-b
Therefore, what is the expected MP of a worker to a firm?
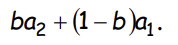
So, as firms will pay each worker the expected MP, each worker gets the wage rate of what? And what is it equivalent to?
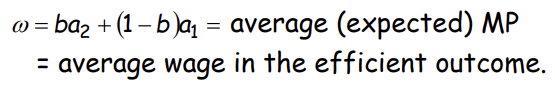
Thus, if everyone is willing to accept the average wage, then what do we see?

Suppose workers can signal their ability by acquiring education. When an unable worker acquires e1 ≥ 0 level of education, the cost he/she incurs is what?
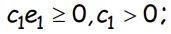
Suppose workers can signal their ability by acquiring education. When an able worker acquires e2 ≥ 0 level of education, the cost he/she incurs is what?
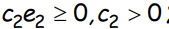
What can each worker do regarding their level of education?
Each worker chooses his/her own level of education
Who decides how to relate wage rates to education levels?
What assumption do we make about education and the ability of a worker?


What does this mean regarding a worker’s MP?


What is Case 1?
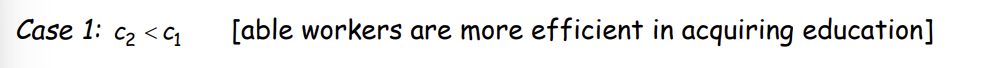
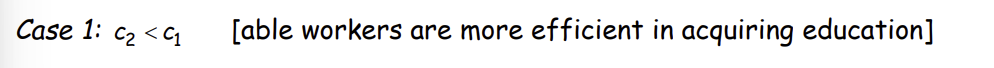
What does this imply?
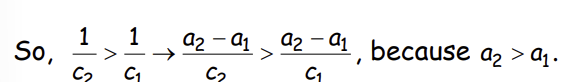
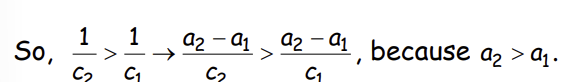
How do we include a level of education between the two outcomes?
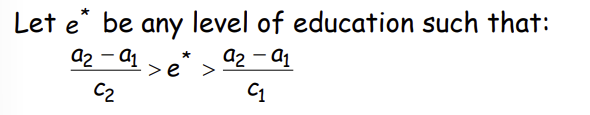

How will this affect the wage choice and behaviour of the firm?


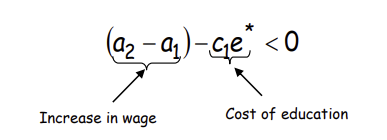
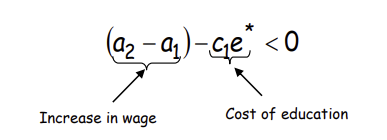
Why is this the case?
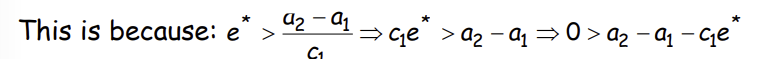
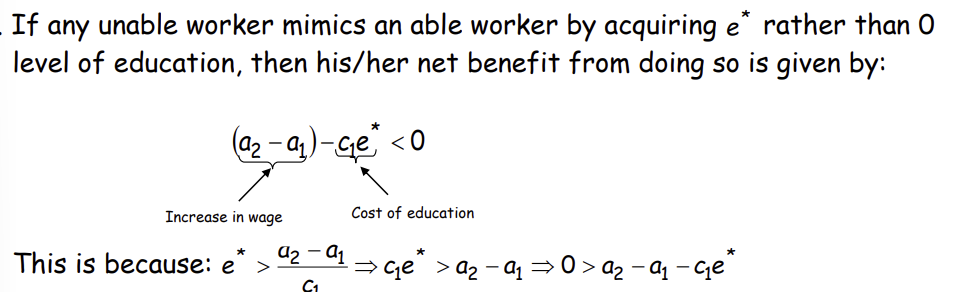
What does this imply in this scenario?
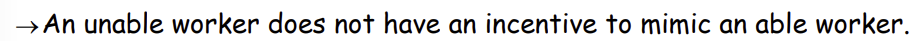

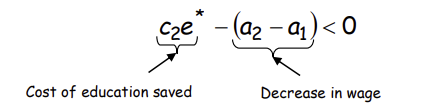
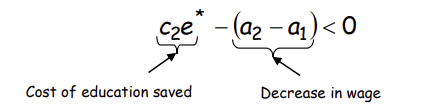
Why is this the case?
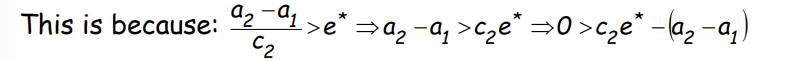

What does this imply in this scenario?
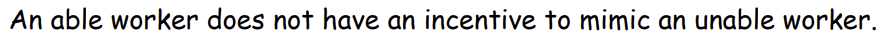

Is what type of outcome and why?
An equilibrium because neither any firm nor any worker has the incentive to behave any differently than at this outcome
What is this type of equilibrium known as and why?
Separating equilibrium; signalling allows the two types of workers to be separated from each other at equilibrium
What is Case 2?


What does this imply?
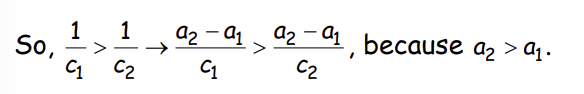

What is implied?
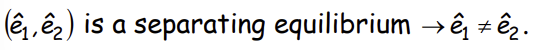
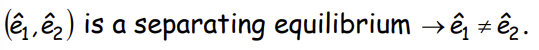
How does this help determine the wage rate and the action of able/unable workers?
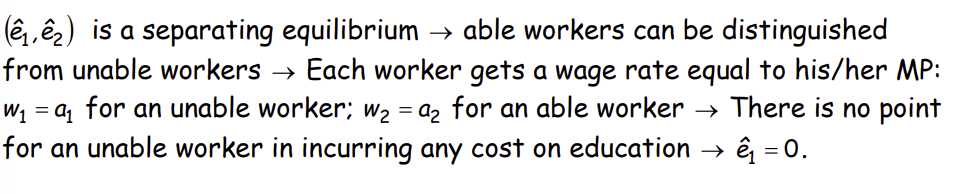
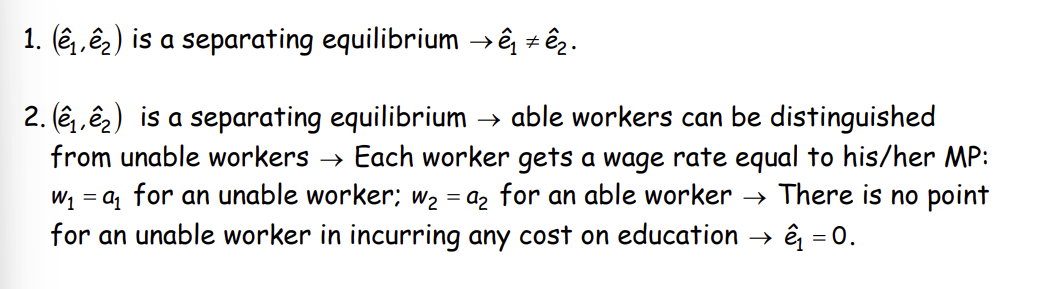
What do both of these imply?
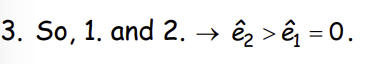

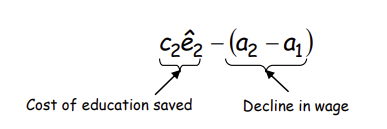
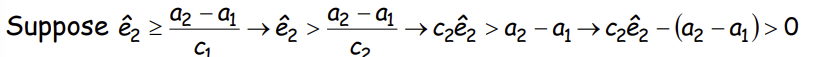
What does this imply about the incentives of an able worker and what must not be true?


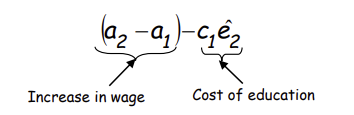
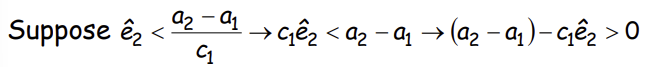
What does this imply about the incentives of an unable worker and what must not be true?


What do 5 and 7 imply?
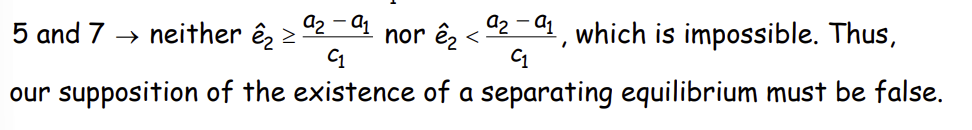
Therefore, what does not exist in Case 2?

What do we know about the level of education acquired by able/unable workers?
Therefore, every worker, able or unable, acquires 0 level of education at the equilibrium of Case 2
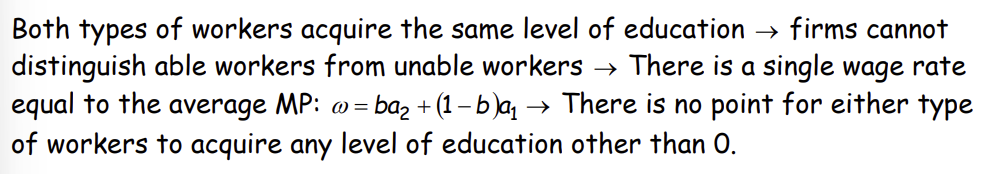
Such an equilibrium in which signalling fails to separate the types is called what?
Pooling equilibrium
In any separating equilibrium of case 1, there is waste of resources on education by able workers but why?
Because education does not enhance anyone’s productivity
Therefore, from a social perspective, the separating equilibria of Case 1 are what?
All inefficient outcomes
However, in any separating equilibrium of case 1, by separating themselves from unable workers by acquiring a positive level of education, able workers earn the wage rate of what?
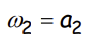
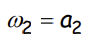
How does this wage rate compare to the average wage?

Thus, in the separating equilibria of case 1, signalling has what kind of benefit for who?

A car seller can send a signal by offering a warranty that promises to pay a certain amount of money back to the buyer if his/her car turns out to be a lemon. How does this lead to an efficient outcome?

Even in the education market, if education enhances a worker’s productivity, then there may not be inefficiencies at the separating equilibrium. Why not?
